
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2026, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (2): 159-176.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250148
• REVIEW • Previous Articles Next Articles
SUN Lian( ), ZHANG Leilei(
), ZHANG Leilei( ), XUE Zexu, WU Kun, CHEN Ye, LI Zhiyuan, WANG Lukai, WANG Zungang(
), XUE Zexu, WU Kun, CHEN Ye, LI Zhiyuan, WANG Lukai, WANG Zungang( )
)
Received:2025-04-08
Revised:2025-05-05
Published:2026-02-20
Online:2025-06-27
Contact:
ZHANG Leilei, assistant professor. E-mail: zhangleilei@sklnbcpc.cn;About author:SUN Lian (1993-), male, assistant professor. E-mail: sunlian12@alumni.nudt.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
SUN Lian, ZHANG Leilei, XUE Zexu, WU Kun, CHEN Ye, LI Zhiyuan, WANG Lukai, WANG Zungang. Research Progress on Zero-dimensional Metal Halide Scintillators towards Radiation Detection Applications[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2026, 41(2): 159-176.
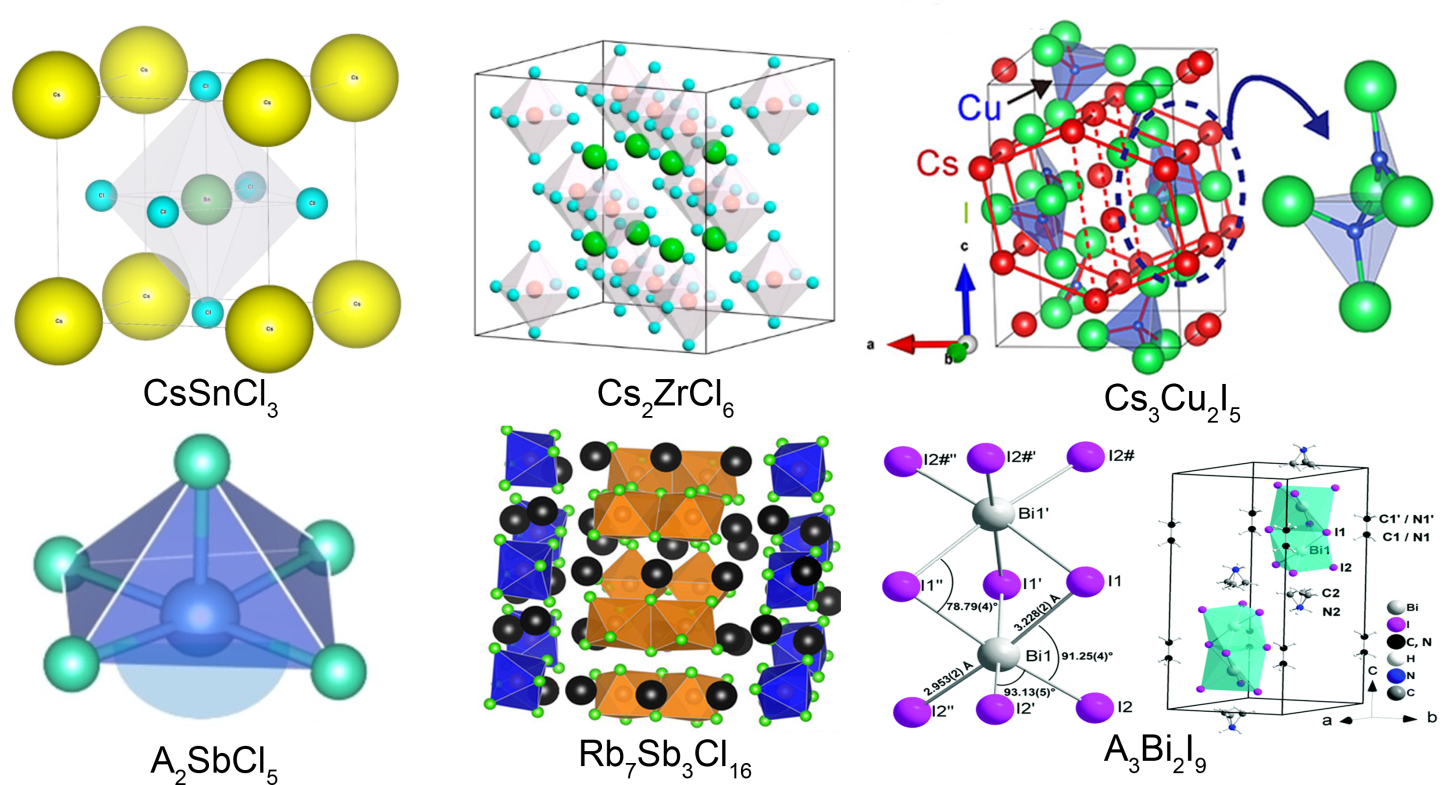
Fig. 2 Crystal structures of several typical 0D metal halides[13-18] CsSnCl3[13]; Cs2ZrCl6[14]; Cs3Cu2I5[15]; A2SbCl5[16]; Rb7Sb3Cl16[17]; A3Bi2I9[18]
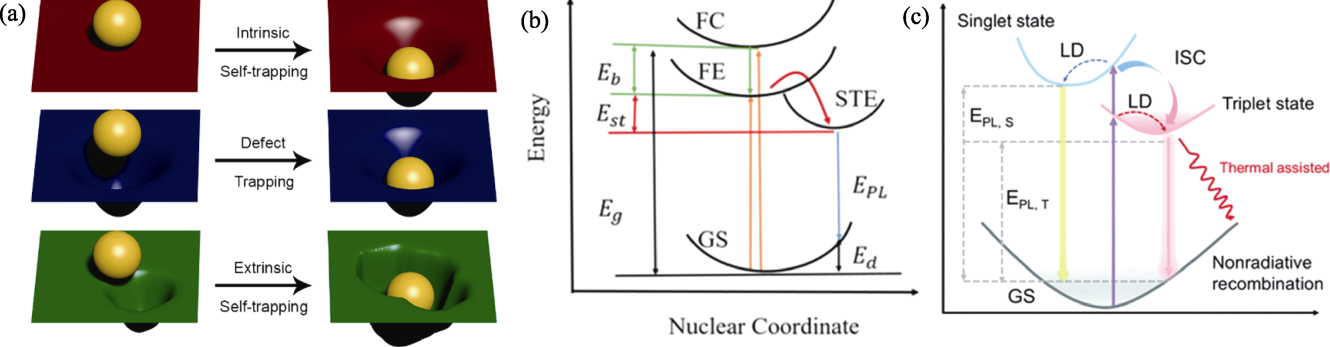
Fig. 4 Formation and luminescence mechanism of STEs[20,25 -26] (a) Self-trapping represented by a ball interacting with a rubber sheet[25]; (b) Schematic of typical STEs process (GS represents ground state, FE represents free exciton state, FC represents free carrier state, STE represents self-trapped exciton state, Eg represents bandgap energy, Eb represents exciton binding energy, Est represents self-trapping energy, Ed represents lattice deformation energy, and EPL represents emission energy)[26]; (c) Schematic of the luminescence processes in 0D perovskites (LD represents lattice distortion, EPL,S represents singlet state emission energy, and EPL,T represents triplet state emission energy)[20]
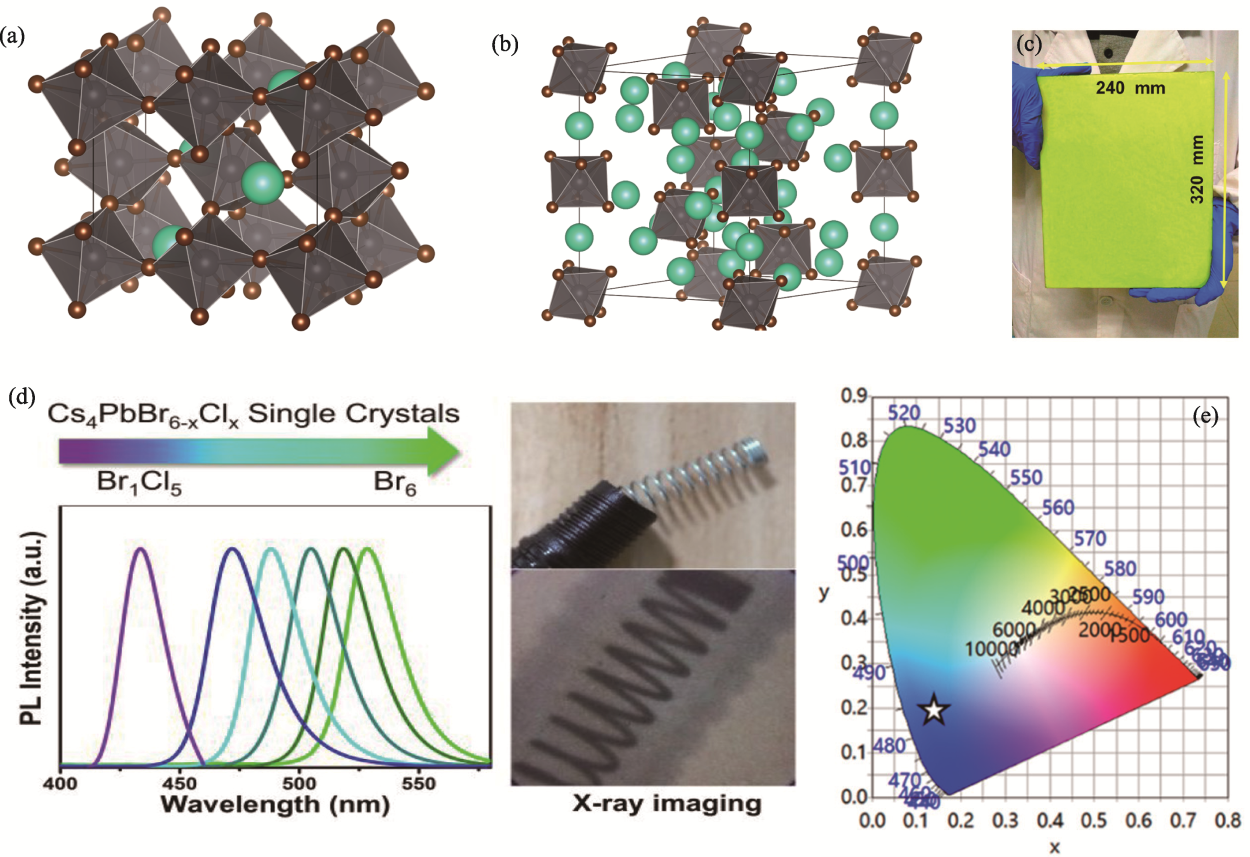
Fig. 6 Pb-based 0D metal halides[44,46,49] (a, b) Crystal structures of (a) CsPbBr3 and (b) Cs4PbBr6; (c) Photo of large-scale CsPbBr3@Cs4PbBr6[44]; (d) PL spectra of Cs4PbBr6-xClx single crystal and application for X-ray imaging[49]; (e) CIE chromaticity coordinates (0.14, 0.19) of the blue emission from (C9NH20)7(PbCl4)Pb3Cl11·CH3CN single crystals[46]
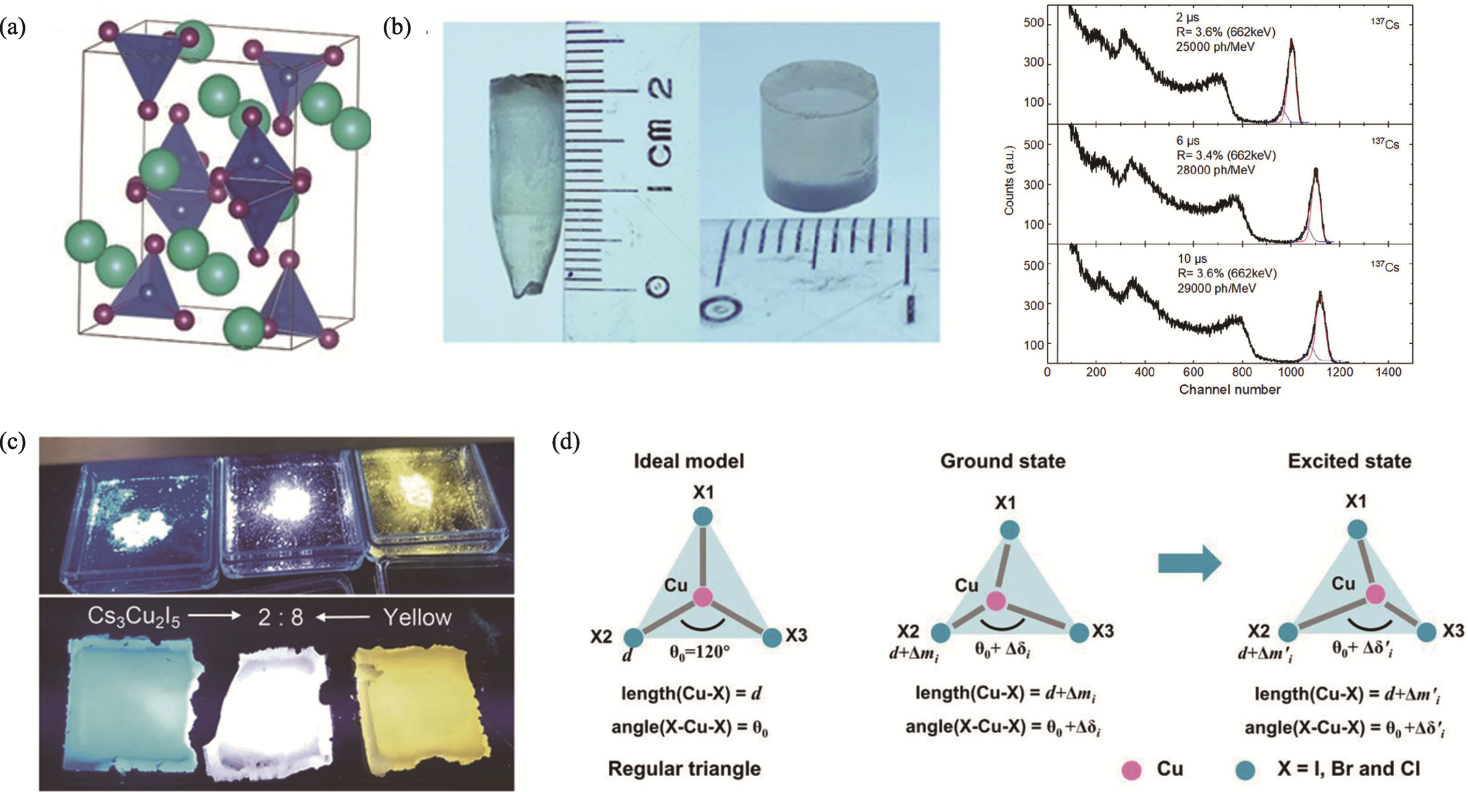
Fig. 7 Cu-based 0D metal halides[56,59,66 -67] (a) Crystal structure of Cs3Cu2I5[56]; (b) As-grown 7 mm diameter Cs3Cu2I5 crystal ingot, a polished sample, and 137Cs gamma-ray spectra of ϕ7 mm×1 mm Cs3Cu2I5 single crystal[59]; (c) Photograph of colloidal solution of Cs3Cu2X5 (X=Cl, Br, I) nanocrystals (NCs) in hexane and their thin films under UV light (λ=254 nm)[66]; (d) An ideal model method used for quantitative analysis of structural deformation for Cs3Cu2X5[67]
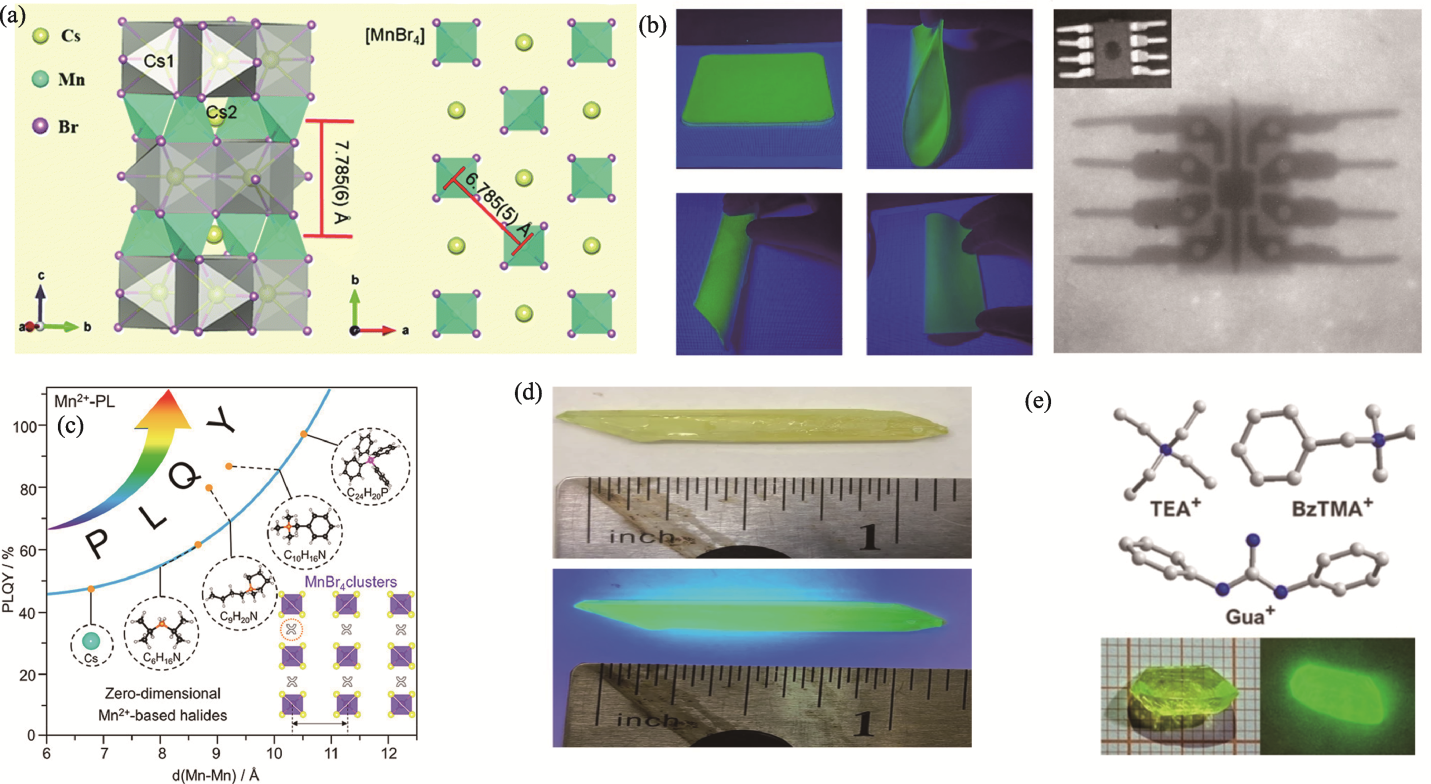
Fig. 8 Mn-based 0D metal halides[76,78 -81] (a) Crystal structure of Cs3MnBr5[76]; (b) Photography of flexible Cs3MnBr5@PDMS film under ambient light, UV light and bending, with X-ray images of chip using Cs3MnBr5@PDMS film[78]; (c) Illustration of the closest Mn-Mn distance and luminescent efficiency for the selected 0D Mn2+-based metal halides[79]; (d) Images of a (C38H34P2)MnBr4 single crystal under daylight and UV light[80]; (e) Illustration of bulky molecules at A site in A2MnBr4, and images of a (Gua)2MnBr4 bulk single crystal under ambient light and UV irradiation (365 nm)[81]
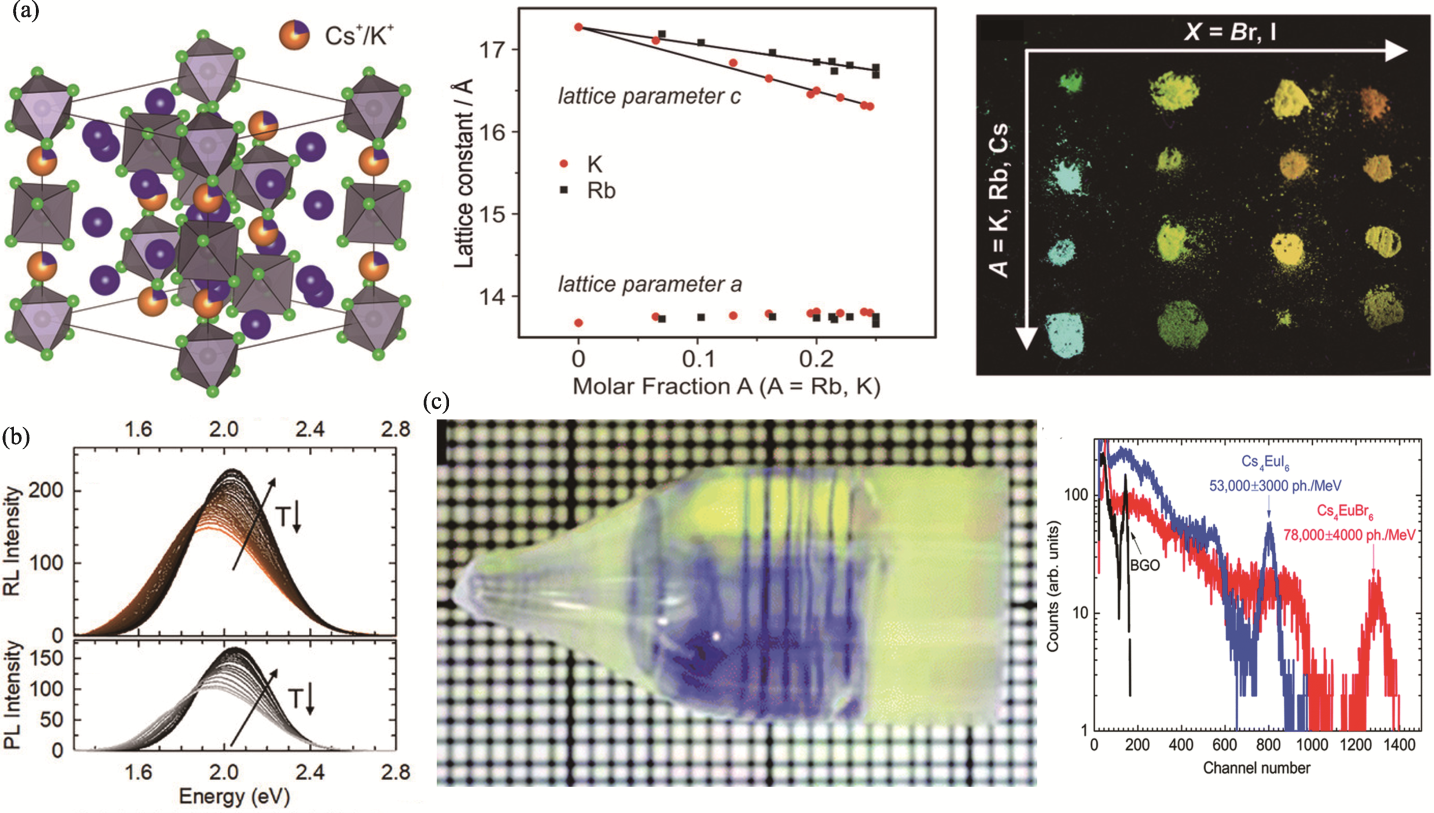
Fig. 9 Other 0D metal halides[86,99,105] (a) Crystal structure of Cs3.2K0.8SnBr6 determined by Rietveld refinement, change in a and c lattice parameters upon Cs+ substitution by Rb+ and K+, and image of Cs4-xAxSn(Br,I)6 powders under 365 nm UV light[86]; (b) Radioluminescence (RL)/PL spectra of Gua3SbCl6 powders as a function of temperature[99]; (c) Picture of 12-mm diameter as-grown Cs4EuBr6 single crystal and 137Cs pulse height spectra measured with Cs4EuBr6[105]
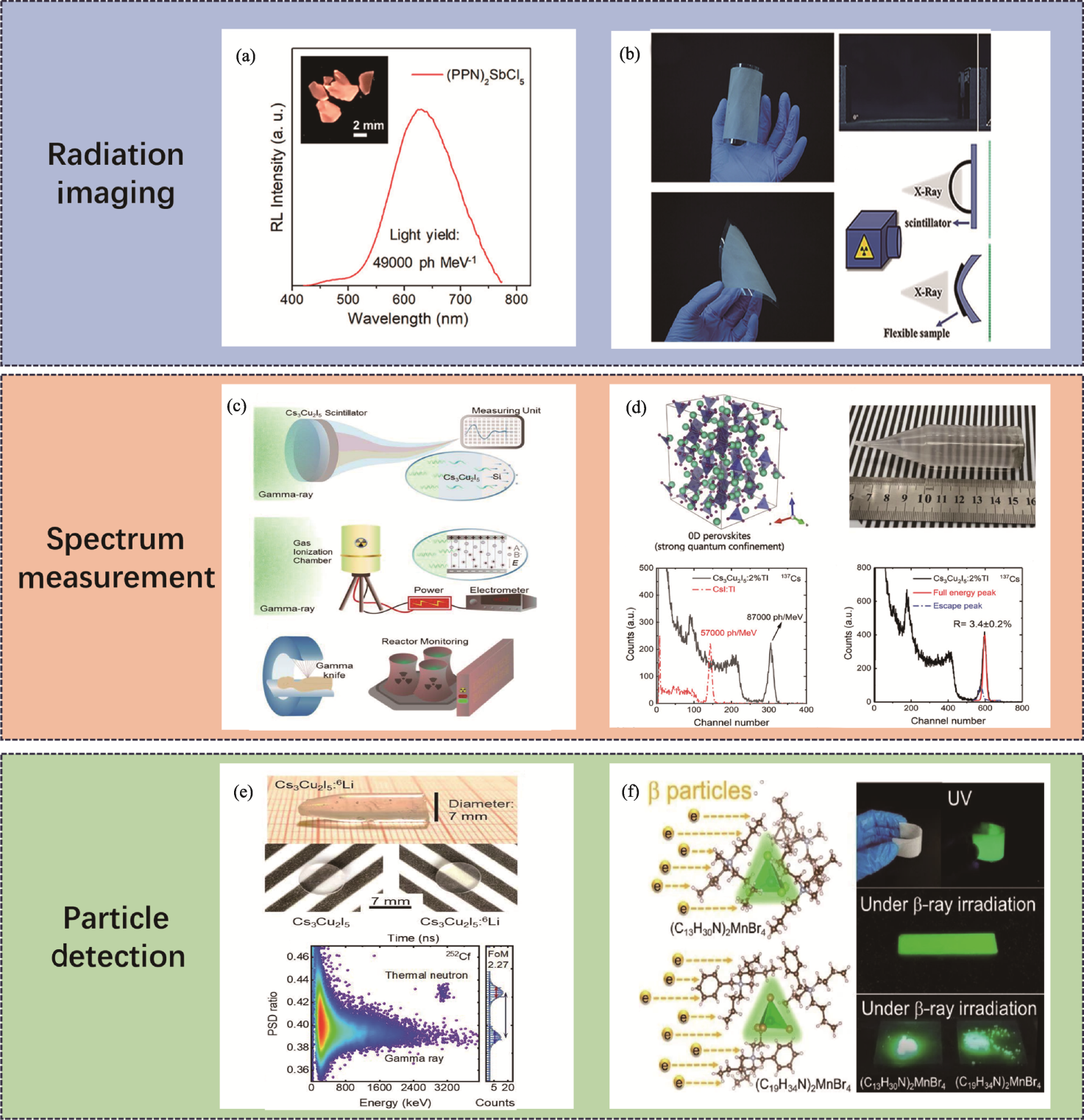
Fig. 10 Applications of 0D metal halides in radiation detection fields[60,112,118,122,127,129] (a) Crystal structure and X-ray radioluminescence of (PPN)2SbCl5[112]; (b) Optical images of Cs3Cu2Cl5 films, and schematic diagram of the sample upright and attached on the Cs3Cu2Cl5 film[118]; (c) Comparison of Cs3Cu2I5 and other scintillators for γ-ray dosimetry[122];(d) Crystal structure, picture of as-grown crystal and pulse height spectra of Cs3Cu2I5:Tl[60]; (e) Neutron detection properties of Cs3Cu2I5:6Li[127]; (f) Crystal structure and photos of (C19H34N)2MnBr4 under β-ray irradiation[129]
| Type | Luminescence emission peak/nm | Light yield/(ph·MeV-1) | Decay time/ns | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cs3Cu2I5:Mn | 445a | 95772a | 3a | [ |
| (C3N3H11O)2PbBr6·4H2O | 568b | - | 15.4c | [ |
| Cs4PbBr6 | 523b | 19000b | 179.6c | [ |
| CsPbBr3@Cs4PbBr6 | 523b | 64000b | 2.1c | [ |
| CsPbBr5Cl | 518b | ~4426b | 0.62c | [ |
| bMOF⊃MAPbBr3 | 517c | - | 37.7c | [ |
| Cs3Cu2I5:Tl | 440b | 87000a | 807.5a | [ |
| [AEPipz]CuBr3·Br·H2O | 500c | 62400b | 1.2×105a | [ |
| Cs3Cu2I5 single crystal | 436b | 32695a | 39a | [ |
| (TBA)CuBr2 | 498c | 24134b | 2.3×105a | [ |
| (Bmpip)2Cu2Br4 | ~650b | 16000b | 56.2a (241Am) | [ |
| [BzTPP]2Cu2I4 | 529c | 27706b | 1.9×103c | [ |
| (C8H20N)2Cu2Br4 | 468b | 91300b | 1.4×106c | [ |
| Cs3MnI5 | 540c | 33600b | 4.0×105c | [ |
| (C10H16N)2MnBr4 | 518c | - | 3.3×105c | [ |
| (C38H34P2)MnBr4 | 517b | ~80000b | 3.2×105c | [ |
| (Gua)2MnBr4 | 520b | 21061b | 2.0×108b | [ |
| (ETP)2MnBr4 | 520b | ~35000±2000b | 3.0×105c | [ |
| Mn(ttpo)Br2 | - | 12840b | 6×105c | [ |
Table 1 Scintillation properties of typical 0D metal halides
| Type | Luminescence emission peak/nm | Light yield/(ph·MeV-1) | Decay time/ns | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cs3Cu2I5:Mn | 445a | 95772a | 3a | [ |
| (C3N3H11O)2PbBr6·4H2O | 568b | - | 15.4c | [ |
| Cs4PbBr6 | 523b | 19000b | 179.6c | [ |
| CsPbBr3@Cs4PbBr6 | 523b | 64000b | 2.1c | [ |
| CsPbBr5Cl | 518b | ~4426b | 0.62c | [ |
| bMOF⊃MAPbBr3 | 517c | - | 37.7c | [ |
| Cs3Cu2I5:Tl | 440b | 87000a | 807.5a | [ |
| [AEPipz]CuBr3·Br·H2O | 500c | 62400b | 1.2×105a | [ |
| Cs3Cu2I5 single crystal | 436b | 32695a | 39a | [ |
| (TBA)CuBr2 | 498c | 24134b | 2.3×105a | [ |
| (Bmpip)2Cu2Br4 | ~650b | 16000b | 56.2a (241Am) | [ |
| [BzTPP]2Cu2I4 | 529c | 27706b | 1.9×103c | [ |
| (C8H20N)2Cu2Br4 | 468b | 91300b | 1.4×106c | [ |
| Cs3MnI5 | 540c | 33600b | 4.0×105c | [ |
| (C10H16N)2MnBr4 | 518c | - | 3.3×105c | [ |
| (C38H34P2)MnBr4 | 517b | ~80000b | 3.2×105c | [ |
| (Gua)2MnBr4 | 520b | 21061b | 2.0×108b | [ |
| (ETP)2MnBr4 | 520b | ~35000±2000b | 3.0×105c | [ |
| Mn(ttpo)Br2 | - | 12840b | 6×105c | [ |
| [1] |
ZHENG Z, WEI Q, TONG Y, et al. Effect of Zr4+ co-doping on neutron/gamma discrimination of Cs2LaLiBr6:Ce crystals. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(5): 539.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
JANA A, CHO S, PATIL S A, et al. Perovskite: scintillators, direct detectors, and X-ray imagers. Materials Today, 2022, 55: 110.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
NIKL M, YOSHIKAWA A. Recent R&D trends in inorganic single-crystal scintillator materials for radiation detection. Advanced Optical Materials, 2015, 3(4): 463.
DOI URL |
| [4] | SHEN Y Q, SHI Y, PAN Y B, et al. Fabrication and 2D-mapping of Pr: Lu3Al5O12 scintillator ceramics with high light yield and fast decay time. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(5): 534. |
| [5] |
GLODO J, WANG Y, SHAWGO R, et al. New developments in scintillators for security applications. Physics Procedia, 2017, 90: 285.
DOI URL |
| [6] | DI FULVIO A, SHIN T H, HAMEL M C, et al. Digital pulse processing for NaI(Tl) detectors. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2016, 806: 69. |
| [7] |
HAWRAMI R, ARIESANTI E, FARSONI A, et al. Growth and evaluation of improved CsI:Tl and NaI:Tl scintillators. Crystals, 2022, 12(11): 1517.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
BIZARRI G, DORENBOS P. Charge carrier and exciton dynamics in LaBr3:Ce3+ scintillators: experiment and model. Physical Review B, 2007, 75(18): 184302.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
MOSZYŃSKI M, NASSALSKI A, SYNTFELD-KAŻUCH A, et al. Temperature dependences of LaBr3(Ce), LaCl3(Ce) and NaI(Tl) scintillators. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2006, 568(2): 739.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
GUO S, LIU K, LIN Z, et al. Temperature dependence of Ce luminescence characteristics in LaBr3:Ce crystal. Journal of Luminescence, 2025, 277: 120956.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
ZHOU L, LIAO J F, KUANG D B. An overview for zero-dimensional broadband emissive metal-halide single crystals. Advanced Optical Materials, 2021, 9(17): 2100544.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
WELLS H L. Über die cäsium- und kalium-bleihalogenide. Zeitschrift fur Anorganische Chemie, 1893, 3(1): 195.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
PAUL D K, HOSSAIN A K M A. A comprehensive DFT + U investigation of electrical, optical, and structural properties of doped CsSnCl3 perovskite: unveiling optoelectronic potential. Computational Materials Science, 2024, 231: 112585.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
CHEN B, GUO Y, WANG Y, et al. Multiexcitonic emission in zero-dimensional Cs2ZrCl6:Sb3+ perovskite crystals. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2021, 143(42): 17599.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
TSUJI M, SASASE M, IIMURA S, et al. Room-temperature solid-state synthesis of Cs3Cu2I5 thin films and formation mechanism for its unique local structure. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2023, 145(21): 11650.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
SUN C, DENG Z, LI Z, et al. Achieving near-unity photoluminescence quantum yields in organic-inorganic hybrid antimony (III) chlorides with the [SbCl5] geometry. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2023, 62(10): e202216720.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
ZHANG B, PINCHETTI V, ZITO J, et al. Isolated [SbCl6]3- octahedra are the only active emitters in Rb7Sb3Cl16 nanocrystals. ACS Energy Letters, 2021, 6(11): 3952.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
ECKHARDT K, BON V, GETZSCHMANN J, et al. Crystallographic insights into (CH3NH3)3(Bi2I9): a new lead-free hybrid organic-inorganic material as a potential absorber for photovoltaics. Chemical Communications, 2016, 52(14): 3058.
DOI PMID |
| [19] |
DING M, WU Q, SHEN Y, et al. (C8H7N2O2)2[Bi2Br8]·2H2O and (C8H7N2O2)6[Bi2Cl10]Cl2·2H2O: exploring birefringent crystals in hybrid halide systems. Inorganic Chemistry, 2024, 63(21): 9701.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
LI M, XIA Z. Recent progress of zero-dimensional luminescent metal halides. Chemical Society Reviews, 2021, 50(4): 2626.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
LIU J, LI M, HAN Q, et al. Theoretical investigation of the structural stability, electronic and optical properties of the double perovskite Cs2ZrX6 (X=Cl, Br, I). Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing, 2024, 171: 107984.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
HAN D, SHI H, MING W, et al. Unraveling luminescence mechanisms in zero-dimensional halide perovskites. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2018, 6(24): 6398.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
HOANG T B, MOSES A F, ZHOU H L, et al. Observation of free exciton photoluminescence emission from single wurtzite GaAs nanowires. Applied Physics Letters, 2009, 94(13): 133105.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
ZHANG Y, TU D, WANG L, et al. Transition metal ion-doped cesium lead halide perovskite nanocrystals: doping strategies and luminescence design. Materials Chemistry Frontiers, 2024, 8(1): 192.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
SMITH M D, KARUNADASA H I. White-light emission from layered halide perovskites. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2018, 51(3): 619.
DOI PMID |
| [26] |
LI S, LUO J, LIU J, et al. Self-trapped excitons in all-inorganic halide perovskites: fundamentals, status, and potential applications. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2019, 10(8): 1999.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
MURRAY R B, MEYER A. Scintillation response of activated inorganic crystals to various charged particles. Physical Review, 1961, 122(3): 815.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
BIZARRI G. Scintillation mechanisms of inorganic materials: from crystal characteristics to scintillation properties. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2010, 312(8): 1213.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
YAO Q, LI J, LI X, et al. Achieving a record scintillation performance by micro-doping a heterovalent magnetic ion in Cs3Cu2I5 single-crystal. Advanced Materials, 2023, 35(44): 2304938.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
TONGUC B T, ARSLAN H, AL-BURIAHI M S. Studies on mass attenuation coefficients, effective atomic numbers and electron densities for some biomolecules. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 2018, 153: 86.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
DORENBOS P, HAAS J, EIJK C. Non-proportionality in the scintillation response and the energy resolution obtainable with scintillation crystals. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 1995, 42(6): 2190.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
MOSZYŃSKI M, SYNTFELD-KAŻUCH A, SWIDERSKI L, et al. Energy resolution of scintillation detectors. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2016, 805: 25.
DOI URL |
| [33] | LECOQ P, KORZNIK M. Scintillator developments for high energy physics and medical imaging. 1999 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference, Seattle, 1999, 1: 1-5. |
| [34] |
RONDA C. Scintillators for medical imaging. Optical Materials: X, 2024, 22: 100293.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
TANG Y, DENG M, LIU Q, et al. Reducing luminescence intensity and suppressing irradiation-induced darkening of Bi4Ge3O12 by Ce-doping for radiation detection. Advanced Optical Materials, 2024, 12(2): 2301332.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
WANG J X, SHEKHAH O, BAKR O M, et al. Energy transfer- based X-ray imaging scintillators. Chem, 2025, 11(1): 102273.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
YIN J, ZHANG Y, BRUNO A, et al. Intrinsic lead ion emissions in zero-dimensional Cs4PbBr6 nanocrystals. ACS Energy Letters, 2017, 2(12): 2805.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
NIKL M, MIHOKOVA E, NITSCH K, et al. Photoluminescence of Cs4PbBr6 crystals and thin films. Chemical Physics Letters, 1999, 306(5): 280.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
AKKERMAN Q A, PARK S, RADICCHI E, et al. Nearly monodisperse insulator Cs4PbX6 (X=Cl, Br, I) nanocrystals, their mixed halide compositions, and their transformation into CsPbX3 nanocrystals. Nano Letters, 2017, 17(3): 1924.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
BAO Z, TSENG Y J, YOU W, et al. Efficient luminescence from CsPbBr3 nanoparticles embedded in Cs4PbBr6. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2020, 11(18): 7637.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
SAIDAMINOV M I, ALMUTLAQ J, SARMAH S, et al. Pure Cs4PbBr6: highly luminescent zero-dimensional perovskite solids. ACS Energy Letters, 2016, 1(4): 840.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
ZHANG H, LIAO Q, WU Y, et al. Pure zero-dimensional Cs4PbBr6 single crystal rhombohedral microdisks with high luminescence and stability. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2017, 19(43): 29092.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
YIN J, YANG H, SONG K, et al. Point defects and green emission in zero-dimensional perovskites. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2018, 9(18): 5490.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
CAO F, YU D, MA W, et al. Shining emitter in a stable host: design of halide perovskite scintillators for X-ray imaging from commercial concept. ACS Nano, 2020, 14(5): 5183.
DOI PMID |
| [45] |
CUI B B, HAN Y, HUANG B, et al. Locally collective hydrogen bonding isolates lead octahedra for white emission improvement. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 5190.
DOI |
| [46] |
ZHOU C, LIN H, WORKU M, et al. Blue emitting single crystalline assembly of metal halide clusters. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2018, 140(41): 13181.
DOI PMID |
| [47] |
PENG G, AN B, CHEN H, et al. Self-organizing pixelated Cs4PbBr6 scintillator plate for large-area, ultra-flexible, high spatial resolution and stable X-Ray imaging. Advanced Optical Materials, 2023, 11(1): 2201751.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
XU Q, WANG J, SHAO W, et al. A solution-processed zero-dimensional all-inorganic perovskite scintillator for high resolution gamma-ray spectroscopy detection. Nanoscale, 2020, 12(17): 9727.
DOI PMID |
| [49] |
WU X, ZHOU Q, WU H, et al. Cs4PbBr6-xClx single crystals with tunable emission for X-ray detection and imaging. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2021, 125(48): 26619.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
WU H, RAN P, YAO L, et al. Confinement of methylammonium lead bromide nanocrystals in metal-organic frameworks as a stable scintillator for high-performance X-ray imaging. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 491: 152098.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
SHI W, ZHANG X, MATRAS-POSTOLEK K, et al. Mn-derived Cs4PbX6 nanocrystals with stable and tunable wide luminescence for white light-emitting diodes. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2022, 10(10): 3886.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
QIU Y, MA Z, DAI G, et al. Doped 0D Cs4PbCl6 single crystals featuring full-visible-region colorful luminescence. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2022, 10(16): 6227.
DOI URL |
| [53] | LI Y, CHEN L, GAO R, et al. Nanosecond and highly sensitive scintillator based on all-inorganic perovskite single crystals. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(1): 1489. |
| [54] |
HAN J, LI Y, SHEN P, et al. Pressure-induced free exciton emission in a quasi-zero-dimensional hybrid lead halide. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2024, 63(1): e202316348.
DOI URL |
| [55] | CHEN S, GAO J, CHANG J, et al. Family of highly luminescent pure ionic copper (I) bromide based hybrid materials. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(19): 17513. |
| [56] |
JUN T, SIM K, IIMURA S, et al. Lead-free highly efficient blue-emitting Cs3Cu2I5 with 0D electronic structure. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(43): 1804547.
DOI URL |
| [57] | YUAN D. Air-stable bulk halide single-crystal scintillator Cs3Cu2I5 by melt growth: intrinsic and Tl doped with high light yield. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(34): 38333. |
| [58] |
STAND L, RUTSTROM D, KOSCHAN M, et al. Crystal growth and scintillation properties of pure and Tl-doped Cs3Cu2I5. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2021, 991: 164963.
DOI URL |
| [59] |
CHENG S, BEITLEROVA A, KUCERKOVA R, et al. Zero-dimensional Cs3Cu2I5 perovskite single crystal as sensitive X-ray and γ-ray scintillator. Physica Status Solidi (RRL) - Rapid Research Letters, 2020, 14(11): 2000374.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
CHENG S, NIKL M, BEITLEROVA A, et al. Ultrabright and highly efficient all-inorganic zero-dimensional perovskite scintillators. Advanced Optical Materials, 2021, 9(13): 2100460.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
WANG Q, ZHOU Q, NIKL M, et al. Highly resolved X-Ray imaging enabled by In(I) doped perovskite-like Cs3Cu2I5 single crystal scintillator. Advanced Optical Materials, 2022, 10(11): 2200304.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
HU Y, YAN X, ZHOU L, et al. Improved energy transfer in Mn-doped Cs3Cu2I5 microcrystals induced by localized lattice distortion. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2022, 13(46): 10786.
DOI URL |
| [63] |
HAPOSAN T, ARRAMEL A, MAULIDA P Y D, et al. All-inorganic copper-halide perovskites for large-Stokes shift and ten-nanosecond-emission scintillators. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2024, 12(7): 2398.
DOI URL |
| [64] |
HUNYADI M, SAMU G F, CSIGE L, et al. Scintillator of polycrystalline perovskites for high-sensitivity detection of charged-particle radiations. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(48): 2206645.
DOI URL |
| [65] |
YANG Q, WEI H, LI G, et al. Spectral adjustable Re-Cs3Cu2I5 nanocrystal-in-glass composite with long-term stability. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 483: 149288.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
LIAN L, ZHENG M, ZHANG W, et al. Efficient and reabsorption-free radioluminescence in Cs3Cu2I5 nanocrystals with self-trapped excitons. Advanced Science, 2020, 7(11): 2000195.
DOI URL |
| [67] |
ZHU W, LI R, LIU X, et al. Photophysical properties of copper halides with strongly confined excitons and their high-performance X-ray imaging. Advanced Functional Materials, 2024, 34(26): 2316449.
DOI URL |
| [68] | LIN N, WANG X, ZHANG H Y, et al. Zero-dimensional copper(I) halide microcrystals as highly efficient scintillators for flexible X-ray imaging. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2024, 16(31): 41165. |
| [69] |
YAO Q, LI J, LI X, et al. High-quality Cs3Cu2I5 single-crystal is a fast-decaying scintillator. Advanced Optical Materials, 2022, 10(23): 2201161.
DOI URL |
| [70] |
LIAN L, WANG X, ZHANG P, et al. Highly luminescent zero-dimensional organic copper halides for X-ray scintillation. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2021, 12(29): 6919.
DOI URL |
| [71] | XU T, LI Y, NIKL M, et al. Lead-free zero-dimensional organic-copper (I) halides as stable and sensitive X-ray scintillators. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(12): 14157. |
| [72] |
LIN N, WANG R C, ZHANG S Y, et al. 0D hybrid cuprous halide as an efficient light emitter and X-ray scintillator. Laser & Photonics Reviews, 2023, 17(12): 2300427.
DOI URL |
| [73] |
SU B, JIN J, HAN K, et al. Ceramic wafer scintillation screen by utilizing near-unity blue-emitting lead-free metal halide (C8H20N)2Cu2Br4. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(5): 2210735.
DOI URL |
| [74] |
KOIDL P. Jahn-Teller effect in the 4T1(1) and 4T2(1) states of tetrahedrally coordinated Mn2+. Physica Status Solidi (b), 1976, 74(2): 477.
DOI URL |
| [75] |
KRETOV M K, ISKANDAROVA I M, POTAPKIN B V, et al. Simulation of structured 4T1→6A1 emission bands of Mn2+ impurity in Zn2SiO4: a first-principle methodology. Journal of Luminescence, 2012, 132(8): 2143.
DOI URL |
| [76] |
SU B, MOLOKEEV M, XIA Z. Mn2+-based narrow-band green-emitting Cs3MnBr5 phosphor and the performance optimization by Zn2+ alloying. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2019, 7(36): 11220.
DOI URL |
| [77] |
KONG Q, MENG X, JI S, et al. Highly reversible cesium manganese iodine for sensitive water detection and X-ray imaging. ACS Materials Letters, 2022, 4(9): 1734.
DOI URL |
| [78] |
XU M, YANG X, YANG X, et al. Heating revival of Cs3MnBr5 for anti-counterfeiting and large-area flexible X-ray imaging. Optical Materials, 2024, 156: 115959.
DOI URL |
| [79] |
ZHOU G, LIU Z, HUANG J, et al. Unraveling the near-unity narrow-band green emission in zero-dimensional Mn2+-based metal halides: a case study of (C10H16N)2Zn1-xMnxBr4 solid solutions. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2020, 11(15): 5956.
DOI URL |
| [80] |
XU L J, LIN X, HE Q, et al. Highly efficient eco-friendly X-ray scintillators based on an organic manganese halide. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 4329.
DOI |
| [81] | WU Y, ZHU Y, AHMED A A, et al. Excitation-dependent anti-thermal quenching in zero-dimensional manganese bromides for photoluminescence and X-ray scintillation. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2025, 137(5): e202417018. |
| [82] |
LI B, XU Y, ZHANG X, et al. Zero-dimensional luminescent metal halide hybrids enabling bulk transparent medium as large-area X-ray scintillators. Advanced Optical Materials, 2022, 10(10): 2102793.
DOI URL |
| [83] |
LU J, GAO J, WANG S, et al. Improving X-ray scintillating merits of zero-dimensional organic-manganese (II) halide hybrids via enhancing the ligand polarizability for high-resolution imaging. Nano Letters, 2023, 23(10): 4351.
DOI URL |
| [84] |
LIU L, HU H, PAN W, et al. Robust organogel scintillator for self-healing and ultra-flexible X-ray imaging. Advanced Materials, 2024, 36(13): 2311206.
DOI URL |
| [85] | ANDREWS R H, CLARK S J, DONALDSON J D, et al. Solid-state properties of materials of the type Cs4MX6 (where M= Sn or Pb and X=Cl or Br). Journal of the Chemical Society, Dalton Transactions, 1983, 4: 767. |
| [86] |
BENIN B M, DIRIN D N, MORAD V, et al. Highly emissive self-trapped excitons in fully inorganic zero-dimensional tin halides. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(35): 11329.
DOI URL |
| [87] |
WANG A, LI J, ZHANG Y, et al. Double-shell encapsulation of lead-free tin halide perovskite for self-powered smart windows. Small, 2024, 20(51): 2404149.
DOI URL |
| [88] |
LIU Y, YANG B, YU Z, et al. Eu3+@Cs4SnBr6 NCs-doped silicate glass with efficient tunable white light emission via energy transfer and multi-emission photoluminescence properties. Materials Today Chemistry, 2024, 42: 102387.
DOI URL |
| [89] |
HUANG Y, LU X, WU H, et al. Improving photoluminescence properties of lead-free Cs4SnBr6 zero-dimensional perovskite via Mn2+/Sb3+ co-doping. Journal of Luminescence, 2025, 277: 120930.
DOI URL |
| [90] |
ZHOU C, LIN H, TIAN Y, et al. Luminescent zero-dimensional organic metal halide hybrids with near-unity quantum efficiency. Chemical Science, 2018, 9(3): 586.
DOI PMID |
| [91] | ZHOU C, TIAN Y, YUAN Z, et al. Highly efficient broadband yellow phosphor based on zero-dimensional tin mixed-halide perovskite. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(51): 44579. |
| [92] |
SONG G, LI M, YANG Y, et al. Lead-free tin(IV)-based organic-inorganic metal halide hybrids with excellent stability and blue-broadband emission. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2020, 11(5): 1808.
DOI URL |
| [93] |
ZHOU L, ZHOU S, LIU X, et al. Embedding Te4+ into Sn4+-based metal halide to passivate structure defects for high-performance light-emitting application. Inorganic Chemistry, 2024, 63(22): 10335.
DOI URL |
| [94] |
LIU X, LI K, SHAO W, et al. Revealing the structure- luminescence relationship in robust Sn(IV)-based metal halides by Sb3+ doping. Inorganic Chemistry, 2024, 63(11): 5158.
DOI URL |
| [95] |
WEI S, TIE S, SHEN K, et al. High-performance X-ray detector based on liquid diffused separation induced Cs3Bi2I9 single crystal. Advanced Optical Materials, 2021, 9(22): 2101351.
DOI URL |
| [96] |
WANG J, LI Y, MA L, et al. Air-stabilized lead-free hexagonal Cs3Bi2I9 nanocrystals for ultrahigh-performance optical detection. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(30): 2203072.
DOI URL |
| [97] |
ZHOU C, WORKU M, NEU J, et al. Facile preparation of light emitting organic metal halide crystals with near-unity quantum efficiency. Chemistry of Materials, 2018, 30(7): 2374.
DOI URL |
| [98] |
MCCALL K M, MORAD V, BENIN B M, et al. Efficient lone-pair-driven luminescence: structure-property relationships in emissive 5s2 metal halides. ACS Materials Letters, 2020, 2(9): 1218.
DOI URL |
| [99] |
ZAFFALON M L, WU Y, COVA F, et al. Zero-dimensional Gua3SbCl6 crystals as intrinsically reabsorption-free scintillators for radiation detection. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(48): 2305564.
DOI URL |
| [100] |
XIE J L, HUANG Z Q, WANG B, et al. New lead-free perovskite Rb7Bi3Cl16 nanocrystals with blue luminescence and excellent moisture-stability. Nanoscale, 2019, 11(14): 6719.
DOI URL |
| [101] |
TANG Y, LIANG M, CHANG B, et al. Lead-free double halide perovskite Cs3BiBr6 with well-defined crystal structure and high thermal stability for optoelectronics. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2019, 7(11): 3369.
DOI URL |
| [102] |
LIU X, ZHANG W, XU R, et al. Bright tunable luminescence of Sb3+ doping in zero-dimensional lead-free halide Cs3ZnCl5 perovskite crystals. Dalton Transactions, 2022, 51(26): 10029.
DOI URL |
| [103] |
MARAYATHUNGAL J H, DAS D K, BAKTHAVATSALAM R, et al. Mn2+-activated zero-dimensional metal (Cd, Zn) halide hybrids with near-unity PLQY and zero thermal quenching. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2023, 127(18): 8618.
DOI URL |
| [104] |
HOU C, LIU X, WANG Z, et al. Designing guanidine-based lead-free hybrid indium perovskites with highly efficient intrinsic broadband emissions. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2024, 12(20): 7426.
DOI URL |
| [105] |
WU Y, HAN D, CHAKOUMAKOS B C, et al. Zero- dimensional Cs4EuX6 (X = Br, I) all-inorganic perovskite single crystals for gamma-ray spectroscopy. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2018, 6(25): 6647.
DOI URL |
| [106] |
SAEKI K, FUJIMOTO Y, KOSHIMIZU M, et al. Comparative study of scintillation properties of Cs2HfCl6 and Cs2ZrCl6. Applied Physics Express, 2016, 9(4): 042602.
DOI |
| [107] |
ZHANG F, ZHOU Y, CHEN Z, et al. Thermally activated delayed fluorescence zirconium-based perovskites for large-area and ultraflexible X-ray scintillator screens. Advanced Materials, 2022, 34(43): 2204801.
DOI URL |
| [108] |
SWIDERSKI L, BRYLEW K, JANIAK L, et al. Cs2ZrCl6 scintillation properties studied using γ-ray spectroscopy and Compton coincidence technique. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2023, 1057: 168735.
DOI URL |
| [109] | ZHU W, MA W, SU Y, et al. Low-dose real-time X-ray imaging with nontoxic double perovskite scintillators. Light: Science & Applications, 2020, 9(1): 112. |
| [110] | YAO S Y, LI H, ZHOU M, et al. Visualization of X-rays with an ultralow detection limit via zero-dimensional perovskite scintillators. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(51): 56957. |
| [111] |
MORAD V, SHYNKARENKO Y, YAKUNIN S, et al. Disphenoidal zero-dimensional lead, tin, and germanium halides: highly emissive singlet and triplet self-trapped excitons and X-ray scintillation. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(25): 9764.
DOI PMID |
| [112] |
HE Q, ZHOU C, XU L, et al. Highly stable organic antimony halide crystals for X-ray scintillation. ACS Materials Letters, 2020, 2(6): 633.
DOI URL |
| [113] | ZHOU W, ZHU X, YU J, et al. High-quality Cs3Cu2I5@PMMA scintillator films assisted by multiprocessing for X-ray imaging. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2023, 15(32): 38741. |
| [114] |
MA W, LIANG D, QIAN Q, et al. Near-unity quantum yield in zero-dimensional lead-free manganese-based halides for flexible X-ray imaging with high spatial resolution. eScience, 2023, 3(2): 100089.
DOI URL |
| [115] |
DUAN R, CHEN Z, XIANG D, et al. Large-area flexible scintillator screen based on copper-based halides for sensitive and stable X-ray imaging. Journal of Luminescence, 2023, 253: 119482.
DOI URL |
| [116] |
YANG B, YIN L, NIU G, et al. Lead-free halide Rb2CuBr3 as sensitive X-ray scintillator. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(44): 1904711.
DOI URL |
| [117] |
HAN L, SUN B, GUO C, et al. Photophysics in zero- dimensional potassium-doped cesium copper chloride Cs3Cu2Cl5 nanosheets and its application for high-performance flexible X-ray detection. Advanced Optical Materials, 2022, 10(6): 2102453.
DOI URL |
| [118] |
QIU F, PENG G, XU Y, et al. Sequential vacuum evaporated copper metal halides for scalable, flexible, and dynamic X-ray detection. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(36): 2303417.
DOI URL |
| [119] |
WANG Z, WEI Y, LIU C, et al. Mn2+-activated Cs3Cu2I5 nano-scintillators for ultra-high resolution flexible X-ray imaging. Laser & Photonics Reviews, 2023, 17(6): 2200851.
DOI URL |
| [120] |
CAO S, ZHU Y, HE P, et al. Cost-effective fabrication of copper(I) halide arrays with mitigated optical crosstalk for high-definition X-ray radiography. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2025, 508: 161139.
DOI URL |
| [121] |
WANG H, ZHANG S, XIA Z. Composition modulation of Cs2ZrCl6-based scintillator film via vapor deposition for large-area X-ray imaging. Small Methods, 2025, 9(8): 2500273.
DOI URL |
| [122] |
SONG X, LIU L, WAN P, et al. Ultrabroad dynamic all-solid-state radiation dose detector based on a 0D Cs3Cu2I5 perovskite-like single crystal. ACS Applied Electronic Materials, 2023, 5(12): 6805.
DOI URL |
| [123] | WANG Q, WANG C, SHI H, et al. Exciton-harvesting enabled efficient charged particle detection in zero-dimensional halides. Light: Science & Applications, 2024, 13(1): 190. |
| [124] |
GAO L, LI Q, SUN J L, et al. Gamma-ray irradiation stability of zero-dimensional Cs3Cu2I5 metal halide scintillator single crystals. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2023, 14(5): 1165.
DOI URL |
| [125] |
MYKHAYLYK V, NAGORNY S S, NAHORNA V V, et al. Growth, structure, and temperature dependent emission processes in emerging metal hexachloride scintillators Cs2HfCl6 and Cs2ZrCl6. Dalton Transactions, 2022, 51(17): 6944.
DOI URL |
| [126] |
WU J, DING J, HUANG X, et al. Fabrication and microstructure of Gd2O2S:Tb scintillation ceramics from water-bath synthesized nano-powders: influence of H2SO4/Gd2O3 molar ratio. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 452.
DOI URL |
| [127] |
WANG Q, WANG C, WANG Z, et al. Achieving efficient neutron and gamma discrimination in a highly stable 6Li-loaded Cs3Cu2I5 perovskite scintillator. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2022, 13(39): 9066.
DOI URL |
| [128] |
YAO L, GUI W, ZHOU X, et al. Bright lead-free Cs3Cu2I5 perovskite scintillators for thermal neutron detection. Materials Advances, 2023, 4(17): 3714.
DOI URL |
| [129] |
LIAN L, QI W, DING H, et al. Highly luminescent zero- dimensional lead-free manganese halides for β-ray scintillation. Nano Research, 2022, 15(9): 8486.
DOI |
| [130] | WEI C H, DONG S, XU Z, et al. Controllable multi-exciton zero-dimensional antimony-based metal halides for white-light emission and β-ray detection. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2024, 63(51): e2024122. |
| [1] | LIU Zhanyi, LI Mian, OUYANG Xiaoping, CHAI Zhifang, HUANG Qing. Recent Progress on Removal of Sr/Cs from Molten Salt in Dry Reprocessing [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2026, 41(2): 150-158. |
| [2] | REN Xianpei, LI Chao, HU Qiwei, XIANG Hui, PENG Yuehong. Research Progress on Mott-Schottky Hydrogen Evolution Catalysts Based on Metal/Transition Metal Compounds [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2026, 41(2): 137-149. |
| [3] | ZHOU Qi, LI Xiang, ZHANG Kaihui, WANG Zeliang, DENG Mingxue, JIA Wenbao, WANG Ke, CHEN Junfeng. Organic-Inorganic Composite Scintillators Loaded with LiF-CaF2:Eu Eutectic Powder: Preparation and Characterization [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2026, 41(2): 201-207. |
| [4] | FAN Yuzhu, WANG Yuan, WANG Linyan, XIANG Meiling, YAN Yuting, LI Benhui, LI Min, WEN Zhidong, WANG Haichao, CHEN Yongfu, QIU Huidong, ZHAO Bo, ZHOU Chengyu. Graphene Oxide-based Adsorbents for Pb(II) Removing in Water: Progresses on Synthesis, Performance and Mechanism [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2026, 41(1): 12-26. |
| [5] | XU Jintao, GAO Pan, HE Weiyi, JIANG Shengnan, PAN Xiuhong, TANG Meibo, CHEN Kun, LIU Xuechao. Recent Progress on Preparation of 3C-SiC Single Crystal [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2026, 41(1): 1-11. |
| [6] | YU Shengyang, SU Haijun, JIANG Hao, YU Minghui, YAO Jiatong, YANG Peixin. A Review of Pore Defects in Ultra-high Temperature Oxide Ceramics by Laser Additive Manufacturing: Formation and Suppression [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(9): 944-956. |
| [7] | LIU Jiangping, GUAN Xin, TANG Zhenjie, ZHU Wenjie, LUO Yongming. Research Progress on Catalytic Oxidation of Nitrogen-containing Volatile Organic Compounds [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(9): 933-943. |
| [8] | XIAO Xiaolin, WANG Yuxiang, GU Peiyang, ZHU Zhenrong, SUN Yong. Advances in Regulation of Damaged Skin Regeneration by Two-dimensional Inorganic Materials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 860-870. |
| [9] | MA Jingge, WU Chengtie. Application of Inorganic Bioceramics in Promoting Hair Follicle Regeneration and Hair Growth [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 901-910. |
| [10] | ZHANG Hongjian, ZHAO Ziyi, WU Chengtie. Inorganic Biomaterials on Regulating Neural Cell Function and Innervated Tissue Regeneration: A Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 849-859. |
| [11] | AI Minhui, LEI Bo. Micro-nanoscale Bioactive Glass: Functionalized Design and Angiogenic Skin Regeneration [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 921-932. |
| [12] | WANG Yutong, CHANG Jiang, XU He, WU Chengtie. Advances in Silicate Bioceramic/Bioglass for Wound Healing: Effects, Mechanisms and Application Ways [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 911-920. |
| [13] | MA Wenping, HAN Yahui, WU Chengtie, LÜ Hongxu. Application of Inorganic Bioactive Materials in Organoid Research [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 888-900. |
| [14] | LUO Xiaomin, QIAO Zhilong, LIU Ying, YANG Chen, CHANG Jiang. Inorganic Bioactive Materials Regulating Myocardial Regeneration [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 871-887. |
| [15] | ZHU Wenjie, TANG Lu, LU Jichang, LIU Jiangping, LUO Yongming. Research Progress on Catalytic Oxidation of Volatile Organic Compounds by Perovskite Oxides [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||