
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2026, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (1): 12-26.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250019
• REVIEW • Previous Articles Next Articles
FAN Yuzhu1( ), WANG Yuan1, WANG Linyan1, XIANG Meiling1, YAN Yuting1, LI Benhui1, LI Min1, WEN Zhidong2,3, WANG Haichao2,4, CHEN Yongfu5, QIU Huidong1, ZHAO Bo6, ZHOU Chengyu1(
), WANG Yuan1, WANG Linyan1, XIANG Meiling1, YAN Yuting1, LI Benhui1, LI Min1, WEN Zhidong2,3, WANG Haichao2,4, CHEN Yongfu5, QIU Huidong1, ZHAO Bo6, ZHOU Chengyu1( )
)
Received:2025-01-14
Revised:2025-04-14
Published:2026-01-20
Online:2025-05-09
Contact:
FAN Yuzhu, associate professor. E-mail: fanyuzhu1010@foxmail.com;About author:FAN Yuzhu (1990-), female, associate professor. E-mail: fanyuzhu1010@foxmail.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
FAN Yuzhu, WANG Yuan, WANG Linyan, XIANG Meiling, YAN Yuting, LI Benhui, LI Min, WEN Zhidong, WANG Haichao, CHEN Yongfu, QIU Huidong, ZHAO Bo, ZHOU Chengyu. Graphene Oxide-based Adsorbents for Pb(II) Removing in Water: Progresses on Synthesis, Performance and Mechanism[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2026, 41(1): 12-26.
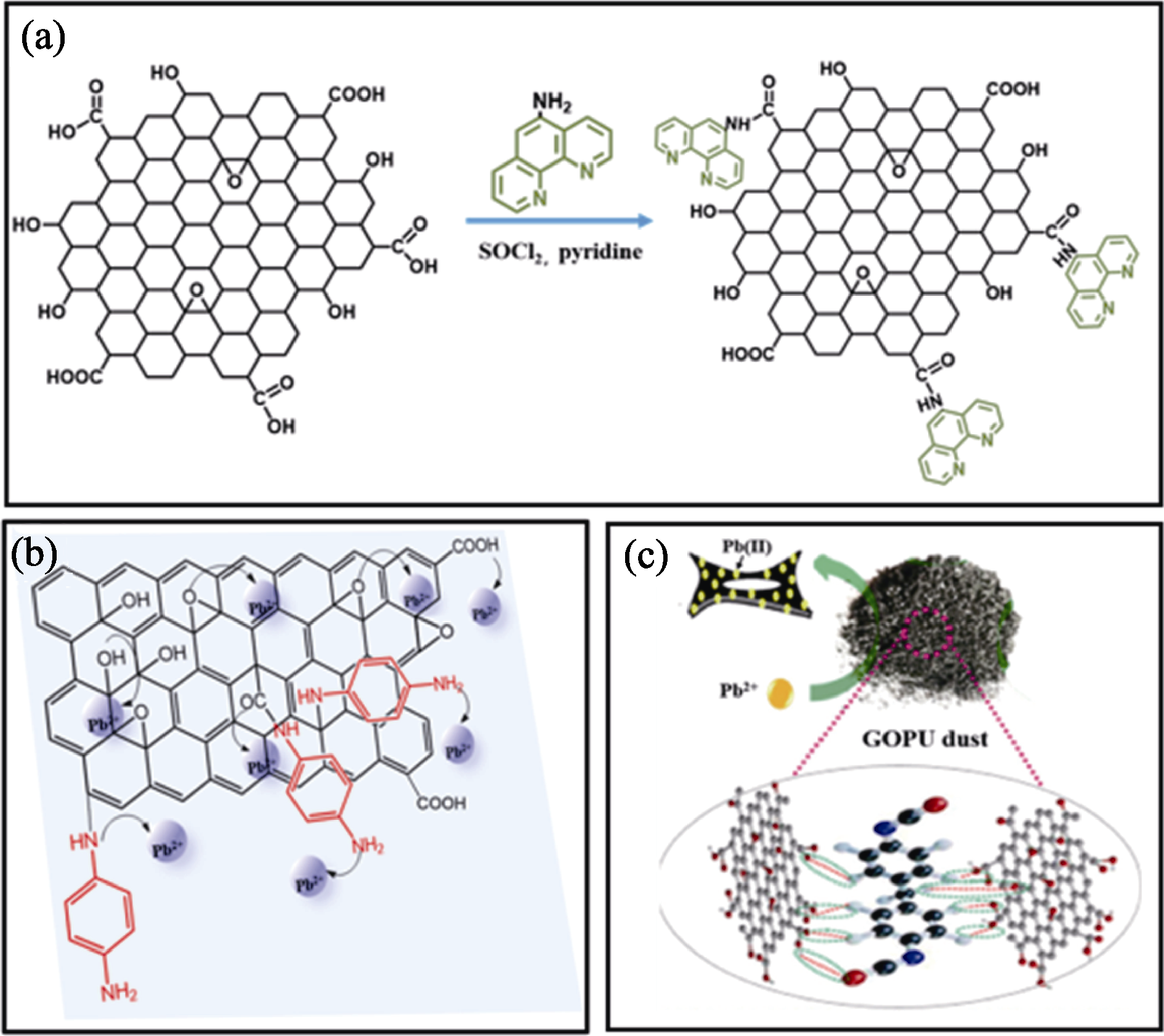
Fig. 2 N modification strategies[22-23,26] (a) Schematic diagram of synthesis of phen-GO[22]; (b, c) Adsorption processes of Pb(II) on (b) PPDG[23] and (c) GOPU[26]
| Type | Adsorbent | Adsorption condition | Adsorption capacity/ (mg·g-1) | Removal efficiency/% | Removal efficiency after desorption (desorption agent, cycle number) | Adsorption mechanism | Isotherm/ kinetic model | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH, time/min | Dosage/ (g·L−1) | |||||||
| N | GO-NH2[ | 4-6, 10 | 1 | 71.89 | − | − | SC, EA, IE | L/PSO |
| IAT-GO[ | 5, 30 | 1 | 124 | 92.3 | >97% (0.4 mol/L HNO3, 5) | SC | L/PSO | |
| IOGO[ | 5, 360 | 0.4 | 798.87 | 87 | − (10% HCl, 5) | SC | L/PSO | |
| GOCAS[ | 5.2, 45 | 0.5 | 138.7 | 93 | >50% (HCl, 4) | − | F/PSO | |
| MGO-EDTA[ | 6.8, 120 | 0.5 | 211.3 | 82.83 | − | SC | F/PSO | |
| phen-GO[ | 6.0, 30 | 1 | 548 | 95 | − | SC | L/PSO | |
| PPDG[ | 4-6, 40 | 0.35 | 800 | − | 30% (0.5 mol/L NaOH, 3) | SC | L/PSO | |
| GO-IIP[ | 6.5, 30 | 0.5 | 40.02 | − | − (2 mol/L HCl, 5) | SC | L/PSO | |
| S | GO/ZnO/CS[ | 5, 120 | 0.5 | 110.88 | 92.4 | − | − | −/PSO |
| GO-SOxR[ | 6.5, 190 | − | 285 | − | − | EA, HB | R/PSO | |
| GOCS[ | 5.5, 30 | 3 | 383.4 | − | 74.26% (0.1 mol/L HNO3, 5) | EA, SC | L/PSO | |
| SH-graphene bio-sponge[ | 5.3, 300 | 1 | 101.01 | 90 | >90% (0.1 mol/L HCl, 5) | EA, SC | L/PSO | |
| MGO@LaS[ | 5, 40 | 0.5 | 123.46 | 95 | − | EA, SC | L/PSO | |
| Fe3S4/rGO[ | 6, − | 2 | 285.71 | 29.59 | 76.88% (0.03 mol/L HNO3, 5) | SC | L/PSO | |
| PVA/GO-SH[ | 6, 60 | 1 | 218.62 | 94.7 | >75% (0.2 mol/L HCl, 5) | SC | L/PSO | |
Table 1 Adsorption characteristics of N/S functional group-modified GO-based adsorbents for Pb(II)[22-23,25,28 -31,33 -40]
| Type | Adsorbent | Adsorption condition | Adsorption capacity/ (mg·g-1) | Removal efficiency/% | Removal efficiency after desorption (desorption agent, cycle number) | Adsorption mechanism | Isotherm/ kinetic model | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH, time/min | Dosage/ (g·L−1) | |||||||
| N | GO-NH2[ | 4-6, 10 | 1 | 71.89 | − | − | SC, EA, IE | L/PSO |
| IAT-GO[ | 5, 30 | 1 | 124 | 92.3 | >97% (0.4 mol/L HNO3, 5) | SC | L/PSO | |
| IOGO[ | 5, 360 | 0.4 | 798.87 | 87 | − (10% HCl, 5) | SC | L/PSO | |
| GOCAS[ | 5.2, 45 | 0.5 | 138.7 | 93 | >50% (HCl, 4) | − | F/PSO | |
| MGO-EDTA[ | 6.8, 120 | 0.5 | 211.3 | 82.83 | − | SC | F/PSO | |
| phen-GO[ | 6.0, 30 | 1 | 548 | 95 | − | SC | L/PSO | |
| PPDG[ | 4-6, 40 | 0.35 | 800 | − | 30% (0.5 mol/L NaOH, 3) | SC | L/PSO | |
| GO-IIP[ | 6.5, 30 | 0.5 | 40.02 | − | − (2 mol/L HCl, 5) | SC | L/PSO | |
| S | GO/ZnO/CS[ | 5, 120 | 0.5 | 110.88 | 92.4 | − | − | −/PSO |
| GO-SOxR[ | 6.5, 190 | − | 285 | − | − | EA, HB | R/PSO | |
| GOCS[ | 5.5, 30 | 3 | 383.4 | − | 74.26% (0.1 mol/L HNO3, 5) | EA, SC | L/PSO | |
| SH-graphene bio-sponge[ | 5.3, 300 | 1 | 101.01 | 90 | >90% (0.1 mol/L HCl, 5) | EA, SC | L/PSO | |
| MGO@LaS[ | 5, 40 | 0.5 | 123.46 | 95 | − | EA, SC | L/PSO | |
| Fe3S4/rGO[ | 6, − | 2 | 285.71 | 29.59 | 76.88% (0.03 mol/L HNO3, 5) | SC | L/PSO | |
| PVA/GO-SH[ | 6, 60 | 1 | 218.62 | 94.7 | >75% (0.2 mol/L HCl, 5) | SC | L/PSO | |
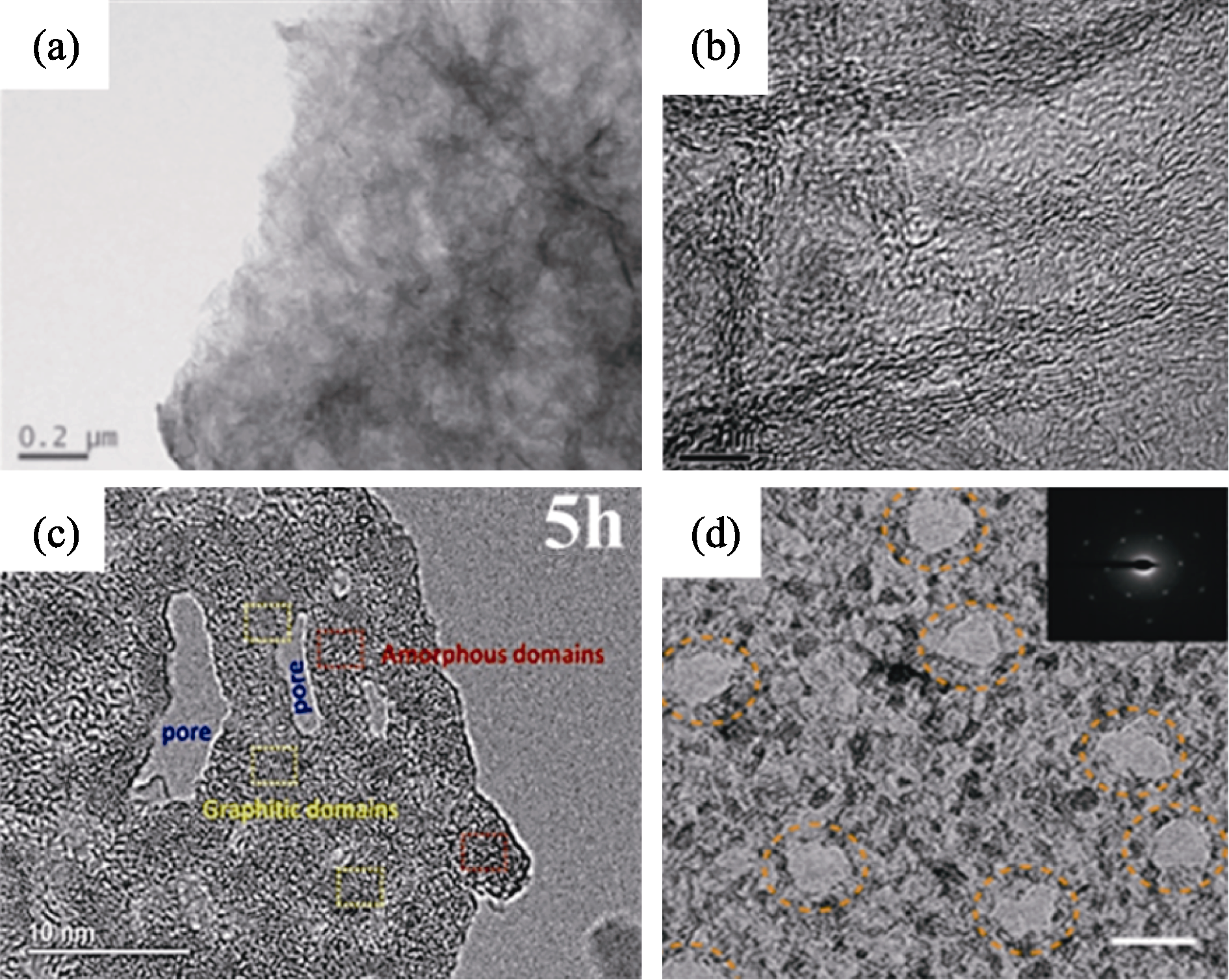
Fig. 4 TEM images of PGO obtained by different preparation methods[41-42,44,46] (a) Hydrothermal method[41]; (b) Template method[42]; (c) Oxidation etching method[46]; (d) High-energy electron irradiation method[44]
| Adsorbent | Adsorption condition | Adsorption capacity/ (mg·g-1) | Removal efficiency/% | Removal efficiency after desorption (desorption agent, cycle number) | Adsorption mechanism | Isotherm/ kinetic model | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH, time/min | Dosage/ (g·L−1) | ||||||
| GO-Si[ | − | 1 | 347.2 | − | − | EA | L/PSO |
| GOCB[ | 5, 120 | 2 | − | − | 48% (0.1 mol/L Na2EDTA, 3) >93% (0.1 mol/L HCl, 3) | PA | −/PFO |
| PGOC[ | − | − | 99 | − | 81% (−, 5) | SC | − |
| NT-CGG[ | 6, <30 | 0.1 | 470 | 99.9998 | 88% (0.05 mol/L EDTA, 5) | SC | L/PSO |
| BC/GO[ | 5, 90 | 0.4 | 224.5 | − | − | SC, EA | F/PSO |
Table 2 Adsorption characteristics of morphology-modified GO-based adsorbents for Pb(II)[49-53]
| Adsorbent | Adsorption condition | Adsorption capacity/ (mg·g-1) | Removal efficiency/% | Removal efficiency after desorption (desorption agent, cycle number) | Adsorption mechanism | Isotherm/ kinetic model | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH, time/min | Dosage/ (g·L−1) | ||||||
| GO-Si[ | − | 1 | 347.2 | − | − | EA | L/PSO |
| GOCB[ | 5, 120 | 2 | − | − | 48% (0.1 mol/L Na2EDTA, 3) >93% (0.1 mol/L HCl, 3) | PA | −/PFO |
| PGOC[ | − | − | 99 | − | 81% (−, 5) | SC | − |
| NT-CGG[ | 6, <30 | 0.1 | 470 | 99.9998 | 88% (0.05 mol/L EDTA, 5) | SC | L/PSO |
| BC/GO[ | 5, 90 | 0.4 | 224.5 | − | − | SC, EA | F/PSO |
| Adsorbent | Adsorption condition | Adsorption capacity/ (mg·g−1) | Removal efficiency/% | Removal efficiency after desorption (desorption agent, cycle number) | Adsorption mechanism | Isotherm /kinetic model | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH, time/min | Dosage/ (g·L−1) | ||||||
| MZIF-8/GO2[ | 4−6, 10 | 0.4 | 625 | 99 | − | − | L/PSO |
| PPy-FG[ | 5, 180 | 0.4 | 93.2 | 85.7 | 85.7% (0.2 mol/L HNO3, 5) | − | L/PSO |
| Fe3O4@C-GO-MOF[ | 6, 60 | 1 | 344.83 | 87 | >85% (5% (in volume) HNO3, 5) | SC | L/PSO |
| MnFe2O4@SiO2-NH2@GO[ | 6.5, 30 | 0.5 | 42.48 | 99.8 | − (0.3 mol/L HCl, 5) | SC | L/PSO |
| MCGO[ | 8, 44 | 0.5 | 372.24 | 93.06 | 68.9% (−, 5) | EA | L/PSO |
| MgFe2O4-NGO[ | 7, 120 | 1 | 930 | 99.7 | 83.6% (0.1 mol/L HCl, 6) | SC, EA, PA | L/PSO |
| SMGI[ | 7, 60 | 0.4 | 1666.66 | − | 75% (0.05 mol/L HCl, 5) | EA | L/F/PSO |
| NH2/β-CD/NH2/β-CD MGO[ | 6.5, 75 | − | 296.16 | − | − (0.1 mol/L HCl, 5) | SC | F/PSO |
Table 3 Adsorption characteristics of magnetization-modified GO-based adsorbents for Pb(II)[54-61]
| Adsorbent | Adsorption condition | Adsorption capacity/ (mg·g−1) | Removal efficiency/% | Removal efficiency after desorption (desorption agent, cycle number) | Adsorption mechanism | Isotherm /kinetic model | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH, time/min | Dosage/ (g·L−1) | ||||||
| MZIF-8/GO2[ | 4−6, 10 | 0.4 | 625 | 99 | − | − | L/PSO |
| PPy-FG[ | 5, 180 | 0.4 | 93.2 | 85.7 | 85.7% (0.2 mol/L HNO3, 5) | − | L/PSO |
| Fe3O4@C-GO-MOF[ | 6, 60 | 1 | 344.83 | 87 | >85% (5% (in volume) HNO3, 5) | SC | L/PSO |
| MnFe2O4@SiO2-NH2@GO[ | 6.5, 30 | 0.5 | 42.48 | 99.8 | − (0.3 mol/L HCl, 5) | SC | L/PSO |
| MCGO[ | 8, 44 | 0.5 | 372.24 | 93.06 | 68.9% (−, 5) | EA | L/PSO |
| MgFe2O4-NGO[ | 7, 120 | 1 | 930 | 99.7 | 83.6% (0.1 mol/L HCl, 6) | SC, EA, PA | L/PSO |
| SMGI[ | 7, 60 | 0.4 | 1666.66 | − | 75% (0.05 mol/L HCl, 5) | EA | L/F/PSO |
| NH2/β-CD/NH2/β-CD MGO[ | 6.5, 75 | − | 296.16 | − | − (0.1 mol/L HCl, 5) | SC | F/PSO |
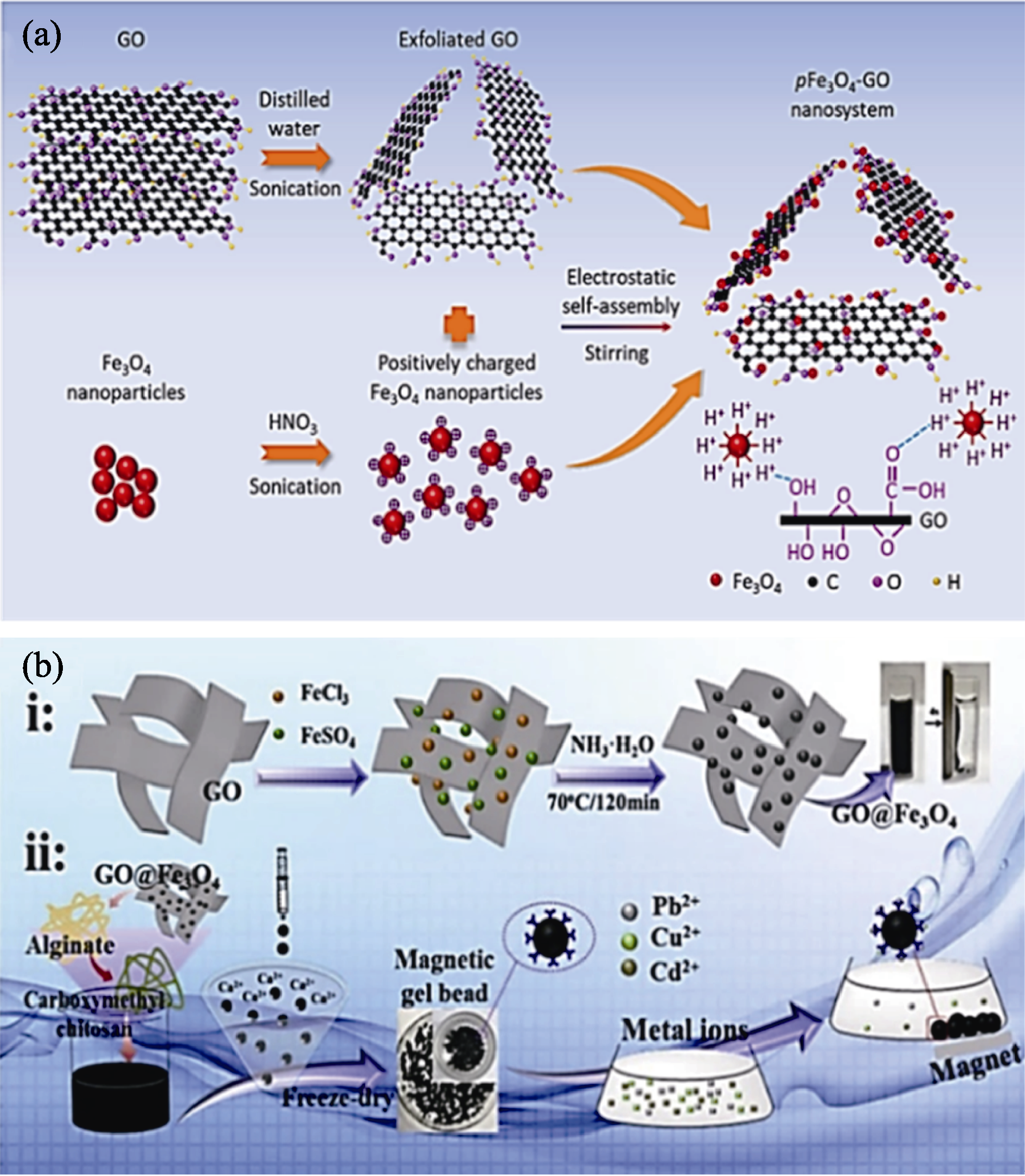
Fig. 5 Schematic diagrams of synthesis routes of different MGO nanocomposites[67,69] (a) pFe3O4-GO[67]; (b) CMC/SA/GO@Fe3O4 (including its adsorption process for Pb(II))[69]
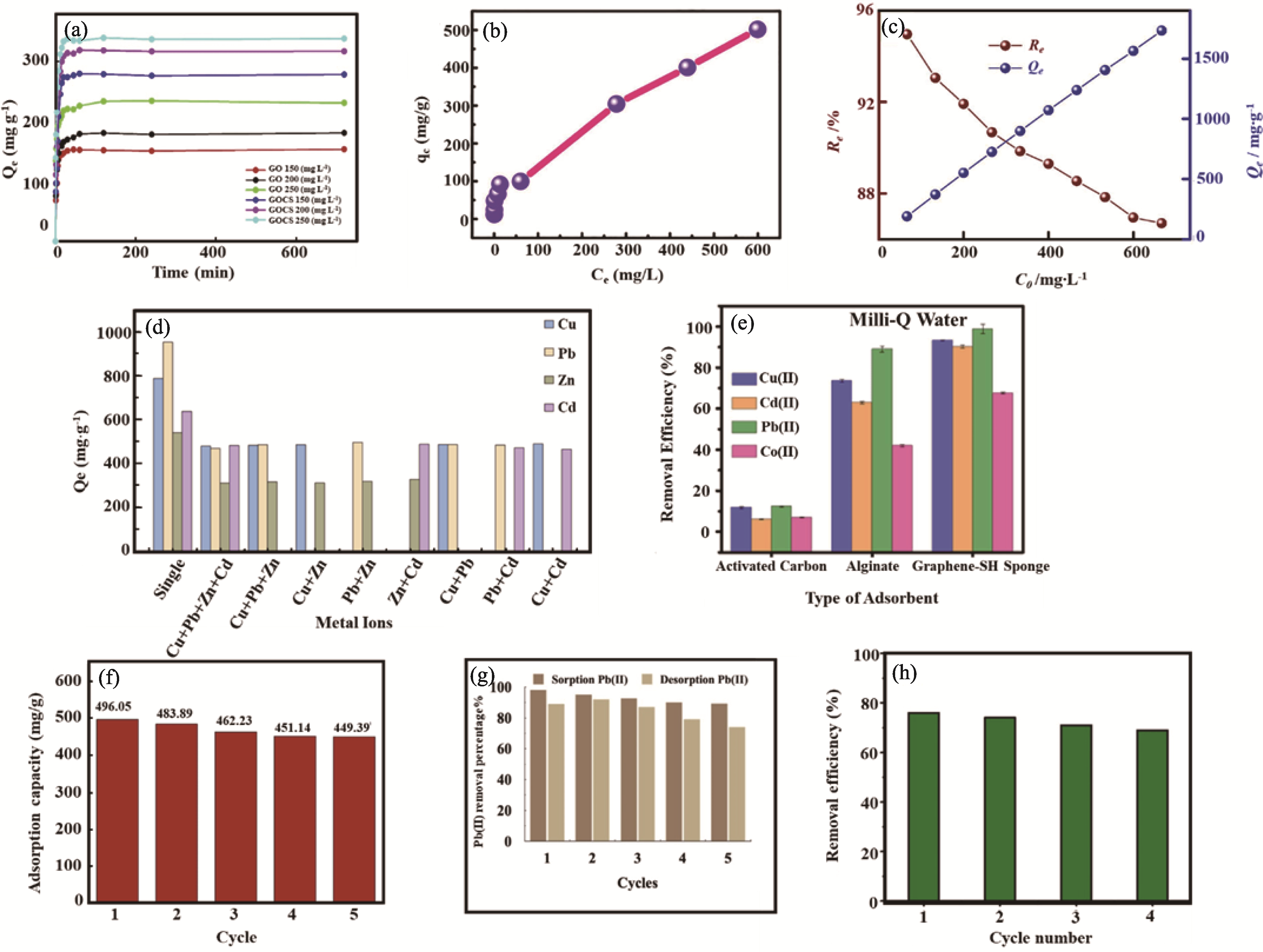
Fig. 6 Adsorption performance of different GO-based adsorbents[29-30,54,71 -72,83 -84,87] (a) Effects of contact time and initial concentration on lead adsorption by GO and GOCS[29]; (b) Effect of Pb(II) initial concentration on adsorption capacity of 3D CA/GO for Pb(II)[71]; (c) Effect of Pb(II) initial concentration on adsorption efficiency of MCGO for Pb(II)[54]; (d) Competitive adsorption of Cu(II), Pb(II), Zn(II), and Cd(II) ions on GO/P(AA-co-AM)[83]; (e) Selectivity of multiple metal ions for SH-graphene bio-sponge in comparison with activated carbon and alginate sponge[30]; (f-h) Recyclability of (f) GOLA[72], (g) GO-MBT[87] and (h) GFC nanosorbent[84] for Pb(II) removal
| Adsorbent | Adsorption condition | Adsorptioncapacity/ (mg·g−1) | Removal efficiency/% | Removal efficiency after desorption (desorption agent, cycle number) | Adsorption mechanism | Isotherm/ kinetic model | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH, time/min | Dosage/ (g·L−1) | ||||||
| OSH[ | 8, 70 | 12 | 6.1 | − | 87% (0.1 mol/L HCl, 3) | EA | F/PSO |
| Zeolite[ | 6, 24 h | 1 | 14 | − | − | PA | L/PSO |
| Calcined MCM-41[ | 5, 120 | 4 | 18.8 | − | − | PA | F/PSO |
| Cu0.5Mg0.5Fe2O4[ | 7, 180 | 2 | 57.7 | 97 | ~90% (2 mol/L NaOH, 5) | − | L/PSO |
| AC/MIL-101(Al)[ | 6, 90 | 0.6 | 241 | − | 92.6% (HCl, 4) | EA, SC, IE | L/PSO |
| Ceramsite[ | 6, 750 | 12 | 46.7 | − | >80% (0.03 mol/L HCl/NaOH, 5) | IE, EA | L/PSO |
| AC from peanut shells[ | 4.5, 50 | 2 | 130.89 | 95 | 66% (NaCl, 4) | EA, IE, PA | L/PSO |
| FmB[ | 6.5, 180 | 1 | 73.68 | 95 | >41.2% (0.1 mol/L HCl, −) | EA, IE | L/PSO |
| PAANa[ | −, 170 | 10 | 173.6 | − | − | IE | F/L/PSO |
| GOLA[ | 5, 20 | 0.12 | 505.8 | − | 90.6% (HNO3, −) | SC | L/PSO |
| 3D CA/GO[ | 3, 240 | 0.4 | 490.2 | 99.8 | 91.6% (1 mol/L HCl, 8) | EA, SC, IE | F/PSO |
| Pip@MGO[ | 6, 27.5 | 0.7 | 558.2 | − | >90% (1 mol/L HNO3, 4) | SC, IE | − |
| FeGO-TiLa[ | 6, 120 | 2 | 109.89 | 93 | 71% (0.1 mol/L HCl, 10) | EA | L/PSO |
Table 4 Comparsion on Pb(II) removal performance of GO-based and other adsorbents[68,71 -82]
| Adsorbent | Adsorption condition | Adsorptioncapacity/ (mg·g−1) | Removal efficiency/% | Removal efficiency after desorption (desorption agent, cycle number) | Adsorption mechanism | Isotherm/ kinetic model | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH, time/min | Dosage/ (g·L−1) | ||||||
| OSH[ | 8, 70 | 12 | 6.1 | − | 87% (0.1 mol/L HCl, 3) | EA | F/PSO |
| Zeolite[ | 6, 24 h | 1 | 14 | − | − | PA | L/PSO |
| Calcined MCM-41[ | 5, 120 | 4 | 18.8 | − | − | PA | F/PSO |
| Cu0.5Mg0.5Fe2O4[ | 7, 180 | 2 | 57.7 | 97 | ~90% (2 mol/L NaOH, 5) | − | L/PSO |
| AC/MIL-101(Al)[ | 6, 90 | 0.6 | 241 | − | 92.6% (HCl, 4) | EA, SC, IE | L/PSO |
| Ceramsite[ | 6, 750 | 12 | 46.7 | − | >80% (0.03 mol/L HCl/NaOH, 5) | IE, EA | L/PSO |
| AC from peanut shells[ | 4.5, 50 | 2 | 130.89 | 95 | 66% (NaCl, 4) | EA, IE, PA | L/PSO |
| FmB[ | 6.5, 180 | 1 | 73.68 | 95 | >41.2% (0.1 mol/L HCl, −) | EA, IE | L/PSO |
| PAANa[ | −, 170 | 10 | 173.6 | − | − | IE | F/L/PSO |
| GOLA[ | 5, 20 | 0.12 | 505.8 | − | 90.6% (HNO3, −) | SC | L/PSO |
| 3D CA/GO[ | 3, 240 | 0.4 | 490.2 | 99.8 | 91.6% (1 mol/L HCl, 8) | EA, SC, IE | F/PSO |
| Pip@MGO[ | 6, 27.5 | 0.7 | 558.2 | − | >90% (1 mol/L HNO3, 4) | SC, IE | − |
| FeGO-TiLa[ | 6, 120 | 2 | 109.89 | 93 | 71% (0.1 mol/L HCl, 10) | EA | L/PSO |
| [28] |
PIRVEYSIAN M, GHIACI M. Synthesis and characterization of sulfur functionalized graphene oxide nanosheets as efficient sorbent for removal of Pb2+, Cd2+, Ni2+ and Zn2+ ions from aqueous solution: a combined thermodynamic and kinetic studies. Applied Surface Science, 2018, 428: 98.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
LIAN Q Y, AHMAD Z U, GANG D D, et al. The effects of carbon disulfide driven functionalization on graphene oxide for enhanced Pb(II) adsorption: investigation of adsorption mechanism. Chemosphere, 2020, 248: 126078.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
YAP P L, AUYOONG Y L, HASSAN K, et al. Multithiol functionalized graphene bio-sponge via photoinitiated thiol-ene click chemistry for efficient heavy metal ions adsorption. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 395: 124965.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
REZANIA S, MOJIRI A, PARK J, et al. Removal of lead ions from wastewater using lanthanum sulfide nanoparticle decorated over magnetic graphene oxide. Environmental Research, 2022, 204: 111959.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
DIAGBOYA P N, MMAKO H K, DIKIO E D, et al. Synthesis of amine and thiol dual functionalized graphene oxide for aqueous sequestration of lead. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2019, 7(6): 103461.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
HUANG H Y, WANG Y, ZHANG Y B, et al. Amino-functionalized graphene oxide for Cr(VI), Cu(II), Pb(II) and Cd(II) removal from industrial wastewater. Open Chemistry, 2020, 18(1): 97.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
BAKRY A M, AMRI N, ADLY M S, et al. Remediation of water containing lead(II) using (3-iminodiacetic acid) propyltriethoxysilane grapheneoxide. Scientific Reports, 2024, 14: 18848.
DOI |
| [35] |
ZOU L, SHANG W, MIN T T, et al. Efficient removal of Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions from wastewater using amidoxime functionalized graphene oxide. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2025, 103(2): 799.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
LOH N Y L, TEE W T, HANSON S, et al. Enhanced removal of lead and zinc by a 3D aluminium sulphate-functionalised graphene aerogel as an effective adsorption system. Chemosphere, 2024, 362: 142537.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
XING C J, XIA A Q, YU L, et al. Enhanced removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solution using EDTA-modified magnetic graphene oxide. CLEAN - Soil, Air, Water, 2021, 49(4): 2000272.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
MANZOOR Q, FARRUKH M A, SAJID A. Optimization of lead (II) and chromium (VI) adsorption using graphene oxide/ZnO/chitosan nanocomposite by response surface methodology. Applied Surface Science, 2024, 655: 159544.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
KONG L, LI Z C, HUANG X Q, et al. Efficient removal of Pb(II) from water using magnetic Fe3S4/reduced graphene oxide composites. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(36): 19333.
DOI URL |
| [40] | ZHANG H N, LIU X M, TIAN L H, et al. Preparation of functionalized graphene oxide composite spheres and removal of Cu2+ and Pb2+ from wastewater. Water,Air, & Soil Pollution, 2022, 233(12): 512. |
| [41] |
TENG J, ZENG X, XU X, et al. Assembly of a novel porous 3D graphene oxide-starch architecture by a facile hydrothermal method and its adsorption properties toward metal ions. Materials Letters, 2018, 214: 31.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
LI Z S, LI B L, DU L J, et al. Three-dimensional oxygen-doped porous graphene: sodium chloride-template preparation, structural characterization and supercapacitor performances. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2021, 40: 304.
DOI |
| [43] |
LIU Z J, ZHANG W H, YIN M J, et al. Tailored GO nanosheets for porous framework to high CO2 adsorption. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 498: 155127.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
OLEJNICZAK A, RYMZHANOV R A. From nanohole to ultralong straight nanochannel fabrication in graphene oxide with swift heavy ions. Nature Communications, 2023, 14: 889.
DOI PMID |
| [45] |
LI B L, LI Z S, PANG Q, et al. Synthesis and characterization of activated 3D graphene via catalytic growth and chemical activation for electrochemical energy storage in supercapacitors. Electrochimica Acta, 2019, 324: 134878.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
WU T R, MOGHADAM F, LI K. High-performance porous graphene oxide hollow fiber membranes with tailored pore sizes for water purification. Journal of Membrane Science, 2022, 645: 120216.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
KONG F X, YOU L, CAO J M, et al. Effect of etching and reduction time on the structure, performance, and stability of GO-based membrane for water purification. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2023, 11(1): 109215.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
LI Y, ZHAO W, WEYLAND M, et al. Thermally reduced nanoporous graphene oxide membrane for desalination. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(14): 8314.
DOI URL |
| [49] | CHENG J H, GAO M L, YANG L, et al. Coral-inspired “nanotentaclization” porous composite gel for efficient removal of lead(II) from aqueous solution. Materials & Design, 2020, 195: 109072. |
| [50] |
MOHARRAM M A K, TOHAMI K, EL HOTABY W M, et al. Graphene oxide porous crosslinked cellulose nanocomposite microspheres for lead removal: kinetic study. Reactive and Functional Polymers, 2016, 101: 9.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
ZHANG X X, XU J, ZHANG Z J, et al. Pb(II) adsorption properties of a three-dimensional porous bacterial cellulose/graphene oxide composite hydrogel subjected to ultrasonic treatment. Materials, 2024, 17(13): 3053.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
PACHIYAPPAN J, GNANASUNDARAM N. Using graphene oxide-silica [GO-Si] nano composite adsorbent, removal of heavy metal ions (lead and mercury) from industrial wastewater and analysing its performance. Rasayan Journal of Chemistry, 2020, 13(3): 2027.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
HE Y Q, ZHANG N N, WANG X D. Adsorption of graphene oxide/chitosan porous materials for metal ions. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2011, 22(7): 859.
DOI |
| [54] |
GUO T, BULIN C K, LI C N, et al. Experimental and statistical physics illumination of Pb(II) adsorption on magnetic chitosan- graphene oxide surface. Separation and Purification Technology, 2025, 354: 128867.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
KIREETI K V M K, CHANDRAKANTH G, KADAM M M, et al. A sodium modified reduced graphene oxide-Fe3O4 nanocomposite for efficient lead(II) adsorption. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(88): 84825.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
AHMAD S Z N, SALLEH W N W, YUSOF N, et al. Efficiency of magnetic zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8) modified graphene oxide for lead adsorption. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2025, 32: 19302.
DOI |
| [57] |
LIU Z M, GAO Z M, XU L C, et al. Polypyrrole modified magnetic reduced graphene oxide composites: synthesis, characterization and application for selective lead adsorption. RSC Advances, 2020, 10(30): 17524.
DOI PMID |
| [1] |
ABDELWAHEB M, JEBALI K, DHAOUADI H, et al. Adsorption of nitrate, phosphate, nickel and lead on soils: risk of groundwater contamination. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 179: 182.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
YAO X, STEVEN X X, YANG Y N, et al. Stratification of population in NHANES 2009-2014 based on exposure pattern of lead, cadmium, mercury, and arsenic and their association with cardiovascular, renal and respiratory outcomes. Environment International, 2021, 149: 106410.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
SALL M L, DIAW A K D, GNINGUE-SALL D, et al. Toxic heavy metals: impact on the environment and human health, and treatment with conducting organic polymers, a review. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2020, 27(24): 29927.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
JOSHI N C, GURURANI P. Advances of graphene oxide based nanocomposite materials in the treatment of wastewater containing heavy metal ions and dyes. Current Research in Green and Sustainable Chemistry, 2022, 5: 100306.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
CHOUDHARI U, RAMGIR N, VAGHELA C, et al. Sensitive and selective electrochemical lead sensor: a synergistic effect of nanobiocomposite. Microchemical Journal, 2024, 202: 110763.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
KAUR S, ROY A. Bioremediation of heavy metals from wastewater using nanomaterials. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 2021, 23(7): 9617.
DOI |
| [7] |
张海虎, 呙润华, 刘喜杰. 改性氧化石墨烯的制备及应用研究进展. 化工新型材料, 2022, 50(12): 12.
DOI |
| [8] | 张笑娟, 魏琦峰, 任秀莲. 氧化石墨烯的制备方法、结构、性质及应用研究进展. 应用化工, 2022, 51(7): 2106. |
| [9] |
GAIDUKEVIC J, AUKSTAKOJYTE R, NAVICKAS T, et al. A novel approach to prepare highly oxidized graphene oxide: structural and electrochemical investigations. Applied Surface Science, 2021, 567: 150883.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
AZIZ K H H, MUSTAFA F S, OMER K M, et al. Heavy metal pollution in the aquatic environment: efficient and low-cost removal approaches to eliminate their toxicity: a review. RSC Advances, 2023, 13(26): 17595.
DOI PMID |
| [11] | 陈玥琪, 张震斌, 单凤君. 氧化石墨烯及其复合材料对重金属离子的吸附研究进展. 辽宁工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 42(5): 325. |
| [58] |
WANG Y, LIN K, LIU Y, et al. Nanocomposites of functionalized metal-organic frameworks and magnetic graphene oxide for selective adsorption and efficient determination of lead(II). Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2022, 313: 123300.
DOI URL |
| [59] |
HOU L, QIN G J, QU Y Q, et al. Fabrication of recoverable magnetic composite material based on graphene oxide for fast removal of lead and cadmium ions from aqueous solution. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology, 2021, 96(5): 1345.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
KAUR M, KAUR M, SINGH D, et al. Magnesium ferrite- nitrogen-doped graphene oxide nanocomposite: effective adsorptive removal of lead(II) and arsenic(III). Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2022, 29(32): 48260.
DOI |
| [61] |
JAVANMIRPOURSHIRZADI Z, HARGALANI F Z, ROBATI M, et al. Removal of lead (II) from aqueous solutions using β-cyclodextrin functionalized magnetic graphene oxide nanocomposite, performance, and optimization with response surface methodology. Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 2023, 25(7): 131.
DOI |
| [62] |
TANG T T, CAO S R, XI C X, et al. Chitosan functionalized magnetic graphene oxide nanocomposite for the sensitive and effective determination of alkaloids in hotpot. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2020, 146: 343.
DOI PMID |
| [63] |
CHAI D, CHEN Y, JIANG Z, et al. Insight on magnetic nitrogen-doped graphene oxide composite electrode constructing heterogeneous electro-Fenton system for treating organophosphorus pesticide wastewater. Separation and Purification Technology, 2024, 345: 127419.
DOI URL |
| [64] |
HE Y, YI C, ZHANG X L, et al. Magnetic graphene oxide: synthesis approaches, physicochemical characteristics, and biomedical applications. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2021, 136: 116191.
DOI URL |
| [65] |
LI S, JI J, SHAN S, et al. Efficient adsorption removal of tetrabromobisphenol A from water by using a magnetic composite Fe3O4/GO/ZIF-67. Crystals, 2024, 14(6): 508.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
BERTRAN A, SANDOVAL S, ORÓ-SOLÉ J, et al. Particle size determination from magnetization curves in reduced graphene oxide decorated with monodispersed superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2020, 566: 107.
DOI PMID |
| [67] |
YANG W J, ZHONG Y C, HE C X, et al. Electrostatic self-assembly of pFe3O4 nanoparticles on graphene oxide: a co-dispersed nanosystem reinforces PLLA scaffolds. Journal of Advanced Research, 2020, 24: 191.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
ZHANG L, ZHANG Z, WANG L, et al. Mechanism and application of sulfhydryl-modified chitosan derivative for decontamination of Pb(II) and Cd(II) in water bodies. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2025, 306: 141535.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
ARYEE A A, MPATANI F M, HAN R P, et al. A review on adsorbents for the remediation of wastewater: antibacterial and adsorption study. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2021, 9(6): 106907.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
YAN H, HU W H, CHENG S, et al. Microwave-assisted preparation of manganese dioxide modified activated carbon for adsorption of lead ions. Water Science and Technology, 2020, 82(1): 170.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
NEOLAKA Y A B, RIWU A A P, AIGBE U O, et al. Potential of activated carbon from various sources as a low-cost adsorbent to remove heavy metals and synthetic dyes. Results in Chemistry, 2023, 5: 100711.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
BESSA R A, FRANÇA A M M, PEREIRA A L S, et al. Hierarchical zeolite based on multiporous zeolite A and bacterial cellulose: an efficient adsorbent of Pb2+. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2021, 312: 110752.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
NEOLAKA Y A B, SUPRIYANTO G, KUSUMA H S. Adsorption performance of Cr(VI)-imprinted poly(4-VP-co-MMA) supported on activated Indonesia (Ende-Flores) natural zeolite structure for Cr(VI) removal from aqueous solution. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2018, 6(2): 3436.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
WANG S F, LI X, LIU Y G, et al. Nitrogen-containing amino compounds functionalized graphene oxide: synthesis, characterization and application for the removal of pollutants from wastewater: a review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2018, 342: 177.
DOI PMID |
| [19] |
YANG X D, WAN Y S, ZHENG Y L, et al. Surface functional groups of carbon-based adsorbents and their roles in the removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions: a critical review. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 366: 608.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
TIWARI S K, SAHOO S, WANG N, et al. Graphene research and their outputs: status andprospect. Journal of Science: Advanced Materials and Devices, 2020, 5(1): 10.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
JIANG X, RUAN G, HUANG Y, et al. Assembly and application advancement of organic-functionalized graphene-based materials: a review. Journal of Separation Science, 2020, 43(8): 1544.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
FEIST B, PILCH M, NYCZ J. Graphene oxide chemically modified with 5-amino-1,10-phenanthroline as sorbent for separation and preconcentration of trace amount of lead(II). Microchimica Acta, 2019, 186(2): 91.
DOI |
| [23] |
ARCHANA S, RADHIKA D, JAYANNA B K, et al. Functionalization and partial grafting of the reduced graphene oxide with p-phenylenediamine: an adsorption and photodegradation studies. FlatChem, 2021, 26: 100210.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
ZHENG B, CHU X X, LI H, et al. Layered graphene oxide membranes functioned by amino acids for efficient separation of metal ions. Applied Surface Science, 2021, 546: 149145.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
HUANG R J, SHAO N, HOU L, et al. Fabrication of an efficient surface ion-imprinted polymer based on sandwich-like graphene oxide composite materials for fast and selective removal of lead ions. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2019, 566: 218.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
SAHU P S, VERMA R P, DABHADE A H, et al. A novel, efficient and economical alternative for the removal of toxic organic, inorganic and pathogenic water pollutants using GO-modified PU granular composite. Environmental Pollution, 2023, 328: 121201.
DOI URL |
| [27] | ZARENEZHAD M, ZAREI M, EBRATKHAHAN M, et al. Synthesis and study of functionalized magnetic graphene oxide for Pb2+ removal from wastewater. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 2021, 22: 101384. |
| [68] |
DE ANDRADE M B, GUERRA A C S, DOS SANTOS T R T, et al. Simplified synthesis of new GO-α-γ-Fe2O3-Sh adsorbent material composed of graphene oxide decorated with iron oxide nanoparticles applied for removing diuron from aqueous medium. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2020, 8(4): 103903.
DOI URL |
| [69] |
WU Z G, DENG W J, ZHOU W, et al. Novel magnetic polysaccharide/graphene oxide @Fe3O4 gel beads for adsorbing heavy metal ions. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2019, 216: 119.
DOI URL |
| [70] |
AZAM M G, KABIR M H, SHAIKH M A A, et al. A rapid and efficient adsorptive removal of lead from water using graphene oxide prepared from waste dry cell battery. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2022, 46: 102597.
DOI URL |
| [71] |
WANG N, SONG F X, NIU Y X, et al. Three-dimensional-printed calcium alginate/graphene oxide porous adsorbent with super-high lead ion adsorption ability in aqueous solution. Separation and Purification Technology, 2023, 326: 124757.
DOI URL |
| [72] |
ZHANG C Z, JIN R H, SHEN Q Q, et al. Synthesis of graphene oxide grafted by diazanyl groups and its application in recovery of lead from lead-acid wastewater. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2023, 30(11): 29844.
DOI |
| [73] |
ALBOGHBEISH M, LARKI A, SAGHANEZHAD S J. Effective removal of Pb(II) ions using piperazine-modified magnetic graphene oxide nanocomposite; optimization by response surface methodology. Scientific Reports, 2022, 12(1): 9658.
DOI PMID |
| [74] | RAKHYM A B, SEILKHANOVA G A, KURMANBAYEVA T S. Adsorption of lead (II) ions from water solutions with natural zeolite and chamotte clay. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2020, 31: 482. |
| [75] |
WEI H, SONG B, HUAN Q, et al. Preparation of iron tailings-based porous ceramsite and its application to lead adsorption: characteristic and mechanism. Separation and Purification Technology, 2024, 342: 126839.
DOI URL |
| [76] |
TRAN C V, QUANG D V, THI H P N, et al. Effective removal of Pb(II) from aqueous media by a new design of Cu-Mg binary ferrite. ACS Omega, 2020, 5(13): 7298.
DOI PMID |
| [77] |
HASHEM H M, EL-MAGHRABEY M, EL-SHAHENY R. Inclusive study of peanut shells derived activated carbon as an adsorbent for removal of lead and methylene blue from water. Scientific Reports, 2024, 14(1): 13515.
DOI PMID |
| [78] |
CHEN Z H, YU C, DONG H F, et al. Sorption-desorption characteristics and internal mechanism of lead ions on polycarboxylic ion exchange resin. Journal of Polymer Research, 2022, 29(12): 512.
DOI |
| [79] | KAUR M, KUMARI S, SHARMA P. Removal of Pb (II) from aqueous solution using nanoadsorbent of Oryza sativa husk: isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Biotechnology Reports, 2020, 25: e00410. |
| [80] |
PUTZ A M, IVANKOV O I, KUKLIN A I, et al. Ordered mesoporous silica prepared in different solvent conditions: application for Cu(II) and Pb(II) adsorption. Gels, 2022, 8(7): 443.
DOI URL |
| [81] |
YAZEED E W S A, MANSOUR B N H, IBRAHIM A A, et al. Activated carbon encapsulated aluminum metal-organic frameworks as an active and recyclable adsorbent for removal of different dyes and lead from aqueous solution. Inorganic Chemistry Communications, 2025, 171: 113558.
DOI URL |
| [82] |
MOSLEH N, AHRANJANI P J, PARANDI E, et al. Titanium lanthanum three oxides decorated magnetic graphene oxide for adsorption of lead ions from aqueous media. Environmental Research, 2022, 214: 113831.
DOI URL |
| [83] |
LIU M, WANG Y, WU Y J, et al. Preparation of graphene oxide hydrogels and their adsorption applications toward various heavy metal ions in aqueous media. Applied Sciences, 2023, 13(21): 11948.
DOI URL |
| [84] | VO L Q, VU A T, LE T D, et al. Fe3O4/graphene oxide/chitosan nanocomposite: a smart nanosorbent for lead(II) ion removal from contaminated water. ACS Omega, 2024, 9(15): 17506. |
| [85] |
BAKHTIARI S, SALARI M, SHAHRASHOUB M, et al. A comprehensive review on green and eco-friendly nano-adsorbents for the removal of heavy metal ions: synthesis, adsorption mechanisms, and applications. Current Pollution Reports, 2024, 10: 1.
DOI |
| [86] |
NICOLA R, COSTIŞOR O, CIOPEC M, et al. Silica-coated magnetic nanocomposites for Pb2+ removal from aqueous solution. Applied Sciences, 2020, 10(8): 2726.
DOI URL |
| [87] |
BHARDWAJ M, TEWARI S, KUMARI N, et al. Adsorption of Pb(II) and Cd(II) by functionalized graphene oxide (GO-MBT): mechanisms, antibacterial activity, and DFT studies. Inorganic Chemistry Communications, 2024, 164: 112464.
DOI URL |
| [88] |
WU W P, GE H C. Preparation of amino-silane and thiosemicarbazide modified graphene oxide composite for high uptake adsorption of Hg(II) and Pb(II). Journal of Dispersion Science and Technology, 2025, 46(7): 1059.
DOI URL |
| [89] |
ZHOU C Y, LI B H, LI Y F, et al. A review of graphene oxide-based adsorbents for removing lead ions in water. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2024, 12(1): 111839.
DOI URL |
| [90] |
WU B L, WAN J, ZHANG Y Y, et al. Selective phosphate removal from water and wastewater using sorption: process fundamentals and removal mechanisms. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(1): 50.
DOI URL |
| [91] | GONZÁLEZ-HERRERO H, RÍO E C, MALLET P, et al. Hydrogen physisorption channel on graphene: a highway for atomic H diffusion. 2D Materials, 2019, 6(2): 021004. |
| [92] | SHARMA P, SINGH A K, SHAHI V K. Selective adsorption of Pb(II) from aqueous medium by cross-linked chitosan-functionalized graphene oxide adsorbent. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2019, 7(1): 1427. |
| [93] |
WEI M P, CHAI H, CAO Y L, et al. Sulfonated graphene oxide as an adsorbent for removal of Pb2+ and methylene blue. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2018, 524: 297.
DOI URL |
| [94] |
FAN Y Z, DONG J X, ZHANG Y, et al. A smartphone-coalesced nanoprobe for high selective ammonia sensing based on the pH-responsive biomass carbon nanodots and headspace single drop microextraction. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2019, 219: 382.
DOI URL |
| [95] |
FAN Y Z, TANG Q, LIU S G, et al. A smartphone-integrated dual-mode nanosensor based on novel green-fluorescent carbon quantum dots for rapid and highly selective detection of 2,4,6- trinitrophenol and pH. Applied Surface Science, 2019, 492: 550.
DOI URL |
| [96] |
DONG X Y, GAO X, SONG J Q, et al. A novel dispersive magnetic solid phase microextraction using ionic liquid-coated amino silanized magnetic graphene oxide nanocomposite for high efficient separation/preconcentration of toxic ions from shellfish samples. Food Chemistry, 2021, 360: 130023.
DOI URL |
| [97] |
CAO Z F, WEN X, WANG J, et al. In situ nano-Fe3O4/ triisopropanolamine functionalized graphene oxide composites to enhance Pb2+ ions removal. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2019, 561: 209.
DOI URL |
| [98] |
HUSEIN D Z, HASSANIEN R, KHAMIS M. Cadmium oxide nanoparticles/graphene composite: synthesis, theoretical insights into reactivity and adsorption study. RSC Advances, 2021, 11(43): 27027.
DOI PMID |
| [99] |
LALMI A, BOUHIDEL K E, SAHRAOUI B, et al. Removal of lead from polluted waters using ion exchange resin with Ca(NO3)2 for elution. Hydrometallurgy, 2018, 178: 287.
DOI URL |
| [100] |
FAN Y Z, HAN L, LIU S G, et al. A ratiometric optical strategy for bromide and iodide ion sensing based on target-induced competitive coordination of a metal-organic nanosystem. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2020, 8(33): 11517.
DOI URL |
| [101] |
FAN Y Z, HAN L, YANG Y Z, et al. Multifunctional binding strategy on nonconjugated polymer nanoparticles for ratiometric detection and effective removal of mercury ions. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(16): 10270.
DOI URL |
| [102] |
LEMMA L, KIFLIE Z, KASSAHUN S K. Adsorption of Pb2+ and Cd2+ on the L-cysteine-functionalized graphene oxide/chitosan/ polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel: kinetic, isotherm, and thermodynamic study. Remediation Journal, 2023, 33(3): 233.
DOI URL |
| [103] | 周博秋, 李慧强, 廖维, 等. GO-LDH复合材料对水中铅离子的吸附性能. 中国给水排水, 2019, 35(17): 105. |
| [1] | WU Boyu, ZHANG Shengen, ZHANG Shengyang, LIU Bo, ZHANG Bolin. Effect of CeO2 on Low-temperature Denitrification Performance of MnOx Catalysts and Its Mechanism [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2026, 41(1): 87-95. |
| [2] | XU Jintao, GAO Pan, HE Weiyi, JIANG Shengnan, PAN Xiuhong, TANG Meibo, CHEN Kun, LIU Xuechao. Recent Progress on Preparation of 3C-SiC Single Crystal [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2026, 41(1): 1-11. |
| [3] | YU Shengyang, SU Haijun, JIANG Hao, YU Minghui, YAO Jiatong, YANG Peixin. A Review of Pore Defects in Ultra-high Temperature Oxide Ceramics by Laser Additive Manufacturing: Formation and Suppression [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(9): 944-956. |
| [4] | LI Fuping, CHU Jiabao, QIU Haibo, DANG Wei, LI Chenxi, ZHAO Kang, TANG Yufei. Compressive Resilience Mechanism of SiO2 Nanofibre Aerogels [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(9): 981-988. |
| [5] | LIU Jiangping, GUAN Xin, TANG Zhenjie, ZHU Wenjie, LUO Yongming. Research Progress on Catalytic Oxidation of Nitrogen-containing Volatile Organic Compounds [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(9): 933-943. |
| [6] | LI Ronghui, QIAN Jun. Nanocrystalline CeO2-ZrO2 Solid Solution: One-step Alcohothermal Synthesis and Arsenic Removal Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(9): 989-996. |
| [7] | XIAO Xiaolin, WANG Yuxiang, GU Peiyang, ZHU Zhenrong, SUN Yong. Advances in Regulation of Damaged Skin Regeneration by Two-dimensional Inorganic Materials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 860-870. |
| [8] | MA Jingge, WU Chengtie. Application of Inorganic Bioceramics in Promoting Hair Follicle Regeneration and Hair Growth [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 901-910. |
| [9] | ZHANG Hongjian, ZHAO Ziyi, WU Chengtie. Inorganic Biomaterials on Regulating Neural Cell Function and Innervated Tissue Regeneration: A Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 849-859. |
| [10] | AI Minhui, LEI Bo. Micro-nanoscale Bioactive Glass: Functionalized Design and Angiogenic Skin Regeneration [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 921-932. |
| [11] | WANG Yutong, CHANG Jiang, XU He, WU Chengtie. Advances in Silicate Bioceramic/Bioglass for Wound Healing: Effects, Mechanisms and Application Ways [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 911-920. |
| [12] | MA Wenping, HAN Yahui, WU Chengtie, LÜ Hongxu. Application of Inorganic Bioactive Materials in Organoid Research [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 888-900. |
| [13] | LUO Xiaomin, QIAO Zhilong, LIU Ying, YANG Chen, CHANG Jiang. Inorganic Bioactive Materials Regulating Myocardial Regeneration [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 871-887. |
| [14] | ZHU Wenjie, TANG Lu, LU Jichang, LIU Jiangping, LUO Yongming. Research Progress on Catalytic Oxidation of Volatile Organic Compounds by Perovskite Oxides [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [15] | WEI Jianwen, ZHANG Lijuan, GENG Linlin, LI Yu, LIAO Lei, WANG Dunqiu. Novel CO2 Adsorbent Prepared with ZSM-5/MCM-48 as Support: High Adsorption Property and Its Mechanism [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 833-839. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||