
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (9): 933-943.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240511
• REVIEW • Next Articles
LIU Jiangping1,2,3( ), GUAN Xin1,2,3, TANG Zhenjie1,2,3, ZHU Wenjie1,2,3, LUO Yongming2,3,4(
), GUAN Xin1,2,3, TANG Zhenjie1,2,3, ZHU Wenjie1,2,3, LUO Yongming2,3,4( )
)
Received:2024-12-10
Revised:2025-03-22
Published:2025-09-20
Online:2025-04-02
Contact:
LUO Yongming, professor. E-mail: environcatalysis@kust.edu.cnAbout author:LIU Jiangping (1991-), male, associate professor. E-mail: liujiangping@kust.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
LIU Jiangping, GUAN Xin, TANG Zhenjie, ZHU Wenjie, LUO Yongming. Research Progress on Catalytic Oxidation of Nitrogen-containing Volatile Organic Compounds[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(9): 933-943.
| N-VOCs | Catalyst | Conversion rate, temperature | N2 selectivity, temperature | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Triethylamine | CuO/Nb2O5-H | 100%, 220 ℃ | 96%, 220 ℃ | [ |
| Diethylamine | CuO/CeO2/ZSM-5 | 100%, 220 ℃ | 100%, 220 ℃ | [ |
| DMF | Cu-Ce/H-MOR | 99%, 220 ℃ | 100%, 220 ℃ | [ |
| DMF | Ag/CeO2 | 90%, 158 ℃ | 80%, 237 ℃ | [ |
| DMF | Cu-ZSM-5 | 100%, 300 ℃ | 95%, 300 ℃ | [ |
| Butylamine | Cu-Mn/ZSM-5 | 100%, 280 ℃ | >82%, 280 ℃ | [ |
| Butylamine | CeCu10%ZrOx | 100%, 250 ℃ | 90%, 250 ℃ | [ |
| Butylamine | Cu-ZSM-5 | 100%, 300 ℃ | >95%, 350 ℃ | [ |
| Butylamine | Cu-Mn/SAPO-34 | 90%, 279 ℃ | 99%, 279 ℃ | [ |
| Butylamine | CuO/Pd@SiO2 | 100%, 260 ℃ | 98.3%, 260 ℃ | [ |
| Acetonitrile | CuCeOx-HZSM-5 | 100%, 225 ℃ | 93%, 225 ℃ | [ |
| Acetonitrile | Cu-Ce/ZSM-5 | 100%, 300 ℃ | 90%, 300 ℃ | [ |
Table 1 Research status of N-VOCs catalytic oxidation in the last 5 years[40,49,54,59-67]
| N-VOCs | Catalyst | Conversion rate, temperature | N2 selectivity, temperature | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Triethylamine | CuO/Nb2O5-H | 100%, 220 ℃ | 96%, 220 ℃ | [ |
| Diethylamine | CuO/CeO2/ZSM-5 | 100%, 220 ℃ | 100%, 220 ℃ | [ |
| DMF | Cu-Ce/H-MOR | 99%, 220 ℃ | 100%, 220 ℃ | [ |
| DMF | Ag/CeO2 | 90%, 158 ℃ | 80%, 237 ℃ | [ |
| DMF | Cu-ZSM-5 | 100%, 300 ℃ | 95%, 300 ℃ | [ |
| Butylamine | Cu-Mn/ZSM-5 | 100%, 280 ℃ | >82%, 280 ℃ | [ |
| Butylamine | CeCu10%ZrOx | 100%, 250 ℃ | 90%, 250 ℃ | [ |
| Butylamine | Cu-ZSM-5 | 100%, 300 ℃ | >95%, 350 ℃ | [ |
| Butylamine | Cu-Mn/SAPO-34 | 90%, 279 ℃ | 99%, 279 ℃ | [ |
| Butylamine | CuO/Pd@SiO2 | 100%, 260 ℃ | 98.3%, 260 ℃ | [ |
| Acetonitrile | CuCeOx-HZSM-5 | 100%, 225 ℃ | 93%, 225 ℃ | [ |
| Acetonitrile | Cu-Ce/ZSM-5 | 100%, 300 ℃ | 90%, 300 ℃ | [ |
| Catalyst category | Vantage | Drawback | Representative substance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Precious metals | High catalytic activity and high stability | Scarce resources and high costs | Pt, Ag, Pd |
| Transition metals | High selectivity, reproducibility, and low costs | Inactivation issues and toxic by-products | Cu, Mn, Fe, Co, Al |
| Molecular sieves | High adsorption capacity, high selectivity, and high temperature resistance | Easy enrichment of NH3 on the surface of pure molecular sieves | ZSM-5, SBA-15 |
| Mineral materials | Unique structure, high adsorption capacity, and low costs | Many ingredients and impurities | Calcite, mullite, spinel |
| SACs | High atom utilization, high selectivity, and reproducibility | Being difficult to prepare | - |
Table 2 Comparison of different catalysts and their applications in catalytic oxidation of N-VOCs
| Catalyst category | Vantage | Drawback | Representative substance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Precious metals | High catalytic activity and high stability | Scarce resources and high costs | Pt, Ag, Pd |
| Transition metals | High selectivity, reproducibility, and low costs | Inactivation issues and toxic by-products | Cu, Mn, Fe, Co, Al |
| Molecular sieves | High adsorption capacity, high selectivity, and high temperature resistance | Easy enrichment of NH3 on the surface of pure molecular sieves | ZSM-5, SBA-15 |
| Mineral materials | Unique structure, high adsorption capacity, and low costs | Many ingredients and impurities | Calcite, mullite, spinel |
| SACs | High atom utilization, high selectivity, and reproducibility | Being difficult to prepare | - |
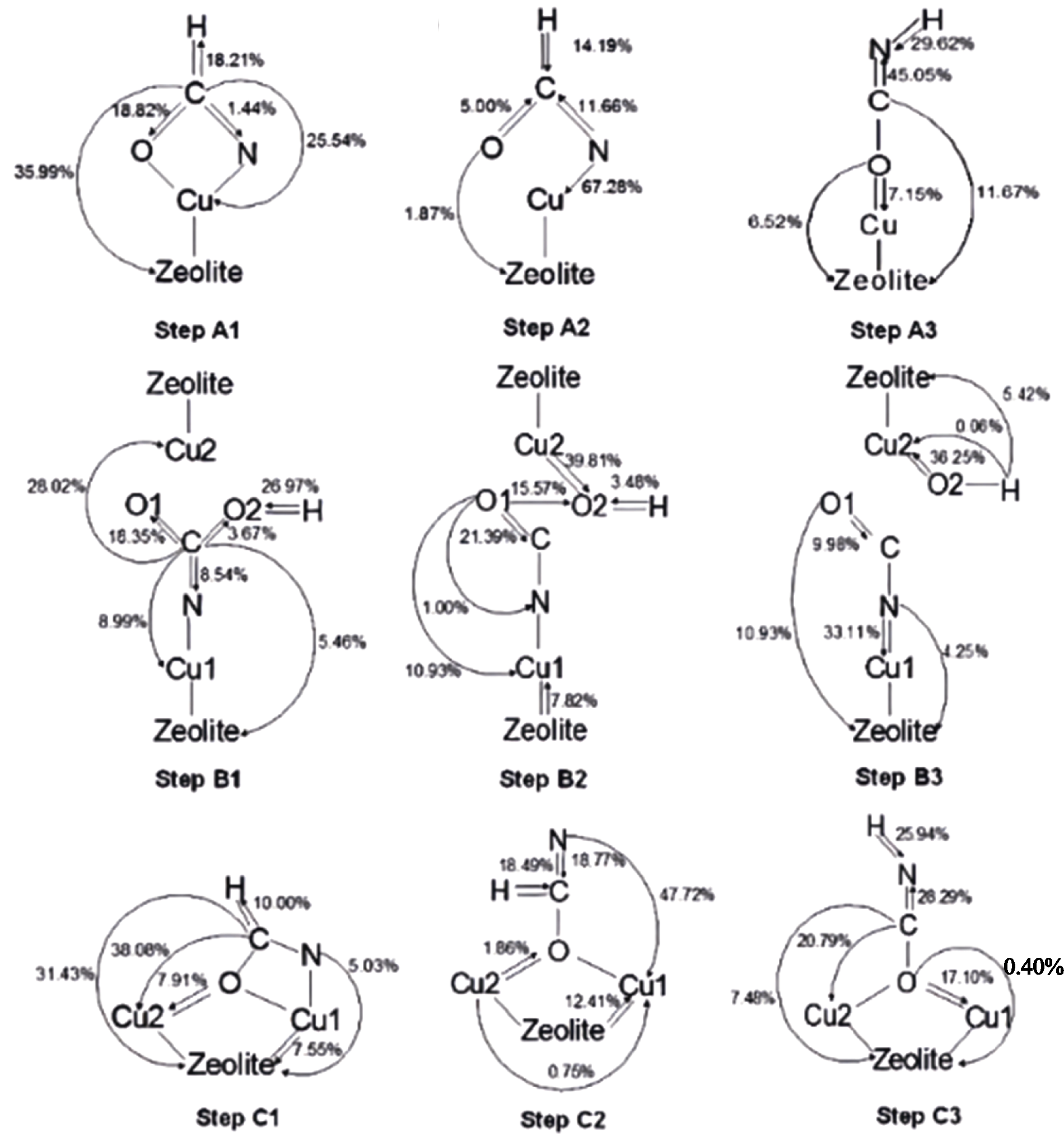
Fig. 6 CT diagram of models included in route I (oxidation of HCN into HNCO or NCO) over Cu-BEA with different active center structures of single [Cu]+, double [Cu]+ and [Cu-O-Cu]2+[81]
| [1] | 苏皓琳, 毕玉赞, 王一航. 空气中挥发性有机污染物的危害及处理工艺综述. 清洗世界, 2024, 40(8): 61. |
| [2] | 曲家福, 李佐习. 空气中挥发性有机污染物的危害及处理工艺综述. 苏州科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 39(3): 1. |
| [3] | 赵飞, 潘帅, 张冲冲. 石油化工行业VOCs治理技术综述. 山东化工, 2024, 53(4): 274. |
| [4] | 高鑫, 荆博宇, 吴琳, 等. 机动车尾气VOCs排放特征及影响因素研究进展. 环境科学与技术, 2023, 46(11): 69. |
| [5] | 潘玉梅, 张敏. 化工企业VOCs治理技术及对策研究. 山东化工, 2024, 53(2): 223. |
| [6] | DUAN X X, ZHAO T, YANG Z W, et al. Oxygen activation- boosted manganese oxide with unique interface for chlorobenzene oxidation: unveiling the roles and dynamic variation of active oxygen species in heterogeneous catalytic oxidation process. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2023, 331: 122719. |
| [7] | CHAI G T, ZHANG W D, LIOTTA L F, et al. Total oxidation of propane over Co3O4-based catalysts: elucidating the influence of Zr dopant. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2021, 298: 120606. |
| [8] | XING X, LI N, CHENG J, et al. Hydrotalcite-derived CuxMg3-xAlO oxides for catalytic degradation of n-butylamine with low concentration NO and pollutant-destruction mechanism. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2019, 58(22): 9362. |
| [9] | WU X Q, HAN R, LIU Q L, et al. A review of confined-structure catalysts in the catalytic oxidation of VOCs: synthesis, characterization, and applications. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2021, 11(16): 5374. |
| [10] | CUI W, CHEN H W, LIU D Q, et al. Mn/Co redox cycle promoted catalytic performance of mesoporous SiO2-confined highly dispersed LaMnxCo1-xO3 perovskite oxides in n-butylamine combustion. ChemistrySelect, 2020, 5(28): 8504. |
| [11] |
HE C, CHENG J, ZHANG X, et al. Recent advances in the catalytic oxidation of volatile organic compounds: a review based on pollutant sorts and sources. Chemical Reviews, 2019, 119(7): 4471.
DOI PMID |
| [12] | WU P, JIN X J, QIU Y C, et al. Recent progress of thermocatalytic and photo/thermocatalytic oxidation for VOCs purification over manganese-based oxide catalysts. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 55(8): 4268. |
| [13] | 王威. 化工行业VOCs废气治理措施分析. 石化技术, 2023, 30(9): 10. |
| [14] | 杨成. 贵阳市机动车大气污染物排放清单的初步研究. 贵阳: 贵州大学硕士学位论文, 2021. |
| [15] | 徐杏, 肖华, 周昕, 等. 畜禽场恶臭VOCs的产生及防控技术进展. 环境工程, 2020, 38(8): 180. |
| [16] | RAJ I, GUPTA A, BANSIWAL A, et al. A bench scale study on the startup, performance and optimization of the biological degradation of obnoxious air containing trimethylamine. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2020, 8(1): 103529. |
| [17] | 牛真真, 孔少飞, 严沁, 等. 薪柴和经济作物秸秆燃烧VOCs排放特征. 环境科学, 2020, 41(3): 1107. |
| [18] | 张靳杰. 武汉市机动车尾气VOCs和颗粒物排放特征研究. 武汉: 华中科技大学硕士学位论文, 2019. |
| [19] | 陈天增, 葛艳丽, 刘永春, 等. 我国机动车排放VOCs及其大气环境影响. 环境科学, 2018, 39(2): 478. |
| [20] | 郭文凯, 刘镇, 刘文博, 等. 兰州生物质燃烧VOCs排放特征及其大气环境影响. 中国环境科学, 2019, 39(1): 40. |
| [21] | 韩昕, 李相贤, 高闽光, 等. 基于SOF-FTIR的机场VOCs污染排放监测分析. 量子电子学报, 2019, 36(1): 101. |
| [22] | 黄碧捷. 武汉市秸秆燃烧VOCs排放估算及管理对策. 环境科学, 2013, 34(12): 4543. |
| [23] | 孙西勃, 廖程浩, 曾武涛, 等. 广东省秸秆燃烧大气污染物及VOCs物种排放清单. 环境科学, 2018, 39(9): 3995. |
| [24] | 张启钧, 吴琳, 刘明月, 等. 南京市机动车排放VOCs的污染特征与健康风险评价. 中国环境科学, 2016, 36(10): 3118. |
| [25] | ZHOU L L, MA C, HORLYCK J, et al. Development of pharmaceutical VOCs elimination by catalytic processes in China. Catalysts, 2020, 10(6): 668. |
| [26] | 程东风, 史彦辉, 张明成, 等. 煤基甲醇中三甲胺类杂质生成机理及脱除方法. 中氮肥, 2017(4): 39. |
| [27] | 胡丽雅. 苏码罐采样-气相色谱-质谱法测定环境空气中三甲胺的含量. 理化检验-化学分册, 2023, 59(4): 394. |
| [28] | 杨睿颖, 朱秋劲, 白晶, 等. 三甲胺表面增强拉曼光谱的密度泛函理论研究. 化学研究与应用, 2021, 33(5): 920. |
| [29] | YAN C, ZHONG M F, HAN J Q, et al. Efficient degradation of trimethylamine in gas phase by petal-shaped Co-MoS2 catalyst in the photo-electrochemical system. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 405: 127034. |
| [30] | 吕道飞, 林洁玲, 许锋, 等. 锌基金属有机框架材料对三甲胺的吸附性能研究. 南方水产科学, 2022, 18(6): 110. |
| [31] | QIU M, CHEN C, LI W. Rapid controllable synthesis of Al-MIL-96 and its adsorption of nitrogenous VOCs. Catalysis Today, 2015, 258: 132. |
| [32] | ZHANG K, DING H L, PAN W G, et al. Research progress of a composite metal oxide catalyst for VOC degradation. Environmental Science & Technology, 2022, 56(13): 9220. |
| [33] | 郭菊花. 生物法在挥发性有机废气处理中的应用研究. 清洗世界, 2023, 39(12): 91. |
| [34] | 李春生. 热力燃烧法处理电子元件厂VOCs研究. 广州化工, 2015, 43(3): 141. |
| [35] | 潘智超. 多相吸收法处理VOCs气体技术研究. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东)硕士学位论文, 2020. |
| [36] | 帅启凡, 董小平, 魏桃, 等. 工业废气中VOCs燃烧处理方法及发展趋势. 2020中国环境科学学会科学技术年会, 南京, 2020: 4411. |
| [37] | 张胜, 王忠海, 文旭, 等. 催化-醚化联合装置污水预处理站VOCs的处理. 化工技术与开发, 2023, 52(10): 91. |
| [38] | WANG F, HE G Z, ZHANG B, et al. Insights into the activation effect of H2 pretreatment on Ag/Al2O3 catalyst for the selective oxidation of ammonia. ACS Catalysis, 2019, 9(2): 1437. |
| [39] |
王嘉, 尤瑞, 千坤, 等. Cl-改性对Ag/Al2O3催化剂结构及其催化C3H6-SCR和H2/C3H6-SCR反应性能的影响. 催化学报, 2021, 42(12): 2242.
DOI |
| [40] | GUO X H, DONG C X, GAO M, et al. Crystal-facet-dependent activity and N2 yield of Ag/CeO2 catalysts for catalytic oxidation of N,N-dimethylformamide. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2024, 341: 123286. |
| [41] | HUANG F Y, YE D S, GUO X H, et al. Effect of ceria morphology on the performance of MnOx/CeO2 catalysts in catalytic combustion of N,N-dimethylformamide. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2020, 10(8): 2473. |
| [42] | ZHANG Y, LU J C, ZHANG L M, et al. Investigation into the catalytic roles of oxygen vacancies during gaseous styrene degradation process via CeO2 catalysts with four different morphologies. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2022, 309: 121249. |
| [43] | ZHANG Y Y, WANG Y X, LIU Y, et al. Insight into the role of cerium in the enhanced performances during catalytic combustion of acetonitrile over core-shell-like Cu-Ce/ZSM-5 catalysts. ACS ES&T Engineering, 2022, 2(9): 1709. |
| [44] | 刘凯鹏, 卢文新. 单原子催化的工业化挑战及现状. 化肥设计, 2023, 61(1): 1. |
| [45] | 刘佳程, 马廷灿. 单原子催化国际研究态势分析. 世界科技研究与发展, 2022, 44(5): 643. |
| [46] | 庄嘉豪, 王定胜. 单原子催化的关键进展与未来挑战. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(5): 31. |
| [47] | WANG Y W, ZHANG J, ZHANG Y F, et al. Single Fe atom- anchored manganese dioxide for efficient removal of volatile organic compounds in refrigerator. Nano Research, 2024, 17(5): 3927. |
| [48] | YE D S, CHENG L, GAO Y Z, et al. Modulating the Mn-O strength of OMS-2 by alkali metal doping for the catalytic oxidation of N,N-dimethylformamide. Separation and Purification Technology, 2024, 351: 128049. |
| [49] | XING X, LI N, LIU D D, et al. Effect of Cu-ZSM-5 catalysts with different CuO particle size on selective catalytic oxidation of N,N-dimethylformamide. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, 2022, 16(10): 125. |
| [50] | LU Y, HU C H, ZHANG W X, et al. Promoting the selective catalytic oxidation of diethylamine over MnOx/ZSM-5 by surface acid centers. Applied Surface Science, 2020, 521: 146348. |
| [51] | HU C H, FANG C T, LU Y, et al. Selective oxidation of diethylamine on CuO/ZSM-5 catalysts: the role of cooperative catalysis of CuO and surface acid sites. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2020, 59(20): 9432. |
| [52] | ZHANG R D, LI P X, XIAO R, et al. Insight into the mechanism of catalytic combustion of acrylonitrile over Cu-doped perovskites by an experimental and theoretical study. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2016, 196: 142. |
| [53] | WANG Y X, YING Q J, ZHANG Y Y, et al. Reaction behaviors of CH3CN catalytic combustion over CuCeOx-HZSM-5 composite catalysts: the mechanism of enhanced N2 selectivity. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2020, 590: 117373. |
| [54] | ZHANG Y Y, WANG Y X, LIU Y, et al. Catalytic combustion of acetonitrile over CuCeOx-HZSM-5 composite catalysts with different mass ratios: the synergism between oxidation and hydrolysis reactions. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2021, 584: 193. |
| [55] | 文红. 单原子掺杂过渡金属基催化剂上NO选择性还原的第一性原理研究. 长春: 吉林大学博士学位论文, 2021. |
| [56] | 柳鑫淼. 单/双原子锚定二维C2N材料降解N2O的理论研究. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学博士学位论文, 2023. |
| [57] | ZHANG R D, SHI D J, LIU N, et al. Catalytic purification of acrylonitrile-containing exhaust gases from petrochemical industry by metal-doped mesoporous zeolites. Catalysis Today, 2015, 258: 17. |
| [58] | ZHANG R D, SHI D J, LIU N, et al. Mesoporous SBA-15 promoted by 3d-transition and noble metals for catalytic combustion of acetonitrile. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2014, 146: 79. |
| [59] | XING X, ZHAO T, CHENG J, et al. Promotional effect of Cu additive for the selective catalytic oxidation of n-butylamine over CeZrOx catalyst. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2022, 33(6): 3065. |
| [60] | XING X, LI N, SUN Y G, et al. Selective catalytic oxidation of n-butylamine over Cu-zeolite catalysts. Catalysis Today, 2020, 339: 192. |
| [61] | MENG L W, MA W H, ZHANG S L, et al. Isolated CuO and medium strong acid on CuO/Nb2O5-H catalyst for efficient enhancement of triethylamine selective catalytic oxidation. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2023, 11(4): 110258. |
| [62] | HE L C, XU H H, LENG X Y, et al. Boosting diethylamine selective oxidation over CuO/ZSM-5 catalyst by CeO2 modification. Fuel, 2023, 342: 127792. |
| [63] | XU H H, XIAN W Y, ZHAO X, et al. Selective catalytic oxidation of DMF over Cu-Ce/H-MOR by modulating the surface active sites. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2024, 474: 134829. |
| [64] | YAN D J, CHEN Z H, MA M D, et al. Hierarchical Cu-Mn/ZSM-5 with boosted activity and selectivity for n-butylamine destruction: synergy of pore structure and surface acidity. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2022, 636: 118579. |
| [65] | XU J W, LIU Q Y, CHEN Z H, et al. Efficient selective combustion of n-butylamine on hierarchical Cu-Mn/SAPO-34 catalysts: the effect of mesoporosity and acidity. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2023, 665: 119354. |
| [66] | MA M D, XU S, LIU Q Y, et al. Rationally engineering a CuO/ Pd@SiO2 core-shell catalyst with isolated bifunctional Pd and Cu active sites for n-butylamine controllable decomposition. Environmental Science & Technology, 2022, 56(22): 16189. |
| [67] | ZHANG Y Y, WANG Y X, LIU Y, et al. The reaction behaviors of acetonitrile and ethyl acetate simultaneous degradation over Cu-Ce/ ZSM-5 catalyst. Applied Surface Science, 2023, 609: 155190. |
| [68] | PENG H G, DONG T, YANG S Y, et al. Intra-crystalline mesoporous zeolite encapsulation-derived thermally robust metal nanocatalyst in deep oxidation of light alkanes. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 295. |
| [69] | ZHANG Y K, WANG Y H, SU K B, et al. The influence of the oxygen vacancies on the Pt/TiO2 single-atom catalyst—a DFT study. Journal of Molecular Modeling, 2022, 28(6): 175. |
| [70] | CHEN X Y, YANG S, REN B P, et al. Copper porphyrin-catalyzed cross dehydrogenative coupling of alkanes with carboxylic acids: esterification and decarboxylation dual pathway. Tetrahedron, 2021, 96: 132377. |
| [71] | 沈宏宇. MFI沸石分子筛的高效合成及其催化性能研究. 大连: 大连理工大学硕士学位论文, 2021. |
| [72] | 孙晶晶. 2-甲基萘酰化反应中改性Hβ分子筛催化性能的研究. 北京: 北京石油化工学院硕士学位论文, 2022. |
| [73] | 王伟都. 沸石分子筛封装Ag纳米粒子的制备、结构分析及催化性能的研究. 沈阳: 沈阳师范大学硕士学位论文, 2021. |
| [74] | 韩文鹏, 王淑娟, 耿付江, 等. 介孔分子筛的合成、改性及催化应用进展. 广州化工, 2025, 53(1): 4. |
| [75] | MONGUEN C K F, DANIEL S, TIAN Z Y. Low-temperature deep oxidation of N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) over CeCu binary oxides. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2023, 13(12): 3517. |
| [76] | ZHU W J, TANG L, LU J C, et al. Research progress in catalytic oxidation of volatile organic compounds by perovskite oxides. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 735. |
| [77] |
沈方燮, 万翔, 王卫超. 基于锰基YMn2O5催化剂室温降解挥发性有机化合污染物. 应用化学, 2023, 40(6): 888.
DOI |
| [78] | HU B T, SUN K A, ZHUANG Z W, et al. Distinct crystal-facet- dependent behaviors for single-atom palladium-on-ceria catalysts: enhanced stabilization and catalytic properties. Advanced Materials, 2022, 34(16): 2107721. |
| [79] | 王愉雄. ZnO基催化剂光催化选择性氧化甲烷制备高值化学品研究. 杭州: 浙江大学博士学位论文, 2024. |
| [80] | 刘璐. 基于单原子铁修饰氮化碳光催化—自Fenton协同体系的构建及其去除NO性能研究. 武汉: 华中农业大学硕士学位论文, 2024. |
| [81] |
LIU N, YUAN X N, ZHANG R D, et al. Mechanistic insight into selective catalytic combustion of HCN over Cu-BEA: influence of different active center structures. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2017, 19(35): 23960.
DOI PMID |
| [82] | CHEN D, SHI J, SHEN H Y. High-dispersed catalysts of core- shell structured Au@SiO2 for formaldehyde catalytic oxidation. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 385: 123887. |
| [1] | YU Shengyang, SU Haijun, JIANG Hao, YU Minghui, YAO Jiatong, YANG Peixin. A Review of Pore Defects in Ultra-high Temperature Oxide Ceramics by Laser Additive Manufacturing: Formation and Suppression [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(9): 944-956. |
| [2] | XIAO Xiaolin, WANG Yuxiang, GU Peiyang, ZHU Zhenrong, SUN Yong. Advances in Regulation of Damaged Skin Regeneration by Two-dimensional Inorganic Materials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 860-870. |
| [3] | MA Jingge, WU Chengtie. Application of Inorganic Bioceramics in Promoting Hair Follicle Regeneration and Hair Growth [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 901-910. |
| [4] | ZHANG Hongjian, ZHAO Ziyi, WU Chengtie. Inorganic Biomaterials on Regulating Neural Cell Function and Innervated Tissue Regeneration: A Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 849-859. |
| [5] | AI Minhui, LEI Bo. Micro-nanoscale Bioactive Glass: Functionalized Design and Angiogenic Skin Regeneration [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 921-932. |
| [6] | WANG Yutong, CHANG Jiang, XU He, WU Chengtie. Advances in Silicate Bioceramic/Bioglass for Wound Healing: Effects, Mechanisms and Application Ways [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 911-920. |
| [7] | MA Wenping, HAN Yahui, WU Chengtie, LÜ Hongxu. Application of Inorganic Bioactive Materials in Organoid Research [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 888-900. |
| [8] | LUO Xiaomin, QIAO Zhilong, LIU Ying, YANG Chen, CHANG Jiang. Inorganic Bioactive Materials Regulating Myocardial Regeneration [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 871-887. |
| [9] | ZHU Wenjie, TANG Lu, LU Jichang, LIU Jiangping, LUO Yongming. Research Progress on Catalytic Oxidation of Volatile Organic Compounds by Perovskite Oxides [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [10] | HU Zhichao, YANG Hongyu, YANG Hongcheng, SUN Chengli, YANG Jun, LI Enzhu. Usage of the P-V-L Bond Theory in Regulating Properties of Microwave Dielectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [11] | WU Qiong, SHEN Binglin, ZHANG Maohua, YAO Fangzhou, XING Zhipeng, WANG Ke. Research Progress on Lead-based Textured Piezoelectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [12] | ZHANG Bihui, LIU Xiaoqiang, CHEN Xiangming. Recent Progress of Hybrid Improper Ferroelectrics with Ruddlesden-Popper Structure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| [13] | WU Jie, YANG Shuai, WANG Mingwen, LI Jinglei, LI Chunchun, LI Fei. Textured PT-based Piezoelectric Ceramics: Development, Status and Challenge [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 575-586. |
| [14] | JIANG Kun, LI Letian, ZHENG Mupeng, HU Yongming, PAN Qinxue, WU Chaofeng, WANG Ke. Research Progress on Low-temperature Sintering of PZT Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| [15] | GUO Ziyu, ZHU Yunzhou, WANG Li, CHEN Jian, LI Hong, HUANG Zhengren. Effect of Zn2+ Catalyst on Microporous Structure of Porous Carbon Prepared from Phenolic Resin/Ethylene Glycol [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 466-472. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||