
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2026, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (2): 201-207.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250163
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHOU Qi1,2( ), LI Xiang2, ZHANG Kaihui1,2, WANG Zeliang3, DENG Mingxue2, JIA Wenbao3, WANG Ke1(
), LI Xiang2, ZHANG Kaihui1,2, WANG Zeliang3, DENG Mingxue2, JIA Wenbao3, WANG Ke1( ), CHEN Junfeng1,2(
), CHEN Junfeng1,2( )
)
Received:2025-04-18
Revised:2025-05-23
Published:2026-02-20
Online:2025-07-16
Contact:
CHEN Junfeng, professor. E-mail: jfchen@mail.sic.ac.cn;About author:ZHOU Qi (2000-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: zqis97@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
ZHOU Qi, LI Xiang, ZHANG Kaihui, WANG Zeliang, DENG Mingxue, JIA Wenbao, WANG Ke, CHEN Junfeng. Organic-Inorganic Composite Scintillators Loaded with LiF-CaF2:Eu Eutectic Powder: Preparation and Characterization[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2026, 41(2): 201-207.
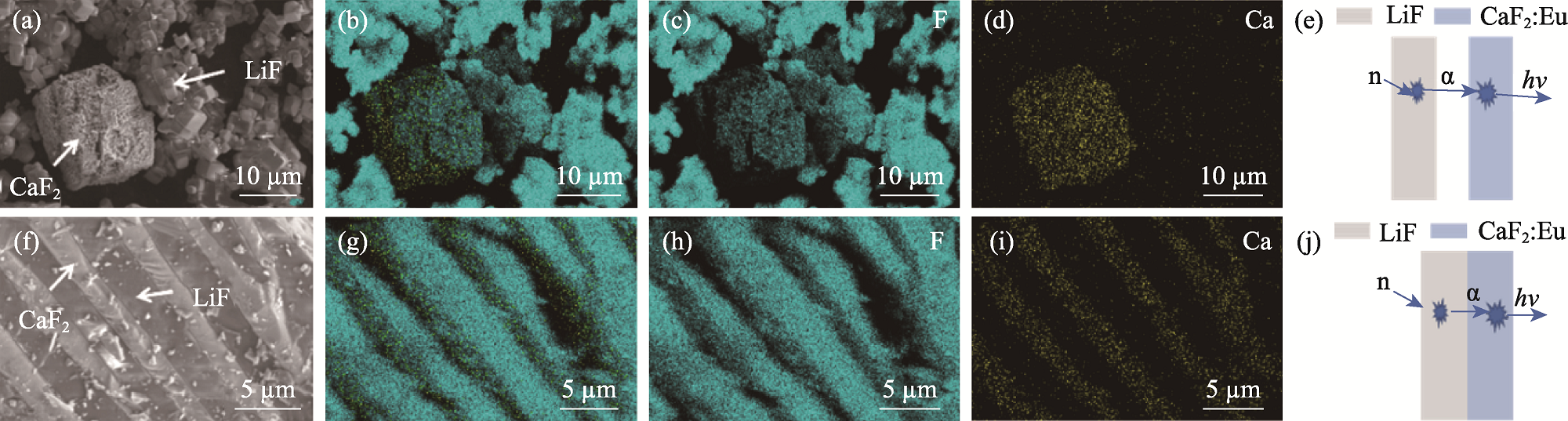
Fig. 3 SEM images and elemental mappings of the synthesized LiF/CaF2:Eu mixed powder and LiF-CaF2:Eu eutectic powder (a) SEM image and (b-d) EDS analyses of LiF/CaF2:Eu mixed powder; (e) Schematic diagram of neutron detection using LiF/CaF2:Eu mixed powder; (f) SEM image and (g-i) EDS analyses of LiF-CaF2:Eu eutectic powder;(j) Schematic diagram of neutron detection using LiF-CaF2:Eu eutectic powder. Colorful figures are available on website
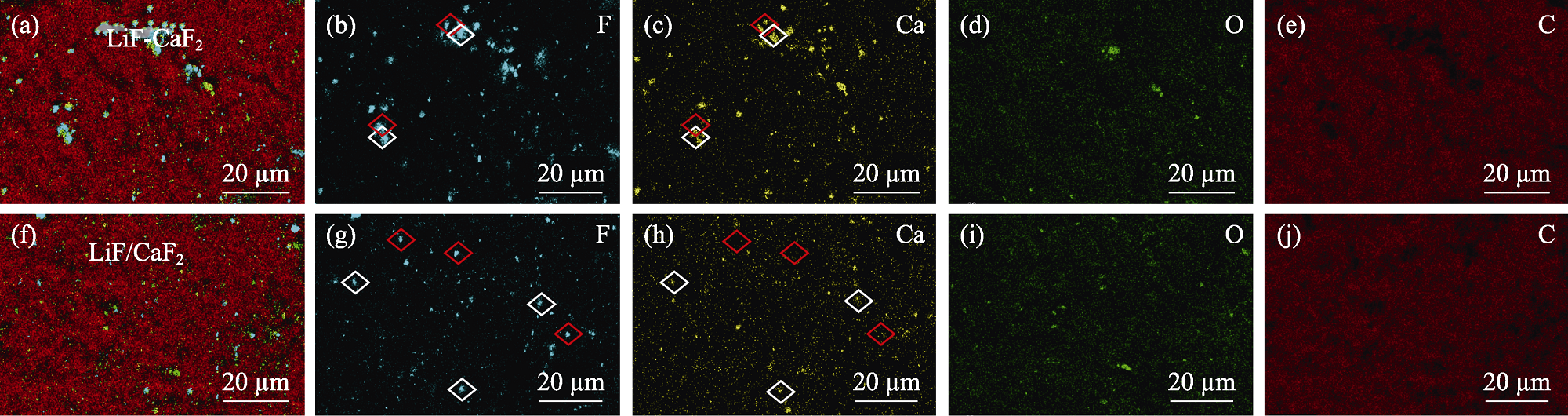
Fig. 4 SEM-EDS analyses of composite scintillators loaded with (a-e) 20% (in mass) LiF-CaF2:Eu eutectic powder and (f-j) 20% (in mass) LiF/CaF2:Eu mixed powder Colorful figures are available on website
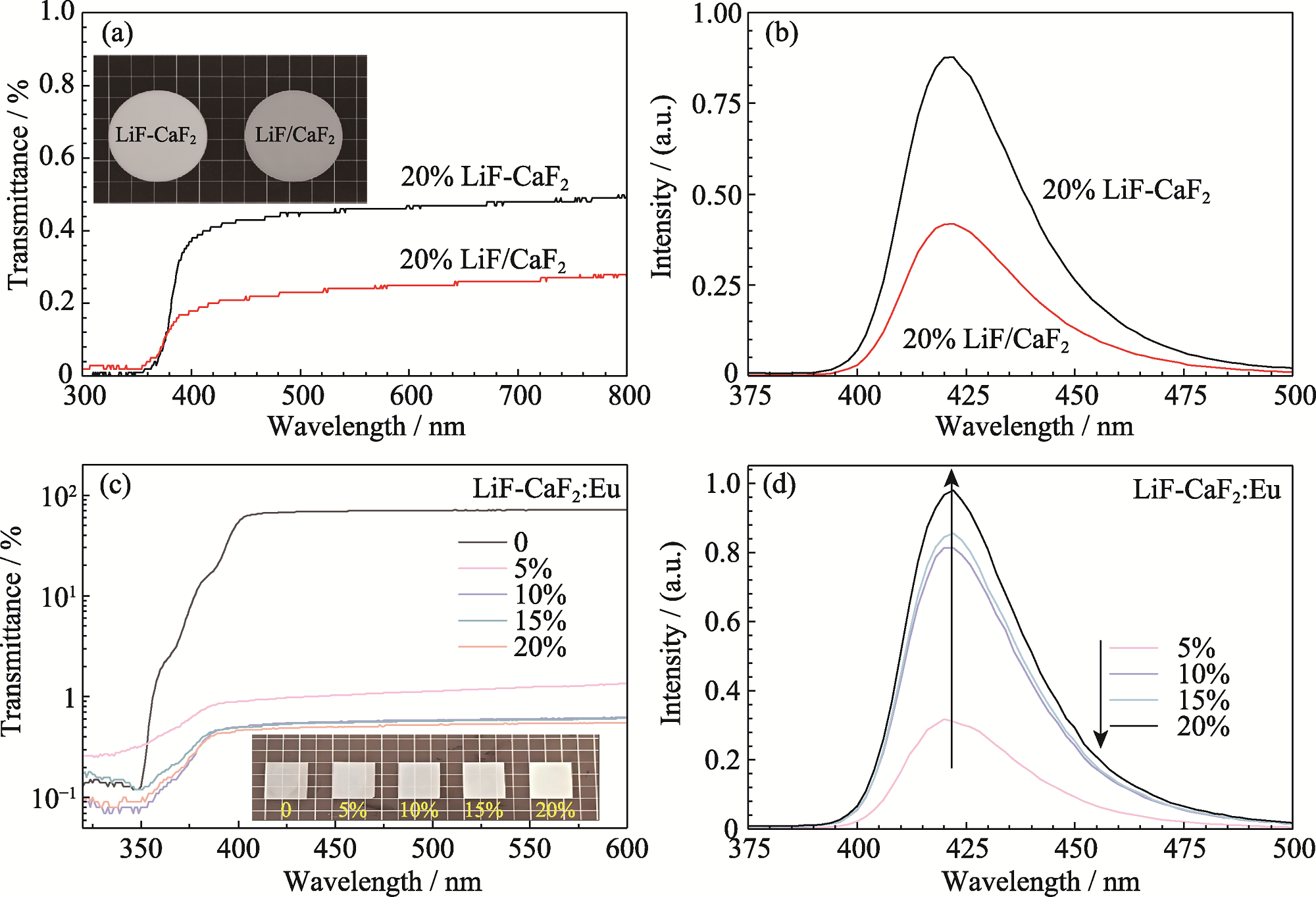
Fig. 5 Optical transmittance spectra and XEL spectra of LiF-CaF2 and LiF/CaF2 composite scintillators (a) Optical transmittance spectra of 20% (in mass) LiF-CaF2 and LiF/CaF2 composite scintillators; (b) XEL spectra of 20% (in mass) LiF-CaF2 and LiF/CaF2 composite scintillators; (c) Optical transmittance spectra of 0-20% (in mass) LiF-CaF2 composite scintillators; (d) XEL spectra of 5%-20% LiF-CaF2 composite scintillators. Colorful figures are available on website
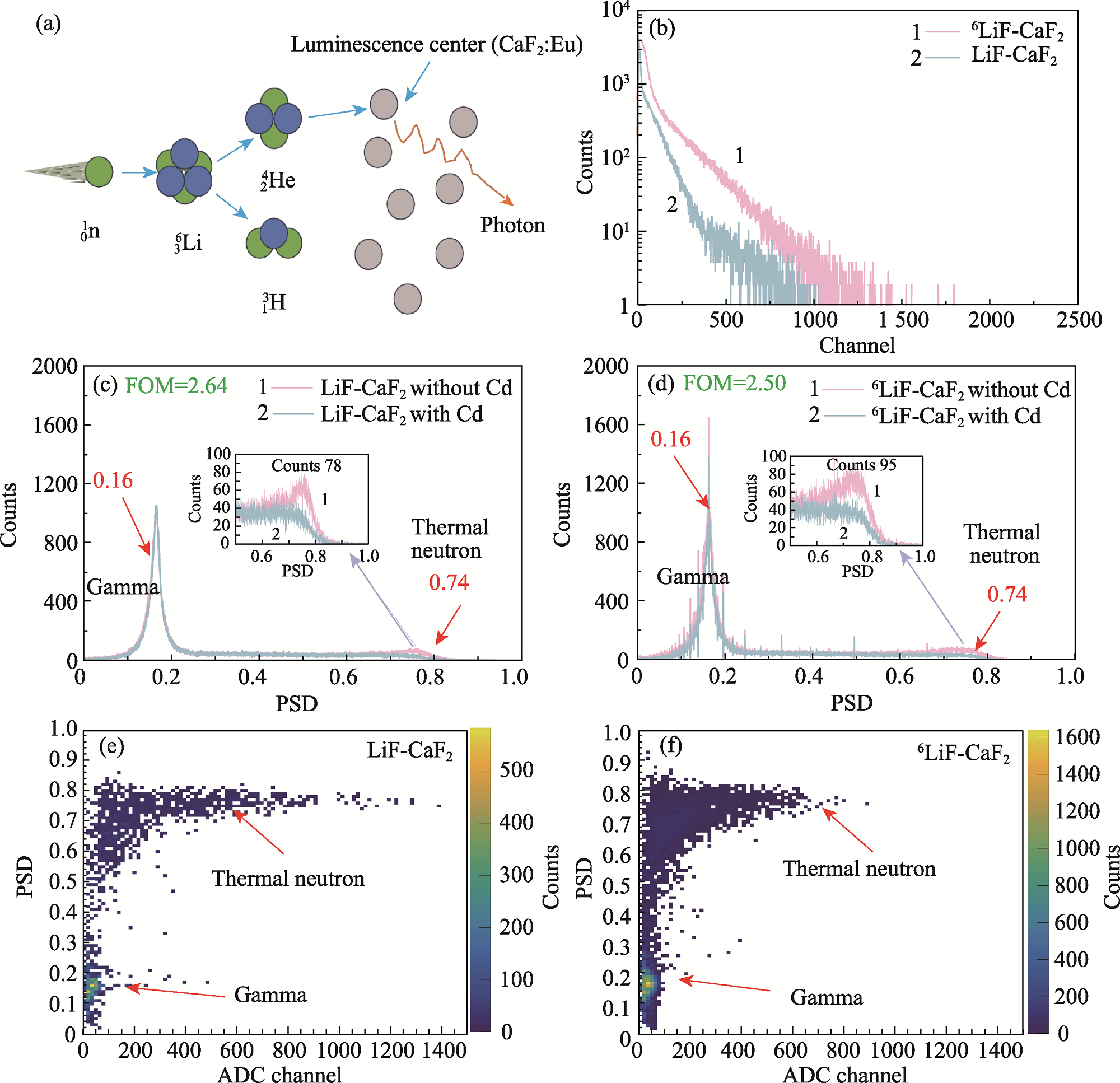
Fig. 6 Thermal neutron response and thermal neutron/gamma discrimination properties of composite scintillator loaded with LiF-CaF2:Eu eutectic powder (a) Schematic diagram of neutron detection process in LiF-CaF2:Eu eutectic powder; (b) Pulse height spectra under irradiation of 241Am-Be source; (c, d) 1D PSD histograms with and without Cd shielding; (e, f) 2D PSD scatter plots
| [1] |
VAN DER ENDE B M, LI L, GODIN D, et al. Stand-off nuclear reactor monitoring with neutron detectors for safeguards and non- proliferation applications. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 1959.
DOI |
| [2] |
SOLTES J, VIERERBL L, LAHODOVA Z, et al. Thermal neutron filter design for the neutron radiography facility at the LVR-15 reactor. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 2016, 63(3): 1640.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
CIEŚLAK M, GAMAGE K, GLOVER R. Critical review of scintillating crystals for neutron detection. Crystals, 2019, 9(9): 480.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
PIETROPAOLO A, ANGELONE M, BEDOGNI R, et al. Neutron detection techniques from μeV to GeV. Physics Reports, 2020, 875: 1.
DOI URL |
| [5] | KOUZES R T. The 3He supply problem. Pacific Northwest National Lab, 2009, 18388: 1. |
| [6] |
KAMADA K, CHIBA H, YOSHINO M, et al. Growth and scintillation properties of Eu doped LiSrI3/LiI eutectics. Optical Materials, 2017, 68: 70.
DOI URL |
| [7] | HOU Y Y, GUI Q, ZHANG C S, et al. Scintillation properties of Cs2LiYCl6:Ce crystal for neutron and gamma dual detection. Journal of Synthetic Crystals, 2021, 50(10): 1933. |
| [8] | ZHANG X, KANG Z, CAI Z, et al. Study on the segregation behavior of Ce in CLYC crystals. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2021, 573: 126308. |
| [9] | HE J Y, LI W, WEI Q H, et al. Growth and properties of 1-inch Cs2LiLaBr6:Ce scintillation crystal. Journal of Synthetic Crystals, 2021, 50(10): 1879. |
| [10] | WOOLF R S, PHLIPS B F, WULF E A. Characterization of the internal background for thermal and fast neutron detection with CLLB. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2016, 838: 147. |
| [11] |
WU C, TANG B, SUN Z J, et al. A study of ZnS(Ag)/6LiF with different mass ratios. Radiation Measurements, 2013, 58: 128.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
STAVE S, BLISS M, KOUZES R, et al. LiF/ZnS neutron multiplicity counter. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2015, 784: 208.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
BEDOGNI R, LEGA A, MENZIO L, et al. A numerical model to predict pulse height distribution of alpha particles in thin ZnS(Ag) scintillators. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2021, 990: 164991.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
WATANABE K, MITSUBOSHI N, ISHIKAWA A, et al. Basic study on a LiF-Eu:CaF2 mixed powder neutron scintillator. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2020, 954: 161244.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
KAWAGUCHI N, KIMURA H, TAKEBUCHI Y, et al. Dosimetric properties of non-doped LiF/CaF2 eutectic. Radiation Measurements, 2020, 132: 106254.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
KAWAGUCHI N, FUKUDA K, YANAGIDA T, et al. Fabrication and characterization of large size 6LiF/CaF2:Eu eutectic composites with the ordered lamellar structure. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2011, 652: 209.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
KAWANO N, KAWAGUCHI N, FUKUDA K, et al. Scintillation and dosimeter properties of 6LiF/CaF2:Eu eutectic composites. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2018, 29(11): 8964.
DOI |
| [18] |
LI X, DENG M, SHI Y, et al. Bulk polystyrene-BaF2 composite scintillators for highly efficient radiation detection. Crystals, 2023, 13(9): 13.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
LI P, CHENG W, ZHOU Y, et al. Large scale BN‐perovskite nanocomposite aerogel scintillator for thermal neutron detection. Advanced Materials, 2023, 35(25): 2209452.
DOI URL |
| [20] | TAUDUL B, TIELENS F, CALATAYUD M. Raman characterization of plastics: a DFT study of polystyrene. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2024, 128(17): 4243. |
| [21] |
TROJAN-PIEGZA J, GLODO J, SARIN V K. CaF2(Eu2+):LiF-structural and spectroscopic properties of a new system for neutron detection. Radiation Measurements, 2010, 45(2): 163.
DOI URL |
| [1] | ZHENG Zhongqiu, WEI Qinhua, TONG Yufeng, TANG Gao, YIN Hang, QIN Laishun. Effect of Zr4+ Co-doping on Neutron/Gamma Discrimination of Cs2LaLiBr6:Ce Crystals [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(5): 539-546. |
| [2] | MENG Bo, XIAO Gang, WANG Xiuli, TU Jiangping, GU Changdong. Ionic Thermal Synthesis and Reversible Heat Storage Performance of Manganese-based Oxides [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(7): 793-799. |
| [3] | LIU Haifang, SU Haijun, SHEN Zhonglin, JIANG Hao, ZHAO Di, LIU Yuan, ZHANG Jun, LIU Lin, FU Hengzhi. Research Progress on Ultrahigh Temperature Oxide Eutectic Ceramics by Laser Additive Manufacturing [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(3): 255-266. |
| [4] | SUN Luchao, ZHOU Cui, DU Tiefeng, WU Zhen, LEI Yiming, LI Jialin, SU Haijun, WANG Jingyang. Directionally Solidified Al2O3/Er3Al5O12 and Al2O3/Yb3Al5O12 Eutectic Ceramics Prepared by Optical Floating Zone Melting [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(6): 652-658. |
| [5] | YANG Ying, ZHANG Zheng, GAO Jing, LIN Ze-Hua, YAN Jing-Yuan, GUO Xue-Yi. Deep Eutectic Solvent Based Polymer Electrolyte for Dye-sensitized Solar Cells [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(1): 25-32. |
| [6] | ZHAO Xin-Hong, LI Xiao-Bin, CHEN Jing, QI Yong-Dong, WEN Juan-Juan, JI Dong. Ambient Pressure Synthesis of Hierarchical Structured SAPO-5 Molecular Sieve with Special Morphology [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(8): 821-826. |
| [7] | YU Jian-Zheng, ZHANG Jun, SU Hai-Jun, SONG Kan, LIU Lin, FU Heng-Zhi. Fabrication and Characterization of Al2O3/Y3Al5O12 Eutectic in situ Composite Ceramics by Double Side Laser Zone Remelting Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(8): 843-848. |
| [8] | DENG Yang-Fang, ZHANG Jun, SU Hai-Jun, SONG Kan, LIU Lin, FU Heng-Zhi. Microstructure and Fracture Toughness of Al2O3/Er3Al5O12 Eutectic Ceramic Prepared by Laser Zone Remelting [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2011, 26(8): 841-846. |
| [9] | LI Jia-Ke,LIU Lei,LIU Yi-Chun,ZHANG Wen-Long,HU Wen-Bin. Preparation of Ti-Si Eutectic Brazes and its Weldability to SiC [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2009, 24(1): 204-208. |
| [10] | CUI Chun-Juan,ZHANG Jun,SU Hai-Jun,WANG Hong,LIU Lin,FU Heng-Zhi. Microstructures of Directionally Solidified Si-TaSi2 Eutectic in situ Composite for Field Emission [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2007, 22(5): 1019-1023. |
| [11] | BAI Yu-Xia,WANG Shu-Lan,LI Ying. Variations of Conductivities of NaOH-KOH Molten Salt during the Process of Synthesis of BaTiO3 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2002, 17(3): 609-612. |
| [12] | PAN Zhen-Su,ZHANG Hui-Feng,GUO Jing-Kun. Status on the Unidirectionally Solidified Eutectic Composite [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 1999, 14(4): 513-519. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||