
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (12): 1433-1442.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240410
• RESEARCH LETTER • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU Hongming1( ), ZHANG Jinke2, CHEN Zhengpeng1, LI Mingfei1, QIAN Xiuyang1, SUN Chuanqi1, XIONG Kai3, RAO Mumin1, CHEN Chuangting1, GAO Yuan2(
), ZHANG Jinke2, CHEN Zhengpeng1, LI Mingfei1, QIAN Xiuyang1, SUN Chuanqi1, XIONG Kai3, RAO Mumin1, CHEN Chuangting1, GAO Yuan2( ), LING Yihan2(
), LING Yihan2( )
)
Received:2024-09-14
Revised:2024-12-11
Published:2025-12-20
Online:2024-12-27
Contact:
GAO Yuan, post doctor. E-mail: tbh371@cumt.edu.cn;About author:LIU Hongmin (1996-), male, PhD. E-mail: liuhongming@geg.com.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
LIU Hongming, ZHANG Jinke, CHEN Zhengpeng, LI Mingfei, QIAN Xiuyang, SUN Chuanqi, XIONG Kai, RAO Mumin, CHEN Chuangting, GAO Yuan, LING Yihan. Enhanced Performance of La0.7Sr0.3FeO3-δ Cathode for SOFC via Implementation of B-site High-entropy Strategy[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(12): 1433-1442.
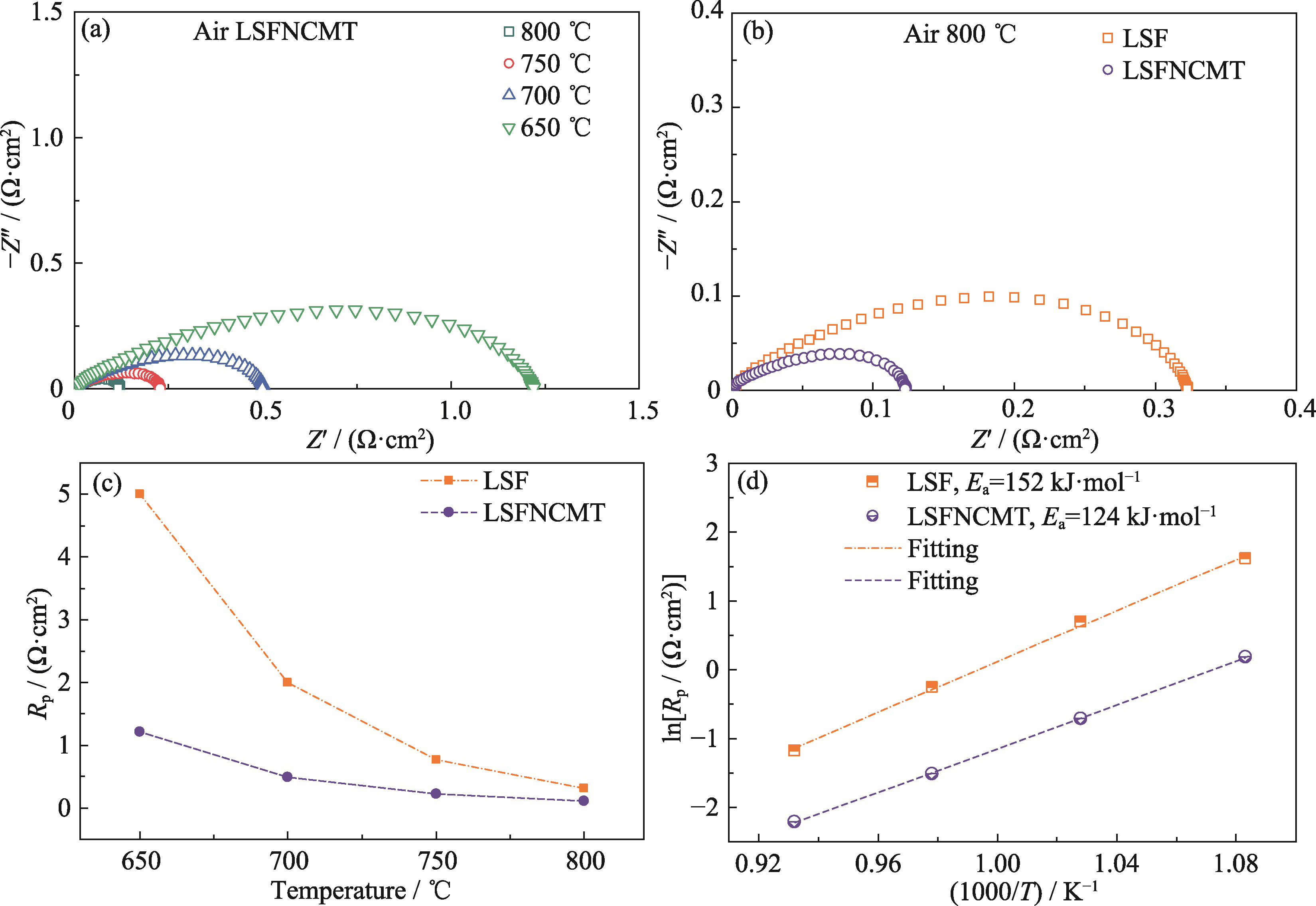
Fig. 3 Electrochemical performance of symmetric cell under different temperatures in air (a) EIS spectra of LSFNCMT electrode; (b) EIS spectra of LSF and LSFNCMT electrodes at 800 ℃; (c) Rp and (d) corresponding Arrhenius plots of two symmetric cells
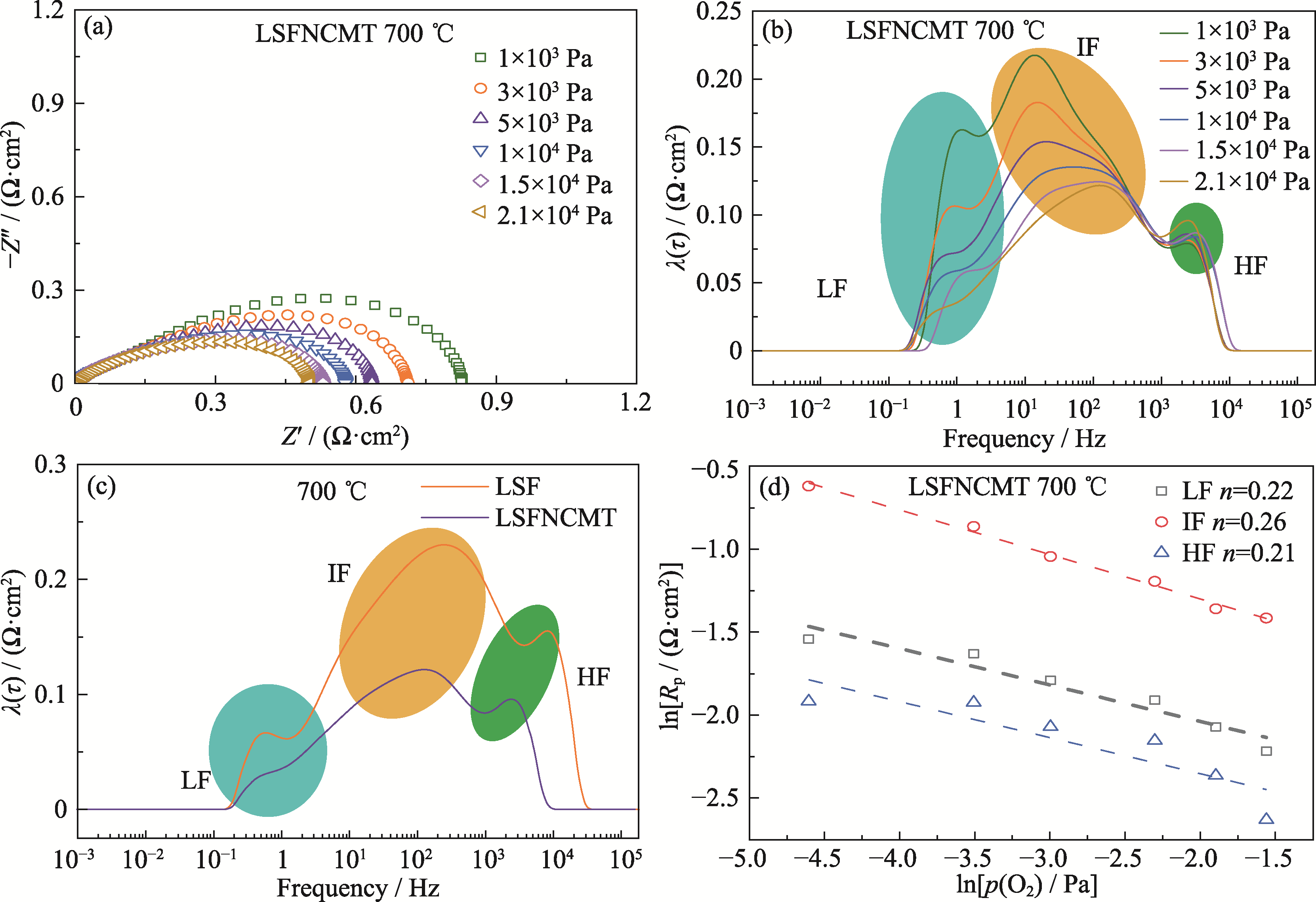
Fig. 4 Electrochemical performance of symmetrical cell under different p(O2) at 700 ℃ (a, b) EIS spectra (a) and DRT curves (b) of LSFNCMT; (c) DRT curves of LSF and LSFNCMT under p(O2) of 2.1×104 Pa at 700 ℃; (d) Dependence of each Rp as a function of p(O2) for LSFNCMT. Colorful figures are available on website
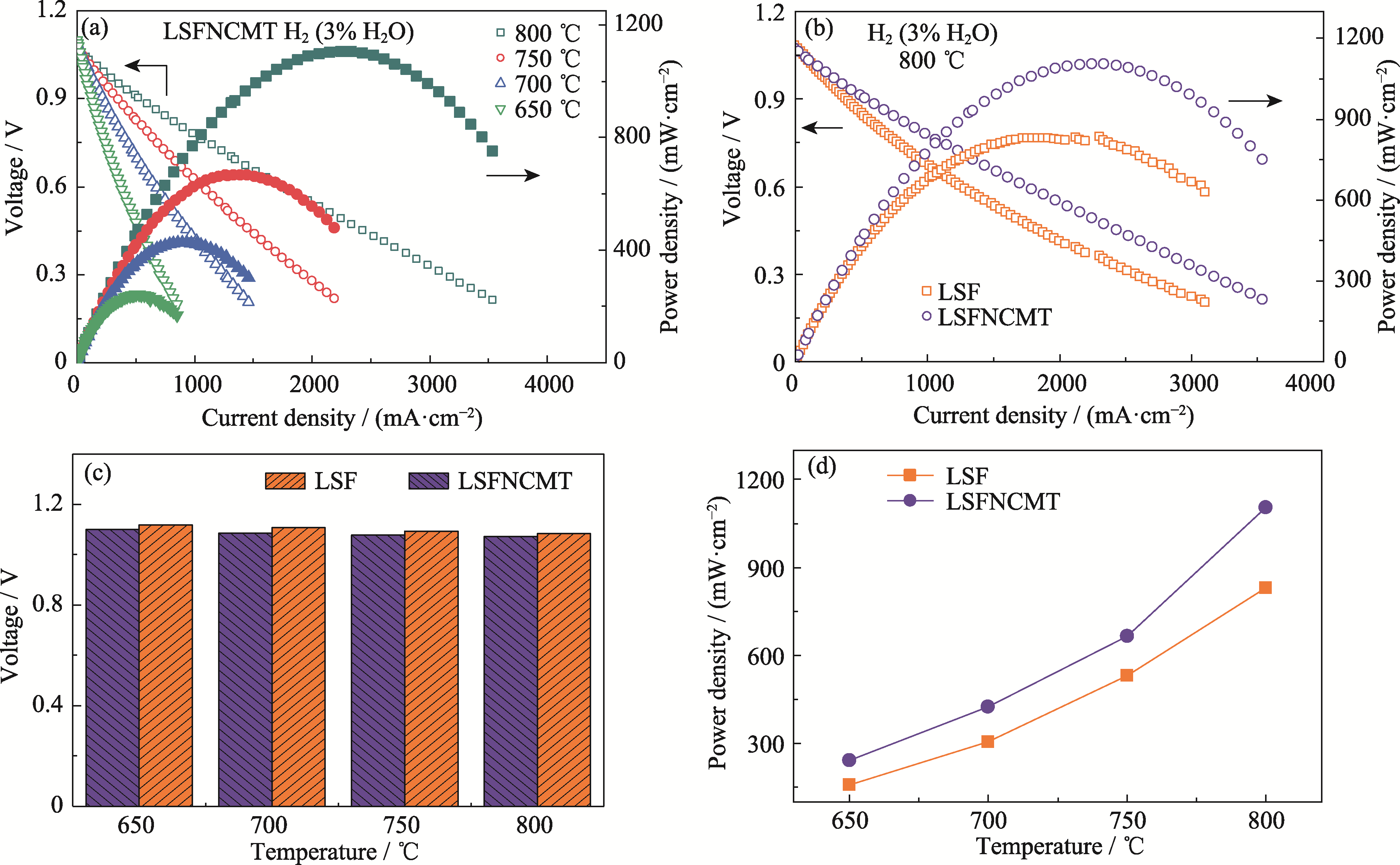
Fig. 6 Electrochemical performance of the single cell at 650-800 ℃ in wet H2 (3% (in volume) H2O) (a) I-V and power density curves of LSFNCMT cathodes; (b) I-V and power density curves of LSF and LSFNCMT cathodes at 800 ℃; (c) OCV and (d) MPD varied with temperature of different single cells
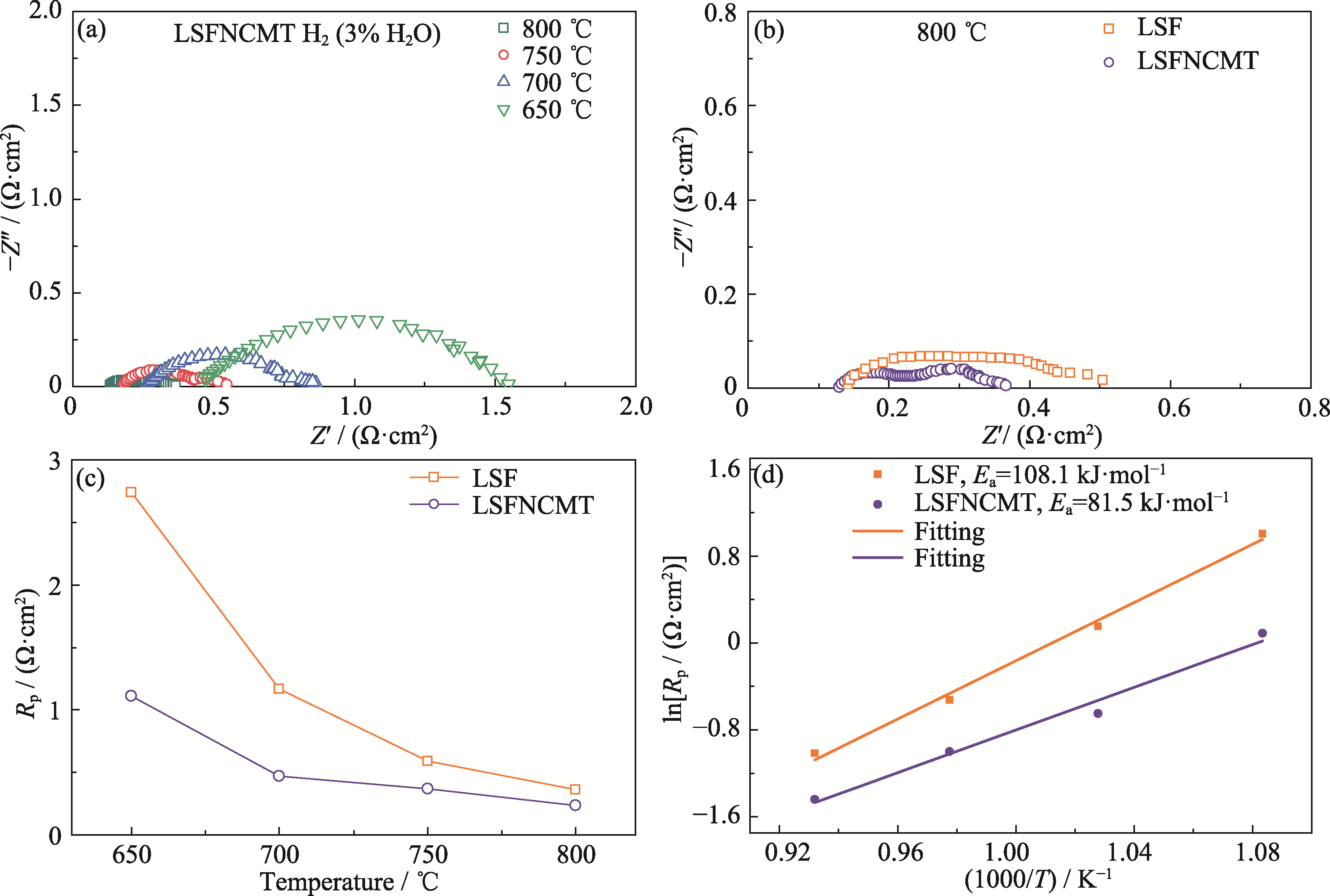
Fig. 7 Electrochemical performance of the anode-supported single cell at 650-800 ℃ in wet H2 (3% (in volume) H2O) (a) EIS spectra of LSFNCMT cathode; (b) EIS spectra of LSF and LSFNCMT cathodes at 800 ℃; (c) Rp at different temperatures and (d) corresponding Arrhenius plots of different single cells
| [1] |
PAN Z, LIU Q, NI M, et al. Activation and failure mechanism of La0.6Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.8O3-δ air electrode in solid oxide electrolyzer cells under high-current electrolysis. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018, 43(11): 5437.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
CAOO D, ZHOU M, LIU Z, et al. Fabrication and characterization of anode-supported solid oxide fuel cell based on proton conductor electrolyte. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(9): 1047.
DOI |
| [3] |
LAGUNA-BERCERO M A, CAMPANA R, LARREA A, et al. Electrolyte degradation in anode supported microtubular yttria stabilized zirconia-based solid oxide steam electrolysis cells at high voltages of operation. Journal of Power Sources, 2011, 196(21): 8942.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
SINGH V, MUROYAMA H, MATSUI T, et al. Feasibility of alternative electrode materials for high temperature CO2 reduction on solid oxide electrolysis cell. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 293: 642.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
LV H, ZHOU Y, ZHANG X, et al. Infiltration of Ce0.8Gd0.2O1.9 nanoparticles on Sr2Fe1.5Mo0.5O6-δ cathode for CO2 electroreduction in solid oxide electrolysis cell. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2019, 35: 71.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
YE Z, ZOU G, WU Q, et al. Preparation and performances of tubular cone-shaped anode-supported segmented-in-series direct carbon solid oxide fuel cell. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(7): 819.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
XUE L, LI S, AN S, et al. Ca-doping cobalt-free double perovskite oxide as a cathode material for intermediate-temperature solid oxide fuel cell. Molecules, 2024, 29(13): 2991.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
PRAŻUCH J, PYZALSKI M, FERNÁNDEZ GONZÁLEZ D, et al. Physicochemical properties of (La,Sr)CoO3 thick films on Fe-25Cr steel under exposure to SOFC cathode operating conditions. Materials, 2024, 17(15): 3791.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
PINSKY R, SABHARWALL P, HARTVIGSEN J, et al. Comparative review of hydrogen production technologies for nuclear hybrid energy systems. Progress in Nuclear Energy, 2020, 123: 103317.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
DING P, LI W, ZHAO H, et al. Review on Ruddlesden-Popper perovskites as cathode for solid oxide fuel cells. Journal of Physics: Materials, 2021, 4(2): 022002.
DOI |
| [11] |
GREELEY J, MARKOVIC N M. The road from animal electricity to green energy: combining experiment and theory in electrocatalysis. Energy and Environmental Science, 2012, 5(11): 9246.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
SHEN R, NIE J, WANG K, et al. Applying multifunctional perovskite LaNiO3 as electrolyte and anode for low‐temperature solid oxide fuel cell. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2021, 32(4): 4196.
DOI |
| [13] |
ZHANG K, WANG Y, ZHU T, et al. LaNi0.6Fe0.4O3 cathode contact material: electrical conducting property manipulation and its effect on SOFC electrochemical performance. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(4): 367.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
ZHANG Y, KNIBBE R, SUNARSO J, et al. Recent progress on advanced materials for solid-oxide fuel cells operating below 500 ℃. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(48): 1700132.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
ISTOMIN S Y, ANTIPOV E V. Cathode materials based on perovskite-like transition metal oxides for intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cells. Russian Chemical Reviews, 2013, 82(7): 686.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
ZHANG J, SONG K, GAO Y, et al. Tuning the thermo-mechanical synergies effect of solid oxide fuel cells with negative thermal expansion NdMnO3 in La0.6Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.8O3-δ-based symmetric electrode. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 491: 152063.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
CHEN Y, ZHU J, XIA T, et al. Improved electrocatalytic activity and CO2 tolerance of iron-based perovskite as an intermediate temperature SOFC cathode. Fuel, 2024, 375: 132546.
DOI URL |
| [18] | XIA Z, ZHANG Y, XIONG X, et al. Realizing B-site high-entropy air electrode for superior reversible solid oxide cells. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2024, 357: 124410. |
| [19] | JIN F, LIU X, TIAN Y, et al. Enhancing oxygen reduction activity and CO2 tolerance by a bismuth doping strategy for solid oxide fuel cell cathodes. Advanced Functional Materials, 2024, 34(29): 2400519. |
| [20] |
CHU Z, GAO J, LI Q, et al. Highly oxygen reduction activity and CO2 resistance of Fe-based cathode electrocatalysts for solid oxide fuel cells. Journal of Materials Science and Technology, 2025, 212: 303.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
ZHANG H X, YAO C G, ZHANG Z, et al. Lithium doping enhanced ORR kinetics and CO2 tolerance of iron-based double perovskite cathode for solid oxide fuel cells. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2024, 980: 173632.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
BAI J, NIU L, ZHU Q, et al. Ni-doped Fe-based perovskite to obtain multifunctional and highly efficient electrocatalytic active IT-SOFC electrode. Fuel, 2024, 365: 131334.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
SUN C, SHEN Y, WANG F, et al. Optimization of a cobalt-free La0.7Sr0.3FeO3-δ-BaZr0.1Ce0.7Y0.2O3-δ composite cathode for proton-conducting solid oxide fuel cells. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2022, 923: 166447.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
YANG C, WANG Z, TAN Y, et al. Interface engineering of La0.6Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.8O3-δ/Gd0.1Ce0.9O1.95 heterostructure oxygen electrode for solid oxide electrolysis cells with enhanced CO2 electrolysis performance. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 498: 155461.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
WANG J, FU L, YANG J, et al. Cerium and ruthenium co-doped La0.7Sr0.3FeO3-δ as a high-efficiency electrode for symmetrical solid oxide fuel cell. Journal of Rare Earths, 2021, 39(9): 1095.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
YUAN M, WANG Z, GAO J, et al. Configuration entropy tailored beneficial surface segregation on double perovskite cathode with enhanced Cr-tolerance for SOFC. Ceramics International, 2024, 50(9): 15076.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
ZHANG X, JIN Y, JIANG Y, et al. Enhancing chromium poisoning tolerance of La0.8Sr0.2Co0.2Fe0.8O3-δ cathode by Ce0.8Gd0.2O1.9-δ coating. Journal of Power Sources, 2022, 547: 231996.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
HUANG K. A thermodynamic perspective on electrode poisoning in solid oxide fuel cells. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy and Materials, 2024, 31(6): 1449.
DOI |
| [29] | JIANG S P, ZHANG S, ZHEN Y D. Deposition of Cr species at (La, Sr)(Co, Fe)O3 cathodes of solid oxide fuel cells. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2006, 153(1): A127. |
| [30] |
GAO Y, HUANG X, YUAN M, et al. A SrCo0.9Ta0.1O3-δ derived medium-entropy cathode with superior CO2 poisoning tolerance for solid oxide fuel cells. Journal of Power Sources, 2022, 540: 231661.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
GAO Y, LING Y, WANG X, et al. Sr-deficient medium-entropy Sr1-xCo0.5Fe0.2Ti0.1Ta0.1Nb0.1O3-δ cathodes with high Cr tolerance for solid oxide fuel cells. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 479: 147665.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
LI Z, GE Y, XIAO Y, et al. Fabrication and performance investigation of high entropy perovskite (Sr0.2Ba0.2Bi0.2La0.2Pr0.2)FeO3 IT-SOFC cathode material. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2024, 989: 174357.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
GUO T M, DONG J B, CHEN Z P, et al. Enhanced compatibility and activity of high-entropy double perovskite cathode material for IT-SOFC. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 38(6): 693.
DOI URL |
| [34] | HAN X, LING Y, YANG Y, et al. Utilizing high entropy effects for developing chromium-tolerance cobalt-free cathode for solid oxide fuel cells. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(43): 230478. |
| [35] |
WANG J, SACCOCCIO M, CHEN D, et al. The effect of A-site and B-site substitution on BaFeO3-δ: an investigation as a cathode material for intermediate-temperature solid oxide fuel cells. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 297: 511.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
KUAI X, YANG G, CHEN Y, et al. Boosting the activity of BaCo0.4Fe0.4Zr0.1Y0.1O3-δ perovskite for oxygen reduction reactions at low-to-intermediate temperatures through tuning B-Site cation deficiency. Advanced Energy Materials, 2019, 9(38): 1902384.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
ZHU C, LIU X, YI C, et al. Novel BaCo0.7Fe0.3-yNbyO3-δ (y=0-0.12) as a cathode for intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cell. Electrochemistry Communications, 2009, 11(5): 958.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
ZHOU Q, WEI T, SHI Y, et al. Evaluation and optimization of SrCo0.9Ta0.1O3-δ perovskite as cathode for solid oxide fuel cells. Current Applied Physics, 2012, 12(4): 1092.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
SHEN Y, WANG F, MA X, et al. SrCo1-yTiyO3-δ as potential cathode materials for intermediate-temperature solid oxide fuel cells. Journal of Power Sources, 2011, 196(18): 7420.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
ZHAO H, TENG D, ZHANG X, et al. Structural and electrochemical studies of Ba0.6Sr0.4Co1-yTiyO3-δ as a new cathode material for IT-SOFCs. Journal of Power Sources, 2009, 186(2): 305.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
YU X, LONG W, JIN F, et al. Cobalt-free perovskite cathode materials SrFe1-xTixO3-δ and performance optimization for intermediate-temperature solid oxide fuel cells. Electrochimica Acta, 2014, 123: 426.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
LI J, SUN N, LIU X, et al. Investigation on Nd1-xCaxBaCo2O5+δ double perovskite as new oxygen electrode materials for reversible solid oxide cells. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2022, 913: 165245.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
CHEN Z P, JIN F J, LI M F, et al. Double perovskite Sr2CoFeO5+δ: preparation and performance as cathode material for intermediate- temperature solid oxide fuel cells. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 39(3): 337.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
ZHANG Z, WANG H, LI X, et al. CO2/Cr-tolerance and oxygen reduction reaction of novel high-entropy perovskite cathode for intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cell. Ceramics International, 2024, 50(7): 11360.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
SCHULER J A, YOKOKAWA H, CALDERONE C F, et al. Combined Cr and S poisoning in solid oxide fuel cell cathodes. Journal of Power Sources, 2012, 201: 112.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
LI Y, ZHANG W, ZHENG Y, et al. Controlling cation segregation in perovskite-based electrodes for high electro-catalytic activity and durability. Chemical Society Reviews, 2017, 46(20): 6345.
DOI PMID |
| [47] |
JEONG N C, LEE J S, TAE E L, et al. Acidity scale for metal oxides and Sanderson's electronegativities of lanthanide elements. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2008, 47(52): 10128.
DOI URL |
| [1] | GAO Yuan, WEI Bo, JIN Fangjun, LÜ Zhe, LING Yihan. Ag Doping Modulating Cathode Acidic Sites to Enhance Chromium Resistance for Intermediate Temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cells [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2026, 41(1): 70-78. |
| [2] | CHAI Runyu, ZHANG Zhen, WANG Menglong, XIA Changrong. Preparation of Ceria Based Metal-supported Solid Oxide Fuel Cells by Direct Assembly Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 765-771. |
| [3] | QU Jifa, WANG Xu, ZHANG Weixuan, ZHANG Kangzhe, XIONG Yongheng, TAN Wenyi. Enhanced Sulfur-resistance for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells Anode via Doping Modification of NaYTiO4 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 489-496. |
| [4] | XUE Ke, CAI Changkun, XIE Manyi, LI Shuting, AN Shengli. Pr1+xBa1-xFe2O5+δ Cathode Materials for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells: Preparation and Electrochemical Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 363-371. |
| [5] | ZHU Zhijie, SHEN Mingyuan, WU Tao, LI Wencui. Inhibition of P2-O2 Phase Transition for P2-Na2/3Ni1/3Mn2/3O2 as Cathode of Sodium-ion Battery via Synergetic Substitution of Cu and Mg [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 184-195. |
| [6] | YANG Hengqiang, ZHANG Xinyue, MA Yichu, ZHOU Qingjun. Iron-based Perovskite Material La0.25M0.75FeO3-δ (M=Ca, Sr, Ba): Preparation and Performance as Cathode for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(12): 1365-1372. |
| [7] | WANG Zhe, HAO Hongru, WU Zonghui, XU Lingling, LÜ Zhe, WEI Bo. Enhancing Cr-tolerance Ability of Double Perovskite Cathodes through Configuration Entropy Engineering [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(12): 1341-1348. |
| [8] | JIANG Yuehong, SONG Yunfeng, ZHANG Leilei, MA Ji, SONG Zhaoyuan, LONG Wen. Fluorination of BaZr0.1Ce0.7Y0.1Yb0.1O3 as Electrolyte Material for Proton-conducting Solid Oxide Fuel Cell [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(12): 1356-1364. |
| [9] | XUE Zixuan, YIN Chaofan, YAO Yuechao, WANG Yanmin, SUN Yueyue, LIU Zhengrong, ZHOU Yucun, ZHOU Jun, WU Kai. Research Progress on Proton-conducting Solid Oxide Fuel Cells with Hydrogen-containing Fuel [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(12): 1324-1340. |
| [10] | LIU Tong, HUANG Su, ZHU Shiyue, ZHA Fanglin, HU Xuelei, WANG Yao. Preparation of Cobalt-free Composite Cathode for Efficient High-temperature Hydrogen Fuel Cell via One-pot Synthesis Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(12): 1349-1355. |
| [11] | ZHANG Jinghui, LU Xiaotong, MAO Haiyan, TIAN Yazhou, ZHANG Shanlin. Effect of Sintering Additives on Sintering Behavior and Conductivity of BaZr0.1Ce0.7Y0.2O3-δ Electrolytes [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 84-90. |
| [12] | PAN Jianlong, MA Guanjun, SONG Lemei, HUAN Yu, WEI Tao. High Stability/Catalytic Activity Co-based Perovskite as SOFC Anode: In-situ Preparation by Fuel Reducing Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(8): 911-919. |
| [13] | YE Zibin, ZOU Gaochang, WU Qiwen, YAN Xiaomin, ZHOU Mingyang, LIU Jiang. Preparation and Performances of Tubular Cone-shaped Anode-supported Segmented-in-series Direct Carbon Solid Oxide Fuel Cell [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(7): 819-827. |
| [14] | ZHANG Kun, WANG Yu, ZHU Tenglong, SUN Kaihua, HAN Minfang, ZHONG Qin. LaNi0.6Fe0.4O3 Cathode Contact Material: Electrical Conducting Property Manipulation and Its Effect on SOFC Electrochemical Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(4): 367-373. |
| [15] | CHENG Jie, ZHOU Yue, LUO Xintao, GAO Meiting, LUO Sifei, CAI Danmin, WU Xueyin, ZHU Licai, YUAN Zhongzhi. Construction and Electrochemical Properties of Yolk-shell Structured FeF3·0.33H2O@N-doped Graphene Nanoboxes [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(3): 299-305. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||