
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (3): 337-344.DOI: 10.15541/jim20230428
Special Issue: 【能源环境】燃料电池(202506)
CHEN Zhengpeng1( ), JIN Fangjun2,3(
), JIN Fangjun2,3( ), LI Mingfei1, DONG Jiangbo1, XU Renci1, XU Hanzhao4, XIONG Kai5, RAO Muming1, CHEN Chuangting1, LI Xiaowei2, LING Yihan2(
), LI Mingfei1, DONG Jiangbo1, XU Renci1, XU Hanzhao4, XIONG Kai5, RAO Muming1, CHEN Chuangting1, LI Xiaowei2, LING Yihan2( )
)
Received:2023-09-20
Revised:2023-11-16
Published:2024-03-20
Online:2023-11-28
Contact:
LING Yihan, professor. E-mail: lyhyy@cumt.edu.cn;About author:CHEN Zhengpeng (1991-), male, Master. E-mail: chenzhengpeng@geg.com.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
CHEN Zhengpeng, JIN Fangjun, LI Mingfei, DONG Jiangbo, XU Renci, XU Hanzhao, XIONG Kai, RAO Muming, CHEN Chuangting, LI Xiaowei, LING Yihan. Double Perovskite Sr2CoFeO5+δ: Preparation and Performance as Cathode Material for Intermediate-temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cells[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(3): 337-344.
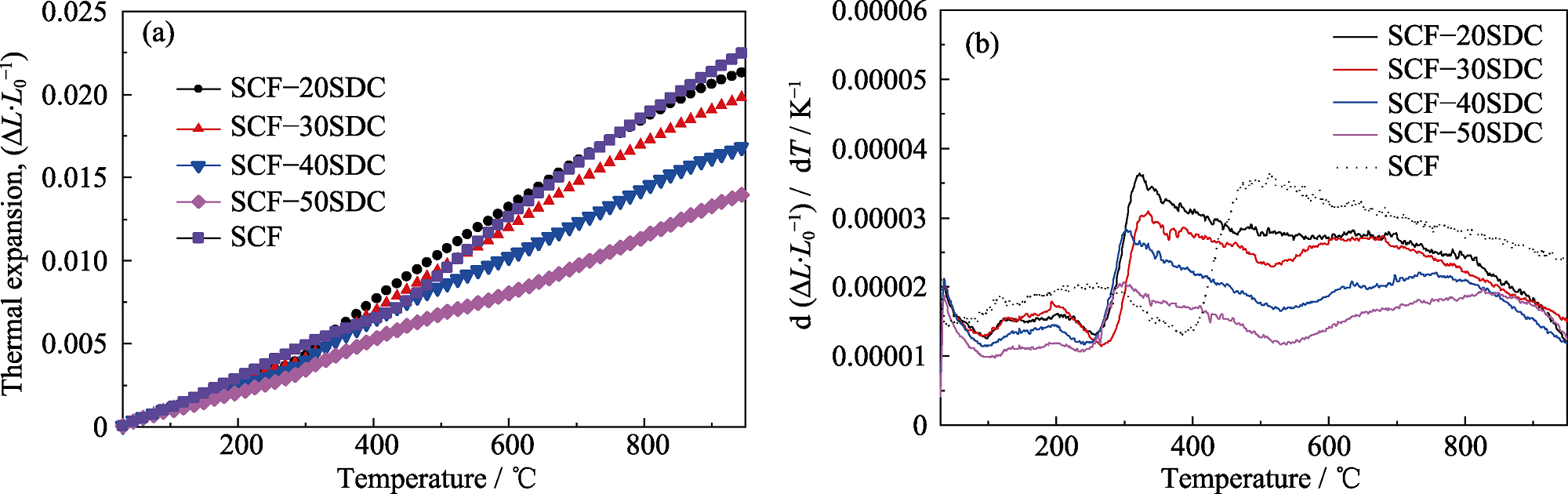
Fig. 4 (a) Thermal expansion behaviors and (b) thermal expansion coefficient curves of SCF-xSDC composite cathodes in the temperature range of 30-950 ℃ Colorful figures are available on website
| Sample | Average TEC/(×10−6, K−1) | |
|---|---|---|
| SCF | 17.4 (30−400 ℃) | 28.8 (400−1000 ℃) |
| SCF−20SDC | 15.6 (30−300 ℃) | 26.3 (300−950 ℃) |
| SCF−30SDC | 15.0 (30−300 ℃) | 24.3 (300−950 ℃) |
| SCF−40SDC | 14.5 (30−300 ℃) | 19.8 (300−950 ℃) |
| SCF−50SDC | 12.5 (30−300 ℃) | 16.3 (300−950 ℃) |
Table 1 TEC of SCF-xSDC composite cathodes
| Sample | Average TEC/(×10−6, K−1) | |
|---|---|---|
| SCF | 17.4 (30−400 ℃) | 28.8 (400−1000 ℃) |
| SCF−20SDC | 15.6 (30−300 ℃) | 26.3 (300−950 ℃) |
| SCF−30SDC | 15.0 (30−300 ℃) | 24.3 (300−950 ℃) |
| SCF−40SDC | 14.5 (30−300 ℃) | 19.8 (300−950 ℃) |
| SCF−50SDC | 12.5 (30−300 ℃) | 16.3 (300−950 ℃) |
| Atom | Wyck. | S.O.F. | x/a | y/b | z/c | U/Å2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sr1 | 8c | 1 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.01083(1) |
| Co1 | 4b | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.01311(1) |
| Fe1 | 4a | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0115(2) |
| O1 | 24e | 1 | 0.2496(5) | 0 | 0 | 0.00995(2) |
Table S1 Atomic occupancy information (atomic parameters) of XRD refinement
| Atom | Wyck. | S.O.F. | x/a | y/b | z/c | U/Å2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sr1 | 8c | 1 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.01083(1) |
| Co1 | 4b | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.01311(1) |
| Fe1 | 4a | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.0115(2) |
| O1 | 24e | 1 | 0.2496(5) | 0 | 0 | 0.00995(2) |
| Cathode | Electrolyte | T/℃ | Power density/(mW·cm-2) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YBaCo2/3Fe2/3Cu2/3O5+δ | LSGM | 800 | 543 | [ |
| SrCo0.7Fe0.2Ta0.1O3−δ | LSGM | 800 | 652.9 | [ |
| PrBaCo2/3Fe2/3Cu2/3O5+δ | GDC | 800 | 659 | [ |
| Pr1.9Ca0.1BaCoFeO5+δ | LSGM | 800 | 728 | [ |
| SCF−40SDC | LSGM | 800 | 757 | This work |
Table S2 Electrochemical performance for cathode materials using hydrogen fuels
| Cathode | Electrolyte | T/℃ | Power density/(mW·cm-2) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YBaCo2/3Fe2/3Cu2/3O5+δ | LSGM | 800 | 543 | [ |
| SrCo0.7Fe0.2Ta0.1O3−δ | LSGM | 800 | 652.9 | [ |
| PrBaCo2/3Fe2/3Cu2/3O5+δ | GDC | 800 | 659 | [ |
| Pr1.9Ca0.1BaCoFeO5+δ | LSGM | 800 | 728 | [ |
| SCF−40SDC | LSGM | 800 | 757 | This work |
| [1] |
GUO T M, DONG J B, CHEN Z P, et al. Enhanced compatibility and activity of high-entropy double perovskite cathode material for IT-SOFC. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 693.
DOI |
| [2] | HAN X, LING Y H, YANG Y, et al. Utilizing high entropy effects for developing chromium-tolerance cobalt-free cathode for solid oxide fuel cells. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(43): 202304728. |
| [3] |
TAI L W, NASRALLAH M M, ANDERSON H U, et al. Structure and electrical properties of La1-xSrxCo1-yFeyO3. Part 1. The system La0.8Sr0.2Co1-yFeyO3. Solid State Ionics, 1995, 76(3/4): 259.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
TAI L W, NASRALLAH M M, ANDERSON H U, et al. Structure and electrical properties of La1-xSrxCo1-yFeyO3. Part 2. The system La1-xSrxCo0.2Fe0.8O3. Solid State Ionics, 1995, 76(3/4): 273.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
SHAO Z, HAILE S M. A high-performance cathode for the next generation of solid-oxide fuel cells. Nature, 2004, 431(7005): 170.
DOI |
| [6] |
WEI B, LU Z, LI S Y, et al. Thermal and electrical properties of new cathode material Ba0.5Sr0.5Co0.8Fe0.2O3-δ for solid oxide fuel cells. Electrochemical and Solid State Letters, 2005, 8(8): A428.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
ZHANG K, GE L, RAN R, et al. Synthesis, characterization and evaluation of cation-ordered LnBaCo2O5+δ as materials of oxygen permeation membranes and cathodes of SOFCs. Acta Materialia, 2008, 56(17): 4876.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
JIN F J, SHEN Y, WANG R, et al. Double-perovskite PrBaCo2/3Fe2/3Cu2/3O5+δ as cathode material for intermediate-temperature solid-oxide fuel cells. Journal of Power Sources, 2013, 234: 244.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
LI J, SUN N, LIU X, et al. Investigation on Nd1-xCaxBaCo2O5+δ double perovskite as new oxygen electrode materials for reversible solid oxide cells. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2022, 913: 165245.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
JIN F, XU H, LONG W, et al. Characterization and evaluation of double perovskites LnBaCoFeO5+δ (Ln=Pr and Nd) as intermediate- temperature solid oxide fuel cell cathodes. Journal of Power Sources, 2013, 243: 10.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
LIU X, JIN F, SUN N, et al. Nd3+-deficiency double perovskite Nd1-xBaCo2O5+s and performance optimization as cathode materials for intermediate-temperature solid oxide fuel cells. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(23): 33886.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
BEZDICKA P, FOURNES L, WATTIAUX A, et al. Mössbauer characteristics of the Sr2CoFeO6 perovskite obtained by electrochemical oxidation. Solid State Communications, 1994, 91(7): 501.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
MARTÍNEZ-LOPE MARÍA J, ALONSO JOSÉ A, CASAIS MARÍA T, et al. Preparation, crystal and magnetic structure of the double perovskites Ba2CoBO6 (B=Mo, W). European Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2002, 2002(9): 2463.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
YOSHII K. Magnetic transition in the perovskite Ba2CoNbO6-δ. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2000, 151(2): 294.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
COX D E, SHIRANE G, FRAZER B C. Neutron-diffraction study of antiferromagnetic Ba2CoWO6 and Ba2NiWO6. Journal of Applied Physics, 1967, 38(3): 1459.
DOI URL |
| [16] | RAMMEH N, EHRENBERG H, FUESS H, et al. Structure and magnetic properties of the double-perovskites Ba2(B,Re)2O6 (B=Fe, Mn, Co and Ni). Physica Status Solidi (c), 2006, 3(9): 3225. |
| [17] |
XIAO G L, LIU Q A, ZHAO F, et al. Sr2Fe1.5Mo0.5O6 as cathodes for intermediate-temperature solid oxide fuel cells with La0.8Sr0.2Ga0.87Mg0.13O3 electrolyte. Journal of Electrochem Society, 2011, 158: B455.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
MENG J L, LIU X J, HAN L, et al. Improved electrochemical performance by doping cathode materials Sr2Fe1.5Mo0.5-xTaxO6-δ (0≤x≤0.15) for solid state fuel cell. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 247: 845.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
DENG Z Q, SMIT J P, NIU H J, et al. B cation ordered double perovskite Ba2CoMo0.5Nb0.5O6-δ as a potential SOFC cathode. Chemistry of Materials, 2009, 21(21): 5154.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
PRADHEESH R, NAIR H S, KUMAR C M N, et al. Observation of spin glass state in weakly ferromagnetic Sr2FeCoO6 double perovskite. Journal of Applied Physics, 2012, 111(5): 053905.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
PRADHEESH R, NAIR HS, SANKARANARAYANAN V, et al. Large magnetoresistance and Jahn-Teller effect in Sr2FeCoO6. The European Physical Journal B, 2012, 85: 260.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
PRADHEESH R, NAIR HS, SANKARANARAYANAN V, et al. Exchange bias and memory effect in double perovskite Sr2FeCoO6. Applied Physics Letters, 2012, 101(14): 142401.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
CONG LG, HE TM, JI YA, et al. Synthesis and characterization of IT-electrolyte with perovskite structure La0.8Sr0.2Ga0.85Mg0.15O3-δ by glycine-nitrate combustion method. Journal of Alloys and Compounds. 2003, 348(1/2): 325.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
WANG Y, JIN F, HAO X, et al. B-site-ordered Co-based double perovskites Sr2Co1-xNbxFeO5+δ as active and stable cathodes for intermediate-temperature solid oxide fuel cells. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 829: 154470.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
WU H, QIAN Y, TAN W, et al. The theoretical search for half- metallic material: the non-stoichiometric perovskite oxide Sr2FeCoO6-δ. Applied Physics Letters, 2011, 99(12): 123116.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
SHAO Z, XIONG G, TONG J, et al. Ba effect in doped Sr(Co0.8Fe0.2)O3-δ on the phase structure and oxygen permeation properties of the dense ceramic membranes. Separation and Purification Technology, 2001, 25(1/2/3): 419.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
SHAO Z, YANG W, CONG Y, et al. Investigation of the permeation behavior and stability of a Ba0.5Sr0.5Co0.8Fe0.2O3-δ oxygen membrane. Journal of Membrane Science, 2000, 172(1/2): 177.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
LIU X, JIN F, LIU X, et al. Effect of calcium doping on Sm1-xCaxBaCo2O5+δ cathode materials for intermediate-temperature solid oxide fuel cells. Electrochim Acta, 2021, 390: 138830.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
LING Y H, GUO T M, GUO Y Y, et al. New two-layer Ruddlesden-Popper cathode materials for protonic ceramics fuel cells. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2021, 10: 1052.
DOI |
| [30] |
JIN F, LIU J, NIU B, et al. Evaluation and performance optimization of double-perovskite LaSrCoTiO5+δ cathode for intermediate-temperature solid-oxide fuel cells. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 41(46): 21439.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
GHAFFARI M, SHANNON M, HUI H, et al. Preparation, surface state and band structure studies of SrTi(1-x)Fe(x)O(3-δ) (x=0-1) perovskite-type nano structure by X-ray and ultraviolet photoelectron spectroscopy. Surface Science, 2012, 606(5/6): 670.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
PIKALOVA EY, MARAGOU VI, DEMINA AN, et al. The effect of co-dopant addition on the properties of Ln0.2Ce0.8O2-δ (Ln=Gd, Sm, La) solid-state electrolyte. Journal of Power Sources, 2008, 181(2): 199
DOI URL |
| [33] |
JIN F, LIU J, SHEN Y, et al. Improved electrochemical performance and thermal expansion compatibility of LnBaCoFeO5+δ- Sm0.2Ce0.8O1.9 (LnPr and Nd) composite cathodes for IT-SOFCs. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016, 685: 483.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
LIU B, SUNARSO J, ZHANG Y, et al. Highly oxygen non- stoichiometric BaSc0.25Co0.75O3-δ as a high-performance cathode for intermediate-temperature solid oxide fuel cells. ChemElectroChem, 2018, 5(5): 785.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
BU Y F, DING D, LAI S Y, et al. Evaluation of La0.4Ba0.6Fe0.8Zn0.2O3-δ+Sm0.2Ce0.8O1.9 as a potential cobalt-free composite cathode for intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cells. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 275: 808.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
LI S L, ZHANG L K, XIA T, et al. Synergistic effect study of EuBa0.98Co2O5+δ-Ce0.8Sm0.2O1.9 composite cathodes for intermediate- temperature solid oxide fuel cells. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 771: 513.
DOI URL |
| [37] | STEELE BCH. Survey of materials selection for ceramic fuel cells II. cathodes and anodes. Solid State Ionics, 1996, 86: 1223. |
| [1] | CHAI Runyu, ZHANG Zhen, WANG Menglong, XIA Changrong. Preparation of Ceria Based Metal-supported Solid Oxide Fuel Cells by Direct Assembly Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 765-771. |
| [2] | QU Jifa, WANG Xu, ZHANG Weixuan, ZHANG Kangzhe, XIONG Yongheng, TAN Wenyi. Enhanced Sulfur-resistance for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells Anode via Doping Modification of NaYTiO4 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 489-496. |
| [3] | WAN Junchi, DU Lulu, ZHANG Yongshang, LI Lin, LIU Jiande, ZHANG Linsen. Structural Evolution and Electrochemical Performance of Na4FexP4O12+x/C Cathode Materials for Sodium-ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 497-503. |
| [4] | XUE Ke, CAI Changkun, XIE Manyi, LI Shuting, AN Shengli. Pr1+xBa1-xFe2O5+δ Cathode Materials for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells: Preparation and Electrochemical Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 363-371. |
| [5] | ZHU Zhijie, SHEN Mingyuan, WU Tao, LI Wencui. Inhibition of P2-O2 Phase Transition for P2-Na2/3Ni1/3Mn2/3O2 as Cathode of Sodium-ion Battery via Synergetic Substitution of Cu and Mg [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 184-195. |
| [6] | ZHANG Jinghui, LU Xiaotong, MAO Haiyan, TIAN Yazhou, ZHANG Shanlin. Effect of Sintering Additives on Sintering Behavior and Conductivity of BaZr0.1Ce0.7Y0.2O3-δ Electrolytes [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 84-90. |
| [7] | WANG Kunpeng, LIU Zhaolin, LIN Cunsheng, WANG Zhiyu. Development of Quasi-solid-state Na-ion Battery Based on Water-minimal Prussian Blue Cathode [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(9): 1005-1012. |
| [8] | PAN Jianlong, MA Guanjun, SONG Lemei, HUAN Yu, WEI Tao. High Stability/Catalytic Activity Co-based Perovskite as SOFC Anode: In-situ Preparation by Fuel Reducing Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(8): 911-919. |
| [9] | YE Zibin, ZOU Gaochang, WU Qiwen, YAN Xiaomin, ZHOU Mingyang, LIU Jiang. Preparation and Performances of Tubular Cone-shaped Anode-supported Segmented-in-series Direct Carbon Solid Oxide Fuel Cell [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(7): 819-827. |
| [10] | ZHANG Kun, WANG Yu, ZHU Tenglong, SUN Kaihua, HAN Minfang, ZHONG Qin. LaNi0.6Fe0.4O3 Cathode Contact Material: Electrical Conducting Property Manipulation and Its Effect on SOFC Electrochemical Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(4): 367-373. |
| [11] | CHENG Jie, ZHOU Yue, LUO Xintao, GAO Meiting, LUO Sifei, CAI Danmin, WU Xueyin, ZHU Licai, YUAN Zhongzhi. Construction and Electrochemical Properties of Yolk-shell Structured FeF3·0.33H2O@N-doped Graphene Nanoboxes [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(3): 299-305. |
| [12] | ZHOU Jingyu, LI Xingyu, ZHAO Xiaolin, WANG Youwei, SONG Erhong, LIU Jianjun. Rate and Cycling Performance of Ti and Cu Doped β-NaMnO2 as Cathode of Sodium-ion Battery [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(12): 1404-1412. |
| [13] | XUE Dingxi, YI Bingyao, LI Guojun, MA Shuai, LIU Keqin. Numerical Simulation of Thermal Stress in Solid Oxide Fuel Cells with Functional Gradient Anode [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(11): 1189-1196. |
| [14] | WANG Machao, TANG Yangmin, DENG Mingxue, ZHOU Zhenzhen, LIU Xiaofeng, WANG Jiacheng, LIU Qian. Cs2Ag0.1Na0.9BiCl6:Tm3+ Double Perovskite: Coprecipitation Preparation and Near-infrared Emission [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(9): 1083-1088. |
| [15] | ZHANG Lun, LYU Mei, ZHU Jun. Research Progress of Cs2AgBiBr6 Perovskite Solar Cell [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(9): 1044-1054. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||