
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2015, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (12): 1283-1290.DOI: 10.15541/jim20150150
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZOU Ai-Hua1, 2, ZHOU Xian-Liang1, 2, HUA Xiao-Zhen2, WU Kai-Yang2
Received:2015-03-26
Revised:2015-07-09
Published:2015-12-20
Online:2015-11-24
About author:ZOU Ai-Hua. E-mail: aihua553030@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
ZOU Ai-Hua, ZHOU Xian-Liang, HUA Xiao-Zhen, WU Kai-Yang. Effect of Continuous-distribution Inter-phase on the Thermal Conductivity of SiCp/Al Composites by Numerical Simulation Method[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(12): 1283-1290.
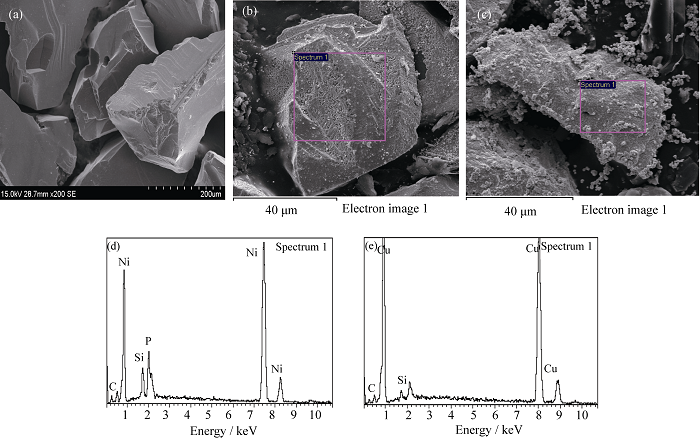
Fig. 1 SEM morphology and EDS analysis of SiC particles with different pre-treatments. (a) after pickling , (b, d) electroless Ni deposition, (c, e) electroless Cu deposition
| Model | Parameter | Value of parameter |
|---|---|---|
| Four particles coated by inter-phase completely | Type of inter-phase | 1.4(SiO2); 5.9(MgAl2O4); 10, 50, 90(Ni); …, 290, 384(Cu) |
| Thickness of inter-phase | 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, …, 4.5 μm |
Table 1 Model of the composites, the simulated parameters and the corresponding values
| Model | Parameter | Value of parameter |
|---|---|---|
| Four particles coated by inter-phase completely | Type of inter-phase | 1.4(SiO2); 5.9(MgAl2O4); 10, 50, 90(Ni); …, 290, 384(Cu) |
| Thickness of inter-phase | 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, …, 4.5 μm |
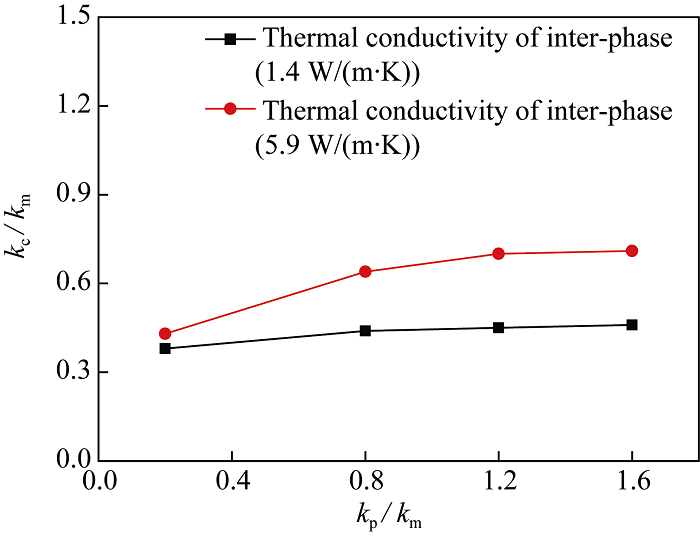
Fig. 8 Variation in the ratio of thermal conductivity of the composites (kc) to the matrix (km) with the ratio of thermal conductivity of the particles (kp) to the matrix (km)
| t/a | t/μm | Kc/(W·m-1·K-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kj1=1.4 (W·m-1·K-1) | Kj2=384 (W·m-1·K-1) | ||
| 1: 300 | 0.5 | 153.53 | 153.59 |
| 3.5 | 153.20 | 154.43 | |
| 1: 30 | 0.5 | 123.92 | 167.60 |
| 3.5 | 73.28 | 170.41 | |
| 1: 3 | 0.5 | 62.20 | 204.29 |
| 3.5 | 61.80 | 204.65 | |
Table 2 Value of thermal conductivity of the composites with different thickness of inter-phase when varying in t/a and intrinsic thermal conductivity of inter-phase
| t/a | t/μm | Kc/(W·m-1·K-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kj1=1.4 (W·m-1·K-1) | Kj2=384 (W·m-1·K-1) | ||
| 1: 300 | 0.5 | 153.53 | 153.59 |
| 3.5 | 153.20 | 154.43 | |
| 1: 30 | 0.5 | 123.92 | 167.60 |
| 3.5 | 73.28 | 170.41 | |
| 1: 3 | 0.5 | 62.20 | 204.29 |
| 3.5 | 61.80 | 204.65 | |
| SiC particle | Experimented/(W·m-1·K-1) | Simulated/(W·m-1·K-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface state | Diameter/μm | Volume fraction/% | ||
| After pickling | 90 | 50 | 161.83 | 162.54 |
| Ni-coated (3.5μm) | 90 | 50 | 152.80 | 156.66 |
| Cu-coated (3.5μm) | 90 | 50 | 168.21 | 170.41 |
Table 3 Comparison of the experimental values with the simulated values for thermal conductivity of SiCp/Al composites
| SiC particle | Experimented/(W·m-1·K-1) | Simulated/(W·m-1·K-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface state | Diameter/μm | Volume fraction/% | ||
| After pickling | 90 | 50 | 161.83 | 162.54 |
| Ni-coated (3.5μm) | 90 | 50 | 152.80 | 156.66 |
| Cu-coated (3.5μm) | 90 | 50 | 168.21 | 170.41 |
| [1] | LAI Y S, WANG T H, LEE C C.Thermal-mechanical coupling analysis for coupled power-and thermal-cycling reliability of board-level electronic packages.IEEE T Device Mat. Re., 2008, 8(1): 122-128. |
| [2] | SONG M, HE Y H.Effects of die-pressing pressure and extrusion on the microstructures and mechanical properties of SiC reinforced pure aluminium composites.Mater. Des., 2010, 31: 985-989. |
| [3] | KACZMAR J W, PIETRZAK K, WLOSIŃSKI W. The production and application of metal matrix composite materials.J. Mater. Process Technol., 2000, 106(1): 58-67. |
| [4] | VETTERLIA M, TAVANGARB R, WEBERB L.Influence of the elastic properties of the phases on the coefficient of thermal expansion of a metal matrix composite.Scripita Mater., 2011, 64(2): 153-156. |
| [5] | REN S B, HE X B, QU X H.Effect of Mg and Si in the aluminum on the thermo-mechanical properties of pressureless infiltrated SiCp/Al composites.Compos. Sci. Technol., 2007, 67(10): 2103-2113. |
| [6] | UREÑA A, MARTÍNEZ E E, RODROGO P, GIL L. Oxidation treatments for SiC particulate used as reinforcement in aluminium matrix composites.Compos. Sci. Technol., 2004, 64(12): 1843-1854. |
| [7] | PECH-CANUL M I, MAKHLOUF M M. Processing of Al-SiCp metal matrix composites by pressureless infiltration of SiC preforms.J. Mater. Synth. Process, 2000, 8(1): 35-53. |
| [8] | LEE H S, HONG S H.Pressure infiltration casting process and thermophysical properties of high volume fraction SiCp/Al metal matrix composites.Mater. Sci. Technol., 2003, 19(8): 1057-1064. |
| [9] | LEÓN C A, DREW R A L. The influence of nickel coating on the wettability of aluminum on ceramics.Compos. Part A, 2002, 33(10): 1429-1432. |
| [10] | MANDAL D, VISWANATHAN S.Effect of heat treatment on microstructure and interface of SiC particle reinforced 2124 Al matrix composite.Mater. Character., 2013, 85: 73-81. |
| [11] | LIU MEI-TAN, CAI XU-SHENG, LI GUO-QIANG.Microstructure and thermal properties of high-performance SiC reinforced Al matrix composite.T. Nonferr. Metal Soc., 2013, 23(4): 1040-1046. |
| [12] | MANDAL D, VISWANATHAN S.Effect of re-melting on particle distribution and interface formation in SiC reinforced 2124Al matrix composite.Mater. Charact., 2013, 86: 21-27. |
| [13] | JEONG J H, KIM Y, LEE J C.Mechanical properties of 2014Al/SiC composites with oxidized SiC particles.Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2003, 34(6): 1361-1369. |
| [14] | DONG R H, YANG W S, WU P, et al.High content SiC nanowires reinforced Al composite with high strength and plasticity.Mater. Sci. Engineer: A, 2015, 630: 8-12. |
| [15] | KAWAI C.Effect of interfacial reaction on the thermal conductivity of Al-SiC composites with SiC dispersions.J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2001, 84(4): 896-898. |
| [16] | JI Y, ZHONG T X, GAO X X, et al.Scanning thermal microscopic analysis of interface thermal conductivity of high thermal conductivity composites for electronic packaging.J. Electron Micros. Soc., 2001, 20(3): 238-243. |
| [17] | YUAN M, YU J K, CHEN D G, et al.Interface and properties of SiCp/ZL101 matrix composites.Chin. J. Nonferrous. Met., 2013, 23(3): 779-785. |
| [18] | ZHANG J Y, WANG Y, CUI X, et al.Numerical simulation of thermal conductivity of SiCp /Al composites. T. Mater. Heat Treat, 2010, 31(8): 146-150. |
| [19] | ZHOU X L, ZHANG J Y, HUA X Z, et al. The proeess and the mechanism of making aluminium matrix partical reinforeed composite by pressureless-infiltration.Hot Working Technology, 1995(3): 25-27. |
| [20] | WANG H Y, SHANG J L, LIU G Q, et al.Overview on description methods for the spatial distribution of the second phase in multi-phase materials.Adv. Mech., 2000, 25(4): 558-570. |
| [1] | WANG Weiming, WANG Weide, SU Yi, MA Qingsong, YAO Dongxu, ZENG Yuping. Research Progress of High Thermal Conductivity Silicon Nitride Ceramics Prepared by Non-oxide Sintering Additives [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(6): 634-646. |
| [2] | JIN Min, MA Yupeng, WEI Tianran, LIN Siqi, BAI Xudong, SHI Xun, LIU Xuechao. Growth and Characterization of Large-size InSe Crystal from Non-stoichiometric Solution via a Zone Melting Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(5): 554-560. |
| [3] | WANG Shuling, JIANG Meng, WANG Lianjun, JIANG Wan. n-Type Pb-free AgBiSe2 Based Thermoelectric Materials with Stable Cubic Phase Structure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(7): 807-814. |
| [4] | CHEN Qiang, BAI Shuxin, YE Yicong. Highly Thermal Conductive Silicon Carbide Ceramics Matrix Composites for Thermal Management: a Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 634-646. |
| [5] | ZHANG Shuo, FU Qiangang, ZHANG Pei, FEI Jie, LI Wei. Influence of High Temperature Treatment of C/C Porous Preform on Friction and Wear Behavior of C/C-SiC Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 561-568. |
| [6] | FU Shi, YANG Zengchao, LI Jiangtao. Progress of High Strength and High Thermal Conductivity Si3N4 Ceramics for Power Module Packaging [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(10): 1117-1132. |
| [7] | SUN Xiaofan, CHEN Xiaowu, JIN Xihai, KAN Yanmei, HU Jianbao, DONG Shaoming. Fabrication and Properties of AlN-SiC Multiphase Ceramics via Low Temperature Reactive Melt Infiltration [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(10): 1223-1229. |
| [8] | FU Shi, YANG Zengchao, LI Honghua, WANG Liang, LI Jiangtao. Mechanical Properties and Thermal Conductivity of Si3N4 Ceramics with Composite Sintering Additives [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 947-953. |
| [9] | HU Jiajun, WANG Kai, HOU Xinguang, YANG Ting, XIA Hongyan. Boron Phosphide with High Thermal Conductivity: Synthesis by Molten Salt Method and Thermal Management Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 933-940. |
| [10] | WANG Pengjiang, KANG Huijun, YANG Xiong, LIU Ying, CHENG Cheng, WANG Tongmin. Inhibition of Lattice Thermal Conductivity of ZrNiSn-based Half-Heusler Thermoelectric Materials by Entropy Adjustment [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 717-723. |
| [11] | RUAN Jing, YANG Jinshan, YAN Jingyi, YOU Xiao, WANG Mengmeng, HU Jianbao, ZHANG Xiangyu, DING Yusheng, DONG Shaoming. Porous SiC Ceramic Matrix Composite Reinforced by SiC Nanowires with High Strength and Low Thermal Conductivity [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(4): 459-466. |
| [12] | LOU Xunuo, DENG Houquan, LI Shuang, ZHANG Qingtang, XIONG Wenjie, TANG Guodong. Thermal and Electrcial Transport Properities of Ge Doped MnTe Thermoelectrics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(2): 209-214. |
| [13] | WANG Weide, CHEN Huanbei, LI Shishuai, YAO Dongxu, ZUO Kaihui, ZENG Yuping. Preparation of Silicon Nitride with High Thermal Conductivity and High Flexural Strength Using YbH2-MgO as Sintering Additive [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(9): 959-966. |
| [14] | WANG Haoxuan, LIU Qiaomu, WANG Yiguang. Research Progress of High Entropy Transition Metal Carbide Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(4): 355-364. |
| [15] | SANG Weiwei, ZHANG Hongsong, CHEN Huahui, WEN Bin, LI Xinchun. Preparation and Thermophysical Properties of (Sm0.2Gd0.2Dy0.2Y0.2Yb0.2)3TaO7 High-entropy Ceramic [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(4): 405-410. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||