|
|
Research Progress in Improvement of Oxygen Permeation Properties for Dual-phase Mixed Conducting Membranes
CHEN Ting, JIANG Wan, JIANG Wei-Hui, LIU Jian-Min, ZHANG Xiao-Jun, XIE Zhi-Xiang
2015 Vol. 30 (12): 1233–1242
 Abstract
Abstract(
945 )
 HTML
HTML(
14)
 PDF
PDF(783KB)(
2093
)
Dual-phase mixed conducting membrane can transport oxygen ions and electrons simultaneously at high temperature. Due to its high stability, low thermal expansion coefficient, high mechanical strength, and tunable component, it shows great potential in application of partial oxidation of methane to syngas (POM). However, how to improve its oxygen permeation flux is a key problem needing to be solved. In this review, the controlled step of the permeation process was analyzed based on the permeation mechanization. The improvements were presented, including utilized mixed conductor as electron conducting phase, reduced electronic threshold and decreased the grain size of the two phases. Meanwhile, fabricating asymmetric membrane, tube membrane and hollow fiber membrane were also efficient ways to reduce the thickness and to increase the surface area of the membrane, resulting in much increased permeation flux. Finally, some key problems to be solved in the future were also outlined.
|
|
|
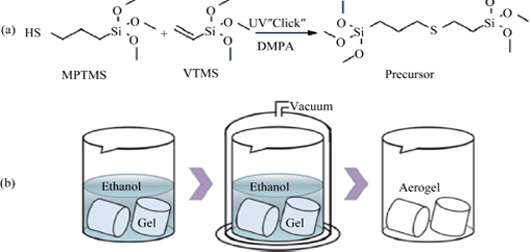
An Overview on Silica Aerogels Synthesized by Siloxane Co-precursors
HE Fei, YU Wan-Jun, FANG Min-Han, HE Xiao-Dong, LI Ming-Wei
2015 Vol. 30 (12): 1243–1253
 Abstract
Abstract(
1298 )
 HTML
HTML(
15)
 PDF
PDF(571KB)(
1570
)
Due to their unique features, such as high specific surface area, high porosity, low density, low thermal conductivity, and high transmittance, aerogels can be widely applied in the fields of thermal insulation, sound insulation and optics. However, aerogels usually tend to be destructive collapse, due to their porous structures constituted by slightly brittle skeletons, which is a negative factor to restrict their applications. According to the number and variety of non-hydrolytic groups in siloxane precursors, an overview of the literatures is presented on silica aerogels synthesized by three kinds of siloxane co-precursors, i.e. integral hydrolytic co-precursors, integral/partial and partial hydrolytic co-precursors. The characteristics of porous structures and properties in mechanics, thermal insulation, optics, and hydrophobicity are analyzed. It is an effective method by choosing appropriate precursors to realize the designs and improve mechanical behaviors of aerogels in respect of structures and properties.
|
|
|
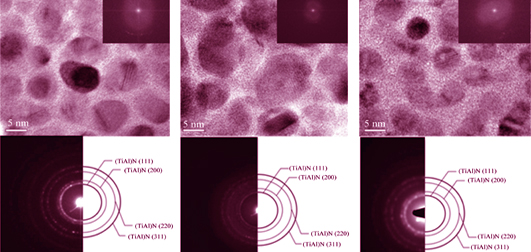
Microstructure Controlling and Properties of TiAlSiN Nanocomposite Coatings Deposited by Modulated Pulsed Power Magnetron Sputtering
WU Zhi-Li, LI Yu-Ge, WU Bi, LEI Ming-Kai
2015 Vol. 30 (12): 1254–1260
 Abstract
Abstract(
969 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(483KB)(
2917
)
TiAlSiN nanocomposite coatings were deposited by modulated pulsed power magnetron sputtering (MPPMS) from TiAlSi targets with the Al/(Al+Ti) atomic ratios (x) of 0.25, 0.5 and 0.67. The targets were powered by average sputtering power of 1-4 kW under work pressure of 0.3 Pa with a nitrogen addition of 25%. All of the TiAlSiN coatings with a nitrogen content of 52.0at%~56.7at% possessed an nc-TiAlN/a-Si3N4/AlN nanocomposite structure. As x increased, the percentage of amorphous phases was increased, meanwhile the hardness of the coatings firstly increased and then decreased. In the TiAlSiN coating with x =0.5, a highest hardness of 28.7 GPa was detected. Improvement in average sputtering power could prompt the formation of a complete phase separation nanocomposite coatings with a constant grain size. With x =0.67 under average sputtering power from 1 kW to 4 kW, the hardness of the coatings increased from 16.4 GPa to 21.3 GPa. A low wear rate of about (0.13-6.25) ×10-5 mm3/(N·m) was detected in the TiAlSiN coatings with different Al contents as a function of the average sputtering power. An optimized wear resistance was identified in the TiAlSiN coatings deposited by MPPMS under average sputtering power of 2 kW at x =0.5.
|
|
|
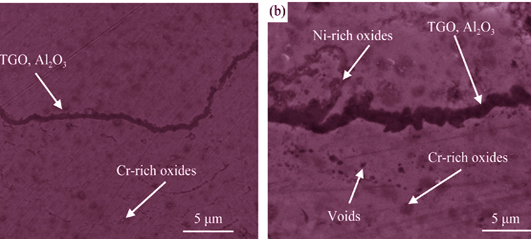
Structure Evolution of 7YSZ Thermal Barrier Coating During Thermal Shock Testing
ZHANG Xiao-Feng, ZHOU Ke-Song, ZHANG Ji-Fu, ZHANG Yong, LIU Min, DENG Chun-Ming
2015 Vol. 30 (12): 1261–1266
 Abstract
Abstract(
783 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(468KB)(
1319
)
Bond coating NiCoCrAlYTa was prepared on nickel-based superalloy by low temperature-high velocity oxygen flame (LT-HVOF). Then 7wt% Y2O3 stabilized ZrO2 ceramic coating was fabricated on bond coating by air plasma spray (APS). Diffusion principles of bond coating were investigated under thermal cycle by using multi-functional flame tester. Sintering and phase transformation of ceramic coating were studied. The experiment results show that with thermal cycle increase, thermally grown oxide (TGO) forms at the interface of ceramic-bond coating and its thickness continuously increases. Besides, the bond coating further diffuses to surface of ceramic coating. Lots of oxides appears on the surface of ceramic coating nearing microcrack. Diffusion of bond coating to surface contributes to sintering of ceramic coating, which leads to increase of microhardness. Additionally, plenty of voids were appeares in bond coating for Kirkendall effect resulting in decrease of microhardness. Large-scale cracks are observed after thermal cycle due to phase transformation and thermal residual stress.
|
|
|
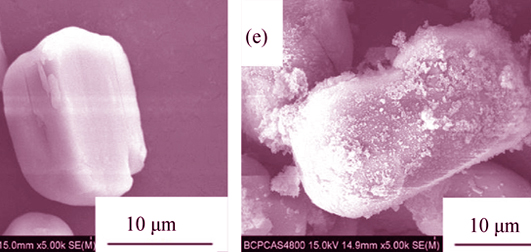
Preparation of Ammonium Polyphosphate Coated with Aluminium Hydroxide and Its Application in Polypropylene as Flame Retardant
QIN Zhao-Lu, LI Ding-Hua, YANG Rong-Jie
2015 Vol. 30 (12): 1267–1272
 Abstract
Abstract(
1428 )
 HTML
HTML(
23)
 PDF
PDF(402KB)(
2039
)
A new surface-modification method was adopted to decrease water solubility and enhance flame retradancy of ammonium polyphosphate (APP) by means of coating with aluminium hydroxide (ATH). The data of X-Ray Fluorescence Spectrometer (XRF) and scanning electron microscope (SEM) demonstrated that ATH was deposited on the surface of APP particles, and lower water resistance and rougher surface were verified. Furthermore, the modified APP was applied with dipentaerythritol (DPER) to prepare flame retarded polypropylene (FR-PP). The combustion behaviors of FR-PP were studied by limiting oxygen index (LOI), UL 94 vertical burning and cone calorimeter tests. Results show that loading of the coated APP has improved flame retardancy of FR-PP composites remarkably. Compared with unmodified APP, PP/DPER/coated APP can pass V-0 in UL 94 test, LOI value increases from 26.6% to 31.8%, and the peak heat release rate (PHRR) decreases from 475 kW/m2 to 308 kW/m2. Finally, study on char residues of FR-PP composites indicates that APP coated with ATH makes char layer more complete and more compact, which contributes to the improvement of flame retardancy.
|
|
|
Low-temperature Synthesis and Characterizations of LaFeAsO Nanocrystals
ZHANG De-Xing, SUN Yun-Lei, ABULIMIT Abuduweli, CAO Guang-Han
2015 Vol. 30 (12): 1273–1277
 Abstract
Abstract(
831 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(422KB)(
1544
)
LaFeAsO as a parent compound of iron-based superconductor was synthesized at low temperatures. The mixtures of La2O3, LaCl3 and BaFe2As2 were ball-milled and the pressed pellets were sintered at 500℃ in vacuum. And nanocrystals of LaFeAsO were formed during the solid-state reaction. The solid-state reaction temperature for preparing LaFeAsO is 200℃ lower than the literature reported. The average crystallite size of the as-prepared LaFeAsO is less than 100 nm, as estimated by the X-ray diffraction Scherrer formula. Meanwhile, the c axis of the unit cell is increased by 0.001 nm, primarily stemming from the nanosize effect. Electrical resistivity measurement shows that the spin-density-wave anomaly becomes unremarkable, accompanied by a significant decrease in the transition temperature. The phenomena are discussed in terms of crystallite-size effect and the influence of lattice parameters.
|
|
|
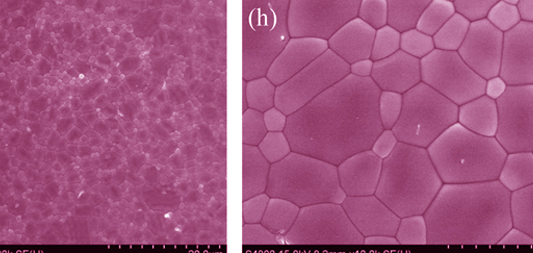
Synthesis of Negative Thermal Expansion Sc2W3O12 Thin Film
ZHANG Zhi-Ping, LIU Hong-Fei, PAN Kun-Min, CHEN Xiao-Bing, ZENG Xiang-Hua
2015 Vol. 30 (12): 1278–1282
 Abstract
Abstract(
865 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(428KB)(
2039
)
Orthorhombic Sc2W3O12 thin films were deposited by pulsed laser deposition method. The microstructure, composition and morphology of the Sc2W3O12 ceramic target and thin films were investigated using the X-ray diffraction (XRD) and field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM). The effects of the substrate temperature and oxygen pressure on the Sc2W3O12 thin films were studied. The negative thermal expansion (NTE) properties of the Sc2W3O12 ceramic target and thin film were characterized using high temperature XRD and thermal mechanical analysis (TMA). Results indicate that the compact orthorhombic Sc2W3O12 ceramic target with excellent NTE can be prepared by sintering at 1000℃ for 6 h. The average thermal expansion coefficient of the orthorhombic Sc2W3O12 ceramic target is -5.28×10-6 K-1 from room temperature to 600℃. All the as-deposited Sc2W3O12 thin films are amorphous. The surface of the as-deposited Sc2W3O12 thin film becomes smoother, but it becomes uneven when the substrate temperature increases. The Sc2W3O12 thin film with excellent NTE is crystallized after annealing at 1000℃ for 7 min. The thermal expansion coefficient of the orthorhombic Sc2W3O12 thin film is calculated to be -7.17×10-6 K-1 in the temperature range from room temperature to 600℃.
|
|
|
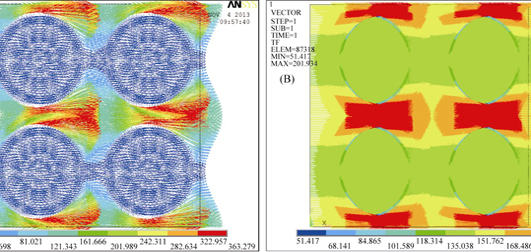
Effect of Continuous-distribution Inter-phase on the Thermal Conductivity of SiCp/Al Composites by Numerical Simulation Method
ZOU Ai-Hua, ZHOU Xian-Liang, HUA Xiao-Zhen, WU Kai-Yang
2015 Vol. 30 (12): 1283–1290
 Abstract
Abstract(
728 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(761KB)(
1443
)
Thermal conductivity of SiC particles-reinforced Al matrix (SiCp/Al) composites was simulated by finite element method (FEM), in which the models of SiC particles coated with inter-phase in the aluminum matrix was established. The effects of inter-phase types and thickness on the thermal conductivity of composites were investigated. The results show that, when the inter-phase combines ideally with SiC and Al which distributes continuously on the surface of SiCp, the thermal conductivity of composites inter-phase acts like a role of iner-layer. With increase of thermal conductivity of inter-layer, the thermal conductivity of the composites increases quickly at first and slowly afferwards. The variation of thermal conductivity of the composites depends on the ratio of inter-layer thickness (t) to the SiCp diameter (a). When the t/a value is very small or very large, the variation of the thermal conductivity is very small, while t/a is small, the variation of thermal conductivity of the composites is related to thermal conductivity of the inter-layer.
|
|
|
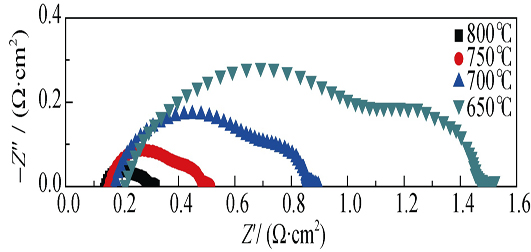
Phase Inversion Tape Casting and Electrochemical Performance of Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Anode
ZHANG Yu-Yue, LIN Jie, MIAO Guo-Shuan, GAO Jian-Feng, CHEN Chu-Sheng, XIA Chang-Rong, ZHAN Zhong-Liang, WANG Shao-Rong
2015 Vol. 30 (12): 1291–1294
 Abstract
Abstract(
1133 )
 HTML
HTML(
16)
 PDF
PDF(461KB)(
2183
)
For an anode-supported solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC), the anode consists of a thick support layer with large pores and a thin functional layer with small pores. In the present work, the anode of NiO and yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ) comprising a porous support layer of ~700 μm thick and a functional layer of ~60 μm thick were formed in a single step using the phase inversion tape casting method. For the as-prepared anode, the support layer contained large open pores which were aligned along the thickness direction. A thin dense YSZ electrolyte layer with a thickness of 15 μm was deposited onto the anode by dip-coating and co-sintering techniques. A composite cathode of YSZ-La0.8Sr0.2MnO3-δ (LSM) with a weight ratio of 50:50 was screen-printed on the surface of the YSZ electrolyte layer. The resulting fuel cell exhibited promising electrochemical performance. A maximum power density of 891 mW/cm2 was obtained at 800 ℃ using H2-3% H2O as the fuel and ambient air as the oxidant. The cell did not show any sign of concentration polarization even at high current densities, which should be attributed to the open straight pore structure and resultant fast gas-phase transport in the anode support.
|
|
|
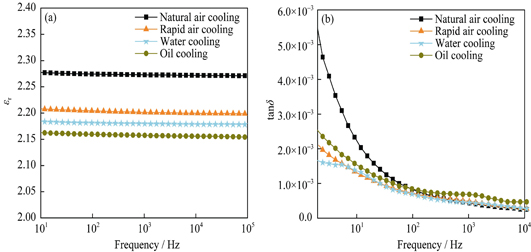
Effects of Cooling Methods on Dielectric Properties of MMT/LDPE
CHENG Yu-Jia, ZHANG Xiao-Hong, ZHOU Xue-Dong, GUO Ning, CHENG Ru-Ru, ZHANG Tian-Xu
2015 Vol. 30 (12): 1295–1302
 Abstract
Abstract(
733 )
 HTML
HTML(
7)
 PDF
PDF(667KB)(
1565
)
The melting intercalation method was used to prepare montmorillonite/low density polyethylene (MMT/LDPE) nano-composites. Through natural air cooling, rapid air cooling, water cooling, and oil cooling methods, the effects of different preparation processes on the dielectric properties of the composites were studied. The MMT/LDPE composite materials were characterized by XRD, FTIR, AFM, PLM, DSC, and TSC test. All experimental results show that the surface modified nano-MMT particles have been exfoliated and uniformly disperse in polyethylene. Different cooling processes have influence on the crystallinity of the composites. The oil cooling sample has higher crystallization rate and smaller crystal size. The density and depth of trap in the composites with nano-MMT are increased, which effectively improves dielectric properties of the polymer. Space charge in the composites by oil cooling process is evidently inhibited under 20 kV/mm and 40 kV/mm field strength. The peak value of positive charge is decreased by 63.57% and 51.39% as compared with that of natural air cooling. The oil cooling sample shows the smallest conductivity, and the largest breakdown strength. In the frequency range of 1-105 Hz, the dielectric constant and dielectric loss angle tangent of other threetypes of rapid air cooling, water cooling and oil cooling samples decrease at different degrees in contrast to natural air cooling sample.
|
|
|
Effect of the Oxidizing Atmosphere on the Microstructure and Dielectric Properties of CaCu3Ti4O12 Ceramics
ZHAO Xue-Tong, REN Lu-Lu, LIAO Rui-Jin, LI Jian-Ying, WANG Fei-Peng
2015 Vol. 30 (12): 1303–1309
 Abstract
Abstract(
741 )
 HTML
HTML(
6)
 PDF
PDF(686KB)(
1390
)
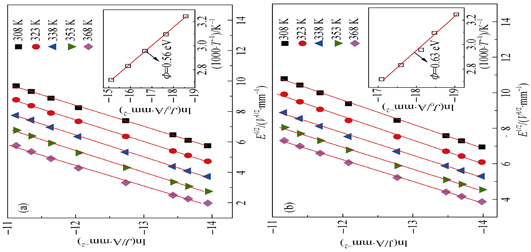
CaCu3Ti4O12 ceramics were synthesized by using the solid-state reaction method, and the roles of heat-treatment in the oxidizing atmosphere on the microstructure and dielectric properties were investigated in this work. It is indicated that after heat-treatment in the oxidizing atmosphere, the dielectric constant is decreased slightly and the dielectric loss tangent is effectively suppressed to 0.03-0.04. In the temperature range of 183-273 K, the dielectric loss is composed of conductance loss and two relaxation loss peaks. It is worth noting that the conductance loss at low frequency is reduced obviously. The result impedance spectra analysis reveals that the grain boundary resistance of CaCu3Ti4O12 ceramics is boosted from 1.8×104 Ω to 8.6×104 Ω at 393 K. Furthermore, the results from volt-ampere characteristics (J-E) exhibit that the breakdown field and nonlinear coefficient of CaCu3Ti4O12 ceramics are increased from 226 V/mm and 3.52 to 397 V/mm and 4.51, respectively. The barrier height is also increased from 0.56 eV to 0.63 eV.
|
|
|
Crystallization Behavior of Glass Ceramic Filler During Joining Process
ZHU Wei-Wei, CHEN Ji-Chun
2015 Vol. 30 (12): 1310–1314
 Abstract
Abstract(
926 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(581KB)(
2486
)
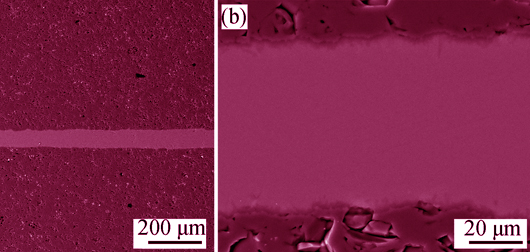
A CaO-Al2O3-SiO2 system glass ceramic with addition of Li2O and Fe2O3 was developed to join alumina ceramics. The crystallization behavior of the glass interlayer during joining process was investigated by DTA, SEM and XRD. The effect of joint microstructure and phase composition on the joint strength was study. The results show that LiAlSi2O6, CaSiO3, Ca3Fe2Si3O12, and CaAl2Si2O8 are formed in the glass during conventional crystallization treatment. However, when the glass was used to join alumina, the crystallization behavior of the glass interlayer is closely related to the heating cycle. Direct cooling from joining temperature leads to completely amorphous interlayer formation, due to the absence of enough nucleation driving force. An extra nucleation-crystallization treatment during cooling contributes to crystallization of the glass interlayer in joints. Meannhile, the phase composition of glass interlayer can be adjusted by changing the crystallization temperature according to the DTA results. In addition, the joint strength is highly sensitive to crystalline phases in the interlayer. When there is only CaAl2Si2O8 formed in the interlayer, the joint strength reaches as high as 247.5 MPa. By contrast, when there is LiAlSi2O6 or Ca3Fe2Si3O12 formed in the interlayer, the joint strength is only 10-135 MPa.
|
|
|
Carbon Supported Pd-Fe Catalyst with Uniform Alloy Structure Prepared with Direct Thermo-decomposition Method for Oxygen Reduction Reaction
WANG Yan-En, WU Xiao-Jie, HE Cheng-Lei, ZHAO Jia-Ning, TANG Ya-Wen, LU Tian-Hong
2015 Vol. 30 (12): 1315–1320
 Abstract
Abstract(
763 )
 HTML
HTML(
1)
 PDF
PDF(440KB)(
1615
)
The Pd3-Fe1/C catalyst was synthesized with the direct thermo-decomposition method using Pd(CH3COO)2 and Fe(CH3COO)2 as precursors. The Pd3-Fe1/C catalyst was characterized with X-ray diffraction(XRD), transmission electron microscope(TEM) and X-photoelectron spectroscope(XPS). The electrocatalytic performance of the Pd3-Fe1/C catalyst was investigated with the cyclic voltammetry and Linear scan voltammograms.The results show that Fe atom has entered into the Pd crystal lattice and formed a single-phase fcc disordered alloyed structure (solid solution). Electrochemical data indicate that the eletrocatalytic activity of the Pd3-Fe1/C electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) is much higher than that of Pd/C electrocatalyst.
|
|
|
Photocatalytic Properties of MOF-derived ZnO/C, Ag/ZnO/C Porous Composite Materials
GUO Yan-Rong, CHANG Wei, ZHANG Wen, WANG Hui
2015 Vol. 30 (12): 1321–1326
 Abstract
Abstract(
1250 )
 HTML
HTML(
12)
 PDF
PDF(457KB)(
2852
)
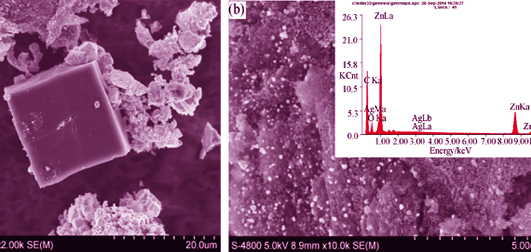
Two photocatalytic materials, ZnO/C and Ag/ZnO/C, were synthesized by high temperature heat-treatment and wet-chemical methods using a typical metal-organic framework (MOF-5) as precursor. The samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Scanning electron microscope (SEM), X-ray energy dispersive spectroscope (EDS), and UV-Vis diffuse reflection spectroscope (UV-Vis DRS), respectively. After heat-treatment under nitrogen, the initial morphology of MOF-5 is mostly retained. As a result, relatively high surface area up to 390 m2/g of ZnO/C and 232 m2/g of Ag/ZnO/C are realized. The size of Ag particles loaded on Ag/ZnO/C is about 30 nm. The photocatalytic efficiencies of both ZnO/C and Ag/ZnO/C composites on photo-degradation of methylene blue (MB) are higher than that of commercial TiO2 powder (Degussa P25). Ag/ZnO/C possesses even higher photocatalytic ability, repeatability and stability than does ZnO/C. The results strongly suggest that high temperature heat-treatment of the MOF properly followed by moderate silver doping is a facile way to improve the photocatalytic properties.
|
|
|
Influence of Al3+/Yb3+/P5+-doping on UV Transmission and Fluorescence Spectra under the UV Excitation of Silica Glasses
SHAO Chong-Yun, XU Wen-Bin, LIU Li-Wan, YANG Qiu-Hong, HU Li-Li, ZHOU Qin-Ling, WANG Shi-Kai
2015 Vol. 30 (12): 1327–1333
 Abstract
Abstract(
992 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(551KB)(
1975
)
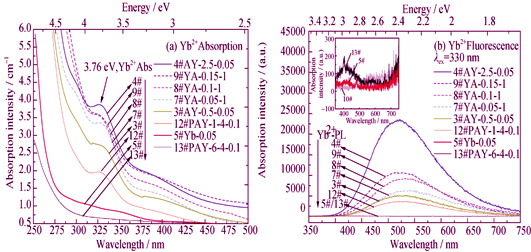
Silica glasses containing different contents of Al2O3, Yb2O3 and P2O5 were fabricated by Sol-Gel method combined with high temperature vacuum sintering. Changes in UV transmission, fluorescence spectra under the UV excitation, and X-ray photoelectron spectra (XPS) of Yb4d caused by P5+ and Al3+ ions co-doping in Yb3+-doped silica glasses were comparatively investigated. The related mechanisms were discussed. Results show that the strong absorption bands in the range of 190 nm to 300 nm in Al3+/Yb3+/P5+-doped silica glasses are largely due to the charge-transfer (CT) from O2- to Yb3+, the positions of CT-absorption bands as well as binding energy of Yb4d are shifted to the higher energy with increasing electro-negativity of the second coordination element (Al, Si, P) of Yb3+ ions. In addition, introduction of Al3+ into Yb3+-doped silica glass leads to the reduction of Yb3+ to Yb2+ ions under vacuum sintering condition. The characteristic absorption of Yb2+ ions is located at 330 nm. Nevertheless, further incorporation P5+ into Al3+/Yb3+-co-doped silica glass with mole ratio of P5+/Al3+>1 can effectively suppress the formation of Yb2+. The IR luminescence (976 nm) under UV excitation originates from a relaxed CT transition, and the visible luminescence (525 nm) is ascribed to 5d→4f transition of Yb2+. The results provide a guidance on technology optimization and composition design for fabricating high-performance Yb3+-doped fiber.
|
|
|
Fabrication of Barium Strontium Titanate Nanophotocatalysts with Gridding Structures and Their Photocatalytic Activities
ZENG Tao, BAI Yang, LI Hao, MAO Chao-Liang, DONG Xian-Lin, GUI Shu-Xiang
2015 Vol. 30 (12): 1334–1338
 Abstract
Abstract(
1145 )
 HTML
HTML(
18)
 PDF
PDF(393KB)(
1597
)
Ba0.7Sr0.3TiO3 (BST) nanocatalysts were prepared by a Sol-Gel method at pH of 2.4 and 4, respectively, both of which were presented as tetragonal phase. TEM images indicated that the BST sample obtained at pH = 2.4 was nanoparticles with an average size of about 100 nm, while that obtained at pH = 4 was gridding structures composed of nanocubes with a mean size of 100 nm. The photocatalytic behavior of BST in the degradation of Rhodamine B (RhB) was investigated. It was found that the BST catalysts with gridding structures showed much better photocatalytic performance than the BST nanoparticles. This could be attributed to the fact that the photo-generated carriers can migrate easily through the gridding-structured BST sample, which would enhance the photocatalytic activity during the degradation process. It was also found that both BST photocatalysts in this work showed good catalytic stability.
|
|
|
VS2 Nanosheets: A Potential Anode Materiral for Li-ion Batteriers
LIU Jian-Zhe, GUO Peng-Fei
2015 Vol. 30 (12): 1339–1344
 Abstract
Abstract(
1904 )
 HTML
HTML(
41)
 PDF
PDF(450KB)(
2677
)
The flower-like VS2 nanosheets were synthesized by a one-step solvothermal method. The X-ray diffraction, Raman, SEM, and TEM studies showed the growth mechanism of VS2 flowers in detail. These experimental results indicate that the reaction temperature and time have the direct effect on the formation of VS2 nanosheets. As anode material for Li-ion batteries, the VS2 nanosheets exhibit an initial discharge and charge capacity are 195.4 and 90.6 mAh/g at current density of 200 mA/g. High Coulombic efficiency over 98% and improved rate capacity are achieved for the VS2 nanosheets. All results suggest that the VS2 nanosheets can be utilized as a promising anode material for Li-ion batteries with high power density and fast charge/discharge rates.
|
|