
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (3): 281-289.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240438
Special Issue: 【结构材料】高导热陶瓷(202506)
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
MU Haojie1( ), ZHANG Yuanjiang1, YU Bin2, FU Xiumei2, ZHOU Shibin2, LI Xiaodong1(
), ZHANG Yuanjiang1, YU Bin2, FU Xiumei2, ZHOU Shibin2, LI Xiaodong1( )
)
Received:2024-10-17
Revised:2024-11-22
Published:2025-03-20
Online:2025-03-12
Contact:
LI Xiaodong, professor. E-mail: xdli@mail.neu.edu.cnAbout author:MU Haojie (1999-), female, PhD candidate. E-mail: 2110169@stu.neu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
MU Haojie, ZHANG Yuanjiang, YU Bin, FU Xiumei, ZHOU Shibin, LI Xiaodong. Preparation and Properties of ZrO2 Doped Y2O3-MgO Nanocomposite Ceramics[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 281-289.
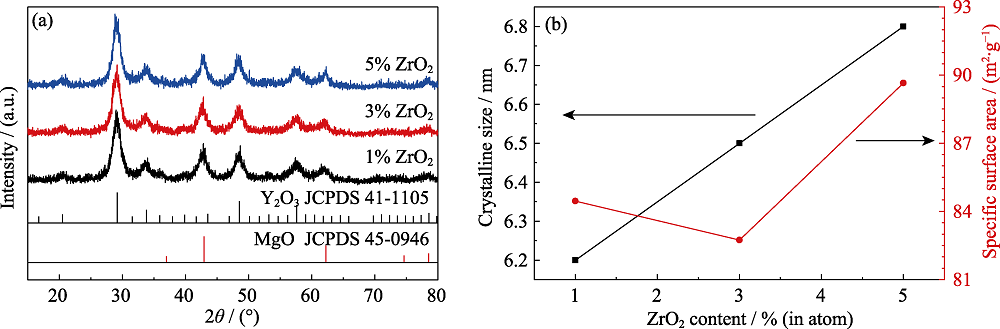
Fig. 2 (a) XRD patterns, (b) crystalline sizes and specific surface areas of Y2O3-MgO nanocomposite powders doped with different ZrO2 concentrations (atom fraction)

Fig. 3 (a) XRD patterns and diffraction peaks of (b) Y2O3 (222) and (c) MgO (200) crystal planes of Y2O3-MgO nanocomposite ceramics doped with different ZrO2concentrations (atom fraction)
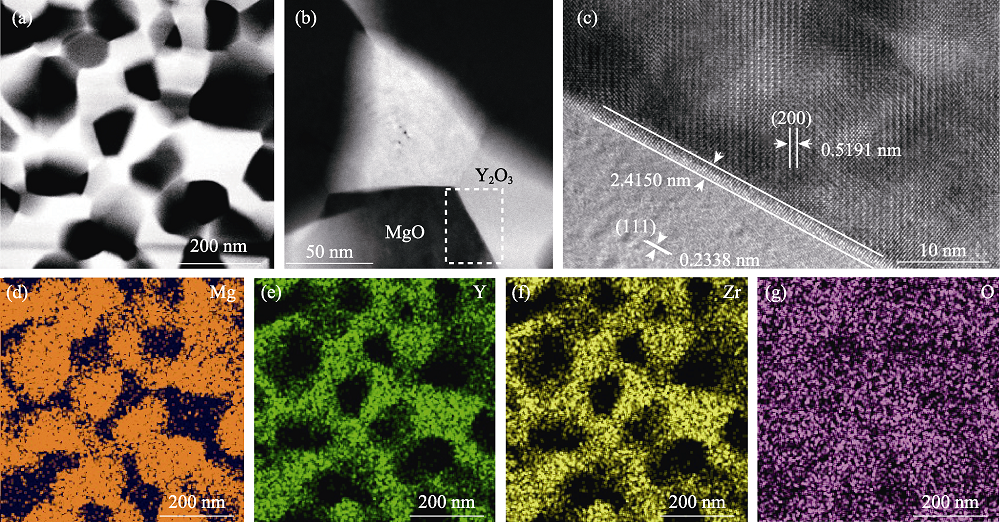
Fig. 4 (a, b) Bright field images of 3%ZrO2:Y2O3-MgO nanocomposite ceramic, (c) high resolution image of grain boundary, and (d-g) element mappings of Mg, Y, Zr, and O
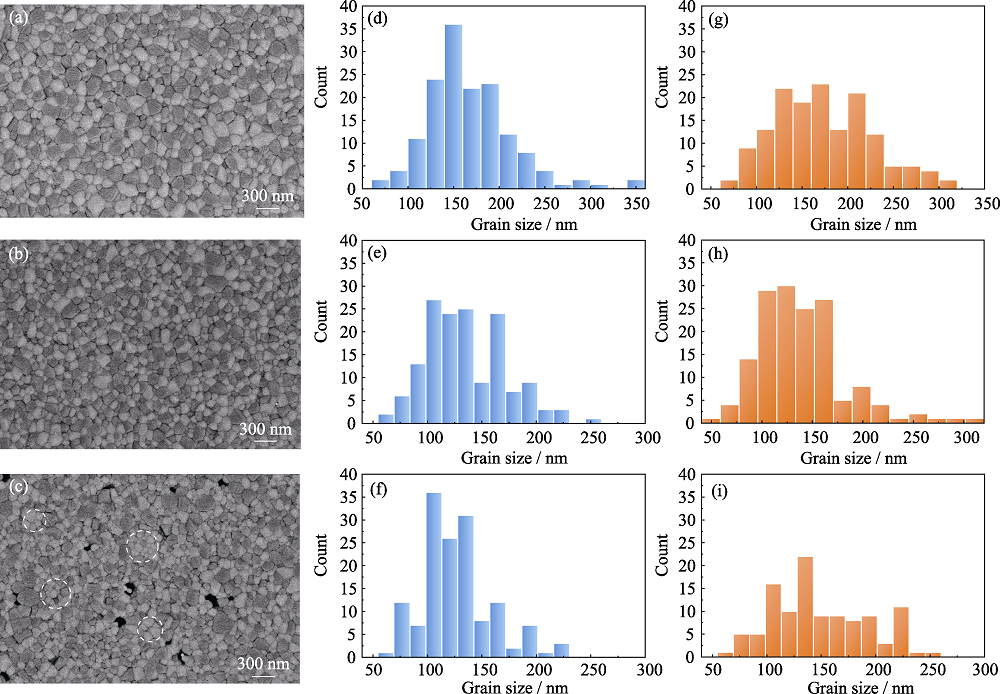
Fig. 5 Surface morphologies and grain size distributions of Y2O3 and MgO phases of ZrO2:Y2O3-MgO nanocomposite ceramics (a-c) Surface morphologies of (a) 1%ZrO2:Y2O3-MgO, (b) 3%ZrO2:Y2O3-MgO and (c) 5%ZrO2:Y2O3-MgO nanocomposite ceramics; (d-f) Grain size distributions of Y2O3 phase in (d) 1%ZrO2:Y2O3-MgO, (e) 3%ZrO2:Y2O3-MgO and (f) 5%ZrO2:Y2O3-MgO nanocomposite ceramics; (g-i) Grain size distributions of MgO phase in (g) 1%ZrO2:Y2O3-MgO, (h) 3%ZrO2:Y2O3-MgO and (i) 5%ZrO2:Y2O3-MgO nanocomposite ceramics
| [1] | LIU Z Y, IKESUE A, LI J. Research progress and prospects of rare-earth doped sesquioxide laser ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(7): 3895. |
| [2] | WANG J, ZHAO Y G, YIN D L, et al. Holmium doped yttria transparent ceramics for 2-μm solid state lasers. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2018, 38(4): 1986. |
| [3] | MA Z Z, CHEN L, CHEN J, et al. Fabrication of Y2O3 transparent ceramics by pressure-assisted alcoholic slip casting. Ceramics International, 2023, 49(23): 37729. |
| [4] | ZHANG L, YANG J, YU H Y, et al. High performance of La- doped Y2O3 transparent ceramics. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2020, 9(4): 493. |
| [5] | 李江, 姜楠, 徐圣泉, 等. 红外透明MgO-Y2O3纳米复相陶瓷研究进展. 硅酸盐学报, 2016, 44(9): 1302. |
| [6] | HARRIS D C, CAMBREA L R, JOHNSON L F, et al. Properties of an infrared-transparent MgO:Y2O3 nanocomposite. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2013, 96(12): 3828. |
| [7] | LIU L H, MORITA K, SUZUKI T S, et al. Synthesis of highly- infrared transparent Y2O3-MgO nanocomposites by colloidal technique and SPS. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(9): 13669. |
| [8] | ABBASLOO M, SHOKROLLAHI H, ALHAJI A. Slip-casting process of MgO-Y2O3 nanocomposite: investigation of powder synthesis method. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2020, 254: 123387. |
| [9] | MA H J, JUNG W K, BAEK C, et al. Influence of microstructure control on optical and mechanical properties of infrared transparent Y2O3-MgO nanocomposite. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2017, 37(15): 4902. |
| [10] | XU S Q, LI J, LI C Y, et al. Infrared-transparent Y2O3-MgO nanocomposites fabricated by the glucose Sol-Gel combustion and hot-pressing technique. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2015, 98(9): 2796. |
| [11] | FURUSE H, HORIUCHI N, KIM B N. Transparent non-cubic laser ceramics with fine microstructure. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1): 10300. |
| [12] | ITATANI K, TSUJIMOTO T, KISHIMOTO A. Thermal and optical properties of transparent magnesium oxide ceramics fabricated by post hot-isostatic pressing. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2006, 26(4/5): 639. |
| [13] | LIU L K, ZHU Q H, ZHU Q Q, et al. Fabrication of fine-grained undoped Y2O3 transparent ceramic using nitrate pyrogenation synthesized nanopowders. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(5): 5339. |
| [14] | YIN D L, WANG J, NI M, et al. Fabrication of highly transparent Y2O3 ceramics with CaO as sintering aid. Materials, 2021, 14(2): 444. |
| [15] | WANG J, YIN D L, MA J, et al. Pump laser induced photodarkening in ZrO2-doped Yb:Y2O3 laser ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(2/3): 635. |
| [16] | ZHU L L, PARK Y J, GAN L, et al. Effects of ZrO2-La2O3 co-addition on the microstructural and optical properties of transparent Y2O3 ceramics. Ceramics International, 2017, 43(11): 8525. |
| [17] | YI Q, ZHOU S M, TENG H, et al. Structural and optical properties of Tm:Y2O3 transparent ceramic with La2O3, ZrO2 as composite sintering aid. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2012, 32(2): 381. |
| [18] | LI X K, MAO X J, FENG M H, et al. Optical absorption and mechanism of vacuum-sintered ZrO2-doped Y2O3 ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2016, 36(16): 4181. |
| [19] | HOU X R, ZHOU S M, LI W J, et al. Study on the effect and mechanism of zirconia on the sinterability of yttria transparent ceramic. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2010, 30(15): 3125. |
| [20] | CAO Y F, LI H Y, ZHENG X Y, et al. Simultaneous precipitation of Zr4+ and Y3+ ions induced refinement of precursors and powders in fabrication of Zr4+ doped Y2O3 transparent ceramics. Optical Materials, 2023, 139: 113802. |
| [21] | WANG J W, ZHANG L C, CHEN D Y, et al. Y2O3-MgO-ZrO2 infrared transparent ceramic nanocomposites. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2012, 95(3): 1033. |
| [22] | LU K. Sintering of nanoceramics. International Materials Reviews, 2008, 53(1): 21. |
| [23] | STANCIU G, VOICU F, BRANDUS C A, et al. Enhancement of the laser emission efficiency of Yb:Y2O3 ceramics via multi-step sintering method fabrication. Optical Materials, 2020, 109: 110411. |
| [24] | ZHANG L, PAN W. Structural and thermo-mechanical properties of Nd:Y2O3 transparent ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2015, 98(10): 3326. |
| [25] | ZHOU H X, YANG Q H, XU J, et al. Preparation and spectroscopic properties of 2%Nd:(Y0.9La0.1)2O3 transparent ceramics. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 471(1/2): 474. |
| [26] | CHEN P L, CHEN I W. Grain boundary mobility in Y2O3: defect mechanism and dopant effects. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1996, 79(7): 1801. |
| [27] | REN Y, LI X D, MU H J, et al. The origin of microstructural inhomogeneity in vacuum-sintered ZrO2‐doped Lu2O3 transparent ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2024, 107(2): 1105. |
| [28] | XU S Q, LI J, KOU H M, et al. Spark plasma sintering of Y2O3-MgO composite nanopowder synthesized by the esterification Sol-Gel route. Ceramics International, 2015, 41(2): 3312. |
| [29] | XU S Q, LI J, LI C Y, et al. Hot pressing of infrared-transparent Y2O3-MgO nanocomposites using Sol-Gel combustion synthesized powders. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2015, 98(3): 1019. |
| [30] | PERMIN D A, BOLDIN M S, BELYAEV A V, et al. IR-transparent MgO-Y2O3 ceramics by self-propagating high-temperature synthesis and spark plasma sintering. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(10): 15786. |
| [31] | ZHANG L P, LIU Q, YU D Z, et al. Effect of sintering process on the properties of transparent Al2O3. Materials Science and Technology, 2023, 39(8): 926. |
| [32] | LU T C, CHANG X H, QI J Q, et al. Low-temperature high- pressure preparation of transparent nanocrystalline MgAl2O4 ceramics. Applied Physics Letters, 2006, 88(21): 213120. |
| [33] | SHAHBAZI H, TATAEI M. Influence of porosity on transparency behavior of MgAl2O4 spinel, experiment vs Mie theory. Optical Materials, 2019, 90: 289. |
| [34] | APETZ R, VAN BRUGGEN M P B. Transparent alumina: a light-scattering model. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2003, 86(3): 480. |
| [35] | ZHAO X M, FANG Q L, XIA C J, et al. Evaluation of pore scattering in transparent ceramics: a simplified model for nanometric spherical pores. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2023, 106(1): 527. |
| [36] | YONG S M, CHOI D H, LEE K, et al. Influence of the SPS heating rate on the optical and mechanical properties of Y2O3-MgO nanocomposites. Journal of Ceramic Processing Research, 2019, 20(1): 59. |
| [37] | ZHANG R, ZHANG K, YUAN M Y, et al. Nitrogen vacancy regulated lattice distortion on improvement of (NbMoTaW)Nx thin films: mechanical properties and wear resistance. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(6): 715. |
| [38] | CHEN Z, HUANG Y, KOUTNÁ N, et al. Large mechanical properties enhancement in ceramics through vacancy-mediated unit cell disturbance. Nature Communications, 2023, 14: 8387. |
| [39] | WANG P, WU Y, LIU J B, et al. Impacts of atomic scale lattice distortion on dislocation activity in high-entropy alloys. Extreme Mechanics Letters, 2017, 17: 38. |
| [40] | ZHU L L, LIU H L, LIN H T, et al. Effects of ZrO2 concentration on the properties of pressureless-sintered highly transparent Er2O3 ceramics. Ceramics International, 2023, 49(23): 39076. |
| [41] | LI C R, LI S, AN D, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of spark plasma sintered SiC ceramics aided by B4C. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(8): 10142. |
| [1] | ZHONG Weimin, ZHAO Ke, WANG Kewei, LIU Dianguang, LIU Jinling, AN Linan. Effect of Oscillatory Pressure Amplitude on Microstructures and Wear Resistance of Tungsten Carbide [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(9): 964-970. |
| [2] | ZHANG Jiawei, CHEN Ning, CHENG Yuan, WANG Bo, ZHU Jianguo, JIN Cheng. Electrical Properties of Bismuth Layered Piezoelectric Bi4Ti3O12 Ceramics with A/B-site Doping [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 690-696. |
| [3] | SUN Yuxuan, WANG Zheng, SHI Xue, SHI Ying, DU Wentong, MAN Zhenyong, ZHENG Liaoying, LI Guorong. Defect Dipole Thermal-stability to the Electro-mechanical Properties of Fe Doped PZT Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 545-551. |
| [4] | CHEN Yi, QIU Haipeng, CHEN Mingwei, XU Hao, CUI Heng. SiC/SiC Composite: Matrix Boron Modification and Mechanical Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 504-510. |
| [5] | CUI Ning, ZHANG Yuxin, WANG Lujie, LI Tongyang, YU Yuan, TANG Huaguo, QIAO Zhuhui. Single-phase Formation Process and Carbon Vacancy Regulation of (TiVNbMoW)Cx High-entropy Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 511-520. |
| [6] | LI Ziwei, GONG Weilu, CUI Haifeng, YE Li, HAN Weijian, ZHAO Tong. (Zr, Hf, Nb, Ta, W)C-SiC Composite Ceramics: Preparation via Precursor Route and Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 271-280. |
| [7] | GAO Chenguang, SUN Xiaoliang, CHEN Jun, LI Daxin, CHEN Qingqing, JIA Dechang, ZHOU Yu. SiBCN-rGO Ceramic Fibers Based on Wet Spinning Technology: Microstructure, Mechanical and Microwave-absorbing Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 290-296. |
| [8] | ZHENG Yuanshun, YU Jian, YE Xianfeng, LIANG Dong, ZHU Wanting, NIE Xiaolei, WEI Ping, ZHAO Wenyu, ZHANG Qingjie. Boosting the Thermoelectric Performance of Full-Heusler Fe2VAl Alloy via Substituting Al Site with V [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(12): 1425-1432. |
| [9] | WANG Yueyue, HUANG Jiahui, KONG Hongxing, LI Huaizhu, YAO Xiaohong. Silver Loaded Radial Mesoporous Silica: Preparation and Application in Dental Resins [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 77-83. |
| [10] | FAN Wugang, CAO Xiong, ZHOU Xiang, LI Ling, ZHAO Guannan, ZHANG Zhaoquan. Anticorrosion Performance of 8YSZ Ceramics in Simulated Aqueous Environment of Pressurized Water Reactor [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(7): 803-809. |
| [11] | CHEN Qian, SU Haijun, JIANG Hao, SHEN Zhonglin, YU Minghui, ZHANG Zhuo. Progress of Ultra-high Temperature Oxide Ceramics: Laser Additive Manufacturing and Microstructure Evolution [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(7): 741-753. |
| [12] | JIANG Lingyi, PANG Shengyang, YANG Chao, ZHANG Yue, HU Chenglong, TANG Sufang. Preparation and Oxidation Behaviors of C/SiC-BN Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(7): 779-786. |
| [13] | WU Yuhao, PENG Renci, CHENG Chunyu, YANG Li, ZHOU Yichun. First-principles Study on Mechanical Properties and Melting Curve of HfxTa1-xC System [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(7): 761-768. |
| [14] | WANG Weiming, WANG Weide, SU Yi, MA Qingsong, YAO Dongxu, ZENG Yuping. Research Progress of High Thermal Conductivity Silicon Nitride Ceramics Prepared by Non-oxide Sintering Additives [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(6): 634-646. |
| [15] | SUN Haiyang, JI Wei, WANG Weimin, FU Zhengyi. Design, Fabrication and Properties of Periodic Ordered Structural Composites with TiB-Ti Units [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(6): 662-670. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||