
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (6): 591-608.DOI: 10.15541/jim20230562
Special Issue: 【结构材料】超高温结构陶瓷(202506); 【结构材料】高熵陶瓷(202506)
• REVIEW • Previous Articles Next Articles
CAI Feiyan1,2,3( ), NI Dewei1,2,4(
), NI Dewei1,2,4( ), DONG Shaoming1,2(
), DONG Shaoming1,2( )
)
Received:2023-12-06
Revised:2024-01-19
Published:2024-06-20
Online:2024-01-22
Contact:
NI Dewei, professor. E-mail: deweini@mail.sic.ac.cn;About author:CAI Feiyan (1998-), female, PhD candidate. E-mail: caifeiyan19@mails.ucas.ac.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
CAI Feiyan, NI Dewei, DONG Shaoming. Research Progress of High-entropy Carbide Ultra-high Temperature Ceramics[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(6): 591-608.
| Composition | EFA/(eV/atom)-1 | Phase |
|---|---|---|
| (VNbTaMoW)C | 125 | Single-phase |
| (TiZrHfNbTa)C | 100 | Single-phase |
| (TiHfVNbTa)C | 100 | Single-phase |
| (TiVNbTaW)C | 77 | Single-phase |
| (TiHfNbTaW)C | 67 | Single-phase |
| (TiZrHfTaW)C | 50 | Single-phase |
| (ZrHfTaMoW)C | 45 | Multi-phase |
| (TiZrHfMoW)C | 38 | Multi-phase |
| (ZrHfVMoW)C | 37 | Multi-phase |
Table 1 EFA values of 9 experimentally validated HECs[31]
| Composition | EFA/(eV/atom)-1 | Phase |
|---|---|---|
| (VNbTaMoW)C | 125 | Single-phase |
| (TiZrHfNbTa)C | 100 | Single-phase |
| (TiHfVNbTa)C | 100 | Single-phase |
| (TiVNbTaW)C | 77 | Single-phase |
| (TiHfNbTaW)C | 67 | Single-phase |
| (TiZrHfTaW)C | 50 | Single-phase |
| (ZrHfTaMoW)C | 45 | Multi-phase |
| (TiZrHfMoW)C | 38 | Multi-phase |
| (ZrHfVMoW)C | 37 | Multi-phase |
| Synthesizing method | Composition (lattice parameter) | Starting materials | Synthesizing conditions | Grain size | Oxygen content/ % (in mass) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical alloying[ | (TiZrHfVNb)C (0.4496 nm) (TiZrHfVTa)C (0.4495 nm) (TiZrHfNbTa)C (0.4526 nm) (TiZrVNbTa)C (0.4440 nm) (TiHfVNbTa)C (0.4425 nm) (ZrHfVNbTa)C (0.4493 nm) | Transition metals + Graphite powder | 50-70 h | 2.5 nm 2.4 nm 3.3 nm 4.0 nm 3.2 nm 3.0 nm | - |
| Carbothermal reduction method[ | (TiZrHfNbTa)C (0.4524 nm) | Metal oxides + Graphite powder or carbon black | Carbothermal reduction (CTR) 1600 ℃, 1 h; Solid solution (SS) 2000 ℃, 1.5 h | 550 nm | 0.2 |
| (TiZrHfNbTa)C (0.4503 nm) | 2200 ℃, 1 h | 0.5-2 μm | - | ||
| Molten salt synthesis[ | (TiVNbTa)C (0.4468 nm) | Metal carbides + Molten salt media KCl | 1300 ℃, 1 h | 50-110 nm | - |
| Liquid precursors method[ | (TiZrHfNbTa)C (-) | Metal chlorides + Furfuryl alcohol | CTR 1400 ℃, 1 h; SS 2000 ℃, 1 h | 132 nm | 0.22 |
| (TiZrHfTa)C (0.4529 nm) | Equiatomic metal containing monomers + Allyl-functional novolac resin | 1800 ℃, 2 h | ~100 nm | - | |
| Direct synthetic method[ | (TiZrHfNbTa)C (0.4508 nm) | Metal carbides | 1950 ℃, 5 min (SPS) | ~2 μm | - |
Table 2 Typical HECs synthesis methods and characteristics
| Synthesizing method | Composition (lattice parameter) | Starting materials | Synthesizing conditions | Grain size | Oxygen content/ % (in mass) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical alloying[ | (TiZrHfVNb)C (0.4496 nm) (TiZrHfVTa)C (0.4495 nm) (TiZrHfNbTa)C (0.4526 nm) (TiZrVNbTa)C (0.4440 nm) (TiHfVNbTa)C (0.4425 nm) (ZrHfVNbTa)C (0.4493 nm) | Transition metals + Graphite powder | 50-70 h | 2.5 nm 2.4 nm 3.3 nm 4.0 nm 3.2 nm 3.0 nm | - |
| Carbothermal reduction method[ | (TiZrHfNbTa)C (0.4524 nm) | Metal oxides + Graphite powder or carbon black | Carbothermal reduction (CTR) 1600 ℃, 1 h; Solid solution (SS) 2000 ℃, 1.5 h | 550 nm | 0.2 |
| (TiZrHfNbTa)C (0.4503 nm) | 2200 ℃, 1 h | 0.5-2 μm | - | ||
| Molten salt synthesis[ | (TiVNbTa)C (0.4468 nm) | Metal carbides + Molten salt media KCl | 1300 ℃, 1 h | 50-110 nm | - |
| Liquid precursors method[ | (TiZrHfNbTa)C (-) | Metal chlorides + Furfuryl alcohol | CTR 1400 ℃, 1 h; SS 2000 ℃, 1 h | 132 nm | 0.22 |
| (TiZrHfTa)C (0.4529 nm) | Equiatomic metal containing monomers + Allyl-functional novolac resin | 1800 ℃, 2 h | ~100 nm | - | |
| Direct synthetic method[ | (TiZrHfNbTa)C (0.4508 nm) | Metal carbides | 1950 ℃, 5 min (SPS) | ~2 μm | - |
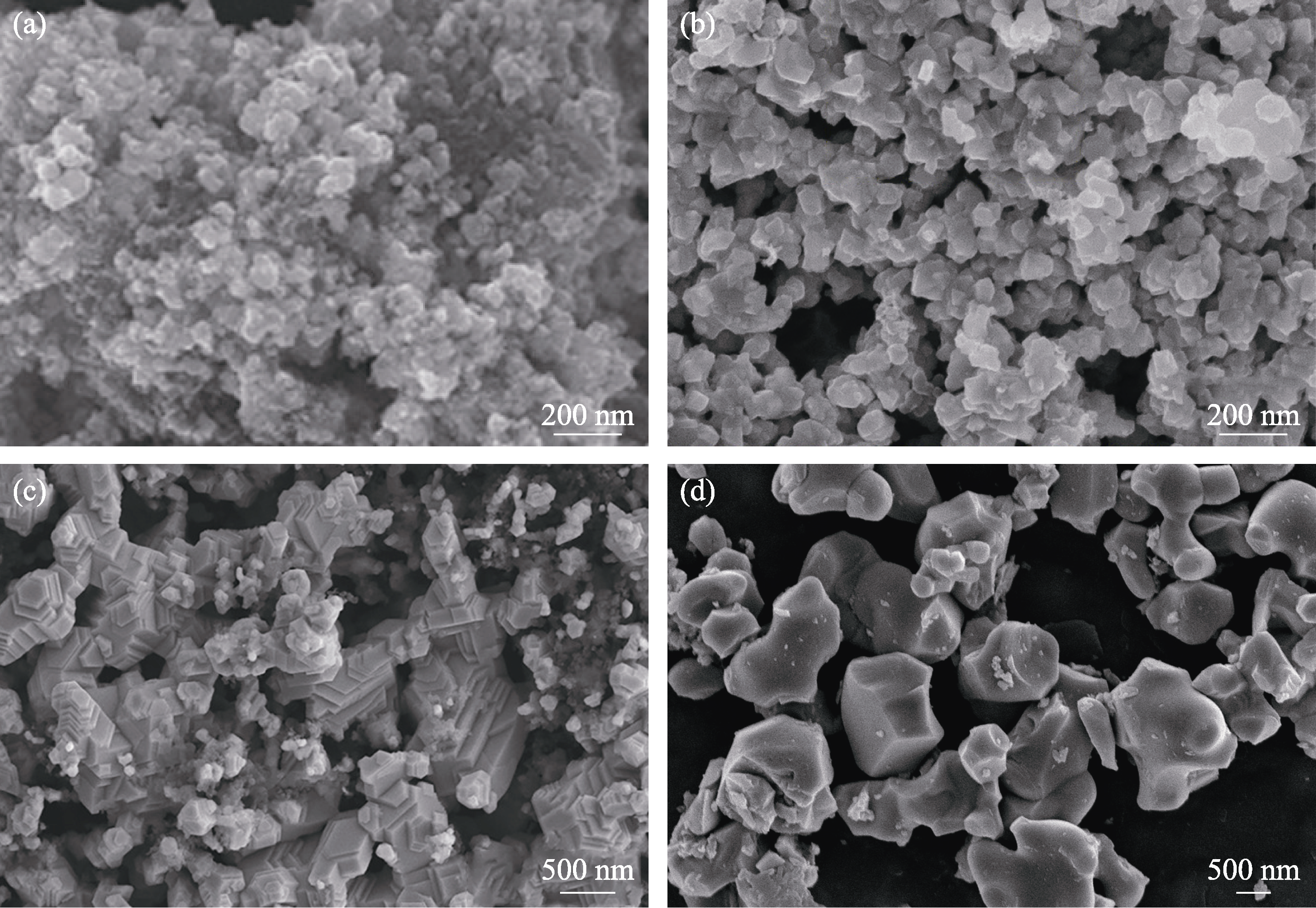
Fig. 1 Morphologies of HECs powders synthesized by several typical methods (a) Liquid precursor method[37]; (b) Molten salt synthesis[36]; (c) Carbothermal reduction method[35]; (d) Direct synthesis method[39]
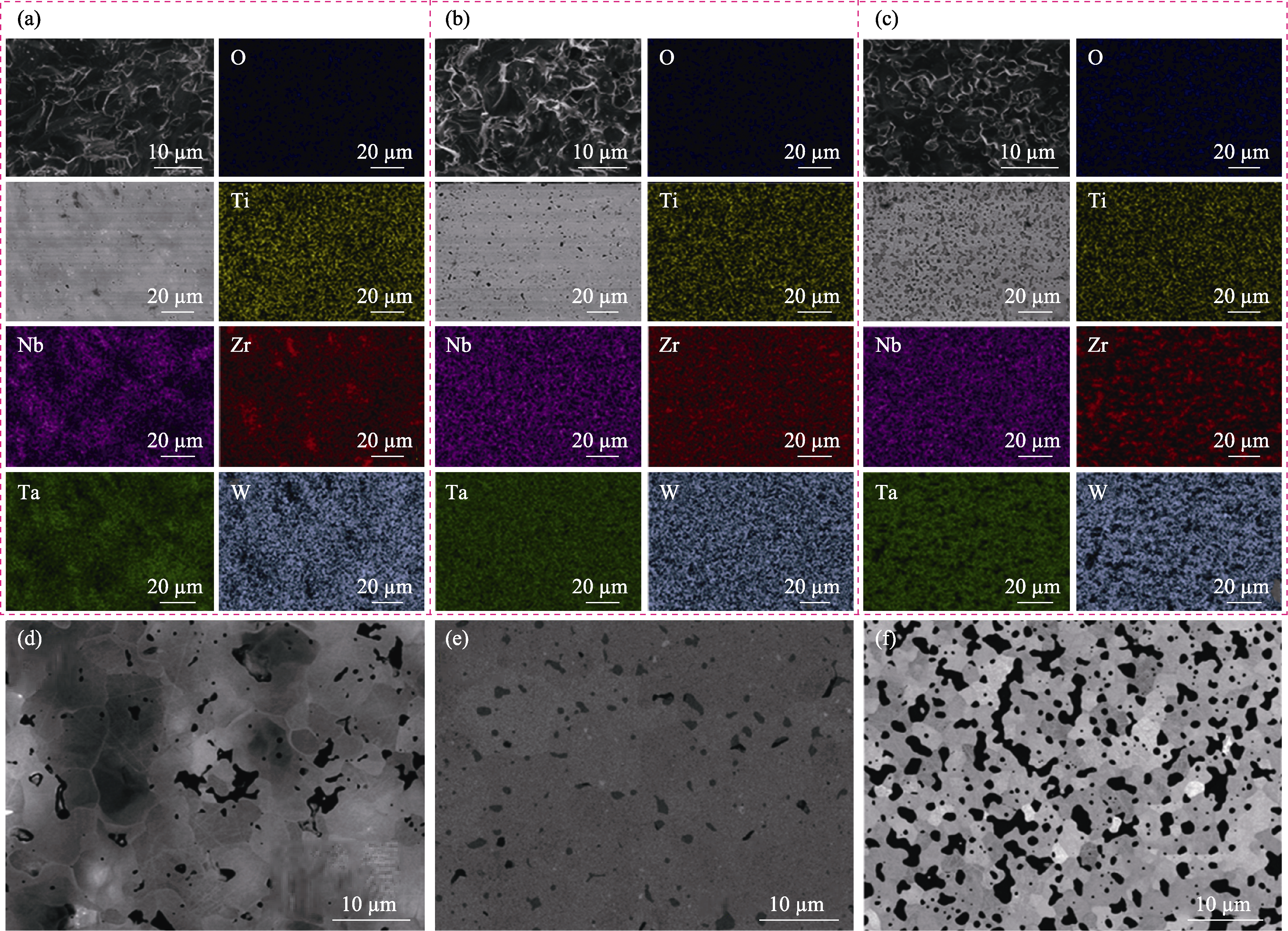
Fig. 2 SEM images and corresponding EDS element mappings of (TiZrNbTaW)C ceramics prepared by three typical processes[67] (a, d) Using metallic powders and graphite as raw materials (HEC-M); (b, e) Using metal carbides as raw materials (HEC-C); (c, f) Using metal oxides and graphite as raw materials (HEC-O)
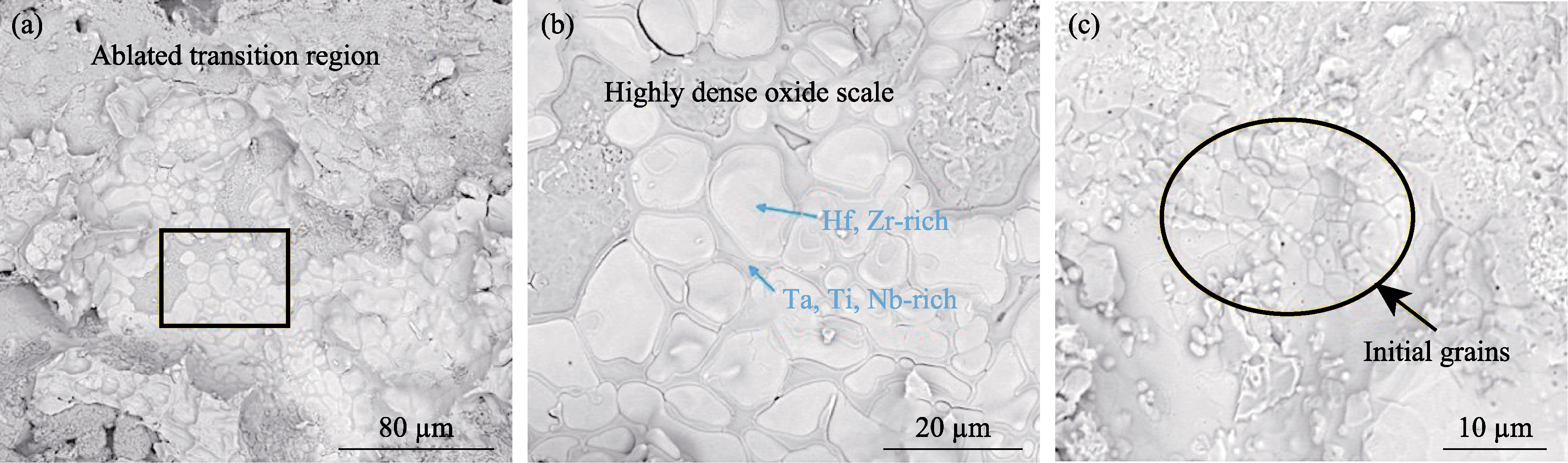

Fig. 9 Elemental enrichment in the ablation transition region of (TiZrHfNbTa)C0.8N0.2[129] (a, b) Highly dense oxide scale embedded in oval Hf/Zr-rich grains; (c) Initial oval grains in the areas away from ablation surface
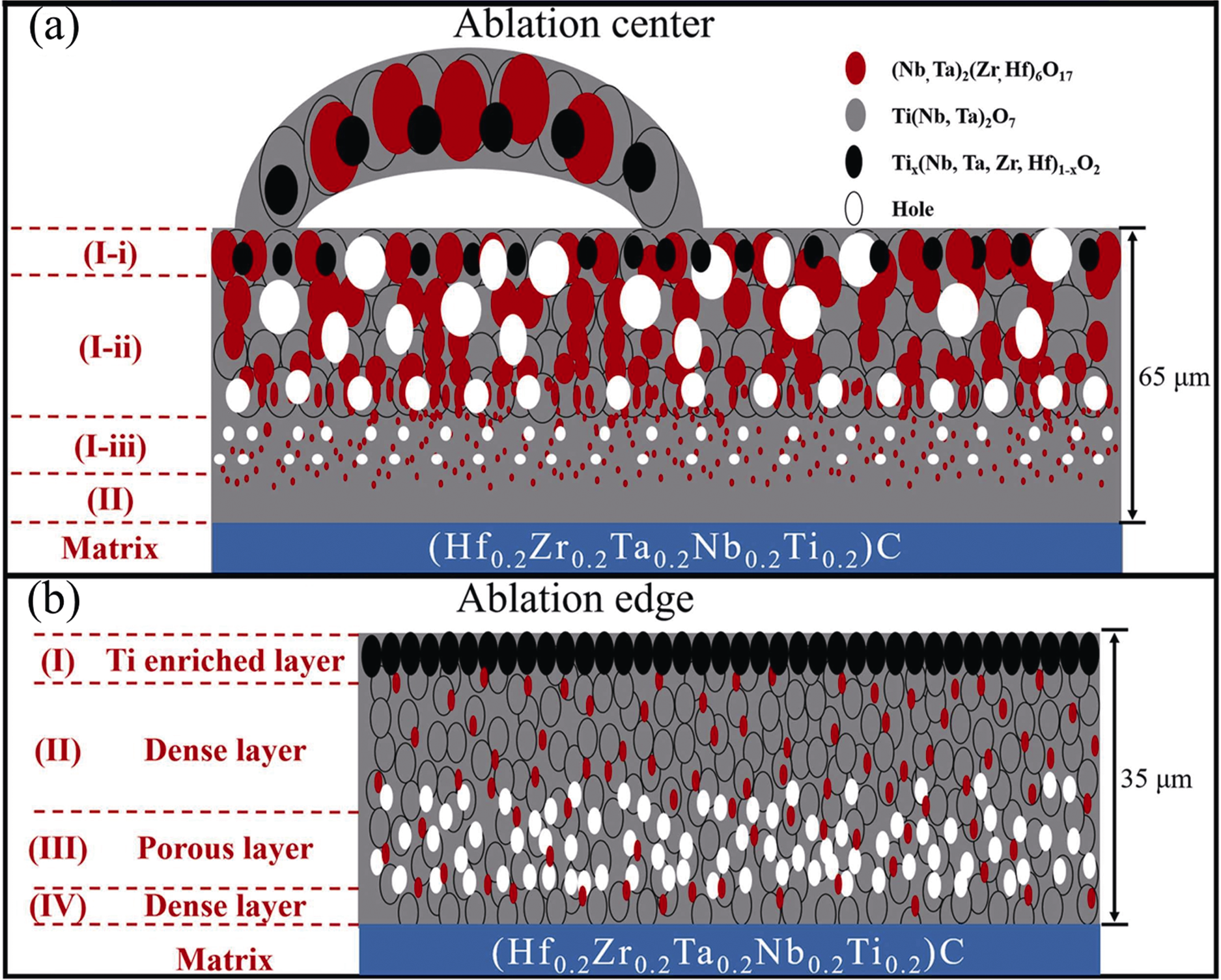
Fig. 10 Schematic diagram of the ablation mechanism of (TiZrHfNbTa)C during oxyacetylene ablation flame (2000 ℃)[56] (a) Ablation center; (b) Ablation edge
| Element | Ti | Zr | Hf | Nb | Ta |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti | TiO2 | HfTiO4[ | |||
| Zr | ZrTiO4[ | ZrO2 | (Hf, Zr)O2[ | ||
| Hf | HfO2 | ||||
| V | ZrV2O7 | VNb9O25[ | VTa9O25[ | ||
| Nb | Nb2TiO7[ Nb10Ti2O29[ Nb6Ti2O19[ TiNb6O17[ | Zr6Nb2O17[ | Hf6Nb2O17[ | Nb2O5 | |
| Ta | TiTa2O7[ | ZrTa6O17[ Zr6Ta2O19[ | Hf6Ta2O17[ | Nb4Ta2O15[ | Ta2O5 |
| Mo | |||||
| W | ZrW2O8[ | HfW2O8[ |
Table 4 Complex oxides that could form in the HECs systems based on a review of available phase diagrams
| Element | Ti | Zr | Hf | Nb | Ta |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti | TiO2 | HfTiO4[ | |||
| Zr | ZrTiO4[ | ZrO2 | (Hf, Zr)O2[ | ||
| Hf | HfO2 | ||||
| V | ZrV2O7 | VNb9O25[ | VTa9O25[ | ||
| Nb | Nb2TiO7[ Nb10Ti2O29[ Nb6Ti2O19[ TiNb6O17[ | Zr6Nb2O17[ | Hf6Nb2O17[ | Nb2O5 | |
| Ta | TiTa2O7[ | ZrTa6O17[ Zr6Ta2O19[ | Hf6Ta2O17[ | Nb4Ta2O15[ | Ta2O5 |
| Mo | |||||
| W | ZrW2O8[ | HfW2O8[ |
| [1] | CHEN B W, NI D W, BAO W C, et al. Engineering Cf/ZrB2- SiC-Y2O3 for thermal structures of hypersonic vehicles with excellent long-term ultrahigh temperature ablation resistance. Adv. Sci., 2023, 10: 202304254. |
| [2] | BINNER J, PORTER M, BAKER B, et al. Selection, processing, properties and applications of ultra-high temperature ceramic matrix composites, UHTCMCs—a review. Int. Mater. Rev., 2019, 65(7):389. |
| [3] | NI D W, CHENG Y, ZHANG J P, et al. Advances in ultra-high temperature ceramics, composites, and coatings. J. Adv. Ceram., 2022, 11(1):1. |
| [4] | OSES C, TOHER C, CURTAROLO S. High-entropy ceramics. Nat. Rev. Mater., 2020, 5(4):295. |
| [5] | WYATT B C, NEMANI S K, HILMAS G E, et al. Ultra-high temperature ceramics for extreme environments. Nat. Rev. Mater., 2023, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41578-023-00619-0. |
| [6] | ZENG Y, WANG D N, XIONG X, et al. Ablation-resistant carbide Zr0.8Ti0.2C0.74B0.26 for oxidizing environments up to 3,000 ℃. Nat. Commun., 2017, 8: 15836. |
| [7] |
WANG H X, WANG Y G, LIU Q M. Research progress of high entropy transition metal carbide ceramics. J. Inorg. Mater., 2021, 36(4):355.
DOI |
| [8] | XIANG H M, XING Y, DAI F Z, et al. High-entropy ceramics: present status, challenges, and a look forward. J. Adv. Ceram., 2021, 10(3):385. |
| [9] | WRIGHT A J, LUO J. A step forward from high-entropy ceramics to compositionally complex ceramics: a new perspective. J. Mater. Sci., 2020, 55(23):9812. |
| [10] | KAUFMANN K, MARYANOVSKY D, MELLOR W M, et al. Discovery of high-entropy ceramics via machine learning. npj Comput. Mater., 2020, 6: 42. |
| [11] | GILD J, ZHANG Y, HARRINGTON T, et al. High-entropy metal diborides: a new class of high-entropy materials and a new type of ultrahigh temperature ceramics. Sci. Rep., 2016, 6: 37946. |
| [12] | ZHANG R Z, REECE M J. Review of high entropy ceramics: design, synthesis, structure and properties. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2019, 7(39):22148. |
| [13] | 顾俊峰, 邹冀, 张帆, 等. 高熵陶瓷研究进展. 中国材料进展, 2019, 38(9):855. |
| [14] | CHEN L, WANG K, SU W T, et al. Research progress of transition metal non-oxide high-entropy ceramics. J. Inorg. Mater., 2019, 35(7):748. |
| [15] | WANG Y C. Processing and properties of high entropy carbides. Adv. Appl. Ceram., 2022, 121(2):57. |
| [16] | CAI F Y, NI D W, CHEN B W, et al. Fabrication and properties of Cf/(Ti0.2Zr0.2Hf0.2Nb0.2Ta0.2)C-SiC high-entropy ceramic matrix composites via precursor infiltration and pyrolysis. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2021, 41(12):5863. |
| [17] | YU D, YIN J, ZHANG B H, et al. Recent development of high- entropy transitional carbides: a review. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn., 2020, 128(7):329. |
| [18] | CASTLE E, CSANADI T, GRASSO S, et al. Processing and properties of high-entropy ultra-high temperature carbides. Sci. Rep., 2018, 8: 8609. |
| [19] | PENG C, GAO X, WANG M Z, et al. Diffusion-controlled alloying of single-phase multi-principal transition metal carbides with high toughness and low thermal diffusivity. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2019, 114(1):011905. |
| [20] | WANG Y C, CSANADI T, ZHANG H F, et al. Enhanced hardness in high-entropy carbides through atomic randomness. Adv. Theory Simul., 2020, 3(9):2000111. |
| [21] | YEH J W, CHEN S K, LIN S J, et al. Nanostructured high- entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater., 2004, 6(5):299. |
| [22] | CANTOR B, CHANG I T H, KNIGHT P, et al. Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. Mater., 2004, 375-377: 213. |
| [23] | ROST C M, SACHET E, BORMAN T, et al. Entropy-stabilized oxides. Nat. Commun., 2015, 6: 8485. |
| [24] | WANG Y J, ZHANG G J. Non-order is the new order: high- entropy ceramics. J. Inorg. Mater., 2021, 36(4):337. |
| [25] | ZHANG W R, LIAW P K, ZHANG Y. Science and technology in high-entropy alloys. Sci. China-Mater., 2018, 61(1):2. |
| [26] | MIRACLE D B, SENKOV O N. A critical review of high entropy alloys and related concepts. Acta Mater., 2017, 122: 448. |
| [27] | HARRINGTON T J, GILD J, SARKER P, et al. Phase stability and mechanical properties of novel high entropy transition metal carbides. Acta Mater., 2019, 166: 271. |
| [28] | YEH J W. Recent progress in high-entropy alloys. Ann. Chim-Sci. Mat., 2006, 31(6):633. |
| [29] | TSAI M H, YEH J W. High-entropy alloys: a critical review. Mater. Res. Lett., 2014, 2(3):107. |
| [30] | YE B L, WEN T Q, HUANG K H, et al. First-principles study, fabrication, and characterization of (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Nb0.2Ti0.2)C high- entropy ceramic. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2019, 102(7):4344. |
| [31] | SARKER P, HARRINGTON T, TOHER C, et al. High-entropy high-hardness metal carbides discovered by entropy descriptors. Nat. Commun., 2018, 9: 4980. |
| [32] | CHICARDI E, GARCÍA-GARRIDO C, HERNÁNDEZ-SAZ J, et al. Synthesis of all equiatomic five-transition metals high entropy carbides of the IVB (Ti, Zr, Hf) and VB (V, Nb, Ta) groups by a low temperature route. Ceram. Int., 2020, 46(13):21421. |
| [33] | CHICARDI E, GARCíA-GARRIDO C, GOTOR F J. Low temperature synthesis of an equiatomic (TiZrHfVNb)C5 high entropy carbide by a mechanically-induced carbon diffusion route. Ceram. Int., 2019, 45(17):21858. |
| [34] | FENG L, FAHRENHOLTZ W G, HILMAS G E, et al. Synthesis of single-phase high-entropy carbide powders. Scr. Mater., 2019, 162: 90. |
| [35] |
YE B L, NING S S, LIU D, et al. One-step synthesis of coral-like high-entropy metal carbide powders. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2019, 102(10):6372.
DOI |
| [36] | NING S S, WEN T Q, YE B L, et al. Low-temperature molten salt synthesis of high-entropy carbide nanopowders. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2019, 103(3):2244. |
| [37] | LI F, LU Y, WANG X G, et al. Liquid precursor-derived high- entropy carbide nanopowders. Ceram. Int., 2019, 45(17):22437. |
| [38] | ZHAO T, LIU W, HAN W J, et al. Synthesis of high entropy carbide nano powders via liquid polymer precursor route. J. Inorg. Mater., 2021, 36(4):393. |
| [39] | ZHOU J Y, ZHANG J Y, ZHANG F, et al. High-entropy carbide: a novel class of multicomponent ceramics. Ceram. Int., 2018, 44(17):22014. |
| [40] | SEDEGOV A, VOROTILO S, TSYBULIN V, et al. Synthesis and study of high-entropy ceramics based on the carbides of refractory metals. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng., 2019, 558(1):012043. |
| [41] | DU B, LIU H H, CHU Y H. Fabrication and characterization of polymer-derived high-entropy carbide ceramic powders. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2020, 103(8):4063. |
| [42] | ŠOLCOVÁ P, NIŽŇANSKÝ M, SCHULZ J, et al. Preparation of high-entropy (Ti, Zr, Hf, Ta, Nb) carbide powder via solution chemistry. Inorg. Chem., 2021, 60(11):7617. |
| [43] | SUN Y N, CHEN F H, QIU W F, et al. Synthesis of rare earth containing single-phase multicomponent metal carbides via liquid polymer precursor route. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2020, 103(11):6081. |
| [44] | CSANÁDI T, VOJTKO M, DANKHÁZI Z, et al. Small scale fracture and strength of high-entropy carbide grains during microcantilever bending experiments. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2020, 40(14):4774. |
| [45] | ZHANG H Z, AKHTAR F. Processing and characterization of refractory quaternary and quinary high-entropy carbide composite. Entropy, 2019, 21(5):474. |
| [46] | DEMIRSKYI D, SUZUKI T S, YOSHIMI K, et al. Synthesis and high-temperature properties of medium-entropy (Ti,Ta,Zr,Nb)C using the spark plasma consolidation of carbide powders. Open Ceram., 2020, 2: 100015. |
| [47] | WANG F, YAN X L, WANG T Y, et al. Irradiation damage in (Zr0.25Ta0.25Nb0.25Ti0.25)C high-entropy carbide ceramics. Acta Mater., 2020, 195: 739. |
| [48] | WANG F, ZHANG X, YAN X L, et al. The effect of submicron grain size on thermal stability and mechanical properties of high- entropy carbide ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2020, 103(8):4463. |
| [49] | LIU D Q, ZHANG A J, JIA J G, et al. Phase evolution and properties of (VNbTaMoW)C high entropy carbide prepared by reaction synthesis. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2020, 40(8):2746. |
| [50] | LU K, LIU J X, WEI X F, et al. Microstructures and mechanical properties of high-entropy (Ti0.2Zr0.2Hf0.2Nb0.2Ta0.2)C ceramics with the addition of SiC secondary phase. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2020, 40(5): 1839. |
| [51] | DUSZA J, CSANáDI T, MEDVEĎ D, et al. Nanoindentation and tribology of a (Hf-Ta-Zr-Nb-Ti)C high-entropy carbide. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2021, 41(11):5417. |
| [52] | YE B L, WEN T Q, NGUYEN M C, et al. First-principles study, fabrication and characterization of (Zr0.25Nb0.25Ti0.25V0.25)C high- entropy ceramics. Acta Mater., 2019, 170: 15. |
| [53] |
FENG L, FAHRENHOLTZ W G, HILMAS G E. Low-temperature sintering of single-phase, high-entropy carbide ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2019, 102(12):7217.
DOI |
| [54] | FENG L, CHEN W T, FAHRENHOLTZ W G, et al. Strength of single-phase high-entropy carbide ceramics up to 2300 ℃. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2020, 104(1):419. |
| [55] | WANG K, CHEN L, XU C G, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of (TiZrNbTaMo)C high-entropy ceramic. J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2020, 39: 99. |
| [56] | NI N, DING Q, SHI Y C, et al. Ablation behavior of high-entropy carbides ceramics (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Nb0.2Ti0.2)C upon exposition to an oxyacetylene torch at 2000 ℃. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2023, 43(6):2306. |
| [57] | LU W Y, CHEN L, ZHANG W, et al. Single-phase formation and mechanical properties of (TiZrNbTaMo)C high-entropy ceramics: first-principles prediction and experimental study. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2022, 42(5): 2021. |
| [58] | PÖTSCHKE J, DAHAL M, HERRMANN M, et al. Preparation of high-entropy carbides by different sintering techniques. J. Mater. Sci., 2021, 56(19):11237. |
| [59] | YU D, YIN J, ZHANG B H, et al. Pressureless sintering and properties of (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Nb0.2Ti0.2)C high-entropy ceramics: the effect of pyrolytic carbon. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2021, 41(6):3823. |
| [60] | CHEN L, ZHANG W, TAN Y Q, et al. Influence of vanadium content on the microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of (TiZrHfVNbTa)C high-entropy carbides processed by pressureless sintering. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2021, 41(16):60. |
| [61] | BRAIC M, BRAIC V, BALACEANU M, et al. Characteristics of (TiAlCrNbY)C films deposited by reactive magnetron sputtering. Surf. Coat. Technol., 2010, 204(12/13): 2010. |
| [62] | BRAIC V, VLADESCU A, BALACEANU M, et al. Nanostructured multi-element (TiZrNbHfTa)N and (TiZrNbHfTa)C hard coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol., 2012, 211: 117. |
| [63] | BRAIC V, PARAU A C, PANA I, et al. Effects of substrate temperature and carbon content on the structure and properties of (CrCuNbTiY)C multicomponent coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol., 2014, 258: 996. |
| [64] | YAN X L, CONSTANTIN L, LU Y F, et al. (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Nb0.2Ti0.2)C high-entropy ceramics with low thermal conductivity. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2018, 101(10):4486. |
| [65] | DUSZA J, ŠVEC P, GIRMAN V, et al. Microstructure of (Hf-Ta-Zr-Nb)C high-entropy carbide at micro and nano/atomic level. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2018, 38(12):4303. |
| [66] | WEI X F, QIN Y, LIU J X, et al. Gradient microstructure development and grain growth inhibition in high-entropy carbide ceramics prepared by reactive spark plasma sintering. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2020, 40(4):935. |
| [67] | WEI X F, LIU J X, LI F, et al. High entropy carbide ceramics from different starting materials. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2019, 39(10):2989. |
| [68] | GILD J, KAUFMANN K, VECCHIO K, et al. Reactive flash spark plasma sintering of high-entropy ultrahigh temperature ceramics. Scr. Mater., 2019, 170: 106. |
| [69] | ZHANG W, CHEN L, XU C G, et al. Densification, microstructure and mechanical properties of multicomponent (TiZrHfNbTaMo)C ceramic prepared by pressureless sintering. J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2021, 72: 23. |
| [70] | YU D, ZHANG B H, YIN J, et al. Densifying (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Nb0.2Ti0.2)C high-entropy ceramics by two-step pressureless sintering. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2022, 105(1):76. |
| [71] | MALINOVSKIS P, FRITZE S, RIEKEHR L, et al. Synthesis and characterization of multicomponent (CrNbTaTiW)C films for increased hardness and corrosion resistance. Mater. Des., 2018, 149: 51. |
| [72] | MUKHERJEE A, VLADESCU A, TITORENCU I, et al. In vitro biocompatibility of Si alloyed multi-principal element carbide coatings. PLOS ONE, 2016, 11(8):e0161151. |
| [73] | BRAIC V, BALACEANU M, BRAIC M, et al. Characterization of multi-principal-element (TiZrNbHfTa)N and (TiZrNbHfTa)C coatings for biomedical applications. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater., 2012, 10: 197. |
| [74] | BRAIC M, BALACEANU M, VLADESCU A, et al. Deposition and characterization of multi-principal-element (CuSiTiYZr)C coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2013, 284: 671. |
| [75] | LIANG S C, TSAI D C, CHANG Z C, et al. Structural and mechanical properties of multi-element (TiVCrZrHf)N coatings by reactive magnetron sputtering. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2011, 258(1):399. |
| [76] | PEI Y T, CHEN C Q, SHAHA K P, et al. Microstructural control of TiC/a-C nanocomposite coatings with pulsed magnetron sputtering. Acta Mater., 2008, 56(4):696. |
| [77] | ROST C M, BORMAN T, HOSSAIN M D, et al. Electron and phonon thermal conductivity in high entropy carbides with variable carbon content. Acta Mater., 2020, 196: 231. |
| [78] | GORBAN’ V F, ANDREYEV A A, KARTMAZOV G N, et al. Production and mechanical properties of high-entropic carbide based on the TiZrHfVNbTa multicomponent alloy. J. Phys. Chem., 2017, 39(3):166. |
| [79] | KAO W H, SU Y L, HORNG J H, et al. Mechanical, tribological, anti-corrosion and anti-glass sticking properties of high-entropy TaNbSiZrCr carbide coatings prepared using radio-frequency magnetron sputtering. Mater. Chem. Phys., 2021, 268: 124741. |
| [80] | JHONG Y S, HUANG C W, LIN S J. Effects of CH4 flow ratio on the structure and properties of reactively sputtered (CrNbSiTiZr) Cx coatings. Mater. Chem. Phys., 2018, 210: 348. |
| [81] | LIN S Y, CHANG S Y, HUANG Y C, et al. Mechanical performance and nanoindenting deformation of (AlCrTaTiZr)NCy multi-component coatings co-sputtered with bias. Surf. Coat. Technol., 2012, 206(24):5096. |
| [82] | XU W J, JIA B S, LIU X H, et al. Structural evolution and mechanical properties of multi-element (TiCrZrVNb)C high entropy ceramics films by multi-arc ion plating. Ceram. Int., 2022, 48(13):19191. |
| [83] | WANG J, ZHANG H, YU X, et al. Insight into the structure and tribological and corrosion performance of high entropy (CrNbSiTiZr) C films: first-principles and experimental study. Surf. Coat. Technol., 2021, 421: 127468. |
| [84] | LI J C, ZHANG Y L, ZHAO Y X, et al. A novel (Hf1/3Zr1/3Ti1/3)C medium-entropy carbide coating with excellent long-life ablation resistance applied above 2100 ℃. Compos. B Eng., 2023, 251: 110467. |
| [85] | CAI F Y, NI D W, CHEN B W, et al. Efficient fabrication and properties of 2D Cf/(Ti0.2Zr0.2Hf0.2Nb0.2Ta0.2)C-SiC high-entropy ceramic matrix composites via slurry infiltration lamination combined with precursor infiltration and pyrolysis. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2023, 43(16):7403. |
| [86] | ZHANG L, WANG W Q, ZHOU N P, et al. Low temperature fabrication of Cf/BNi/(Ti0.2Zr0.2Hf0.2Nb0.2Ta0.2)C-SiCm high entropy ceramic matrix composite by slurry coating and laminating combined with precursor infiltration and pyrolysis. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2022, 42(7):3099. |
| [87] | GUO W J, HU J, FANG W, et al. A novel strategy for rapid fabrication of continuous carbon fiber reinforced (TiZrHfNbTa)C high-entropy ceramic composites: high-entropy alloy in-situ reactive melt infiltration. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2023, 43(6):2295. |
| [88] | BAO W C, WANG X G, DING H J, et al. High-entropy M2AlC-MC (M=Ti, Zr, Hf, Nb, Ta) composite: synthesis and microstructures. Scr. Mater., 2020, 183: 33. |
| [89] | CHEN L, LI Y B, CHEN K, et al. Synthesis and characterization of medium-/high-entropy M2SnC (M = Ti/V/Nb/Zr/Hf) MAX phases. Small Struct., 2023, 4: 2200161. |
| [90] | NEMANI S K, ZHANG B, WYATT B C, et al. High-entropy 2D carbide MXenes: TiVNbMoC3 and TiVCrMoC3. ACS Nano, 2021, 15(8):12815. |
| [91] | CHEN L, LI Y B, LIANG K, et al. Two-dimensional MXenes derived from medium/high-entropy MAX phases M2GaC (M = Ti/V/Nb/Ta/Mo) and their electrochemical performance. Small Methods, 2023, 7(8):2300054 |
| [92] | DU Z G, WU C, CHEN Y C, et al. High-entropy atomic layers of transition-metal carbides (MXenes). Adv. Mater., 2021, 33(39):2101473. |
| [93] | LIU J B, XIONG J, GUO Z X, et al. Preparation of high-entropy (Zr0.25Hf0.25Ta0.25Ti0.25)C-Ni-Co composite by spark plasma sintering. Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2020, 51(12):6706. |
| [94] | WANG Y C, YU D, YIN J, et al. Ablation behavior of (Hf-Ta-Zr-Nb-Ti)C high-entropy carbide and (Hf-Ta-Zr-Nb-Ti)C- xSiC composites. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2022, 105(10):6395. |
| [95] | WANG H X, WANG S Y, CAO Y J, et al. Oxidation behaviors of (Hf0.25Zr0.25Ta0.25Nb0.25)C and (Hf0.25Zr0.25Ta0.25Nb0.25)C-SiC at 1300-1500 ℃. J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2021, 60: 147. |
| [96] | NAUGHTON-DUSZOVÁ A, ŠVEC P, KOVALČÍKOVÁ A, et al. On the phase and grain boundaries in dual phase carbide/boride ceramics from micro to atomic level. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2023, 43(15):6765. |
| [97] | QIN M D, GILD J, HU C Z, et al. Dual-phase high-entropy ultra- high temperature ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2020, 40(15):5037. |
| [98] | HUO S J, CHEN L, LIU X R, et al. Reactive sintering of dual- phase high-entropy ceramics with superior mechanical properties. J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2022, 129: 223. |
| [99] | QIN M D, VEGA H D, ZHANG D W, et al. 21-Component compositionally complex ceramics: discovery of ultrahigh-entropy weberite and fergusonite phases and a pyrochlore-weberite transition. J. Adv. Ceram., 2022, 11(4):641. |
| [100] | WANG Y C, WANG X C, LI S, et al. Improved oxidation resistance of (Zr-Nb-Hf-Ta)(C, N) high entropy carbonitrides. Corros. Sci., 2023, 225: 111583. |
| [101] | DIPPO O F, MESGARZADEH N, HARRINGTON T J, et al. Bulk high-entropy nitrides and carbonitrides. Sci. Rep., 2020, 10: 21288. |
| [102] | BALASUBRAMANIAN K, KHARE S V, GALL D. Valence electron concentration as an indicator for mechanical properties in rocksalt structure nitrides, carbides and carbonitrides. Acta Mater., 2018, 152: 175. |
| [103] | MOSKOVSKIKH D O, VOROTILO S, SEDEGOV A S, et al. High-entropy (HfTaTiNbZr)C and (HfTaTiNbMo)C carbides fabricated through reactive high-energy ball milling and spark plasma sintering. Ceram. Int., 2020, 46(11):19008. |
| [104] | 王达飞, 刘宁, 张晓玲. 四元高熵碳化物陶瓷的组织和性能研究. 热处理, 2020, 35(2):8. |
| [105] | LIU D Q, ZHANG A J, JIA J G, et al. Reaction synthesis and characterization of a new class high entropy carbide (NbTaMoW)C. Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. Mater., 2021, 804: 140520. |
| [106] | YU H, BAHADORI M, THOMPSON G B, et al. Understanding dislocation slip in stoichiometric rocksalt transition metal carbides and nitrides. J. Mater. Sci., 2017, 52(11):6235. |
| [107] | KIANI S, YANG J M, KODAMBAKA S, et al. Nanomechanics of refractory transition-metal carbides: a path to discovering plasticity in hard ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2015, 98(8):2313. |
| [108] | CSANáDI T, CASTLE E, REECE M J, et al. Strength enhancement and slip behaviour of high-entropy carbide grains during micro-compression. Sci. Rep., 2019, 9: 10200. |
| [109] | HAN X X, GIRMAN V, SEDLAK R, et al. Improved creep resistance of high entropy transition metal carbides. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2020, 40(7):2709. |
| [110] | CHENG Z L, LU W Y, CHEN L, et al. Compressive creep properties and mechanisms of (Ti-Zr-Nb-Ta-Mo)C high entropy ceramics at high temperatures. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2022, 42(13):5280. |
| [111] | KÖRMANN F, IKEDA Y, GRABOWSKI B, et al. Phonon broadening in high entropy alloys. npj Comput. Mater., 2017, 3: 36. |
| [112] | ZHANG Y W, STOCKS G M, JIN K, et al. Influence of chemical disorder on energy dissipation and defect evolution in concentrated solid solution alloys. Nat. Commun., 2015, 6: 8736. |
| [113] | CHEN H, XIANG H M, DAI F Z, et al. High porosity and low thermal conductivity high entropy (Zr0.2Hf0.2Ti0.2Nb0.2Ta0.2)C. J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2019, 35(8):1700. |
| [114] | GASPARRINI C, RANA D S, LE BRUN N, et al. On the stoichiometry of zirconium carbide. Sci. Rep., 2020, 10: 6347. |
| [115] | WEI X F, LIU J X, BAO W C, et al. High-entropy carbide ceramics with refined microstructure and enhanced thermal conductivity by the addition of graphite. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2021, 41(9):4747. |
| [116] | GILD J, SAMIEE M, BRAUN J L, et al. High-entropy fluorite oxides. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2018, 38(10):3578. |
| [117] | BACKMAN L, OPILA E J. Thermodynamic assessment of the group IV, V and VI oxides for the design of oxidation resistant multi-principal component materials. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2019, 39(5):1796. |
| [118] | BACKMAN L, GILD J, LUO J, et al. Part I: theoretical predictions of preferential oxidation in refractory high entropy materials. Acta Mater., 2020, 197: 20. |
| [119] | BACKMAN L, GILD J, LUO J, et al. Part II: experimental verification of computationally predicted preferential oxidation of refractory high entropy ultra-high temperature ceramics. Acta Mater., 2020, 197: 81. |
| [120] | YE B L, WEN T Q, LIU D, et al. Oxidation behavior of (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Nb0.2Ti0.2)C high-entropy ceramics at 1073-1473 K in air. Corros. Sci., 2019, 153: 327. |
| [121] | YE B L, WEN T Q, CHU Y H. High-temperature oxidation behavior of (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Nb0.2Ti0.2)C high-entropy ceramics in air. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2019, 103(1):500. |
| [122] | WANG Y C, ZHANG R Z, ZHANG B H, et al. The role of multi- elements and interlayer on the oxidation behaviour of (Hf-Ta- Zr-Nb)C high entropy ceramics. Corros. Sci., 2020, 176: 109019. |
| [123] | WANG H X, HAN X, LIU W, et al. Oxidation behavior of high-entropy carbide (Hf0.2Ta0.2Zr0.2Ti0.2Nb0.2)C at 1400-1600 °C. Ceram. Int., 2021, 47(8):10848. |
| [124] | WANG H X, CAO Y J, LIU W, et al. Oxidation behavior of (Hf0.2Ta0.2Zr0.2Ti0.2Nb0.2)C-xSiC ceramics at high temperature. Ceram. Int., 2020, 46(8):11160. |
| [125] | TAN Y Q, CHEN C, LI S G, et al. Oxidation behaviours of high-entropy transition metal carbides in 1200 ℃ water vapor. J. Alloys Compd., 2020, 816: 152523. |
| [126] | WANG Y C, REECE M J. Oxidation resistance of (Hf-Ta-Zr-Nb)C high entropy carbide powders compared with the component monocarbides and binary carbide powders. Scr. Mater., 2021, 193: 86. |
| [127] | MELLOR W M, KAUFMANN K, DIPPO O F, et al. Development of ultrahigh-entropy ceramics with tailored oxidation behavior. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2021, 41(12):5791. |
| [128] | WANG Y C, CSANADI T, ZHANG H F, et al. Synthesis, microstructure, and mechanical properties of novel high entropy carbonitrides. Acta Mater., 2022, 231: 117887. |
| [129] | PENG Z, SUN W, XIONG X, et al. Novel refractory high-entropy ceramics: transition metal carbonitrides with superior ablation resistance. Corros. Sci., 2021, 184: 109359. |
| [130] | WANG Y C, ZHANG B H, ZHANG C Y, et al. Ablation behaviour of (Hf-Ta-Zr-Nb)C high entropy carbide ceramic at temperatures above 2100 °C. J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2022, 113: 40. |
| [131] | GUO W J, HU J, YE Y C, et al. Ablation behavior of (TiZrHfNbTa)C high-entropy ceramics with the addition of SiC secondary under an oxyacetylene flame. Ceram. Int., 2022, 48(9):12790. |
| [132] | YE Z M, ZENG Y, XIONG X, et al. Elucidating the role of preferential oxidation during ablation: insights on the design and optimization of multicomponent ultra-high temperature ceramics. J. Adv. Ceram., 2022, 11(12): 1956. |
| [133] | CHEN Z Z, WANG H X, LI C R, et al. Oxyacetylene ablation of (Hf0.2Ti0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Nb0.2)C at 1350-2050 ℃. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2023, 43(6):2700. |
| [134] | MCCORMACK S J, TSENG K P, WEBER R J K, et al. In-situ determination of the HfO2-Ta2O5-temperature phase diagram up to 3000 ℃. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2019, 102(8):4848. |
| [135] | WANG F, NORTHWOOD D O. Oxides formed between ZrO2 and Nb2O5. J. Mater. Sci., 1995, 30: 4003. |
| [136] | CAI F Y, NI D W, BAO W C, et al. Ablation behavior and mechanisms of Cf/(Ti0.2Zr0.2Hf0.2Nb0.2Ta0.2)C-SiC high-entropy ceramic matrix composites. Compos. B Eng., 2022, 243: 110177. |
| [137] | COUTURES J P, COUTURES J. The system HfO2-TiO2. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1987, 70(6):383. |
| [138] | MCHALE A E, ROTH R S. Investigation of the phase transition in ZrTiO4 and ZrTiO4-SnO2 solid solutions. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1983, 66(2):C-18. |
| [139] | KREBS M A, CONDRATE S R A. Vibrational spectra of HfO2-ZrO2 solid solutions. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1982, 65(9):c144. |
| [140] |
WARING J L, ROTH R S. Phase equilibria in the system vanadium oxide-niobium oxide. J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand A Phys. Chem., 1965, 69a(2):119.
DOI PMID |
| [141] | SCHADOW H, OPPERMANN H, WEHNER B. Investigations on the quasi-binary system V2O5-Ta2O5. Cryst. Res. Technol., 2006, 27(5):691. |
| [142] | JONGEJAN A, WILKINS A. A re-examination of the system Nb2O5-TiO2 at liquidus temperatures. J. Less-Common Met., 1969, 19(3):185. |
| [143] | ROTH R S, COUGHANOUR L W. Phase equilibrium relations in the systems titania-niobia. J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand, 1955, 55(4):209. |
| [144] | WARING J L, ROTH R S. Effect of oxide additions on the polymorphism of tantalum pentoxide (system Ta2O5-TiO2). J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand A Phys. Chem., 1968, 72(2):175. |
| [145] | ROTH R, WARING J. Effect of oxide additions on the polymorphism of tantalum pentoxide III. Stabilization of the low temperature structure type. J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand A Phys. Chem., 1970, 74(4):485. |
| [146] | HOLTZBERG F, REISMAN A. Sub-solidus equilibria in the system Nb2O5-Ta2O5. J. Phys. Chem., 1961, 65(7):1192. |
| [147] | CHANG L L Y, SCROGER M G, PHILLIPS B. Condensed phase relations in the systems ZrO2-WO2-WO3 and HfO2-WO2-WO3. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1967, 50(4):211. |
| [148] | WANG F, YAN X L, SHAO L, et al. Irradiation damage behavior in novel high-entropy carbide ceramics. Trans. Am. Nucl. Soc., 2019, 120: 327. |
| [149] | XIN X T, BAO W C, WANG X G, et al. Reduced He ion irradiation damage in ZrC-based high-entropy ceramics. J. Adv. Ceram., 2023, 12(5):916. |
| [150] | ZHOU Y C, ZHAO B, CHEN H, et al. Electromagnetic wave absorbing properties of TMCs (TM = Ti, Zr, Hf, Nb and Ta) and high entropy (Ti0.2Zr0.2Hf0.2Nb0.2Ta0.2)C. J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2021, 74: 105. |
| [151] | ZHANG W M, XIANG H M, DAI F Z, et al. Achieving ultra- broadband electromagnetic wave absorption in high-entropy transition metal carbides (HE TMCs). J. Adv. Ceram., 2022, 11(4):545. |
| [152] | HU Y, NI D W, CHEN B W, et al. Cf/(CrZrHfNbTa)C-SiC high- entropy ceramic matrix composites for potential multi-functional applications. J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2024, 182: 132. |
| [1] | ZHU Wenjie, TANG Lu, LU Jichang, LIU Jiangping, LUO Yongming. Research Progress on Catalytic Oxidation of Volatile Organic Compounds by Perovskite Oxides [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [2] | HU Zhichao, YANG Hongyu, YANG Hongcheng, SUN Chengli, YANG Jun, LI Enzhu. Usage of the P-V-L Bond Theory in Regulating Properties of Microwave Dielectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [3] | WU Qiong, SHEN Binglin, ZHANG Maohua, YAO Fangzhou, XING Zhipeng, WANG Ke. Research Progress on Lead-based Textured Piezoelectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [4] | ZHANG Bihui, LIU Xiaoqiang, CHEN Xiangming. Recent Progress of Hybrid Improper Ferroelectrics with Ruddlesden-Popper Structure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| [5] | WU Jie, YANG Shuai, WANG Mingwen, LI Jinglei, LI Chunchun, LI Fei. Textured PT-based Piezoelectric Ceramics: Development, Status and Challenge [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 575-586. |
| [6] | JIANG Kun, LI Letian, ZHENG Mupeng, HU Yongming, PAN Qinxue, WU Chaofeng, WANG Ke. Research Progress on Low-temperature Sintering of PZT Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| [7] | SUN Yuxuan, WANG Zheng, SHI Xue, SHI Ying, DU Wentong, MAN Zhenyong, ZHENG Liaoying, LI Guorong. Defect Dipole Thermal-stability to the Electro-mechanical Properties of Fe Doped PZT Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 545-551. |
| [8] | CHEN Yi, QIU Haipeng, CHEN Mingwei, XU Hao, CUI Heng. SiC/SiC Composite: Matrix Boron Modification and Mechanical Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 504-510. |
| [9] | CUI Ning, ZHANG Yuxin, WANG Lujie, LI Tongyang, YU Yuan, TANG Huaguo, QIAO Zhuhui. Single-phase Formation Process and Carbon Vacancy Regulation of (TiVNbMoW)Cx High-entropy Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 511-520. |
| [10] | TIAN Ruizhi, LAN Zhengyi, YIN Jie, HAO Nanjing, CHEN Hangrong, MA Ming. Microfluidic Technology Based Synthesis of Inorganic Nano-biomaterials: Principles and Progress [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 337-347. |
| [11] | ZHANG Jiguo, WU Tian, ZHAO Xu, YANG Fan, XIA Tian, SUN Shien. Improvement of Cycling Stability of Cathode Materials and Industrialization Process for Sodium-ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 348-362. |
| [12] | YIN Jie, GENG Jiayi, WANG Kanglong, CHEN Zhongming, LIU Xuejian, HUANG Zhengren. Recent Advances in 3D Printing and Densification of SiC Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 245-255. |
| [13] | LI Ziwei, GONG Weilu, CUI Haifeng, YE Li, HAN Weijian, ZHAO Tong. (Zr, Hf, Nb, Ta, W)C-SiC Composite Ceramics: Preparation via Precursor Route and Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 271-280. |
| [14] | GAO Chenguang, SUN Xiaoliang, CHEN Jun, LI Daxin, CHEN Qingqing, JIA Dechang, ZHOU Yu. SiBCN-rGO Ceramic Fibers Based on Wet Spinning Technology: Microstructure, Mechanical and Microwave-absorbing Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 290-296. |
| [15] | CHEN Guangchang, DUAN Xiaoming, ZHU Jinrong, GONG Qing, CAI Delong, LI Yuhang, YANG Donglei, CHEN Biao, LI Xinmin, DENG Xudong, YU Jin, LIU Boya, HE Peigang, JIA Dechang, ZHOU Yu. Advanced Ceramic Materials in Helicopter Special Structures: Research Progress and Application Prospect [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 225-244. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||