
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (4): 387-398.DOI: 10.15541/jim20220760
Special Issue: 【信息功能】忆阻器材料与器件(202506)
• Topical Section on Neuromorphic Materials and Devices (Contributing Editor: WAN Qing) • Previous Articles Next Articles
YOU Junqi1( ), LI Ce1, YANG Dongliang1, SUN Linfeng1,2(
), LI Ce1, YANG Dongliang1, SUN Linfeng1,2( )
)
Received:2022-12-19
Revised:2023-01-18
Published:2023-04-20
Online:2023-04-18
Contact:
SUN Linfeng, professor. E-mail: sunlinfeng@bit.edu.cnAbout author:YOU Junqi (2000-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: 3120221530@bit.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
YOU Junqi, LI Ce, YANG Dongliang, SUN Linfeng. Double Dielectric Layer Metal-oxide Memristor: Design and Applications[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 387-398.

Fig. 1 Comparison of the structure and performance between the single/double dielectric layer metal-oxide memristor (a, d) Schematic diagrams for (a) single and (d) double dielectric layer metal-oxide memristors; (b, e) Comparison of I-V curves between (b) ZrO2-based memristor and (e) Ta2O5/ZrO2-based memristor with bi-layer structure exhibiting more uniform switching voltage[17]; (c, f) Comparison of the endurance between (c) HfO2-based memristor and (f) HfO2:Al/HfO2-based memristor with double dielectric layer exhibiting better cycling endurance[18]
| Memristor structure | Range of Set voltage, ΔVSet/V | Range of Reset voltage, ΔVReset/V | Endurance | On/Off ratio | Retention/s | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single dielectric layer | Ta/ZrO2/TiN | -1.0 ~-1.6 (0.6) | 0.8 ~ 1.5 (0.7) | 100 | 102 | - | [ |
| Cu/Al2O3/Pt | 0.4 ~ 1.2 (0.8) | -0.1 ~-0.8 (0.7) | 2×103 | 105 | 105 | [ | |
| Ag/ZnO/Pt | 0.3 ~ 1.0 (0.7) | -0.4 ~-0.8 (0.4) | 102 | 50 | 104 | [ | |
| TaN/Ta2O5/Pt | 2.0 ~ 4.5 (2.5) | -2.5 ~-4.5 (2) | 104 | - | 104 | [ | |
| Ta/ZrO2/Pt | 0.4 ~ 2.0 (1.6) | -0.4 ~-1.0 (0.6) | 100 | - | - | [ | |
| Double dielectric layer | Ag/SiO2/Ta2O5/Pt | 0.14 ~ 0.24 (0.1) | -0.06 ~-0.14 (0.08) | 103 | 103 | 104 | [ |
| Ta/ZrO2/ZTO/TiN | -0.8 ~-1.2 (0.4) | 0.8 ~ 1.2 (0.4) | 105 | 102 | 3×103 | [ | |
| Ta/Ta2O5/ZrO2/Pt | 0.7 ~ 1.2 (0.5) | -0.5 ~-0.8 (0.3) | 106 | 102 | 104 | [ | |
| TaN/Ta2O5/WO3/Pt | 1.6 ~ 2.3 (0.7) | -1.9 ~-2.5 (0.6) | 109 | - | 106 | [ | |
| Ti/HfO2/TiOx/Pt | -0.8 ~-1.1 (0.3) | 1.4 ~ 1.5 (0.1) | 107 | 103 | 105 | [ | |
Table 1 Performance comparison of the single/double dielectric layer metal-oxide memristors
| Memristor structure | Range of Set voltage, ΔVSet/V | Range of Reset voltage, ΔVReset/V | Endurance | On/Off ratio | Retention/s | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single dielectric layer | Ta/ZrO2/TiN | -1.0 ~-1.6 (0.6) | 0.8 ~ 1.5 (0.7) | 100 | 102 | - | [ |
| Cu/Al2O3/Pt | 0.4 ~ 1.2 (0.8) | -0.1 ~-0.8 (0.7) | 2×103 | 105 | 105 | [ | |
| Ag/ZnO/Pt | 0.3 ~ 1.0 (0.7) | -0.4 ~-0.8 (0.4) | 102 | 50 | 104 | [ | |
| TaN/Ta2O5/Pt | 2.0 ~ 4.5 (2.5) | -2.5 ~-4.5 (2) | 104 | - | 104 | [ | |
| Ta/ZrO2/Pt | 0.4 ~ 2.0 (1.6) | -0.4 ~-1.0 (0.6) | 100 | - | - | [ | |
| Double dielectric layer | Ag/SiO2/Ta2O5/Pt | 0.14 ~ 0.24 (0.1) | -0.06 ~-0.14 (0.08) | 103 | 103 | 104 | [ |
| Ta/ZrO2/ZTO/TiN | -0.8 ~-1.2 (0.4) | 0.8 ~ 1.2 (0.4) | 105 | 102 | 3×103 | [ | |
| Ta/Ta2O5/ZrO2/Pt | 0.7 ~ 1.2 (0.5) | -0.5 ~-0.8 (0.3) | 106 | 102 | 104 | [ | |
| TaN/Ta2O5/WO3/Pt | 1.6 ~ 2.3 (0.7) | -1.9 ~-2.5 (0.6) | 109 | - | 106 | [ | |
| Ti/HfO2/TiOx/Pt | -0.8 ~-1.1 (0.3) | 1.4 ~ 1.5 (0.1) | 107 | 103 | 105 | [ | |

Fig. 2 Advantages of the double dielectric layer metal-oxide memristor in building neural network (a) I-V curves of Pt/Al2O3/TaOx/Ta memristor with self-rectifying characteristic[26]; (b) Comparison of the pulse response between the HfO2 and the AlOx/HfO2-based memristor[30]
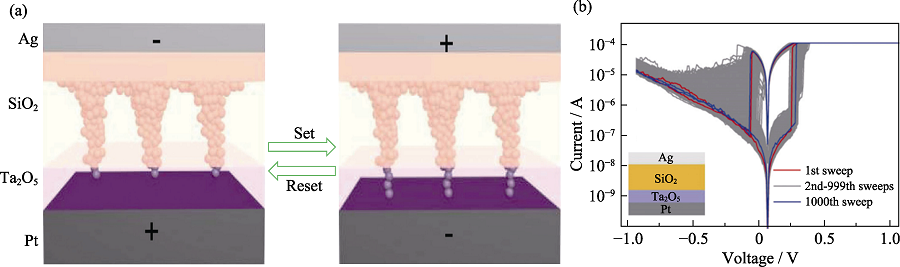
Fig. 3 Mechanism and characteristic of the double dielectric layer metal-oxide memristor based on the localization effect of electric field[14] (a) Schematic illustration for the switching mechanism of Ag/SiO2/Ta2O5/Pt memristor; (b) I-V characteristic of Ag/SiO2/Ta2O5/Pt memristor

Fig. 4 Two mechanisms and characteristics comparison of the double dielectric layer metal-oxide memristor based on oxygen vacancy gradient (a, b) Schematic diagrams of the resistance switching mechanism with (a) the structure of W/AlOx/AlOy/Pt memristor[47], (b) Ti/HfO2/TiOx/Pt memristor[23]; (c, d) Endurance of W/AlOx/AlOy/Pt memristor[47] and Ti/HfO2/TiOx/Pt memristor[23], and the Ti/HfO2/TiOx/Pt memristor with transition layer exhibiting more stable resistance states

Fig. 5 Mechanism and performance of the double dielectric layer metal-oxide memristor based on Joule heating effect[57] (a) Schematic diagrams of the switching mechanism of Ta/ZrO2(Y)/Ta2O5/TiN memristor; (b) I-V characteristic of Ta/ZrO2(Y)/Ta2O5/TiN memristor with nonlinear low-resistance state

Fig. 6 Mechanism of the double dielectric layer metal-oxide memristor with the linear symmetrical pulse response[58] (a) Schematic representation of the switching mechanism of Ag/SiO2/VOx/Pt memristor; (b) Pulse response of Ag/SiO2/VOx/Pt memristor represents highly linear and symmetric properties
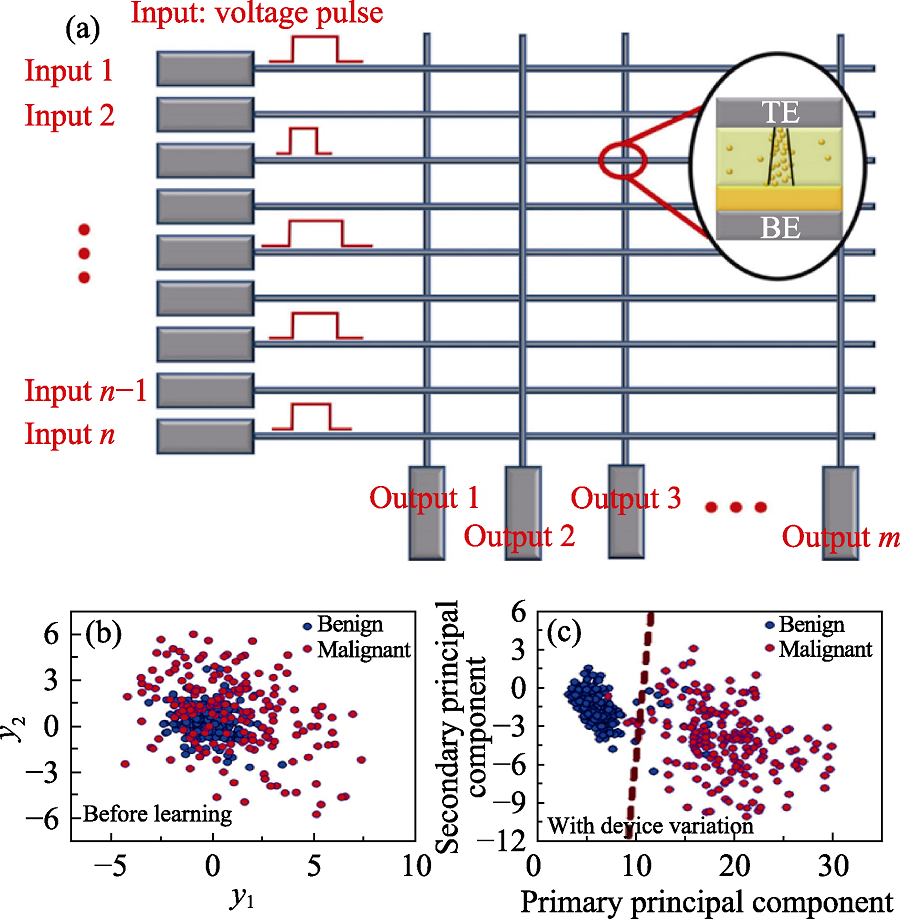
Fig. 7 Data set classification using memristor based on double dielectric layer metal-oxide[51] (a) Schematic of Pd/TaOx/Ta2O5/Pd memristor crossbar array; (b, c) The initial data and classification results of the data set
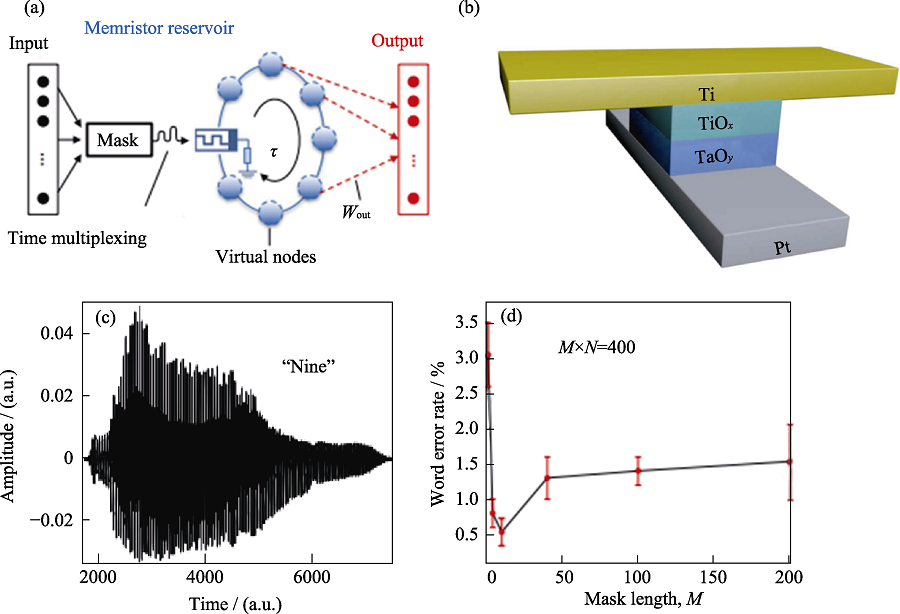
Fig. 8 Demonstration of speech recognition using double dielectric layer metal-oxide memristor[61] (a) Schematic of the memristor-based reservoir computing system; (b) Diagram of Ti/TiOx/TaOy/Pt memristor structure; (c) Typical audio waveform of digit 9; (d) Recognition error rate of speech varies as a function of the mask length with error bar representing variation between memristor devices
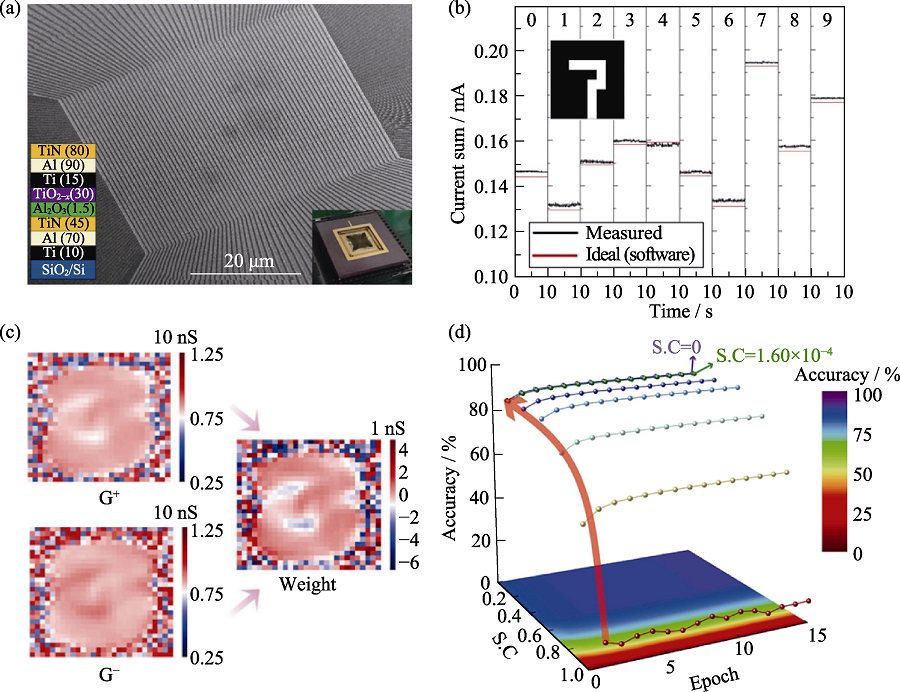
Fig. 9 Demonstration of image recognition using double dielectric layer metal-oxide memristor (a) SEM image of the 64×64 memristor crossbar array; (b) All experimental output currents for the digit “7”[59]; (c) Recognition diagrams of conductance and synaptic weights of digit “3”; (d) Evolution of the recognition accuracy of the MNIST under different synaptic coupling and training epochs[62]
| [1] |
CHUA L. Memristor-the missing circuit element. IEEE Trans. Circuit Theory, 1971, 18(5):507.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
STRUKOV D B, SNIDER G S, STEWART D R, et al. The missing memristor found. Nature, 2008, 453(7191):80.
DOI |
| [3] | KANG J, KIM T, HU S, et al. Cluster-type analogue memristor by engineering redox dynamics for high-performance neuromorphic computing. Nat. Commun., 2022, 13: 4040. |
| [4] |
CHANG T, JO S H, LU W. Short-term memory to long-term memory transition in a nanoscale memristor. ACS Nano, 2011, 5(9):7669.
DOI PMID |
| [5] |
JO S H, CHANG T, EBONG I, et al. Nanoscale memristor device as synapse in neuromorphic systems. Nano Lett., 2010, 10(4):1297.
DOI PMID |
| [6] |
WRIGHT C D, WANG L, AZIZ M M, et al. Phase-change processors, memristors and memflectors. Phys. Status Solidi B, 2012, 249(10): 1978.
DOI URL |
| [7] | YOSHIDA M, SUZUKI R, ZHANG Y, et al. Memristive phase switching in two-dimensional 1T-TaS2 crystals. Sci Adv., 2015, 1(9):e1500606. |
| [8] |
SOUSA R C, PREJBEANU I L. Non-volatile magnetic random access memories (MRAM). Comptes Rendus Physique, 2005, 6(9):1013.
DOI URL |
| [9] | SHIH M C, WANG C Y, LEE Y H, et al. Reliability study of perpendicular STT-MRAM as emerging embedded memory qualified for reflow soldering at 260 ℃. 2016 IEEE Symposium on VLSI Technology, Honolulu, 2016: 1-2. |
| [10] |
MANCHON A, ŽELEZNÝ J, MIRON I M. Current-induced spin-orbit torques in ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic systems. Rev. Mod. Phys., 2019, 91(3):035004.
DOI URL |
| [11] | HUANG Y T, CHEN N K, LI Z Z, et al. Two-dimensional In2Se3: a rising advanced material for ferroelectric data storage. InfoMat, 2022, 4(8):e12341. |
| [12] |
SETTER N, DAMJANOVIC D, ENG L M, et al. Ferroelectric thin films: review of materials, properties and applications. J. Appl. Phys., 2006, 100(10):051606.
DOI URL |
| [13] | VU Q A, KIM H, NGUYEN V L, et al. A high-on/off-ratio floating-gate memristor array on a flexible substrate via CVD-grown large-area 2D layer stacking. Adv. Mater., 2017, 29(44):1703363. |
| [14] |
GUO X, WANG Q, LÜ X, et al. SiO2/Ta2O5 heterojunction ECM memristors: physical nature of their low voltage operation with high stability and uniformity. Nanoscale, 2020, 12(7):4320.
DOI URL |
| [15] | ISMAIL M, ABBAS H, CHOI C, et al. Stabilized and reset-voltage controlled multi-level switching characteristics in ZrO2-based memristors by inserting a-ZTO interface layer. J. Alloys Compd., 2020, 835: 155256. |
| [16] |
ANDREEVA N, MAZING D, ROMANOV A, et al. Contact engineering approach to improve the linearity of multilevel memristive devices. Micromachines, 2021, 12(12):1567.
DOI URL |
| [17] | ISMAIL M, ABBAS H, MAHATA C, et al. Optimizing the thickness of Ta2O5 interfacial barrier layer to limit the oxidization of Ta ohmic interface and ZrO2 switching layer for multilevel data storage. J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2022, 106: 98. |
| [18] | ZHU Y L, XUE K H, CHENG X M, et al. Uniform and robust TiN/HfO2/Pt memristor through interfacial Al-doping engineering. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2021, 550: 149274. |
| [19] | SU C, SHAN L, YANG D, et al. Effects of heavy ion irradiation on Cu/Al2O3/Pt CBRAM devices. Microelectronic Eng., 2021, 247: 111600. |
| [20] | WU M C, TING Y H, CHEN J Y, et al. Low power consumption nanofilamentary ECM and VCM cells in a single sidewall of high-density VRRAM arrays. Adv. Sci., 2019, 6(24):1902363. |
| [21] |
RAJASEKARAN S, SIMANJUNTAK F M, CHANDRASEKARAN S, et al. Flexible Ta2O5/WO3-based memristor synapse for wearable and neuromorphic applications. IEEE Electron Device Lett., 2021, 43(1):9.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
ISMAIL M, ABBAS H, SOKOLOV A, et al. Emulating synaptic plasticity and resistive switching characteristics through amorphous Ta2O5 embedded layer for neuromorphic computing. Ceram. Int., 2021, 47(21):30764.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
LIU J, YANG H, JI Y, et al. An electronic synaptic device based on HfO2TiOx bilayer structure memristor with self-compliance and deep-RESET characteristics. Nanotechnology, 2018, 29(41):415205.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
XIA Q, YANG J J. Memristive crossbar arrays for brain-inspired computing. Nat. Mater., 2019, 18(4):309.
DOI PMID |
| [25] |
CHEN Y C, LIN C C, CHANG Y F. Post-moore memory technology: sneak path current (SPC) phenomena on RRAM crossbar array and solutions. Micromachines, 2021, 12(1):50.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
REN S G, NI R, HUANG X D, et al. Pt/Al2O3/TaOx/Ta self-rectifying memristor with record-low operation current (<2 pA), low power (fJ), and high scalability. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices, 2022, 69(2):838.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
XI Y, GAO B, TANG J, et al. In-memory learning with analog resistive switching memory: a review and perspective. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2021, 109(1):14.
DOI URL |
| [28] | CHEN P Y, PENG X, YU S. NeuroSim+: an integrated device-to-algorithm framework for benchmarking synaptic devices and array architectures. 2017 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), San Francisco, 2017: 6.1.1-6.1.4. |
| [29] | CHEN P Y, YU S. Technological benchmark of analog synaptic devices for neuroinspired architectures. IEEE Des. Test, 2019, 36(3):31. |
| [30] |
WOO J, MOON K, SONG J, et al. Improved synaptic behavior under identical pulses using AlOx/HfO2 bilayer RRAM array for neuromorphic systems. IEEE Electron Device Lett., 2016, 37(8):994.
DOI URL |
| [31] | 李策, 杨栋梁, 孙林锋. 基于二维层状材料的神经形态器件研究进展. 物理学报, 2022, 71(21):218504. |
| [32] |
YANG J J, MIAO F, PICKETT M D, et al. The mechanism of electroforming of metal oxide memristive switches. Nanotechnology, 2009, 20(21):215201.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
MAO G Q, XUE K H, SONG Y Q, et al. Oxygen migration around the filament region in HfOxmemristors. AIP Advances, 2019, 9(10):105007.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
YANG Y, LU W. Nanoscale resistive switching devices: mechanisms and modeling. Nanoscale, 2013, 5(21):10076.
DOI PMID |
| [35] |
ZHANG Z, YANG D, LI H, et al. 2D materials and van der Waals heterojunctions for neuromorphic computing. Neuromorph. Comput. Eng., 2022, 2(3):032004.
DOI |
| [36] |
CELANO U, GOUX L, BELMONTE A, et al. Three-dimensional observation of the conductive filament in nanoscaled resistive memory devices. Nano Lett., 2014, 14(5):2401.
DOI PMID |
| [37] | YANG Y, GAO P, GABA S, et al. Observation of conducting filament growth in nanoscale resistive memories. Nat. Commun., 2012, 3: 732. |
| [38] | LI C, GAO B, YAO Y, et al. Direct observations of nanofilament evolution in switching processes in HfO2 based resistive random access memory by in situ TEM studies. Adv. Mater., 2017, 29(10):1602976. |
| [39] |
MIAO F, STRACHAN J P, YANG J J, et al. Anatomy of a nanoscale conduction channel reveals the mechanism of a high performance memristor. Adv. Mater., 2011, 23(47):5633.
DOI URL |
| [40] | 栗苹, 许玉堂. 氧空位迁移造成的氧化物介质层时变击穿的蒙特卡罗模拟. 物理学报, 2017, 66(21):217701. |
| [41] | DESHMUKH S, ROJO M M, YALON E, et al. Direct measurement of nanoscale filamentary hot spots in resistive memory devices. Sci. Adv., 2022, 8(13):eabk1514. |
| [42] |
STRACHAN J P, STRUKOV D B, BORGHETTI J, et al. The switching location of a bipolar memristor: chemical, thermal and structural mapping. Nanotechnology, 2011, 22(25):254015.
DOI URL |
| [43] | WU F, SI S, CAO P, et al. Interface engineering via MoS2insertion layer for improving resistive switching of conductive bridging random access memory. Adv. Electron. Mater., 2019, 5(4):1800747. |
| [44] | CHEN Y Y, ROELOFS R, REDOLFI A, et al. Tailoring switching and endurance/retention reliability characteristics of HfO2/Hf RRAM with Ti, Al, Si dopants. 2014 Symposium on VLSI Technology: Digest of Technical Papers, Honolulu, 2014: 1-2. |
| [45] |
WANG B, XUE K H, SUN H J, et al. Performance enhancement of TaOx resistive switching memory using graded oxygen content. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2018, 113(18):183501.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
LANDON C D, WILKE R H T, BRUMBACH M T, et al. Thermal transport in tantalum oxide films for memristive applications. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2015, 107(2):023108.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
HUANG X D, LI Y, LI H Y, et al. Enhancement of DC/AC resistive switching performance in AlOx memristor by two technique bilayer approach. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2020, 116(17):173504.
DOI URL |
| [48] | DUAN Q, XU L, ZHU J, et al. Resistive switching and synaptic plasticity in HfO2-based memristors with single-layer and bilayer structures. 2018 China Semiconductor Technology International Conference (CSTIC), Shanghai, 2018: 1-3. |
| [49] |
HUANG X D, LI Y, LI H Y, et al. Forming-free, fast, uniform, and high endurance resistive switching from cryogenic to high temperatures in W/AlOx/Al2O3/Pt bilayer memristor. IEEE Electron Device Lett., 2020, 41(4):549.
DOI URL |
| [50] | HUANG X D, LI Y, LI H Y, et al. Low-power, high speed and high uniform switching in AlOx-based memristor using homogeneous bilayer structure for memcomputing. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Integrated Circuits, Technologies and Applications (ICTA), Chengdu, 2019: 113. |
| [51] | CHOI S, SHERIDAN P, LU W D. Data clustering using memristor networks. Sci. Rep., 2015, 5: 10492. |
| [52] | WANG X, LIAO W, RAO T, et al. Resistive switching in sputtered ZnO/IGZO heterostructure memristor. 2022 IEEE 5th International Conference on Electronics Technology (ICET), Chengdu, 2022: 113. |
| [53] |
XU Z, YU L, XU X, et al. Effect of oxide/oxide interface on polarity dependent resistive switching behavior in ZnO/ZrO2 heterostructures. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2014, 104(19):192903.
DOI URL |
| [54] | ZHU J, LEE J W, LEE H, et al. Probing vacancy behavior across complex oxide heterointerfaces. Sci. Adv., 2019, 5(2):eaau8467. |
| [55] |
CHANDRASEKARAN S, SIMANJUNTAK F M, SAMINATHAN R, et al. Improving linearity by introducing Al in HfO2 as a memristor synapse device. Nanotechnology, 2019, 30(44):445205.
DOI URL |
| [56] | ZHANG Z, CAI Y, YU M, et al. A tantalum oxide memristor for artificial synapse applications. 2014 12th IEEE International Conference on Solid-State and Integrated Circuit Technology (ICSICT), Guilin, 2014: 1. |
| [57] | MIKHAYLOV A, BELOV A, KOROLEV D, et al. Multilayer metal-oxide memristive device with stabilized resistive switching. Adv. Mater. Technol., 2020, 5(1):1900607. |
| [58] |
BOUSOULAS P, SAKELLAROPOULOS D, TSOUKALAS D, et al. Tuning the analog synaptic properties of forming free SiO2 memristors by material engineering. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2021, 118(14):143502.
DOI URL |
| [59] | KIM H, MAHMOODI M R, NILI H, et al. 4K-memristor analog-grade passive crossbar circuit. Nat. Commun., 2021, 12: 5198. |
| [60] |
WU F, CAO P, PENG Z, et al. Memristor based on TiOx/Al2O3 bilayer as flexible artificial synapse for neuromorphic electronics. IEEE Trans. Electron Device, 2021, 69(1):375.
DOI URL |
| [61] | ZHONG Y, TANG J, LI X, et al. Dynamic memristor-based reservoir computing for high-efficiency temporal signal processing. Nat. Commun., 2021, 12: 408. |
| [62] |
CHOI S, JANG S, MOON J H, et al. A self-rectifying TaOy/ nanoporous TaOx memristor synaptic array for learning and energy-efficient neuromorphic systems. NPG Asia Mater., 2018, 10(12):1097.
DOI |
| [63] | KIM H J, PARK T H, YOON K J, et al. Fabrication of a Cu-cone-shaped cation source inserted conductive bridge random access memory and its improved switching reliability. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2019, 29(8):1806278. |
| [64] | KIM H J, KIM J, PARK T G, et al. Multi-level control of conductive filament evolution and enhanced resistance controllability of the Cu-cone structure embedded conductive bridge random access memory. Adv. Electron. Mater., 2022, 8(8):2100209. |
| [1] | ZHU Wenjie, TANG Lu, LU Jichang, LIU Jiangping, LUO Yongming. Research Progress on Catalytic Oxidation of Volatile Organic Compounds by Perovskite Oxides [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [2] | HU Zhichao, YANG Hongyu, YANG Hongcheng, SUN Chengli, YANG Jun, LI Enzhu. Usage of the P-V-L Bond Theory in Regulating Properties of Microwave Dielectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [3] | WU Qiong, SHEN Binglin, ZHANG Maohua, YAO Fangzhou, XING Zhipeng, WANG Ke. Research Progress on Lead-based Textured Piezoelectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [4] | ZHANG Bihui, LIU Xiaoqiang, CHEN Xiangming. Recent Progress of Hybrid Improper Ferroelectrics with Ruddlesden-Popper Structure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| [5] | WU Jie, YANG Shuai, WANG Mingwen, LI Jinglei, LI Chunchun, LI Fei. Textured PT-based Piezoelectric Ceramics: Development, Status and Challenge [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 575-586. |
| [6] | JIANG Kun, LI Letian, ZHENG Mupeng, HU Yongming, PAN Qinxue, WU Chaofeng, WANG Ke. Research Progress on Low-temperature Sintering of PZT Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| [7] | TIAN Ruizhi, LAN Zhengyi, YIN Jie, HAO Nanjing, CHEN Hangrong, MA Ming. Microfluidic Technology Based Synthesis of Inorganic Nano-biomaterials: Principles and Progress [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 337-347. |
| [8] | ZHANG Jiguo, WU Tian, ZHAO Xu, YANG Fan, XIA Tian, SUN Shien. Improvement of Cycling Stability of Cathode Materials and Industrialization Process for Sodium-ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 348-362. |
| [9] | YIN Jie, GENG Jiayi, WANG Kanglong, CHEN Zhongming, LIU Xuejian, HUANG Zhengren. Recent Advances in 3D Printing and Densification of SiC Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 245-255. |
| [10] | CHEN Guangchang, DUAN Xiaoming, ZHU Jinrong, GONG Qing, CAI Delong, LI Yuhang, YANG Donglei, CHEN Biao, LI Xinmin, DENG Xudong, YU Jin, LIU Boya, HE Peigang, JIA Dechang, ZHOU Yu. Advanced Ceramic Materials in Helicopter Special Structures: Research Progress and Application Prospect [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 225-244. |
| [11] | FAN Xiaobo, ZU Mei, YANG Xiangfei, SONG Ce, CHEN Chen, WANG Zi, LUO Wenhua, CHENG Haifeng. Research Progress on Proton-regulated Electrochemical Ionic Synapses [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 256-270. |
| [12] | HAIREGU Tuxun, GUO Le, DING Jiayi, ZHOU Jiaqi, ZHANG Xueliang, NUERNISHA Alifu. Research Progress of Optical Bioimaging Technology Assisted by Upconversion Fluorescence Probes in Tumor Imaging [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 145-158. |
| [13] | SUN Shujuan, ZHENG Nannan, PAN Haokun, MA Meng, CHEN Jun, HUANG Xiubing. Research Progress on Preparation Methods of Single-atom Catalysts [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 113-127. |
| [14] | TAO Guilong, ZHI Guowei, LUO Tianyou, OUYANG Peidong, YI Xinyan, LI Guoqiang. Progress on Key Technologies of Cavity-structured Thin Film Bulk Acoustic Wave Filter [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 128-144. |
| [15] | ZHOU Fan, TIAN Zhilin, LI Bin. Research Progress on Carbide Ultra-high Temperature Ceramic Anti-ablation Coatings for Thermal Protection System [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 1-16. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||