
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (6): 609-622.DOI: 10.15541/jim20230581
Special Issue: 【结构材料】陶瓷基复合材料(202506)
• REVIEW • Previous Articles Next Articles
WU Xiaochen1( ), ZHENG Ruixiao1(
), ZHENG Ruixiao1( ), LI Lu2(
), LI Lu2( ), MA Haolin2, ZHAO Peihang1, MA Chaoli2
), MA Haolin2, ZHAO Peihang1, MA Chaoli2
Received:2023-12-18
Revised:2024-01-25
Published:2024-06-20
Online:2024-01-31
Contact:
ZHENG Ruixiao, associate professor. E-mail: zhengruixiao@buaa.edu.cn;About author:WU Xiaochen (1998-), male, PhD candidate. E-mail: wuxiaochen@buaa.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
WU Xiaochen, ZHENG Ruixiao, LI Lu, MA Haolin, ZHAO Peihang, MA Chaoli. Research Progress on In-situ Monitoring of Damage Behavior of SiCf/SiC Ceramic Matrix Composites at High Temperature Environments[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(6): 609-622.
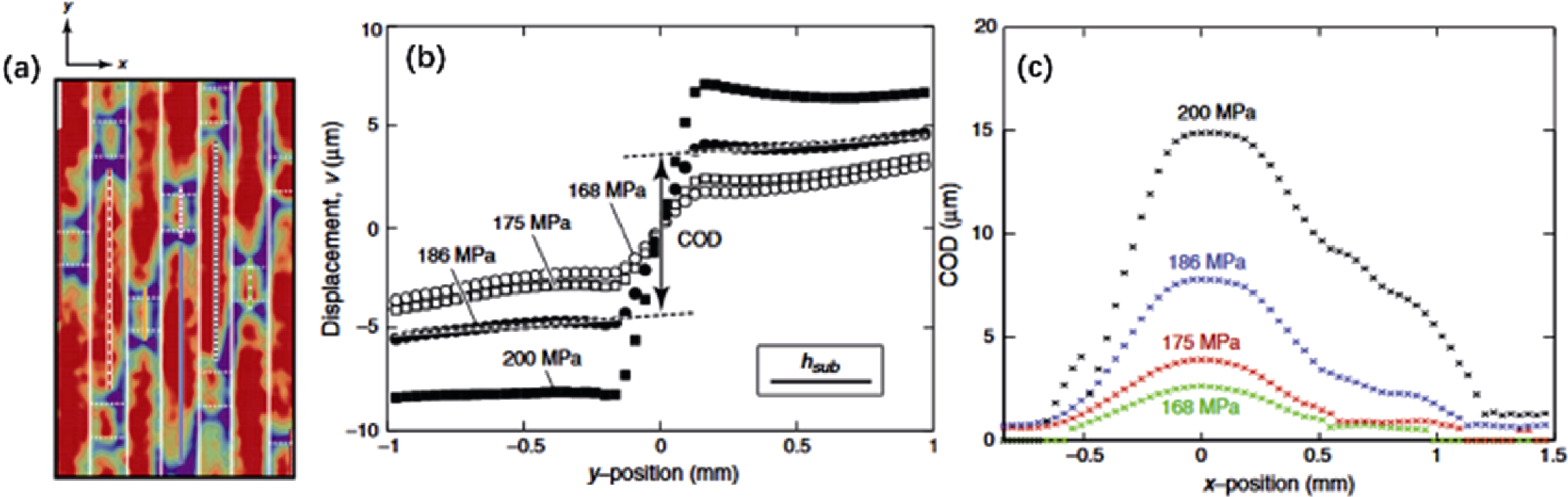
Fig. 1 DIC strain measurement results of two-dimensional woven SiCf/SiC composites[18] (a) Distribution of surface strain field; (b) Demonstration of COD determination procedure; (c) Distribution of COD at different stress levels
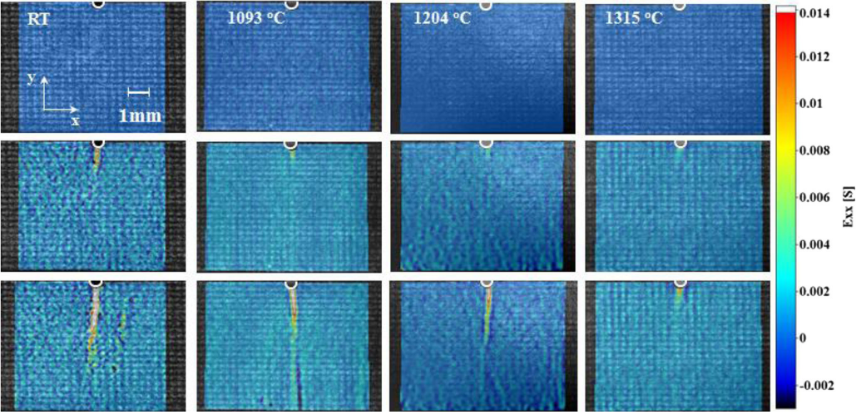
Fig. 2 Full field strain maps of single-notched SiCf/SiC samples monotonically loaded in tension at room temperature, 1093, 1204 and 1315 ℃ showing crack propagation[25]
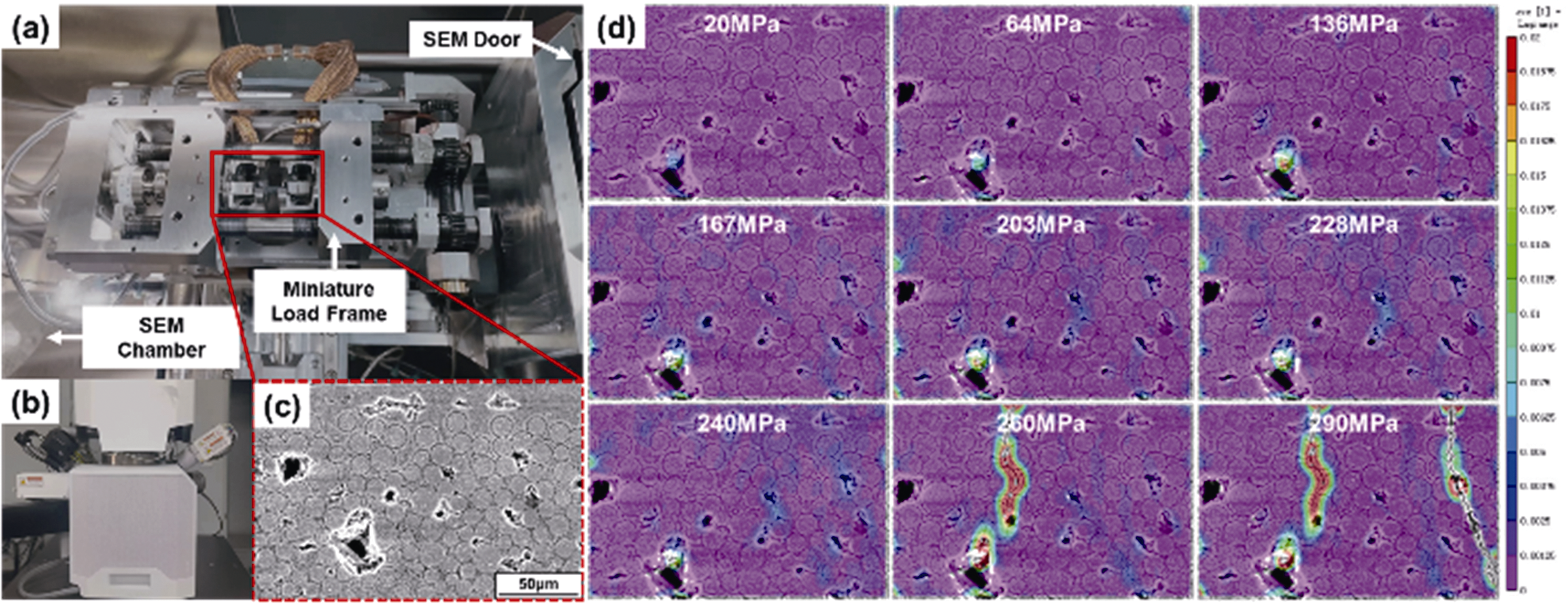
Fig. 4 Strain evolution of the micro-zone in weft yarn under tensile load in 2.5D-SiCf/SiC composites (a) Elevated-temperature in-situ micro-loading stage; (b) SEM equipment; (c) Distribution of speckles on the surface of the sample at the weft yarn; (d) Evolution process of strain cloud map in the microzone within the weft yarn of the composite specimen

Fig. 5 High-temperature in -situ Lab-μ-CT device developed by using a laboratory X-ray source[46] (a) Schematic diagram of the elevated-temperature in-situ μ-CT apparatus; (b) Schematic of the dynamic seal structure; (c) Schematic of the heating chamber with the specimen mounted in grips
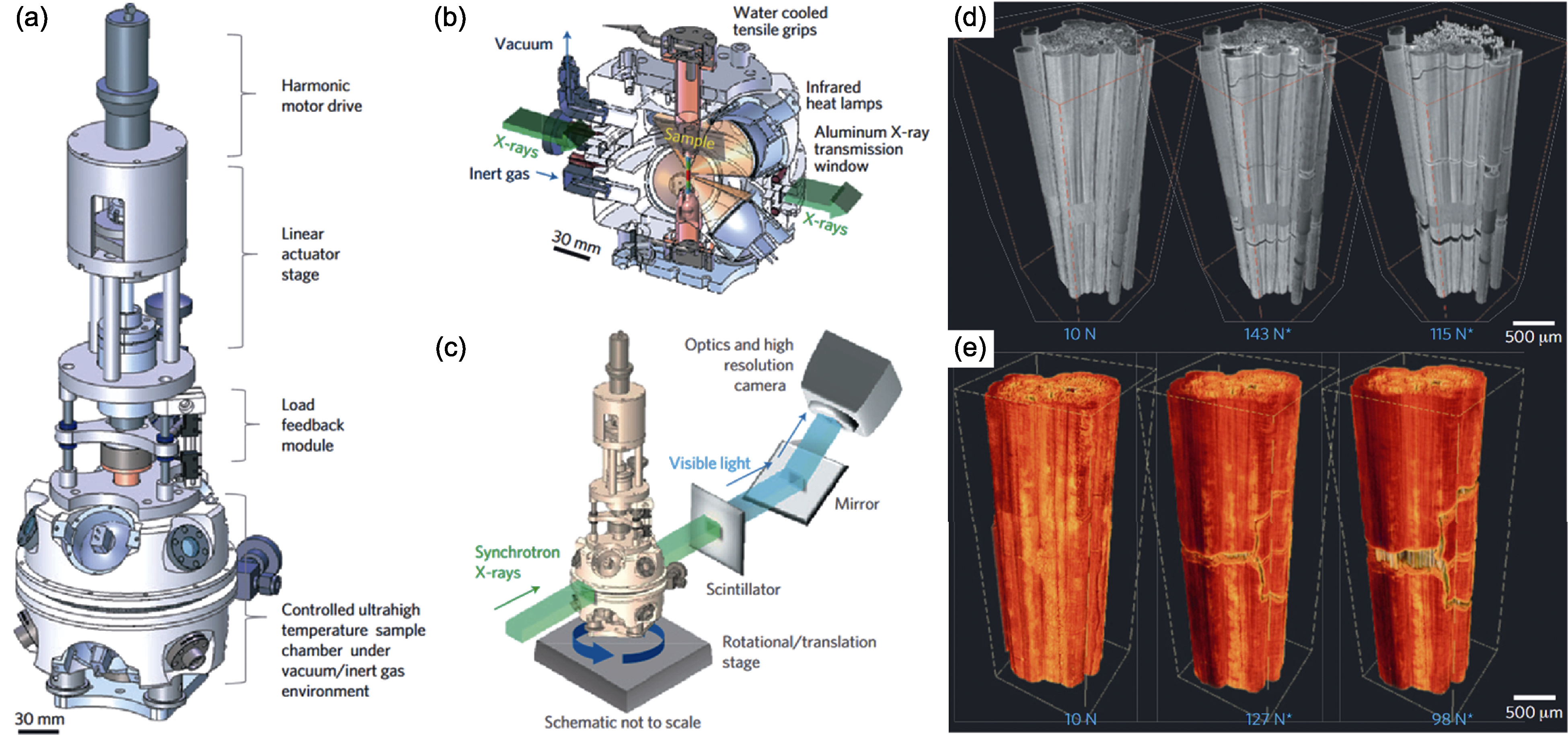
Fig. 6 SR-μ-CT in -situ tensile/compression test rig to quantitatively analyze the internal matrix crack and damage evolution of SiCf/SiC composites under ultrahigh temperature[49] (a) Schematic illustration of in-situ ultrahigh temperature tensile test rig for synchrotron X-ray computed microtomography; (b) Sectional view of the heating chamber illustrating X-ray transmission path through the heating chamber and sample; (c) Schematic of the rig in transmission mode for X-ray computed tomography; (d, e) 3D volume-rendered µ-CT images from specimens tested at (d) room temperature and (e) 1750 ℃ at several applied tensile loads
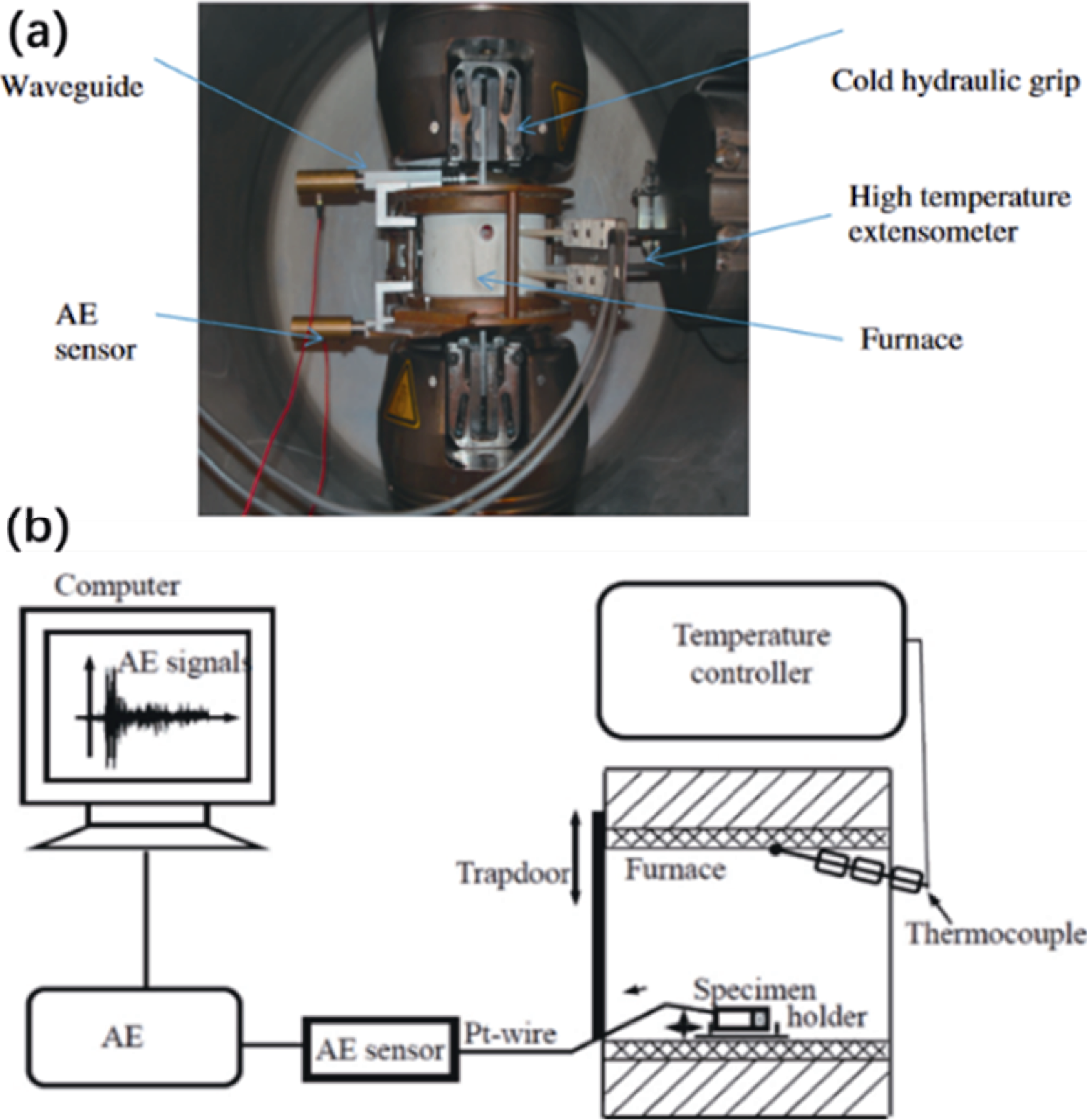
Fig. 8 (a) Instrumentation with waveguide rod during mechanical test on CMC at high temperature[59]and (b) schematic of the experimental set-up for cyclic heating and cooling tests and AE measurements using waveguide wire[68]
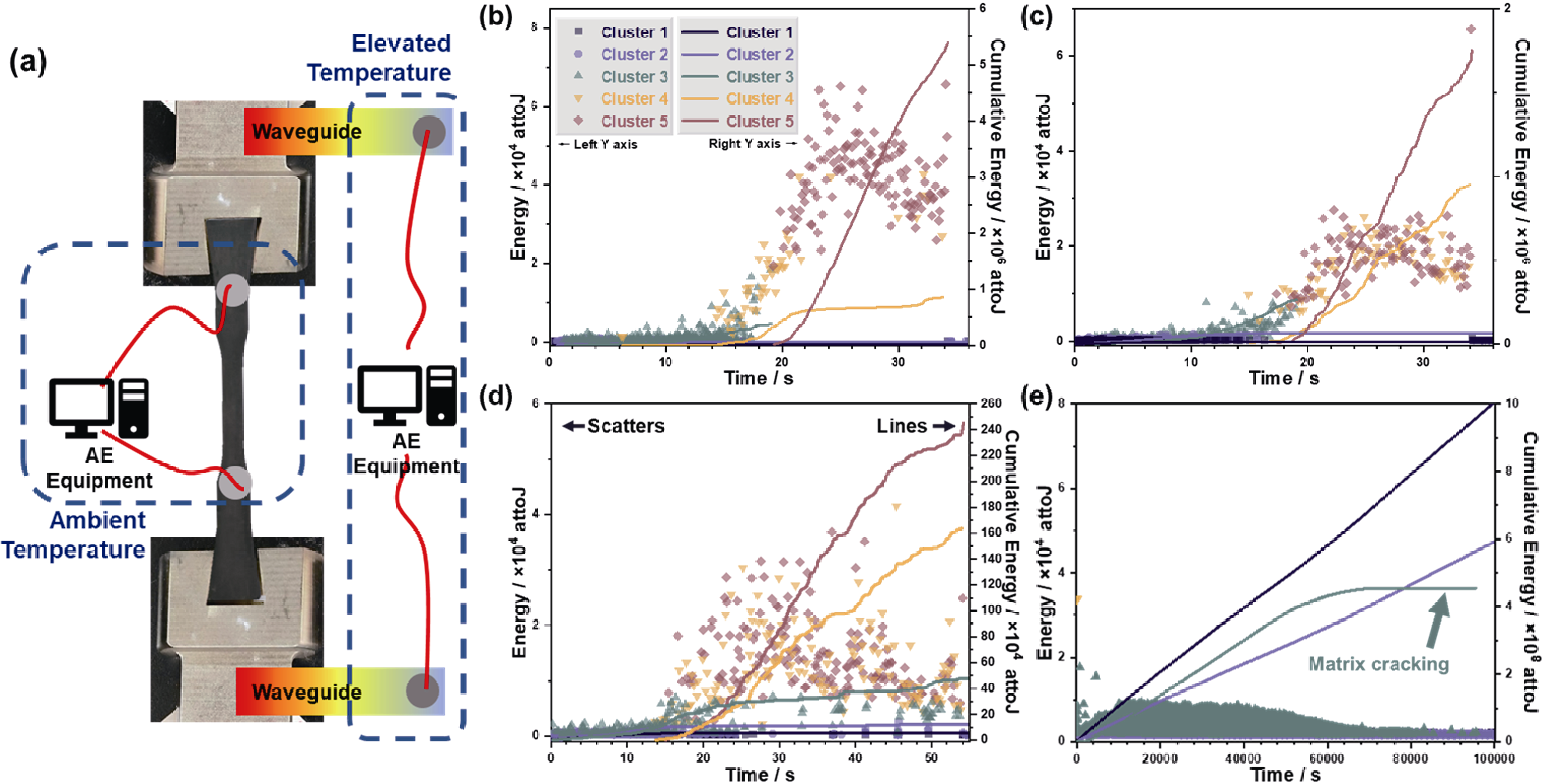
Fig. 9 In-situ AE monitoring results of 2D-SiCf/SiC composites at ambient temperature, high temperature tensile and high temperature fatigue (a) Placement of AE sensors at ambient temperature and high temperature; (b-e) Energy and cumulative energy-time diagrams after classification of AE signals (b) without and (c) with waveguides at ambient temperature tensile, and after classification of AE signals at 1350 ℃/air environment (d) tensile and (e) fatigue
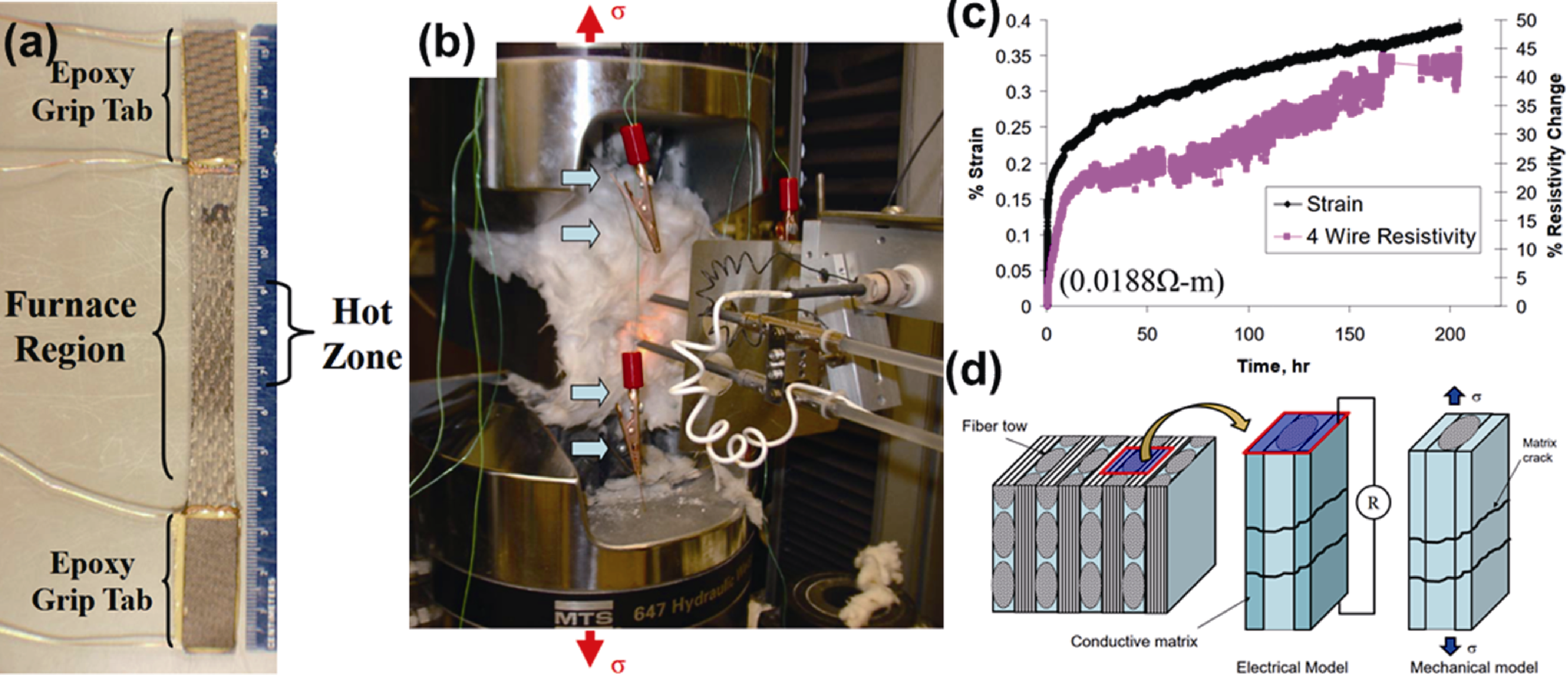
Fig. 10 In-situ ER monitoring of high-temperature creep test at 1315 ℃[79] (a) Four-probe method for sample resistance wiring arrangement; (b) Arrangement of high-temperature creep equipment device; (c) Creep curve and corresponding resistance curve; (d) Physical principle diagram of resistance method for creep damage monitoring
| [1] | 刘巧沐, 黄顺洲, 何爱杰. 碳化硅陶瓷基复合材料在航空发动机上的应用需求及挑战. 材料工程, 2019, 47(2): 1. |
| [2] | 沙建军, 代吉祥, 张兆甫. 纤维增韧高温陶瓷基复合材料(Cf, SiCf/SiC)应用研究进展. 航空制造技术, 2017(19): 16. |
| [3] | XU S, ZHENG C, BI Y, et al. In-situ TEM investigations on the microstructural evolution of SiC fibers under ion irradiation: amorphization and grain growth. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2023, 43(4): 1376. |
| [4] | SONG C, YE F, CHENG L, et al. Long-term ceramic matrix composite for aeroengine. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2022, 11(9): 1343. |
| [5] | CHATEAU C, GÉLÉBART L, BORNERT M, et al. Modeling of damage in unidirectional ceramic matrix composites and multi-scale experimental validation on third generation SiC/SiC minicomposites. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 2014, 63: 298. |
| [6] | HAN D, YE F, CHENG L, et al. Matrix cracking of 2D SiC/SiC composite characterized by in situ SEM and nano-CT. Ceramics International, 2023, 49(8): 12508. |
| [7] | DELAGE J, SAIZ E, AL NASIRI N. Fracture behaviour of SiC/SiC ceramic matrix composite at room temperature. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2022, 42(7): 3156. |
| [8] | ZHAO S, ZHOU X, YU J, et al. Mechanical properties and in situ crack growth observation of SiC/SiC composites. Ceramics International, 2014, 40(5): 7481. |
| [9] | 梁杰存, 韩琦男, 贺志武, 等. 扫描显微环境下原位高温力学测量技术及其应用研究. 中国科学: 物理学力学天文学, 2018, 48(9): 71. |
| [10] | 祺跃科技. 祺跃自研产品系列: 原位高温拉伸台(2022-12-15) [2024-01-21]. http://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzA4NTgzMzc1Ng==&mid=2247484072&idx=1&sn=5f947cc76feb36074fd722279b89c4ca&chksm=9fd0a3dba8a72acd159cf2064eb5ff511b9e89e8724cdc6dd8f14544a01588e45f91c00ae710#rd. |
| [11] | 马晋遥, 王晋, 赵云松, 等. 一种第二代镍基单晶高温合金1150 ℃原位拉伸断裂机制研究. 金属学报, 2019, 55(8): 987. |
| [12] | DETWILER K, HUNT R, OPILA E. In-situ observation of micro-cracking in a SiC/BN/SiC ceramic matrix composite under tension. Open Ceramics, 2023, 14: 100366. |
| [13] | MIYASHITA Y, KANDA K, ZHU S, et al. Observations of fatigue damage process in SiC/SiC composites at room and elevated temperatures. International Journal of Fatigue, 2002, 24(2): 241. |
| [14] | 罗雅煊, 董亚丽, 李露, 等. 基于数字图像相关方法的SiCf/SiC陶瓷基复合材料力学行为表征. 航空材料学报, 2023, 43(3): 60. |
| [15] | HOLMES J, SOMMACAL S, DAS R, et al. Digital image and volume correlation for deformation and damage characterisation of fibre-reinforced composites: a review. Composite Structures, 2023, 315: 116994. |
| [16] | YAMAGUCHI I. Speckle displacement and decorrelation in the diffraction and image fields for small object deformation. Optica Acta: International Journal of Optics, 1981, 28(10): 1359. |
| [17] | PETERS W H, RANSON W F. Digital imaging techniques in experimental stress analysis. Optical Engineering, 1982, 21(3): 427. |
| [18] | RAJAN V P, ROSSOL M N, ZOK F W. Optimization of digital image correlation for high-resolution strain mapping of ceramic composites. Experimental Mechanics, 2012, 52(9): 1407. |
| [19] | BERNACHY-BARBE F, GÉLÉBART L, BORNERT M, et al. Characterization of SiC/SiC composites damage mechanisms using digital image correlation at the tow scale. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2015, 68: 101. |
| [20] | BUMGARDNER C H, HEIM F M, ROACHE D C, et al. Unveiling hermetic failure of ceramic tubes by digital image correlation and acoustic emission. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2020, 103(3): 2146. |
| [21] | BUMGARDNER C H, HEIM F M, ROACHE D C, et al. Characterizing environment-dependent fracture mechanisms of ceramic matrix composites via digital image correlation. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2021, 104(12): 6545. |
| [22] | PRESBY M J, KANNAN M, MORSCHER G N, et al. An investigation of the end-notched flexure and end-loaded split tests applied to the mode II interlaminar fracture of a SiC/SiC ceramic matrix composite. Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power, 2020, 142: 041027. |
| [23] | TABLEAU N, ABOURA Z, KHELLIL K, et al. Accurate measurement of in-plane and out-of-plane shear moduli on 3D woven SiC-SiBC material. Composite Structures, 2017, 172: 319. |
| [24] | MORSCHER G N, MAXWELL R. Monitoring tensile fatigue crack growth and fiber failure around a notch in laminate SIC/SIC composites utilizing acoustic emission, electrical resistance, and digital image correlation. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(2): 229. |
| [25] | MEYER P, WAAS A M. Mesh-objective two-scale finite element analysis of damage and failure in ceramic matrix composites. Integrating Materials and Manufacturing Innovation, 2015, 4(1): 63. |
| [26] | MEYER P, WAAS A M. Experimental results on the elevated temperature tensile response of SiC/SiC ceramic matrix notched composites. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2018, 143: 26. |
| [27] | 陈俊, 佀明森, 张人发, 等. 高温下C/SiC复合材料弯曲断裂性能实时测试和微观结构表征分析. 实验力学, 2016, 31(2): 243. |
| [28] | MAO W G, CHEN J, SI M S, et al. High temperature digital image correlation evaluation of in-situ failure mechanism: an experimental framework with application to C/SiC composites. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2016, 665: 26. |
| [29] | TRACY J, DALY S, SEVENER K. Multiscale damage characterization in continuous fiber ceramic matrix composites using digital image correlation. Journal of Materials Science, 2015, 50(15): 5286. |
| [30] | SEVENER K M, TRACY J M, CHEN Z, et al. Crack opening behavior in ceramic matrix composites. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2017, 100(10): 4734. |
| [31] | TRACY J, WAAS A, DALY S. A new experimental approach for in situ damage assessment in fibrous ceramic matrix composites at high temperature. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2015, 98(6): 1898. |
| [32] | LOVAAS N. Minimizing noise and bias in DIC(2020-11-25) [2023-11-30]. https://correlated.kayako.com/article/25-minimizing-noise-and-bias-in-dic. |
| [33] | 王龙, 冯国林, 李志强, 等. X射线断层扫描在材料力学行为研究中的应用. 强度与环境, 2017, 44(6): 43. |
| [34] | LI Q, CHEN Y, CHEN Y, et al. Effects of void defects on fracture features and tensile strength of C/SiC composites: an image-based FEM study. Applied Composite Materials, 2022, 29(3): 1021. |
| [35] | GAO Y, WANG Y, YANG X, et al. Synchrotron X-ray tomographic characterization of CVI engineered 2D-woven and 3D-braided SiCf/SiC composites. Ceramics International, 2016, 42(15): 17137. |
| [36] | SAUCEDO-MORA L, LOWE T, ZHAO S, et al. In situ observation of mechanical damage within a SiC-SiC ceramic matrix composite. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2016, 481: 13. |
| [37] | CHEN Y, GÉLÉBART L, CHATEAU C, et al. Analysis of the damage initiation in a SiC/SiC composite tube from a direct comparison between large-scale numerical simulation and synchrotron X-ray micro-computed tomography. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2019, 161: 111. |
| [38] | YANG H, XU S, ZHANG D, et al. In-situ tensile damage and fracture behavior of PIP SiC/SiC minicomposites at room temperature. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(14): 6869. |
| [39] | GUO W, GAO Y, SUN L. In-situ CT characterization of 2D woven SiCf/SiC composite loading under compression. Science and Engineering of Composite Materials, 2022, 29(1): 394. |
| [40] | CHATEAU C, GÉLÉBART L, BORNERT M, et al. In situ X-ray microtomography characterization of damage in SiCf/SiC minicomposites. Composites Science and Technology, 2011, 71(6): 916. |
| [41] | HILMAS A M, SEVENER K M, HALLORAN J W. Damage evolution in SiC/SiC unidirectional composites by X-ray tomography. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2020, 103(5): 3436. |
| [42] | 刘海龙, 张大旭, 祁荷音, 等. 基于X射线CT原位试验的平纹SiC/SiC复合材料拉伸损伤演化. 上海交通大学学报, 2020, 54(10): 1074. |
| [43] | 冯宇琦, 张毅, 张大旭, 等. 基于深度学习的2.5D陶瓷基复合材料损伤识别与评估. 硅酸盐学报, 2021, 49(8): 1765. |
| [44] | ZHANG D, LIU Y, LIU H, et al. Characterisation of damage evolution in plain weave SiC/SiC composites using in situ X-ray micro-computed tomography. Composite Structures, 2021, 275: 114447. |
| [45] | YANG C, WU S, WU S, et al. In-situ characterization on crack propagation behavior of SiCf/SiC composites during monotonic tensile loading. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2022, 42(15): 6836. |
| [46] | ZHU R, QU Z, YANG S, et al. An in situ microtomography apparatus with a laboratory X-ray source for elevated temperatures of up to 1000 ℃. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2021, 92(3): 033704. |
| [47] | ZHU R, NIU G, QU Z, et al. In-situ quantitative tracking of micro- crack evolution behavior inside CMCs under load at high temperature: a deep learning method. Acta Materialia, 2023, 255: 119073. |
| [48] | HABOUB A, BALE H A, NASIATKA J R, et al. Tensile testing of materials at high temperatures above 1700 ℃ with in situ synchrotron X-ray micro-tomography. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2014, 85(8): 083702. |
| [49] | BALE H A, HABOUB A, MACDOWELL A A, et al. Real-time quantitative imaging of failure events in materials under load at temperatures above 1600 ℃. Nature Materials, 2013, 12(1): 40. |
| [50] | MAZARS V, CATY O, COUÉGNAT G, et al. Damage investigation and modeling of 3D woven ceramic matrix composites from X-ray tomography in-situ tensile tests. Acta Materialia, 2017, 140: 130. |
| [51] | LIU C, CHEN Y, SHI D, et al. In situ investigation of failure in 3D braided SiCf/SiC composites under flexural loading. Composite Structures, 2021, 270: 114067. |
| [52] | CROOM B P, XU P, LAHODA E J, et al. Quantifying the three-dimensional damage and stress redistribution mechanisms of braided SiC/SiC composites by in situ volumetric digital image correlation. Scripta Materialia, 2017, 130: 238. |
| [53] | CHEN Y, GÉLÉBART L, CHATEAU C, et al. 3D detection and quantitative characterization of cracks in a ceramic matrix composite tube using X-ray computed tomography. Experimental Mechanics, 2020, 60(3): 409. |
| [54] | CHEN Y, GÉLÉBART L, CHATEAU C, et al. Crack initiation and propagation in braided SiC/SiC composite tubes: effect of braiding angle. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(13): 4403. |
| [55] | FORNA-KREUTZER J P, ELL J, BARNARD H, et al. Full-field characterisation of oxide-oxide ceramic-matrix composites using X-ray computed micro-tomography and digital volume correlation under load at high temperatures. Materials & Design, 2021, 208: 109899. |
| [56] | GAO X, LEI B, ZHANG Y, et al. Identification of microstructures and damages in silicon carbide ceramic matrix composites by deep learning. Materials Characterization, 2023, 196: 112608. |
| [57] | DU Y, ZHANG D, WANG L, et al. Damage mechanism characterisation of plain weave ceramic matrix composites under in-plane shear using in-situ X-ray micro-CT and deep-learning-based image segmentation. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2024, 44(1): 142. |
| [58] | BADRAN A, MARSHALL D, LEGAULT Z, et al. Automated segmentation of computed tomography images of fiber-reinforced composites by deep learning. Journal of Materials Science, 2020, 55(34): 16273. |
| [59] | GROSSE C U, OHTSU M, AGGELIS D G, et al. Acoustic emission testing:basics for research-applications in engineering. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2022. |
| [60] | MAILLET E, GODIN N, R’MILI M, et al. Damage monitoring and identification in SiC/SiC minicomposites using combined acousto-ultrasonics and acoustic emission. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2014, 57: 8. |
| [61] | MOEVUS M, GODIN N, R’MILI M, et al. Analysis of damage mechanisms and associated acoustic emission in two SiCf/[Si-B-C] composites exhibiting different tensile behaviours. Part II: unsupervised acoustic emission data clustering. Composites Science and Technology, 2008, 68(6): 1258. |
| [62] | SHAN Q, XUE Y, HU J. The anti-oxidation mechanism of SiCf/SiC-B4C modified with Al2O3 in wet atmosphere based on machine learning. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2022, 105(9): 5853. |
| [63] | SHAN Q, XU Q, XUE Y, et al. The tensile damage behavior of SiCf/SiC-B4C after oxidation in wet atmosphere based on acoustic emission pattern recognition. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2021, 104(8): 4131. |
| [64] | MUIR C, TULSHIBAGWALE N, FURST A, et al. Quantitative benchmarking of acoustic emission machine learning frameworks for damage mechanism identification. Integrating Materials and Manufacturing Innovation, 2023, 12(1): 70. |
| [65] | MORSCHER G N. Modal acoustic emission of damage accumulation in a woven SiC/SiC composite. Composites Science and Technology, 1999, 59(5): 687. |
| [66] | SWAMINATHAN B, MCCARTHY N R, ALMANSOUR A S, et al. Microscale characterization of damage accumulation in CMCs. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(5): 3082. |
| [67] | NOZAWA T, KOYANAGI T, KATOH Y, et al. Failure evaluation of neutron-irradiated SiC/SiC composites by underwater acoustic emission. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2022, 566: 153787. |
| [68] | YANG L, ZHOU Y C, LU C. Damage evolution and rupture time prediction in thermal barrier coatings subjected to cyclic heating and cooling: an acoustic emission method. Acta Materialia, 2011, 59(17): 6519. |
| [69] | 宫永辉, 武小峰, 尹晓峰, 等. 高温条件下波导杆的在线损伤检测. 无损检测, 2019, 41(09): 70. |
| [70] | 杨丽, 周益春, 朱旺. 热障涂层失效的声发射实时表征技术研究进展. 中国材料进展, 2020, 39(11): 878. |
| [71] | MOMON S, MOEVUS M, GODIN N, et al. Acoustic emission and lifetime prediction during static fatigue tests on ceramic- matrix-composite at high temperature under air. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2010, 41(7): 913. |
| [72] | MOMON S, GODIN N, REYNAUD P, et al. Unsupervised and supervised classification of AE data collected during fatigue test on CMC at high temperature. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2012, 43(2): 254. |
| [73] | MAILLET E. Analysis of acoustic emission energy release during static fatigue tests at intermediate temperatures on ceramic matrix composites: towards rupture time prediction. Composites Science and Technology, 2012, 72(9): 1001. |
| [74] | MAILLET E, GODIN N, R’MILI M, et al. Real-time evaluation of energy attenuation: a novel approach to acoustic emission analysis for damage monitoring of ceramic matrix composites. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2014, 34(7): 1673. |
| [75] | GODIN N, REYNAUD P, FANTOZZI G. Challenges and limitations in the identification of acoustic emission signature of damage mechanisms in composites materials. Applied Sciences, 2018, 8(8): 1267. |
| [76] | SMITH C E, MORSCHER G N, XIA Z H. Monitoring damage accumulation in ceramic matrix composites using electrical resistivity. Scripta Materialia, 2008, 59(4): 463. |
| [77] | MANSOUR R, MAILLET E, MORSCHER G N. Monitoring interlaminar crack growth in ceramic matrix composites using electrical resistance. Scripta Materialia, 2015, 98: 9. |
| [78] | XIA Z, SUJIDKUL T, NIU J, et al. Modeling of electromechanical behavior of woven SiC/SiC composites. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2012, 43(10): 1730. |
| [79] | SMITH C, MORSCHER G, XIA Z. Electrical resistance of SiC/SiC ceramic matrix composites for damage detection and life-prediction: E-17375. Cleveland: NASA Glenn Research Center, 2009: 9-18. |
| [80] | APPLEBY M, MORSCHER G, ZHU D. Correlation of electrical resistance to CMC stress-strain and fracture behavior under high heat-flux thermal and stress gradients: GRC-E-DAA-TN20638. Cleveland: NASA Glenn Research Center, 2015: 16. |
| [81] | SIMON C, REBILLAT F, CAMUS G. Electrical resistivity monitoring of a SiC/[Si-B-C] composite under oxidizing environments. Acta Materialia, 2017, 132: 586. |
| [82] | MEI H, CHENG L. Damage analysis of 2D C/SiC composites subjected to thermal cycling in oxidizing environments by mechanical and electrical characterization. Materials Letters, 2005, 59(26): 3246. |
| [83] | 栾新刚.3D C/SiC在复杂耦合环境中的损伤机理与寿命预测. 西安: 西北工业大学博士学位论文, 2007. |
| [84] | 魏婷婷.基于电阻抗成像的陶瓷基复合材料高温燃气损伤检测方法. 南京: 南京航空航天大学硕士学位论文, 2020. |
| [85] | WANG F, TENG X, HU X, et al. Damage and failure analysis of a SiCf/SiC ceramic matrix composite using digital image correlation and acoustic emission. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(4): 4699. |
| [86] | DUAN Y, QIU H, YANG T, et al. Flexural failure mechanism of 2.5D woven SiCf/SiC composites: combination of acoustic emission, digital image correlation and X-ray tomography. Composites Communications, 2021, 28: 100921. |
| [87] | MAILLET E, SINGHAL A, HILMAS A, et al. Combining in-situ synchrotron X-ray microtomography and acoustic emission to characterize damage evolution in ceramic matrix composites. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(13): 3546. |
| [88] | EL RASSI J, HEGEMAN A L, MORSCHER G N. A ply-level electrical resistance approach to monitor crack evolution in a laminate SiC/SiC composites. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2022, 42(13): 5355. |
| [89] | WHITLOW T, JONES E, PRZYBYLA C. In-situ damage monitoring of a SiC/SiC ceramic matrix composite using acoustic emission and digital image correlation. Composite Structures, 2016, 158: 245. |
| [90] | SIMON C, REBILLAT F, HERB V, et al. Monitoring damage evolution of SiCf/[SiBC]m composites using electrical resistivity: crack density-based electromechanical modeling. Acta Materialia, 2017, 124: 579. |
| [91] | MORSCHER G N, GORDON N A. Acoustic emission and electrical resistance in SiC-based laminate ceramic composites tested under tensile loading. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2017, 37(13): 3861. |
| [92] | APPLEBY M P, ZHU D, MORSCHER G N. Mechanical properties and real-time damage evaluations of environmental barrier coated SiC/SiC CMCs subjected to tensile loading under thermal gradients. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2015, 284: 318. |
| [93] | BROCKMAN C, SWITZER C, ALMANSOUR A, et al. High-temperature mechanical tensile testing of unidirectional SiCf/SiC composites using a versatile lamp furnace. 11th International Conference on High Temperature Ceramic Matrix Composites, Jeju, 2023: 315. |
| [1] | ZHU Wenjie, TANG Lu, LU Jichang, LIU Jiangping, LUO Yongming. Research Progress on Catalytic Oxidation of Volatile Organic Compounds by Perovskite Oxides [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [2] | HU Zhichao, YANG Hongyu, YANG Hongcheng, SUN Chengli, YANG Jun, LI Enzhu. Usage of the P-V-L Bond Theory in Regulating Properties of Microwave Dielectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [3] | WU Qiong, SHEN Binglin, ZHANG Maohua, YAO Fangzhou, XING Zhipeng, WANG Ke. Research Progress on Lead-based Textured Piezoelectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [4] | ZHANG Bihui, LIU Xiaoqiang, CHEN Xiangming. Recent Progress of Hybrid Improper Ferroelectrics with Ruddlesden-Popper Structure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| [5] | WU Jie, YANG Shuai, WANG Mingwen, LI Jinglei, LI Chunchun, LI Fei. Textured PT-based Piezoelectric Ceramics: Development, Status and Challenge [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 575-586. |
| [6] | JIANG Kun, LI Letian, ZHENG Mupeng, HU Yongming, PAN Qinxue, WU Chaofeng, WANG Ke. Research Progress on Low-temperature Sintering of PZT Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| [7] | TIAN Ruizhi, LAN Zhengyi, YIN Jie, HAO Nanjing, CHEN Hangrong, MA Ming. Microfluidic Technology Based Synthesis of Inorganic Nano-biomaterials: Principles and Progress [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 337-347. |
| [8] | ZHANG Jiguo, WU Tian, ZHAO Xu, YANG Fan, XIA Tian, SUN Shien. Improvement of Cycling Stability of Cathode Materials and Industrialization Process for Sodium-ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 348-362. |
| [9] | YIN Jie, GENG Jiayi, WANG Kanglong, CHEN Zhongming, LIU Xuejian, HUANG Zhengren. Recent Advances in 3D Printing and Densification of SiC Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 245-255. |
| [10] | CHEN Guangchang, DUAN Xiaoming, ZHU Jinrong, GONG Qing, CAI Delong, LI Yuhang, YANG Donglei, CHEN Biao, LI Xinmin, DENG Xudong, YU Jin, LIU Boya, HE Peigang, JIA Dechang, ZHOU Yu. Advanced Ceramic Materials in Helicopter Special Structures: Research Progress and Application Prospect [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 225-244. |
| [11] | FAN Xiaobo, ZU Mei, YANG Xiangfei, SONG Ce, CHEN Chen, WANG Zi, LUO Wenhua, CHENG Haifeng. Research Progress on Proton-regulated Electrochemical Ionic Synapses [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 256-270. |
| [12] | HAIREGU Tuxun, GUO Le, DING Jiayi, ZHOU Jiaqi, ZHANG Xueliang, NUERNISHA Alifu. Research Progress of Optical Bioimaging Technology Assisted by Upconversion Fluorescence Probes in Tumor Imaging [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 145-158. |
| [13] | SUN Shujuan, ZHENG Nannan, PAN Haokun, MA Meng, CHEN Jun, HUANG Xiubing. Research Progress on Preparation Methods of Single-atom Catalysts [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 113-127. |
| [14] | TAO Guilong, ZHI Guowei, LUO Tianyou, OUYANG Peidong, YI Xinyan, LI Guoqiang. Progress on Key Technologies of Cavity-structured Thin Film Bulk Acoustic Wave Filter [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 128-144. |
| [15] | ZHOU Fan, TIAN Zhilin, LI Bin. Research Progress on Carbide Ultra-high Temperature Ceramic Anti-ablation Coatings for Thermal Protection System [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 1-16. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||