无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (12): 1379-1386.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250080 CSTR: 32189.14.jim20250080
收稿日期:2025-02-24
修回日期:2025-05-16
出版日期:2025-12-20
网络出版日期:2025-06-10
通讯作者:
俎喜红, 教授. E-mail: xhzu@gdut.edu.cn作者简介:易国刚(1982-), 男, 正高级工程师. E-mail: tadd.yi@gdnhec.com
基金资助:
YI Guogang1,2( ), WU Yaoying2, ZU Xihong2(
), WU Yaoying2, ZU Xihong2( )
)
Received:2025-02-24
Revised:2025-05-16
Published:2025-12-20
Online:2025-06-10
Contact:
ZU Xihong, professor. E-mail: xhzu@gdut.edu.cnAbout author:YI Guogang (1982-), male, professor. E-mail: tadd.yi@gdnhec.com
Supported by:摘要: 针对锂离子电池硅碳负极体积膨胀大、循环稳定性差、导电性不佳、能耗高等问题, 本研究以纳米硅为活性物质、石墨为导电载体、沥青为碳前驱体、氯化钾为造孔模板剂, 采用绿色节能的无溶剂法在较低温度下制备了多孔硅碳负极材料P-Si@G@C, 并研究了其作为锂离子电池负极的性能, 对比分析了不同结构硅碳负极的性能差异, 阐明了构效关系。结果表明, 用石墨载体锚定硅纳米颗粒(Si@G), 有利于提高电极材料整体导电性, 加快电子传输速率, 并抑制纳米硅的体积膨胀; 在Si@G表面包覆多孔碳壳层, 大大减少了硅的体积膨胀, 并加快了锂离子和电子的传输速率。相比Si@G和未造孔的Si@G@C硅碳负极材料, P-Si@G@C负极材料所构建的电池呈现出更优异的电性能。电池的首次库仑效率高达85.8%; 在0.1、0.2、0.5、1.0、2.0、5.0 A·g-1电流密度下, 电池比容量分别高达1403.6、1291.7、1206.1、1093.6、868.4和609.5 mAh·g-1, 且比容量恢复率达98.3%, 倍率性能优异; 在1.0 A·g-1下循环200圈仍具有770.7 mAh·g-1的比容量, 表现出优异的长循环稳定性。
中图分类号:
易国刚, 吴耀应, 俎喜红. 无溶剂法低温制备双碳包覆多孔硅碳负极材料及储锂性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(12): 1379-1386.
YI Guogang, WU Yaoying, ZU Xihong. Non-solvent and Low-temperature Preparation of Porous Silicon-carbon Anodes for Enhanced Lithium Storage[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(12): 1379-1386.
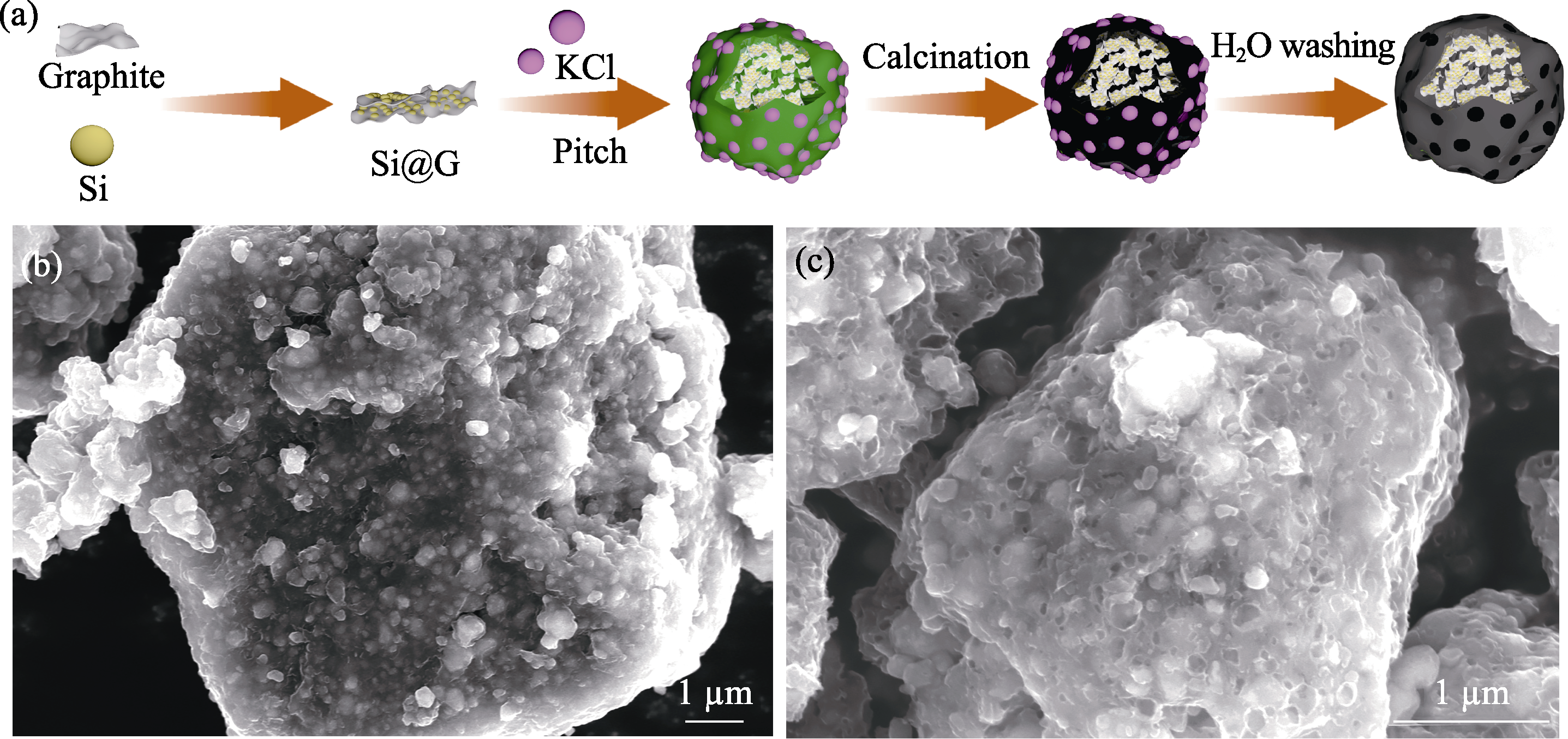
图1 (a) P-Si@G@C复合材料的制备示意图; (b) Si@G@C和(c) P-Si@G@C复合材料的SEM照片
Fig. 1 (a) Schematic of preparation of P-Si@G@C composite; (b, c) SEM images of (b) Si@G@C and (c) P-Si@G@C

图2 P-Si@G@C的(a) TEM照片、(b) HRTEM照片、(c) SAED图像、(d~h) TEM照片及EDS元素分布图
Fig. 2 (a) TEM image, (b) HRTEM image, (c) SAED pattern, (d-h) TEM image and their corresponding EDS elemental maps of P-Si@G@C
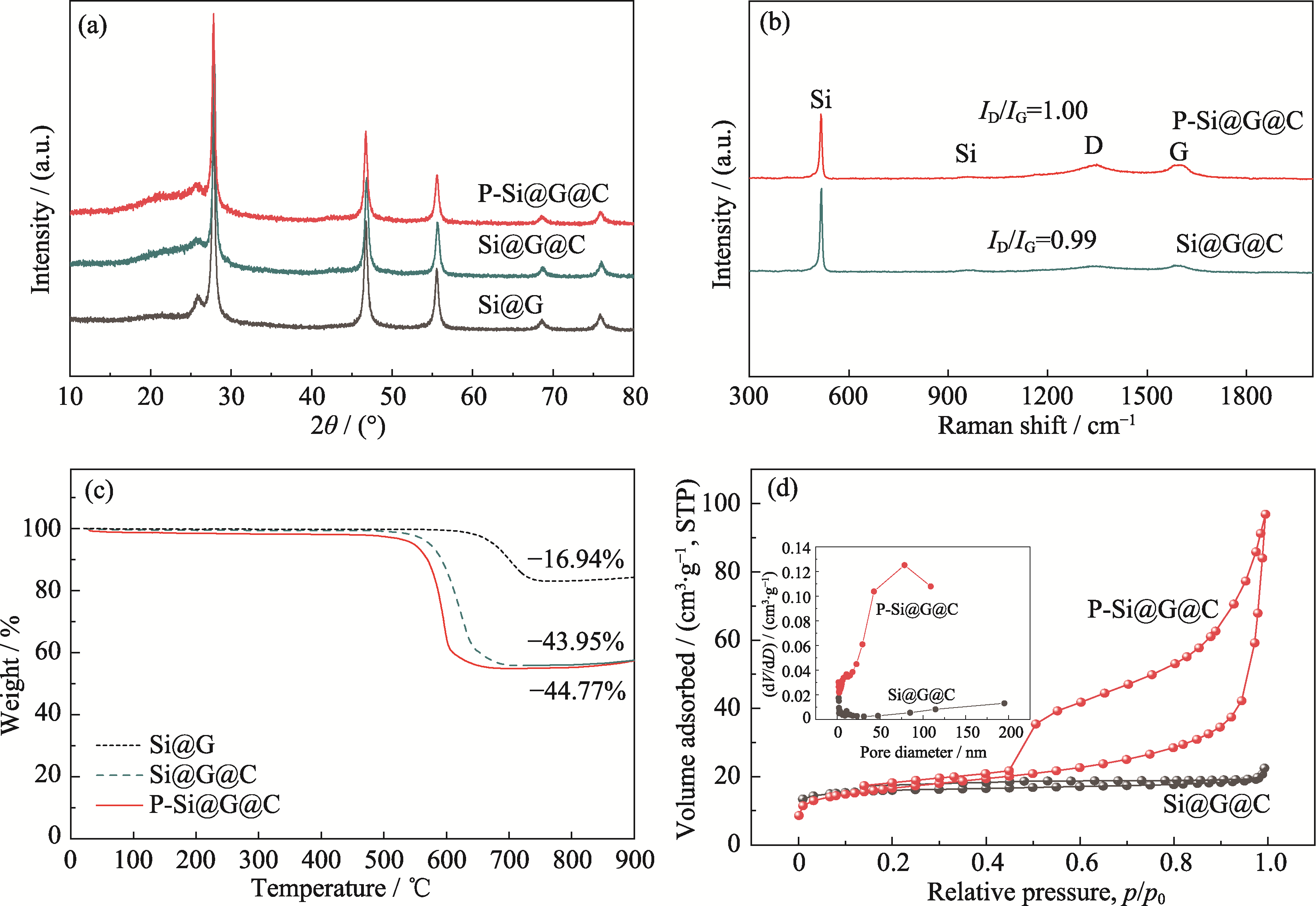
图3 不同复合材料的结构表征
Fig. 3 Structure characterization of different composite materials (a) XRD patterns; (b) Raman spectra; (c) Thermogravimetric curves; (d) N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms
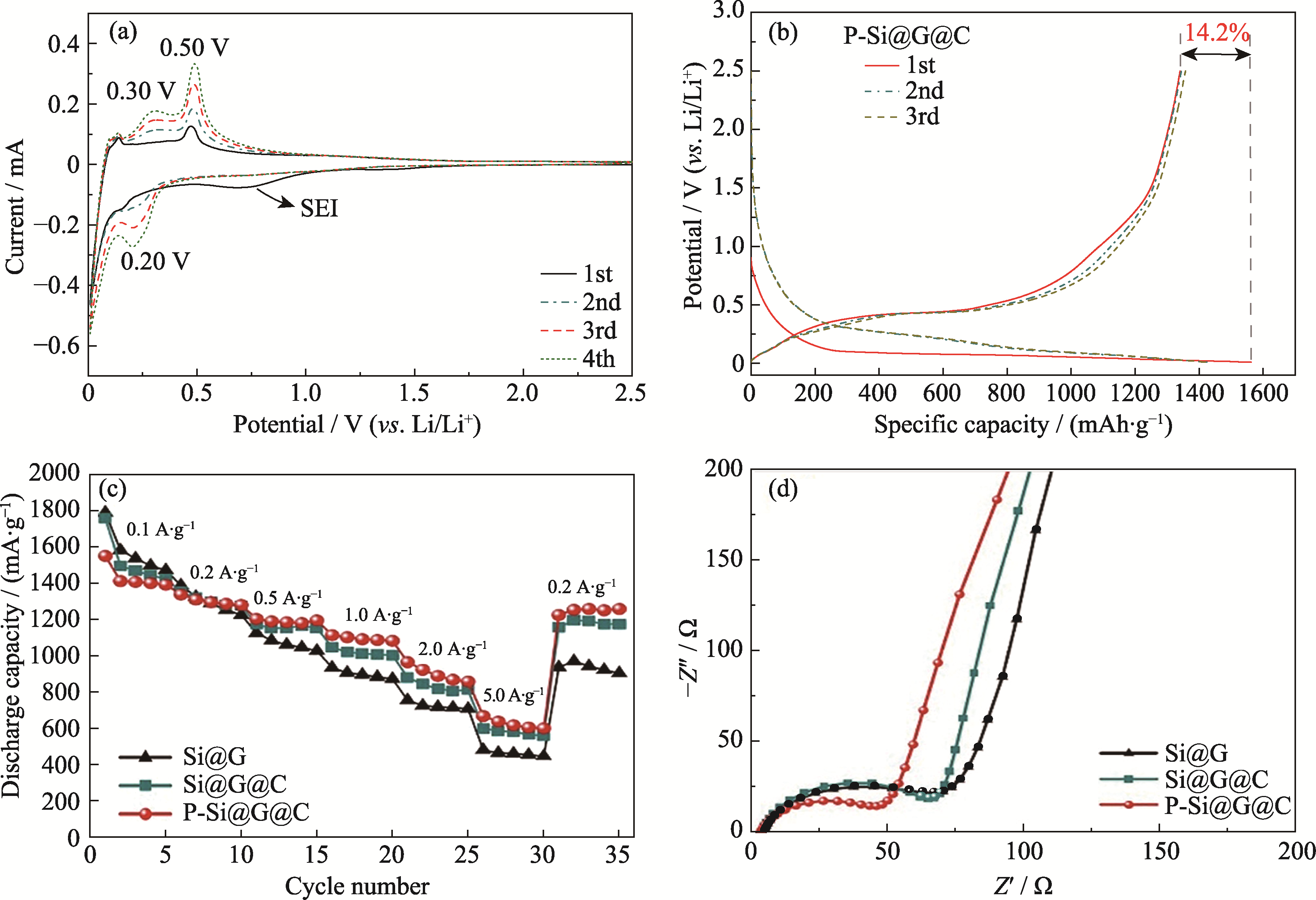
图5 不同负极材料电池的电化学性能
Fig. 5 Electrochemical performance of batteries with different anode materials (a) CV curves of initial 4 cycles of P-Si@G@C battery; (b) Charging-discharging curves of initial 3 cycles of P-Si@G@C battery; (c) Rate performances and (d) EIS spectra of Si@G, Si@G@C and P-Si@G@C batteries
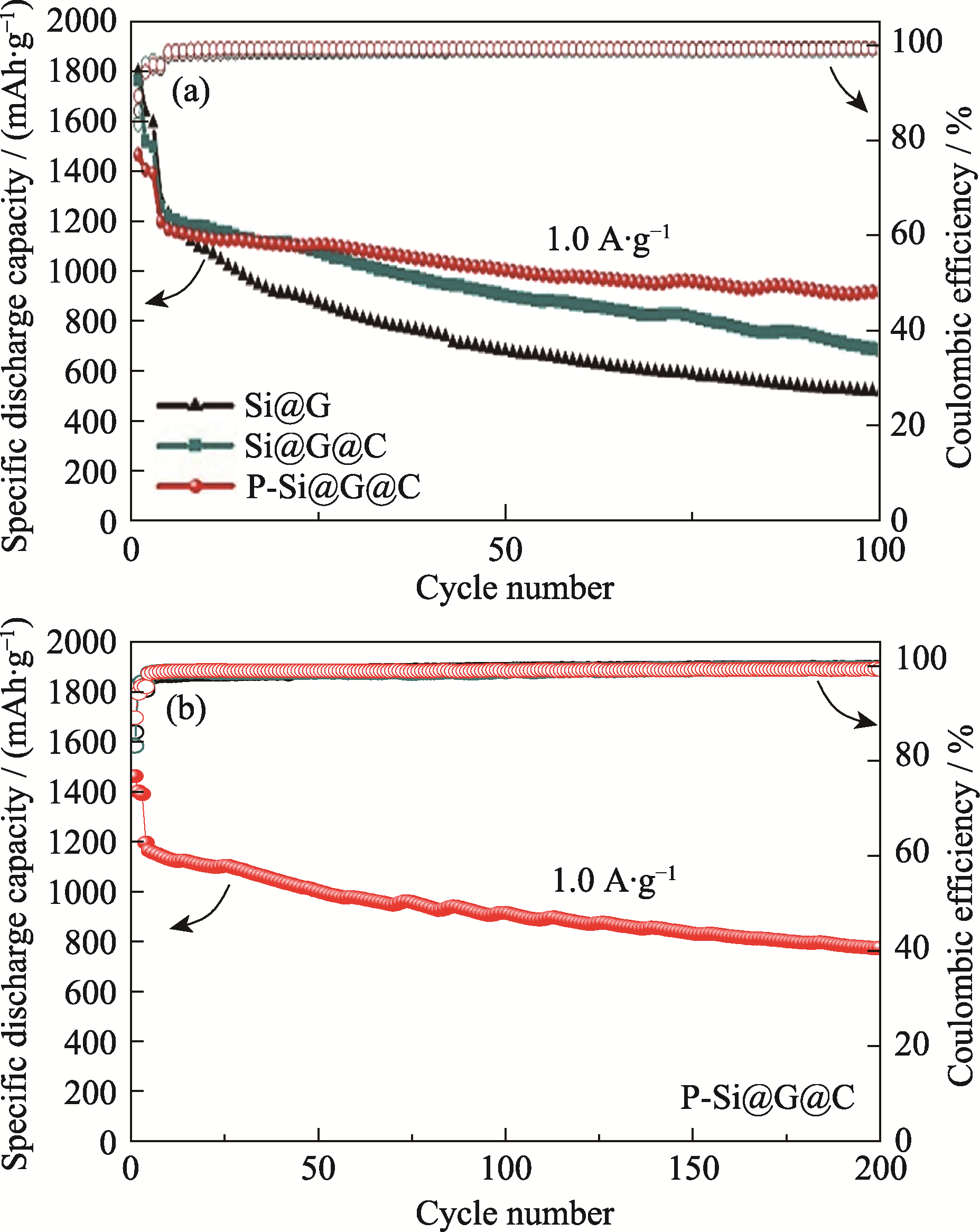
图6 (a) Si@G、Si@G@C和P-Si@G@C电池在1.0 A·g-1下循环100圈的循环性能; (b) P-Si@G@C电池在1.0 A·g-1下循环200圈的长循环性能
Fig. 6 (a) Cycling performances of Si@G, Si@G@C and P-Si@G@C batteries at 1.0 A·g-1 for 100 cycles; (b) Long cycling performance of P-Si@G@C battery at 1.0 A·g-1 for 200 cycles
| [38] |
LU J, LIU S, LIU J, et al. Millisecond conversion of photovoltaic silicon waste to binder-free high silicon content nanowires electrodes. Adv. Energy Mater., 2021, 11(40): 2102103.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
LIU G X, TIAN J X, WAN J, et al. Revealing the high salt concentration manipulated evolution mechanism on the lithium anode in quasi-solid-state lithium sulfur batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2022, 61(12): e202212744.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
ZHANG J H, LIU G X, ZHAI P B, et al. Stabilizing the interface of Li1.3Al0.3Ti1.7(PO4)3 and lithium electrodes via an interlayer strategy in solid-state batteries. Chem. Comm., 2025, 61(14): 2949.
DOI URL |
| [1] |
DING J W, JI D F, YUE Y Z, et al. Amorphous materials for lithium- ion and post-lithium-ion batteries. Small, 2024, 20(5): 2304270.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
JELLA G, PANDA D K, SAPKOTA N, et al. Electrochemical performance of polymer-derived silicon-oxycarbide/graphene nanoplatelet composites for high-performance Li-ion batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf., 2023, 15(25): 30039.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
KIM M J, LEE I, LEE J W, et al. A novel structured Si-based composite with 2D structured graphite for high-performance lithium-ion batteries. Small, 2024, 20: 2405005.
DOI URL |
| [4] | SUN L, LIU Y X, SHAO R, et al. Recent progress and future perspective on practical silicon anode-based lithium ion batteries. Energy Storage Mater., 2022, 46: 482. |
| [5] | LI P, ZHAO G, ZHENG X, et al. Recent progress on silicon-based anode materials for practical lithium-ion battery applications. Energy Storage Mater., 2018, 15: 422. |
| [6] |
LIU W J, SU S X, WANG Y, et al. Constructing a stable conductive network for high-performance silicon-based anode in lithium-ion batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf., 2024, 16: 10703.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
SHI H F, ZHANG W Y, WANG D H, et al. Facile preparation of silicon/carbon composite with porous architecture for advanced lithium-ion battery anode. J. Electroanal. Chem., 2023, 937: 117427.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
LI H, YAO B H, LI M, et al. Three-dimensional carbon nanotubes buffering interfacial stress of the silicon/carbon anodes for long-cycle lithium storage. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf., 2024, 16: 53665.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
GAO J F, LIU Y, CHEN J Q, et al. Fabrication of honeycomb-like amorphous carbon-encapsulated Si nanoparticles/graphene composite for superior lithium storage. J. Energy Storage, 2023, 74: 109351.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
GAO Y J, SONG S S, HE F, et al. Controllable synthesis of hollow dodecahedral Si@C core-shell structures for ultrastable lithium- ion batteries. Small, 2024, 20: 2406489.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
LI X Z, ZHANG M, YUAN S X, et al. Research progress of silicon/carbon anode materials for lithium-ion batteries: structure design and synthesis method. ChemElectroChem, 2020, 7: 4289.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
LUO W, CHEN X Q, XIA Y, et al. Surface and interface engineering of silicon-based anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Energy Mater., 2017, 7: 1701083.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
SU N, QIU J S, WANG Z Y. F-doped carbon coated nano-Si anode with high capacity: preparation by gaseous fluorination and performance for lithium storage. J. Inorg. Mater., 2023, 38(8): 947.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
HU M F, HUANG L P, LI H, et al. Research progress on hard carbon anode for Li/Na-ion batteries. J. Inorg. Mater., 2024, 39(1): 32.
DOI URL |
| [15] | MA Q, ZHAO Z, ZHAO Y, et al. A self-driven alloying/dealloying approach to nanostructuring micro-silicon for high-performance lithium-ion battery anodes. Energy Storage Mater., 2021, 34: 768. |
| [16] |
ZHANG L, HUANG Q, LIAO X, et al. Scalable and controllable fabrication of CNTs improved yolk-shelled Si anodes with advanced in operando mechanical quantification. Energ. Environ. Sci., 2021, 14(6): 3502.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
TAO H, FAN L Z, SONG W L, et al. Hollow core-shell structured Si/C nanocomposites as high-performance anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Nanoscale, 2014, 6(6): 3138.
DOI PMID |
| [18] | LIU N, LIU J, JIA D, et al. Multi-core yolk-shell like mesoporous double carbon-coated silicon nanoparticles as anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Energy Storage Mater., 2019, 18: 165. |
| [19] |
SU H, LI X, LIU C, et al. Scalable synthesis of micrometer-sized porous silicon/carbon composites for high-stability lithium-ion battery anodes. Chem. Eng. J., 2023, 451: 138394.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
SUN Y Q, ZU X H, LIU B W, et al. Low-cost integrated silicon-carbon anode based on Si-Cu bonds and asphalt-derived carbon towards high-performance lithium-ion battery. ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2023, 6: 11376.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
KONG X, XI Z, JIANG Y, et al. Fe-NC decorated fibrous network-wrapped biomass SiOx/C with gradient conductive structure for high performance Li-ion battery anodes. Chem. Eng. J., 2023, 477: 147178.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
PEI Y, WANG Y, CHANG A Y, et al. Nanofiber-in-microfiber carbon/silicon composite anode with high silicon content for lithium-ion batteries. Carbon, 2023, 203: 436.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
HU L, LUO B, WU C, et al. Yolk-shell Si/C composites with multiple Si nanoparticles encapsulated into double carbon shells as lithium-ion battery anodes. J. Energy Chem., 2019, 32: 124.
DOI |
| [24] |
ZHANG L, HU X, CHEN C, et al. In operando mechanism analysis on nanocrystalline silicon anode material for reversible and ultrafast sodium storage. Adv. Mater., 2017, 29: 1604708.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
ZHAO M, MCCORMACK A, KESWANI M. The formation mechanism of gradient porous Si in a contactless electrochemical process. J Mater. Chem. C, 2016, 4(19): 4204.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
DONG H, FU X, WANG J, et al. In-situ construction of porous Si@C composites with LiCl template to provide silicon anode expansion buffer. Carbon, 2021, 173: 687.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
CHAE S, XU Y, YI R, et al. A micrometer-sized silicon/carbon composite anode synthesized by impregnation of petroleum pitch in nanoporous silicon. Adv. Mater., 2021, 33(40): 2103095.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
MU T, ZUO P, LOU S, et al. A two-dimensional nitrogen-rich carbon/silicon composite as high performance anode material for lithium ion batteries. Chem. Eng. J., 2018, 341: 37.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
LI X, YANG D, HOU X, et al. Scalable preparation of mesoporous silicon@C/graphite hybrid as stable anodes for lithium-ion batteries. J. Alloys Compd., 2017, 728: 1.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
SHIN H J, HWANG J Y, KWON H J, et al. Sustainable encapsulation strategy of silicon nanoparticles in microcarbon sphere for high-performance lithium-ion battery anode. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng., 2020, 8(37): 14150.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
LI P, HWANG J Y, SUN Y K. Nano/microstructured silicon-graphite composite anode for high-energy-density Li-ion battery. ACS Nano, 2019, 13(2): 2624.
DOI PMID |
| [32] |
ZHANG H, ZHANG X, JIN H, et al. A robust hierarchical 3D Si/CNTs composite with void and carbon shell as Li-ion battery anodes. Chem. Eng. J., 2019, 360: 974.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
WEI Q, CHEN Y M, HONG X J, et al. Novel bread-like nitrogen-doped carbon anchored nano-silicon as high-stable anode for lithium-ion batteries. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2020, 511: 145609.
DOI URL |
| [34] | XIN X, ZHOU X, WANG F, et al. A 3D porous architecture of Si/graphene nanocomposite as high-performance anode materials for Li-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2012, 22(16): 7724. |
| [35] |
PAN Q, ZUO P, LOU S, et al. Micro-sized spherical silicon@carbon@graphene prepared by spray drying as anode material for lithium-ion batteries. J. Alloys Compd., 2017, 723: 434.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
FU L, XU A, SONG Y, et al. Pinecone-like silicon@carbon microspheres covered by Al2O3 nano-petals for lithium-ion battery anode under high temperature. Electrochim. Acta, 2021, 387: 138461.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
GAO R, TANG J, YU X, et al. In situ synthesis of MOF-derived carbon shells for silicon anode with improved lithium-ion storage. Nano Energy, 2020, 70: 104444.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 文伸豪, 彭德招, 林喆与, 郭霞, 黄培鑫, 章志珍. 基于LLZTO电解质的固态锂金属电池负极界面调控[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(9): 1013-1021. |
| [2] | 谭博文, 耿双龙, 张锴, 郑百林. 硅电极组分梯度设计抑制力-化学耦合劣化[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 772-780. |
| [3] | 张宇婷, 李晓斌, 刘尊义, 李宁, 赵鹬. 复合蛋黄壳型NiCo2V2O8@TiO2@NC材料用作锂离子电池负极研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(11): 1221-1228. |
| [4] | 刘鹏东, 王桢, 刘永锋, 温广武. 硅泥在锂离子电池中的应用研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(9): 992-1004. |
| [5] | 程节, 周月, 罗薪涛, 高美婷, 骆思妃, 蔡丹敏, 吴雪垠, 朱立才, 袁中直. 蛋黄壳结构FeF3·0.33H2O@N掺杂碳纳米笼正极材料的构筑及其电化学性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(3): 299-305. |
| [6] | 胡梦菲, 黄丽萍, 李贺, 张国军, 吴厚政. 锂/钠离子电池硬碳负极材料的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(1): 32-44. |
| [7] | 苏楠, 邱介山, 王治宇. 高容量氟掺杂碳包覆纳米硅负极材料: 气相氟化法制备及其储锂性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(8): 947-953. |
| [8] | 杨卓, 卢勇, 赵庆, 陈军. X射线衍射Rietveld精修及其在锂离子电池正极材料中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 589-605. |
| [9] | 宿拿拿, 韩静茹, 郭印毫, 王晨宇, 石文华, 吴亮, 胡执一, 刘婧, 李昱, 苏宝连. 基于ZIF-8的三维网络硅碳复合材料锂离子电池性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(9): 1016-1022. |
| [10] | 王洋, 范广新, 刘培, 尹金佩, 刘宝忠, 朱林剑, 罗成果. 钾离子掺杂提高锂离子电池正极锰酸锂性能的微观机制[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(9): 1023-1029. |
| [11] | 朱河圳, 王选朋, 韩康, 杨晨, 万睿哲, 吴黎明, 麦立强. 超高镍LiNi0.91Co0.06Al0.03O2@Ca3(PO4)2正极材料的储锂稳定性的提升机制[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(9): 1030-1036. |
| [12] | 冯锟, 朱勇, 张凯强, 陈长, 刘宇, 高彦峰. 勃姆石纳米片增强锂离子电池隔膜性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(9): 1009-1015. |
| [13] | 陈莹, 栾伟玲, 陈浩峰, 朱轩辰. 基于应力场的锂离子电池正极多尺度失效研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(8): 918-924. |
| [14] | 江依义, 沈旻, 宋半夏, 李南, 丁祥欢, 郭乐毅, 马国强. 双功能电解液添加剂对锂离子电池高温高电压性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 710-716. |
| [15] | 苏东良, 崔锦, 翟朋博, 郭向欣. 石榴石型Li6.4La3Zr1.4Ta0.6O12对Si/C负极表面固体电解质中间相的调控机制研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 802-808. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||