无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (7): 772-780.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240472 CSTR: 32189.14.jim20240472
收稿日期:2024-11-11
修回日期:2025-01-21
出版日期:2025-07-20
网络出版日期:2025-02-19
通讯作者:
郑百林, 教授. E-mail: blzheng@tongji.edu.cn;作者简介:谭博文(1998-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: tan_bowen@tongji.edu.cn
基金资助:
TAN Bowen( ), GENG Shuanglong, ZHANG Kai(
), GENG Shuanglong, ZHANG Kai( ), ZHENG Bailin(
), ZHENG Bailin( )
)
Received:2024-11-11
Revised:2025-01-21
Published:2025-07-20
Online:2025-02-19
Contact:
ZHENG Bailin, professor. E-mail: blzheng@tongji.edu.cn;About author:TAN Bowen (1998-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: tan_bowen@tongji.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
作为锂离子电池负极, 硅材料具有高能量密度的优点, 但其充放电循环中的体积效应会引发活性涂层的上下表面不稳定, 且内部极化会诱导产生扩散应力, 两者共同导致结构退化和容量衰减。受功能梯度材料启发, 本研究提出了一种五层复合组分梯度硅电极。通过实验与多尺度力-电-化学耦合仿真发现, 本研究所设计的对称组分梯度硅电极和线性组分梯度硅电极在减缓力-化学耦合劣化方面效果显著, 较传统的均匀电极表现出更好的循环和倍率性能。对称梯度电极锂离子电池在0.2C(1C=2.65 mA·cm-2)倍率下循环100次后, 比容量剩余2065 mAh·g-1, 容量保持率为81%, 而均匀电极为51%。线性梯度电极在1C倍率下的平均放电容量则是均匀电极的1.5倍, 且两类梯度电极循环前后的阻抗变化均小于均匀电极。上述组分梯度电极采用多层复合涂布工艺制备, 无需材料改性便能提高电极的结构稳定性和电化学性能, 为高性能锂离子电池的设计与制造提供了参考。
中图分类号:
谭博文, 耿双龙, 张锴, 郑百林. 硅电极组分梯度设计抑制力-化学耦合劣化[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 772-780.
TAN Bowen, GENG Shuanglong, ZHANG Kai, ZHENG Bailin. Composition-gradient Design of Silicon Electrodes to Mitigate Mechanochemical Coupling Degradation[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 772-780.
| Si/% | SP/% | SA/% |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | 70 | 20 |
| 20 | 60 | 20 |
| 30 | 50 | 20 |
| 40 | 40 | 20 |
| 50 | 30 | 20 |
表1 不同Si质量分数的组分配比(%, 质量分数)
Table 1 Composition ratios of different Si mass fractions (%, in mass)
| Si/% | SP/% | SA/% |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | 70 | 20 |
| 20 | 60 | 20 |
| 30 | 50 | 20 |
| 40 | 40 | 20 |
| 50 | 30 | 20 |
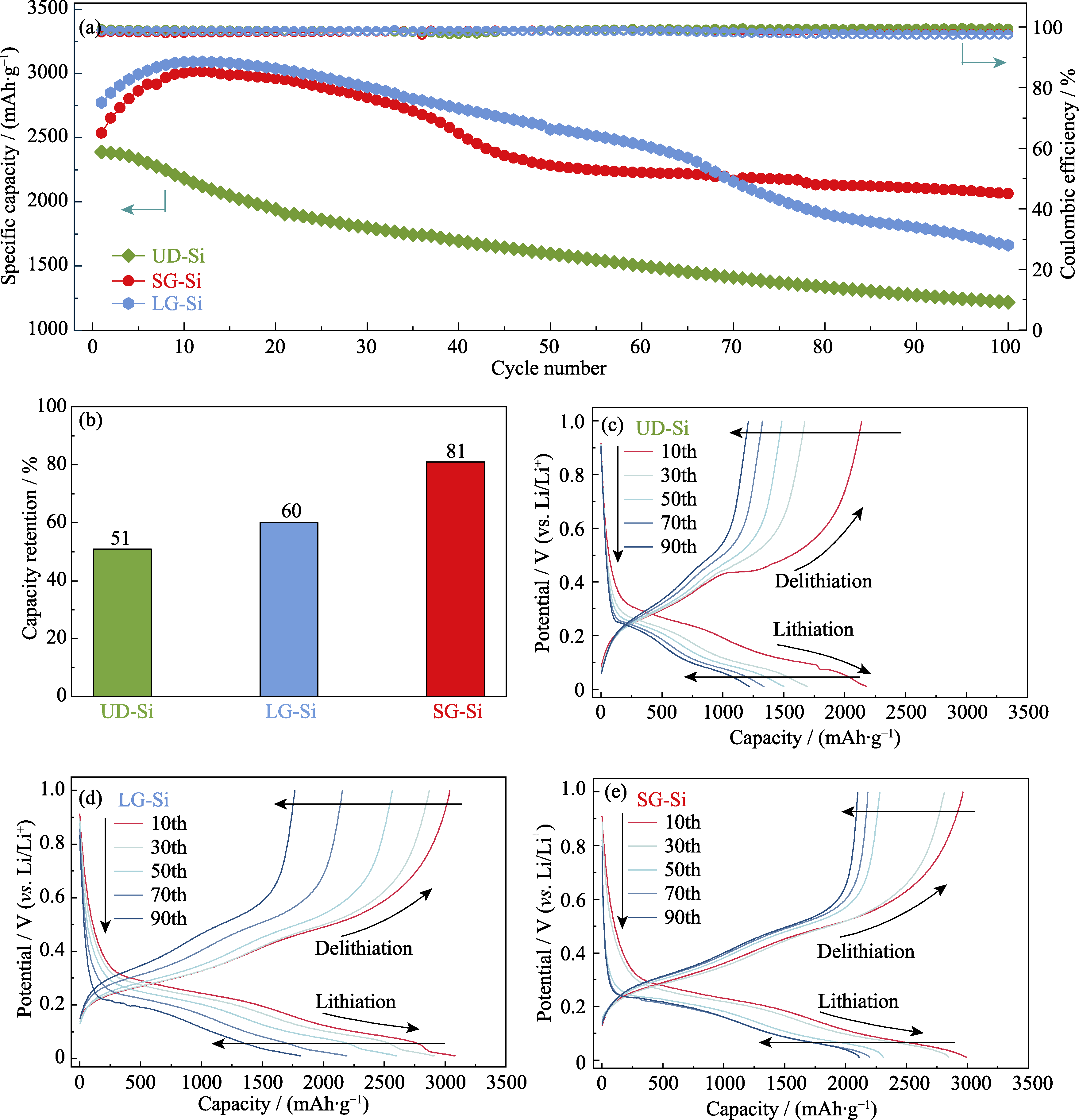
图4 不同锂离子电池的电化学性能
Fig. 4 Electrochemical performance of different lithium-ion batteries (a) Cycling performance at 0.2C; (b) Capacity retentions after 100 cycles; (c-e) Charging-discharging curves of (c) UD-Si, (d) LG-Si and (e) SG-Si. Colorful figures are available on website
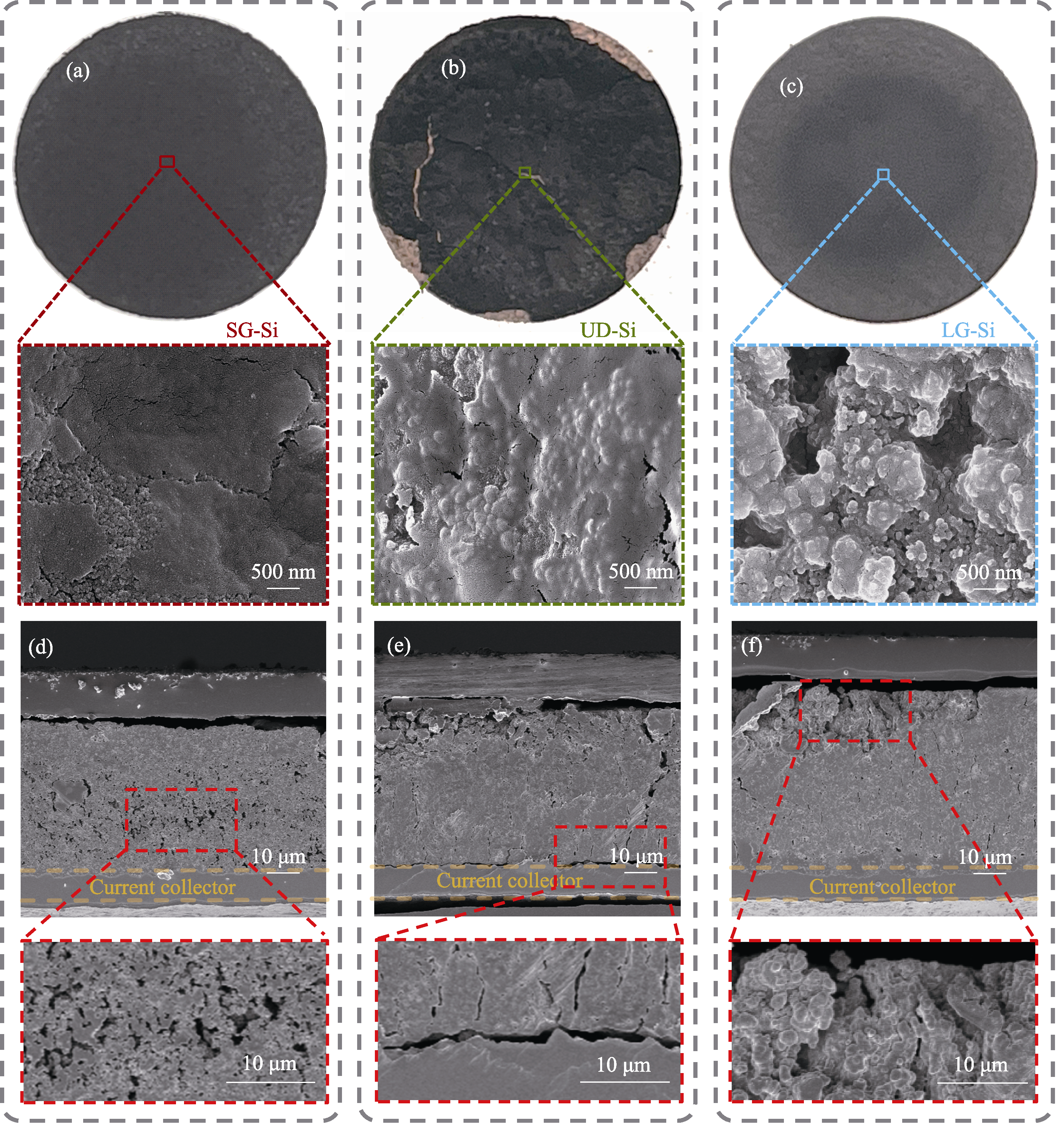
图6 循环后电极表面和横截面的SEM照片
Fig. 6 SEM images of the electrode surfaces and cross-sections after cycling (a-c) Surface: (a) SG-Si, (b) UD-Si, and (c) LG-Si; (d-f) Cross-section: (d) SG-Si, (e) UD-Si, and (f) LG-Si
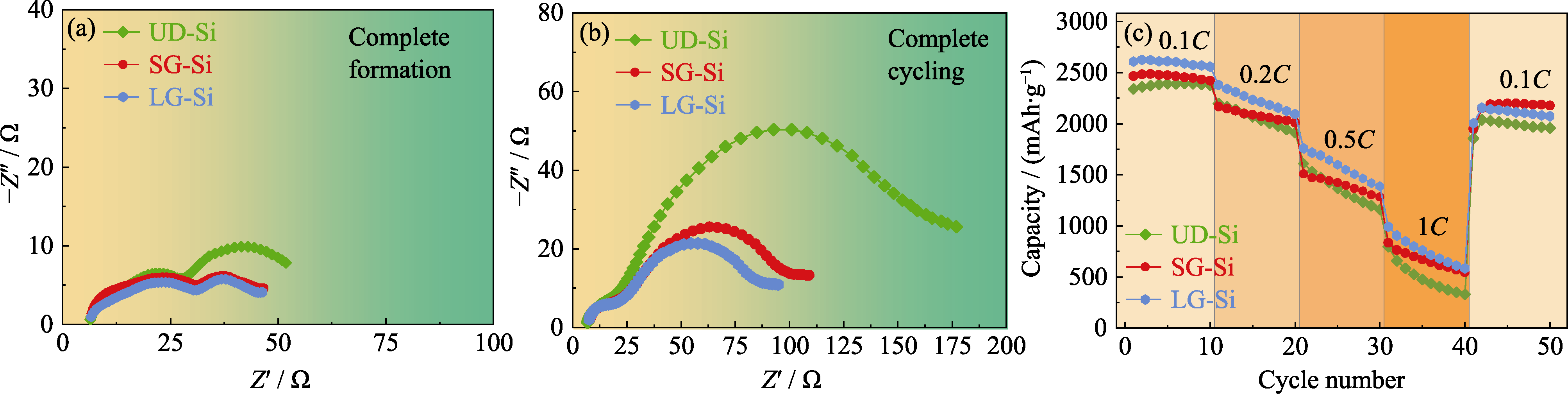
图7 锂离子电池的倍率性能与电极阻抗
Fig. 7 Rate performance of lithium-ion batteries and resistances of electrodes (a, b) Nyquist plots of the electrode after (a) formation and (b) cycling; (c) Rate performance of the electrode
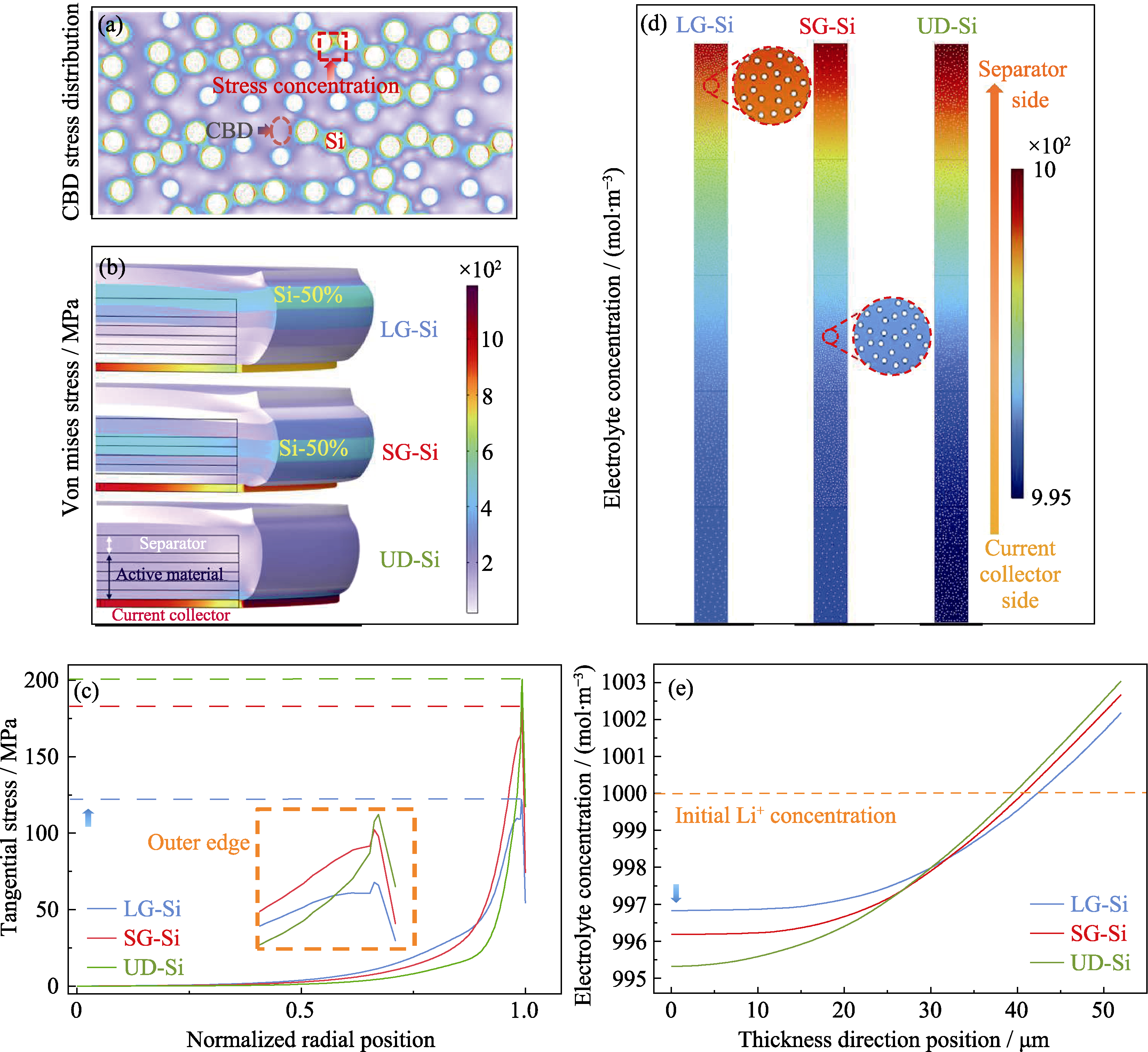
图8 多尺度力-电-化学耦合仿真结果
Fig. 8 Results of multi-scale electro-chemo-mechanical coupled model (a) Stress distribution of CBD in the surface layer of LG-Si; (b) Stress-strain plots of Si electrodes; (c) Comparison of tangential stresses at the active layer & current collector interfaces; (d) Electrolyte concentration distributions of Si electrodes; (e) Comparison of electrolyte concentration gradients in the thickness direction. Colorful figures are available on website
| [1] | LI M, LU J, CHEN Z, et al. 30 years of lithium-ion batteries. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(33): 1800561. |
| [2] | ZENG X, LI M, EL-HADY D A, et al. Commercialization of lithium battery technologies for electric vehicles. Advanced Energy Materials, 2019, 9(27): 1900161. |
| [3] | VISWANATHAN V, EPSTEIN A H, CHIANG Y M, et al. The challenges and opportunities of battery-powered flight. Nature, 2022, 601(7894): 519. |
| [4] |
DIXIT M, BISHT A, ESSEHLI R, et al. Lithium-ion battery power performance assessment for the climb step of an electric vertical takeoff and landing (eVTOL) application. ACS Energy Letters, 2024, 9(3): 934.
DOI PMID |
| [5] | GREY C P, HALL D S. Prospects for lithium-ion batteries and beyond—a 2030 vision. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 6279. |
| [6] | GAO Y, PAN Z, SUN J, et al. High-energy batteries: beyond lithium-ion and their long road to commercialization. Nano-micro Letters, 2022, 14: 94. |
| [7] | XU J, CAI X, CAI S, et al. High-energy lithium-ion batteries: recent progress and a promising future in applications. Energy Environmental Materials, 2023, 6(5): e12450. |
| [8] | ZUO X, ZHU J, MULLER-BUSCHBAUM P, et al. Silicon based lithium-ion battery anodes: a chronicle perspective review. Nano Energy, 2017, 31: 113. |
| [9] | TAN Y, WANG K. Silicon-based anode materials applied in high specific energy lithium-ion batteries: a review. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(4): 349. |
| [10] | PRUSSIN S. Generation and distribution of dislocations by solute diffusion. Journal of Applied Physics, 1961, 32(10): 1876. |
| [11] |
WANG Y N, LI H, WANG Z K, et al. Progress on failure mechanism of lithium ion battery caused by diffusion induced stress. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(10): 1071.
DOI |
| [12] | LI Y, ZHANG K, YANG F. Generalized theory for DISes in a large deformed solid. International Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2022, 14(4): 2250024. |
| [13] | CHRISTENSEN J, NEWMAN J. Stress generation and fracture in lithium insertion materials. Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 2007, 10(5): 2939. |
| [14] | MCDOWELL M T, LEE S W, NIX W D, et al. 25th anniversary article: understanding the lithiation of silicon and other alloying anodes for lithium-ion batteries. Advanced Materials, 2013, 25(36): 4966. |
| [15] | SUN L, LIU Y, SHAO R, et al. Recent progress and future perspective on practical silicon anode-based lithium ion batteries. Energy Storage Materials, 2022, 46: 482. |
| [16] | DE VASCONCELOS L S, XU R, XU Z R, et al. Chemomechanics of rechargeable batteries: status, theories, and perspectives. Chemical Reviews, 2022, 122(15): 13043. |
| [17] | LU B, YUAN Y, BAO Y H, et al. Mechanics-based design of lithium-ion batteries: a perspective. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2022, 24(48): 29279. |
| [18] | 吕浡, 陈鑫松, 周志宇, 等. 锂离子电池的劣化: 力-电化学耦合机理与模型. 力学季刊, 2024, 45(2): 287. |
| [19] |
LIU X H, ZHONG L, HUANG S, et al. Size-dependent fracture of silicon nanoparticles during lithiation. ACS Nano, 2012, 6(2): 1522.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
WANG J, CHENG Z N, GUO Y Z, et al. Preparation and electrochemical performance of ordered mesoporous Si/C composite for anode material. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(3): 313.
DOI |
| [21] | 朱思颖, 李辉阳, 胡忠利, 等. 锂离子电池氧化亚硅负极结构优化和界面改性研究进展. 物理化学学报, 2022, 38(6): 39. |
| [22] | CHAN C K, PENG H, LIU G, et al. High-performance lithium battery anodes using silicon nanowires. Nature Nanotechnology, 2007, 3(1): 31. |
| [23] | SU N, QIU J S, WANG Z Y. F-doped carbon coated nano-Si anode with high capacity: preparation by gaseous fluorination and performance for lithium storage. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(8): 947. |
| [24] | WANG J, CUI Y, WANG D. Design of hollow nanostructures for energy storage, conversion and production. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(38): 1801993. |
| [25] | 温变英. 自然界中的梯度材料及其仿生研究. 材料导报, 2008, 22(S2): 351. |
| [26] | YANG Z, XIA Y, JI J, et al. Superior cycling performance of a sandwich structure Si/C anode for lithium ion batteries. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(15): 12107. |
| [27] | GUO Z Z, YAO L M. Improving the electrochemical performance of Si-based anode via gradient Si concentration. Materials & Design, 2019, 177: 107851. |
| [28] | ZHANG W, GUI S, LI W, et al. Functionally gradient silicon/graphite composite electrodes enabling stable cycling and high capacity for lithium-ion batteries. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(46): 51954. |
| [29] | DENG J, REN X, LIN H, et al. Functionally gradient materials for sustainable and high-energy rechargeable lithium batteries: design principles, progress, and perspectives. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2024, 99: 426. |
| [30] | SUO Y, YANG F. One-dimensional analysis of the coupling between diffusion and deformation in a bilayer electrode. Acta Mechanica Sinica, 2019, 35(3): 589. |
| [31] |
ZHAO Y, STEIN P, BAI Y, et al. A review on modeling of electro-chemo-mechanics in lithium-ion batteries. Journal of Power Sources, 2019, 413: 259.
DOI |
| [32] | XU Y, ZHENG B, ZHANG K, et al. Effect of combining local velocity and chemical reaction on the interaction between diffusion and stresses in large deformed electrodes. AIP Advances, 2019, 9(10): 105103. |
| [33] |
CHEN Y, LUAN W L, CHEN H F, et al. Multi-scale failure behavior of cathode in lithium-ion batteries based on stress field. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(8): 918.
DOI |
| [34] | SUTHAR B, NORTHROP P W C, RIFE D, et al. Effect of porosity, thickness and tortuosity on capacity fade of anode. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2015, 162(9): A1708. |
| [35] | CHEN Y, SANG M, JIANG W, et al. Fracture predictions based on a coupled chemo-mechanical model with strain gradient plasticity theory for film electrodes of Li-ion batteries. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2021, 253: 107866. |
| [36] | GENG S L, ZHOU J W, TAN B W, et al. Impact of thickness and charge rate on the electrochemical performance of Si-based electrodes. Cell Reports Physical Science, 2024, 5(12): 102305. |
| [1] | 文伸豪, 彭德招, 林喆与, 郭霞, 黄培鑫, 章志珍. 基于LLZTO电解质的固态锂金属电池负极界面调控[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(9): 1013-1021. |
| [2] | 易国刚, 吴耀应, 俎喜红. 无溶剂法低温制备双碳包覆多孔硅碳负极材料及储锂性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(12): 1379-1386. |
| [3] | 张宇婷, 李晓斌, 刘尊义, 李宁, 赵鹬. 复合蛋黄壳型NiCo2V2O8@TiO2@NC材料用作锂离子电池负极研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(11): 1221-1228. |
| [4] | 刘鹏东, 王桢, 刘永锋, 温广武. 硅泥在锂离子电池中的应用研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(9): 992-1004. |
| [5] | 程节, 周月, 罗薪涛, 高美婷, 骆思妃, 蔡丹敏, 吴雪垠, 朱立才, 袁中直. 蛋黄壳结构FeF3·0.33H2O@N掺杂碳纳米笼正极材料的构筑及其电化学性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(3): 299-305. |
| [6] | 薛顶喜, 伊炳尧, 李国君, 马帅, 刘克勤. 功能梯度阳极固体氧化物燃料电池热应力数值模拟研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(11): 1189-1196. |
| [7] | 胡梦菲, 黄丽萍, 李贺, 张国军, 吴厚政. 锂/钠离子电池硬碳负极材料的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(1): 32-44. |
| [8] | 苏楠, 邱介山, 王治宇. 高容量氟掺杂碳包覆纳米硅负极材料: 气相氟化法制备及其储锂性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(8): 947-953. |
| [9] | 杨卓, 卢勇, 赵庆, 陈军. X射线衍射Rietveld精修及其在锂离子电池正极材料中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 589-605. |
| [10] | 宿拿拿, 韩静茹, 郭印毫, 王晨宇, 石文华, 吴亮, 胡执一, 刘婧, 李昱, 苏宝连. 基于ZIF-8的三维网络硅碳复合材料锂离子电池性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(9): 1016-1022. |
| [11] | 王洋, 范广新, 刘培, 尹金佩, 刘宝忠, 朱林剑, 罗成果. 钾离子掺杂提高锂离子电池正极锰酸锂性能的微观机制[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(9): 1023-1029. |
| [12] | 朱河圳, 王选朋, 韩康, 杨晨, 万睿哲, 吴黎明, 麦立强. 超高镍LiNi0.91Co0.06Al0.03O2@Ca3(PO4)2正极材料的储锂稳定性的提升机制[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(9): 1030-1036. |
| [13] | 冯锟, 朱勇, 张凯强, 陈长, 刘宇, 高彦峰. 勃姆石纳米片增强锂离子电池隔膜性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(9): 1009-1015. |
| [14] | 陈莹, 栾伟玲, 陈浩峰, 朱轩辰. 基于应力场的锂离子电池正极多尺度失效研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(8): 918-924. |
| [15] | 江依义, 沈旻, 宋半夏, 李南, 丁祥欢, 郭乐毅, 马国强. 双功能电解液添加剂对锂离子电池高温高电压性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 710-716. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||