
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2020, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (6): 633-646.DOI: 10.15541/jim20190308
Special Issue: 封面文章; 功能陶瓷论文精选(二)
Previous Articles Next Articles
YU Ying1,DU Hongliang1,2( ),YANG Zetian1,JIN Li2,QU Shaobo1
),YANG Zetian1,JIN Li2,QU Shaobo1
Received:2019-06-25
Revised:2019-09-03
Published:2020-06-20
Online:2019-12-04
Supported by:CLC Number:
YU Ying, DU Hongliang, YANG Zetian, JIN Li, QU Shaobo. Electrocaloric Effect of Lead-free Bulk Ceramics: Current Status and Challenges[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(6): 633-646.
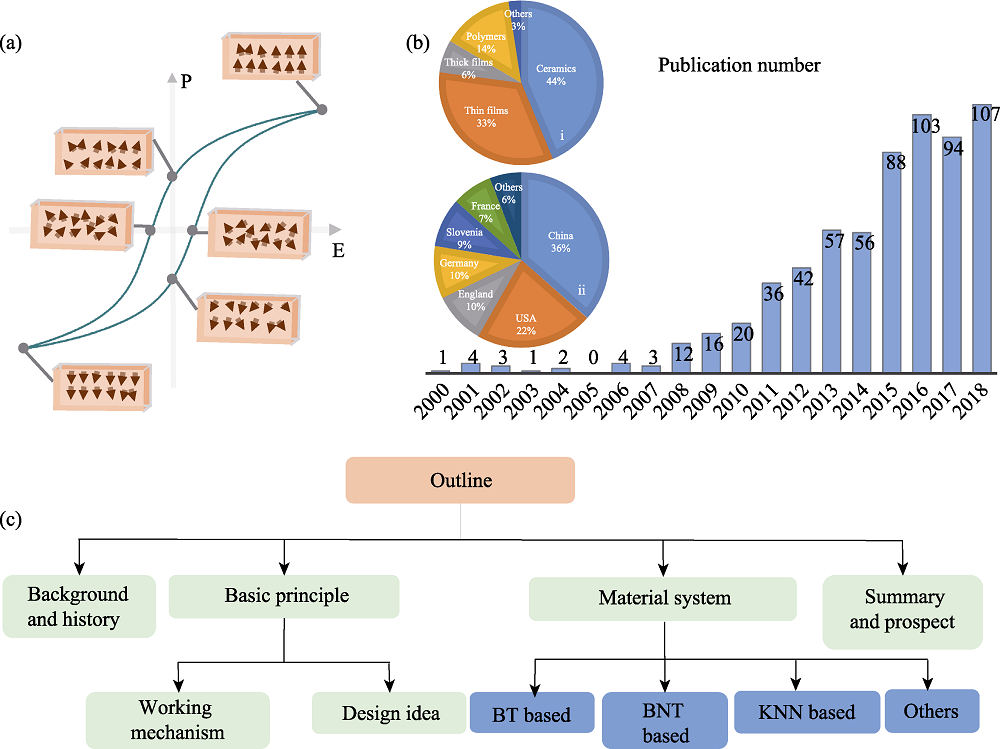
Fig. 1 The influence of changing electric field to polarization states of a ferroelectric (a), publication numbers on Web of Science database from 2000 to 2018 (b) and structure of the review (c) Theme searching of (b): “electrocaloric effect”, “electrocaloric effect” and “bulk ceramic”, “electrocaloric effect” and “thin film”, “electrocaloric effect” and “polymer”, “electrocaloric effect”, and “thick film”
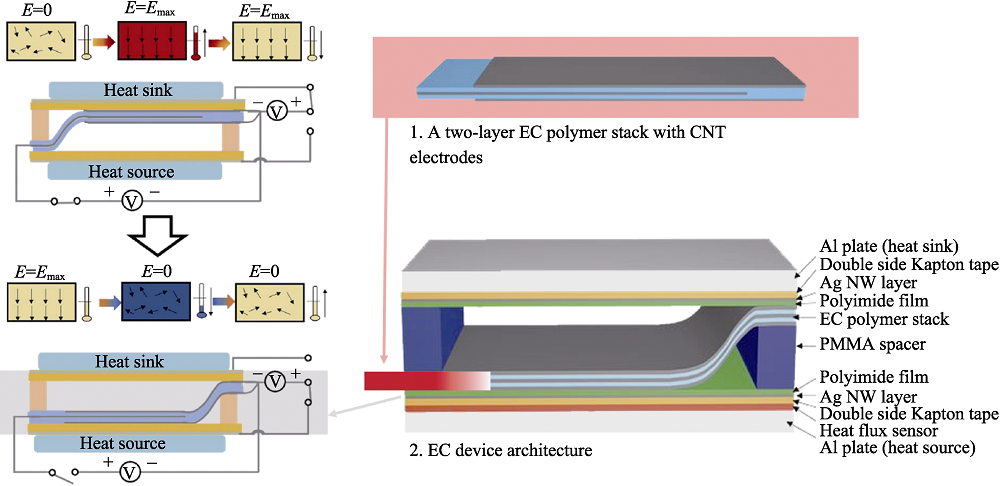
Fig. 3 A solid-state EC cooling device and working mechanism of P(VDF-TrFE-CFE) cooling device to move heat from heat source to heat sink by electrostatic actuation[59]
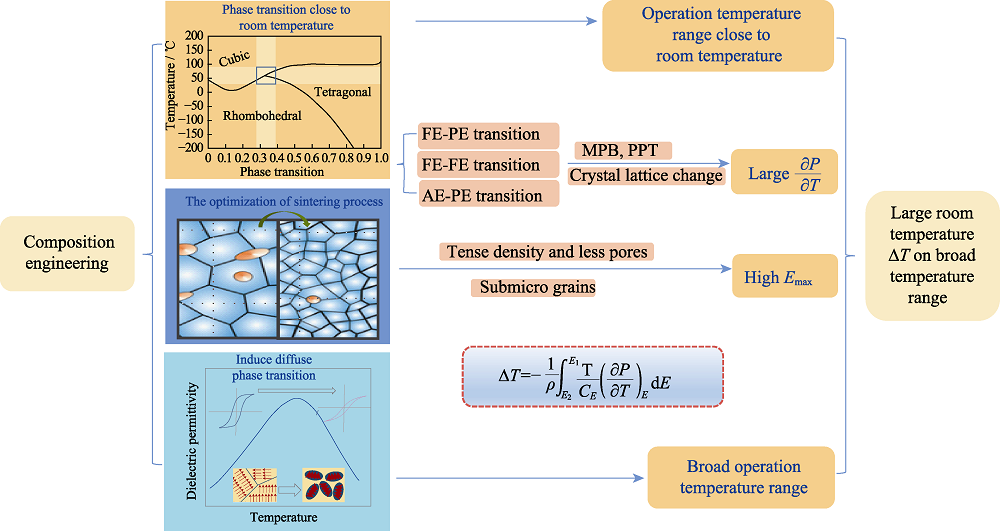
Fig. 5 Schematic diagram of composition design for achieving a large ?T near room temperature and a wide using range FE: ferroelectric; AE: antiferroelectric; PE: paraelectric
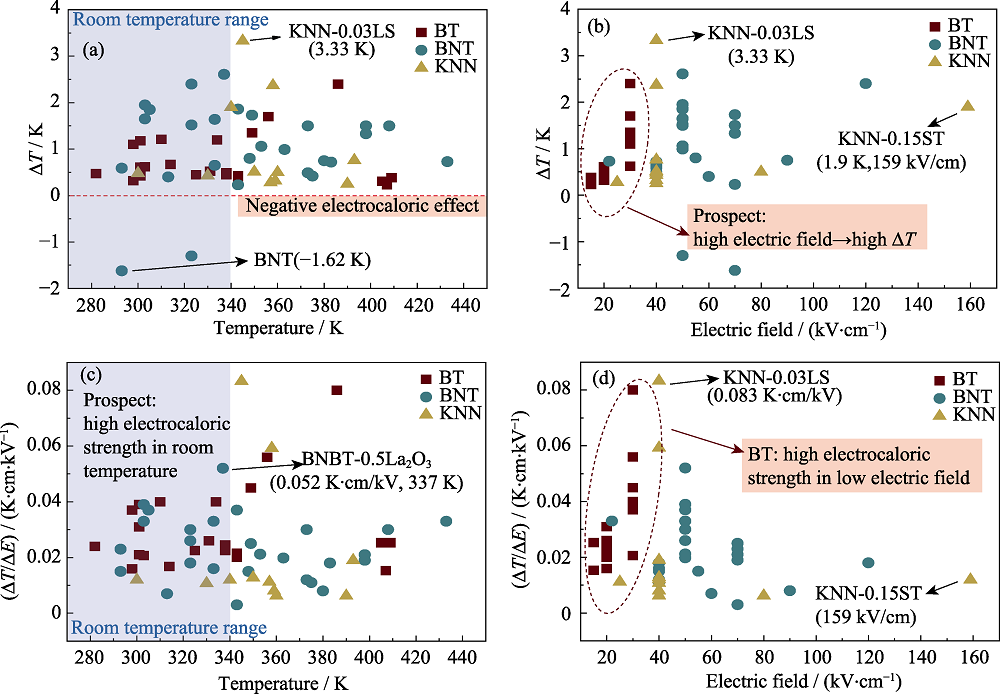
Fig. 8 The EC properties of BT, BNT and KNN based lead-free bulk ceramics[50-52,63-65,67,74, 89-98,101,107,108,110-118,121-126] (a) ΔT and temperature; (b) ΔT and electric field; (c) ΔT/ΔE and temperature; (d) ΔT/ΔE and electric field
| [1] |
SHI J Y, HAN D L, LI Z C , et al. Electrocaloric cooling materials and devices for zero-global-warming-potential, high-efficiency refrigeration. Joule, 2019,3:1-26.
DOI URL |
| [2] | SUCHANECK G, GERLACH G . Lead-free relaxor ferroelectrics for electrocaloric cooling. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2016,3(2):622-631. |
| [3] | CORREIA T, ZHANG Q . Electrocaloric Materials: New Generation of Coolers. Berlin: Spinger, 2014: 1-3. |
| [4] |
DU G, LIANG R H, LI T , et al. Recent progress on defect dipoles characteristics in piezoelectric materials. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013,28(2):123-130.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
MISCHENKO A S, ZHANG Q, SCOTT J F , et al. Giant electrocaloric effect in thin-film PbZr0.95Ti0.05O3. Science, 2006,311(5765):1270-1271.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
ZHANG G Z, ZHANG X S, YANG T N , et al. Colossal room-temperature electrocaloric effect in ferroelectric polymer nanocomposites using nanostructured barium strontium titanates. ACS Nano, 2015,9(7):7164-7174.
DOI URL |
| [7] | ZHANG G Z, LI Q, GU H M , et al. Ferroelectric polymer nanocomposites for room temperature electrocaloric refrigeration. Adv. Mater., 2015,27(8):1450-1454. |
| [8] |
WANG D, CHEN X, YUAN G L , et al. Toward artificial intelligent self-cooling electronic skins: large electrocaloric effect in all-inorganic flexible thin films at room temperature. J. Materiomics, 2019,5(1):66-72.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
DARBANIYAN F, DAYAL K, LIU L P , et al. Designing soft pyroelectric and electrocaloric materials using electrets. Soft Matter., 2019,15(2):262-277.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
LI Q, ZHANG G Z, ZHAN X S , et al. Relaxor ferroelectric-based electrocaloric polymer nanocomposites with a broad operating temperature range and high cooling energy. Adv. Mater., 2015,27(13):2236-2241.
DOI URL |
| [11] | KLEIN L, APARICIO M, JITIANU A . Handbook of Sol-Gel Science and Technology: Processing, Characterization and Applications. 2nd ed. Springer: Switzerland, 2018: 667-693. |
| [12] | BAI Y, WEI D, QIAO L J. Control multiple electrocaloric effect peak in Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-PbTiO3 by phase composition and crystal orientation. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2015, 107(19): 192904-1-4. |
| [13] | YE H J, QIAN X S, JEONG D Y , et al. Giant electrocaloric effect in BaZr0.2Ti0.8O3 thick film. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2014, 105(15): 152908-1-4. |
| [14] | LI F, CHEN G R, LIU X , et al. Type-I pseudo-first-order phase transition induced electrocaloric effect in lead-free Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3- 0.06BaTiO3 ceramics. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2017, 110(18): 182904-1-5. |
| [15] |
VALANT M, AXELSSON A K, LE GOUPIL F , et al. Electrocaloric temperature change constrained by the dielectric strength. Mater. Chem. Phys., 2012,136(2/3):277-280.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
NEESE B, CHU B J, LU S G , et al. Large electrocaloric effect in ferroelectric polymers near room temperature. Science, 2008,321(5890):821-823.
DOI URL |
| [17] | ZHANG G Z, WENG L X, HU Z Y , et al. Nanoconfinement-induced giant electrocaloric effect in ferroelectric polymer nanowire array integrated with aluminum oxide membrane to exhibit record cooling power density. Adv. Mater., 2019, 31(8): 1806642-1-8. |
| [18] | ZHUO F P, LI Q, GAO J H, et al. Coexistence of multiple positive and negative electrocaloric responses in (Pb, La)(Zr, Sn, Ti)O3 single crystal. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2016, 108(8): 082904-1-5. |
| [19] | KUTNJAK Z ROŽIČ B, PIRC R , Wiley Encyclopedia of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (John Wiley& Sons)., 2015: 1-19. |
| [20] | LIU Y, SCOTT J F, DKHIL B. Direct and indirect measurements on electrocaloric effect: recent developments and perspectives. Appl. Phys. Rev., 2016, 3(3): 031102-1-18. |
| [21] |
LI X Y, LU S G, CHEN X Z , et al. Pyroelectric and electrocaloric materials. J. Mater. Chem. C, 2013,1:23-37.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
VALANT M . Electrocaloric materials for future solid-state refrigeration technologies. Prog. Mater Sci., 2012,57(6):980-1009.
DOI URL |
| [23] | LIU Y, SCOTT J F, DKHIL B. Some strategies for improving caloric responses with ferroelectrics. APL Mater., 2016, 4(6): 064109-1-9. |
| [24] |
SINYAVSKY Y V, BRODYANSKY V M . Experimental testing of electrocaloric cooling with transparent ferroelectric ceramic as a working body. Ferroelectrics, 1992,131(1):321-325.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
CAZORLA C . In the search of new electrocaloric materials: fast ion conductors. Results Phys., 2015,5:262-263.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
SCOTT J F . Electrocaloric materials. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res., 2011,41:229-240.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
FÄHLER S, RÖßLER U K, KASTNER O , et al. Caloric effects in ferroic materials: new concepts for cooling. Adv. Eng. Mater., 2012,14(1/2):10-19.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
MANOSA L, PLANES A, ACET M . Advanced materials for solid-state refrigeration. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2013,1(16):4925-4936.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
LU S G, TANG X G, WU S H , et al. Large electrocaloric effect in ferroelectric materials. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014,29(1):6-12.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
ALPAY S P, MANTESE J, TROLIER-MCKINSTRY S , et al. Next-generation electrocaloric and pyroelectric materials for solid-state electrothermal energy interconversion. MRS Bull., 2014,39(12):1099-1111.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
MOYA X, KAR-NARAYAN S, MATHUR N D . Caloric materials near ferroic phase transitions. Nat. Mater., 2014,13:439-450.
DOI URL |
| [32] | BAI Y, LI J T, QIN S Q , et al. Ferroelectric ceramics for high-efficient solid-state refrigeration. Advanced Ceramics, 2018,39(6):369-389. |
| [33] | THOMSON W, KELVIN L. On the thermoelastic, thermomagnetic, and pyroelectric properties of matter. Phil. Mag., 1878,5(28):4-27. |
| [34] | KOBEKO P, KURTSCHATOV J . Dielektrische eigenschaften der seignettesalzkristalle. Z. Phys., 1930,66(3/4):192-205. |
| [35] | HAUTZENLAUB J F . Electrocaloric and Dielectric Behavior of Potassium Dihydrogen Phosphate. Massachusetts: Massachusetts Institute of Technology Doctoral Dissertation, 1943. |
| [36] |
RADEBAUGH R, LAWLESS W N, SIEGWARTH J D , et al. Feasibility of electrocaloric refrigeration for the 4-15 K temperature range. Cryogenics, 1979,19(4):187-208.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
KIMURA T, NEWNHAM R E, CROSS L E . Shape-memory effect in PLZT ferroelectric ceramics. Phase Transit., 1981,2(2):113-130.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
BIRKS E, SHEBANOV L, STERNBERG A . Electrocaloric effect in PLZT ceramics. Ferroelectrics, 1986,69(1):125-129.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
LAWLESS W N . Specific heat and electrocaloric properties of KTaO3 at low temperatures. Phys. Rev. B, 1977,16(1):433-439.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
SINYAVSKY Y V, PASHKOV N D, GOROVOY Y M , et al. The optical ferroelectric ceramic as working body for electrocaloric refrigeration. Ferroelectrics, 1989,90(1):213-217.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
XIAO D Q, YANG B, PENG S Q , et al. Analyses and syntheses of ferroelectric refrigeration ceramics. Ferroelectrics, 1997,195(1):93-96.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
ZHAO Y, HAO X H, ZHANG Q . A giant electrocaloric effect of Pb0.97La0.02(Zr0.75Sn0.18Ti0.07)O3 antiferroelectric thick film at room temperature near room temperature. J. Mater. Chem. C, 2015,3:1694-1699.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
ROŽIČ B, MALIČ B, URŠIČ H , et al. Direct measurements of the electrocaloric effect in bulk PbMg1/3Nb2/3O3 (PMN) ceramics. Ferroelectrics, 2011,421(1):103-107.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
HAN L Y, GUO S B, YAN S G , et al. Electrocaloric effect in Pb0.3CaxSr0.7-xTiO3 ceramics near room temperature. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019,34(9):1011-1014.
DOI URL |
| [45] | PERÄNTIE J, TAILOR H N, HAGBERG J , et al. Electrocaloric properties in relaxor ferroelectric (1-x)Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-xPbTiO3 system. J. Appl. Phys., 2013, 114(17): 174105-1-6. |
| [46] | GENG W P, LIU Y, MENG X J. Giant negative electrocaloric effect in antiferroelectric La-doped Pb(ZrTi)O3 thin films near room temperature. Adv. Mater., 2015, 27(20): 3164-1-5. |
| [47] | BAI Y, ZHENG G P, DING K , et al. The giant electrocaloric effect and high effective cooling power near room temperature for BaTiO3 thick film. J. Appl. Phys., 2011, 110(9): 094103-1-3. |
| [48] |
JIANG X J, LUO L H, WANG B Y , et al. Electrocaloric effect based on the depolarization transition in (1-x)Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3-xKNbO3 lead-free ceramics. Ceram. Int., 2014,40(2):2627-2634.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
KUMAR S, SINGH S . Study of electrocaloric effect in lead-free 0.9K0.5Na0.5NbO3-0.1CaZrO3 solid solution ceramics. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron., 2019,30(14):12924-12928.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
NOVAK N, PIRC R, KUTNJAK Z . Effect of electric field on ferroelectric phase transition in BaTiO3 ferroelectric. Ferroelectrics, 2014,469(1):61-66.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
QIAN X S, YE H J, ZHANG Y T , et al. Giant electrocaloric response over a broad temperature range in modified BaTiO3 ceramics. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2014,24(9):1300-1305.
DOI URL |
| [52] | BAI Y, HAN X, ZHENG X C , et al. Both high reliability and giant electrocaloric strength in BaTiO3 ceramics. Sci. Rep., 2013, 3: 2895-1-5. |
| [53] |
BAI Y, ZHENG G P, SHI S Q . Abnormal electrocaloric effect of Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3-BaTiO3 lead-free ferroelectric ceramics above room temperature. Mater. Res. Bull., 2011,46(11):1866-1869.
DOI URL |
| [54] | PLAZNIK U, KITANOVSKI A, ROŽIČ B , et al. Bulk relaxor ferroelectric ceramics as a working body for an electrocaloric cooling device. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2015, 106(4): 043903-1-4. |
| [55] | CHUKKA R, VANDRANGI S, SHANNIGRAHI S , et al. An electrocaloric device demonstrator for solid-state cooling. EPL-Europhys. Lett., 2013, 103: 47011-1-4. |
| [56] | ZHANG T, QIAN X S, GU H M , et al. An electrocaloric refrigerator with direct solid to solid regeneration. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2017, 110(24): 243503-1-4. |
| [57] |
BLUMENTHAL P, RAATZ A . Design methodology for electrocaloric cooling systems. Energy Technol., 2018,6(8):1560-1566.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
MOYA X, DEFAY E, MATHUR N D , et al. Electrocaloric effects in multilayer capacitors for cooling applications. MRS Bulletin, 2018,43(4):291-294.
DOI URL |
| [59] |
MA R J, ZHANG Z Y, TONG K , et al. Highly efficient electrocaloric cooling with electrostatic actuation. Science, 2017,357(6356):1130-1134.
DOI URL |
| [60] | Li X Y . Electrocaloric Effect in Relaxor Ferroelectric Materials. Pennsylvania: The Pennsylvania State University Doctoral Dissertation, 2013. |
| [61] |
ROŽIČ B, MALIČ B, URŠIČ H , et al. Direct measurements of the giant electrocaloric effect in soft and solid ferroelectric materials. Ferroelectrics, 2010,405(1):26-31.
DOI URL |
| [62] | SANLIALP M, MOLIN C, SHVARTSMAN V V , et al. Modified differential scanning calorimeter for direct electrocaloric measurements. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectrics, 2016,63(10):1690-1696. |
| [63] |
QI S, ZHANG G H, DUAN L H , et al. Electrocaloric effect in Pb-free Sr-doped BaTi0.9Sn0.1O3 ceramics. Mater. Res. Bull., 2017,91:31-35.
DOI URL |
| [64] | LI J T, BAI Y, QIN S Q , Direct and indirect characterization of electrocaloric effect in (Na, K)NbO3 based lead-free ceramics. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2016, 109(16): 162902-1-4. |
| [65] | ZHOU Y Z, LIN Q R, LIU W F , et al. Compositional dependence of electrocaloric effect in lead-free (1-x)Ba(Zr0.2Ti0.8)O3-x(Ba0.7Ca0.3)TiO3 ceramics. RCS Adv., 2016,6(17):14084-14089. |
| [66] | ROSE M C, COHEN R E. Giant electrocaloric effect around TC. Phys. Rev. Lett., 2012, 109(18): 187604-1-5. |
| [67] |
ZHAO L, KE X Q, ZHOU Z J , et al. Large electrocaloric effect over a wide temperature range in BaTiO3-modified lead-free ceramics. J. Mater. Chem. C, 2019,7:1353-1358.
DOI URL |
| [68] | NIE X, YAN S G, CHEN X F, et al. Correlation between electrocaloric response and polarization behavior: slim-like and square-like hysteresis loop. Phys. Status Solidi A, 2018, 215(13): 1700971-1-7. |
| [69] | 张良莹, 姚熹 . 电介质物理. 西安: 西安交通大学, 2008: 432-480. |
| [70] | 王国梅, 万发荣 . 材料物理. 武汉:武汉理工大学出版社, 2004: 179-192. |
| [71] | 殷之文 . 电介质物理学. 北京: 科学出版社, 2003: 473-483. |
| [72] | 钟维烈 . 铁电体物理学. 北京: 科学出版社, 2018: 68-148. |
| [73] | KARAKI T, KATAYAMA T, YOSHIDA K , et al. Morphotropic phase boundary slope of (K, Na, Li)NbO3-BaZrO3 binary system adjusted using third component (Bi, Na)TiO3 additive. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 2013, 52(9S1): 09KD11-1-4. |
| [74] |
SASAKI A, CHIBA T, MAMIYA Y , et al. Dielectric and piezoelectric properties of (Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3-(Bi0.5K0.5)TiO3 systems. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 1999,38(9):5564-5567.
DOI URL |
| [75] | CHUKKA R, CHEAH J W, CHEN Z H , et al. Enhanced cooling capacities of ferroelectric materials at morphotropic phase boundaries. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2011, 98(24): 242902-1-3. |
| [76] | ZHANG T D, LI W L, CAO W P , et al. Giant electrocaloric effect in PZT bilayer thin films by utilizing the electric field engineering. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2016, 108(216): 162902-1-5. |
| [77] |
YAO F Z, YU Q, WANG K , et al. Ferroelectric domain morphology and temperature-dependent piezoelectricity of (K, Na, Li)(Nb, Ta, Sb)O3 lead-free piezoceramics. RSC Adv., 2014,4:20062-20068.
DOI URL |
| [78] | GOTTSCHALL T, BENKE D, FRIES M , et al. A matter of size and stress: understanding the first-order transition in materials for solid-state refrigeration. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2017, 27(32): 1606735-1-6. |
| [79] |
WANG D W, HUSSAIN F, KHESRO A , et al. Composition and temperature dependence of structure and piezoelectricity in (1-x)(K1-yNay)NbO3-x(Bi1/2Na1/2)ZrO3 lead-free ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2017,100:627-637.
DOI URL |
| [80] |
SRIKANTH K S, SINGH V P, VAISH R . Enhanced pyroelectric figure of merits of porous BaSn0.05Ti0.95O3 ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2017,37(13):3943-3950.
DOI URL |
| [81] | KIM H K, SHI F G . Thickness dependent dielectric strength of a low-permittivity dielectric film. IEEE Trans. Electr. In., 2001,8(2):248-252. |
| [82] | CHEN G, ZHAO J W, LI S T , et al. Origin of thickness dependent dc electrical breakdown in dielectrics. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2012, 100(22): 222904-1-4. |
| [83] |
LIU X Q, CHEN T T, FU M S , et al. Electrocaloric effects in spark plasma sintered Ba0.7Sr0.3TiO3-based ceramics: effects of domain sizes and phase constitution. Ceram. Int., 2014,40(7):11269-11276.
DOI URL |
| [84] | 内野研二 . 铁电器件, 2版. 西安: 西安交通大学出版社, 2017: 15-17. |
| [85] | MARATHE M, GRÜNEBOHM A, NISHIMATSU T , et al. First-principles-based calculation of the electrocaloric effect in BaTiO3: a comparison of direct and indirect methods. Phys. Rev. B, 2016, 93: 054110-1-10. |
| [86] | NOVAK N, PIRC R, KUTNJAK Z. Impact of critical point on piezoelectric and electrocaloric response in barium titanate. Phys. Rev. B, 2013, 87: 104102-1-5. |
| [87] | NISHIMATSU T, BARR J A, BECKMAN S P. Direct molecular dynamics simulation of electrocaloric effect BaTiO3. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn., 2013, 82(11): 114605-1-5. |
| [88] |
HAN F, BAI Y, QIAO L J , et al. A systematic modification of the large electrocaloric effect within a broad temperature range in rare-earth doped BaTiO3 ceramics. J. Mater. Chem. C, 2016,4(9):1842-1849.
DOI URL |
| [89] |
BAI Y, HAN F, XIE S , et al. Thickness dependence of electrocaloric effect in high-temperature sintered Ba0.8Sr0.2TiO3 ceramics. J. Alloys Compd., 2018,736:57-61.
DOI URL |
| [90] |
YU Z, ANG C, GUO R , et al. Piezoelectric and strain properties of Ba(Ti1-xZrx)O3 ceramics. J. Appl. Phys., 2002,92(3):1489-1493.
DOI URL |
| [91] | YAO Y G, ZHOU C, LYU D C , et al. Large piezoelectricity and dielectric permittivity in BaTiO3-xBaSnO3 system: the role of phase coexisting. Europhysics Letters, 2012, 98(2): 27008-1-6. |
| [92] |
WEYLAND F, EISELE T, STEINER S , et al. Long term stability of electrocaloric response in barium zirconate titanate. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2017,38(2):551-556.
DOI URL |
| [93] | ZHANG X, WU L, GAO S , et al. Large electrocaloric effect in Ba(Ti1-xSnx)O3 ceramics over a broad temperature region. AIP Adv., 2015, 5: 047134-1-7. |
| [94] | SANLIALP M, LUO Z D, SHVARTSMAN V V , et al. Direct measurement of electrocaloric effect in lead-free Ba(SnxTi1-x)O3 ceramics. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2017, 111(17): 173903-1-5. |
| [95] | HIROSHI M. Temperature dependences of the electromechanical and electrocaloric properties of Ba(Zr, Ti)O3 and (Ba, Sr)TiO3 ceramics. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 2017, 56: 10PC05-1-8. |
| [96] |
JIAN X D, LU B, LI D D , et al. Direct measurement of large electrocaloric effect in Ba(ZrxTi1-x)O3 ceramics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018,10(5):4801-4807.
DOI URL |
| [97] | LUO Z D, ZHANG D W, YANG L , et al. Enhanced electrocaloric effect in lead-free BaTi1-xSnxO3 ceramics near room temperature. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2014, 105(10): 102904-1-5. |
| [98] | LIU W F, REN X B. Large piezoelectric effect in Pb-free ceramics. Phys. Rev. Lett., 2009, 103(25): 257602-1-4. |
| [99] |
XU Z P, QIANG H, CHEN Y , et al. Room-temperature electrocaloric effect in (1-x)Ba0.67Sr0.33TiO3-xBa0.9Ca0.1Ti0.9Zr0.1O3 ceramics under moderate electric field. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron., 2018,29(9):7227-7232.
DOI URL |
| [100] | TSAI C C, CHAO W H, CHU S Y, et al. Enhanced temperature stability and quality factor with Hf substitution for Sn and MnO2 doping of (Ba0.97Ca0.03)(Ti0.96Sn0.04)O3 lead-free piezoelectric ceramics with high Curie temperature. AIP Advances, 2016, 6(12): 125024-1-16. |
| [101] |
NIE X, YAN S, GUO S , et al. The influence of phase transition on electrocaloric effect in lead-free (Ba0.9Ca0.1)(Ti1-xZrx)O3 ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2017,100(11):5202-5210.
DOI URL |
| [102] |
PATEL S, VAISH R . Effect of sintering temperature and dwell time on electrocaloric properties of Ba0.85Ca0.075Sr0.075Ti0.90Zr0.10O3 ceramics. Phase Transit., 2017,90(5):465-474.
DOI URL |
| [103] |
HAO J G, XU Z J, CHU R Q , et al. Fatigue-resistant, temperature- insensitive strain behavior and strong red photoluminescence in Pr-modified 0.92(Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3-0.08(Ba0.90Ca0.10)(Ti0.92Sn0.08)O3 lead-free ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2017,37(2):877-882.
DOI URL |
| [104] |
FAN Z M, LIU X M, TAN X L . Large electrocaloric responses in [Bi1/2(Na, K)1/2]TiO3-based ceramics with giant electrostrains. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2017,100(5):2088-2097.
DOI URL |
| [105] |
RIEMER L M, LALITHA K V, JIANG X J , et al. Stress-induced phase transition in lead-free relaxor ferroelectric composites. Acta Mater., 2017,136:271-280.
DOI URL |
| [106] |
CHAUHAN A, PATEL S, VAISH R . Enhanced electrocaloric effect in pre-stressed ferroelectric materials. Energy Technol., 2015,3(2):177-186.
DOI URL |
| [107] |
CAO W P, LI W L, XU D , et al. Enhanced electrocaloric effect in lead-free NBT-based ceramics. Ceram. Int., 2014,40(7):9273-9278.
DOI URL |
| [108] |
CAO W P, LI W L, DAI X F , et al. Large electrocaloric response and high energy-storage properties over a broad temperature range in lead-free NBT-ST ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2016,36(3):593-600.
DOI URL |
| [109] | PONOMAREVA I, LISENKOV S. Bridging the macroscopic and atomistic descriptions of the electrocaloric effect. Phys. Rev. Lett., 2012, 108(16): 167604-1-5. |
| [110] |
ZANNEN M, LAHMAR A, KUTNJAK Z , et al. Electrocaloric effect and energy storage in lead free Gd0.02Na0.5Bi0.48TiO3 ceramic. Solid State Sci., 2017,66:31-37.
DOI URL |
| [111] |
LUO L H, JIANG X J, ZHANG Y Y , et al. Electrocaloric effect and pyroelectric energy harvesting of (0.94-x)Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3- 0.06BaTiO3-xSrTiO3 ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2017,37(8):2803-2812.
DOI URL |
| [112] | LE GOUPIL F, BENNETT J, AXELSSON A K , et al. Electrocaloric enhancement near the morphotropic phase boundary in lead-free NBT-KBT ceramics. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2015, 107(17): 172903-1-4. |
| [113] | LE GOUPIL F, ALFORD N M. Upper limit of the electrocaloric peak in lead-free ferroelectric relaxor ceramics. APL Mater., 2016, 4(6): 064104-1-6. |
| [114] | LE GOUPIL F, MCKINNON R, KOVAL V , et al. Tuning the electrocaloric enhancement near the morphotropic phase boundary in lead-free ceramics. Sci. Rep., 2016, 6: 28251-1-6. |
| [115] |
WEYLAND F, ACOSTA M, KORUZA J , et al. Criticality: concept to enhance the piezoelectric and electrocaloric properties of ferroelectrics. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2016,26(40):7326-7333.
DOI URL |
| [116] |
LI F, CHEN G R, LIU X , et al. Phase-composition and temperature dependence of electrocaloric effect in lead-free Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3- BaTiO3-(Sr0.7Bi0.2□0.1)TiO3 ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2017,37(15):4732-4740.
DOI URL |
| [117] |
LI J L, ZHAO X B, XU Z , et al. Electrocaloric effect in lead-free relaxor (1-x)(Sr0.7Bi0.2)TiO3+x(Na0.5Bi0.5)TiO3 material system. Mater. Lett., 2017,187:68-71.
DOI URL |
| [118] |
LI Q, WANG J, MA L T , et al. Large electrocaloric effect in (Bi0.5Na0.5)0.94Ba0.06TiO3 lead-free ferroelectric ceramics by La2O3 addition. Mater. Res. Bull., 2016,74:57-61.
DOI URL |
| [119] |
TUNKASIRI T, RUJIJANAGUL G . Dielectric strength of fine grained barium titanate ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. Lett., 1996,15(20):1767-1769.
DOI URL |
| [120] |
DU H L, YANG Z T, GAO F , et al. Lead-free nonlinear dielectric ceramics for energy storage application: current status and challenges. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018,33(10):1046-1058.
DOI URL |
| [121] |
ROŽIČ B, KORUZA J, KUTNJAK Z , et al. The electrocaloric effect in lead-free K0.5Na0.5NbO3-SrTiO3 ceramics. Ferroelectrics, 2013,446(1):39-45.
DOI URL |
| [122] | KORUZA J, ROŽIČ B, CORDOYIANNIS G , et al. Large electrocaloric effect in lead-free K0.5Na0.5NbO3-SrTiO3 ceramics. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2015, 106(20): 202905-1-4. |
| [123] |
GUPTA A, KUMAR R, SINGH S . Coexistence of negative and positive electrocaloric effect in lead-free 0.9(K0.5Na0.5)NbO3-0.1SrTiO3 nanocrystalline ceramics. Scripta Mater., 2018,143:5-9.
DOI URL |
| [124] |
KUMAR R, SINGH S . Enhanced electrocaloric effect in lead-free 0.9(K0.5Na0.5)NbO3-0.1Sr(Sc0.5Nb0.5)O3 ferroelectric nanocrystalline ceramics. Alloys Compd., 2017,723:589-594.
DOI URL |
| [125] | WANG X J, WU J G, DKHIL B , et al. Enhanced electrocaloric effect near polymorphic phase boundary in lead-free potassium sodium niobate ceramics. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2017, 110(6): 063904-1-5. |
| [126] | KUMAR R, SINGH S . Giant electrocaloric and energy storage performance of [(K0.5Na0.5)NbO3](1-x)-(LiSbO3)x nanocrystalline ceramics. Sci. Rep., 2018, 8(1): : 3186-1-9. |
| [127] |
LI F, LU B, ZHAI J W , et al. Enhanced piezoelectric properties and electrocaloric effect in novel lead-free (Bi0.5K0.5)TiO3-La(Mg0.5Ti0.5)O3 ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2018,101(12):5503-5513.
DOI URL |
| [128] | TAO H, YANG J L, LYU X , et al. Electrocaloric behavior and piezoelectric effect in relaxor NaNbO3-based ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2019,102(5):2578-2586. |
| [129] |
YU Y, GAO F, WEYLAND F , et al. Significantly enhanced room temperature electrocaloric response with superior thermal stability in sodium niobate-based bulk ceramics. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2019,7(19):11665-11672.
DOI URL |
| [130] |
AXELSSON A K, LE GOUPIL F, VALANT M , et al. Electrocaloric effect in lead-free Aurivillius relaxor ferroelectric ceramics. Acta Mater., 2017,124:120-126.
DOI URL |
| [1] | ZHU Wenjie, TANG Lu, LU Jichang, LIU Jiangping, LUO Yongming. Research Progress on Catalytic Oxidation of Volatile Organic Compounds by Perovskite Oxides [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [2] | HU Zhichao, YANG Hongyu, YANG Hongcheng, SUN Chengli, YANG Jun, LI Enzhu. Usage of the P-V-L Bond Theory in Regulating Properties of Microwave Dielectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [3] | WU Qiong, SHEN Binglin, ZHANG Maohua, YAO Fangzhou, XING Zhipeng, WANG Ke. Research Progress on Lead-based Textured Piezoelectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [4] | ZHANG Bihui, LIU Xiaoqiang, CHEN Xiangming. Recent Progress of Hybrid Improper Ferroelectrics with Ruddlesden-Popper Structure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| [5] | WU Jie, YANG Shuai, WANG Mingwen, LI Jinglei, LI Chunchun, LI Fei. Textured PT-based Piezoelectric Ceramics: Development, Status and Challenge [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 575-586. |
| [6] | JIANG Kun, LI Letian, ZHENG Mupeng, HU Yongming, PAN Qinxue, WU Chaofeng, WANG Ke. Research Progress on Low-temperature Sintering of PZT Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| [7] | WAN Junchi, DU Lulu, ZHANG Yongshang, LI Lin, LIU Jiande, ZHANG Linsen. Structural Evolution and Electrochemical Performance of Na4FexP4O12+x/C Cathode Materials for Sodium-ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 497-503. |
| [8] | TIAN Ruizhi, LAN Zhengyi, YIN Jie, HAO Nanjing, CHEN Hangrong, MA Ming. Microfluidic Technology Based Synthesis of Inorganic Nano-biomaterials: Principles and Progress [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 337-347. |
| [9] | ZHANG Jiguo, WU Tian, ZHAO Xu, YANG Fan, XIA Tian, SUN Shien. Improvement of Cycling Stability of Cathode Materials and Industrialization Process for Sodium-ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 348-362. |
| [10] | YIN Jie, GENG Jiayi, WANG Kanglong, CHEN Zhongming, LIU Xuejian, HUANG Zhengren. Recent Advances in 3D Printing and Densification of SiC Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 245-255. |
| [11] | CHEN Guangchang, DUAN Xiaoming, ZHU Jinrong, GONG Qing, CAI Delong, LI Yuhang, YANG Donglei, CHEN Biao, LI Xinmin, DENG Xudong, YU Jin, LIU Boya, HE Peigang, JIA Dechang, ZHOU Yu. Advanced Ceramic Materials in Helicopter Special Structures: Research Progress and Application Prospect [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 225-244. |
| [12] | FAN Xiaobo, ZU Mei, YANG Xiangfei, SONG Ce, CHEN Chen, WANG Zi, LUO Wenhua, CHENG Haifeng. Research Progress on Proton-regulated Electrochemical Ionic Synapses [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 256-270. |
| [13] | HAIREGU Tuxun, GUO Le, DING Jiayi, ZHOU Jiaqi, ZHANG Xueliang, NUERNISHA Alifu. Research Progress of Optical Bioimaging Technology Assisted by Upconversion Fluorescence Probes in Tumor Imaging [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 145-158. |
| [14] | SUN Shujuan, ZHENG Nannan, PAN Haokun, MA Meng, CHEN Jun, HUANG Xiubing. Research Progress on Preparation Methods of Single-atom Catalysts [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 113-127. |
| [15] | TAO Guilong, ZHI Guowei, LUO Tianyou, OUYANG Peidong, YI Xinyan, LI Guoqiang. Progress on Key Technologies of Cavity-structured Thin Film Bulk Acoustic Wave Filter [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 128-144. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||