
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (4): 337-347.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240431
Special Issue: 【生物材料】骨骼与齿类组织修复(202506)
• REVIEW • Next Articles
TIAN Ruizhi1,2( ), LAN Zhengyi1, YIN Jie1,2, HAO Nanjing3, CHEN Hangrong1,2, MA Ming1,2(
), LAN Zhengyi1, YIN Jie1,2, HAO Nanjing3, CHEN Hangrong1,2, MA Ming1,2( )
)
Received:2024-10-12
Revised:2024-11-05
Published:2025-04-20
Online:2024-11-25
Contact:
MA Ming, professor. E-mail: mma@mail.sic.ac.cnAbout author:TIAN Ruizhi (2001-), male, PhD candidate. E-mail: tianruizhi23@mails.ucas.ac.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TIAN Ruizhi, LAN Zhengyi, YIN Jie, HAO Nanjing, CHEN Hangrong, MA Ming. Microfluidic Technology Based Synthesis of Inorganic Nano-biomaterials: Principles and Progress[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 337-347.
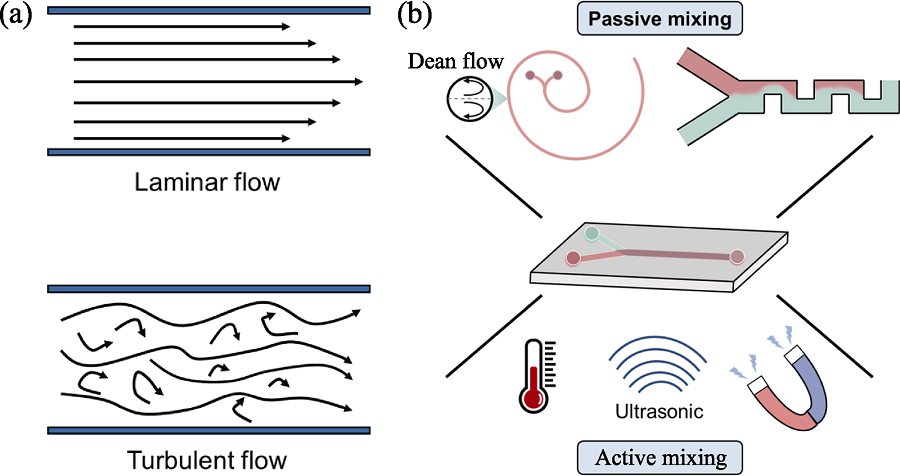
Fig. 1 Flow patterns and fluid mixing strategies in microfluidic devices (a) Diagram of laminar flow and turbulent flow in a microchannel; (b) Schematic diagram of active and passive mixing strategies in microfluidic device
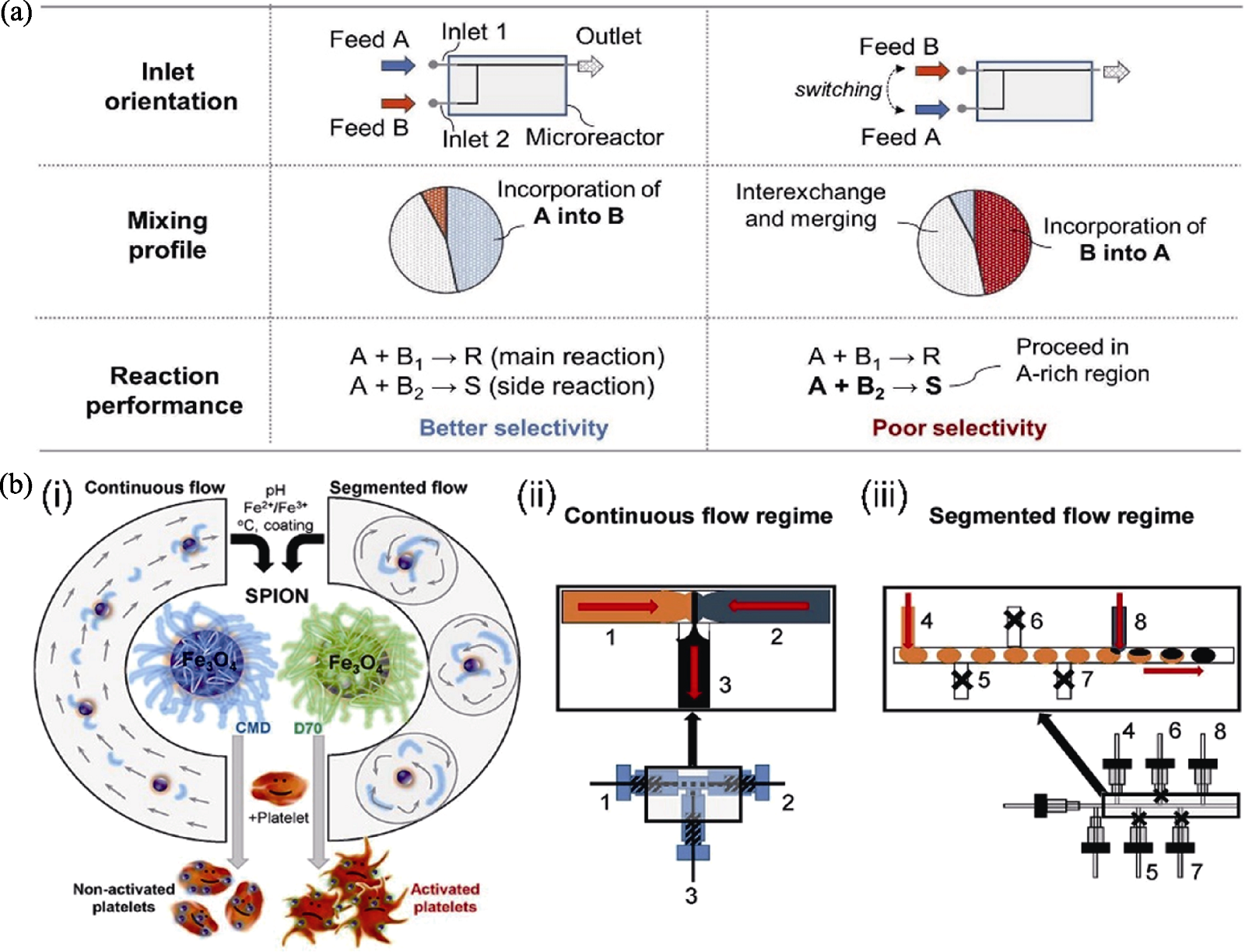
Fig. 2 Fluid mixing in T-shaped microfluidic device and its application in synthesis of inorganic nano-biomaterials[25,35] (a) Influence of inlet orientation on the mixing profile and reaction selectivity[25]; (b) Schematic diagrams of SPION synthesis and labeling of human platelets (i), continuous flow (ii), and segmented flow (iii) used in the synthesis of SPION[35]
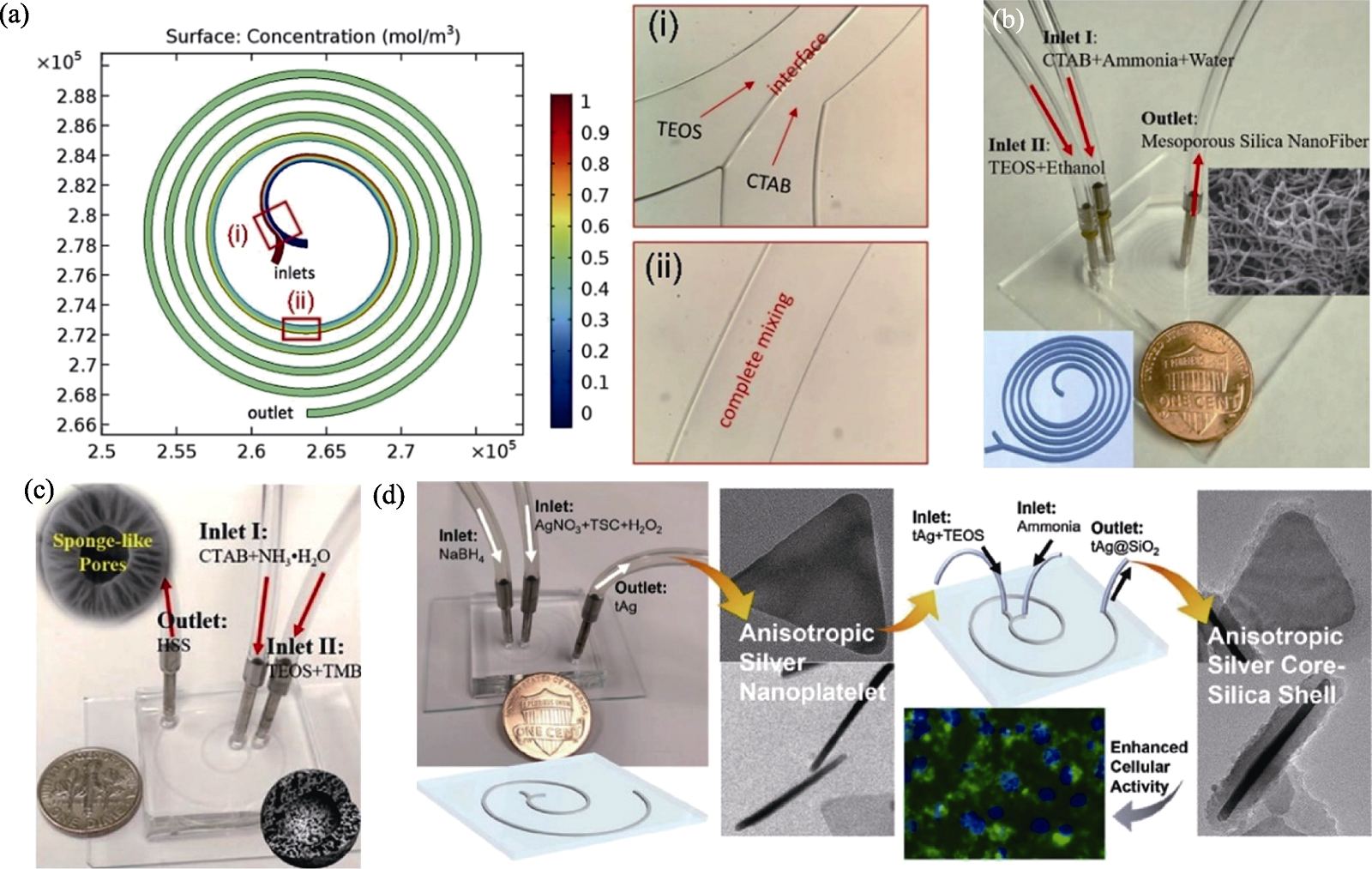
Fig. 3 Application of planar spiral microfluidic devices in the preparation of inorganic nano-biomaterials[42⇓⇓-45] (a) Simulatied and experimental results of mixing in spiral microchannel utilized in the microfluidic synthesis of smHSS[42]; (b) Spiral microreactor used for the preparation of MSNF[43]; (c) Spiral microreactor with three arcs and generation of spherical hollow SiO2 with hierarchical sponge-like porous structure[44]; (d) Schematic diagram showing the synthesis of triangular core-shell tAg@SiO2 with spiral microreactor[45]
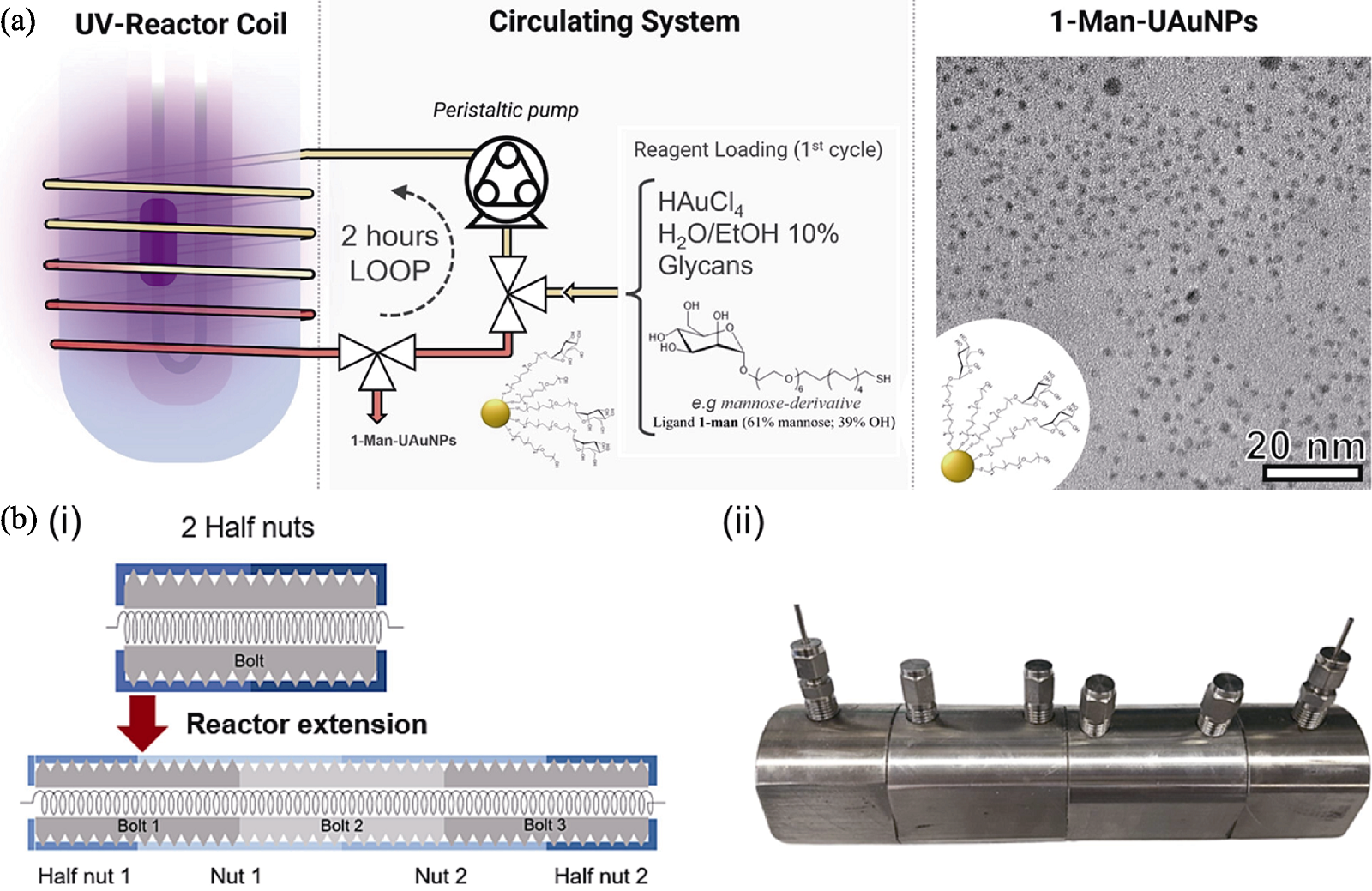
Fig. 4 Application of three-dimensional helical microfluidic devices in the preparation of inorganic nano-biomaterials[48-49] (a) Schematic diagram for the synthesis of 1-Man-UAuNPs (left) and their TEM image (right)[48]; (b) Schematic diagram (i) and photograph (ii) of the bolt-nut microfluidic device made of stainless steel[49]
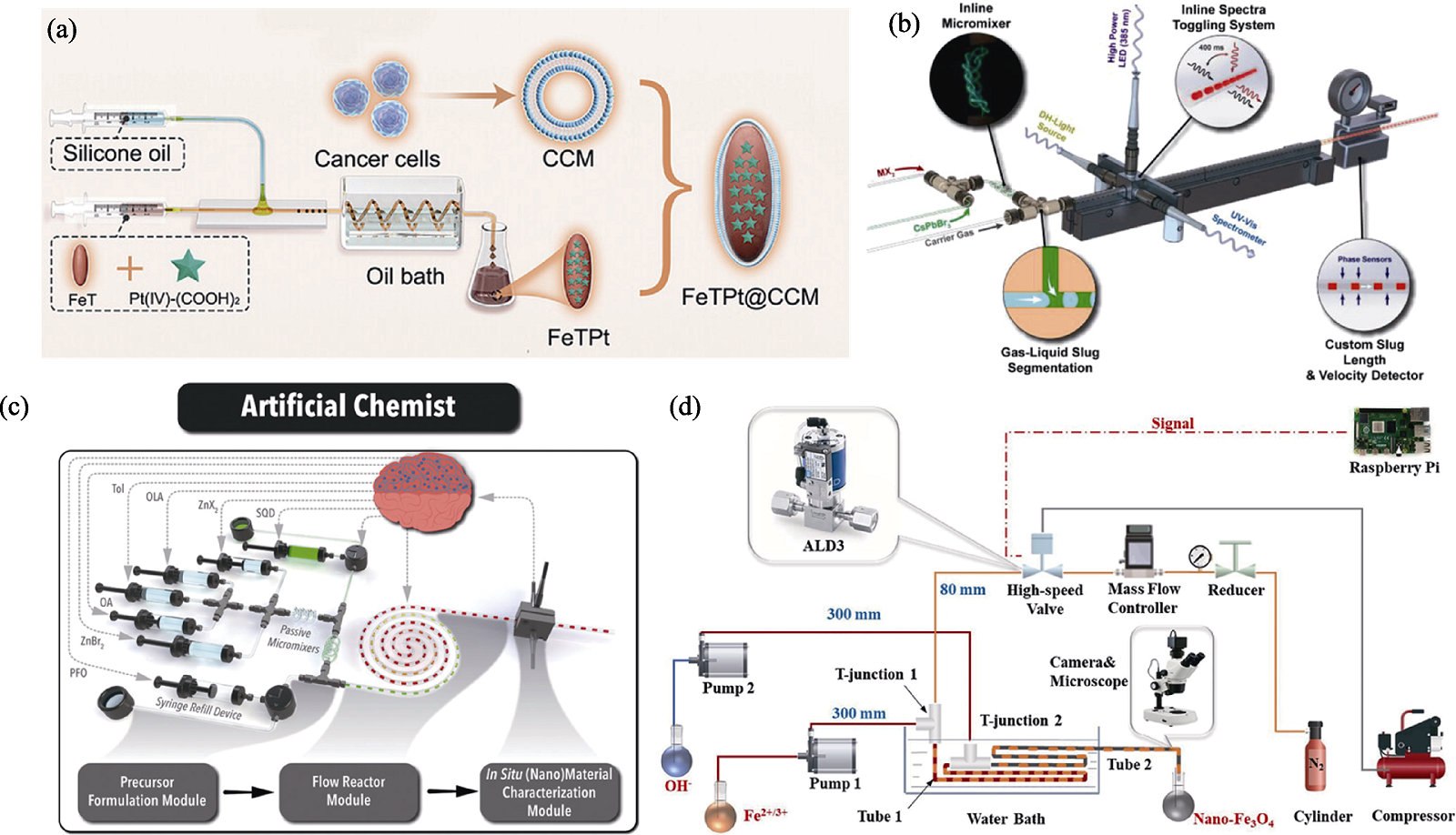
Fig. 5 Application of segmented flow microfluidic systems in the preparation of inorganic nano-biomaterials[61,66⇓ -68] (a) Schematic diagram showing the segmented flow microfluidic preparation of FeTPt, and the generation of FeTPt@CCM via CCM coating[61]; (b) Schematic illustration of the modular automated microfluidic platform based on gas-liquid segmented flow[66]; (c) Schematic of the self-driving “Artificial Chemist” for autonomous synthetic path discovery and optimization of colloidal quantum dots[67]; (d) Schematic of the gas-liquid segmented flow based microfluidic device for high-throughput and continuous synthesis of nano-Fe3O4[68]
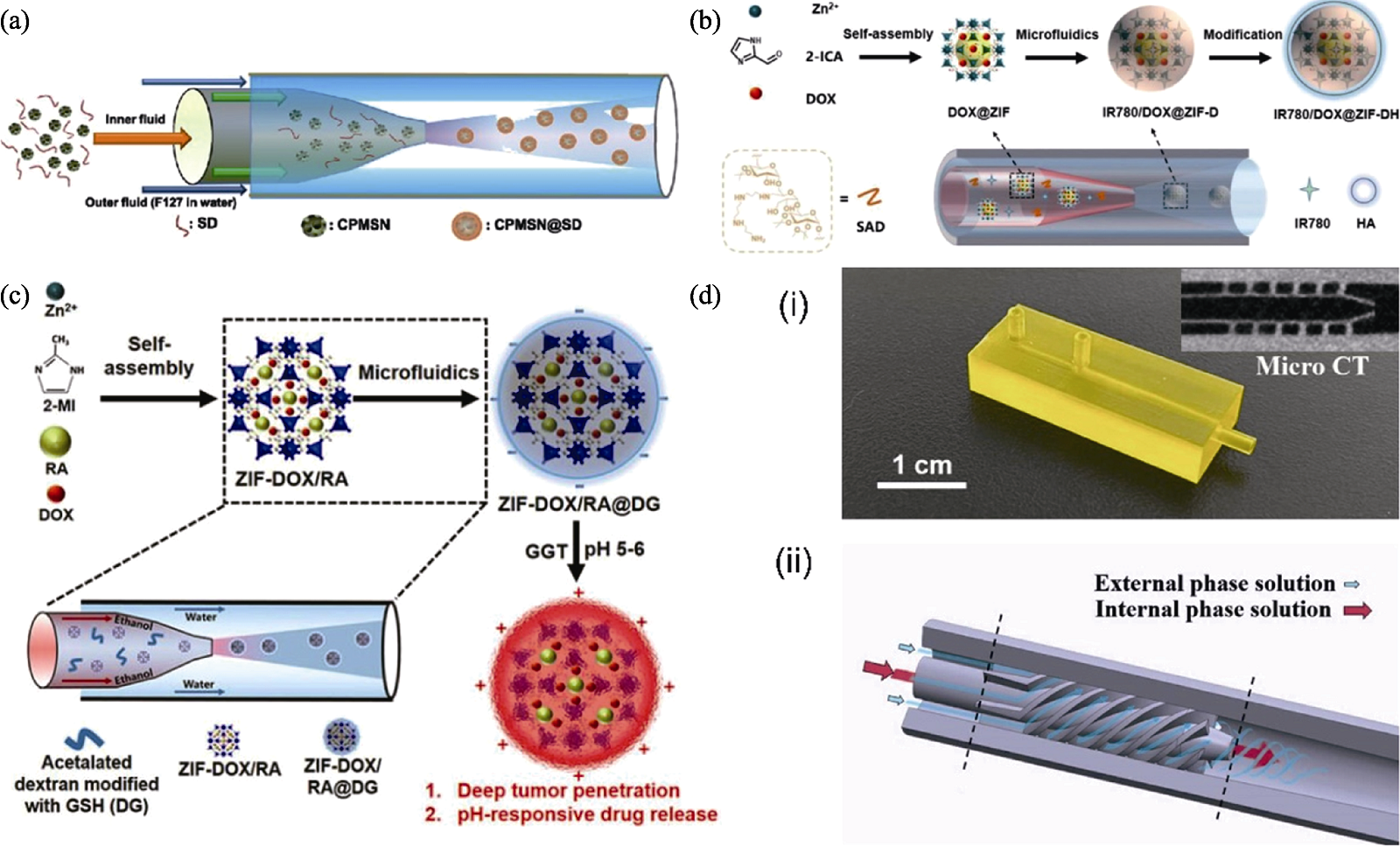
Fig. 6 Application of flow-focusing microfluidic devices in the preparation and surface modification of inorganic nano-biomaterials[24,74⇓ -76] (a) Schematic illustration of the synthesis of CPMSN@SD using a flow-focusing microfluidic device[74]; (b) Schematic illustration of the microfluidic synthesis of IR780/DOX@ZIF-DH[75]; (c) Schematic illustration of the synthesis of pH/enzyme dual-environment responsive ZIF-DOX/RA@DG[76]; (d) Physical picture of the HBSCF device and micro CT image of the fluid mixing area (i), along with the enlarged cross-sectional view of the core hybrid structure within the HBSCF device (ii)[24]
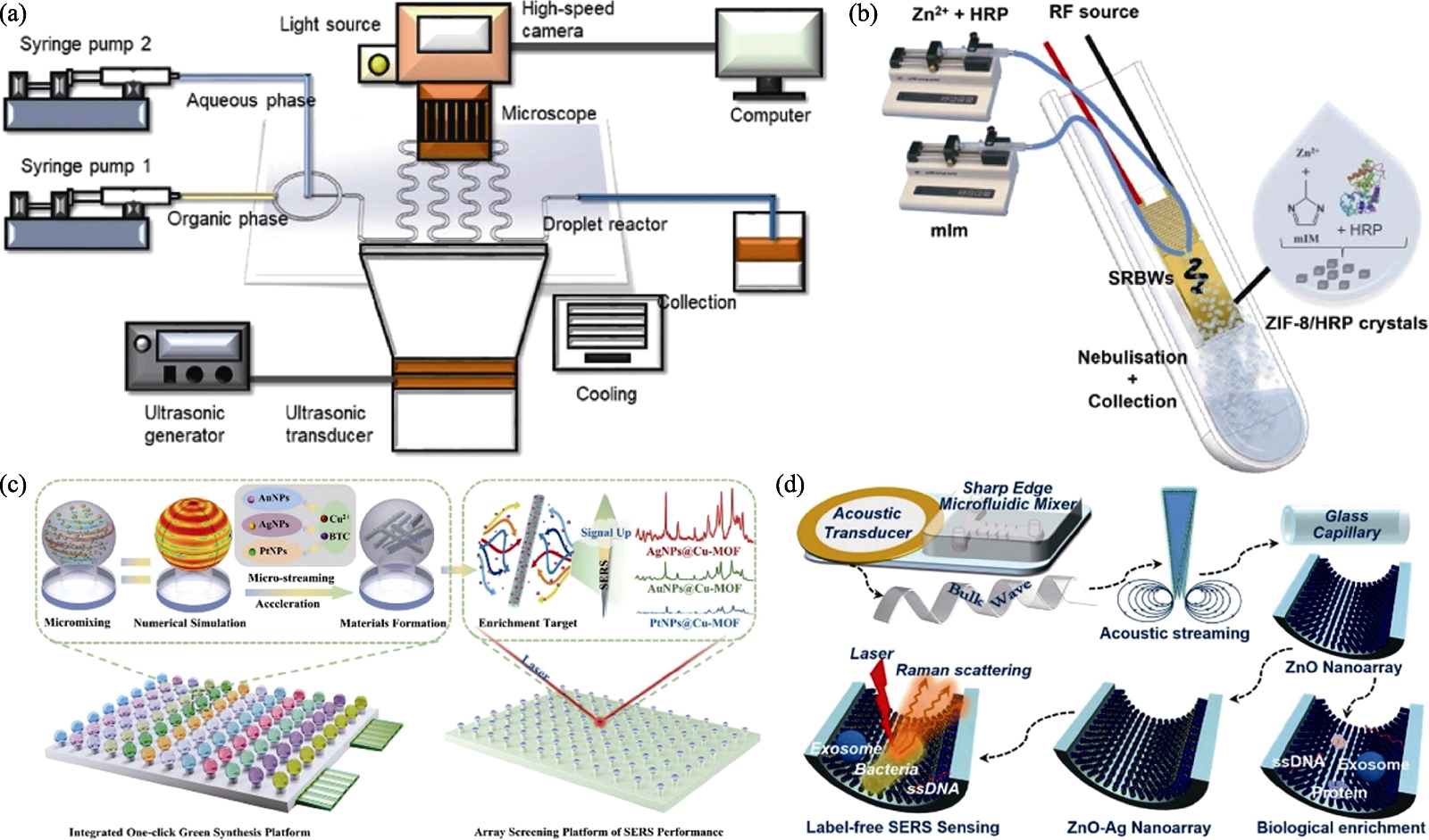
Fig. 7 Application of ultrasound-enhanced microfluidic devices in the preparation and surface modification of inorganic nano-biomaterials[84⇓⇓-87] (a) Schematic diagram of ultrasound-enhanced microdroplet reaction system for the synthesis of Ag2S quantum dots[84]; (b) Schematic illustration of the microfluidic device employed for the simultaneous synthesis of ZIF-8 and encapsulation of HRP[85]; (c) Schematic illustration of the one-click green and integrated platform incorporating ultrasound-enhanced droplet arrays synthesis system and high-throughput screening system via Raman performance [86]; (d) Schematic diagram showing the construction of ZnO-Ag nanoarray inside of confined capillary microchannel as multifunctional biological enrichment and sensing platform[87]
| [1] | CONG Y, BAIMANOV D, ZHOU Y, et al. Penetration and translocation of functional inorganic nanomaterials into biological barriers. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2022, 191: 114615. |
| [2] | FENG Z, XIANG X, HUANG J, et al. Intelligent sonocatalytic nanoagents for energy conversion-based therapies. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(45):2302579. |
| [3] | WANG J, FAN X, HAN X, et al. Ultrasmall inorganic mesoporous nanoparticles: preparation, functionalization, and application. Advanced Materials, 2024, 36(28):2312374. |
| [4] | SONG Z, SHAFIQ M, TIAN R, et al. Microfluidic production of inorganic nanoparticles//LAMPROU D A, WEAVER E. Microfluidics in pharmaceutical sciences: formulation, drug delivery, screening, and diagnostics. Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland, 2024: 133. |
| [5] | XU M, QI Y, LIU G, et al. Size-dependent in vivo transport of nanoparticles: implications for delivery, targeting, and clearance. ACS Nano, 2023, 17(21):20825. |
| [6] |
KAMAT V, DEY P, BODAS D, et al. Active microfluidic reactor-assisted controlled synthesis of nanoparticles and related potential biomedical applications. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2023, 11(25):5650.
DOI PMID |
| [7] | RAN J, WANG X, LIU Y, et al. Microreactor-based micro/ nanomaterials: fabrication, advances, and outlook. Materials Horizons, 2023, 10(7):2343. |
| [8] | MARK D, HAEBERLE S, ROTH G, et al. Microfluidic lab-on-a- chip platforms: requirements, characteristics and applications. Chemical Society Reviews, 2010, 39(3):1153. |
| [9] | ILLATH K, KAR S, GUPTA P, et al. Microfluidic nanomaterials: from synthesis to biomedical applications. Biomaterials, 2022, 280: 121247. |
| [10] |
ZHANG L, CHEN Q, MA Y, et al. Microfluidic methods for fabrication and engineering of nanoparticle drug delivery systems. ACS Applied Bio Materials, 2020, 3(1):107.
DOI PMID |
| [11] | FABOZZI A, SALA F D, GENNARO M, et al. Design of functional nanoparticles by microfluidic platforms as advanced drug delivery systems for cancer therapy. Lab on a Chip, 2023, 23(5):1389. |
| [12] | LIU Z, FONTANA F, PYTHON A, et al. Microfluidics for production of particles: mechanism, methodology, and applications. Small, 2020, 16(9):1904673. |
| [13] | ZHANG Q, KUANG G, WANG L, et al. Tailoring drug delivery systems by microfluidics for tumor therapy. Materials Today, 2024, 73: 151. |
| [14] |
TOMEH M A, ZHAO X. Recent advances in microfluidics for the preparation of drug and gene delivery systems. Molecular Pharmaceutics, 2020, 17(12):4421.
DOI PMID |
| [15] | CONVERY N, GADEGAARD N. 30 years of microfluidics. Micro and Nano Engineering, 2019, 2: 76. |
| [16] | FERNANDES P. Basic principles of microfluidics//LAMPROU D A, WEAVER E. Microfluidics in pharmaceutical sciences: formulation, drug delivery, screening, and diagnostics. Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland, 2024: 1. |
| [17] | KLEIN A K, DIETZEL A. A primer on microfluidics: from basic principles to microfabrication//BAHNEMANN J, GRÜNBERGER A. Microfluidics in biotechnology. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2022: 17. |
| [18] | MARTINS J P, TORRIERI G, SANTOS H A. The importance of microfluidics for the preparation of nanoparticles as advanced drug delivery systems. Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery, 2018, 15(5):469. |
| [19] | MARTINS J P, SANTOS H A. Microfluidics as a tool for the synthesis of advanced drug delivery systems//LAMPROU D. Nano- and microfabrication techniques in drug delivery: recent developments and future prospects. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2023: 321. |
| [20] |
LIU Y, SUN L, ZHANG H, et al. Microfluidics for drug development: from synthesis to evaluation. Chemical Reviews, 2021, 121(13):7468.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
MA Q, CAO J, GAO Y, et al. Microfluidic-mediated nano-drug delivery systems: from fundamentals to fabrication for advanced therapeutic applications. Nanoscale, 2020, 12(29):15512.
DOI PMID |
| [22] | LIU Y, YANG G, HUI Y, et al. Microfluidic nanoparticles for drug delivery. Small, 2022, 18(36):2106580. |
| [23] |
ZHANG H, YANG J, SUN R, et al. Microfluidics for nano-drug delivery systems: from fundamentals to industrialization. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, 2023, 13(8):3277.
DOI PMID |
| [24] | WANG H, LAN Z, TIAN R, et al. Combined helical-blade- strengthened co-flow focusing and high-throughput screening for the synthesis of highly homogeneous nanoliposomes. Nano Today, 2024, 56: 102301. |
| [25] | ASANO S, MAKI T, INOUE S, et al. Incorporative mixing in microreactors: influence on reactions and importance of inlet designation. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 451: 138942. |
| [26] | FAN J, LI S, WU Z, et al. Diffusion and mixing in microfluidic devices//Microfluidics for pharmaceutical applications. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2019: 79. |
| [27] | BAYAREH M, ASHANI M N, USEFIAN A. Active and passive micromixers: a comprehensive review. Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensification, 2020, 147: 107771. |
| [28] | WANG X, LIU Z, WANG B, et al. An overview on state-of-art of micromixer designs, characteristics and applications. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2023, 1279: 341685. |
| [29] | CORTES-QUIROZ C A, AZARBADEGAN A, ZANGENEH M. Effect of channel aspect ratio of 3-D T-mixer on flow patterns and convective mixing for a wide range of Reynolds number. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2017, 239: 1153. |
| [30] | MARIOTTI A, ANTOGNOLI M, GALLETTI C, et al. A study on the effect of flow unsteadiness on the yield of a chemical reaction in a T micro-reactor. Micromachines, 2021, 12(3):242. |
| [31] | AGARWAL T, WANG L. Numerical analysis of vortex T micromixer with diffuser plates and obstacles. Thermal Science and Engineering Progress, 2022, 28: 101156. |
| [32] | MATSUNAGA T, NISHINO K. Swirl-inducing inlet for passive micromixers. RSC Advances, 2013, 4(2):824. |
| [33] | ZHAO S, HU R, NIE Y, et al. Intensification of mixing efficiency and reduction of pressure drop in a millimeter scale T-junction mixer optimized by an elliptical array hole structure. Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensification, 2022, 178: 109034. |
| [34] | KURNIA J C, AHMADIHOSSEINI A, SASMITO A P. Flow behavior and mixing of single-phase laminar Newtonian miscible fluid in T-junction micromixer with twisted mixing channel - a numerical study. Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensification, 2022, 181: 109171. |
| [35] | SCHEMBERG J, ABBASSI A E, LINDENBAUER A, et al. Synthesis of biocompatible superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPION) under different microfluidic regimes. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(42):48011. |
| [36] | ZHAN T, SONG Y, YANG Q, et al. Structure and catalytic activity of hemoglobin assembled with layered double hydroxide nanosheets by coprecipitation using a T-shaped microreactor. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 306: 1143. |
| [37] |
NIVEDITA N, LIGRANI P, PAPAUTSKY I. Dean flow dynamics in low-aspect ratio spiral microchannels. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1):44072.
DOI PMID |
| [38] | NGO I L, LAI T K, CHOI H J, et al. A study on mixing performance of dean flows through spiral micro-channel under various effects. Physics of Fluids, 2020, 32(2):022004. |
| [39] | CHEN H, ZHANG Y, HUANG L, et al. Microfluidic production of silica nanofluids for highly efficient two-phase cooling with micro pin-fins structure. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 465: 142799. |
| [40] |
HAO N, NIE Y, SHEN T, et al. Microfluidics-enabled rational design of immunomagnetic nanomaterials and their shape effect on liquid biopsy. Lab on a Chip, 2018, 18(14): 1997.
DOI PMID |
| [41] | YANG H, AKINOGLU E M, GUO L, et al. A PTFE helical capillary microreactor for the high throughput synthesis of monodisperse silica particles. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 401: 126063. |
| [42] | NIE Y, HAO N, ZHANG J X J. Ultrafast synthesis of multifunctional submicrometer hollow silica spheres in microfluidic spiral channels. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 12616. |
| [43] | HAO N, NIE Y, ZHANG J X J. Microfluidic flow synthesis of functional mesoporous silica nanofibers with tunable aspect ratios. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2018, 6(2):1522. |
| [44] | HAO N, NIE Y, XU Z, et al. Microfluidic continuous flow synthesis of functional hollow spherical silica with hierarchical sponge-like large porous shell. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 366: 433. |
| [45] | HAO N, NIE Y, XU Z, et al. Ultrafast microfluidic synthesis of hierarchical triangular silver core-silica shell nanoplatelet toward enhanced cellular internalization. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2019, 542: 370. |
| [46] | SINGH J, KOCKMANN N, NIGAM K D P. Novel three- dimensional microfluidic device for process intensification. Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensification, 2014, 86: 78. |
| [47] | KOCKMANN N, ROBERGE D M. Transitional flow and related transport phenomena in curved microchannels. Heat Transfer Engineering, 2011, 32(7/8):595. |
| [48] | SCHMIDT P P, PAGANO K, LENARDI C, et al. Photo-induced microfluidic production of ultrasmall glyco gold nanoparticles. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2023, 62(1):e202210140. |
| [49] | KIM H, KIM D H, KIM S H. Robust and versatile bolt-nut microreactors designed for controlled synthesis of quantum dots. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 474: 145761. |
| [50] | HU G, YANG L, LI Y, et al. Continuous and scalable fabrication of stable and biocompatible MOF@SiO2 nanoparticles for drug loading. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2018, 6(47):7936. |
| [51] | MAHIN J, TORRENTE-MURCIANO L. Continuous synthesis of monodisperse iron@iron oxide core@shell nanoparticles. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 396: 125299. |
| [52] | GAO Y, PINHO B, TORRENTE-MURCIANO L. Tailoring the size of silver nanoparticles by controlling mixing in microreactors. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 432: 134112. |
| [53] | WU K J, DE VARINE BOHAN G M, TORRENTE-MURCIANO L. Synthesis of narrow sized silver nanoparticles in the absence of capping ligands in helical microreactors. Reaction Chemistry & Engineering, 2017, 2(2):116. |
| [54] | LUO X, SU P, ZHANG W, et al. Microfluidic devices in fabricating nano or micromaterials for biomedical applications. Advanced Materials Technologies, 2019, 4(12):1900488. |
| [55] | SONG H, CHEN D L, ISMAGILOV R F. Reactions in droplets in microfluidic channels. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2006, 45(44):7336. |
| [56] |
DING Y, HOWES P D, DEMELLO A J. Recent advances in droplet microfluidics. Analytical Chemistry, 2020, 92(1):132.
DOI PMID |
| [57] | KUMAR D V R, PRASAD B L V, KULKARNI A A. Segmented flow synthesis of Ag nanoparticles in spiral microreactor: role of continuous and dispersed phase. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2012, 192: 357. |
| [58] | PENG Z, WANG G, MOGHTADERI B, et al. A review of microreactors based on slurry Taylor (segmented) flow. Chemical Engineering Science, 2022, 247: 117040. |
| [59] | FU Q, NIU W, YAN L, et al. A versatile microfluidic strategy using air-liquid segmented flow for continuous and efficient synthesis of metal-organic frameworks. Materials Letters, 2023, 343: 134344. |
| [60] | PASETA L, SEOANE B, JULVE D, et al. Accelerating the controlled synthesis of metal-organic frameworks by a microfluidic approach: a nanoliter continuous reactor. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2013, 5(19):9405. |
| [61] | ZHANG Q, KUANG G, WANG H, et al. Multi-bioinspired MOF delivery systems from microfluidics for tumor multimodal therapy. Advanced Science, 2023, 10(33):2303818. |
| [62] | BAGI S, YUAN S, ROJAS-BUZO S, et al. A continuous flow chemistry approach for the ultrafast and low-cost synthesis of MOF-808. Green Chemistry, 2021, 23(24):9982. |
| [63] |
LIGNOS I, STAVRAKIS S, NEDELCU G, et al. Synthesis of cesium lead halide perovskite nanocrystals in a droplet-based microfluidic platform: fast parametric space mapping. Nano Letters, 2016, 16(3): 1869.
DOI PMID |
| [64] | BATENI F, SADEGHI S, OROUJI N, et al. Smart dope: a self- driving fluidic lab for accelerated development of doped perovskite quantum dots. Advanced Energy Materials, 2024, 14(1):2302303. |
| [65] | VOLK A A, EPPS R W, YONEMOTO D, et al. Continuous biphasic chemical processes in a four-phase segmented flow reactor. Reaction Chemistry & Engineering, 2021, 6(8):1367. |
| [66] | ABDEL-LATIF K, EPPS R W, KERR C B, et al. Facile room- temperature anion exchange reactions of inorganic perovskite quantum dots enabled by a modular microfluidic platform. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29(23):1900712. |
| [67] | EPPS R W, BOWEN M S, VOLK A A, et al. Artificial chemist: an autonomous quantum dot synthesis bot. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(30):2001626. |
| [68] | JIANG X, LI S, SOTOWA K I, et al. High throughput continuous synthesis of size-controlled nanoFe3O4 in segmented flow. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 471: 144546. |
| [69] | SHEPHERD S J, ISSADORE D, MITCHELL M J. Microfluidic formulation of nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Biomaterials, 2021, 274: 120826. |
| [70] | LE P T, AN S H, JEONG H H. Microfluidic Tesla mixer with 3D obstructions to exceptionally improve the curcumin encapsulation of PLGA nanoparticles. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 483: 149377. |
| [71] | TROFIMOV A D, IVANOVA A A, ZYUZIN M V, et al. Porous inorganic carriers based on silica, calcium carbonate and calcium phosphate for controlled/modulated drug delivery: fresh outlook and future perspectives. Pharmaceutics, 2018, 10(4):167. |
| [72] | SAYED E, HAJ-AHMAD R, RUPARELIA K, et al. Porous inorganic drug delivery systems—a review. AAPS PharmSciTech, 2017, 18(5):1507. |
| [73] | ZOU Y, HUANG B, CAO L, et al. Tailored mesoporous inorganic biomaterials: assembly, functionalization, and drug delivery engineering. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(2):2005215. |
| [74] | YAO M, SHI X, ZUO C, et al. Engineering of SPECT/photoacoustic imaging/antioxidative stress triple-function nanoprobe for advanced mesenchymal stem cell therapy of cerebral ischemia. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(34):37885. |
| [75] | SHEN J, MA M, ZHANG H, et al. Microfluidics-assisted surface trifunctionalization of a zeolitic imidazolate framework nanocarrier for targeted and controllable multitherapies of tumors. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(41):45838. |
| [76] | SHEN J, MA M, SHAFIQ M, et al. Microfluidics-assisted engineering of pH/enzyme dual-activatable ZIF@polymer nanosystem for co-delivery of proteins and chemotherapeutics with enhanced deep-tumor penetration. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2022, 61(14):e202113703. |
| [77] | LIU Z, YANG M, YAO W, et al. Microfluidic ultrasonic cavitation enables versatile and scalable synthesis of monodisperse nanoparticles for biomedical application. Chemical Engineering Science, 2023, 280: 119052. |
| [78] | ZHAO S, YAO C, DONG Z, et al. Role of ultrasonic oscillation in chemical processes in microreactors: a mesoscale issue. Particuology, 2020, 48: 88. |
| [79] | ZHAO S, YAO C, LIU L, et al. Parametrical investigation of acoustic cavitation and extraction enhancement in ultrasonic microreactors. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 450: 138185. |
| [80] | LIU Z, YANG M, DONG Z, et al. Cavitation behavior and mixing performance of antisolvent precipitation process in an ultrasonic micromixer. AIChE Journal, 2023, 69(7):e18080. |
| [81] | ZHAO S, YAO C, ZHANG Q, et al. Acoustic cavitation and ultrasound-assisted nitration process in ultrasonic microreactors: the effects of channel dimension, solvent properties and temperature. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 374: 68. |
| [82] | CHEN Z, PEI Z, ZHAO X, et al. Acoustic microreactors for chemical engineering. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 433: 133258. |
| [83] | LIU Z, YANG M, ZHAO Q, et al. Scale-up of antisolvent precipitation process with ultrasonic microreactors: cavitation patterns, mixing characteristics and application in nanoparticle manufacturing. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 475: 146040. |
| [84] | ZHANG Z, XU C, SONG S, et al. Ultrasonic enhancement of microdroplet-based interfacial reaction for improving the synthesis of Ag2S QDs. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 2023, 95: 106411. |
| [85] | MASSAHUD E, AHMED H, AMBATTU L A, et al. Acoustomicrofluidic synthesis of ZIF-8/HRP metal-organic framework composites with enhanced enzymatic activity and stability. Materials Today Chemistry, 2023, 33: 101694. |
| [86] | FAN C, LUO Y, TIAN M, et al. Integrated microsystem toward high-throughput automated green synthesis and Raman enhancement performance screening of noble-metal@Cu-MOF. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(11):2211845. |
| [87] |
HAO N, LIU P, BACHMAN H, et al. Acoustofluidics-assisted engineering of multifunctional three-dimensional zinc oxide nanoarrays. ACS Nano, 2020, 14(5):6150.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | YU Shengyang, SU Haijun, JIANG Hao, YU Minghui, YAO Jiatong, YANG Peixin. A Review of Pore Defects in Ultra-high Temperature Oxide Ceramics by Laser Additive Manufacturing: Formation and Suppression [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(9): 944-956. |
| [2] | LIU Jiangping, GUAN Xin, TANG Zhenjie, ZHU Wenjie, LUO Yongming. Research Progress on Catalytic Oxidation of Nitrogen-containing Volatile Organic Compounds [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(9): 933-943. |
| [3] | XIAO Xiaolin, WANG Yuxiang, GU Peiyang, ZHU Zhenrong, SUN Yong. Advances in Regulation of Damaged Skin Regeneration by Two-dimensional Inorganic Materials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 860-870. |
| [4] | MA Jingge, WU Chengtie. Application of Inorganic Bioceramics in Promoting Hair Follicle Regeneration and Hair Growth [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 901-910. |
| [5] | ZHANG Hongjian, ZHAO Ziyi, WU Chengtie. Inorganic Biomaterials on Regulating Neural Cell Function and Innervated Tissue Regeneration: A Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 849-859. |
| [6] | AI Minhui, LEI Bo. Micro-nanoscale Bioactive Glass: Functionalized Design and Angiogenic Skin Regeneration [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 921-932. |
| [7] | WANG Yutong, CHANG Jiang, XU He, WU Chengtie. Advances in Silicate Bioceramic/Bioglass for Wound Healing: Effects, Mechanisms and Application Ways [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 911-920. |
| [8] | MA Wenping, HAN Yahui, WU Chengtie, LÜ Hongxu. Application of Inorganic Bioactive Materials in Organoid Research [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 888-900. |
| [9] | LUO Xiaomin, QIAO Zhilong, LIU Ying, YANG Chen, CHANG Jiang. Inorganic Bioactive Materials Regulating Myocardial Regeneration [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 871-887. |
| [10] | ZHU Wenjie, TANG Lu, LU Jichang, LIU Jiangping, LUO Yongming. Research Progress on Catalytic Oxidation of Volatile Organic Compounds by Perovskite Oxides [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [11] | HU Zhichao, YANG Hongyu, YANG Hongcheng, SUN Chengli, YANG Jun, LI Enzhu. Usage of the P-V-L Bond Theory in Regulating Properties of Microwave Dielectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [12] | WU Qiong, SHEN Binglin, ZHANG Maohua, YAO Fangzhou, XING Zhipeng, WANG Ke. Research Progress on Lead-based Textured Piezoelectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [13] | ZHANG Bihui, LIU Xiaoqiang, CHEN Xiangming. Recent Progress of Hybrid Improper Ferroelectrics with Ruddlesden-Popper Structure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| [14] | WU Jie, YANG Shuai, WANG Mingwen, LI Jinglei, LI Chunchun, LI Fei. Textured PT-based Piezoelectric Ceramics: Development, Status and Challenge [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 575-586. |
| [15] | JIANG Kun, LI Letian, ZHENG Mupeng, HU Yongming, PAN Qinxue, WU Chaofeng, WANG Ke. Research Progress on Low-temperature Sintering of PZT Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||