
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (6): 627-638.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240513
• REVIEW • Previous Articles Next Articles
JIANG Kun1,5( ), LI Letian1,5, ZHENG Mupeng2(
), LI Letian1,5, ZHENG Mupeng2( ), HU Yongming1(
), HU Yongming1( ), PAN Qinxue3, WU Chaofeng4, WANG Ke5
), PAN Qinxue3, WU Chaofeng4, WANG Ke5
Received:2024-12-10
Revised:2025-02-25
Published:2025-06-20
Online:2025-03-06
Contact:
ZHENG Mupeng, associate professor. E-mail: mpzheng@bjut.edu.cn;About author:JIANG Kun (2000-), male, Master candidate. E-maill: 202321119012904@stu.hubu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
JIANG Kun, LI Letian, ZHENG Mupeng, HU Yongming, PAN Qinxue, WU Chaofeng, WANG Ke. Research Progress on Low-temperature Sintering of PZT Ceramics[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 627-638.
| Material | d33/ (pC•N-1) | kp | Qm | Curie temperature/℃ | tanδ/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PZT-4 | 300 | 0.60 | 600 | 320 | 0.5 |
| PZT-8 | 200 | 0.50 | 1000 | 300 | 0.3 |
| PZT-5 | 400 | 0.60 | 80 | 260 | 2.0 |
| PZT-5H | 700 | 0.70 | 70 | 200 | 2.0 |
Table 1 Electrical properties of commercial PZT ceramics
| Material | d33/ (pC•N-1) | kp | Qm | Curie temperature/℃ | tanδ/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PZT-4 | 300 | 0.60 | 600 | 320 | 0.5 |
| PZT-8 | 200 | 0.50 | 1000 | 300 | 0.3 |
| PZT-5 | 400 | 0.60 | 80 | 260 | 2.0 |
| PZT-5H | 700 | 0.70 | 70 | 200 | 2.0 |
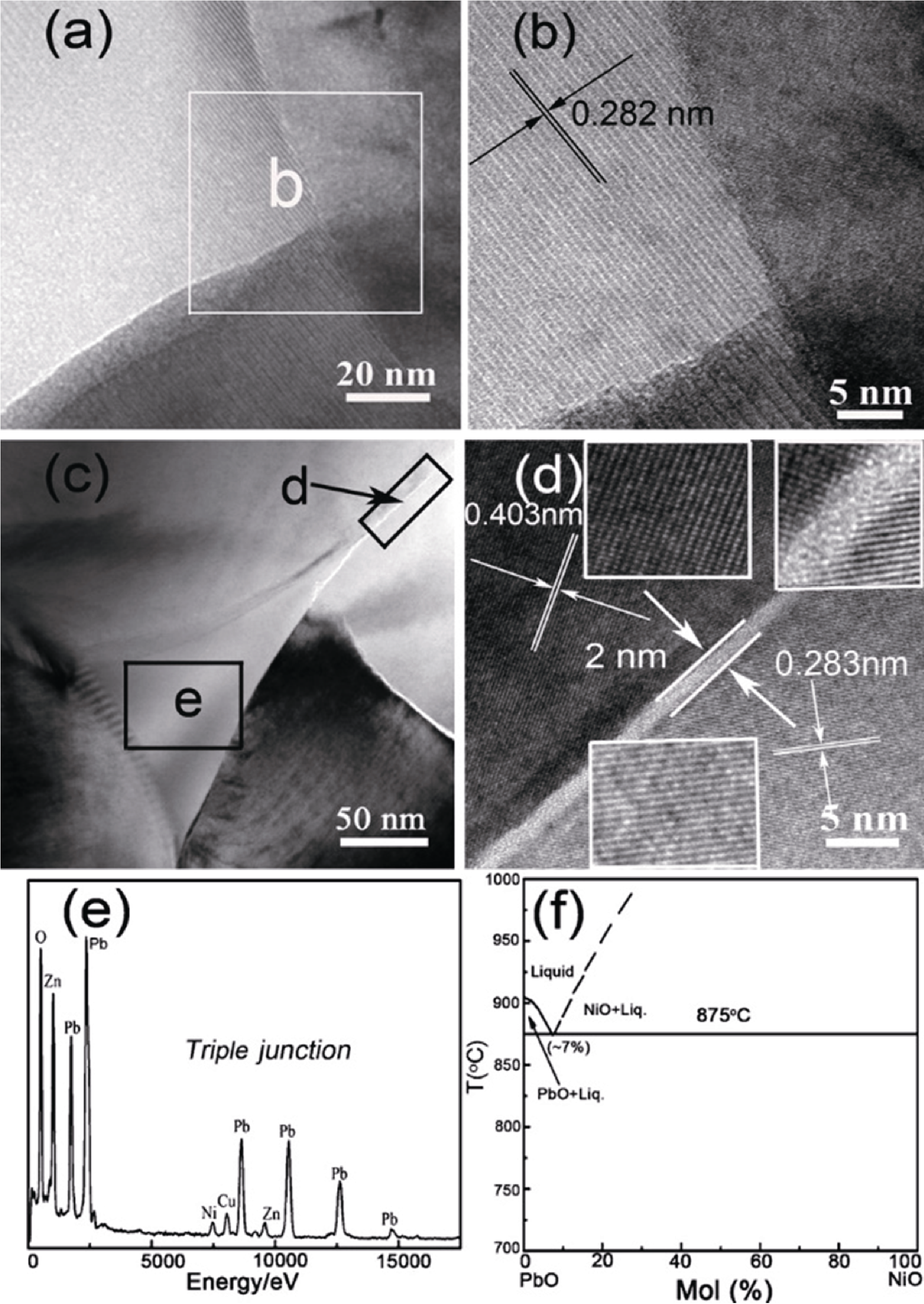
Fig. 6 Microstructure of NiO-doped PZN-PZT ceramics[68] (a) TEM image of pure 0.2PZN-0.8PZT specimen; (b) High resolution TEM (HRTEM) image of the interface region between PZN-PZT grains without NiO addition; (c) TEM image of 1.0% NiO-doped 0.2PZN-0.8PZT specimen; (d) HRTEM image of the interface region between PZT-PZT grains with 1.0% NiO addition; (e) Energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) spectrum of the triple junction of 1.0% NiO-doped 0.2PZN-0.8PZT specimen with the Cu peak indicating the sample holder; (f) Partial phase equilibrium diagram of PbO-NiO system
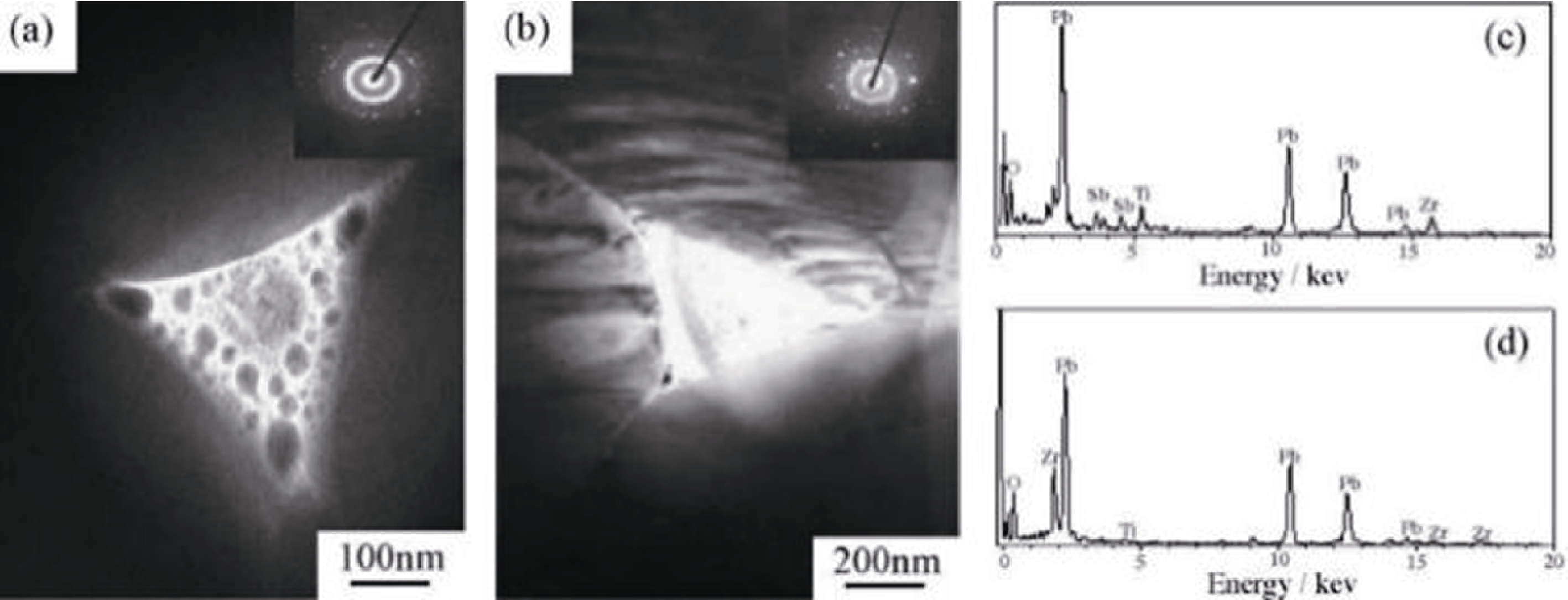
Fig. 7 Charaterizations of grain boundary of PMS-PZT ceramics[71] (a, b) TEM images and selected-area diffraction patterns of grain boundary in ceramics sintered at (a) 1100 and (b) 1260 ℃; (c, d) Energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS) spectra of grain boundary in ceramics sintered at (c) 1100 and (d) 1260 ℃
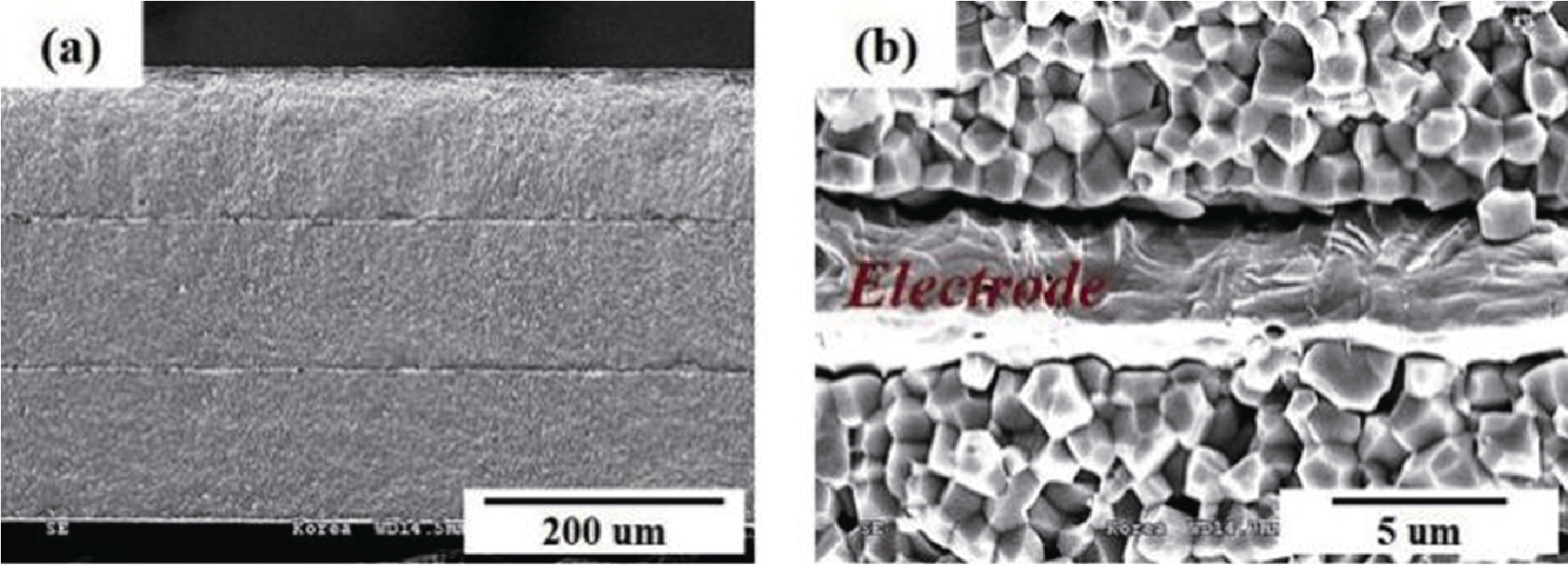
Fig. 8 SEM images of multilayer structure of piezoelectric ceramics[79] (a) Three-layer MLC sintered at 900 ℃; (b) Interface between Ag electrode and ceramic layers
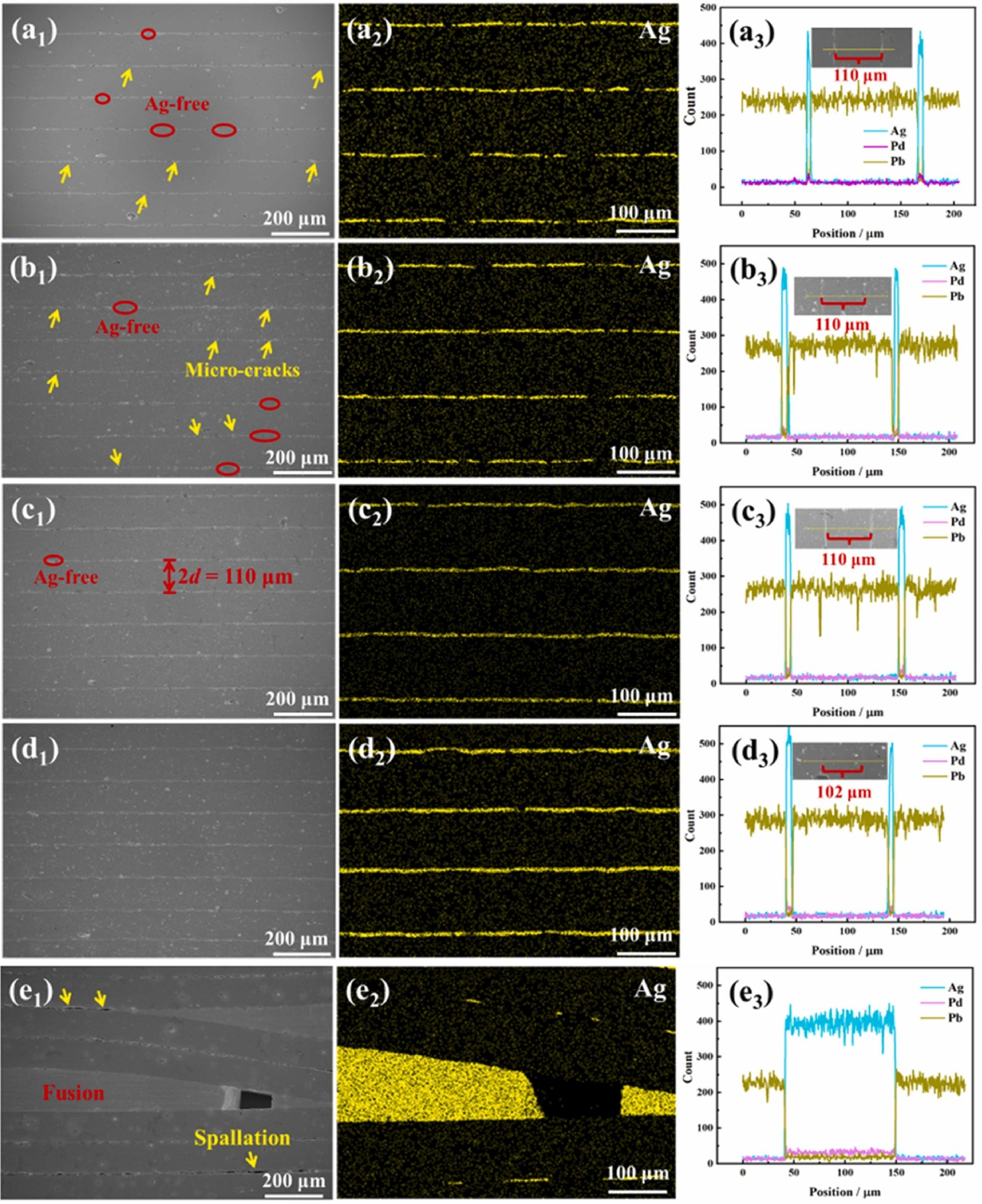
Fig. 9 SEM images and Ag elemental distributions of MLCs co-fired at varying temperatures[80] (a1-a3) 900 ℃; (b1-b3) 920 ℃; (c1-c3) 940 ℃; (d1-d3) 960 ℃; (e1-e3) 980 ℃
| Sintering method | Principle of low-temperature sintering | Sintering temperature/℃ | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPS | Pulse current heating+ pressure | 900-1000 | Low sintering temperature, short sintering time, high dense fine- grained structure | High equipment cost, complicated process |
| HP | Heating+pressure | 1000-1200 | Moderate sintering temperature, short sintering time, excellent electrical property, high density | Complicated equipment, high mold requirements, high cost |
| CSP | Liquid phase sintering+ pressure | 200-400 | Extremely low sintering temperature, short sintering time, simple equipment | High pressure requirement, uneven microstructure, poor mechanical and electrical properties |
| Introducing sintering additives | Formation of solid solution | 950-1100 | Reduced sintering temperature, increased density | Introducing impurities affects electrical properties, high requirements for composition control |
| Liquid phase sintering | 950-1100 | Reduced sintering temperature, increased density | Introducing impurities affects electrical properties, high requirements for composition control | |
| Transient liquid phase sintering | 950-1100 | Reduced sintering temperature, increased density, optimized electrical performance | High requirements for composition control |
Table 2 Comparison of sintering temperature and advantages and disadvantages of PZT ceramics prepared by different sintering techniques
| Sintering method | Principle of low-temperature sintering | Sintering temperature/℃ | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPS | Pulse current heating+ pressure | 900-1000 | Low sintering temperature, short sintering time, high dense fine- grained structure | High equipment cost, complicated process |
| HP | Heating+pressure | 1000-1200 | Moderate sintering temperature, short sintering time, excellent electrical property, high density | Complicated equipment, high mold requirements, high cost |
| CSP | Liquid phase sintering+ pressure | 200-400 | Extremely low sintering temperature, short sintering time, simple equipment | High pressure requirement, uneven microstructure, poor mechanical and electrical properties |
| Introducing sintering additives | Formation of solid solution | 950-1100 | Reduced sintering temperature, increased density | Introducing impurities affects electrical properties, high requirements for composition control |
| Liquid phase sintering | 950-1100 | Reduced sintering temperature, increased density | Introducing impurities affects electrical properties, high requirements for composition control | |
| Transient liquid phase sintering | 950-1100 | Reduced sintering temperature, increased density, optimized electrical performance | High requirements for composition control |
| [1] | HAO J G, LI W, ZHAI J W, et al. Progress in high-strain perovskite piezoelectric ceramics. Materials Science and Engineering: R: Reports, 2019, 135: 1. |
| [2] | ZHENG T, WU J G, XIAO D Q, et al. Recent development in lead-free perovskite piezoelectric bulk materials. Progress in Materials Science, 2018, 98: 552. |
| [3] | CHEN L, LIU H, QI H, et al. High-electromechanical performance for high-power piezoelectric applications: fundamental, progress, and perspective. Progress in Materials Science, 2022, 127: 100944. |
| [4] | DONG Y Z, ZOU K, LIANG R H, et al. Review of BiScO3-PbTiO3 piezoelectric materials for high temperature applications: fundamental, progress, and perspective. Progress in Materials Science, 2023, 132: 101026. |
| [5] | WANG B, LIU W, ZHAO T L, et al. Promising lead-free BiFeO3-BaTiO3 ferroelectric ceramics: optimization strategies and diverse device applications. Progress in Materials Science, 2024, 146: 101333. |
| [6] | JAFFE B, ROTH R S, MARZULLO S. Piezoelectric properties of lead zirconate-lead titanate solid-solution ceramics. Journal of Applied Physics, 1954, 25(6): 809. |
| [7] | JAFFE B, ROTH R S, MARZULLO S. Properties of piezoelectric ceramics in the solid-solution series lead titanate-lead zirconate- lead oxide: tin oxide and lead titanate-lead hafnate. Journal of Research of the National Bureau of Standards, 1955, 55(5): 239. |
| [8] | 北京恒州博智国际信息咨询有限公司.2024—2030年全球与中国压电陶瓷行业调研及趋势分析报告: 3889852, 北京: 北京恒州博智国际信息咨询有限公司, 2024: 122. |
| [9] | KINGON A I, CLARK J B. Sintering of PZT ceramics: II, effect of PbO content on densification kinetics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1983, 66(4): 256. |
| [10] | RYU J, CHOI J J, KIM H E. Effect of heating rate on the sintering behavior and the piezoelectric properties of lead zirconate titanate ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2001, 84(4): 902. |
| [11] | FAN H Q, KIM H E. Effect of lead content on the structure and electrical properties of Pb((Zn1/3Nb2/3)0.5(Zr0.47Ti0.53)0.5)O3 ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2001, 84(3): 636. |
| [12] | HOU Y D, ZHU M K, WANG H, et al. Effects of atmospheric powder on microstructure and piezoelectric properties of PMZN-PZT quaternary ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2004, 24(15/16): 3731. |
| [13] | KONG L B, MA J, HUANG H, et al. Effect of excess PbO on microstructure and electrical properties of PLZT7/60/40 ceramics derived from a high-energy ball milling process. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2002, 345(1/2): 238. |
| [14] | JAFFE B, COOK W R, JAFFE H. The piezoelectric effect in ceramics// JAFFE B, COOK W R, JAFFE H. Piezoelectric ceramics. New York: Elsevier, 1971: 7-21. |
| [15] | SOARES M R, SENOS A M R, MANTAS P Q. Phase coexistence region and dielectric properties of PZT ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2000, 20(3): 321. |
| [16] |
GUO R, CROSS L E, PARK S E, et al. Origin of the high piezoelectric response in PbZr1-xTixO3. Physical Review Letters, 2000, 84(23): 5423.
PMID |
| [17] | GENG W P, LIU Y, MENG X J, et al. Giant negative electrocaloric effect in antiferroelectric La-doped Pb(ZrTi)O3 thin films near room temperature. Advanced Materials, 2015, 27(20): 3165. |
| [18] | BABU T A, RAMESH K V, BADAPANDA T, et al. Structural and electrical studies of excessively Sm2O3 substituted soft PZT nanoceramics. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(22): 31294. |
| [19] | YAN S H, SUN C C, CUI Q Y, et al. Dielectric, piezoelectric and DC bias characteristics of Bi-doped PZT multilayer ceramic actuator. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2020, 255: 123605. |
| [20] | ZHAO C H, HOU D, CHUNG C C, et al. Deconvolved intrinsic and extrinsic contributions to electrostrain in high performance, Nb-doped Pb(ZrxTi1-x)O3 piezoceramics (0.50≤x≤0.56). Acta Materialia, 2018, 158: 369. |
| [21] | LI Q, WANG X, WANG F A, et al. Effect of neodymium substitution on crystalline orientation, microstructure and electric properties of Sol-Gel derived PZT thin films. Ceramics International, 2018, 44(7): 7709. |
| [22] | GUPTA A K, SIL A. Dielectric and energy storage characteristics of 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8 wt% Cr2O3 doped PbZr0.52Ti0.48O3 ceramics synthesized by spark plasma sintering. Materials Science and Engineering: B, 2022, 281: 115738. |
| [23] | THAKRE A, KUMAR A, JEONG D Y, et al. Enhanced mechanical quality factor of 32 mode Mn doped 71Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3- 29PbZrTiO3 piezoelectric single crystals. Electronic Materials Letters, 2020, 16(2): 156. |
| [24] | LI L L, LIU J T, XU J, et al. Effect of MnO2 on the microstructure and electrical properties of 0.83Pb(Zr0.5Ti0.5)O3-0.11Pb(Zn1/3Nb2/3)O3- 0.06Pb(Ni1/3Nb2/3)O3 piezoelectric ceramics. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(1): 180. |
| [25] | BIESUZ M, GRASSO S, SGLAVO V M. What’s new in ceramics sintering? A short report on the latest trends and future prospects. Current Opinion in Solid State and Materials Science, 2020, 24(5): 100868. |
| [26] | TAKAHASHI S. Sintering Pb(Zr,Ti)O3 ceramics at low temperature. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 1980, 19(4): 771. |
| [27] | LI L T, DENG W T, CHAI J H, et al. Lead zirconate titanate ceramics and monolithic piezoelectric transformer of low firing temperature. Ferroelectrics, 1990, 101(1): 193. |
| [28] | ZHENG M P, HOU Y D, YAN X D, et al. A highly dense structure boosts energy harvesting and cycling reliabilities of a high- performance lead-free energy harvester. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2017, 5(31): 7862. |
| [29] | LI C C, YIN C Z, KHALIQ J, et al. Ultralow-temperature synthesis and densification of Ag2CaV4O12 with improved microwave dielectric performances. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2021, 9(43): 14461. |
| [30] | LIU J, SHEN Z J, NYGREN M, et al. SPS processing of bismuth-layer structured ferroelectric ceramics yielding highly textured microstructures. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2006, 26(15): 3233. |
| [31] | ZHANG S P, WANG X H, WANG H, et al. Grain boundary region and local piezoelectric response of BiScO3-PbTiO3 nanoceramics prepared by combination of SPS and two-step sintering. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2014, 34(10): 2317. |
| [32] | NIEMIEC P, BOCHENEK D, BRZEZIŃSKA D. Effect of various sintering methods on the properties of PZT-type ceramics. Ceramics International, 2023, 49(22): 35687. |
| [33] | AMORÍN H, RICOTE J, JIMÉNEZ R, et al. Submicron and nanostructured 0.8Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-0.2PbTiO3 ceramics by hot pressing of nanocrystalline powders. Scripta Materialia, 2008, 58(9): 755. |
| [34] | BRZEZIŃSKA D, BOCHENEK D, ZUBKO M, et al. Properties of Sn-doped PBZT ferroelectric ceramics sintered by hot-pressing method. Materials, 2024, 17(20): 5072. |
| [35] | DENG B Y, MA Y M, CHEN T X, et al. Elevating electrical properties of (K, Na)NbO3 ceramics via cold sintering process and post-annealing. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2022, 105(1): 461. |
| [36] | GALOTTA A, SGLAVO V M. The cold sintering process: a review on processing features, densification mechanisms and perspectives. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(16): 1. |
| [37] | SI M M, HAO J Y, ZHAO E D, et al. Preparation of zinc oxide/poly-ether-ether-ketone (PEEK) composites via the cold sintering process. Acta Materialia, 2021, 215: 117036. |
| [38] | JIA Y J, SU X H, WU Y J, et al. Fabrication of lead zirconate titanate ceramics by reaction flash sintering of PbO-ZrO2-TiO2 mixed oxides. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(13): 3915. |
| [39] | ARYA K S, SINGH R P, CHAKRABARTI T. Novel liquid-phase flash sintering of lead zirconate titanate piezo-ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2024, 107(12): 8007. |
| [40] | ARYA K S, KALYANI A K, CHAKRABARTI T. Flash sintering of lead zirconate titanate (PZT) with minimal lead oxide loss and enhanced dielectric properties. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2024, 44(5): 2797. |
| [41] | CHENG L Q, XU Z, THONG H C, et al. Influence of spark plasma sintering temperature on piezoelectric properties of PZT-PMnN piezoelectric ceramics. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2019, 30(6): 5691. |
| [42] | CHENG L Q, XU Z, ZHAO C L, et al. Significantly improved piezoelectric performance of PZT-PMnN ceramics prepared by spark plasma sintering. RSC Advances, 2018, 8(62): 35594. |
| [43] |
LIU K, WANG W, LIU Q, et al. Photostriction properties of PLZT (4/52/48) ceramics sintered by SPS. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(2): 2097.
DOI |
| [44] | HAERTLING G H, LAND C E. Hot-pressed (Pb, La)(Zr, Ti)O3 ferroelectric ceramics for electrooptic applications. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1971, 54(1): 1. |
| [45] | GUO H Z, BAKER A, GUO J, et al. Cold sintering process: a novel technique for low-temperature ceramic processing of ferroelectrics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2016, 99(11): 3489. |
| [46] | GUO D J, GUO D H, BAKER A L, et al. Cold sintering: a paradigm shift for processing and integration of ceramics. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2016, 55(38): 11457. |
| [47] | YANG C, LI J P, SHI H F, et al. Effects of the liquid phase content on the microstructure and properties of the ZrW2O8 ceramics with negative thermal expansion fabricated by the cold sintering process. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(15): 6079. |
| [48] | HÉRISSON DE BEAUVOIR T, TSUJI K, ZHAO X T, et al. Cold sintering of ZnO-PTFE: utilizing polymer phase to promote ceramic anisotropic grain growth. Acta Materialia, 2020, 186: 511. |
| [49] | LI Y Q, ZHENG M P, ZHU M K, et al. Microwave dielectric properties and low-temperature sintering mechanism in (Ca, Bi)(Mo, V)O4 ceramics. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 889: 161644. |
| [50] | LI Y Q, ZHENG M P, ZANG M Y, et al. Cold sintering co-firing of (Ca, Bi)(Mo, V)O4-PTFE composites in a single step. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2022, 105(10): 6262. |
| [51] | TSUJI K, FAN Z M, BANG S H, et al. Cold sintering of the ceramic potassium sodium niobate, (K0.5Na0.5)NbO3, and influences on piezoelectric properties. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2022, 42(1): 105. |
| [52] | WANG D X, DURSUN S, GAO L S, et al. Fabrication of bimorph lead zirconate titanate thick films on metal substrates via the cold sintering-assisted process. Acta Materialia, 2020, 195: 482. |
| [53] | WANG D X, GUO H Z, MORANDI C S, et al. Cold sintering and electrical characterization of lead zirconate titanate piezoelectric ceramics. APL Materials, 2018, 6(1): 016101. |
| [54] | NIU L, HAN X T, WANG H T, et al. Flash sintering of lead zirconate titanate ceramics under high voltage at room temperature. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2024, 44(10): 6169. |
| [55] | KAMIYA T, SUZUKI T, TSURUMI T, et al. Effects of manganese addition on piezoelectric properties of Pb(Zr0.5Ti0.5)O3. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 1992, 31(9S): 3058. |
| [56] | WANG H H, MA M, XIA S, et al. Giant piezoelectric properties of the [110]-oriented PZT-5H single crystals grown by solid state crystal growth. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2023, 11(7): 2664. |
| [57] | GAO X Y, JIN H N, XIN B J, et al. Low temperature sintering of Li2CO3 added Pb(Ni1/3Nb2/3)-Pb(Zr,Ti)O3 ceramics with high piezoelectric properties. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2022, 892: 162132. |
| [58] | SANGAWAR S R, PRAVEENKUMAR B. Structural and electrical properties of low temperature sintered PZT ceramics. Ferroelectrics, 2017, 517(1): 66. |
| [59] | CORKER D L, WHATMORE R W, RINGGAARD E, et al. Liquid-phase sintering of PZT ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2000, 20(12): 2039. |
| [60] | KIM B S, JI J H, KOH J H. Improved strain and transduction values of low-temperature sintered CuO-doped PZT-PZNN soft piezoelectric materials for energy harvester applications. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(5): 6683. |
| [61] | OUCHI H, NAGANO K, HAYAKAWA S. Piezoelectric properties of Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-PbTiO3-PbZrO3 solid solution ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1965, 48(12): 630. |
| [62] | 侯育冬, 郑木鹏. 压电陶瓷掺杂调控. 北京: 科学出版社, 2018. |
| [63] | ZHANG J B, LIU H, SUN S D, et al. Crystal structure and actuation mechanisms in morphotropic phase boundary Pb(Zn1/3Nb2/3)O3-Pb(Zr1/2Ti1/2)O3 piezoelectric ceramic. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2021, 104(6): 2621. |
| [64] | CHANG L M, HOU Y D, ZHU M K, et al. Effect of sintering temperature on the phase transition and dielectrical response in the relaxor-ferroelectric-system 0.5PZN-0.5PZT. Journal of Applied Physics, 2007, 101(3): 034101. |
| [65] | ZHENG M P, HOU Y, ZHU M K, et al. Shift of morphotropic phase boundary in high-performance fine-grained PZN-PZT ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2014, 34(10): 2275. |
| [66] | SEO S B, LEE S H, YOON C B, et al. Low-temperature sintering and piezoelectric properties of 0.6Pb(Zr0.47Ti0.53)O3·0.4Pb(Zn1/3Nb2/3)O3 ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2004, 87(7): 1238. |
| [67] | HOU Y D, CHANG L M, ZHU M K, et al. Effect of Li2CO3 addition on the dielectric and piezoelectric responses in the low-temperature sintered 0.5PZN-0.5PZT systems. Journal of Applied Physics, 2007, 102(8): 084507. |
| [68] | ZHENG M P, HOU Y D, GE H Y, et al. Effect of NiO additive on microstructure, mechanical behavior and electrical properties of 0.2PZN-0.8PZT ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2013, 33(8): 1447. |
| [69] | ZHENG M P, HOU Y D, GE H Y, et al. The formation of (Zn, Ni)TiO3 secondary phase in NiO-modified Pb(Zn1/3Nb2/3)O3- PbZrO3-PbTiO3 ceramics. Scripta Materialia, 2013, 68(9): 707. |
| [70] | YOO J, LEE C, JEONG Y, et al. Microstructural and piezoelectric properties of low temperature sintering PMN-PZT ceramics with the amount of Li2CO3 addition. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2005, 90(2/3): 386. |
| [71] | ZHU Z G, LI B S, LI G R, et al. Microstructure and piezoelectric properties of PMS-PZT ceramics. Materials Science and Engineering: B, 2005, 117(2): 216. |
| [72] | LI S, FU J, ZUO R Z. Middle-low temperature sintering and piezoelectric properties of CuO and Bi2O3 doped PMS-PZT based ceramics for ultrasonic motors. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(14): 20117. |
| [73] | LI J P, HUANG H, MORITA T. Stepping piezoelectric actuators with large working stroke for nano-positioning systems: a review. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 2019, 292: 39. |
| [74] | TAMBURRANO P, SCIATTI F, PLUMMER A R, et al. A review of novel architectures of servovalves driven by piezoelectric actuators. Energies, 2021, 14(16): 4858. |
| [75] | GAO X Y, YANG J K, WU J G, et al. Piezoelectric actuators and motors: materials, designs, and applications. Advanced Materials Technologies, 2020, 5(1): 1900716. |
| [76] |
AABID A, HRAIRI M, ALI S J M, et al. Review of piezoelectric actuator applications in damaged structures: challenges and opportunities. ACS Omega, 2023, 8(3): 2844.
DOI PMID |
| [77] | CHEN J Y, TEO E H T, YAO K. Electromechanical actuators for haptic feedback with fingertip contact. Actuators, 2023, 12(3): 104. |
| [78] | MA X F, LIU J K, ZHANG S J, et al. Recent trends in bionic stepping piezoelectric actuators for precision positioning: a review. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 2023, 364: 114830. |
| [79] | SEO I T, LEE T G, KIM D H, et al. Multilayer piezoelectric haptic actuator with CuO-modified PZT-PZNN ceramics. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 2016, 238: 71. |
| [80] | ZHANG J, CHEN Y J, GUO Y X, et al. Low-temperature co-fired PNN-PZT-based multilayer piezoelectric actuator with low cost and high reliability. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2024, 44(15): 116744. |
| [1] | YU Shengyang, SU Haijun, JIANG Hao, YU Minghui, YAO Jiatong, YANG Peixin. A Review of Pore Defects in Ultra-high Temperature Oxide Ceramics by Laser Additive Manufacturing: Formation and Suppression [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(9): 944-956. |
| [2] | LIU Jiangping, GUAN Xin, TANG Zhenjie, ZHU Wenjie, LUO Yongming. Research Progress on Catalytic Oxidation of Nitrogen-containing Volatile Organic Compounds [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(9): 933-943. |
| [3] | XIAO Xiaolin, WANG Yuxiang, GU Peiyang, ZHU Zhenrong, SUN Yong. Advances in Regulation of Damaged Skin Regeneration by Two-dimensional Inorganic Materials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 860-870. |
| [4] | MA Jingge, WU Chengtie. Application of Inorganic Bioceramics in Promoting Hair Follicle Regeneration and Hair Growth [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 901-910. |
| [5] | ZHANG Hongjian, ZHAO Ziyi, WU Chengtie. Inorganic Biomaterials on Regulating Neural Cell Function and Innervated Tissue Regeneration: A Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 849-859. |
| [6] | AI Minhui, LEI Bo. Micro-nanoscale Bioactive Glass: Functionalized Design and Angiogenic Skin Regeneration [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 921-932. |
| [7] | WANG Yutong, CHANG Jiang, XU He, WU Chengtie. Advances in Silicate Bioceramic/Bioglass for Wound Healing: Effects, Mechanisms and Application Ways [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 911-920. |
| [8] | MA Wenping, HAN Yahui, WU Chengtie, LÜ Hongxu. Application of Inorganic Bioactive Materials in Organoid Research [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 888-900. |
| [9] | LUO Xiaomin, QIAO Zhilong, LIU Ying, YANG Chen, CHANG Jiang. Inorganic Bioactive Materials Regulating Myocardial Regeneration [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 871-887. |
| [10] | ZHU Wenjie, TANG Lu, LU Jichang, LIU Jiangping, LUO Yongming. Research Progress on Catalytic Oxidation of Volatile Organic Compounds by Perovskite Oxides [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [11] | CHEN Xiangjie, LI Ling, LEI Tianfu, WANG Jiajia, WANG Yaojin. Enhanced Piezoelectric Properties of (1-x)(0.8PZT-0.2PZN)-xBZT Ceramics via Phase Boundary and Domain Engineering [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 729-734. |
| [12] | HU Zhichao, YANG Hongyu, YANG Hongcheng, SUN Chengli, YANG Jun, LI Enzhu. Usage of the P-V-L Bond Theory in Regulating Properties of Microwave Dielectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [13] | ZHANG Jiawei, CHEN Ning, CHENG Yuan, WANG Bo, ZHU Jianguo, JIN Cheng. Electrical Properties of Bismuth Layered Piezoelectric Bi4Ti3O12 Ceramics with A/B-site Doping [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 690-696. |
| [14] | WU Qiong, SHEN Binglin, ZHANG Maohua, YAO Fangzhou, XING Zhipeng, WANG Ke. Research Progress on Lead-based Textured Piezoelectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [15] | ZHANG Bihui, LIU Xiaoqiang, CHEN Xiangming. Recent Progress of Hybrid Improper Ferroelectrics with Ruddlesden-Popper Structure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||