
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2020, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (6): 647-653.DOI: 10.15541/jim20190307
• REVIEW • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHENG Yun1,2,CHEN Yilin1,GAO Bifen1,LIN Bizhou1
Received:2019-06-24
Revised:2019-08-23
Published:2020-06-20
Online:2019-09-18
Supported by:CLC Number:
ZHENG Yun,CHEN Yilin,GAO Bifen,LIN Bizhou. Progress on Phosphorene for Photocatalytic Water Splitting[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(6): 647-653.
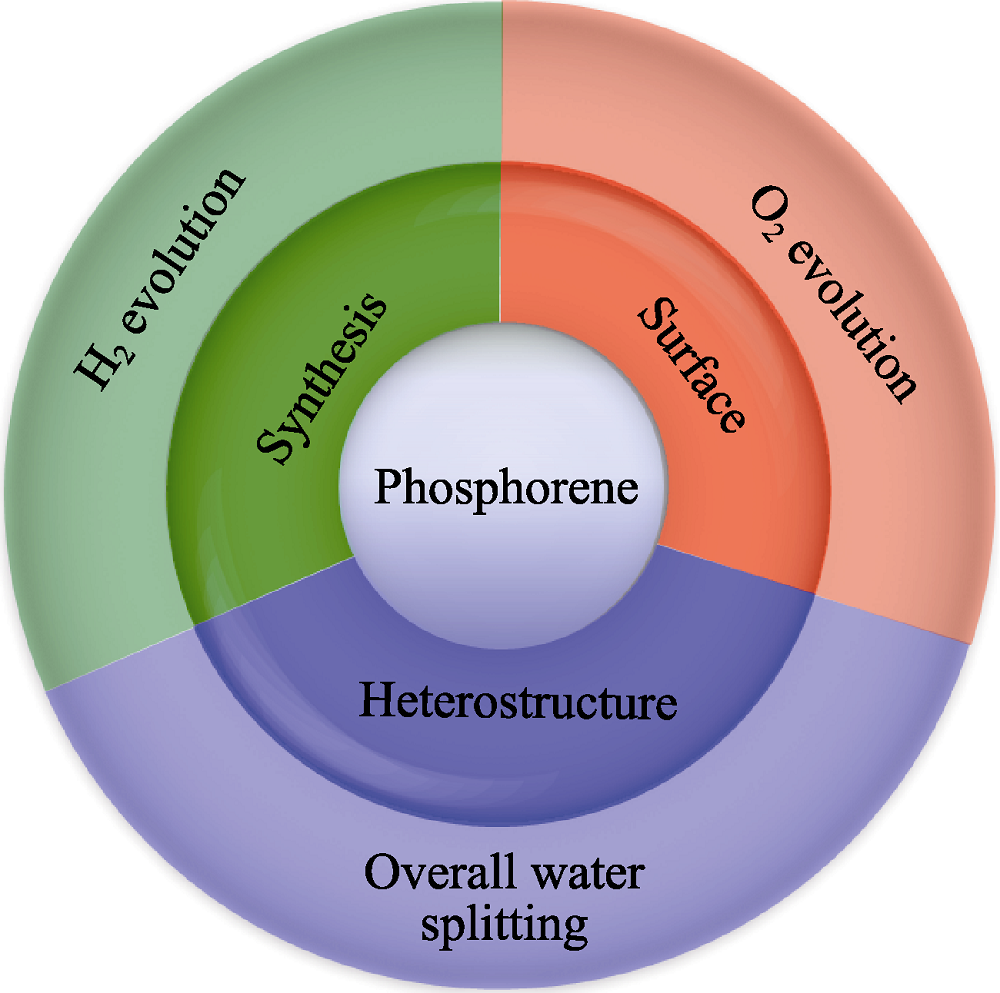
Fig. 1 Synthesis, surface modification and heterostructure design of phosphorene-based photocatalysts for half-reactions and overall reactions of water splitting
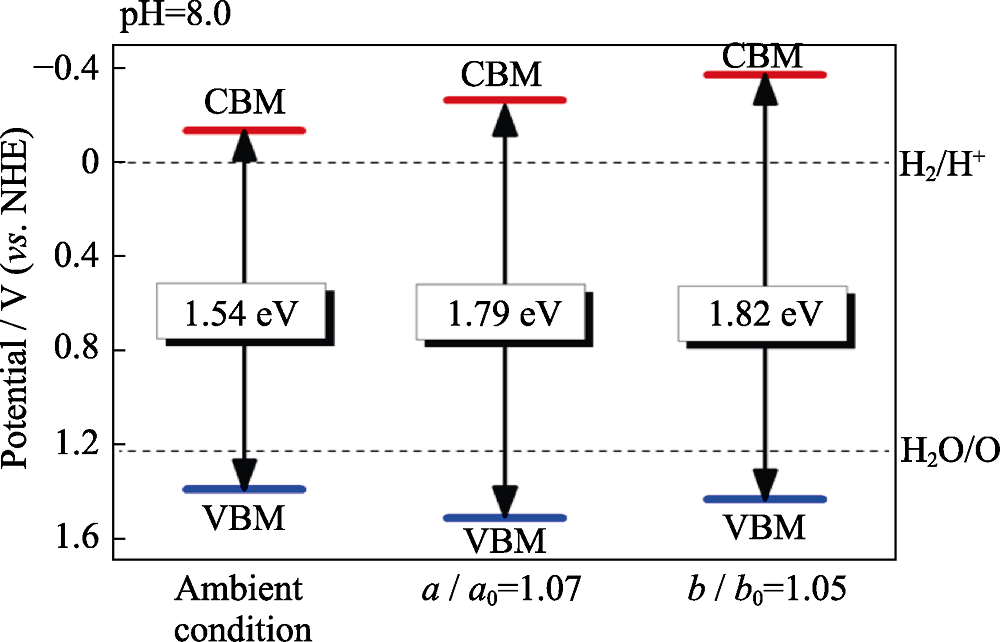
Fig. 2 Band edge alignments of phosphorene at ambient condition, under 7% tensile strain along a axis and 5% tensile strain along b axis when pH=8.0[13]
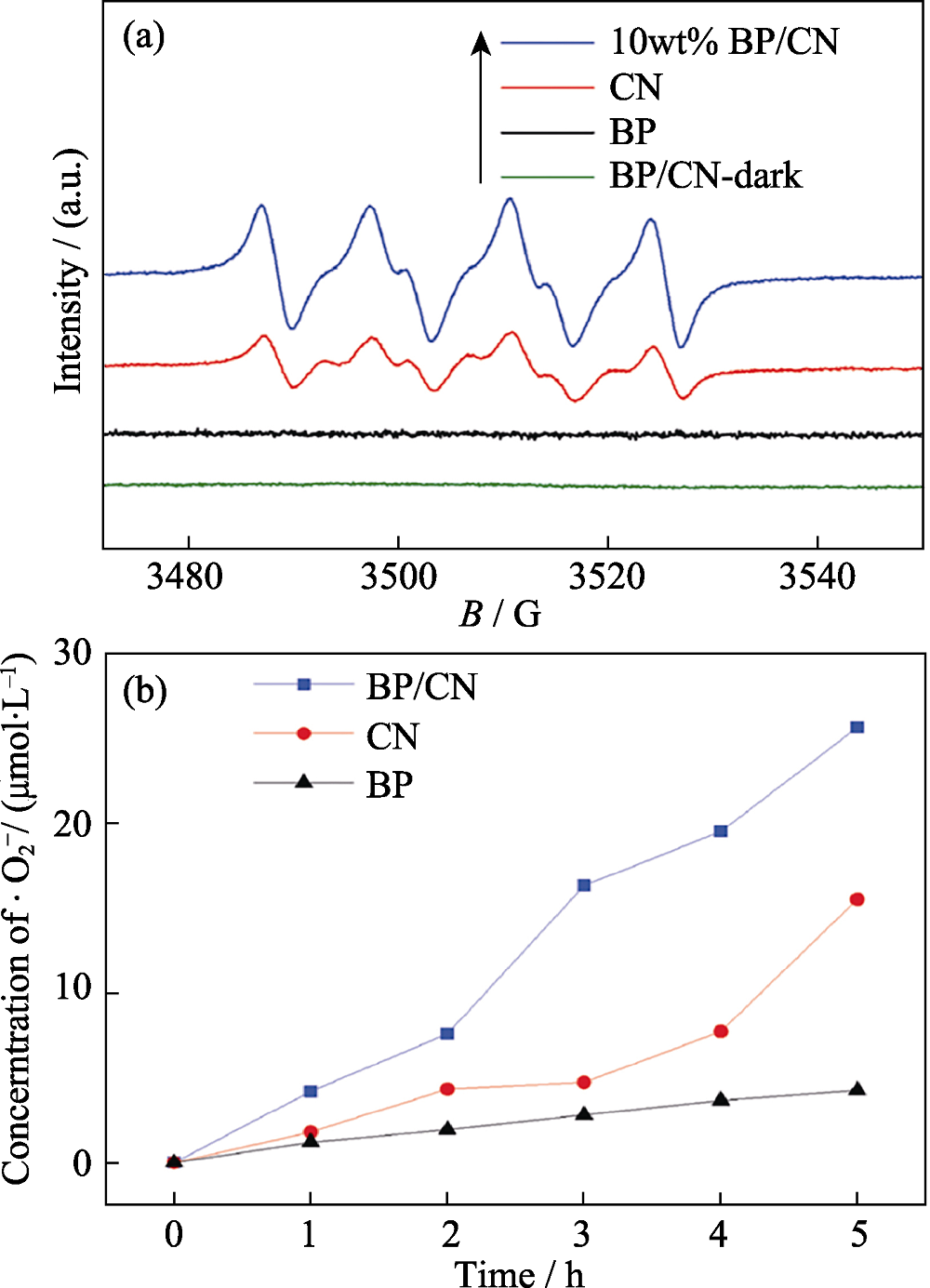
Fig. 9 (a) Electron spin resonance spectra of ·O2- radicals over BP/CN hybrid with visible-light irradiation, and (b) time-dependent degradation of nitroblue tetrazolium solution to detect ·O2- evolution over BP/CN hybrid under visible-light irradiation[46]
| [1] |
FUJISHIMA A, HONDA K . Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode. Nature, 1972,238(5358):37-38.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
ZHENG D, ZHANG G, WANG X . Integrating CdS quantum dots on hollow graphitic carbon nitride nanospheres for hydrogen evolution photocatalysis. Appl. Catal. B-Environ, 2015,179:479-488.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
LU Q, HUA L, CHEN Y , et al. Preparation and property of oxygen- deficient Bi2WO6-x photocatalyst active in visible light. J. Inorg. Mater., 2015,30(4):413-419.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
WAN J, HU D, LU P , et al. Preparation of anatase TiO2 nanocube with exposed (001) facet and its photocatalytic properties. J. Inorg. Mater., 2016,31(8):845-849.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
YI Z, YE J, KIKUGAWA N , et al. An orthophosphate semiconductor with photooxidation properties under visible-light irradiation. Nat. Mater., 2010,9:559.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
WANG X, MAEDA K, THOMAS A , et al. A metal-free polymeric photocatalyst for hydrogen production from water under visible light. Nat. Mater., 2008,8:76.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
BAI Y, WILBRAHAM L, SLATER B J , et al. Accelerated discovery of organic polymer photocatalysts for hydrogen evolution from water through the integration of experiment and theory. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019,141(22):9063-9071.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
ZHAO C, CHEN Z, XU J , et al. Probing supramolecular assembly and charge carrier dynamics toward enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen evolution in 2D graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets. Appl. Catal. B-Environ, 2019,256:117867.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
YANG X, TIAN L, ZHAO X , et al. Interfacial optimization of g- C3N4-based Z-scheme heterojunction toward synergistic enhancement of solar-driven photocatalytic oxygen evolution. Appl. Catal. B-Environ, 2019,244:240-249.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
LI J, LI H, ZHAN G , et al. Solar water splitting and nitrogen fixation with layered bismuth oxyhalides. Acc. Chem. Res., 2017,50(1):112-121.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
LI B, LAI C, ZENG G , et al. Black phosphorus, a rising star 2D nanomaterial in the post-graphene era: synthesis, properties, modifications, and photocatalysis applications. Small, 2019,15(8):1804565.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
YAN J, VERMA P, KUWAHARA Y , et al. Recent progress on black phosphorus-based materials for photocatalytic water splitting. Small Methods, 2018,2(12):1800212.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
SA B, LI Y L, QI J , et al. Strain engineering for phosphorene: the potential application as a photocatalyst. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2014,118(46):26560-26568.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
RAHMAN MZ, BATMUNKH M, BAT-ERDENE M , et al. p-type BP nanosheet photocatalyst with AQE of 3.9% in the absence of a noble metal cocatalyst: investigation and elucidation of photophysical properties. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2018,6(38):18403-18408.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
ZHU X, ZHANG T, SUN Z , et al. Black phosphorus revisited: a missing metal-free elemental photocatalyst for visible light hydrogen evolution. Adv. Mater., 2017,29(17):1605776.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
TIAN B, TIAN B, SMITH B , et al. Facile bottom-up synthesis of partially oxidized black phosphorus nanosheets as metal-free photocatalyst for hydrogen evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 2018,115(17):4345-4350.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
ZHAO G, WANG T, SHAO Y , et al. A novel mild phase-transition to prepare black phosphorus nanosheets with excellent energy applications. Small, 2017,13(7):1602243.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
ZHU M, ZHAI C, FUJITSUKA M , et al. Noble metal-free near- infrared-driven photocatalyst for hydrogen production based on 2D hybrid of black phosphorus/WS2. Appl. Catal. B-Environ, 2018,221:645-651.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
YUAN Y J, WANG P, LI Z , et al. The role of bandgap and interface in enhancing photocatalytic H2 generation activity of 2D-2D black phosphorus/MoS2 photocatalyst. Appl. Catal. B-Environ, 2019,242:1-8.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
TIAN B, TIAN B, SMITH B , et al. Supported black phosphorus nanosheets as hydrogen-evolving photocatalyst achieving 5.4% energy conversion efficiency at 353 K. Nat. Commun., 2018,9:1397.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
LIANG Q, SHI F, XIAO X , et al. In situ growth of CoP nanoparticles anchored on black phosphorus nanosheets for enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen production. ChemCatChem, 2018,10(10):2179-2183.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
VISHNOI P, GUPTA U, PANDEY R , et al. Stable functionalized phosphorenes with photocatalytic HER activity. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2019,7(12):6631-6637.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
WU J, HUANG S, JIN Z , et al. Black phosphorus: an efficient co- catalyst for charge separation and enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. J. Mater. Sci., 2018,53(24):16557-16566.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
ELBANNA O, ZHU M, FUJITSUKA M , et al. Black phosphorus sensitized TiO2 mesocrystal photocatalyst for hydrogen evolution with visible and near-infrared light irradiation. ACS Catal., 2019,9(4):3618-3626.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
ZHAO H, LIU H, SUN R , et al. A Zn0.5Cd0.5S photocatalyst modified by 2D black phosphorus for efficient hydrogen evolution from water. ChemCatChem, 2018,10(19):4395-4405.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
ZHENG Y, LIN L, YE X , et al. Helical graphitic carbon nitrides with photocatalytic and optical activities. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2014,53(44):11926-11930.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
ZHENG Y, LIN L, WANG B , et al. Graphitic carbon nitride polymers toward sustainable photoredox catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2015,54(44):12868-12884.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
ZHENG Y, YU Z, LIN F , et al. Sulfur-doped carbon nitride polymers for photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutant and reduction of Cr(VI). Molecules, 2017,22(4):572.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
ZHU M, KIM S, MAO L , et al. Metal-free photocatalyst for H2 evolution in visible to near-infrared region: black phosphorus/graphitic carbon nitride. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017,139(37):13234-13242.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
WEN M, WANG J, TONG R , et al. A low-cost metal-free photocatalyst based on black phosphorus. Adv. Sci., 2019,6(1):1801321.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
RAN J R, GUO W W, WANG H L , et al. Metal-free 2D/2D phosphorene/g-C3N4 van der Waals heterojunction for highly enhanced visible-light photocatalytic H2 production. Adv. Mater., 2018,30(25):1800128.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
DU H, LIU Y, SHEN C , et al. Nanoheterostructured photocatalysts for improving photocatalytic hydrogen production. Chin. J. Catal., 2017,38(8):1295-1306.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
LEI W, MI Y, FENG R , et al. Hybrid 0D-2D black phosphorus quantum dots-graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets for efficient hydrogen evolution. Nano Energy, 2018,50:552-561.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
RAN J, ZHU B, QIAO S Z . Phosphorene co-catalyst advancing highly efficient visible-light photocatalytic hydrogen production. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2017,56(35):10373-10377.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
HU J, CHEN D , MO Z et al. Z-scheme 2D/2D heterojunction of black phosphorus/monolayer Bi2WO6 nanosheets with enhanced photocatalytic activities. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2019,58(7):2073-2077.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
ZHANG Y, WANG L, PARK S H , et al. Single near-infrared-laser driven Z-scheme photocatalytic H2 evolution on upconversion material@Ag3PO4@black phosphorus. Chem. Eng. J., 2019,375:121967.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
ZHU M, OSAKADA Y, KIM S , et al. Black phosphorus: a promising two dimensional visible and near-infrared-activated photocatalyst for hydrogen evolution. Appl. Catal. B-Environ, 2017,217:285-292.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
ZHU M, FUJITSUKA M, ZENG L , et al. Dual function of graphene oxide for assisted exfoliation of black phosphorus and electron shuttle in promoting visible and near-infrared photocatalytic H2 evolution. Appl. Catal. B-Environ, 2019,256:117864.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
ZHU M, CAI X, FUJITSUKA M , et al. Au/La2Ti2O7 nanostructures sensitized with black phosphorus for plasmon-enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen production in visible and near-infrared light. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2017,56(8):2064-2068.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
RAN J, WANG X, ZHU B , et al. Strongly interactive 0D/2D heterostructure of a ZnxCd1-xS nanoparticle decorated phosphorene nanosheet for enhanced visible-light photocatalytic H2 production. Chem. Commun., 2017,53(71):9882-9885.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
REDDY DA, KIM E H, GOPANNAGARI M , et al. Few layered black phosphorus/MoS2 nanohybrid: a promising co-catalyst for solar driven hydrogen evolution. Appl. Catal. B-Environ, 2019,241:491-498.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
BOPPELLA R, YANG W, TAN J , et al. Black phosphorus supported Ni2P co-catalyst on graphitic carbon nitride enabling simultaneous boosting charge separation and surface reaction. Appl. Catal. B-Environ, 2019,242:422-430.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
HU J, JI Y, MO Z , et al. Engineering black phosphorus to porous g-C3N4-metal-organic framework membrane: a platform for highly boosting photocatalytic performance. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2019,7(9):4408-4414.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
YAN J, JI Y, KONG L , et al. Black phosphorus-based compound with few layers for photocatalytic water oxidation. ChemCatChem, 2018,10(16):3424-3428.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
ZHU M, SUN Z, FUJITSUKA M , et al. Z-scheme photocatalytic water splitting on a 2D heterostructure of black phosphorus/bismuth vanadate using visible light. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2018,57(8):2160-2164.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
ZHENG Y, YU Z, OU H , et al. Black phosphorus and polymeric carbon nitride heterostructure for photoinduced molecular oxygen activation. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2018,28(10):1705407.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
RUDENKO A N, KATSNELSON M I . Quasiparticle band structure and tight-binding model for single- and bilayer black phosphorus. Phys. Rev. B, 2014,89(20):201408.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
TRAN V, SOKLASKI R, LIANG Y , et al. Layer-controlled band gap and anisotropic excitons in few-layer black phosphorus. Phys. Rev. B, 2014,89(23):235319.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
ZHOU Q, CHEN Q, TONG Y , et al. Light-induced ambient degradation of few-layer black phosphorus: mechanism and protection. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2016,55(38):11437-11441.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
QIU M, WANG D, LIANG W , et al. Novel concept of the smart NIR-light-controlled drug release of black phosphorus nanostructure for cancer therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 2018,115(3):501-506.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
PENG X, WEI Q, COPPLE A . Strain-engineered direct-indirect band gap transition and its mechanism in two-dimensional phosphorene. Phys. Rev. B, 2014,90(8):085402.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
TANG X, LIANG W, ZHAO J , et al. Fluorinated phosphorene: electrochemical synthesis, atomistic fluorination, and enhanced stability. Small, 2017,13(47):1702739.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
MAO L, CAI X, YANG S , et al. Black phosphorus-CdS-La2Ti2O7 ternary composite: effective noble metal-free photocatalyst for full solar spectrum activated H2 production. Appl. Catal. B-Environ, 2019,242:441-448.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
FENG R, LEI W, LIU G , et al. Visible- and NIR-light responsive black-phosphorus-based nanostructures in solar fuel production and environmental remediation. Adv. Mater., 2018,30(49):1804770.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
ZHANG K, JIN B, PARK C , et al. Black phosphorene as a hole extraction layer boosting solar water splitting of oxygen evolution catalysts. Nat. Commun., 2019,10(1):2001.
DOI URL |
| [1] | ZHU Wenjie, TANG Lu, LU Jichang, LIU Jiangping, LUO Yongming. Research Progress on Catalytic Oxidation of Volatile Organic Compounds by Perovskite Oxides [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [2] | HU Zhichao, YANG Hongyu, YANG Hongcheng, SUN Chengli, YANG Jun, LI Enzhu. Usage of the P-V-L Bond Theory in Regulating Properties of Microwave Dielectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [3] | WU Qiong, SHEN Binglin, ZHANG Maohua, YAO Fangzhou, XING Zhipeng, WANG Ke. Research Progress on Lead-based Textured Piezoelectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [4] | ZHANG Bihui, LIU Xiaoqiang, CHEN Xiangming. Recent Progress of Hybrid Improper Ferroelectrics with Ruddlesden-Popper Structure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| [5] | WU Jie, YANG Shuai, WANG Mingwen, LI Jinglei, LI Chunchun, LI Fei. Textured PT-based Piezoelectric Ceramics: Development, Status and Challenge [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 575-586. |
| [6] | JIANG Kun, LI Letian, ZHENG Mupeng, HU Yongming, PAN Qinxue, WU Chaofeng, WANG Ke. Research Progress on Low-temperature Sintering of PZT Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| [7] | FAN Xiaoxuan, ZHENG Yonggui, XU Lirong, YAO Zimin, CAO Shuo, WANG Kexin, WANG Jiwei. Organic Pollutant Fenton Degradation Driven by Self-activated Afterglow from Oxygen-vacancy-rich LiYScGeO4: Bi3+ Long Afterglow Phosphor [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 481-488. |
| [8] | TIAN Ruizhi, LAN Zhengyi, YIN Jie, HAO Nanjing, CHEN Hangrong, MA Ming. Microfluidic Technology Based Synthesis of Inorganic Nano-biomaterials: Principles and Progress [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 337-347. |
| [9] | ZHANG Jiguo, WU Tian, ZHAO Xu, YANG Fan, XIA Tian, SUN Shien. Improvement of Cycling Stability of Cathode Materials and Industrialization Process for Sodium-ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 348-362. |
| [10] | JIA Xianghua, ZHANG Huixia, LIU Yanfeng, ZUO Guihong. Cu2O/Cu Hollow Spherical Heterojunction Photocatalysts Prepared by Wet Chemical Approach [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 397-404. |
| [11] | YIN Jie, GENG Jiayi, WANG Kanglong, CHEN Zhongming, LIU Xuejian, HUANG Zhengren. Recent Advances in 3D Printing and Densification of SiC Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 245-255. |
| [12] | CHEN Guangchang, DUAN Xiaoming, ZHU Jinrong, GONG Qing, CAI Delong, LI Yuhang, YANG Donglei, CHEN Biao, LI Xinmin, DENG Xudong, YU Jin, LIU Boya, HE Peigang, JIA Dechang, ZHOU Yu. Advanced Ceramic Materials in Helicopter Special Structures: Research Progress and Application Prospect [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 225-244. |
| [13] | FAN Xiaobo, ZU Mei, YANG Xiangfei, SONG Ce, CHEN Chen, WANG Zi, LUO Wenhua, CHENG Haifeng. Research Progress on Proton-regulated Electrochemical Ionic Synapses [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 256-270. |
| [14] | HAIREGU Tuxun, GUO Le, DING Jiayi, ZHOU Jiaqi, ZHANG Xueliang, NUERNISHA Alifu. Research Progress of Optical Bioimaging Technology Assisted by Upconversion Fluorescence Probes in Tumor Imaging [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 145-158. |
| [15] | SUN Shujuan, ZHENG Nannan, PAN Haokun, MA Meng, CHEN Jun, HUANG Xiubing. Research Progress on Preparation Methods of Single-atom Catalysts [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 113-127. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||