
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2026, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (1): 37-44.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250146
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Yongheng1,2( ), CHEN Jixin1(
), CHEN Jixin1( )
)
Received:2025-04-07
Revised:2025-05-10
Published:2026-01-20
Online:2025-05-22
Contact:
CHEN Jixin, associate professor. E-mail: jxchen@imr.ac.cnAbout author:ZHANG Yongheng (1994-), male, PhD candidate. E-mail: yhzhang18s@imr.ac.cn
CLC Number:
ZHANG Yongheng, CHEN Jixin. Preparation and Properties of Ytterbium Aluminosilicate Glass and SiC Modified h-BN-based Composites[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2026, 41(1): 37-44.
| Sample | SiC/ % (in volume) | YbAS glass/ % (in volume) | h-BN/ % (in volume) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BYbSi5 | 5 | 30 | 65 |
| BYbSi10 | 10 | 30 | 60 |
| BYbSi20 | 20 | 30 | 50 |
| BYbSi30 | 30 | 30 | 40 |
Table 1 Sample notations and compositions of raw powders
| Sample | SiC/ % (in volume) | YbAS glass/ % (in volume) | h-BN/ % (in volume) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BYbSi5 | 5 | 30 | 65 |
| BYbSi10 | 10 | 30 | 60 |
| BYbSi20 | 20 | 30 | 50 |
| BYbSi30 | 30 | 30 | 40 |

Fig. 3 Microstructure and element mappings of the BYbSi30 composite (a) Bright field image; (b) HAADF image; (c-e) Diffraction patterns of h-BN (c), SiC (d) and YbAS glass (e); (f-l) Distributions of B, N, Yb, Al, O, Si and C elements in Fig. (b); (m, n) High-resolution images of area A (m) and area B (n) in Fig. (a)
| Composite | BYbSi5 | BYbSi10 | BYbSi20 | BYbSi30 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density/(g·cm-3) | 2.763 | 2.813 | 2.910 | 3.015 |
| Relative density/% | 96.12 | 96.30 | 96.55 | 97.04 |
Table 2 Densities and relative densities of the h-BN/YbAS/SiC composites
| Composite | BYbSi5 | BYbSi10 | BYbSi20 | BYbSi30 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density/(g·cm-3) | 2.763 | 2.813 | 2.910 | 3.015 |
| Relative density/% | 96.12 | 96.30 | 96.55 | 97.04 |
| Composite | BYbSi5 | BYbSi10 | BYbSi20 | BYbSi30 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flexural strength/MPa | 377±41 | 348±29 | 447±10 | 462±5 |
| Fracture toughness/(MPa·m1/2) | 4.9±0.2 | 5.1±0.1 | 5.3±0.1 | 5.5±0.3 |
| Compressive strength/MPa | 1067±55 | 1046±91 | 1288±64 | 1465±58 |
| Elasticity modulus/GPa | 104 | 108 | 125 | 140 |
| Vickers hardness/GPa | 2.5±0.1 | 2.8±0.3 | 3.3±0.2 | 4.7±0.3 |
Table 3 Room-temperature mechanical properties of the h-BN/YbAS/SiC composites
| Composite | BYbSi5 | BYbSi10 | BYbSi20 | BYbSi30 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flexural strength/MPa | 377±41 | 348±29 | 447±10 | 462±5 |
| Fracture toughness/(MPa·m1/2) | 4.9±0.2 | 5.1±0.1 | 5.3±0.1 | 5.5±0.3 |
| Compressive strength/MPa | 1067±55 | 1046±91 | 1288±64 | 1465±58 |
| Elasticity modulus/GPa | 104 | 108 | 125 | 140 |
| Vickers hardness/GPa | 2.5±0.1 | 2.8±0.3 | 3.3±0.2 | 4.7±0.3 |
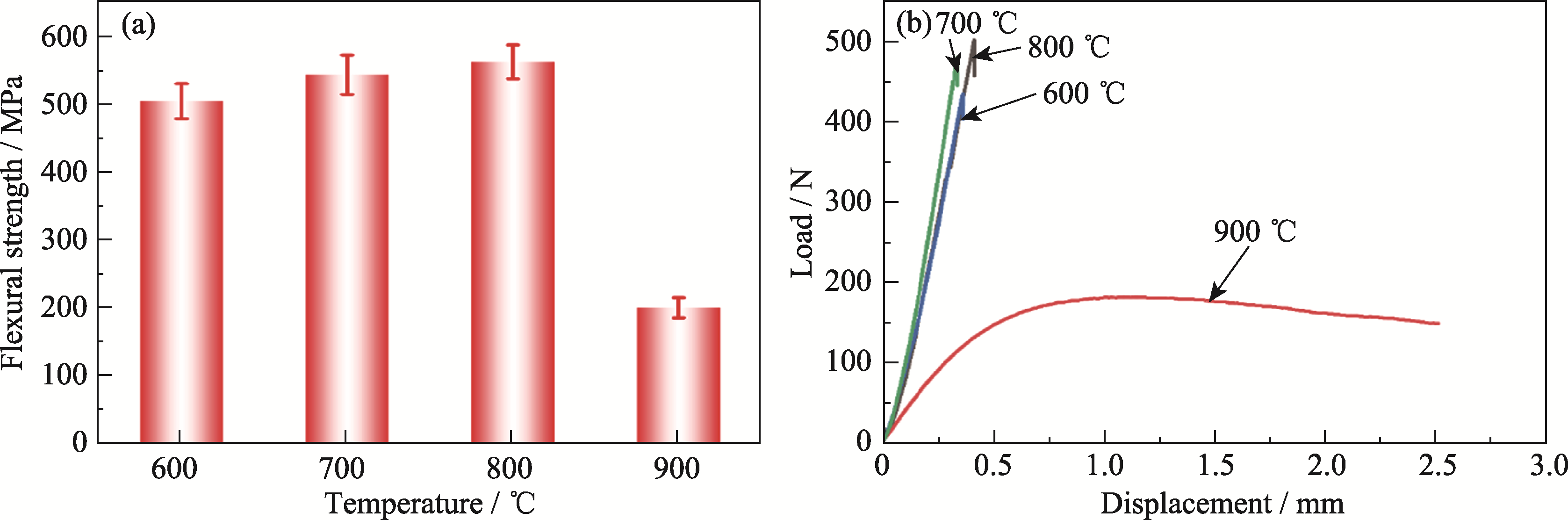
Fig. 6 (a) Flexural strength of the BYbSi30 composite at different temperatures and (b) load-displacement curves for testing flexural strength at elevated temperature
| [1] |
LIPP A, SCHWETZ K A, HUNOLD K. Hexagonal boron nitride fabrication, properties and applications. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 1989, 5(1): 3.
DOI URL |
| [2] | HAUBNER R, WILHELM M, WEISSENBACHER R, et al. Boron nitrides properties, synthesis and applications. Structure and Bonding, 2002, 102: 14. |
| [3] | RUSANOVA L N, ROMASHLN A G, KULLKOVA G I, et al. Boron nitride ceramics: problems and development perspectives. Powder Metallurgy and Metal Ceramics, 1988, 1: 23. |
| [4] |
QIAO W, YANG J, QIAO J, et al. Pressureless-sintered boron nitride nanosheets/glass composite ceramics for excellent mechanical, dielectric and thermo-conductive performances. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2023, 43(9): 3998.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
FREDERIKSE H P R, KAHN A H, DRAGOO A L, et al. Electrical resistivity and microwave transmission of hexagonal boron nitride. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1985, 68(3): 131.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
SINCLAIR W, SIMMONS H. Microstructure and thermal-shock behavior of BN composites. Journal of Materials Science Letters, 1987, 6(6): 627.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
TAHARA H, IMANAKA K, YUGE S. Effects of channel wall material on thrust performance and plasma characteristics of Hall-effect thrusters. Vacuum, 2006, 80(11/12): 1216.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
EICHLER J, LESNIAK C, CHRISTOPH L. Boron nitride (BN) and BN composites for high-temperature applications. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2008, 28(5): 1105.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
RIZAKHANOV R N B, IVANOV A A, IVLIEVA A V, et al. Ceramic composite based on boron nitride with enhanced resistance to ion bombardment for application in hall thruster. Inorganic Materials: Applied Research, 2015, 6(2): 156.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
LI Y L, QIAO G J, JIN Z H. Machinable Al2O3/BN composite ceramics with strong mechanical properties. Materials Research Bulletin, 2002, 37(8): 1401.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
DUAN X M, JIA D C, ZHOU Y, et al. Mechanical properties and plasma erosion resistance of BNp/Al2O3-SiO2 composite ceramics. Journal of Central South University, 2013, 20(6): 1462.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
TIAN Z, DUAN X M, YANG Z, et al. Ablation mechanism and properties of in-situ SiAlON reinforced BN-SiO2 ceramic composite under an oxyacetylene torch environment. Ceramics International, 2014, 40(7): 11149.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
ZHANG X, CHEN J X, LI X C, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of h-BN/Y2SiO5 composites. Ceramics International, 2015, 41(1): 1279.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
CAI D, YANG Z, DUAN X M, et al. A novel BN-MAS system composite ceramics with greatly improved mechanical properties prepared by low temperature hot-pressing. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2015, 633: 194.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
CHEN J J, CHEN J X, ZHANG H, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of h-BN/Yb4Si2O7N2 composites. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2018, 7(4): 317.
DOI |
| [16] |
ZHANG X, ZHANG R, CHEN G, et al. Microstructure, mechanical properties and thermal shock resistance of hot-pressed ZrO2(3Y)-BN composites. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2008, 497(1/2): 195.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
CHEN L, HUANG Y, WANG Y, et al. Effect of ZrO2 content on microstructure, mechanical properties and thermal shock resistance of (ZrB2+3Y-ZrO2)/BN composites. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2013, 573: 106.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
CHEN L, WANG Y, SHEN H, et al. Effect of SiC content on mechanical properties and thermal shock resistance of BN-ZrO2-SiC composites. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2014, 590: 346.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
ZHAI F R, LI S, SUN J L, et al. Microstructure, mechanical properties and thermal shock behavior of h-BN-SiC ceramic composites prepared by spark plasma sintering. Ceramics International, 2017, 43(2): 2413.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
WANG J, LU D, XUAN W, et al. Boron nitride microribbons strengthened and toughened alumina composite ceramics with excellent mechanical, dielectric, and thermal conductivity properties. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2024, 13(4): 496.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
WEN G, WU G L, LEI T Q, et al. Co-enhanced SiO2-BN ceramics for high-temperature dielectric applications. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2000, 20(12): 1923.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
CHEN J J, CHEN J, ZHANG X, et al. Fabrication and mechanical properties of h-BN based composites containing dual glass phases. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2018, 38(9): 3210.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
QIU B F, DUAN X M, ZHANG Z, et al. Microstructure and room/elevated-temperature mechanical properties of hot-pressed h-BN composite ceramics with La2O3-Al2O3-SiO2 addition. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(6): 2260.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
ZHANG Y H, CHEN J X, ZHANG H, et al. Hexagonal boron nitride ceramic reinforced with a dispersed glass phase and microdomain-extruded glass fibers. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2025 45(10): 117362.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
ZHANG Y H, CHEN J X, ZHANG H, et al. Bulk ytterbium aluminosilicate glass with excellent mechanical properties and plasma etching resistance. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2024, 642: 123159.
DOI URL |
| [26] | 李文新, 李文辉. 常压烧结碳化硅陶瓷的力学性能与质密度. 哈尔滨理工大学学报, 2002, 7: 80. |
| [27] |
LI Z, BRADT R C. Thermal expansion of the hexagonal (6H) polytype of silicon carbide. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2005, 69(12): 863.
DOI URL |
| [28] | 武安华, 曹文斌, 李江涛, 等. 固相烧结SiC陶瓷. 材料工程, 2001, 4: 3. |
| [29] |
PEASE R S. An X-ray study of boron nitride. Acta Crystallographica, 1952, 5(3): 356.
DOI URL |
| [30] | SIMPSON A, STUCKES A D. The thermal conductivity of highly oriented pyrolytic boron nitride. Journal of Physics Part C Solid State Physics, 1971, 4(13): 1710. |
| [31] | WANG F F, ZENG X L, YAO Y M, et al. Silver nanoparticle- deposited boron nitride nanosheets as fillers for polymeric composites with high thermal conductivity. Scientific Report, 2016, 6: 19394. |
| [1] | YUAN Wang, HU Jianbao, ZHOU Liang, KAN Yanmei, ZHANG Xiangyu, DONG Shaoming. Effect of Argon Atmosphere Heat Treatment on Mechanical Properties and Microstructural Evolution of Shicolon-II SiC Fibers [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2026, 41(1): 119-128. |
| [2] | XU Jintao, GAO Pan, HE Weiyi, JIANG Shengnan, PAN Xiuhong, TANG Meibo, CHEN Kun, LIU Xuechao. Recent Progress on Preparation of 3C-SiC Single Crystal [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2026, 41(1): 1-11. |
| [3] | CHEN Bin, REN Ke, WANG Yiguang. Evolution of Mechanical Properties of Mini-SiCf/SiC Composites at High Temperatures over a Long Period of Time [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(9): 971-980. |
| [4] | TAN Bowen, GENG Shuanglong, ZHANG Kai, ZHENG Bailin. Composition-gradient Design of Silicon Electrodes to Mitigate Mechanochemical Coupling Degradation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 772-780. |
| [5] | SUN Yuxuan, WANG Zheng, SHI Xue, SHI Ying, DU Wentong, MAN Zhenyong, ZHENG Liaoying, LI Guorong. Defect Dipole Thermal-stability to the Electro-mechanical Properties of Fe Doped PZT Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 545-551. |
| [6] | CHEN Yi, QIU Haipeng, CHEN Mingwei, XU Hao, CUI Heng. SiC/SiC Composite: Matrix Boron Modification and Mechanical Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 504-510. |
| [7] | CUI Ning, ZHANG Yuxin, WANG Lujie, LI Tongyang, YU Yuan, TANG Huaguo, QIAO Zhuhui. Single-phase Formation Process and Carbon Vacancy Regulation of (TiVNbMoW)Cx High-entropy Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 511-520. |
| [8] | GOU Yanzi, KANG Weifeng, WANG Pengren. Influence of Sintering Conditions on Preparation of Nearly Stoichiometric SiC Fibers with Highly Crystalline Microstructure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 405-414. |
| [9] | MU Shuang, MA Qin, ZHANG Yu, SHEN Xu, YANG Jinshan, DONG Shaoming. Oxidation Behavior of Yb2Si2O7 Modified SiC/SiC Mini-composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 323-328. |
| [10] | YIN Jie, GENG Jiayi, WANG Kanglong, CHEN Zhongming, LIU Xuejian, HUANG Zhengren. Recent Advances in 3D Printing and Densification of SiC Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 245-255. |
| [11] | LI Ziwei, GONG Weilu, CUI Haifeng, YE Li, HAN Weijian, ZHAO Tong. (Zr, Hf, Nb, Ta, W)C-SiC Composite Ceramics: Preparation via Precursor Route and Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 271-280. |
| [12] | GAO Chenguang, SUN Xiaoliang, CHEN Jun, LI Daxin, CHEN Qingqing, JIA Dechang, ZHOU Yu. SiBCN-rGO Ceramic Fibers Based on Wet Spinning Technology: Microstructure, Mechanical and Microwave-absorbing Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 290-296. |
| [13] | MU Haojie, ZHANG Yuanjiang, YU Bin, FU Xiumei, ZHOU Shibin, LI Xiaodong. Preparation and Properties of ZrO2 Doped Y2O3-MgO Nanocomposite Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 281-289. |
| [14] | HOU Jiaqi, CHEN Ruicong, ZENG Yaoying, ZHOU Lei, ZHANG Jiaping, FU Qiangang. Thermal Shock and Ablation Resistance of SiC Coating Repaired by Gaseous Silicon Infiltration [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 168-176. |
| [15] | LI Wei, XU Zhiming, GOU Yanzi, YIN Senhu, YU Yiping, WANG Song. Preparation and Performance of Sintered SiC Fiber-bonded Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 177-183. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||