
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (11): 1173-1187.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250023
• REVIEW • Next Articles
ZOU Minmin( ), LIU Jingxin, HU Haolin, ZENG Dongmei, ZHANG Ting, ZHANG You
), LIU Jingxin, HU Haolin, ZENG Dongmei, ZHANG Ting, ZHANG You
Received:2025-01-15
Revised:2025-04-19
Published:2025-11-20
Online:2025-05-21
About author:ZOU Minmin (1985-), female, lecturer. E-mail: zouminmin@bipt.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
ZOU Minmin, LIU Jingxin, HU Haolin, ZENG Dongmei, ZHANG Ting, ZHANG You. Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution Performance of Two-dimensional Mo2CTx MXene Materials: A Review from Preparation to Application[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(11): 1173-1187.
| Method | MAX | Etching solution | Temperature/℃ | Time/h | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fluoride etching | Mo2Ga2C | 50% HF | 50 | 3 | [ |
| LiF+HCl | 35 | 384 | [ | ||
| HF | 55 | 158.4 | [ | ||
| LiF+HCl, NaF+HCl, KF+HCl & NH4F+HCl | 140 | 24 | [ | ||
| 48% HF | 140 | 96 | [ | ||
| Mo2SnC | HF | 60 | 72 | [ | |
| Alkali etching | Mo3AlC2 | NaOH+Na2S | 220 | 2 | [ |
| Mo2Ga2C | 20 mol/L NaOH | 180 | 24 | [ | |
| Molten salt etching | Mo2Ga2C | NaCl, KCl & CuCl2 | 600 | 0.5 | [ |
| Mo inks | KCl salt template | 900 | 3 | [ | |
| UV induced etching | Mo2Ga2C | UV+H2PO4 | RT | 3-5 | [ |
| Mo-In-C | 85% H3PO4+UV | RT | 3-5 | [ | |
| Other etching | Mo2Ga2C | CTAB+HCl | 160 | 24 | [ |
| HBr | 220 | 72 | [ | ||
| LiBr+HBr, NaBr+HBr & NH4Br+HBr | 180 | 24 | [ |
Table 1 Experimental parameters of Mo2CTx prepared by different etching methods[11,31,34 -44]
| Method | MAX | Etching solution | Temperature/℃ | Time/h | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fluoride etching | Mo2Ga2C | 50% HF | 50 | 3 | [ |
| LiF+HCl | 35 | 384 | [ | ||
| HF | 55 | 158.4 | [ | ||
| LiF+HCl, NaF+HCl, KF+HCl & NH4F+HCl | 140 | 24 | [ | ||
| 48% HF | 140 | 96 | [ | ||
| Mo2SnC | HF | 60 | 72 | [ | |
| Alkali etching | Mo3AlC2 | NaOH+Na2S | 220 | 2 | [ |
| Mo2Ga2C | 20 mol/L NaOH | 180 | 24 | [ | |
| Molten salt etching | Mo2Ga2C | NaCl, KCl & CuCl2 | 600 | 0.5 | [ |
| Mo inks | KCl salt template | 900 | 3 | [ | |
| UV induced etching | Mo2Ga2C | UV+H2PO4 | RT | 3-5 | [ |
| Mo-In-C | 85% H3PO4+UV | RT | 3-5 | [ | |
| Other etching | Mo2Ga2C | CTAB+HCl | 160 | 24 | [ |
| HBr | 220 | 72 | [ | ||
| LiBr+HBr, NaBr+HBr & NH4Br+HBr | 180 | 24 | [ |
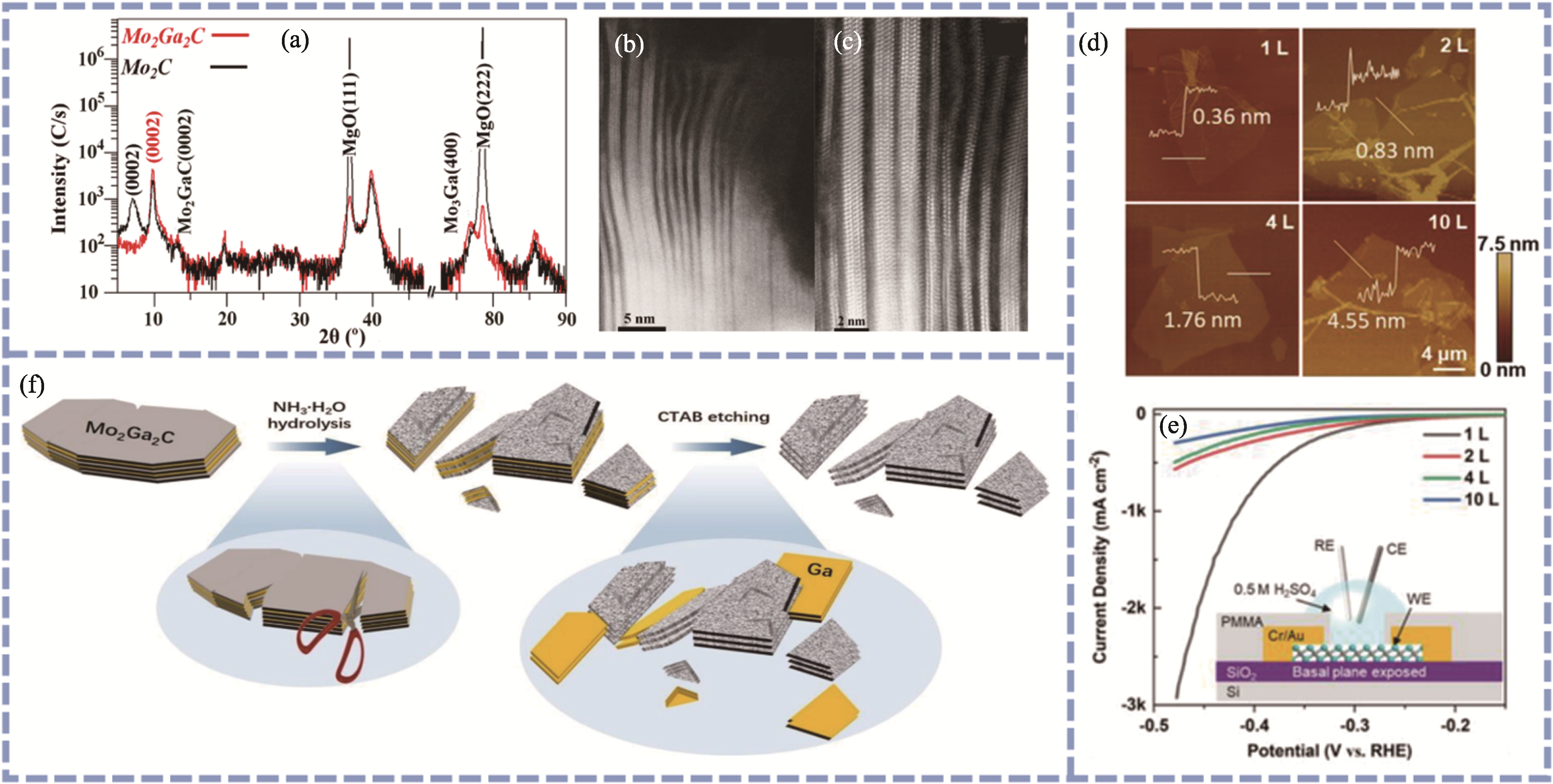
Fig. 2 Preparation of Mo2CTx by the top-down method[34,39 -40] (a) XRD patterns and (b, c) TEM images of Mo2C prepared by HF etching[34]; (d) Representative AFM images of 2D Mo2C flakes of different thicknesses[40]; (e) Polarization curves obtained from 2D Mo2C microcell devices with flake thickness from 10 layers down to monolayer[40]; (f) Schematic diagram of the preparation of Mo2C MXene by CTAB etching[39]

Fig. 3 Preparation of Mo2CTx by the bottom-up method[50,53,55] (a) Synthesis of Mo2C by CVD[50]; (b) Optical microscopy image of Mo2C[53]; (c) Optical microscopy images of 2D ultrathin α-Mo2C crystals with a uniform thickness of ~3 nm[53]; (d) LSV curves and (e) Tafel plots of Mo2CTx/G[50]; (f, g) Cross-sectional HRTEM images of (f) Mo2C-MoS2 junction and (g) fully converted Mo2C[55]
| Electrocatalyst | Electrolyte | Overpotential@ 10 mA·cm-2/mV | Tafel slope/(mV·dec-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mo2CTx | 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 | 283 | - | [ |
| Mo2CTx-F | 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 | 189 | 75 | [ |
| P-Mo2CTx | 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 | 186 | - | [ |
| N-Mo2CTx | 1 mol/L KOH | 191 | 88 | [ |
| Ru/Mo2CTx | 1 mol/L PBS | 73 | 57 | [ |
| Co-MoS2/Mo2CTx | 1 mol/L KOH | 112 | 82 | [ |
| MoS2/Mo2CTx | 1 mol/L KOH | 176 | - | [ |
| MoS2/Mo2CTx | 1 mol/L KOH | 110±7 | 65 | [ |
| Mo2CTx/2H-MoS2 | 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 | 119 | 60 | [ |
| MoS2/Mo2CTx | 1 mol/L KOH | 150 | 70 | [ |
| MoS2/Mo2CTx | 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 | 243 | 81 | [ |
| MoSe2/Mo2CTx | 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 | 108.3 | 70.7 | [ |
| Pt/NBF-ReS2/Mo2CTx | 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 | 29 | 24 | [ |
| 1 mol/L KOH | 37 | 36 | [ | |
| NBF-CoSe/Mo2CTx | 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 | 70 | 30 | [ |
| 1 mol/L KOH | 81 | 29 | [ | |
| Ru/NBF-NiSe2/Mo2CTx | 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 | 30 | 25 | [ |
| 1 mol/L KOH | 39 | 29 | [ | |
| NiS/Mo2CTx | 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 | 157 | 77 | [ |
| CoP/Mo2CTx | 1 mol/L KOH | 78 | 66 | [ |
| NBF-BiOBr/Bi2Se3/Mo2CTx | 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 | 109 | 36 | [ |
| Mo2CTx/PDTDA/rGO | 1 mol/L KOH | 59 | 44 | [ |
Table 2 Electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution performance of Mo2CTx and its composites[14,20 -21,23 -24,38,61 -73]
| Electrocatalyst | Electrolyte | Overpotential@ 10 mA·cm-2/mV | Tafel slope/(mV·dec-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mo2CTx | 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 | 283 | - | [ |
| Mo2CTx-F | 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 | 189 | 75 | [ |
| P-Mo2CTx | 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 | 186 | - | [ |
| N-Mo2CTx | 1 mol/L KOH | 191 | 88 | [ |
| Ru/Mo2CTx | 1 mol/L PBS | 73 | 57 | [ |
| Co-MoS2/Mo2CTx | 1 mol/L KOH | 112 | 82 | [ |
| MoS2/Mo2CTx | 1 mol/L KOH | 176 | - | [ |
| MoS2/Mo2CTx | 1 mol/L KOH | 110±7 | 65 | [ |
| Mo2CTx/2H-MoS2 | 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 | 119 | 60 | [ |
| MoS2/Mo2CTx | 1 mol/L KOH | 150 | 70 | [ |
| MoS2/Mo2CTx | 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 | 243 | 81 | [ |
| MoSe2/Mo2CTx | 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 | 108.3 | 70.7 | [ |
| Pt/NBF-ReS2/Mo2CTx | 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 | 29 | 24 | [ |
| 1 mol/L KOH | 37 | 36 | [ | |
| NBF-CoSe/Mo2CTx | 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 | 70 | 30 | [ |
| 1 mol/L KOH | 81 | 29 | [ | |
| Ru/NBF-NiSe2/Mo2CTx | 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 | 30 | 25 | [ |
| 1 mol/L KOH | 39 | 29 | [ | |
| NiS/Mo2CTx | 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 | 157 | 77 | [ |
| CoP/Mo2CTx | 1 mol/L KOH | 78 | 66 | [ |
| NBF-BiOBr/Bi2Se3/Mo2CTx | 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 | 109 | 36 | [ |
| Mo2CTx/PDTDA/rGO | 1 mol/L KOH | 59 | 44 | [ |
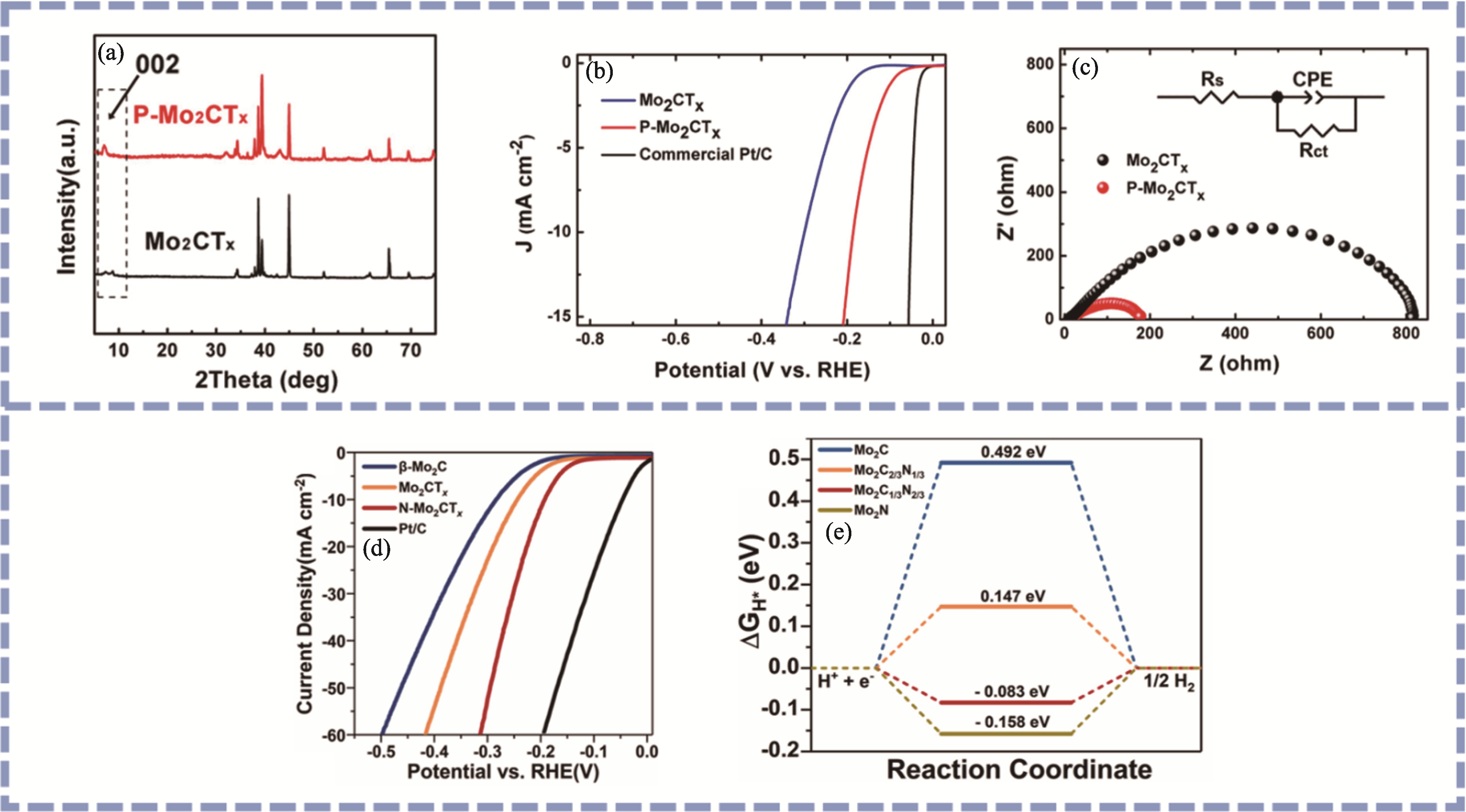
Fig. 5 Characterization of heteroatom-doped Mo2CTx materials[21,61] (a) XRD patterns, (b) LSV curves and (c) Nyquist plots of P-Mo2CTx[21]; (d) LSV curves of N-Mo2CTx[61]; (e) H atoms free energy barriers for different structures[61]

Fig. 6 Characterization of Mo2CTx/precious metal hybrid materials[62,76] (a) SEM image, (b) LSV curves and (c) Tafel plots of Ru/Mo2CTx[62]; (d-f) Top and side views of the geometry of Pd4-6 on bare Mo2C, Mo2CO2 and Mo2CF2 with blue, red, purple, brown, and cyan dots representing Pd, O, F, C, and Mo atoms, respectively[76]; (g-i) Top and side views of the geometry of Au4-6 on bare Mo2C, Mo2CO2 and Mo2CF2 with yellow, red, purple, brown, and cyan dots representing Au, O, F, C, and Mo atoms, respectively[76]
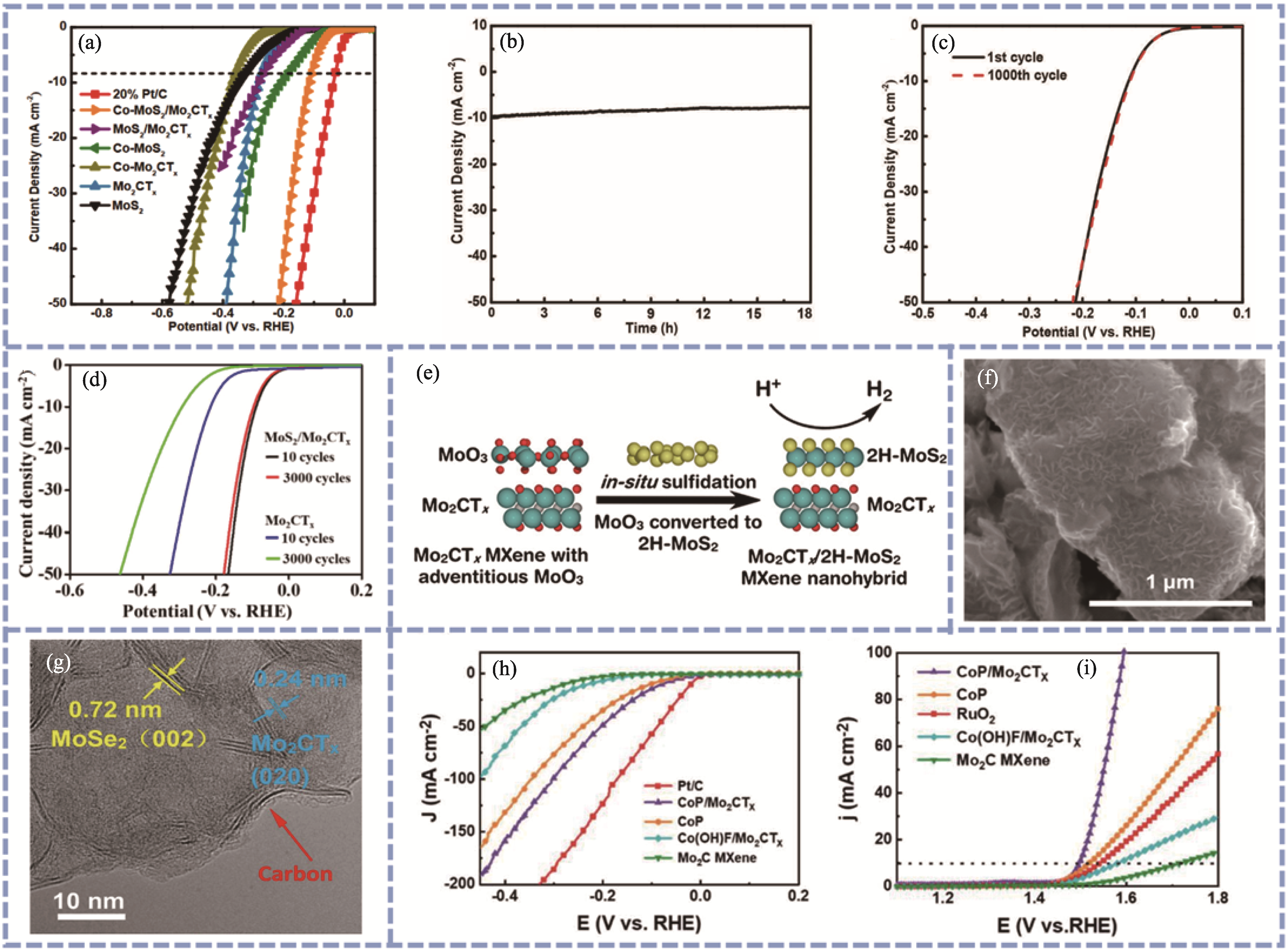
Fig. 7 Characterization of Mo2CTx/transition metal compound hybrid materials[24,38,63 -64,66,71] (a) LSV curves of Co-MoS2/Mo2CTx[63]; (b) Stability of Co-MoS2/Mo2CTx nano-arrays measured by chronocurrent method[63]; (c) Polarization curves of Co-MoS2/Mo2CTx electrode before and after 1000 CV cycles at 100 mV·s-1[63]; (d) HER polarization curves after 10 and 3000 cycles of Mo2CTx and MoS2/Mo2CTx[38]; (e) Schematic diagram of Mo2CTx/2H-MoS2 synthesis[64]; (f) SEM image of MoS2/Mo2CTx[66]; (g) HRTEM image of MoSe2/Mo2CTx@C nanohybrids[24]; (h) HER and (i) OER polarization curves of CoP/Mo2CTx[71]
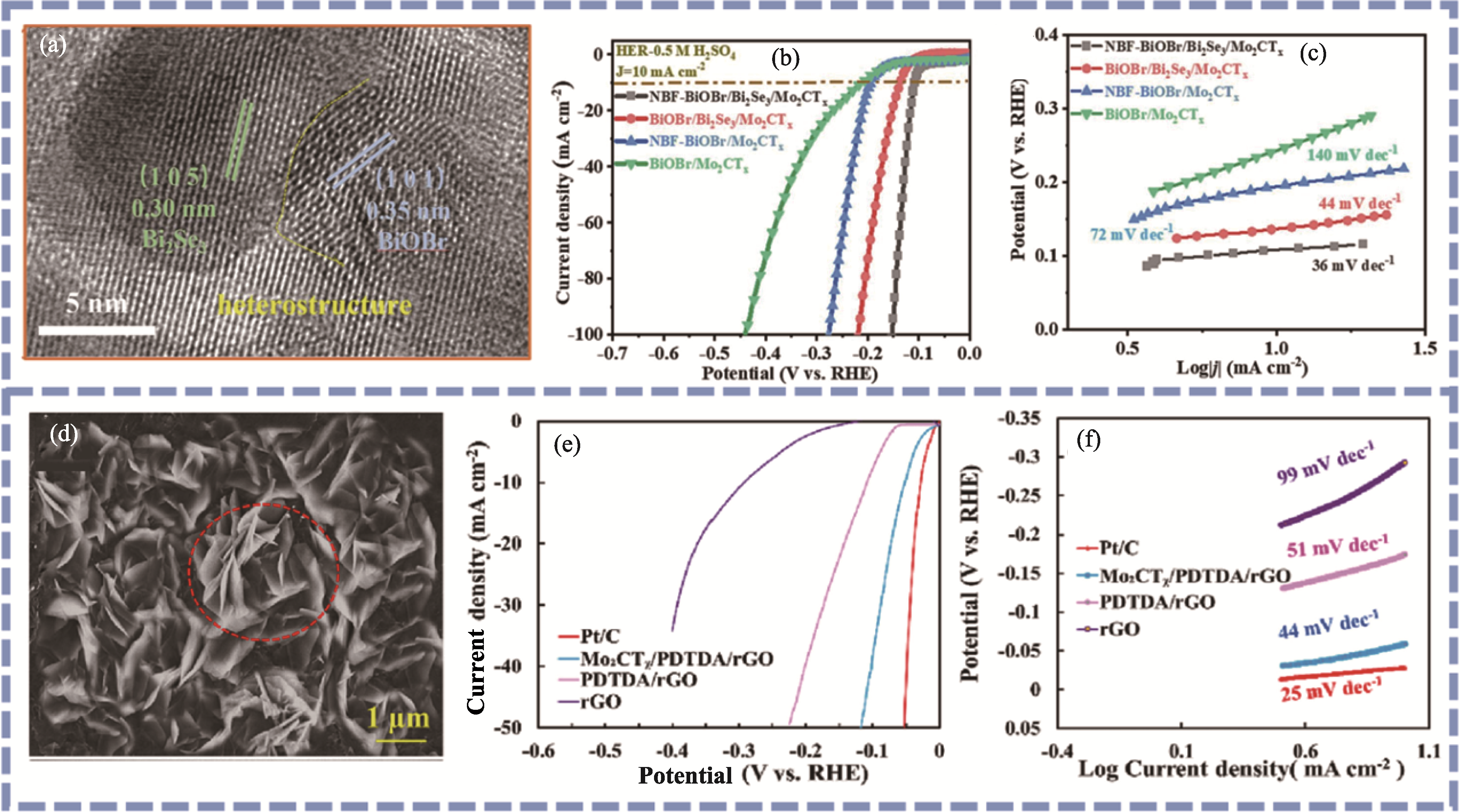
Fig. 8 Characterization of other Mo2CTx-based hybrid materials[72-73] (a) HRTEM image, (b) LSV curves and (c) Tafel plots of NBF-BiOBr/Bi2Se3/Mo2CTx[72]; (d) SEM image, (e) LSV curves and (f) Tafel plots of Mo2CTx/PDTDA/rGO[73]
| [1] |
HUANG Q. MXene: coming up roses. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(2): 113.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
LI N, KONG Z, CHEN X Z, et al. Research progress of novel two-dimensional materials in photocatalysis and electrocatalysis. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(7): 735.
DOI |
| [3] |
GOGOTSI Y, ANASORI B. The rise of MXenes. ACS Nano, 2019, 13(8): 8491.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
LI L, CHENG Q. Recent advances in the high performance MXenes nanocomposites. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(2): 153.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
IBRAGIMOVA R, ERHART P, RINKE P, et al. Surface func- tionalization of 2D MXenes: trends in distribution, composition, and electronic properties. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2021, 12(9): 2377.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
MOZAFARI M, SOROUSH M. Surface functionalization of MXenes. Materials Advances, 2021, 2(22): 7277.
DOI URL |
| [7] | LI M, HUANG Q. Recent progress and prospects of ternary layered carbides/nitrides MAX phases and their derived two- dimensional nanolaminates MXenes. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(1): 1. |
| [8] |
PERSSON I, EL GHAZALY A, TAO Q, et al. Tailoring structure, composition, and energy storage properties of MXenes from selective etching of in-plane, chemically ordered MAX phases. Small, 2018, 14(17): 1703676.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
WANG X, DING J, SONG W, et al. Cation vacancy clusters in Ti3C2Tx MXene induce ultra-strong interaction with noble metal clusters for efficient electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Advanced Energy Materials, 2023, 13(23): 2300148.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
ZHAO X, LI W P, CAO Y, et al. Dual-atom Co/Ni electrocatalyst anchored at the surface-modified Ti3C2Tx MXene enables efficient hydrogen and oxygen evolution reactions. ACS Nano, 2024, 18(5): 4256.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
LI Y, LAN B, GUAN B, et al. Molten salt derived Mo2CTx MXene with excellent catalytic performance for hydrogen evolution reaction. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2024, 40(9): 2306031.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
KUMAR J A, PRAKASH P, KRITHIGA T, et al. Methods of synthesis, characteristics, and environmental applications of MXene: a comprehensive review. Chemosphere, 2022, 286: 131607.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
LEI J C, ZHANG X, ZHOU Z. Recent advances in MXene: preparation, properties, and applications. Frontiers of Physics, 2015, 10(3): 276.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
SEH Z W, FREDRICKSON K D, ANASORI B, et al. Two-dimensional molybdenum carbide (MXene) as an efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution. ACS Energy Letters, 2016, 1(3): 589.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
SEH Z W, KIBSGAARD J, DICKENS C F, et al. Combining theory and experiment in electrocatalysis: insights into materials design. Science, 2017, 355(6321): eaad4998.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
LING C, SHI L, OUYANG Y, et al. Searching for highly active catalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction based on O-terminated MXenes through a simple descriptor. Chemistry of Materials, 2016, 28: 9026.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
PANDEY M T, THYGESEN K S. Two-dimensional MXenes as catalysts for electrochemical hydrogen evolution: a computational screening study. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2017, 121: 13593.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
JIN D, JOHNSON L R, RAMAN A S, et al. Computational screening of 2D ordered double transition-metal carbides (MXenes) as electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2020, 124: 10584.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
LI H, CHEN Y, TANG Q. Surface termination (-O, -F or -OH) and metal doping on the HER activity of Mo2CTx MXene. ChemPhysChem, 2024, 25(18): e202400255.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
HANDOKO A D, FREDRICKSON K D, ANASORI B, et al. Tuning the basal plane functionalization of two-dimensional metal carbides (MXenes) to control hydrogen evolution activity. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2018, 1(1): 173.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
QU G, ZHOU Y, WU T, et al. Phosphorized MXene-phase molybdenum carbide as an earth-abundant hydrogen evolution electrocatalyst. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2018, 1(12): 7206.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
PAN H. Ultra-high electrochemical catalytic activity of MXenes. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 32531.
DOI PMID |
| [23] |
REN J, ZONG H, SUN Y, et al. 2D organ-like molybdenum carbide (MXene) coupled with MoS2 nanoflowers enhances the catalytic activity in the hydrogen evolution reaction. CrystEngComm, 2020, 22(8): 1395.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
TAN Y, YI M, ZHU Z, et al. Carbon-coated MoSe2/Mo2CTx (MXene) heterostructure for efficient hydrogen evolution. Materials Science and Engineering: B, 2021, 271: 115239.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
HUANG S, MOCHALIN V N. Combination of high pH and an antioxidant improves chemical stability of two-dimensional transition-metal carbides and carbonitrides (MXenes) in aqueous colloidal solutions. Inorganic Chemistry, 2022, 61(26): 9877.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
ZHAO X, VASHISTH A, BLIVIN J, et al. pH, nanosheet concentration, and antioxidant affect the oxidation of Ti3C2Tx and Ti2CTx MXene dispersions. Advanced Materials Interfaces, 2020, 7(20): 2000845.
DOI URL |
| [27] | DOO S, CHAE A, KIM D, et al. Mechanism and kinetics of oxidation reaction of aqueous Ti3C2Tx suspensions at different pHs and temperatures. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(19): 22855. |
| [28] |
WAN P, TANG Q. Theoretical progress of MXenes as electrocatalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction. Materials Chemistry Frontiers, 2024, 8(2): 507.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
WANG K, ZHOU Y, XU W, et al. Fabrication and thermal stability of two-dimensional carbide Ti3C2 nanosheets. Ceramics International, 2016, 42(7): 8419.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
DALL'AGNESE C, DALL'AGNESE Y, ANASORI B, et al. Oxidized Ti3C2 MXene nanosheets for dye-sensitized solar cells. New Journal of Chemistry, 2018, 42(20): 16446.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
GUO Y, JIN S, WANG L, et al. Synthesis of two-dimensional carbide Mo2CTx MXene by hydrothermal etching with fluorides and its thermal stability. Ceramics International, 2020, 46: 19550.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
PEERA S G, KOUTAVARAPU R, CHAO L, et al. 2D MXene nanomaterials as electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction (HER): a review. Micromachines, 2022, 13(9): 1499.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
HANAN A, AWAN H T A, BIBI F, et al. MXenes and heterostructures-based electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction: recent developments and future outlook. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2024, 92: 176.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
MESHKIAN R, NÄSLUND L Å, HALIM J, et al. Synthesis of two-dimensional molybdenum carbide, Mo2C, from the gallium based atomic laminate Mo2Ga2C. Scripta Materialia, 2015, 108: 147.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
HALIM J, KOTA S, LUKATSKAYA M, et al. Synthesis and characterization of 2D molybdenum carbide (MXene). Advanced Functional Materials, 2016, 26(18): 3118.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
MEI J, AYOKO G A, HU C, et al. Two-dimensional fluorine-free mesoporous Mo2C MXene via UV-induced selective etching of Mo2Ga2C for energy storage. Sustainable Materials and Technologies, 2020, 25: e00156.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
THOMAS T, PUSHPAN S, AGUILAR MARTÍNEZ J A, et al. UV-assisted safe etching route for the synthesis of Mo2CTx MXene from Mo-In-C non-MAX phase. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(24): 35384.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
UNNIKRISHNAN B, WU C W, SANGILI A, et al. Synthesis and in situ sulfidation of molybdenum carbide MXene using fluorine- free etchant for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution reactions. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2022, 628: 849.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
JIN S, WU J, JIANG J, et al. Boosting photocatalytic performance of CdxZn1-xS for H2 production by Mo2C MXene with large interlayer distance. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2023, 11(11): 5851.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
WU J B, SU J W, WU T, et al. Scalable synthesis of 2D Mo2C and thickness-dependent hydrogen evolution on its basal plane and edges. Advanced Materials, 2023, 35(25): 2209954.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
WANG F, JIN S, DU Y, et al. Preparation of Mo2CTx MXene as co-catalyst for H2 production by etching of pure/mixed HBr solution. Diamond and Related Materials, 2023, 136: 109922.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
DEEVA E B, KURLOV A, ABDALA P M, et al. In situ XANES/XRD study of the structural stability of two-dimensional molybdenum carbide Mo2CTx: implications for the catalytic activity in the water-gas shift reaction Chemistry of Materials, 2019, 31(12): 4505.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
LV L P, GUO C, SUN W, et al. Strong surface-bound sulfur in carbon nanotube bridged hierarchical Mo2C-based MXene nanosheets for lithium-sulfur batteries. Small, 2019, 15(3): 1804338.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
GUO Y, ZHANG X, JIN S, et al. Synthesis of Mo2C MXene with high electrochemical performance by alkali hydrothermal etching. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2023, 12(10): 1889.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
LI G, TAN L, ZHANG Y, et al. Highly efficiently delaminated single-layered MXene nanosheets with large lateral size. Langmuir, 2017, 33(36): 9000.
DOI PMID |
| [46] |
XIE X, XUE Y, LI L, et al. Surface Al leached Ti3AlC2 as a substitute for carbon for use as a catalyst support in a harsh corrosive electrochemical system. Nanoscale, 2014, 6(19): 11035.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
LI M, LU J, LUO K, et al. Element replacement approach by reaction with Lewis acidic molten salts to synthesize nanolaminated MAX phases and MXenes. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(11): 4730.
DOI PMID |
| [48] |
WANG Y, ZHOU B, TANG Q, et al. Ultrafast synthesis of MXenes in minutes via low-temperature molten salt etching. Advanced Materials, 2024, 36(49): 2410736.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
ALI M A, KHATUN M R, JAHAN N, et al. Comparative study of Mo2Ga2C with superconducting MAX phase Mo2GaC: first- principles calculations. Chinese Physics B, 2017, 26(3): 033102.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
GENG D, ZHAO X, CHEN Z, et al. Direct synthesis of large-area 2D Mo2C on in situ grown graphene. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(35): 1700072.
DOI URL |
| [51] | ÖPER M, YORULMAZ U, SEVIK C, et al. Controlled CVD growth of ultrathin Mo2C (MXene) flakes. Journal of Applied Physics, 2022, 131(2): 5304. |
| [52] |
RAVURI S, WROBEL P S, GORANTLA S, et al. High yield and wide lateral size growth of α-Mo2C: exploring the boundaries of CVD growth of bare MXene analogues. Nanotechnology, 2024, 35(15): 155601.
DOI |
| [53] |
XU C, WANG L, LIU Z, et al. Large-area high-quality 2D ultrathin Mo2C superconducting crystals. Nature Materials, 2015, 14(11): 1135.
DOI PMID |
| [54] |
SUN W, WANG X, FENG J, et al. Controlled synthesis of 2D Mo2C/graphene heterostructure on liquid Au substrates as enhanced electrocatalytic electrodes. Nanotechnology, 2019, 30(38): 385601.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
JEON J, PARK Y, CHOI S, et al. Epitaxial synthesis of molybdenum carbide and formation of a Mo2C/MoS2 hybrid structure via chemical conversion of molybdenum disulfide. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(1): 338.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
ZHANG F, ZHANG Z, WANG H, et al. Plasma-enhanced pulsed- laser deposition of single-crystalline Mo2C ultrathin superconducting films. Physical Review Materials, 2017, 1(3): 034002.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
HART J L, HANTANASIRISAKUL K, LANG A C, et al. Control of MXenes’ electronic properties through termination and intercalation. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 522.
DOI |
| [58] |
FENG W, WANG R, ZHOU Y, et al. Ultrathin molybdenum carbide MXene with fast biodegradability for highly efficient theory-oriented photonic tumor hyperthermia. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29: 1901942.
DOI URL |
| [59] |
CHOI J, CHACON B, PARK H, et al. N-p-conductor transition of gas sensing behaviors in Mo2CTx MXene. ACS Sensors, 2022, 7(8): 2225.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
LI J, ZHANG W, GE X, et al. Etching-courtesy NH4+ pre-intercalation enables highly-efficient Li+ storage of MXenes via the renaissance of interlayer redox. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2022, 72: 26.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
JIANG W, GAO Z, SHEN M, et al. Molten salt N-modified Mo2CTx as a non-precious metal catalyst for efficient hydrogen evolution reaction. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 57: 1.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
WU Y, WANG L, BO T, et al. Boosting hydrogen evolution in neutral medium by accelerating water dissociation with Ru clusters loaded on Mo2CTx MXene. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(16): 2214375.
DOI URL |
| [63] |
LIANG J, DING C, LIU J, et al. Heterostructure engineering of Co-doped MoS2 coupled with Mo2CTx MXene for enhanced hydrogen evolution in alkaline media. Nanoscale, 2019, 11(22): 10992.
DOI URL |
| [64] |
LIM K R G, HANDOKO A D, JOHNSON L R, et al. 2H-MoS2 on Mo2CTx MXene nanohybrid for efficient and durable electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. ACS Nano, 2020, 14(11): 16140.
DOI URL |
| [65] |
BENCHAKAR M, NATU V, ELMELEGY T A, et al. On a two-dimensional MoS2/Mo2CTx hydrogen evolution catalyst obtained by the topotactic sulfurization of Mo2CTx MXene. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2020, 167(12): 124507.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
WU Y, WANG L, CHAI Z, et al. Heterostructure engineering of MoS2/Mo2CTx nanoarray via molten salt synthesis for enhanced hydrogen evolution reaction. Journal of Materiomics, 2023, 9(6): 1122.
DOI URL |
| [67] |
YI M, LI N, LU B, et al. Single-atom Pt decorated in heteroatom (N, B, and F)-doped ReS2 grown on Mo2CTx for efficient pH-universal hydrogen evolution reaction and flexible Zn-air batteries. Energy Storage Materials, 2021, 42: 418.
DOI URL |
| [68] |
YI M, HU S, LI N, et al. Selenium vacancy-rich and heteroatom-doped CoSe/Mo2CTx MXene prepared using ionic liquid dopants for pH-universal hydrogen evolution and flexible supercapacitors. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2022, 72: 453.
DOI URL |
| [69] | YI M, ZHANG X, CHEN Y, et al. Ionic liquid dopant induced abundant Ni-vacancies in N, B, F tri-doped NiSe2/Mo2CTx stabilizing of single-atom Ru for efficient hydrogen evolution reactions and flexible Zn-air batteries. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2023, 11(9): 3687. |
| [70] |
WU N, LIU J, ZHAO W, et al. Molybdenum carbide MXene embedded with nickel sulfide clusters as an efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2023, 48(46): 17526.
DOI URL |
| [71] |
LIU S, LIN Z, WAN R, et al. Cobalt phosphide supported by two-dimensional molybdenum carbide (MXene) for the hydrogen evolution reaction, oxygen evolution reaction, and overall water splitting. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2021, 9(37): 21259.
DOI URL |
| [72] |
YI M, REN Y, ZHANG X, et al. Ionic liquid-assisted synthesis of N, F, and B co-doped BiOBr/Bi2Se3 on Mo2CTx for enhanced performance in hydrogen evolution reaction and supercapacitors. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2024, 658: 334.
DOI URL |
| [73] |
ABDOLAHI B, GHOLIVAND M B, SHAMSIPUR M, et al. Introduction of a three-dimensional flower-like Mo2CTx/poly (2, 2′-dithiodianiline) on reduced graphene oxide as an efficient electrode for supercapacitor and hydrogen evolution reaction. Journal of Energy Storage, 2023, 62: 106906.
DOI URL |
| [74] |
DING B, ONG W J, JIANG J, et al. Uncovering the electrochemical mechanisms for hydrogen evolution reaction of heteroatom doped M2C MXene (M = Ti, Mo). Applied Surface Science, 2020, 500: 143987.
DOI URL |
| [75] |
KUZNETSOV D A, CHEN Z, KUMAR P V, et al. Single site cobalt substitution in 2D molybdenum carbide (MXene) enhances catalytic activity in the hydrogen evolution reaction. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(44): 17809.
DOI PMID |
| [76] |
ZHAO C, QIU C, DENG S, et al. 2D-3D transformation of palladium and gold nanoparticles on functionalized Mo2C by multiscale simulation. Applied Surface Science, 2019, 481: 554.
DOI URL |
| [1] | YU Shengyang, SU Haijun, JIANG Hao, YU Minghui, YAO Jiatong, YANG Peixin. A Review of Pore Defects in Ultra-high Temperature Oxide Ceramics by Laser Additive Manufacturing: Formation and Suppression [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(9): 944-956. |
| [2] | LIU Jiangping, GUAN Xin, TANG Zhenjie, ZHU Wenjie, LUO Yongming. Research Progress on Catalytic Oxidation of Nitrogen-containing Volatile Organic Compounds [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(9): 933-943. |
| [3] | XIAO Xiaolin, WANG Yuxiang, GU Peiyang, ZHU Zhenrong, SUN Yong. Advances in Regulation of Damaged Skin Regeneration by Two-dimensional Inorganic Materials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 860-870. |
| [4] | MA Jingge, WU Chengtie. Application of Inorganic Bioceramics in Promoting Hair Follicle Regeneration and Hair Growth [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 901-910. |
| [5] | ZHANG Hongjian, ZHAO Ziyi, WU Chengtie. Inorganic Biomaterials on Regulating Neural Cell Function and Innervated Tissue Regeneration: A Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 849-859. |
| [6] | AI Minhui, LEI Bo. Micro-nanoscale Bioactive Glass: Functionalized Design and Angiogenic Skin Regeneration [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 921-932. |
| [7] | WANG Yutong, CHANG Jiang, XU He, WU Chengtie. Advances in Silicate Bioceramic/Bioglass for Wound Healing: Effects, Mechanisms and Application Ways [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 911-920. |
| [8] | MA Wenping, HAN Yahui, WU Chengtie, LÜ Hongxu. Application of Inorganic Bioactive Materials in Organoid Research [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 888-900. |
| [9] | LUO Xiaomin, QIAO Zhilong, LIU Ying, YANG Chen, CHANG Jiang. Inorganic Bioactive Materials Regulating Myocardial Regeneration [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 871-887. |
| [10] | ZHU Wenjie, TANG Lu, LU Jichang, LIU Jiangping, LUO Yongming. Research Progress on Catalytic Oxidation of Volatile Organic Compounds by Perovskite Oxides [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [11] | HU Zhichao, YANG Hongyu, YANG Hongcheng, SUN Chengli, YANG Jun, LI Enzhu. Usage of the P-V-L Bond Theory in Regulating Properties of Microwave Dielectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [12] | WU Qiong, SHEN Binglin, ZHANG Maohua, YAO Fangzhou, XING Zhipeng, WANG Ke. Research Progress on Lead-based Textured Piezoelectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [13] | ZHANG Bihui, LIU Xiaoqiang, CHEN Xiangming. Recent Progress of Hybrid Improper Ferroelectrics with Ruddlesden-Popper Structure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| [14] | WU Jie, YANG Shuai, WANG Mingwen, LI Jinglei, LI Chunchun, LI Fei. Textured PT-based Piezoelectric Ceramics: Development, Status and Challenge [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 575-586. |
| [15] | JIANG Kun, LI Letian, ZHENG Mupeng, HU Yongming, PAN Qinxue, WU Chaofeng, WANG Ke. Research Progress on Low-temperature Sintering of PZT Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||