
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (9): 1022-1028.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250022
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Liangjun1( ), OUYANG Yuzhao1, ZHAO Junliang2, YANG Chang1(
), OUYANG Yuzhao1, ZHAO Junliang2, YANG Chang1( )
)
Received:2025-01-15
Revised:2025-02-13
Published:2025-09-20
Online:2025-03-19
Contact:
YANG Chang, professor. E-mail: cyang@phy.ecnu.edu.cnAbout author:WANG Liangjun (1998-), male, PhD candidate. E-mail: 1134420548@qq.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
WANG Liangjun, OUYANG Yuzhao, ZHAO Junliang, YANG Chang. Cu-Mn-I Solid Solution Thin Films: Preparation and Control of p-type Transparent Conductive Properties[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(9): 1022-1028.
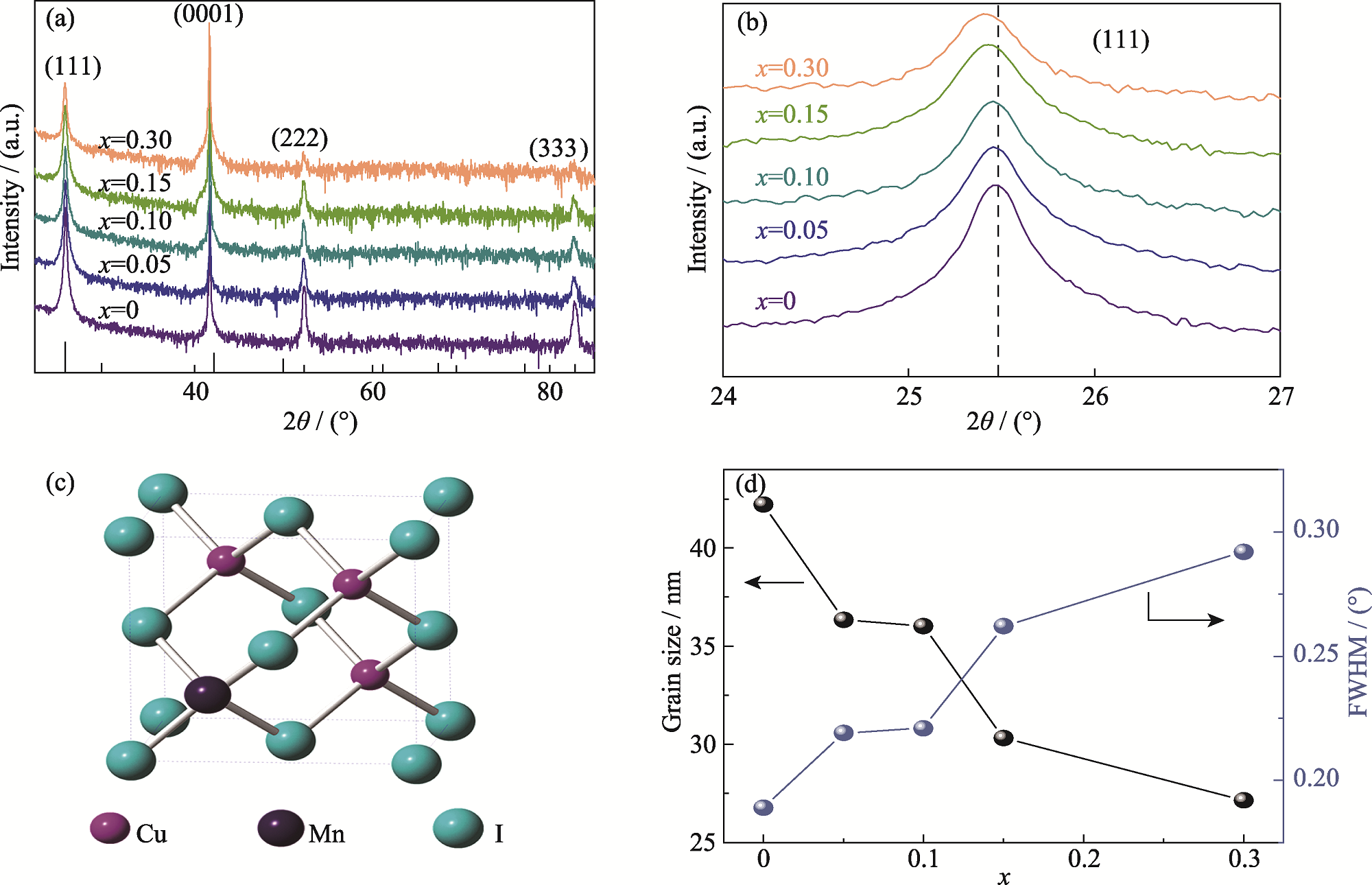
Fig. 2 Crystal structure analyses of Cu1-xMnxI thin films (a) XRD patterns; (b) Localized magnified patterns of diffraction peak (111); (c) Schematic diagram of manganese ions replacing copper ions; (d) Dependence of grain size and FWHM on x
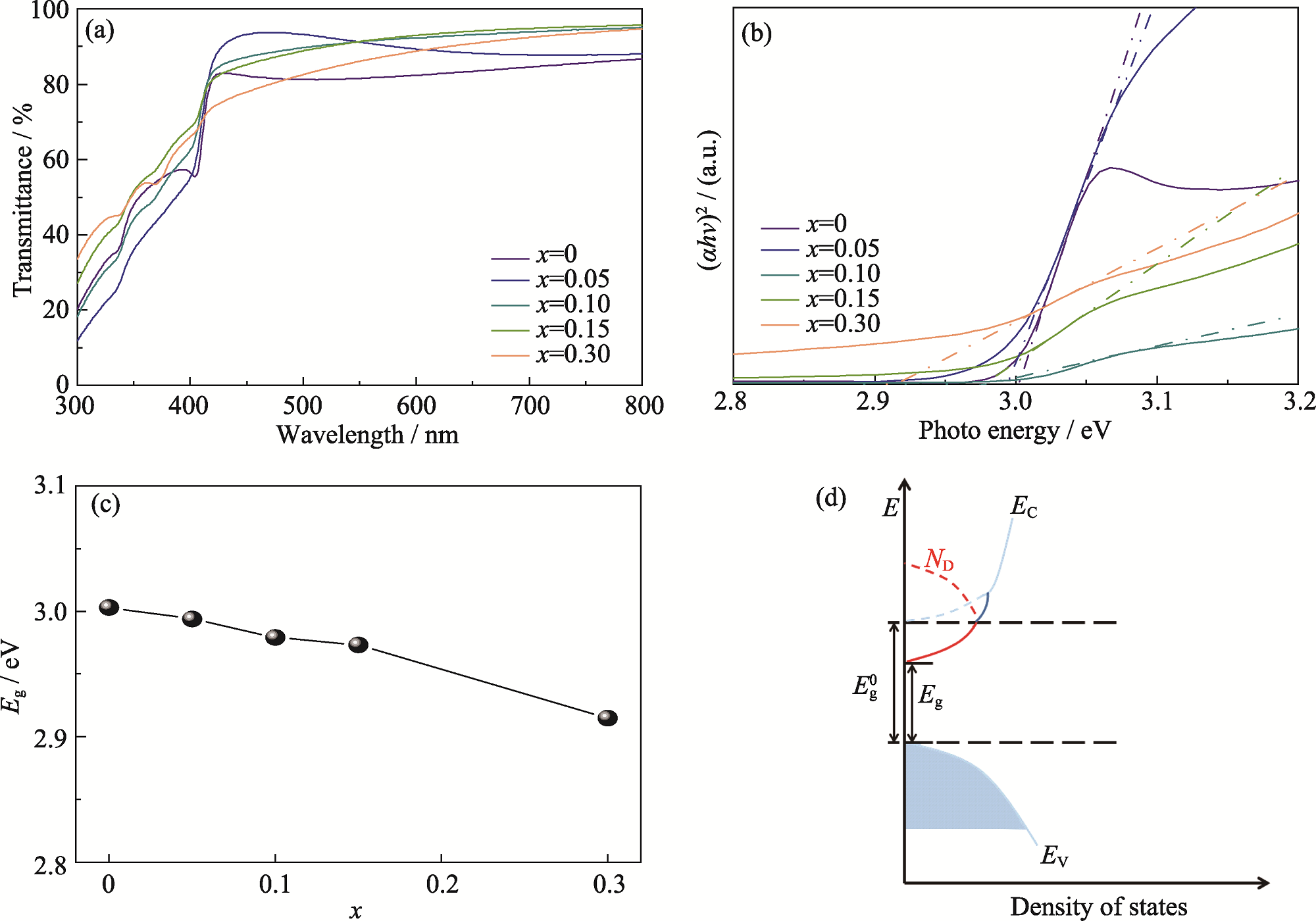
Fig. 3 Analyses of optical bandgap of Cu1-xMnxI thin films (a) UV-Vis transmission spectra; (b) Tauc plots; (c) Dependence of Eg on x; (d) Schematic diagram of the influence of donor energy levels on Eg. Colorful figures are available on website
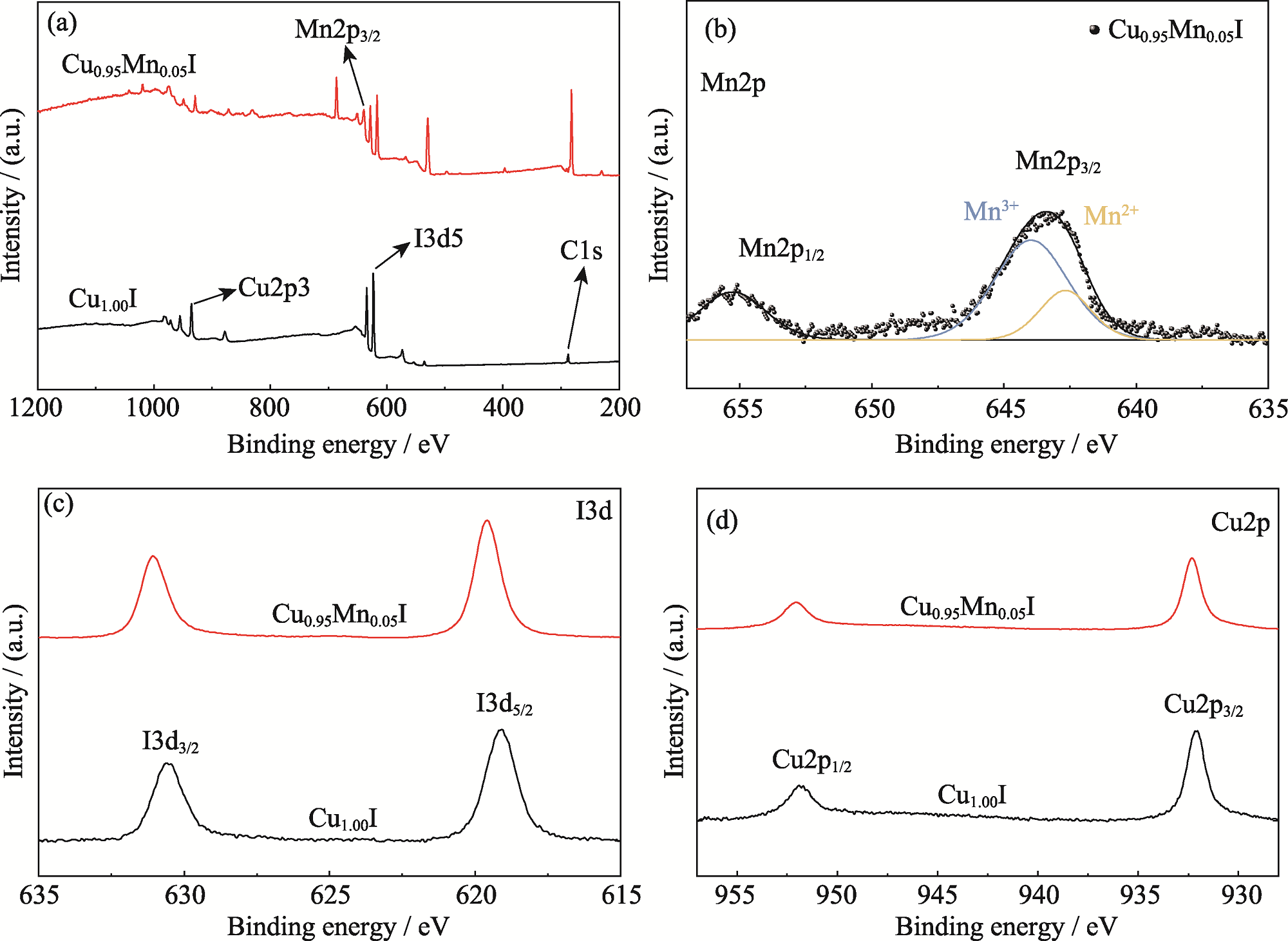
Fig. 4 XPS spectra of Cu1.00I and Cu0.95Mn0.05I thin films (a) XPS survey spectra; (b) High-resolution Mn2p XPS spectra of Cu0.95Mn0.05I films; (c, d) High-resolution I3d (c) and Cu2p (d) XPS spectra of Cu1.00I and Cu0.95Mn0.05I thin films
| [1] | LIU A, ZHU H H, KIM M G, et al. Engineering copper iodide (CuI) for multifunctional p-type transparent semiconductors and conductors. Advanced Science, 2021, 8(14): 2100546. |
| [2] | THOMAS G. Invisible circuits. Nature, 1997, 389(6654): 907. |
| [3] | KAWAZOE H, YASUKAWA M, HYODO H, et al. P-type electrical conduction in transparent thin films of CuAlO2. Nature, 1997, 389(6654): 939. |
| [4] | UEDA K, HASE T, YANAGI H, et al. Epitaxial growth of transparent p-type conducting CuGaO2 thin films on sapphire (001) substrates by pulsed laser deposition. Journal of Applied Physics, 2001, 89(3): 1790. |
| [5] | YANAGI H, HASE T, IBUKI S, et al. Bipolarity in electrical conduction of transparent oxide semiconductor CuInO2 with delafossite structure. Applied Physics Letters, 2001, 78(11): 1583. |
| [6] | KUDO A, YANAGI H, HOSONO H, et al. SrCu2O2: a p-type conductive oxide with wide band gap. Applied Physics Letters, 1998, 73(2): 220. |
| [7] | RAGHUPATHY R K M, KÜHNE T D, FELSER C, et al. Rational design of transparent p-type conducting non-oxide materials from high-throughput calculations. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2018, 6(3): 541. |
| [8] | YANG C, KNEIß M, LORENZ M, et al. Room-temperature synthesized copper iodide thin film as degenerate p-type transparent conductor with a boosted figure of merit. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2016, 113(46): 12929. |
| [9] | GENG F J, WANG L J, STRALKA, et al. (111)-oriented growth and acceptor doping of transparent conductive CuI:S thin films by spin coating and radio frequency-sputtering. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2023, 25(11): 2201666. |
| [10] | YANG J L, JIANG X L, RUAN S Y, et al. Highly weak-light sensitive and dual-band switchable photodetector based on CuI/Si unilateral heterojunction. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(9): 1063. |
| [11] | GRUNDMANN M, SCHEIN F L, LORENZ M, et al. Cuprous iodide - a p-type transparent semiconductor: history and novel applications. Physica Status Solidi A, 2013, 210(9): 1671. |
| [12] | GRUNDMANN M. Karl Bädeker (1877-1914) and the discovery of transparent conductive materials. Physica Status Solidi A, 2015, 212(7): 1409. |
| [13] | CHEN D, WANG Y, LIN Z, et al. Growth strategy and physical properties of the high mobility p-type CuI crystal. Crystal Growth & Design, 2010, 10(5): 2057. |
| [14] | JUN T, KIM J, SASASE M, et al. Material design of p-type transparent amorphous semiconductor, Cu-Sn-I. Advance Materials, 2018, 30(12): 1706573. |
| [15] | YANG C, SOUCHAY D, KNEIß M, et al. Transparent flexible thermoelectric material based on non-toxic earth-abundant p-type copper iodide thin film. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 16076. |
| [16] | ZENG G X, DOU W, GAN X M, et al. Low-voltage solution-processed NaxCu1-xI thin-film transistors for mimicking synaptic plasticity. Applied Physical Letters, 2024, 124(12): 123508. |
| [17] | JIANG G G, DOU W, GAN X M, et al. Low-voltage solution- processed p-type Mg-doped CuI thin film transistors with NAND logic function. Applied Physical Letters, 2023, 122(21): 213501. |
| [18] | GHAZAL N, MADKOUR M, NAZEER A A, et al. Electrochemical capacitive performance of thermally evaporated Al-doped CuI thin films. RSC Advance, 2021, 11(62): 39262. |
| [19] | MIRZA A S, VISHAL B, DALLY P, et al. Cs-doped and Cs-S co-doped CuI p-type transparent semiconductors with enhanced conductivity. Advanced Functional Materials, 2024, 34(30): 2316144. |
| [20] | MUDE N N, BUKKE R N, JIANG J. Transparent, p-channel CuISn thin-film transistor with field effect mobility of 45 cm2·V-1·s-1 and excellent bias stability. Advanced Materials Technologies, 2022, 7(8): 2101434. |
| [21] | TAREY R D, RAJU T A. A method for the deposition of transparent conducting thin films of tin oxide. Thin Solid Films, 1985, 128(3/4): 181. |
| [22] | LIU A, ZHU H H, PARK W T, et al. Room-temperature solution-synthesized p-type copper(I) iodide semiconductors for transparent thin-film transistors and complementary electronics. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(34): 1802379. |
| [23] | STRELCHUNK V, KOLOMYS O, RARATA S, et al. Raman submicron spatial mapping of individual Mn-doped ZnO nanorods. Nano Epress, 2017, 12: 1. |
| [24] | ZI M, LI J, ZHANG Z C, et al. Effect of deposition temperature on transparent conductive properties of γ-CuI film prepared by vacuum thermal evaporation. Physica Status Solidi A, 2015, 212(7): 1466. |
| [25] | SUNG S Y, KIM S Y, JO K M, et al. Fabrication of p-channel thin-film transistors using CuO active layers deposited at low temperature. Applied Physical Letters, 2010, 97(22): 222109. |
| [26] | KYKYNESHI R, MCINTYRE D H, TATE J, et al. Electrical and optical properties of epitaxial transparent conductive BaCuTeF thin films deposited by pulsed laser deposition. Solid State Sciences, 2008, 10(7): 921. |
| [27] | ZAKUTAYEV A, MCINTYRE D H, SCHNEIDER G, et al. Tunable properties of wide-band gap p-type BaCu(Ch1-xChx′)F (Ch=S, Se, Te) thin-film solid solutions. Thin Solid Films, 2010, 518(19): 5494. |
| [28] | YANG C, KNEIß M, SCHEIN F L, et al. Room-temperature domain-epitaxy of copper iodide thin films for transparent CuI/ZnO heterojunctions with high rectification ratios larger than 109. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 21937. |
| [29] | YANG C, ROSE E, YU W L, et al. Controllable growth of copper iodide for high-mobility thin films and self-assembled microcrystals. ACS Applied Electronic Materials, 2020, 2(11): 3627. |
| [1] | LING Yihan, GUO Sheng, CAO Zhiqiang, TIAN Yunfeng, LIU Fangsheng, JIN Fangjun, GAO Yuan. Research Progress on Preparation Technologies and Performance of Straight-pore Electrode Structures for Solid Oxide Cells [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(12): 1311-1323. |
| [2] | ZHANG Haifeng, JIANG Meng, SUN Tingting, WANG Lianjun, JIANG Wan. Preparation of p-type GeMnTe2 Based Thermoelectric Materials with Stable Cubic Phase [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(11): 1245-1251. |
| [3] | LI Chengming, ZHOU Chuang, LIU Peng, ZHENG Liping, LAI Yongji, CHEN Liangxian, LIU Jinlong, WEI Junjun. Stress in CVD Diamond Films: Generation, Suppression, Application, and Measurement [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(11): 1188-1200. |
| [4] | WU Mingxuan, LI Junjie, CHEN Shuo, YAN Yonggao, SU Xianli, ZHANG Qingjie, TANG Xinfeng. Homogeneity of Zone-melted n-type Bi1.96Sb0.04Te2.70Se0.30 Thermoelectric Material [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(11): 1252-1260. |
| [5] | YUAN Long, JIA Ru, YUAN Meng, ZHANG Jian, DUAN Yu, MENG Xiangdong. Mechanism and Application of X-ray Induced Photochromic Materials: A Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(10): 1097-1110. |
| [6] | AI Yizhaotong, REN Jiulong, QIANG Linya, ZHANG Xiaozhen, YANG Kai, GAO Yanfeng. Friction and Wear Properties of Al2O3-GdAlO3 (GAP) Amorphous Ceramic Coatings under High Load Capacity [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(10): 1111-1118. |
| [7] | CAO Luhan, MENG Jia, XUE Yudong, SHENG Xiaochen, CUI Yuanyuan, LE Jun, SONG Lixin. Effect of SiC Transition Layer on Bonding Properties of MoSi2-SABB Coating on SiC/SiC Ceramic Matrix Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(10): 1119-1128. |
| [8] | WAN Xinyi, WANG Wenqi, LI Jiacheng, ZHAO Junliang, MA Dongyun, WANG Jinmin. Colorless/Black Switching Electrochromic Device Based on WO3·xH2O and Reversible Metal Electrodeposition [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(10): 1163-1174. |
| [9] | ZHAO Lihua, WANG Yanshuai, YIN Xinwu, MAO Yeqiong, NIU Dechao. Bismuth Sulfide Nanoclusters-loaded Silica-based Hybrid Micelles: Preparation and Photothermal Antibacterial Property [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(10): 1129-1136. |
| [10] | WU Huaxin, ZHANG Qihao, YAN Haixue, WANG Lianjun, JIANG Wan. Optimization of Thermoelectric Transport Properties in Nanocomposite MgAgSb-based Alloys [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(9): 997-1004. |
| [11] | YU Shengyang, SU Haijun, JIANG Hao, YU Minghui, YAO Jiatong, YANG Peixin. A Review of Pore Defects in Ultra-high Temperature Oxide Ceramics by Laser Additive Manufacturing: Formation and Suppression [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(9): 944-956. |
| [12] | LI Tingsong, WANG Wenli, LIU Qiang, WANG Yanbin, ZHOU Zhenzhen, HU Chen, LI Jiang. Influence of Cr3+ Doping Concentration on the Persistent Performance of YAGG:Ce3+,Cr3+ Luminescent Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(9): 1037-1044. |
| [13] | MA Jingge, WU Chengtie. Application of Inorganic Bioceramics in Promoting Hair Follicle Regeneration and Hair Growth [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 901-910. |
| [14] | ZHANG Hongjian, ZHAO Ziyi, WU Chengtie. Inorganic Biomaterials on Regulating Neural Cell Function and Innervated Tissue Regeneration: A Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 849-859. |
| [15] | MA Wenping, HAN Yahui, WU Chengtie, LÜ Hongxu. Application of Inorganic Bioactive Materials in Organoid Research [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(8): 888-900. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||