
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (6): 707-714.DOI: 10.15541/jim20230588
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHENG Yawen( ), ZHANG Cuiping(
), ZHANG Cuiping( ), ZHANG Ruijie, XIA Qian, RU Hongqiang
), ZHANG Ruijie, XIA Qian, RU Hongqiang
Received:2023-12-21
Revised:2024-03-17
Published:2024-06-20
Online:2024-03-22
Contact:
ZHANG Cuiping, lecturer. E-mail: zhangcp@smm.neu.edu.cnAbout author:ZHENG Yawen (2000-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: zheng_ya_wen@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
ZHENG Yawen, ZHANG Cuiping, ZHANG Ruijie, XIA Qian, RU Hongqiang. Fabrication of Boron Carbide Ceramic Composites by Boronic Acid Carbothermal Reduction and Silicon Infiltration Reaction Sintering[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(6): 707-714.

Fig. 2 SEM secondary electron images of synthesized powders under different nC/nB conditions (a) nC/nB=1.35; (b) nC/nB=1.75; (c) nC/nB=1.93; (d) nC/nB=2.01
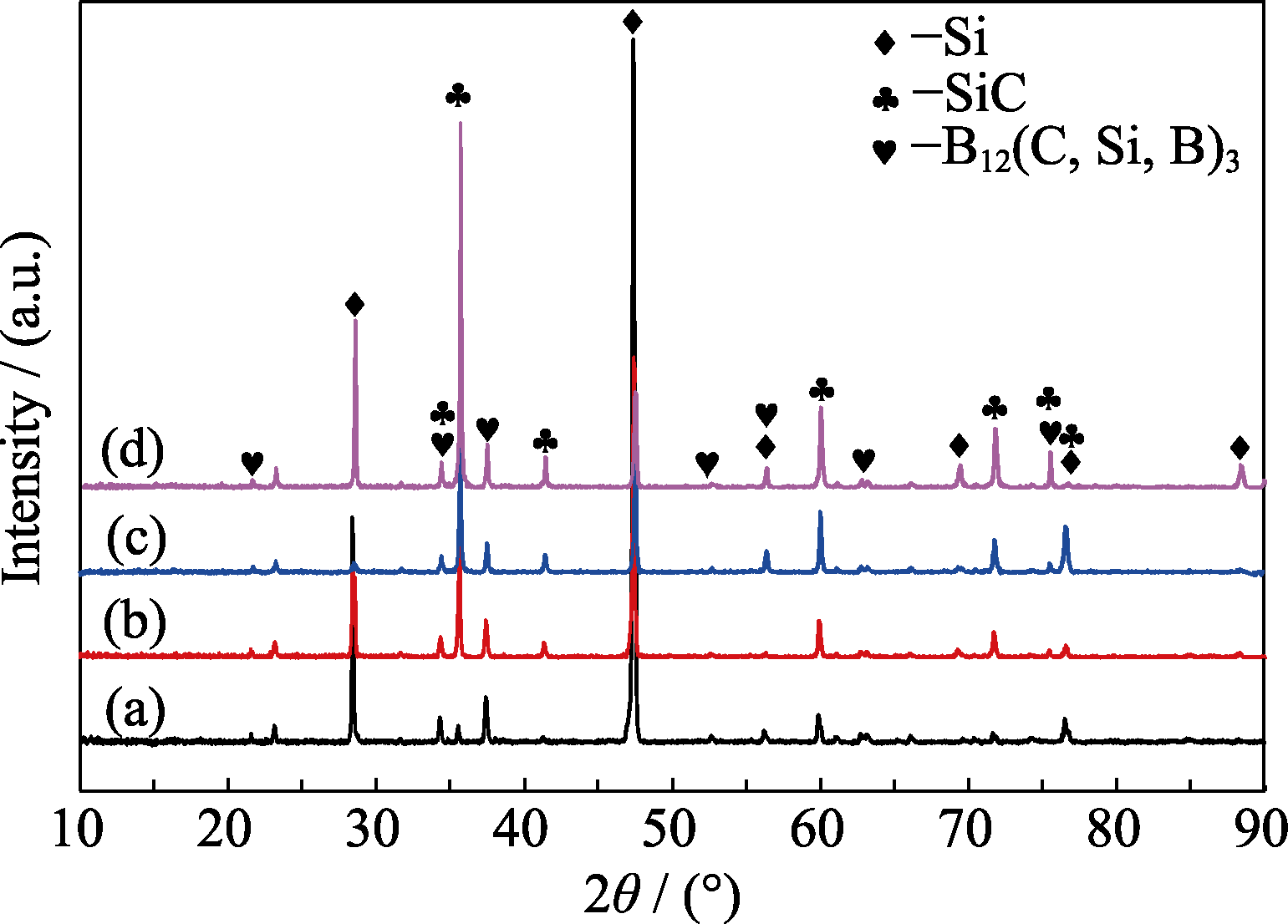
Fig. 3 XRD patterns of B4C composite materials prepared under different nC/nB conditions (a) nC/nB=1.35; (b) nC/nB=1.75; (c) nC/nB=1.93; (d) nC/nB=2.01
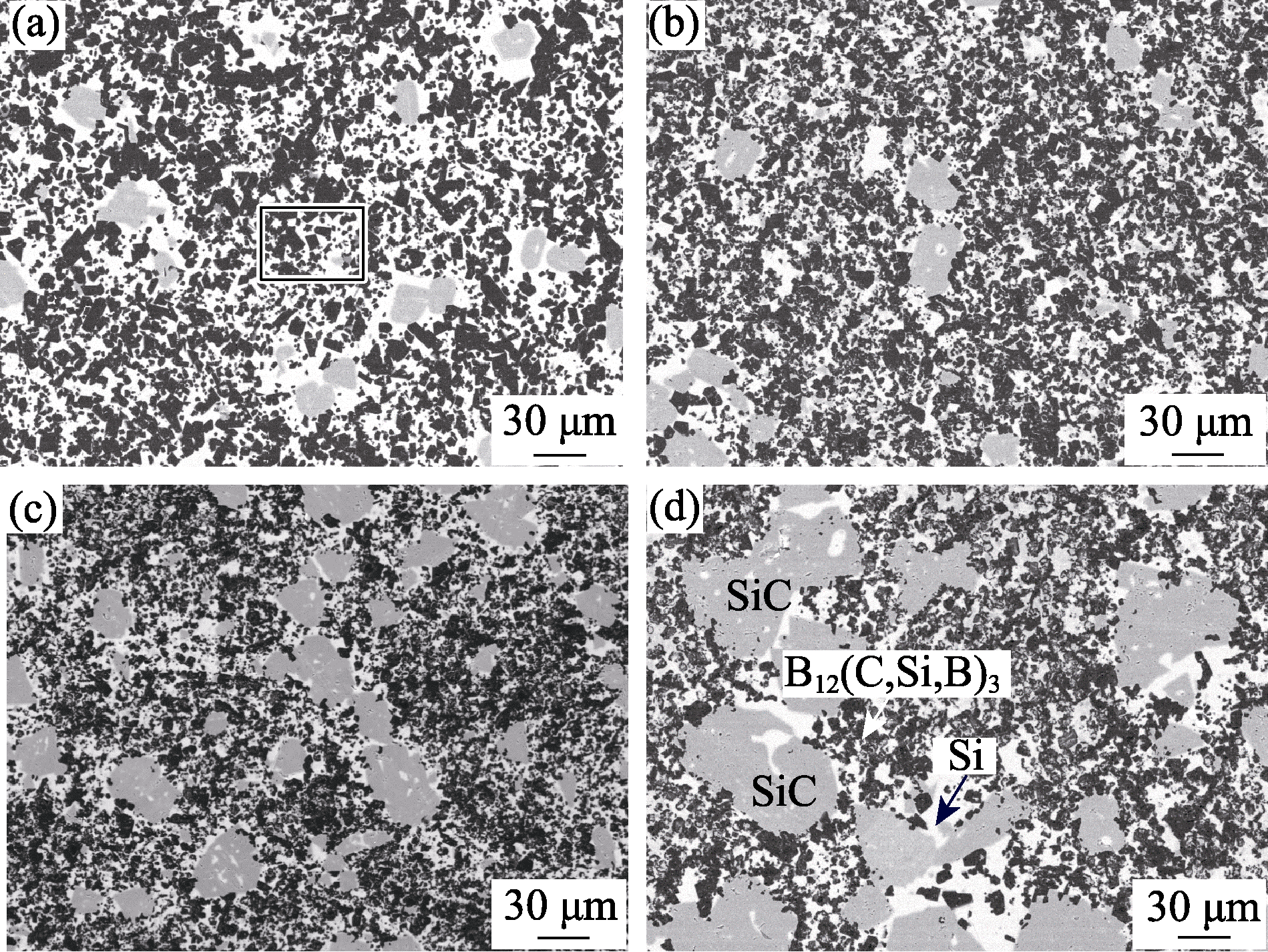
Fig. 4 SEM backscatter images of B4C composite materials prepared under different nC/nB conditions (a) nC/nB=1.35; (b) nC/nB=1.75; (c) nC/nB=1.93; (d) nC/nB=2.01
| nC/nB | Volume fraction/% | Dmean/μm | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B12(B,C,Si)3 | SiC | Si | SiC | |
| 1.35 | 57.21 | 19.47 | 23.32 | 5.32 |
| 1.75 | 56.71 | 24.68 | 18.61 | 5.59 |
| 1.93 | 52.57 | 36.24 | 11.18 | 6.18 |
| 2.01 | 51.98 | 38.07 | 9.95 | 5.99 |
Table 1 Volume fraction of B4C composite materials and phase size of SiC under different nC/nB conditions
| nC/nB | Volume fraction/% | Dmean/μm | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B12(B,C,Si)3 | SiC | Si | SiC | |
| 1.35 | 57.21 | 19.47 | 23.32 | 5.32 |
| 1.75 | 56.71 | 24.68 | 18.61 | 5.59 |
| 1.93 | 52.57 | 36.24 | 11.18 | 6.18 |
| 2.01 | 51.98 | 38.07 | 9.95 | 5.99 |
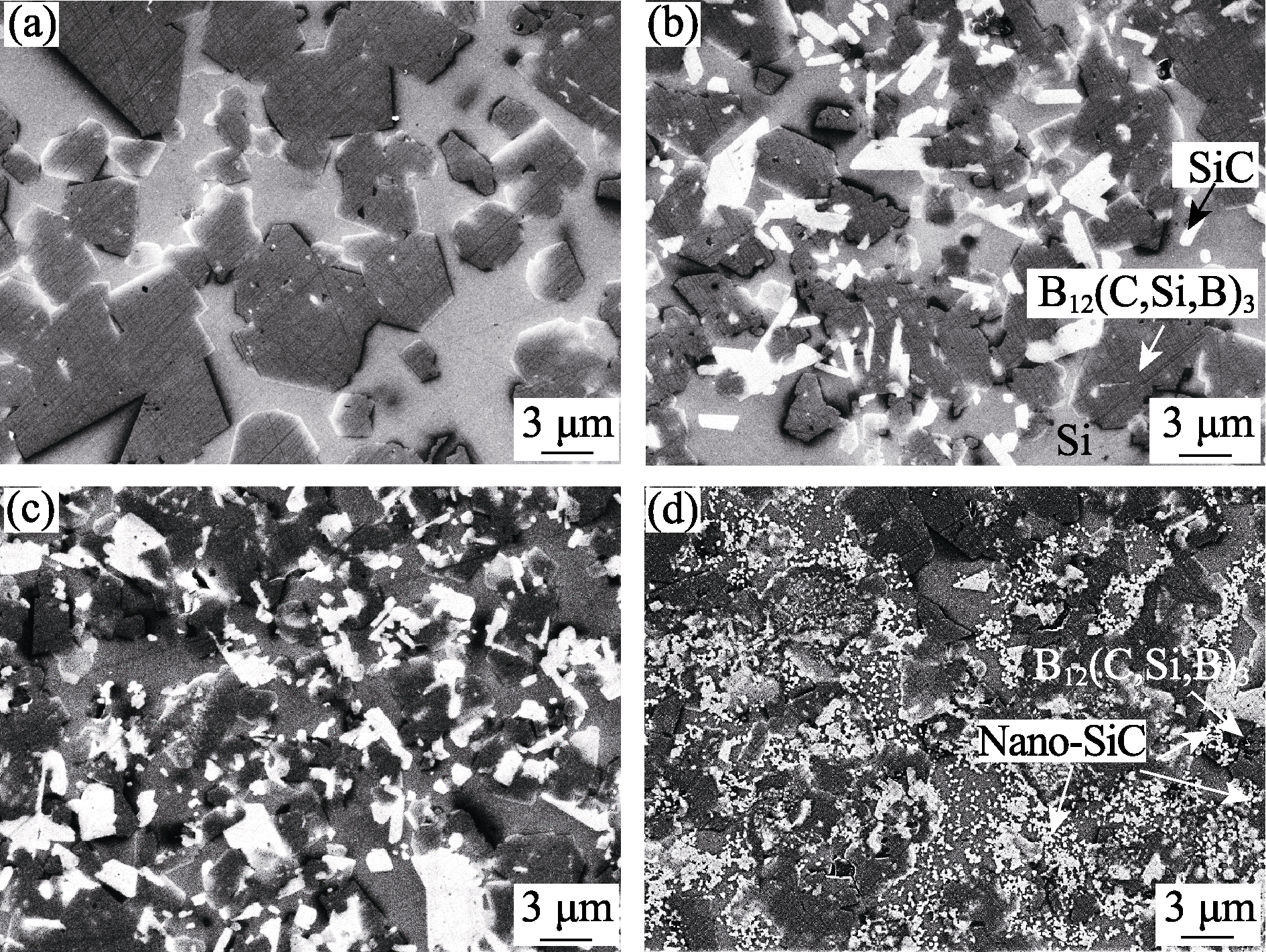
Fig. 5 SEM secondary electron images of B4C composite materials prepared under different nC/nB conditions (a) nC/nB=1.35; (b) nC/nB=1.75; (c) nC/nB=1.93; (d) nC/nB=2.01
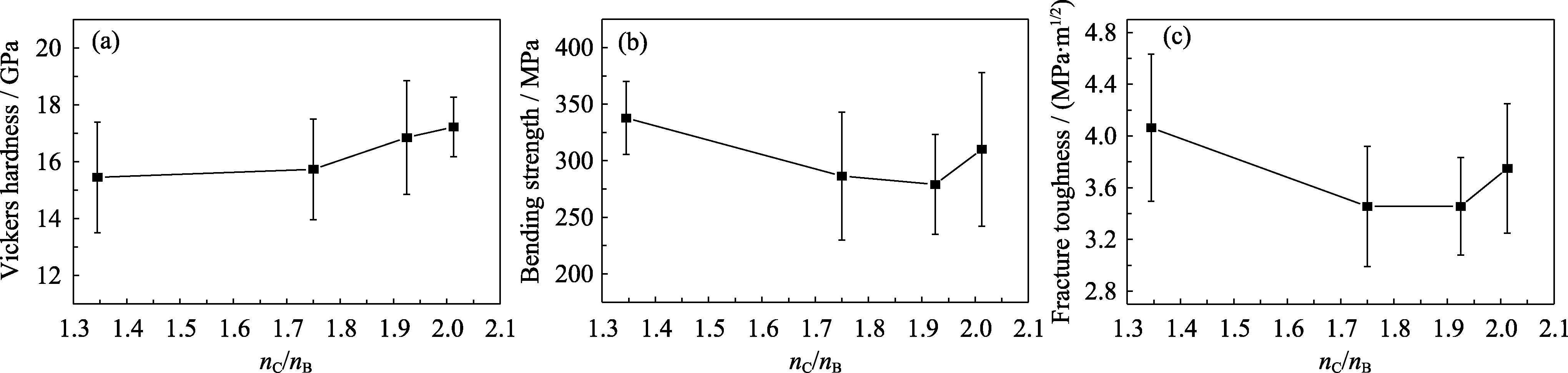
Fig. 7 Mechanical properties of boron carbide composite materials under different nC/nB conditions (a) Vickers hardness; (b) Bending strength; (c) Fracture toughness
| [1] | SONG Q, ZHANG Z H, HU Z Y, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of super-hard B4C ceramic fabricated by spark plasma sintering with (Ti3SiC2+Si) as sintering aid. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(7):8790. |
| [2] | SONG S, BAO C, WANG B. Effect of the addition of carbon fibres on the microstructure and mechanical properties of reaction bonded B4C/SiC composites. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2016, 36(8): 1905. |
| [3] | MOSHTAGHIOUN B M, CUMBRERA-HERNÁNDEZ F L, GÓMEZ-GARCÍA D, et al. Effect of spark plasma sintering parameters on microstructure and room-temperature hardness and toughness of fine-grained boron carbide (B4C). Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2013, 33(2):361. |
| [4] | ZHAO X, ZOU J, JI W, et al. Processing and mechanical properties of B4C-SiCw ceramics densified by spark plasma sintering. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2022, 42(5): 2004. |
| [5] | WANG S, GAO S, XING P, et al. Pressureless liquid-phase sintering of B4C with MoSi2 as a sintering aid. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(10):13502. |
| [6] | BARICK P, JANA D C, THIYAGARAJAN N. Effect of particle size on the mechanical properties of reaction bonded boron carbide ceramics. Ceramics International, 2013, 39(1):763. |
| [7] | SURI A K, SUBRAMANIAN C, SONBER J K, et al. Synthesis and consolidation of boron carbide: a review. International Materials Reviews, 2013, 55(1):4. |
| [8] | FOROUGHI P, CHENG Z. Understanding the morphological variation in the formation of B4C via carbothermal reduction reaction. Ceramics International, 2016, 42(14):15189. |
| [9] | AHMED Y M Z, EL-SHEIKH S M, EWAIS E M M, et al. Controlling the morphology and oxidation resistance of boron carbide synthesized via carbothermic reduction reaction. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2017, 26(3):1444. |
| [10] | 董开朝.Na2CO3添加剂对碳化硼制备的影响及其作用机理的研究. 沈阳: 东北大学硕士学位论文, 2019. |
| [11] | 于国强, 刘维良, 欧阳瑞丰, 等. 碳热还原法制备碳化硼粉末的工艺研究. 中国陶瓷, 2012, 48(6):58. |
| [12] | ALIZADEH A, TAHERI-NASSAJ E, EHSANI N. Synthesis of boron carbide powder by a carbothermic reduction method. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2004, 24(10/11):3227. |
| [13] | KANANATHAN J, SOFIAH A G N, SAMYKANO M, et al. Influence of boric acid (H3BO3) concentration on the physical properties of electrochemical deposited nickel (Ni) nanowires. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2017, 257: 012033. |
| [14] | HAYUN S, WEIZMANN A, DARIEL M P, et al. Microstructural evolution during the infiltration of boron carbide with molten silicon. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2010, 30(4):1007. |
| [15] | HAYUN S, FRAGE N, DARIEL M P. The morphology of ceramic phases in BxC-SiC-Si infiltrated composites. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2006, 179(9):2875. |
| [16] | HAYUN S, WEIZMANN A, DARIEL M P, et al. The effect of particle size distribution on the microstructure and the mechanical properties of boron carbide-based reaction-bonded composites. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2009, 6(4):492. |
| [17] | ZHANG C, XIA Q, HAN L, et al. Fabrication of carbon-coated boron carbide particle and its role in the reaction bonding of boron carbide by silicon infiltration. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2022, 42(3):860. |
| [18] | CHEN Z F, SU Y C, CHENG Y B. Formation and sintering mechanisms of reaction bonded silicon carbide-boron carbide composites. Key Engineering Materials, 2007, 352: 207. |
| [19] | 赵祖德. 复合材料固-液成形理论与工艺. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2008. |
| [20] | PATEL M, SUBRAHMANYAM J, PRASAD V V B, et al. Processing and characterization of B4C-SiC-Si-TiB2 composites. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2010, 527(16/17):4109. |
| [21] | CHAIM R, HEFETZ M. Effect of grain size on elastic modulus and hardness of nanocrystalline ZrO2-3 wt%Y2O3 ceramic. Journal of Materials Sciences, 2004, 39(9):3057. |
| [22] | THÉVENOT F. Boron carbide-a comprehensive review. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 1990, 6(4):205. |
| [23] | DOWLING N. Mechanical behavior of materials:engineering methods for deformation, fracture, and fatigue. Upper Saddle River: Pearson Education Inc., 2012. |
| [24] | BARSOUM M, BARSOUM M W. Fundamentals of Ceramics. New York: The McGraw-Hill Companies Inc., 2002. |
| [25] | GUO S, TODD R I. Quantitative optical fluorescence microprobe measurements of stresses around indentations in Al2O3 and Al2O3/SiC nanocomposites: the influence of depth resolution and specimen translucency. Acta Materialia, 2011, 59(7):2637. |
| [26] | ZHANG C, RU H, WANG W, et al. The role of infiltration temperature in the reaction bonding of boron carbide by silicon infiltration. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2014, 97(10):3286. |
| [1] | MU Haojie, ZHANG Yuanjiang, YU Bin, FU Xiumei, ZHOU Shibin, LI Xiaodong. Preparation and Properties of ZrO2 Doped Y2O3-MgO Nanocomposite Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 281-289. |
| [2] | FAN Wugang, CAO Xiong, ZHOU Xiang, LI Ling, ZHAO Guannan, ZHANG Zhaoquan. Anticorrosion Performance of 8YSZ Ceramics in Simulated Aqueous Environment of Pressurized Water Reactor [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(7): 803-809. |
| [3] | CHEN Qian, SU Haijun, JIANG Hao, SHEN Zhonglin, YU Minghui, ZHANG Zhuo. Progress of Ultra-high Temperature Oxide Ceramics: Laser Additive Manufacturing and Microstructure Evolution [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(7): 741-753. |
| [4] | JIANG Lingyi, PANG Shengyang, YANG Chao, ZHANG Yue, HU Chenglong, TANG Sufang. Preparation and Oxidation Behaviors of C/SiC-BN Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(7): 779-786. |
| [5] | XUE Yifan, LI Weijie, ZHANG Zhongwei, PANG Xu, LIU Yu. Process Control of PyC Interphases Microstructure and Uniformity in Carbon Fiber Cloth [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(4): 399-408. |
| [6] | SUN Chuan, HE Pengfei, HU Zhenfeng, WANG Rong, XING Yue, ZHANG Zhibin, LI Jinglong, WAN Chunlei, LIANG Xiubing. SiC-based Ceramic Materials Incorporating GNPs Array: Preparation and Mechanical Characterization [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(3): 267-273. |
| [7] | ZHENG Jiaqian, LU Xiao, LU Yajie, WANG Yingjun, WANG Zhen, LU Jianxi. Functional Bioadaptability in Medical Bioceramics: Biological Mechanism and Application [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(1): 1-16. |
| [8] | HE Danqi, WEI Mingxu, LIU Ruizhi, TANG Zhixin, ZHAI Pengcheng, ZHAO Wenyu. Heavy-Fermion YbAl3 Materials: One-step Synthesis and Enhanced Thermoelectric Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 577-582. |
| [9] | WU Shuang, GOU Yanzi, WANG Yongshou, SONG Quzhi, ZHANG Qingyu, WANG Yingde. Effect of Heat Treatment on Composition, Microstructure and Mechanical Property of Domestic KD-SA SiC Fibers [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 569-576. |
| [10] | XIE Jiaye, LI Liwen, ZHU Qiang. Contrastive Study on in Vitro Antibacterial Property and Biocompatibility of Three Clinical Pulp Capping Agents [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(12): 1449-1456. |
| [11] | LI Jianbo, TIAN Zhen, JIANG Quanwei, YU Lifeng, KANG Huijun, CAO Zhiqiang, WANG Tongmin. Effects of Different Element Doping on Microstructure and Thermoelectric Properties of CaTiO3 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(12): 1396-1404. |
| [12] | WU Dongjiang, ZHAO Ziyuan, YU Xuexin, MA Guangyi, YOU Zhulin, REN Guanhui, NIU Fangyong. Direct Additive Manufacturing of Al2O3-TiCp Composite Ceramics by Laser Directed Energy Deposition [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(10): 1183-1192. |
| [13] | ZHANG Ye, ZENG Yuping. Progress of Porous Silicon Nitride Ceramics Prepared via Self-propagating High Temperature Synthesis [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(8): 853-864. |
| [14] | XIA Qian, SUN Shihao, ZHAO Yiliang, ZHANG Cuiping, RU Hongqiang, WANG Wei, YUE Xinyan. Effect of Boron Carbide Particle Size Distribution on the Microstructure and Properties of Reaction Bonded Boron Carbide Ceramic Composites by Silicon Infiltration [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(6): 636-642. |
| [15] | HONG Du, NIU Yaran, LI Hong, ZHONG Xin, ZHENG Xuebin. Tribological Properties of Plasma Sprayed TiC-Graphite Composite Coatings [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(6): 643-650. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||