
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (12): 1449-1456.DOI: 10.15541/jim20220465
Special Issue: 【生物材料】抗菌与肿瘤治疗(202506); 【生物材料】骨骼与齿类组织修复(202506)
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
XIE Jiaye1( ), LI Liwen1, ZHU Qiang2(
), LI Liwen1, ZHU Qiang2( )
)
Received:2022-08-05
Revised:2023-06-30
Published:2023-07-28
Online:2023-07-28
Contact:
ZHU Qiang, associate professor. E-mail: txzdzq1979@163.comAbout author:XIE Jiaye (1979-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: xpony171207@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
XIE Jiaye, LI Liwen, ZHU Qiang. Contrastive Study on in Vitro Antibacterial Property and Biocompatibility of Three Clinical Pulp Capping Agents[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(12): 1449-1456.
| Sample | Components | |
|---|---|---|
| ZnO | Zinc oxide powder Eugenol solution | |
| Dycal | Paste A (13 g) | 1,3-butanediol bis(salicylic acid) vinegar Zinc oxide Calcium phosphate Calcium tungstate Iron oxide pigment |
| Paste B (11 g, with catalyst) | Calcium hydroxide N-ethyl-o/p-toluenesulfonamide Zinc oxide Iron dioxide Zinc stearate Iron oxide pigment | |
| Calcimol | Urethane dimethacrylate Barium aluminosilicate Barium sulfonate; Silica Triethylene glycol dimethacrylate Calcium hydroxide | |
Table 1 Content of the three samples
| Sample | Components | |
|---|---|---|
| ZnO | Zinc oxide powder Eugenol solution | |
| Dycal | Paste A (13 g) | 1,3-butanediol bis(salicylic acid) vinegar Zinc oxide Calcium phosphate Calcium tungstate Iron oxide pigment |
| Paste B (11 g, with catalyst) | Calcium hydroxide N-ethyl-o/p-toluenesulfonamide Zinc oxide Iron dioxide Zinc stearate Iron oxide pigment | |
| Calcimol | Urethane dimethacrylate Barium aluminosilicate Barium sulfonate; Silica Triethylene glycol dimethacrylate Calcium hydroxide | |
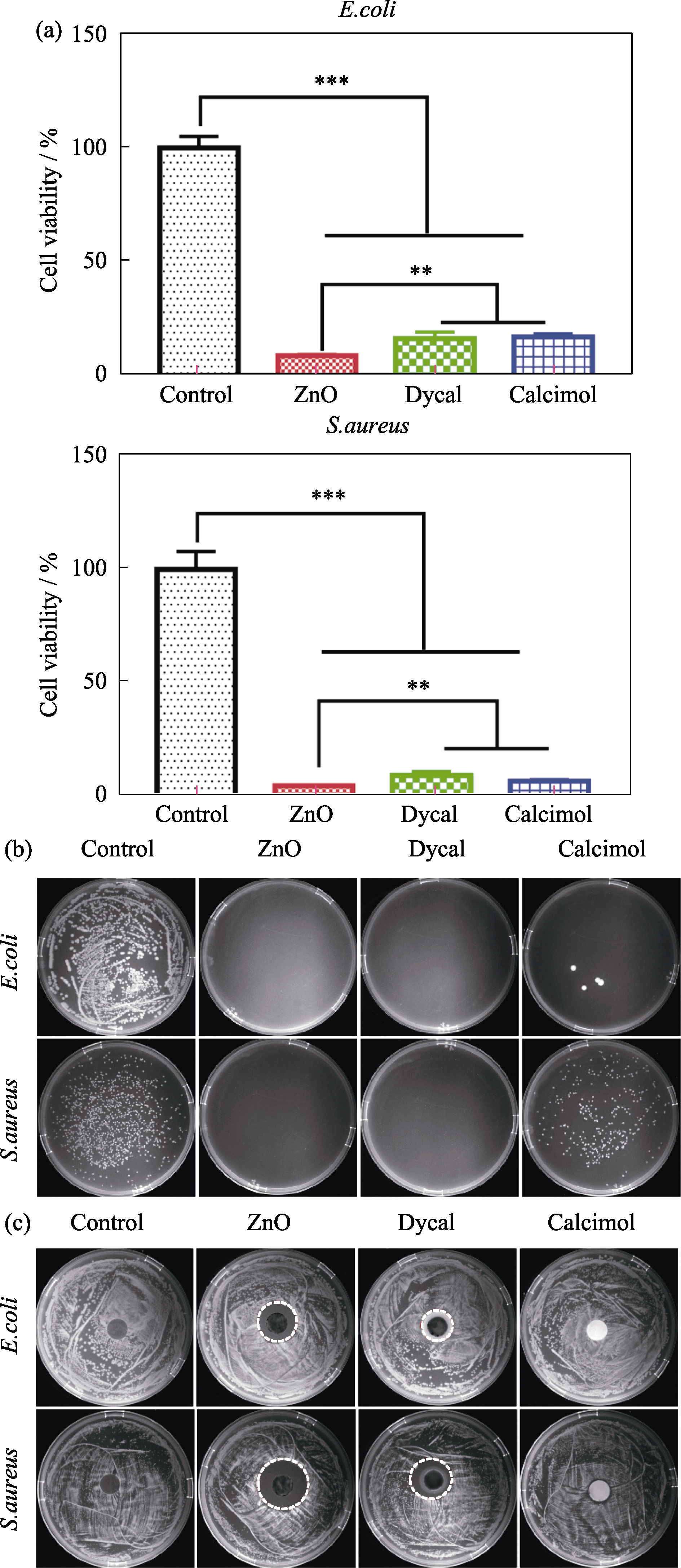
Fig. 5 Antibacterial ability of all samples on E.coli and S.aureus (a) Cell viability; (b) Photos of bacterial colony; (c) Photos of antibacterial ring
| Property | ZnO | Dycal | Calcimol |
|---|---|---|---|
| Morphology | Smooth surface | Smooth surface | Porous |
| Element | C, O, Zn | C, O, Ca, Zn | C, O, Ca |
| Water contact angle | 90° | 75° | 22° |
| pH | 6.66 | 9.16 | 7.90 |
| Antibacteria effect/% | 92.6 | 84.5 | 82.7 |
| HDPSCs activity/% | 6.82 | 44.54 | 137.87 |
| Hemolysis ratio/% | 8.14 | 0.99 | 1.42 |
Table 2 Comparisons on physicochemical and biological properties of clinical three common pulp capping agents
| Property | ZnO | Dycal | Calcimol |
|---|---|---|---|
| Morphology | Smooth surface | Smooth surface | Porous |
| Element | C, O, Zn | C, O, Ca, Zn | C, O, Ca |
| Water contact angle | 90° | 75° | 22° |
| pH | 6.66 | 9.16 | 7.90 |
| Antibacteria effect/% | 92.6 | 84.5 | 82.7 |
| HDPSCs activity/% | 6.82 | 44.54 | 137.87 |
| Hemolysis ratio/% | 8.14 | 0.99 | 1.42 |
| [1] |
BJØRNDAL L, SIMON S, TOMSON P L, et al. Management of deep caries and the exposed pulp. International Endodontic Journal, 52(7): 949.
DOI URL |
| [2] | 周学东, 黄定明, 刘建国, 等. 牙髓损伤的活髓保存治疗. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2017, 35(4): 339. |
| [3] |
RANLY D M, GARCIA-GODOY F. Current and potential pulp therapies for primary and young permanent teeth. Journal of Dentistry, 2000, 28(3): 153.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
KOMABAYASHI T, COLMENAR D, CVACH N, et al. Comprehensive review of current endodontic sealers. Dental Materials Journal, 2020, 39(5): 703.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
SONMEZ D, DURUTURK L. Success rate of calcium hydroxide pulpotomy in primary molars restored with amalgam and stainless steel crowns. British Dental Journal, 2010, 208(9): E18.
DOI |
| [6] | 王子扬, 左恩俊. 生物材料在活髓保存中的应用. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 27(3): 427. |
| [7] | LEYE BENOIST F, GAYE NDIAYE F, KANE AW, et al. Evaluation of mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) versus calcium hydroxide cement (Dycal(®)) in the formation of a dentine bridge: a randomised controlled trial. International Endodontic Journal, 2012, 62(1): 33. |
| [8] |
APPLEROT G, LIPOVSKY A, DROR R, et al. Enhanced antibacterial activity of nanocrystalline ZnO due to increased ROS- mediated cell injury. Advanced Functional Materials, 2009, 19(6): 842.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
FISHER F J. The effect of a calcium hydroxide-water paste on micro-organisms in carious dentine. British Dental Journal, 1972, 133(1): 19.
PMID |
| [10] |
GEROSA R, BORIN M, MENEGAZZI G, et al. In vitro evaluation of the cytotoxicity of pure eugenol. Journal of Endodontics, 1996, 22(10): 532.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
JENG J H, HAHN L J, LU F J, et al. Eugenol triggers different pathobiological effects on human oral mucosal fibroblasts. Journal of Dental Research, 1994, 73(5): 1050.
PMID |
| [12] |
JUN S K, KIM H W, LEE H H, et al. Zirconia-incorporated zinc oxide eugenol has improved mechanical properties and cytocompatibility with human dental pulp stem cells. Dental Materials, 2018, 34(1): 132.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
TAN J, WANG D H, CAO H L, et al. Effect of local alkaline microenvironment on the behaviors of bacteria and osteogenic cells. ACS Applied Materials Interfaces, 2018, 10(49): 42018.
DOI URL |
| [14] | WANG N, MA Y T, SHI H X, et al. Mg-, Zn-, and Fe-based alloys with antibacterial properties as orthopedic implant materials. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2022, 10: 888084. |
| [15] | MIYASHITA H, WORTHINGTON H V, QUALTROUGH A, et al. Pulp management for caries in adults: maintaining pulp vitality. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 2007, 18(2): CD004484. |
| [16] |
BEEGUM M S F, GEORGE S, ANANDARAJ S, et al. Comparative evaluation of diffused calcium and hydroxyl ion release from three different indirect pulp capping agents in permanent teeth-an in vitro study. Saudi Dental Journal, 2021, 33(8): 1149.
DOI URL |
| [1] | WANG Yueyue, HUANG Jiahui, KONG Hongxing, LI Huaizhu, YAO Xiaohong. Silver Loaded Radial Mesoporous Silica: Preparation and Application in Dental Resins [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 77-83. |
| [2] | LI Kun-Qiang,QIAO Yu-Qin,LIU Xuan-Yong. Titanium Modified by Copper Ion Implantation: Anti-bacterial and Cellular Behaviors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(2): 158-164. |
| [3] | LIU Yu-Ling, WANG Rui-Li, LI Nan, LIU Mei, ZHANG Qing-Hong. Preparation of Zinc Oxide Mesocrystal Filler and Its Properties as Dental Composite Resin [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(10): 1077-1084. |
| [4] | LIANG Hong-Pei, WANG Ying-Bo, SU Zhi, LU Xiong, WANG Shuai. Electrospinning Gelatin/Chitosan/Hydroxyapatite/Graphene Oxide Composite Nanofibers with Antibacterial Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(5): 516-522. |
| [5] | TAN Ying, Tan Guo-Xin, NING Cheng-Yun, RONG Xi-Cang, ZHANG Yu, ZHOU Lei. Bioinspired Polydopamine Functionalization of Titanium Surface for Silver Nanoparticles Immobilization with Antibacterial Property [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(12): 1320-1326. |
| [6] | YANG Guo-Jing, LIN Mian, ZHANG Lei, GOU Zhong-Ru. Progress of Calcium Sulfate and Inorganic Composites for Bone Defect Repair [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(8): 795-803. |
| [7] | ZENG Xiao-Bo, HU Hao, XIE Li-Qin, LAN Fang, WU Yao, GU Zhong-Wei. Preparation and Properties of Supermagnetic Calcium Phosphate Composite Scaffold [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(1): 79-84. |
| [8] | Lü Xiao-Ying, HUANG Yan, YU Ya-Dong, YANG Ya-Min. Application of Genomics/Proteomics Technologies in the Research of Biocompatibility of Biomaterials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(1): 21-28. |
| [9] | ZHANG Xiang-Yu, JIANG Li, HUANG Xiao-Bo, MA Yong, FAN Ai-Lan, TANG Bin. Improvement of Antibacterial Properties of Stainless Steel by Combining Plasma Cu and Thermal Diffusion [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(5): 519-523. |
| [10] | CHEN Yu, LI Wen-Rui, XU Can, SU Jia-Can, LI Ming, LIU Chang-Sheng. Study on Hemostatic Materials of Mesoporous Silicon Dioxide Doped Ca and Ag with Antibacterial Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(5): 513-518. |
| [11] | HAN Xue, CHEN Xiao-Feng, MENG Yong-Chun, ZHOU Jia-An, LIN Cai, JIANG Xiao-Rui, ZHANG Xin-Xin. Biocompatibility of the Composite Scaffold of Sol-Gel Bioactive Glass/Collagen [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2011, 26(8): 869-873. |
| [12] | CAO Lie-Hui, YU Bao-Qing, WU Guo-Sheng, SU Jia-Can. Study on Adulterate Sodium Silica Apatite Cement Porous Scaffolds for Bone Defect Repair [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2011, 26(6): 591-596. |
| [13] | WANG Ying-Bo,LU Xiong*, FENG Bo,QU Shu-Xin, WENG Jie. Calcium Phosphate/ Gelatin Composite Coatings on Titanium Surfaces by ElectrochemicalDepositon [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2011, 26(1): 61-67. |
| [14] | JIANGXiao-Xin, QU Shu-Xin, LIN Sun-Zhong, DUANKe, WENG Jie. Influenceof Drynaria on Physicochemical and <>in vitro Biological Properties ofCalcium Phosphate Cement [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2011, 26(1): 29-37. |
| [15] | ZHENG Yi-Fan, LU Yue-Ping, MO Wei-Min, LI Guo-Hua, ZHAO Na. Microstructure Characterization and Electrocatalytic Properties of WC/TiO2 Nanocomposites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2010, 25(11): 1139-1144. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||