无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (2): 184-195.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240325 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20240325
所属专题: 【能源环境】储能电池(202506)
收稿日期:2024-07-10
修回日期:2024-09-09
出版日期:2025-02-20
网络出版日期:2024-10-17
通讯作者:
李文翠, 教授. E-mail: wencuili@dlut.edu.cn作者简介:朱志杰(2001-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: 374470898@mail.dlut.edu.cn
基金资助:
ZHU Zhijie( ), SHEN Mingyuan, WU Tao, LI Wencui(
), SHEN Mingyuan, WU Tao, LI Wencui( )
)
Received:2024-07-10
Revised:2024-09-09
Published:2025-02-20
Online:2024-10-17
Contact:
LI Wencui, professor. E-mail: wencuili@dlut.edu.cnAbout author:ZHU Zhijie (2001-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: 374470898@mail.dlut.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
研究钠离子电池(SIBs)对开发新能源和新储能方式具有重要意义。P2型层状氧化物Na2/3Ni1/3Mn2/3O2正极材料具有容量和工作电压较高的优点, 但在高电压下发生的P2-O2不可逆相变会导致体积急剧变化, 容量迅速衰减。针对这个问题, 本研究采用Cu和Mg协同取代的策略, 通过固相反应法合成了P2-Na0.67Ni0.18Cu0.10Mg0.05Mn0.67O2 (NCMM-10-05)正极材料。结果表明, 掺入Cu和Mg有效抑制了P2-O2相变, 转而形成了可逆程度更高的OP4相, 提高了材料结构的可逆稳定性, 且电化学性能得到了显著提升。在2.00~4.35 V(vs. Na+/Na)电压窗口内NCMM-10-05初始放电容量为113 mAh·g-1, 在8C(1C=100 mA·g-1)电流密度下仍有64.1 mAh·g-1的可逆容量, 在1C电流密度下循环200圈后容量保持率可以达到88.9%。本研究探讨了Cu和Mg协同取代对P2型层状氧化物结构与电化学性能的影响, 并通过原位X射线衍射(XRD)分析与密度泛函理论(DFT)计算进一步探究了Cu、Mg元素在结构演变中的具体作用, 为合理设计具备Na+快速传输能力和高稳定性的SIBs正极材料提供了参考。
中图分类号:
朱志杰, 申明远, 吴涛, 李文翠. Cu和Mg协同取代抑制钠离子电池正极材料P2-Na2/3Ni1/3Mn2/3O2的P2-O2相变[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 184-195.
ZHU Zhijie, SHEN Mingyuan, WU Tao, LI Wencui. Inhibition of P2-O2 Phase Transition for P2-Na2/3Ni1/3Mn2/3O2 as Cathode of Sodium-ion Battery via Synergetic Substitution of Cu and Mg[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 184-195.
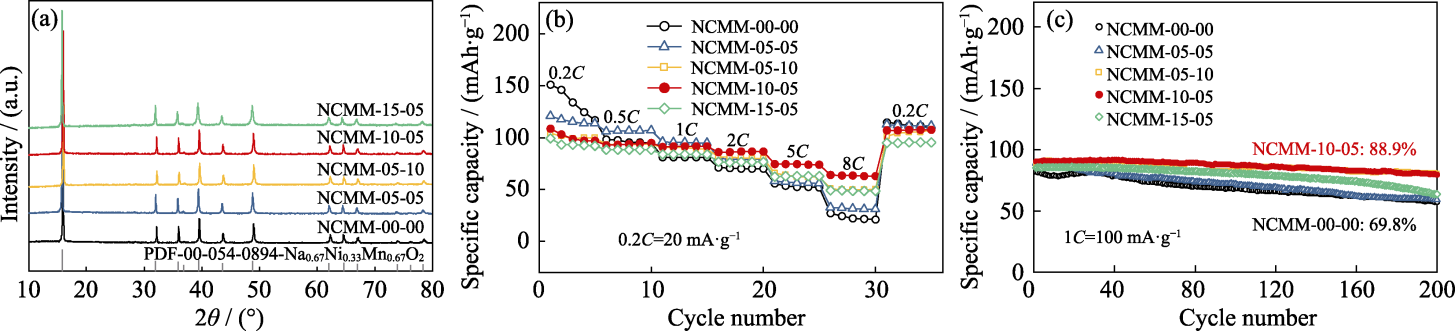
图1 NCMM的XRD图谱及电化学性能
Fig. 1 XRD patterns and electrochemical performances of NCMM (a) XRD patterns; (b) Rate performances; (c) Cycling performances for 200 cycles at 1C
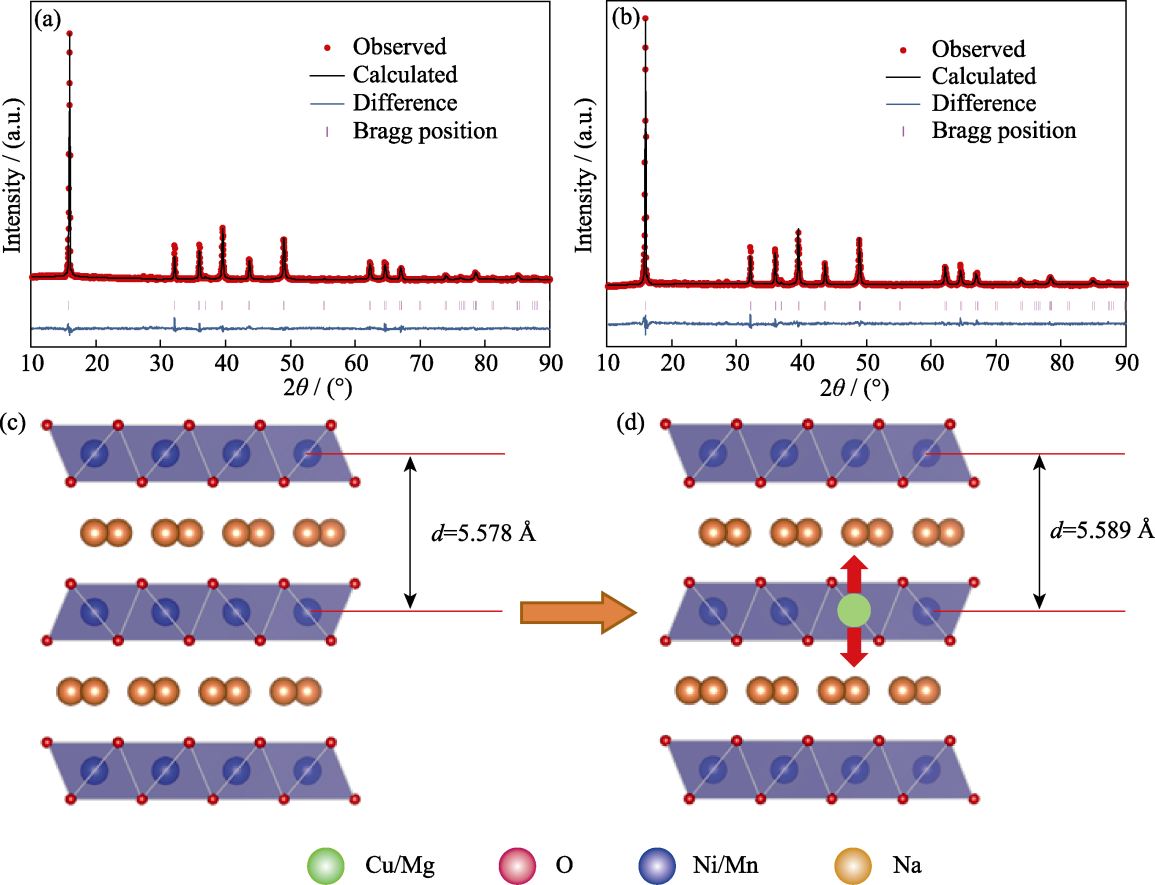
图2 NCMM-00-00和NCMM-10-05的晶体结构信息
Fig. 2 Crystal structure information of NCMM-00-00 and NCMM-10-05 (a, b) Rietveld refinement results and (c, d) crystal structure diagrams of (a, c) NCMM-00-00 and (b, d) NCMM-10-05. Colorful figures are available on website
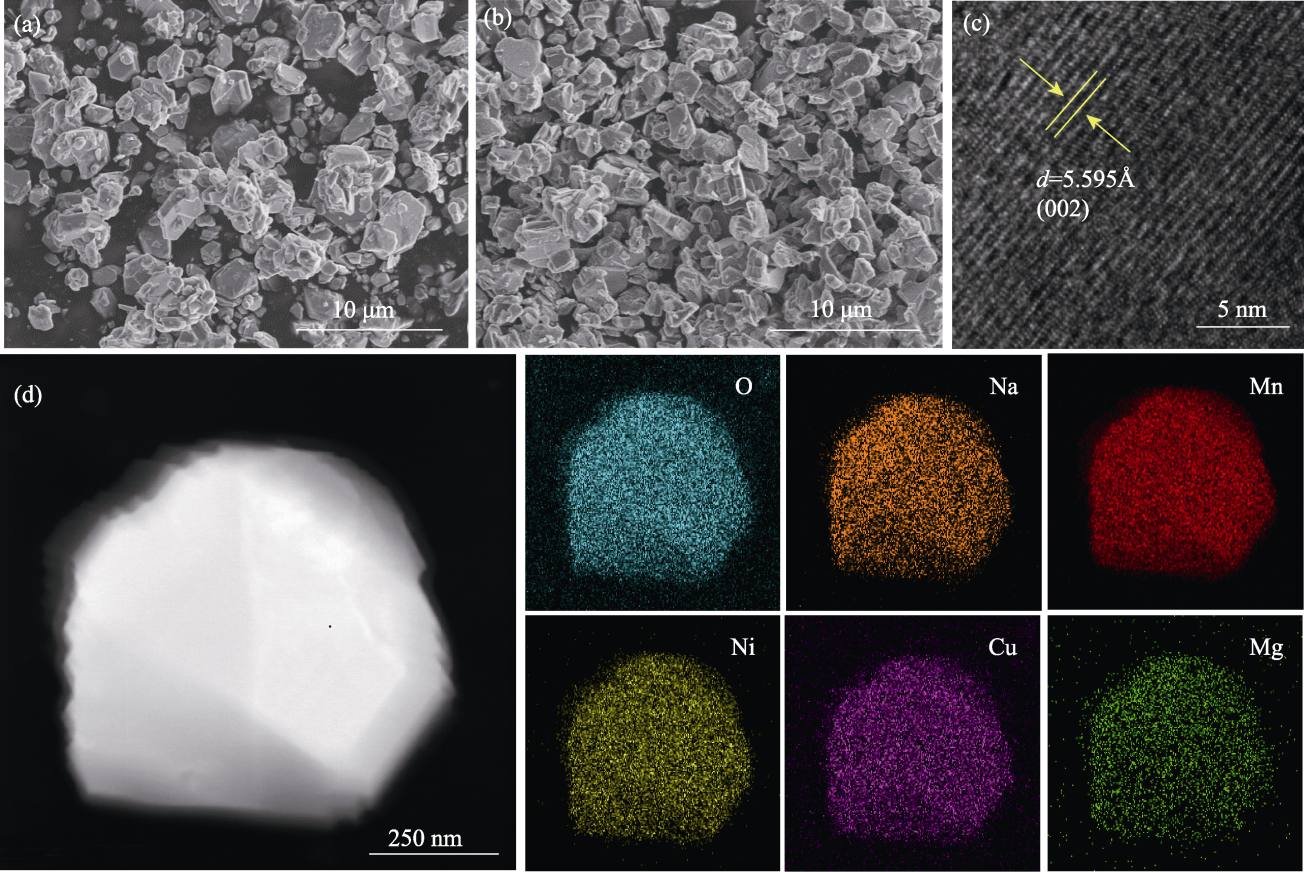
图3 NCMM-00-00和NCMM-10-05的晶体形貌
Fig. 3 Morphologies of NCMM-00-00 and NCMM-10-05 (a) SEM image of NCMM-00-00; (b) SEM, (c) HRTEM images and (d) EDS elemental mappings of NCMM-10-05
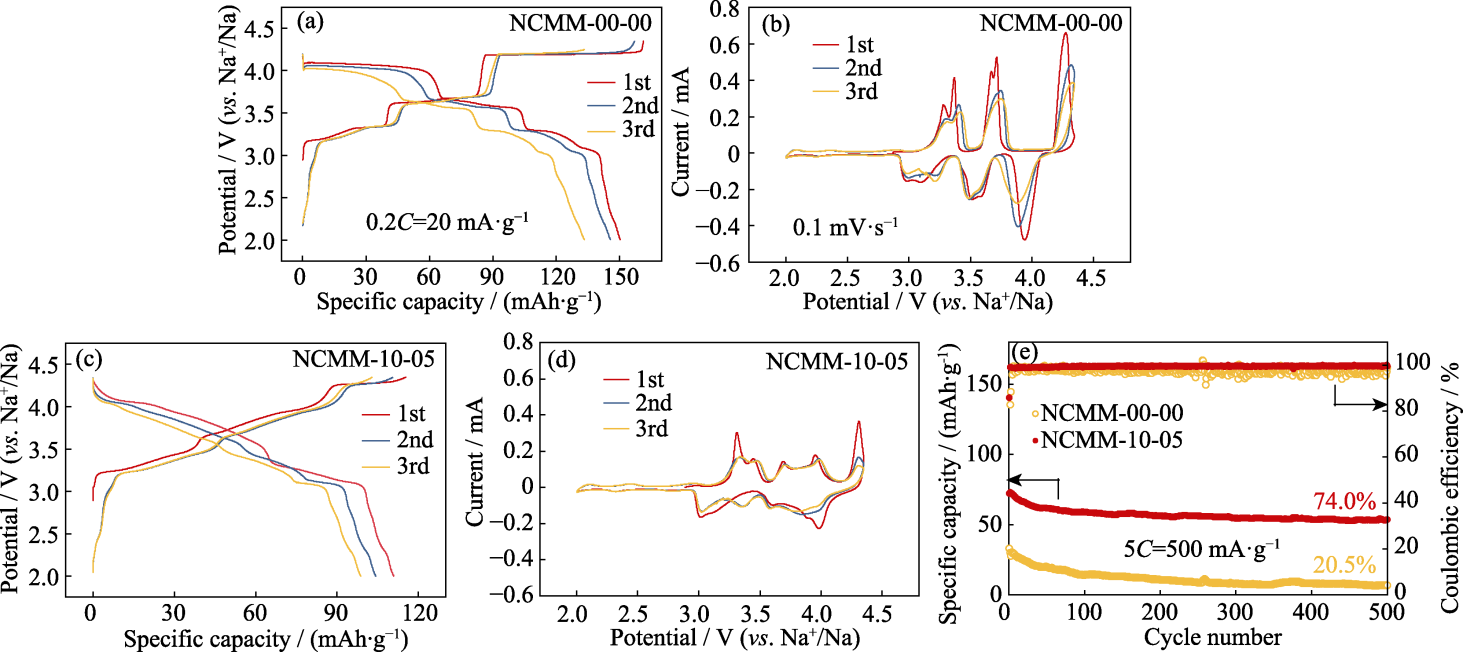
图4 NCMM-00-00和NCMM-10-05的电化学性能
Fig. 4 Electrochemical performance of NCMM-00-00 and NCMM-10-05 (a, c) GCD curves of (a) NCMM-00-00 and (c) NCMM-10-05 at 0.2C; (b, d) CV curves for initial 3 cycles at 0.1 mV·s−1 of (b) NCMM-00-00 and (d) NCMM-10-05; (e) Cycling performance for 500 cycles at 5C of NCMM-00-00 and NCMM-10-05. Colorful figures are available on website
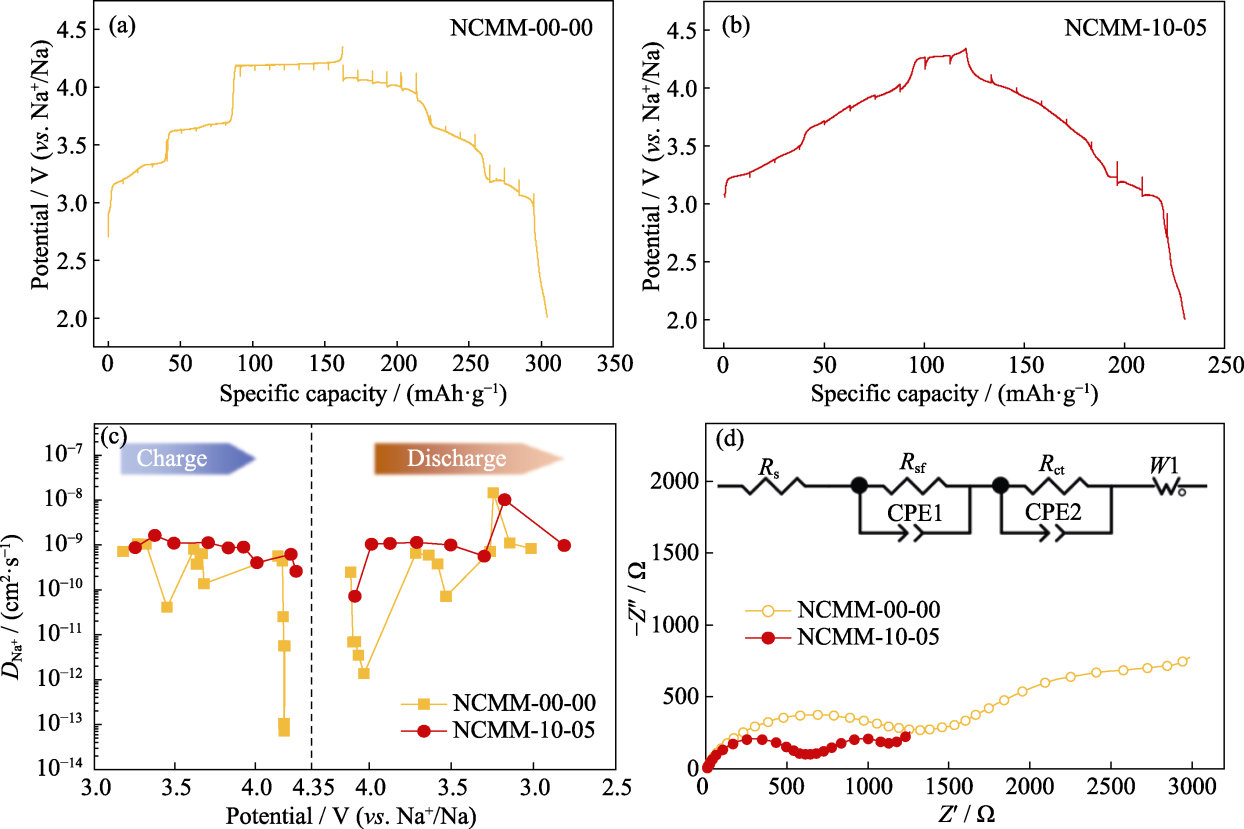
图5 NCMM-00-00和NCMM-10-05的电化学性能
Fig. 5 Electrochemical performance of NCMM-00-00 and NCMM-10-05 (a, b) First-lap GITT curves of (a) NCMM-00-00 and (b) NCMM-10-05; (c) Variation of DNa+ as a function of potential determined by GITT; (d) Nyquist plots
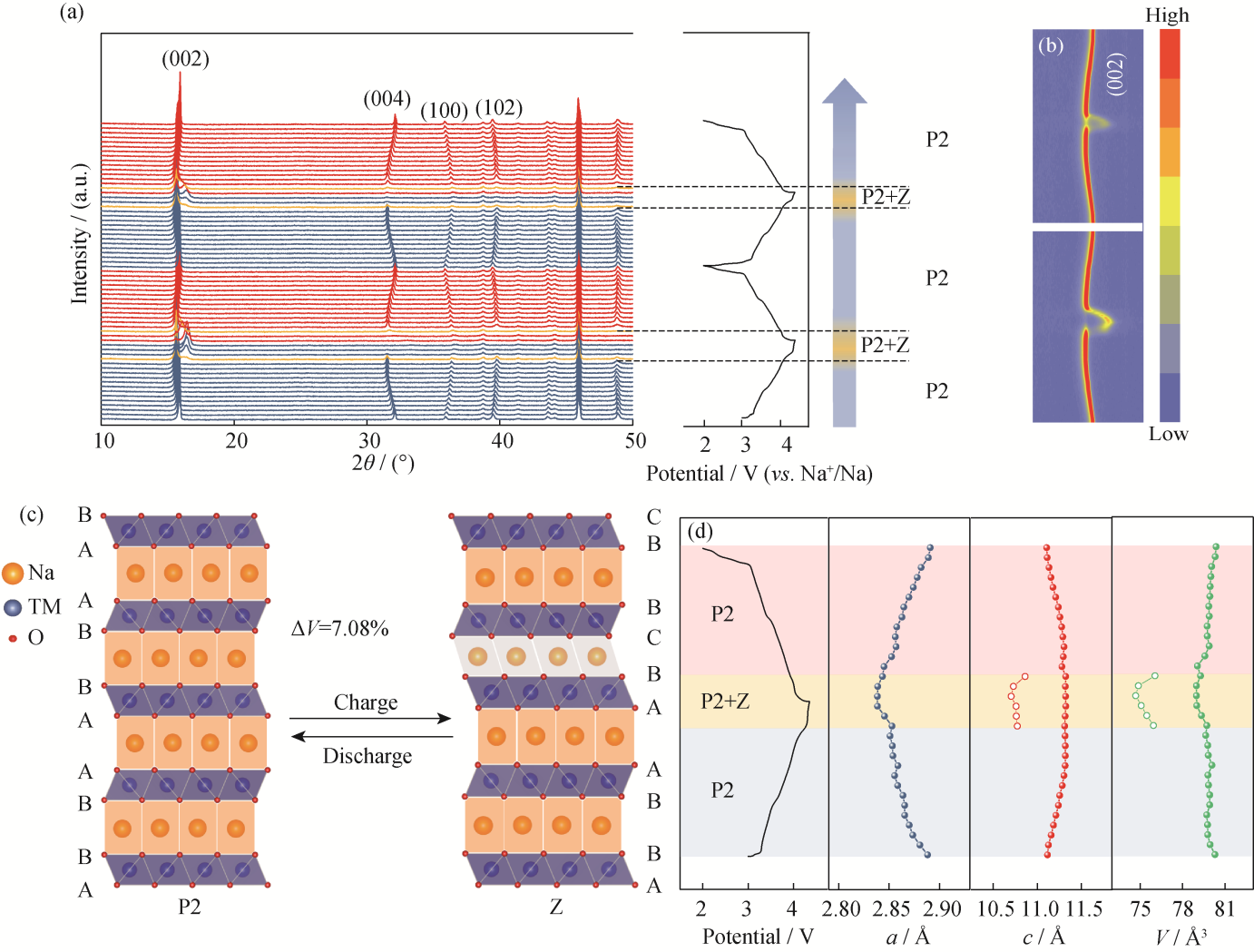
图6 NCMM-10-05的结构演变规律
Fig. 6 Structure evolution of NCMM-10-05 (a) In situ XRD patterns during the first and second charging/discharging cycles at 2.00-4.35 V (0.2C=20 mA·g-1); (b) Contour plots of (002) diffraction peaks; (c) P2-Z phase transition during the first cycling; (d) Evolution of lattice parameters. Colorful figures are available on website

图7 DFT计算结果
Fig. 7 Results of DFT calculations (a) Model structures of discharging and charging states for NCMM-10-05; (b, c) Electronic localization function maps and (e, f) PDOS of (b, e) NCMM-00-00 and (c, f) NCMM-10-05; (d) Na+ migration energy barriers in NCMM-00-00 and NCMM-10-05; (g) Schematic of the orbital energy levels of Cu3d and O2p in NCMM-10-05 (EF: Fermi level); (h) Two possible local structures around Mg atom at 4.2 V. Colorful figures are available on website
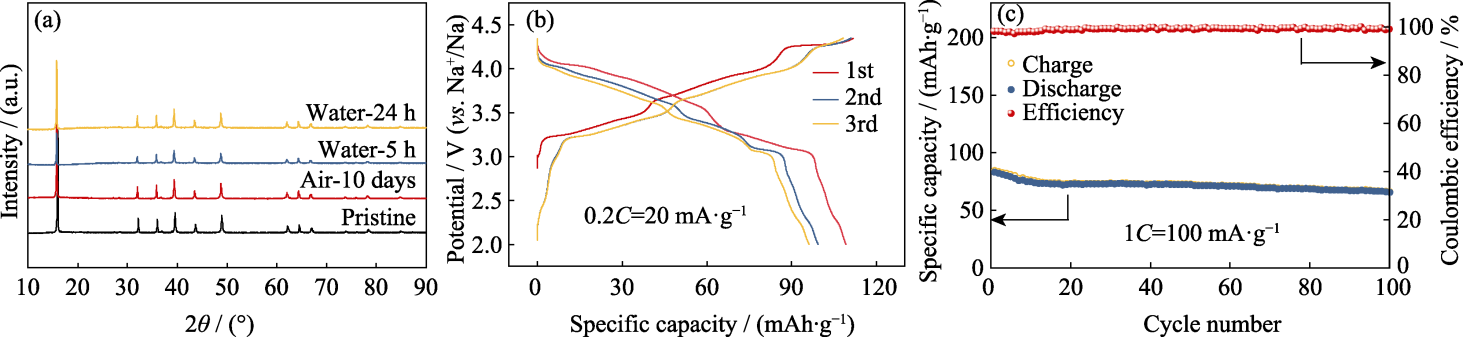
图8 NCMM-10-05经过水和空气处理后的晶体结构及电化学性能
Fig. 8 Crystal structure and electrochemical performance of NCMM-10-05 treated in water and air (a) XRD patterns; (b) GCD curves at 0.2C and (c) cycling performance at 1C of NCMM-10-05 after soaking in water for 24 h. Colorful figures are available on website
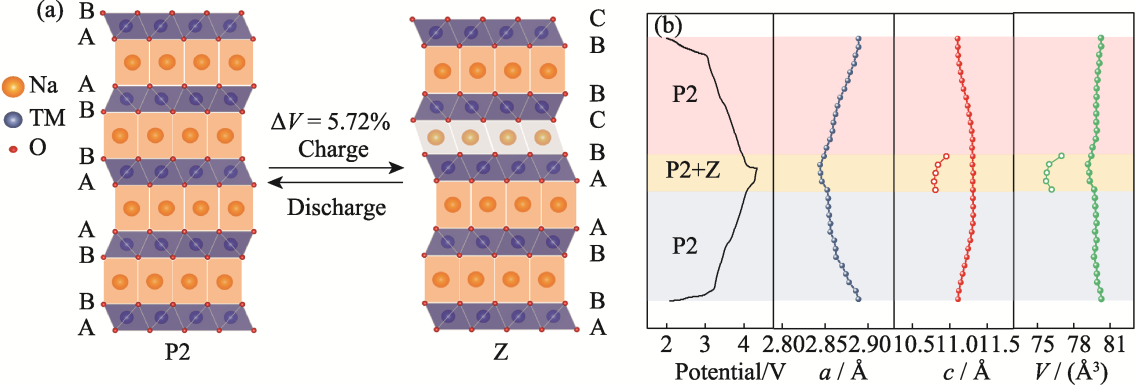
图S4 NCMM-10-05在2.00~4.35 V(0.2C=20 mA·g-1)条件下第二圈充放电过程的(a)P2-Z相变结构示意图和(b)晶格参数演变
Fig. S4 (a) P2-Z phase transition and (b) evolution of lattice parameters during the second cycling at 2.00-4.35 V(0.2C=20 mA·g-1)
| Sample | Composition | QR*(0.2C)/(mAh·g-1) | QR*(8C)/(mAh·g-1) | Capacity retention (1C, 200 cycles)/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCMM-00-00 | Na0.67Ni0.33Mn0.67O2 | 150 | 21 | 69.8 |
| NCMM-05-05 | Na0.67Ni0.23Cu0.05Mg0.05Mn0.67O2 | 120 | 31 | 67.0 |
| NCMM-05-10 | Na0.67Ni0.18Cu0.05Mg0.10Mn0.67O2 | 104 | 49 | 88.5 |
| NCMM-10-05 | Na0.67Ni0.18Cu0.10Mg0.05Mn0.67O2 | 113 | 64 | 88.9 |
| NCMM-15-05 | Na0.67Ni0.13Cu0.15Mg0.05Mn0.67O2 | 99 | 49 | 74.6 |
表S1 NCMM样品的化学组成及电化学性能
Table S1 Compositions and electrochemical performance of NCMM samples
| Sample | Composition | QR*(0.2C)/(mAh·g-1) | QR*(8C)/(mAh·g-1) | Capacity retention (1C, 200 cycles)/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCMM-00-00 | Na0.67Ni0.33Mn0.67O2 | 150 | 21 | 69.8 |
| NCMM-05-05 | Na0.67Ni0.23Cu0.05Mg0.05Mn0.67O2 | 120 | 31 | 67.0 |
| NCMM-05-10 | Na0.67Ni0.18Cu0.05Mg0.10Mn0.67O2 | 104 | 49 | 88.5 |
| NCMM-10-05 | Na0.67Ni0.18Cu0.10Mg0.05Mn0.67O2 | 113 | 64 | 88.9 |
| NCMM-15-05 | Na0.67Ni0.13Cu0.15Mg0.05Mn0.67O2 | 99 | 49 | 74.6 |
| Atom | Wyckoff position | x | y | z | Uiso | Occupancy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na1 | 2b | 0 | 0 | 1/4 | 0.004 | 0.171 |
| Na2 | 2d | 1/3 | 2/3 | 1/4 | 0.188 | 0.490 |
| Mn1 | 2a | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.013 | 0.668 |
| Ni1 | 2a | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.013 | 0.332 |
| O1 | 4f | 2/3 | 1/3 | 0.42320 | 0.004 | 1 |
表S2 XRD精修得到的NCMM-00-00晶体结构信息
Table S2 Crystal structure information of NCMM-00-00 obtained by XRD refinement
| Atom | Wyckoff position | x | y | z | Uiso | Occupancy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na1 | 2b | 0 | 0 | 1/4 | 0.004 | 0.171 |
| Na2 | 2d | 1/3 | 2/3 | 1/4 | 0.188 | 0.490 |
| Mn1 | 2a | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.013 | 0.668 |
| Ni1 | 2a | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.013 | 0.332 |
| O1 | 4f | 2/3 | 1/3 | 0.42320 | 0.004 | 1 |
| Atom | Wyckoff position | x | y | z | Uiso | Occupancy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na1 | 2b | 0 | 0 | 1/4 | 0.051 | 0.245 |
| Na2 | 2d | 1/3 | 2/3 | 1/4 | 0.090 | 0.425 |
| Mn1 | 2a | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.007 | 0.670 |
| Ni1 | 2a | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.007 | 0.181 |
| Cu1 | 2a | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.007 | 0.100 |
| Mg1 | 2a | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.007 | 0.050 |
| O1 | 4f | 2/3 | 1/3 | 0.42063 | 0.007 | 1 |
表S3 XRD精修得到的NCMM-10-05晶体结构信息
Table S3 Crystal structure information of NCMM-10-05 obtained by XRD refinement
| Atom | Wyckoff position | x | y | z | Uiso | Occupancy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na1 | 2b | 0 | 0 | 1/4 | 0.051 | 0.245 |
| Na2 | 2d | 1/3 | 2/3 | 1/4 | 0.090 | 0.425 |
| Mn1 | 2a | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.007 | 0.670 |
| Ni1 | 2a | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.007 | 0.181 |
| Cu1 | 2a | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.007 | 0.100 |
| Mg1 | 2a | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.007 | 0.050 |
| O1 | 4f | 2/3 | 1/3 | 0.42063 | 0.007 | 1 |
| Sample | Resistance/Ω | |
|---|---|---|
| NCMM-00-00 | Rsf | 1088 |
| Rct | 2638 | |
| NCMM-10-05 | Rsf | 596.2 |
| Rct | 688.5 | |
表S4 NCMM-00-00和NCMM-10-05的阻抗
Table S4 Impedance of NCMM-00-00 and NCMM-10-05
| Sample | Resistance/Ω | |
|---|---|---|
| NCMM-00-00 | Rsf | 1088 |
| Rct | 2638 | |
| NCMM-10-05 | Rsf | 596.2 |
| Rct | 688.5 | |
| State | Type | Charge | Zval* | Valence state |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Discharge | O | 7.04 | 6 | -1.04 |
| Ni | 8.84 | 10 | 1.16 | |
| Mn | 5.27 | 7 | 1.73 | |
| Charge | O | 6.84 | 6 | -0.84 |
| Ni | 8.71 | 10 | 1.29 | |
| Mn | 5.25 | 7 | 1.75 |
表S5 NCMM-00-00在充电/放电状态下的Bader电荷分析结果
Table S5 Bader charge analysis of NCMM-00-00
| State | Type | Charge | Zval* | Valence state |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Discharge | O | 7.04 | 6 | -1.04 |
| Ni | 8.84 | 10 | 1.16 | |
| Mn | 5.27 | 7 | 1.73 | |
| Charge | O | 6.84 | 6 | -0.84 |
| Ni | 8.71 | 10 | 1.29 | |
| Mn | 5.25 | 7 | 1.75 |
| State | Type | Charge | Zval* | Valence state |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Discharge | O | 7.05 | 6 | -1.05 |
| Ni | 8.85 | 10 | 1.15 | |
| Cu | 9.79 | 11 | 1.21 | |
| Mg | 0.35 | 2 | 1.65 | |
| Mn | 5.28 | 7 | 1.72 | |
| Charge | O | 6.89 | 6 | -0.89 |
| Ni | 8.75 | 10 | 1.25 | |
| Cu | 9.76 | 11 | 1.24 | |
| Mg | 0.35 | 2 | 1.65 | |
| Mn | 5.25 | 7 | 1.75 |
表S6 NCMM-10-05在充电/放电状态下的Bader电荷分析结果
Table S6 Bader charge analysis of NCMM-10-05
| State | Type | Charge | Zval* | Valence state |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Discharge | O | 7.05 | 6 | -1.05 |
| Ni | 8.85 | 10 | 1.15 | |
| Cu | 9.79 | 11 | 1.21 | |
| Mg | 0.35 | 2 | 1.65 | |
| Mn | 5.28 | 7 | 1.72 | |
| Charge | O | 6.89 | 6 | -0.89 |
| Ni | 8.75 | 10 | 1.25 | |
| Cu | 9.76 | 11 | 1.24 | |
| Mg | 0.35 | 2 | 1.65 | |
| Mn | 5.25 | 7 | 1.75 |
| [1] |
WHITTINGHAM M S. Lithium batteries and cathode materials. Chemical Reviews, 2004, 104(10): 4271.
PMID |
| [2] | RAMASAMY H V, KALIYAPPAN K, THANGAVEL R, et al. Cu-doped P2-Na0.5Ni0.33Mn0.67O2 encapsulated with MgO as a novel high voltage cathode with enhanced Na-storage properties. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(18): 8408. |
| [3] | HWANG J Y, MYUNG S T, SUN Y K. Sodium-ion batteries: present and future. Chemical Society Reviews, 2017, 46(12): 3529. |
| [4] | XIA J L, YAN D, GUO L P, et al. Hard carbon nanosheets with uniform ultramicropores and accessible functional groups showing high realistic capacity and superior rate performance for sodium- ion storage. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(21): 2000447. |
| [5] |
JIN T, LI H X, ZHU K J, et al. Polyanion-type cathode materials for sodium-ion batteries. Chemical Society Reviews, 2020, 49(8): 2342.
DOI PMID |
| [6] | HOU H S, QIU X Q, WEI W F, et al. Carbon anode materials for advanced sodium-ion batteries. Advanced Energy Materials, 2017, 7(24): 1602898. |
| [7] | CAO D, YIN C, SHI D, et al. Cubic perovskite fluoride as open framework cathode for Na-ion batteries. Advanced Functional Materials, 2017, 27(28): 1701130. |
| [8] | HAN Y, HU J, YIN C, et al. Iron-based fluorides of tetragonal tungsten bronze structure as potential cathodes for Na-ion batteries. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2016, 4(19): 7382. |
| [9] | YUAN Y, WEI Q Y, YANG S K, et al. Towards high-performance phosphate-based polyanion-type materials for sodium-ion batteries. Energy Storage Materials, 2022, 50: 760. |
| [10] | AVDEEV M, MOHAMED Z, LING C D, et al. Magnetic structures of NaFePO4 maricite and triphylite polymorphs for sodium-ion batteries. Inorganic Chemistry, 2013, 52(15): 8685. |
| [11] | JIAN Z L, ZHAO L, PAN H L, et al. Carbon coated Na3V2(PO4)3 as novel electrode material for sodium ion batteries. Electrochemistry Communications, 2012, 14(1): 86. |
| [12] | CHOTARD J N, ROUSSE G, DAVID R, et al. Cheminform abstract: discovery of a sodium-ordered form of Na3V2(PO4)3 below ambient temperature. Chemistry of Materials, 2015, 27(17): 5982. |
| [13] | LIU Q N, HU Z, CHEN M Z, et al. The cathode choice for commercialization of sodium-ion batteries: layered transition metal oxides versus Prussian blue analogs. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(14): 1909530. |
| [14] | PAOLELLA A, FAURE C, TIMOSHEVSKII V, et al. A review on hexacyanoferrate-based materials for energy storage and smart windows: challenges and perspectives. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(36): 18919. |
| [15] | LIU X Y, CAO Y, SUN J. Defect engineering in Prussian blue analogs for high-performance sodium-ion batteries. Advanced Energy Materials, 2022, 12(46): 2202532. |
| [16] | WEI F, ZHANG Q, ZHANG P, et al. Review—research progress on layered transition metal oxide cathode materials for sodium ion batteries. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2021, 168(5): 050524. |
| [17] | LI W, HAN C, WANG W, et al. Stress distortion restraint to boost the sodium ion storage performance of a novel binary hexacyanoferrate. Advanced Energy Materials, 2020, 10(4): 1903006. |
| [18] | HASA I, BUCHHOLZ D, PASSERINI S, et al. High performance Na0.5[Ni0.23Fe0.13Mn0.63]O2 cathode for sodium-ion batteries. Advanced Energy Materials, 2014, 4(15): 1400083. |
| [19] | KONG G Q, LENG M Z, ZHOU Z R, et al. Sb doped O3 type Na0.9Ni0.5Mn0.3Ti0.2O2 cathode material for Na-ion battery. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 656. |
| [20] | DAI K, MAO J, SONG X, et al. Na0.44MnO2 with very fast sodium diffusion and stable cycling synthesized via polyvinylpyrrolidone- combustion method. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 285: 161. |
| [21] | KUBOTA K, KUMAKURA S, YODA Y, et al. Electrochemistry and solid-state chemistry of NaMeO2 (Me = 3d transition metals). Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(17): 1703415. |
| [22] | BIANCHINI M, WANG J, CLEMENT R J, et al. The interplay between thermodynamics and kinetics in the solid-state synthesis of layered oxides. Nature Materials, 2020, 19(10): 1088. |
| [23] | LU Z, DAHN J R. In situ X-ray diffraction study of P2-Na2/3[Ni1/3Mn2/3]O2. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2001, 148(11): A1225. |
| [24] | YOU Y, MANTHIRAM A. Progress in high-voltage cathode materials for rechargeable sodium-ion batteries. Advanced Energy Materials, 2017, 8(2): 1701785. |
| [25] |
ZHAO C, WANG Q, YAO Z, et al. Rational design of layered oxide materials for sodium-ion batteries. Science, 2020, 370(6517): 708.
DOI PMID |
| [26] | WANG F, PENG B, ZENG S Y, et al. Activating oxygen redox in layered NaxMnO2 to suppress intrinsic deficient behavior and enable phase-transition-free sodium ion cathode. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(35): 2202665. |
| [27] | LIU Z B, SHEN J D, FENG S H, et al. Ultralow volume change of P2-type layered oxide cathode with controlled phase transition by regulating distribution of Na. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(38): 20960. |
| [28] | ZHENG W, LIU Q, WANG Z, et al. Oxygen redox activity with small voltage hysteresis in Na0.67Cu0.28Mn0.72O2 for sodium-ion batteries. Energy Storage Materials, 2020, 28: 300. |
| [29] | CHENG Z, ZHAO B, GUO Y, et al. Mitigating the large-volume phase transition of P2-type cathodes by synergetic effect of multiple ions for improved sodium-ion batteries. Advanced Energy Materials, 2022, 12(14): 2103461. |
| [30] | BAI X, SATHIYA M, MENDOZA-SANCHEZ B, et al. Anionic redox activity in a newly Zn-doped sodium layered oxide P2-Na2/3Mn1-yZnyO2 (0<y<0.23). Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(32): 1802379. |
| [31] | SHEN M Y, WANG J S, REN Z, et al. Quasi-zero volume strain cathode materials for sodium ion battery through synergetic substitution effect of Li and Mg. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(41): 2303812. |
| [32] | ZHANG X J, LI J L, QIU W J, et al. Electrochemical activity of positive electrode material of P2-Nax[Mg0.33Mn0.67]O2 sodium ion battery. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(6): 623. |
| [33] | WANG P F, YOU Y, YIN Y X, et al. Suppressing the P2-O2 phase transition of Na0.67Mn0.67Ni0.33O2 by magnesium substitution for improved sodium-ion batteries. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2016, 55(26): 7445. |
| [34] | TAPIA-RUIZ N, DOSE W M, SHARMA N, et al. High voltage structural evolution and enhanced Na-ion diffusion in P2-Na2/3Ni1/3-xMgxMn2/3O2 (0≤x≤0.2) cathodes from diffraction, electrochemical and ab initio studies. Energy & Environmental Science, 2018, 11(6): 1470. |
| [35] | LU Z, DAHN J R. Intercalation of water in P2, T2 and O2 structure Az[CoxNi1/3-xMn2/3]O2. Chemistry of Materials, 2001, 13(4): 1252. |
| [36] | LI L, XU M, YAO Q, et al. Alleviating surface degradation of nickel-rich layered oxide cathode material by encapsulating with nanoscale Li-ions/electrons superionic conductors hybrid membrane for advanced Li-ion batteries. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(45): 30879. |
| [37] | KRESSE G, FURTHMULLER J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Physical Review B, 1996, 54(16): 11169. |
| [38] | KRESSE G, JOUBERT D. From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method. Physical Review B, 1999, 59(3): 1758. |
| [39] |
PERDEW J P, BURKE K, ERNZERHOF M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Physical Review Letters, 1996, 77(18): 3865.
DOI PMID |
| [40] | GRIMME S, J ANTONY, S EHRLICH, et al. A consistent and accurate ab initio parametrization of density functional dispersion correction (DFT-D) for the 94 elements H-Pu. Journal of Chemical Physics, 2010, 132(5): 154104. |
| [41] |
GRIMME S, EHRLICH S, GOERIGK L. Effect of the damping function in dispersion corrected density functional theory. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2011, 32(7): 1456.
DOI PMID |
| [42] | DUDAREV S L, BOTTON G A, SAVRASOV S Y, et al. Electron- energy-loss spectra and the structural stability of nickel oxide: an LSDA+U study. Physical Review B, 1998, 57(3): 1505. |
| [43] | WANG V, XU N, LIU J C, et al. VASPKIT: a user-friendly interface facilitating high-throughput computing and analysis using VASP code. Computer Physics Communications, 2021, 267: 108033. |
| [44] | HENKELMAN G, ARNALDSSON A, JÓNSSON H. A fast and robust algorithm for Bader decomposition of charge density. Computational Materials Science, 2006, 36(3): 354. |
| [45] | HU Z, NIU Y, RONG X, et al. Suppression of voltage decay through Ni3+ barrier in anionic-redox active cathode for Na-ion batteries. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2024, 40(6): 2306005. |
| [46] | YANG L, LI X, MA X, et al. Design of high-performance cathode materials with single-phase pathway for sodium ion batteries: a study on P2-Nax(LiyMn1-y)O2 compounds. Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 381: 171. |
| [47] | LI C, ZHAO C, HU B, et al. Unraveling the critical role of Ti substitution in P2-NaxLiyMn1-yO2 cathodes for highly reversible oxygen redox chemistry. Chemistry of Materials, 2020, 32(3): 1054. |
| [48] | YANG L, KUO L Y, JUAN M L DEL A, et al. Structural aspects of P2-type Na0.67Mn0.6Ni0.2Li0.2O2 (MNL) stabilization by lithium defects as a cathode material for sodium-ion batteries. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 31(38): 2102939. |
| [49] | PEER B, MARTIN W, JESUS G J, et al. Solvent co-intercalation- induced activation and capacity fade mechanism of few-/multi- layered MXenes in lithium ion batteries. Small, 2021, 17(47): 2104130. |
| [50] | JAMES W S, ADAM S, NURIA T R, et al. Nature of the “Z”-phase in layered Na-ion battery cathodes. Energy & Environmental Science, 2019, 12(7): 2223. |
| [1] | 闫共芹, 王晨, 蓝春波, 洪雨昕, 叶维超, 付向辉. Al掺杂P2型Na0.8Ni0.33Mn0.67-xAlxO2钠离子电池正极材料的制备与电化学性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(9): 1005-1012. |
| [2] | 万俊池, 杜路路, 张永上, 李琳, 刘建德, 张林森. Na4FexP4O12+x/C钠离子电池正极材料的结构演变及其电化学性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 497-503. |
| [3] | 张继国, 吴田, 赵旭, 杨钒, 夏天, 孙士恩. 钠离子电池正极材料循环稳定性提升策略及产业化进程[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 348-362. |
| [4] | 杨舒琪, 杨存国, 牛慧祝, 石唯一, 舒珂维. GeP3/科琴黑复合材料作为钠离子电池高性能负极材料[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 329-336. |
| [5] | 王琨鹏, 刘兆林, 林存生, 王治宇. 基于低含水量普鲁士蓝正极的准固态钠离子电池[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(9): 1005-1012. |
| [6] | 孔剑锋, 黄杰成, 刘兆林, 林存生, 王治宇. 基于DPEPA聚合物凝胶电解质的准固态钠离子电池[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(12): 1331-1338. |
| [7] | 周靖渝, 李兴宇, 赵晓琳, 王有伟, 宋二红, 刘建军. Ti和Cu掺杂β-NaMnO2正极材料:钠离子电池的倍率和循环性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(12): 1404-1412. |
| [8] | 胡梦菲, 黄丽萍, 李贺, 张国军, 吴厚政. 锂/钠离子电池硬碳负极材料的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(1): 32-44. |
| [9] | 孔国强, 冷明哲, 周战荣, 夏池, 沈晓芳. Sb掺杂O3型Na0.9Ni0.5Mn0.3Ti0.2O2钠离子电池正极材料[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 656-662. |
| [10] | 杨卓, 卢勇, 赵庆, 陈军. X射线衍射Rietveld精修及其在锂离子电池正极材料中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 589-605. |
| [11] | 李涛, 曹鹏飞, 胡力涛, 夏勇, 陈一, 刘跃军, 孙翱魁. NH4+扩层MoS2的制备及其储锌性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(1): 79-86. |
| [12] | 王洋, 范广新, 刘培, 尹金佩, 刘宝忠, 朱林剑, 罗成果. 钾离子掺杂提高锂离子电池正极锰酸锂性能的微观机制[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(9): 1023-1029. |
| [13] | 李文博, 黄民松, 李月明, 李驰麟. 双盐镁电池CoS2正极材料的电化学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(2): 173-181. |
| [14] | 赵伟, 徐阳, 万颖杰, 蔡天逊, 穆金潇, 黄富强. 金属氰胺化合物的结构、合成及电化学储能应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(2): 140-151. |
| [15] | 王晶, 徐守冬, 卢中华, 赵壮壮, 陈良, 张鼎, 郭春丽. 钠离子电池中空结构CoSe2/C负极材料的制备及储钠性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(12): 1344-1350. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||