无机材料学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (12): 1404-1412.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240204 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20240204
所属专题: 【能源环境】储能电池(202506)
• 研究快报 • 上一篇
周靖渝1,2,3( ), 李兴宇2, 赵晓琳2,3, 王有伟2,3, 宋二红2,3(
), 李兴宇2, 赵晓琳2,3, 王有伟2,3, 宋二红2,3( ), 刘建军1,2,3
), 刘建军1,2,3
收稿日期:2024-04-22
修回日期:2024-06-15
出版日期:2024-07-16
网络出版日期:2024-07-16
通讯作者:
宋二红, 副研究员. E-mail: ehsong@mail.sic.ac.cn作者简介:周靖渝(1998-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: zhoujingyu211@mails.ucas.ac.cn
ZHOU Jingyu1,2,3( ), LI Xingyu2, ZHAO Xiaolin2,3, WANG Youwei2,3, SONG Erhong2,3(
), LI Xingyu2, ZHAO Xiaolin2,3, WANG Youwei2,3, SONG Erhong2,3( ), LIU Jianjun1,2,3
), LIU Jianjun1,2,3
Received:2024-04-22
Revised:2024-06-15
Published:2024-07-16
Online:2024-07-16
Contact:
SONG Erhong, associate professor. E-mail: ehsong@mail.sic.ac.cnAbout author:ZHOU Jingyu (1998-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: zhoujingyu211@mails.ucas.ac.cn
Supported by:摘要:
钠离子电池是一种经济且环境可持续的储能电池。其中, β-NaMnO2作为前景广阔的钠离子正极材料, 是一种具有波纹形层状结构的锰基氧化物, 因其结构坚固和比容量相对较高而备受关注。然而, β-NaMnO2存在循环寿命短、倍率性能不佳的问题。为了解决这些问题, 本研究通过第一性原理计算和晶体轨道哈密顿布局(COHP)分析, 在β-NaMnO2中掺入了可以提高材料结构稳定性的Ti原子和有利于钠离子脱出的Cu原子。β-NaMn0.8Ti0.1Cu0.1O2的可逆比容量显著增长, 并且具有卓越的倍率性能。在0.2C电流密度(1C=219 mA·g-1)、1.8~4.0 V电压范围内, 改性材料的初始放电比容量为132 mAh·g-1。分别在0.2C、0.5C、1C、3C和0.2C的电流密度下进行充放电测试后, 该材料仍能保持110 mAh·g-1的比容量。掺入Ti减缓了晶体结构的变化, 晶格常数c/a在脱钠过程中仅有微小变化。Mn和Cu分别在3.0 V以下和3.5 V左右发生可逆氧化还原反应, 在放电曲线中, 3.0 V以下的长平台表明Mn是电池容量的主要贡献者。本工作深入研究了改性β-NaMnO2正极材料的工作机理, 为提高钠离子电池的性能提供了实验依据和理论指导。
中图分类号:
周靖渝, 李兴宇, 赵晓琳, 王有伟, 宋二红, 刘建军. Ti和Cu掺杂β-NaMnO2正极材料:钠离子电池的倍率和循环性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(12): 1404-1412.
ZHOU Jingyu, LI Xingyu, ZHAO Xiaolin, WANG Youwei, SONG Erhong, LIU Jianjun. Rate and Cycling Performance of Ti and Cu Doped β-NaMnO2 as Cathode of Sodium-ion Battery[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(12): 1404-1412.
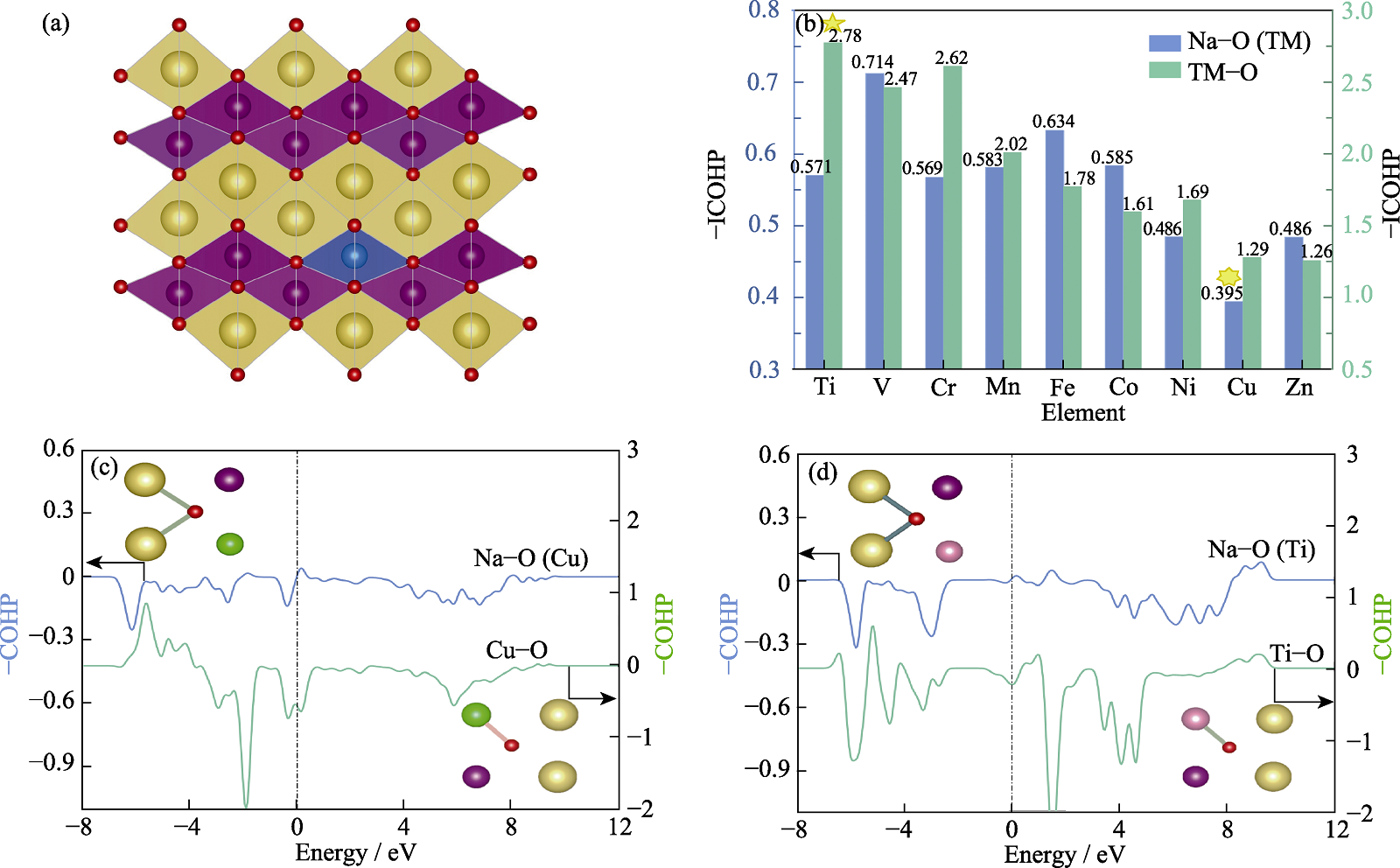
Fig. 1 Screening of doped atoms in β-NaMnO2 (a) Schematic crystal structure of β-NaMnO2 doped by 3d transition metal atoms; (b) -ICOHP of Na-O and TM-O (TM=Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn); (c) -COHP of Na-O and Cu-O in Cu doped β-NaMnO2; (d) -COHP of Na-O and Ti-O in Ti doped β-NaMnO2. Colorful figures are available on website

Fig. 2 Structure and morphology of β-MTC811 (a) Crystal structure modeling of β-MTC811 that obtained by calculation; (b) Comparison of calculated and experimental XRD patterns of β-MTC811; (c) SEM image of β-MTC811; (d) EDS mappings of β-MTC811; (e) TEM image of β-MTC811; (f) Enlarged image of zig-zag layered structure in (e)
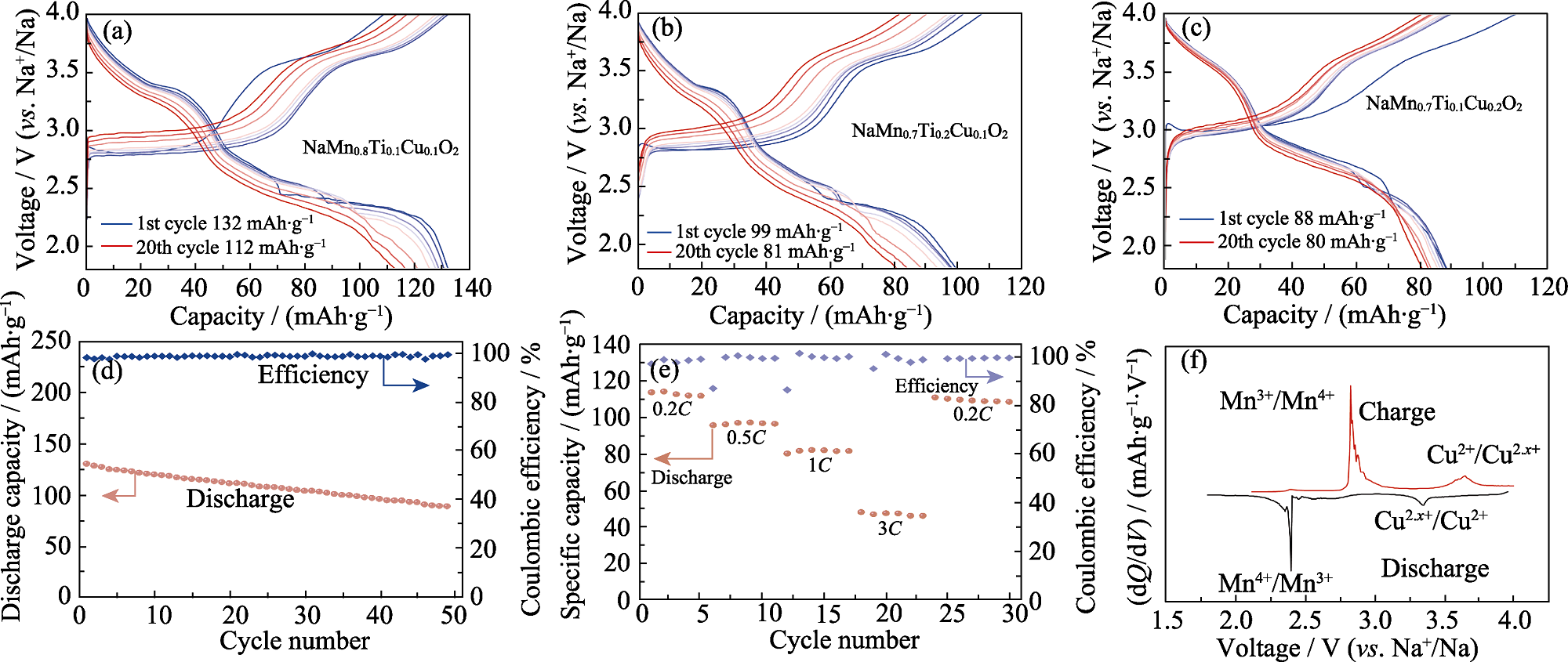
Fig. 3 Electrochemical performance of β-MTC811 cathode (a-c) Charge/discharge curves of (a) β-MTC811, (b) β-MTC721 and (c) β-MTC712 at 0.2C; (d) Cycling performance, (e) rate performance and (f) dQ/dV curves of β-MTC811 Colorful figures are available on website

Fig. 4 Electrochemical reaction mechanisms (a) Mn2p and (b) Cu2p XPS spectra of β-MTC811 in different charging and discharging states. Colorful figures are available on website

Fig. 5 First-principles calculations of β-MTC811 cathode (a) Schematic diagram of desodiation process; (b) Lattice constant c/a during desodiation; (c) Calculated and fitted voltage plateaus, and experimental voltage curve; (d) Bader charge of Mn and Cu; (e-g) pDOS of Mn3d and Cu3d during different desodiation processes Colorful figures are available on website

Fig. S5 Electrochemical performance of (a-c) β-MTC721 and (d-f) β-MTC712 cathodes (a, d) Cycling performance during 50 cycles; (b, e) rate performance; (c, f) dQ/dV curves
| Element | Na-O/Å | TM-O/Å |
|---|---|---|
| Ti | 2.37641 | 1.95505 |
| V | 2.32810 | 1.98783 |
| Cr | 2.36871 | 1.98479 |
| Mn | 2.33621 | 1.97821 |
| Fe | 2.34627 | 2.00070 |
| Co | 2.36626 | 1.94259 |
| Ni | 2.35691 | 1.91536 |
| Cu | 2.39119 | 1.98934 |
| Zn | 2.36493 | 2.08207 |
Table S1 Bond lengths of Na-O (in Na-O-TM) and TM-O
| Element | Na-O/Å | TM-O/Å |
|---|---|---|
| Ti | 2.37641 | 1.95505 |
| V | 2.32810 | 1.98783 |
| Cr | 2.36871 | 1.98479 |
| Mn | 2.33621 | 1.97821 |
| Fe | 2.34627 | 2.00070 |
| Co | 2.36626 | 1.94259 |
| Ni | 2.35691 | 1.91536 |
| Cu | 2.39119 | 1.98934 |
| Zn | 2.36493 | 2.08207 |
| Sample | Measured atomic ration | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Mn | Ti | Cu | |
| β-MTC811 | 0.8 | 0.09 | 0.1 |
| β-MTC712 | 0.7 | 0.08 | 0.2 |
| β-MTC721 | 0.7 | 0.19 | 0.1 |
Table S2 ICP-OES results of β-MTC811, β-MT712 and β-MTC721
| Sample | Measured atomic ration | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Mn | Ti | Cu | |
| β-MTC811 | 0.8 | 0.09 | 0.1 |
| β-MTC712 | 0.7 | 0.08 | 0.2 |
| β-MTC721 | 0.7 | 0.19 | 0.1 |
| Material | Cathodes’ mass loading/mg | Electrolyte amount/μL | Radius/mm |
|---|---|---|---|
| β-MTC811 | 4.192 | 160 | 14 |
| β-MTC721 | 4.360 | 160 | 14 |
| β-MTC712 | 5.696 | 160 | 14 |
Table S3 Parameters for button cell batteries
| Material | Cathodes’ mass loading/mg | Electrolyte amount/μL | Radius/mm |
|---|---|---|---|
| β-MTC811 | 4.192 | 160 | 14 |
| β-MTC721 | 4.360 | 160 | 14 |
| β-MTC712 | 5.696 | 160 | 14 |
| [1] |
DUNN B, KAMATH H, TARASCON J M. Electrical energy storage for the grid: a battery of choices. Science, 2011, 334(6058):928.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
CANEPA P, GAUTAM G S, HANNAH D C, et al. Odyssey of multivalent cathode materials: open questions and future challenges. Chemical Reviews, 2017, 117(5):4287.
DOI PMID |
| [3] | HE T Q, KANG X Y, WANG F J, et al. Capacitive contribution matters in facilitating high power battery materials toward fast- charging alkali metal ion batteries. Materials Science & Engineering R-Reports, 2023, 154: 100737. |
| [4] | SINGH A N, ISLAM M, MEENA A, et al. Unleashing the potential of sodium-ion batteries: current state and future directions for sustainable energy storage. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(46):2304617. |
| [5] | YANG H, WANG D, LIU Y L, et al. Improvement of cycle life for layered oxide cathodes in sodium-ion batteries. Energy & Environmental Science, 2024, 17(5):1756. |
| [6] | PANG X W, AN B G, ZHENG S M, et al. Cathode materials of metal-ion batteries for low-temperature applications. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2022, 912: 165142. |
| [7] | LI J Q, LIANG Z X, JIN Y Q, et al. A high-voltage cathode material with ultralong cycle performance for sodium-ion batteries. Small Methods, 2024, 8(10):2301742. |
| [8] | XU S T, YANG Y, TANG F, et al. Vanadium fluorophosphates: advanced cathode materials for next-generation secondary batteries. Materials Horizons, 2023, 10(6): 1901. |
| [9] | ZHANG Y C, ZHOU X, YANG C, et al. Air-stable prussian white cathode materials for sodium-ion batteries enabled by ZnO surface modification. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2024, 16(13):15649. |
| [10] | ZHOU J E, REDDY R C K, ZHONG A, et al. Metal-organic framework-based materials for advanced sodium storage: development and anticipation. Advanced Materials, 2024, 36(16):2312471. |
| [11] | WU Z H, NI Y X, TAN S, et al. Realizing high capacity and zero strain in layered oxide cathodes via lithium dual-site substitution for sodium-ion batteries. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2023, 145(17):9596. |
| [12] | DELMAS C, FOUASSIER C, HAGENMULLER P. Structural classification and properties of the layered oxides. Physica B & C, 1980, 99(1-4):81. |
| [13] | MENDIBOURE A, DELMAS C, HAGENMULLER P. Electrochemical intercalation and deintercalation of NaxMnO2 bronzes. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 1985, 57(3):323. |
| [14] |
BILLAUD J, CLÉMENT R J, ARMSTRONG A R, et al. β-NaMnO2: a high-performance cathode for sodium-ion batteries. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2014, 136(49):17243.
DOI PMID |
| [15] | CLÉMENT R J, MIDDLEMISS D S, SEYMOUR I D, et al. Insights into the nature and evolution upon electrochemical cycling of planar defects in the β-NaMnO2 Na-ion battery cathode: an NMR and first-principles density functional theory approach. Chemistry of Materials, 2016, 28(22):8228. |
| [16] | GU Z Y, HENG Y L, GUO J Z, et al. Nano self-assembly of fluorophosphate cathode induced by surface energy evolution towards high-rate and stable sodium-ion batteries. Nano Research, 2023, 16(1):439. |
| [17] | HUANG Z X, ZHANG X L, ZHAO X X, et al. Hollow Na0.62K0.05Mn0.7Ni0.2Co0.1O2 polyhedra with exposed stable {001} facets and K riveting for sodium-ion batteries. Science China- Materials, 2023, 66(1):79. |
| [18] | HUANG Z X, ZHANG X L, ZHAO X X, et al. Suppressing oxygen redox in layered oxide cathode of sodium-ion batteries with ribbon superstructure and solid-solution behavior. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2023, 160: 9. |
| [19] | SHISHKIN M, KUMAKURA S, SATO S, et al. Unraveling the role of doping in selective stabilization of NaMnO2 polymorphs: combined theoretical and experimental study. Chemistry of Materials, 2018, 30(4):1257. |
| [20] | JIANG L W, LU Y X, WANG Y S, et al. A high-temperature β-phase NaMnO2 stabilized by Cu doping and its Na storage properties. Chinese Physics Letters, 2018, 35(4):048801. |
| [21] | WANG H J, GAO X, ZHANG S, et al. High-entropy Na-deficient layered oxides for sodium-ion batteries. ACS Nano, 2023, 17(13):12530. |
| [22] | KRESSE G, FURTHMULLER J. Efficiency of ab-initio total energy calculations for metals and semiconductors using a plane-wave basis set. Computational Materials Science, 1996, 6(1):15. |
| [23] |
PERDEW J P, BURKE K, ERNZERHOF M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Physical Review Letters, 1996, 77(18):3865.
DOI PMID |
| [24] | MONKHORST H J, PACK J D. Special points for brillouin-zone integrations. Physical Review B, 1976, 13(12):5188. |
| [25] | OKHOTNIKOV K, CHARPENTIER T, CADARS S. Supercell program: a combinatorial structure-generation approach for the local- level modeling of atomic substitutions and partial occupancies in crystals. Journal of Cheminformatics, 2016, 8: 17. |
| [26] |
DERINGER V L, TCHOUGRÉEFF A L, DRONSKOWSKI R. Crystal orbital Hamilton population (COHP) analysis as projected from plane-wave basis sets. Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2011, 115(21):5461.
DOI PMID |
| [27] | MAINTZ S, DERINGER V L, TCHOUGRÉEFF A L, et al. LOBSTER: a tool to extract chemical bonding from plane-wave based DFT. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2016, 37(11):1030. |
| [28] | HENKELMAN G, ARNALDSSON A, JÓNSSON H. A fast and robust algorithm for Bader decomposition of charge density. Computational Materials Science, 2006, 36(3):354. |
| [29] |
SANVILLE E, KENNY S D, SMITH R, et al. Improved grid-based algorithm for bader charge allocation. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2007, 28(5):899.
PMID |
| [30] | MOMMA K, IZUMI F. VESTA3 for three-dimensional visualization of crystal, volumetric and morphology data. Journal of Applied Crystallography, 2011, 44: 1272. |
| [31] | ZHANG T, REN M, HUANG Y H, et al. Negative lattice expansion in an O3-type transition-metal oxide cathode for highly stable sodium-ion batteries. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2024, 63(8):202316949. |
| [32] | VANAPHUTI P, YAO Z Y, LIU Y T, et al. Achieving high stability and performance in P2-type Mn-based layered oxides with tetravalent cations for sodium-ion batteries. Small, 2022, 18(19):2201086. |
| [33] | LI J C, ZHU G Z, LIANG P, et al. Analysis of Si, Cu, and their oxides by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Journal of Chemical Education, 2024, 101(3):1162. |
| [34] | URBAN A, SEO D H, CEDER G. Computational understanding of Li-ion batteries. npj Computational Materials, 2016, 2: 16002. |
| [35] | ZHANG Z H, WU D H, ZHANG X, et al. First-principles computational studies on layered Na2Mn3O7 as a high-rate cathode material for sodium ion batteries. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2018, 6(14):6107. |
| [1] | 万俊池, 杜路路, 张永上, 李琳, 刘建德, 张林森. Na4FexP4O12+x/C钠离子电池正极材料的结构演变及其电化学性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 497-503. |
| [2] | 张继国, 吴田, 赵旭, 杨钒, 夏天, 孙士恩. 钠离子电池正极材料循环稳定性提升策略及产业化进程[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 348-362. |
| [3] | 杨舒琪, 杨存国, 牛慧祝, 石唯一, 舒珂维. GeP3/科琴黑复合材料作为钠离子电池高性能负极材料[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 329-336. |
| [4] | 朱志杰, 申明远, 吴涛, 李文翠. Cu和Mg协同取代抑制钠离子电池正极材料P2-Na2/3Ni1/3Mn2/3O2的P2-O2相变[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 184-195. |
| [5] | 王琨鹏, 刘兆林, 林存生, 王治宇. 基于低含水量普鲁士蓝正极的准固态钠离子电池[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(9): 1005-1012. |
| [6] | 吴玉豪, 彭仁赐, 程春玉, 杨丽, 周益春. HfxTa1-xC体系力学性能及熔化曲线的第一性原理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 761-768. |
| [7] | 靳宇翔, 宋二红, 朱永福. 3d过渡金属单原子掺杂石墨烯缺陷电催化还原CO2的第一性原理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 845-852. |
| [8] | 王伟华, 张磊宁, 丁峰, 代兵, 韩杰才, 朱嘉琦, 贾怡, 杨宇. 铱衬底上金刚石外延形核与生长: 第一性原理计算[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(4): 416-422. |
| [9] | 张宇晨, 陆知遥, 赫晓东, 宋广平, 朱春城, 郑永挺, 柏跃磊. 硫族MAX相硼化物的物相稳定性和性能预测[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 225-232. |
| [10] | 孔剑锋, 黄杰成, 刘兆林, 林存生, 王治宇. 基于DPEPA聚合物凝胶电解质的准固态钠离子电池[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(12): 1331-1338. |
| [11] | 陈梦杰, 王倩倩, 吴成铁, 黄健. 基于DFT的描述符预测生物陶瓷的降解性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(10): 1175-1181. |
| [12] | 周云凯, 刁亚琪, 王明磊, 张宴会, 王利民. 聚苯胺改性Ti3C2(OH)2抗氧化性的第一性原理计算研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(10): 1151-1158. |
| [13] | 胡梦菲, 黄丽萍, 李贺, 张国军, 吴厚政. 锂/钠离子电池硬碳负极材料的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(1): 32-44. |
| [14] | 吴晓维, 张涵, 曾彪, 明辰, 孙宜阳. 杂化泛函HSE和PBE0计算CsPbI3缺陷性质的比较研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(9): 1110-1116. |
| [15] | 孔国强, 冷明哲, 周战荣, 夏池, 沈晓芳. Sb掺杂O3型Na0.9Ni0.5Mn0.3Ti0.2O2钠离子电池正极材料[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 656-662. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||