无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (12): 1341-1348.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240542 CSTR: 32189.14.jim20240542
• 专栏:高温燃料电池关键材料(客座编辑:凌意瀚) • 上一篇 下一篇
王哲1( ), 郝鸿儒1, 吴宗辉1, 徐玲玲2, 吕喆1, 魏波1(
), 郝鸿儒1, 吴宗辉1, 徐玲玲2, 吕喆1, 魏波1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-12-27
修回日期:2025-02-02
出版日期:2025-12-20
网络出版日期:2025-03-06
通讯作者:
魏 波, 教授. E-mail: bowei@hit.edu.cn作者简介:王 哲(1998-), 男, 博士研究生. E-mail: 1020881070@qq.com
基金资助:
WANG Zhe1( ), HAO Hongru1, WU Zonghui1, XU Lingling2, LÜ Zhe1, WEI Bo1(
), HAO Hongru1, WU Zonghui1, XU Lingling2, LÜ Zhe1, WEI Bo1( )
)
Received:2024-12-27
Revised:2025-02-02
Published:2025-12-20
Online:2025-03-06
Contact:
WEI Bo, professor. E-mail: bowei@hit.edu.cnAbout author:WANG Zhe (1998-), male, PhD candidate. E-mail: 1020881070@qq.com
Supported by:摘要:
固体氧化物燃料电池(SOFCs)作为一种高效清洁的发电装置, 其阴极性能对于电池的商业化应用来说至关重要。其中阴极表面的阳离子偏析会对电池的性能和稳定性产生不利影响。双钙钛矿氧化物PrBa0.8Ca0.2Co2O5+δ (PBCC)是一种高活性阴极, 但其依然存在偏析显著和Cr耐受力不足问题。为提高阴极稳定性, 本研究设计了由PBCC衍生的A位中熵双钙钛矿阴极材料Pr0.6La0.1Nd0.1Sm0.1Gd0.1Ba0.8Ca0.2Co2O5+δ(ME-PBCC), 并系统探究了其在含Cr气氛下的偏析情况及耐Cr性能。与传统PBCC阴极相比, ME-PBCC材料表面的BaCrO4和Co3O4偏析得到了显著抑制, 这归因于其具有较高的构型熵。电导弛豫(ECR)和电化学交流阻抗谱(EIS)结果表明, ME-PBCC阴极的电化学稳定性得到了明显提高。中熵阴极在Cr沉积48 h后的氧表面交换系数kchem从4.4×10-4 cm·s-1降至1.8×10-4 cm·s-1, 其kchem减小量明显低于PBCC(从7.3×10-4 cm·s-1降至1.2×10-4 cm·s-1)。此外, 在700 ℃含Cr空气中处理48 h后的EIS结果显示, ME-PBCC的极化电阻(Rp)仅为0.07 Ω·cm2, 明显小于PBCC的0.11 Ω·cm2, 证实了中熵阴极的运行稳定性与耐Cr能力显著提高。本研究提供了一种具有应用前景的SOFCs阴极材料。
中图分类号:
王哲, 郝鸿儒, 吴宗辉, 徐玲玲, 吕喆, 魏波. 构型熵工程增强双钙钛矿型氧电极抗Cr中毒能力[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(12): 1341-1348.
WANG Zhe, HAO Hongru, WU Zonghui, XU Lingling, LÜ Zhe, WEI Bo. Enhancing Cr-tolerance Ability of Double Perovskite Cathodes through Configuration Entropy Engineering[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(12): 1341-1348.

图1 PBCC和ME-PBCC的晶体结构和XRD图谱
Fig. 1 Crystal structures and XRD patterns of PBCC and ME-PBCC (a) Schematic demonstrations of structures and (b) XRD patterns for PBCC and ME-PBCC; (c) Rietveld XRD pattern for ME-PBCC
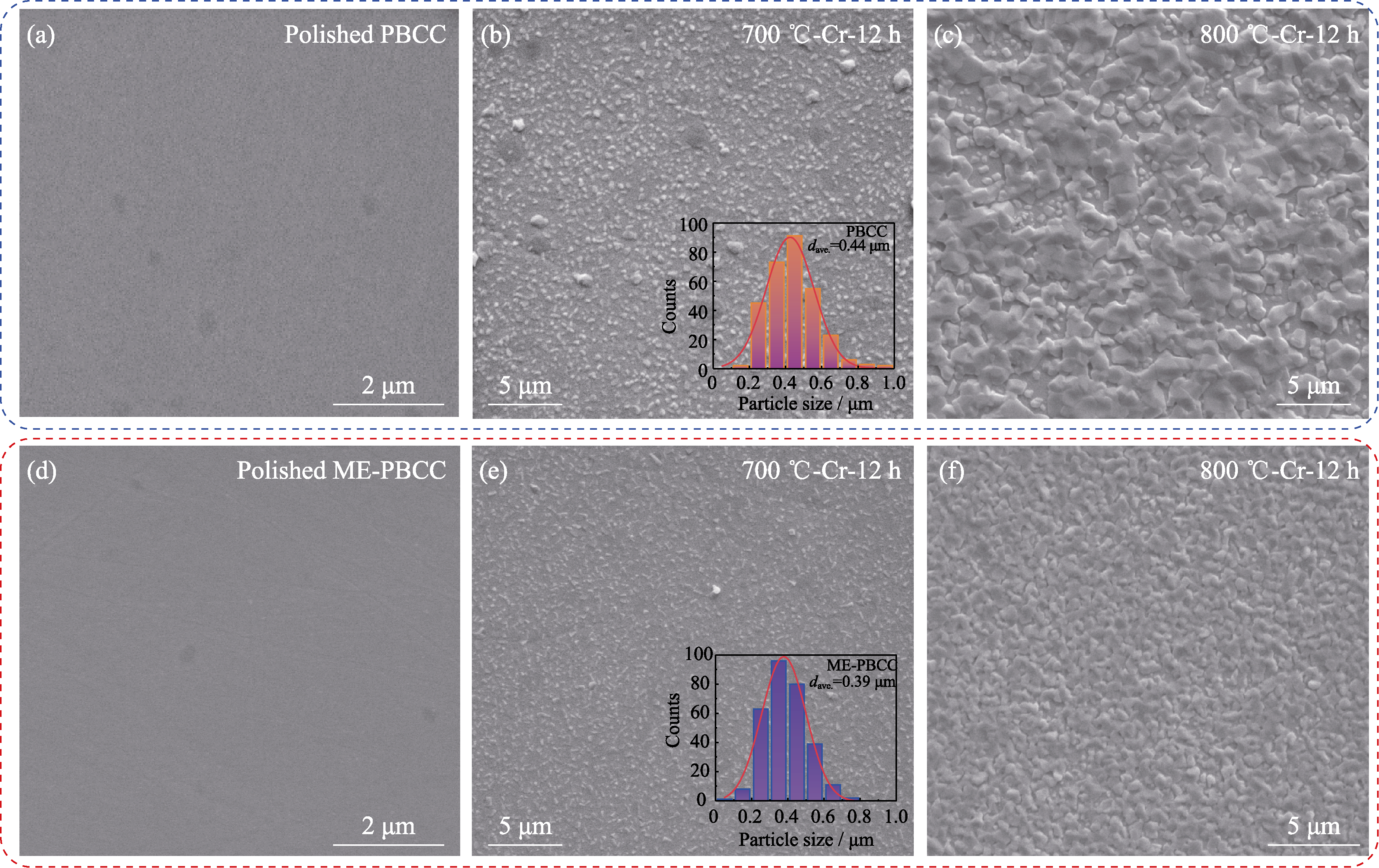
图2 PBCC和ME-PBCC片体在不同处理条件下的SEM照片
Fig. 2 SEM images of PBCC and ME-PBCC pellets treated under different conditions (a-c) SEM images of PBCC after (a) polishing and heat treatment in dry Cr-containing air at (b) 700 and (c) 800 ℃ for 12 h; (d-f) SEM images of ME-PBCC after (d) polishing and heat treatment in dry Cr-containing air at (e) 700 and (f) 800 ℃ for 12 h. Inserts in (b, e): corresponding distributions of particle sizes
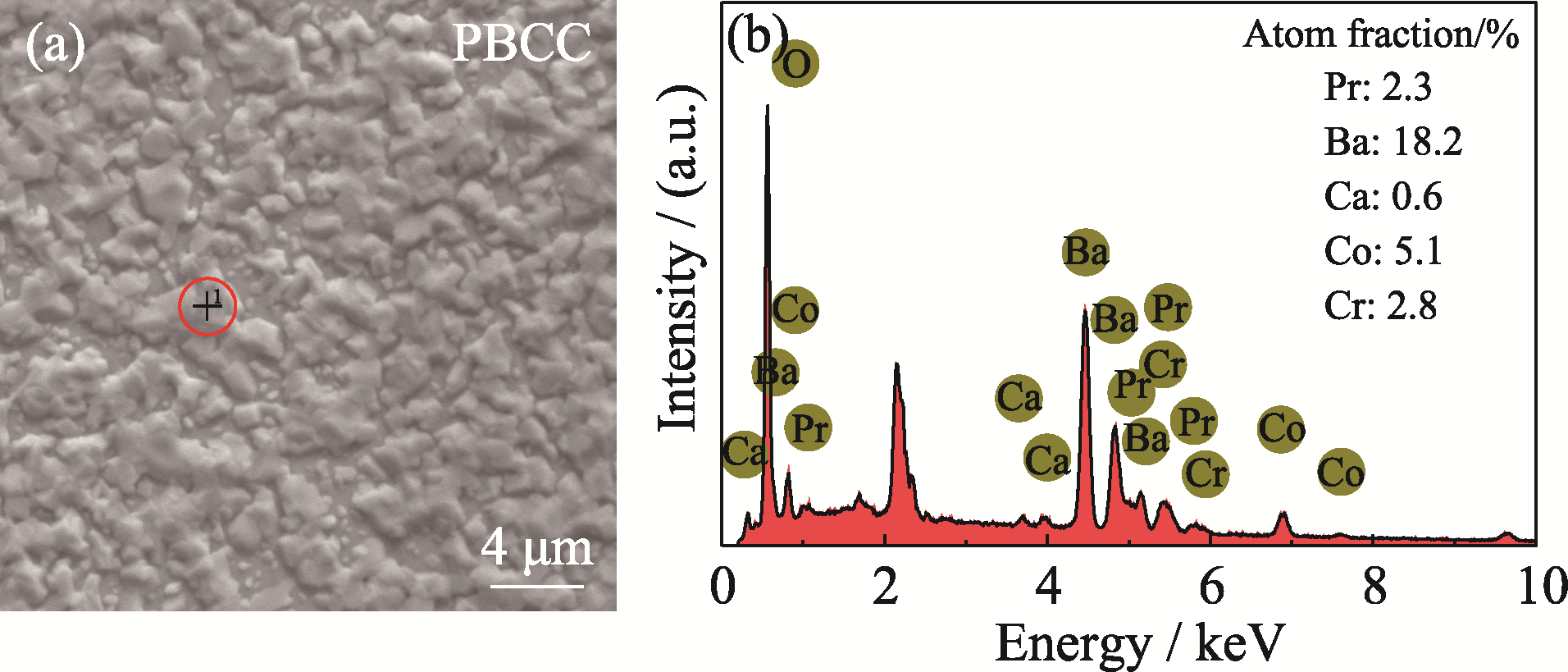
图3 在800 ℃含Cr空气条件下处理12 h后PBCC样品表面的(a) SEM照片及(b) EDS元素分析
Fig. 3 (a) SEM image and (b) corresponding EDS elemental analysis of the surface of PBCC sample after treatment in Cr-containing air for 12 h at 800 ℃
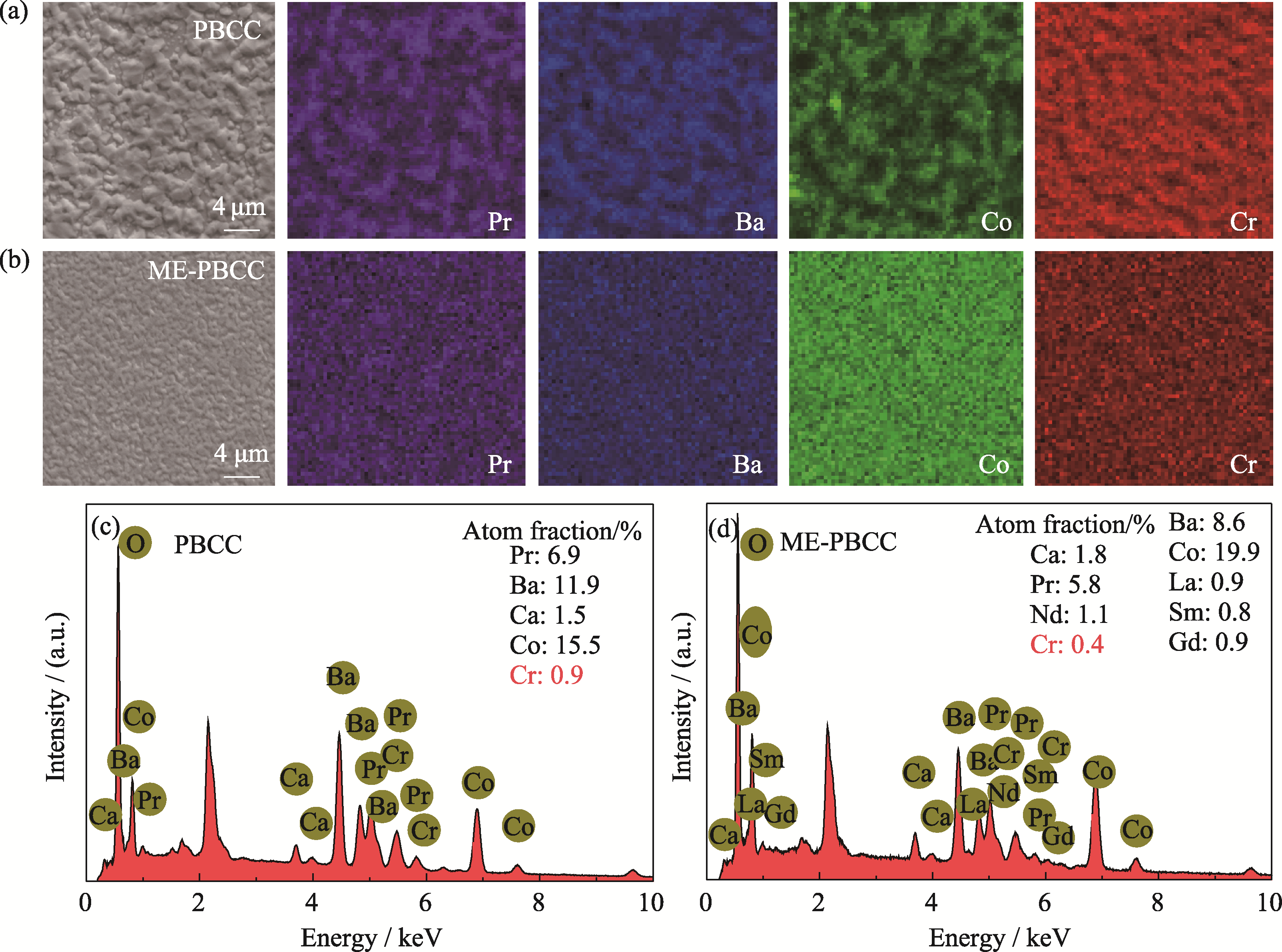
图4 (a, c) PBCC和(b, d) ME-PBCC表面的(a, b) SEM-EDS元素分布及(c, d)相关谱图
Fig. 4 (a, b) SEM-EDS elemental mappings and (c, d) corresponding spectra for the surface of (a, c) PBCC and (b, d) ME-PBCC
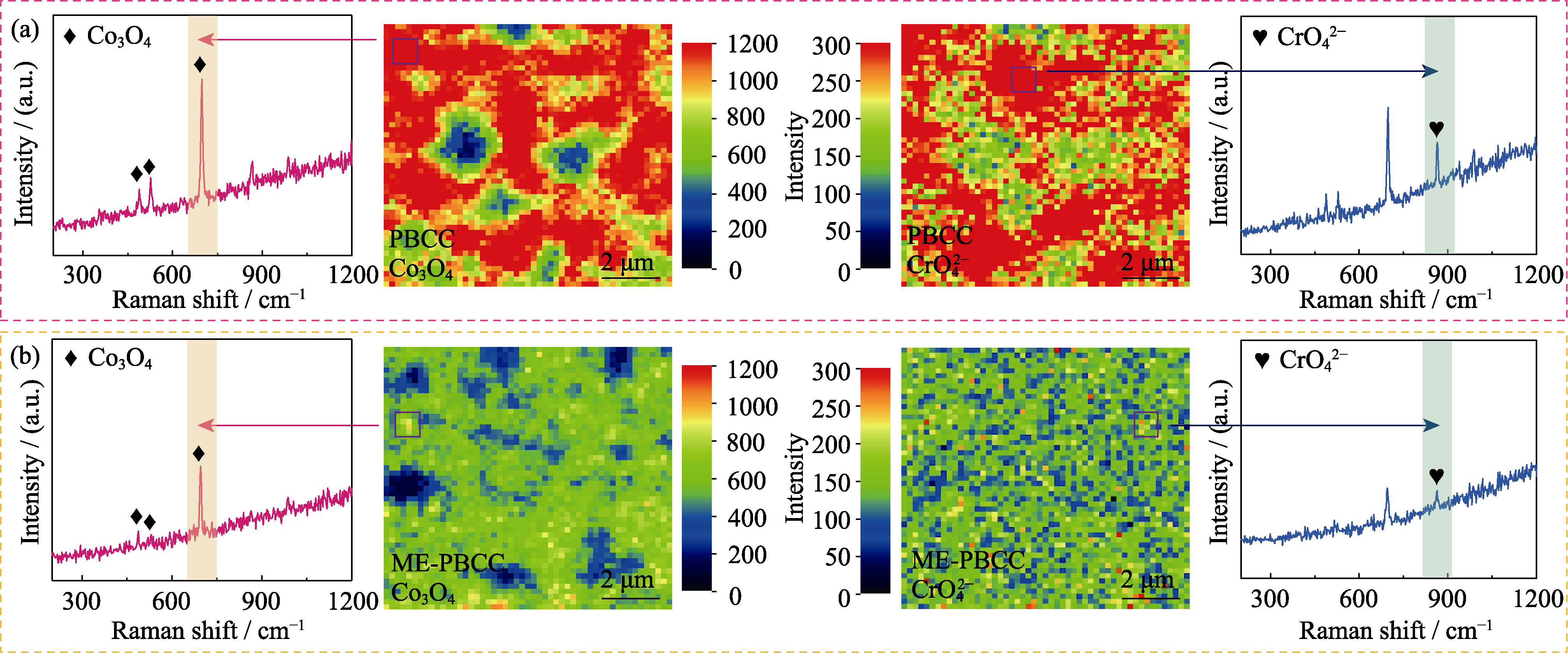
图5 在800 ℃ Cr毒化12 h后(a) PBCC和(b) ME-PBCC样品片上Co3O4和CrO42-的拉曼映射和相应谱图
Fig. 5 Raman mappings and corresponding spectra from marked points of Co3O4 and CrO42- for (a) PBCC and (b) ME-PBCC pellets after Cr-poisoning at 800 ℃ for 12 h Colorful figures are available on website

图6 ECR曲线及氧表面交换系数(kchem)和体相扩散系数(Dchem)结果
Fig. 6 ECR curves, oxygen surface exchange coefficients (kchem) and bulk diffusion coefficients (Dchem) (a, b) ECR curves for (a) PBCC and (b) ME-PBCC before and after Cr deposition at 700 ℃; (c, d) Results for (c) kchem and (d) Dchem
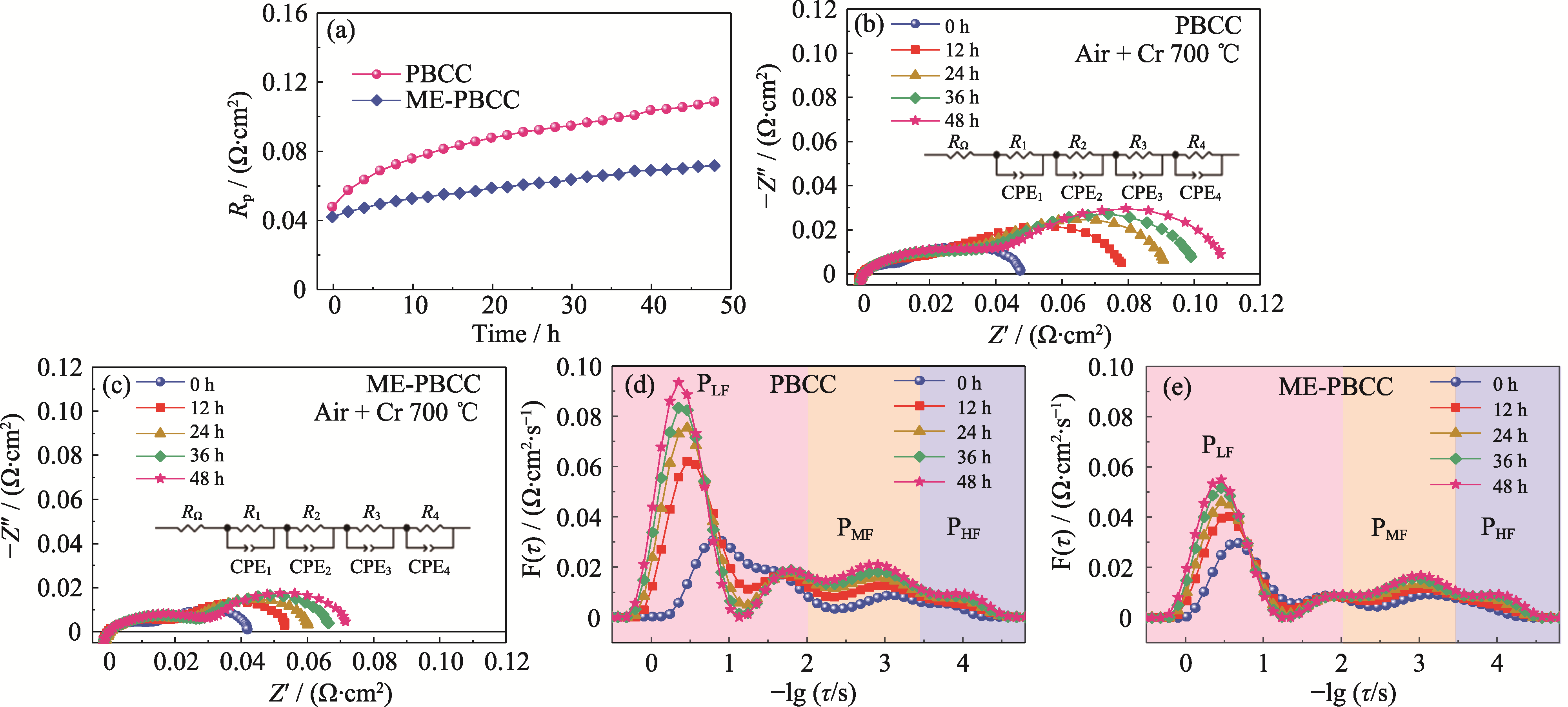
图7 PBCC与ME-PBCC的EIS谱图及相应的DRT分析
Fig. 7 EIS spectra and corresponding DRT analysis of PBCC and ME-PBCC (a) Variation curves of Rp with time at 700 ℃ in Cr-containing air; (b, c) EIS spectra of (b) PBCC and (c) ME-PBCC; (d, e) DRT curves of (d) PBCC and (e) ME-PBCC
| Sample | Space group | a/Å | b/Å | c/Å | Volume/Å3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PBCC | P4/mmm | 3.878 | 3.878 | 7.628 | 114.72 |
| ME-PBCC | P4/mmm | 3.877 | 3.877 | 7.606 | 114.33 |
表S1 PBCC和ME-PBCC精修后的晶胞参数
Table S1 Results of the refined cell parameters of PBCC and ME-PBCC
| Sample | Space group | a/Å | b/Å | c/Å | Volume/Å3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PBCC | P4/mmm | 3.878 | 3.878 | 7.628 | 114.72 |
| ME-PBCC | P4/mmm | 3.877 | 3.877 | 7.606 | 114.33 |
图S3 (a) PBCC和(b) ME-PBCC的SEM照片与除Pr、Ba、Co和Cr元素以外的EDS元素分布图
Fig. S3 SEM images and EDS elemental distribution mappings excluding Pr, Ba, Co, and Cr elements of (a) PBCC and (b) ME-PBCC
| [1] |
KAUR P, SINGH K. Review of perovskite-structure related cathode materials for solid oxide fuel cells. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(5): 5521.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
HANIF M B, MOTOLA M, QAYYUM S, et al. Recent advancements, doping strategies and the future perspective of perovskite-based solid oxide fuel cells for energy conversion. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 428: 132603.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
GAO Y, LING Y H, WANG X X, et al. Sr-deficient medium- entropy Sr1-xCo0.5Fe0.2Ti0.1Ta0.1Nb0.1O3-δ cathodes with high Cr tolerance for solid oxide fuel cells. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 479: 147665.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
GAO J T, WEI Z Y, YUAN M K, et al. Boosting oxygen reduction activity and CO2 resistance on bismuth ferrite-based perovskite cathode for low-temperature solid oxide fuel cells below 600 ℃. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2024, 90: 600.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
HAO H R, WANG J H, WANG Z, et al. Elucidating the superwetting FeOOH-modified NiMoO4 electrodes for efficient alkaline oxygen evolution reaction: an in-situ spectroscopy study. Applied Catalysis B-Environmental and Energy, 2025, 363: 124814.
DOI URL |
| [6] | XIE M Y, CAI C K, LIU X J, et al. Improved durability of high-performance intermediate-temperature solid oxide fuel cells with a Ba-doped La0.6Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.8O3-δ cathode. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(29): 33052. |
| [7] |
LI J, LI J, YAN D, et al. Promoted Cr-poisoning tolerance of La2NiO4+δ-coated PrBa0.5Sr0.5Co1.5Fe0.5O5+δ cathode for intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cells. Electrochimica Acta, 2018, 270: 294.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
CHEN Y, YOO S, LI X X, et al. An effective strategy to enhancing tolerance to contaminants poisoning of solid oxide fuel cell cathodes. Nano Energy, 2018, 47: 474.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
WANG C C, BECKER T, CHEN K F, et al. Effect of temperature on the chromium deposition and poisoning of La0.6Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.8O3-δ cathodes of solid oxide fuel cells. Electrochimica Acta, 2014, 139: 173.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
HUANG J Y, LIU Q, JIANG S P, et al. Promotional role of BaCO3 on the chromium-tolerance of La0.6Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.8O3-δ cathodes of solid oxide fuel cells. Applied Catalysis B-Environment and Energy, 2023, 321: 122080.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
YANG Z B, XIA T, DONG Z W, et al. Considerable oxygen reduction activity and durability of BaO nanoparticles-decorated Ln0.94BaCo2O5+δ electrocatalysts. Separation and Purification Technology, 2023, 317: 123936.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
SUN C W, HUI R, ROLLER J. Cathode materials for solid oxide fuel cells: a review. Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 2010, 14(7): 1125.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
SUN C W. Advances in nanoengineering of cathodes for next-generation solid oxide fuel cells. Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers, 2024, 11(23): 8164.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
CHEN Z P, JIN F J, LI M F, et al. Double perovskite Sr2CoFeO5+δ: preparation and performance as cathode material for intermediate- temperature solid oxide fuel cells. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(3): 337.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
YUAN M K, GAO Y, LIU L M, et al. High entropy double perovskite cathodes with enhanced activity and operational stability for solid oxide fuel cells. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2024, 44(5): 3267.
DOI URL |
| [16] | WEI B, SCHROEDER M, MARTIN M. Surface cation segregation and chromium deposition on the double-perovskite oxide PrBaCo2O5+δ. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(10): 8621. |
| [17] | SEO H G, STAERZ A, KIM D S, et al. Reactivation of chromia poisoned oxygen exchange kinetics in mixed conducting solid oxide fuel cell electrodes by serial infiltration of lithia. Energy & Environmental Science, 2022, 15(10): 4038. |
| [18] |
PEI K, ZHOU Y C, XU K, et al. Enhanced Cr-tolerance of an SOFC cathode by an efficient electro-catalyst coating. Nano Energy, 2020, 72: 104704.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
XIONG C Y, XU S, LI X T, et al. Surface regulating and hetero-interface engineering of an LSCF cathode by CVD for solid oxide fuel cells: integration of improved electrochemical performance and Cr-tolerance. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2023, 11(29): 15760.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
GUO T M, DONG J B, CHEN Z P, et al. Enhanced compatibility and activity of high-entropy double perovskite cathode material for IT-SOFC. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 693.
DOI |
| [21] |
CHEN Z H, MA B, DANG C, et al. Entropy engineering strategies for optimizing solid oxide cell air electrode performance: a review. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2025, 1010: 177585.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
HE F, ZHU F, LIU D L, et al. A reversible perovskite air electrode for active and durable oxygen reduction and evolution reactions via the A-site entropy engineering. Materials Today, 2023, 63: 89.
DOI URL |
| [23] | WANG Z, LI J W, YUAN M K, et al. A medium-entropy engineered double perovskite oxide for efficient and CO2-tolerant cathode of solid oxide fuel cells. Sustainable Materials and Technologies, 2024, 40: e00969. |
| [24] |
OSES C, TOHER C, CURTAROLO S. High-entropy ceramics. Nature Reviews Materials, 2020, 5(4): 295.
DOI |
| [25] | AKRAMI S, EDALATI P, FUJI M, et al. High-entropy ceramics: review of principles, production and applications. Materials Science & Engineering R-Reports, 2021, 146: 100644. |
| [26] |
YANG Y, BAO H, NI H, et al. A novel facile strategy to suppress Sr segregation for high-entropy stabilized La0.8Sr0.2MnO3-δ cathode. Journal of Power Sources, 2021, 482: 228959.
DOI URL |
| [27] | LI Z Q, GUAN B, XIA F, et al. High-entropy perovskite as a high-performing chromium-tolerant cathode for solid oxide fuel cells. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(21): 24363. |
| [28] |
SHEN L Y, DU Z H, ZHANG Y, et al. Medium-entropy perovskites Sr(FeαTiβCoγMnζ)O3-δ as promising cathodes for intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cell. Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 2021, 295: 120264.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
ZHAO L, DRENNAN J, KONG C, et al. Insight into surface segregation and chromium deposition on La0.6Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.8O3-δ cathodes of solid oxide fuel cells. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(29): 11114.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
WANG Y H, ROBSON M J, MANZOTTI A, et al. High-entropy perovskites materials for next-generation energy applications. Joule, 2023, 7(5): 848.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
DABROWA J, OLSZEWSKA A, FALKENSTEIN A, et al. An innovative approach to design SOFC air electrode materials: high entropy La1-xSrx(Co,Cr,Fe,Mn,Ni)O3-δ (x=0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3) perovskites synthesized by the Sol-Gel method. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2020, 8(46): 24455.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
LIU Z Q, TANG Z J, SONG Y F, et al. High-entropy perovskite oxide: a new opportunity for developing highly active and durable air electrode for reversible protonic ceramic electrochemical cells. Nano-Micro Letters, 2022, 14(1): 217.
DOI PMID |
| [33] | ALBEDWAWI S H, ALJABERI A, HAIDEMENOPOULOS G N, et al. High entropy oxides-exploring a paradigm of promising catalysts: a review. Materials & Design, 2021, 202: 109534. |
| [34] |
ZHANG Y, SHEN L Y, WANG Y H, et al. Enhanced oxygen reduction kinetics of IT-SOFC cathode with PrBaCo2O5+δ Gd0.1Ce1.9O2-δ coherent interface. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2022, 10(7): 3495.
DOI URL |
| [35] | KIM J H, YOO S, MURPHY R, et al. Promotion of oxygen reduction reaction on a double perovskite electrode by a water-induced surface modification. Energy & Environmental Science, 2021, 14(3): 1506. |
| [36] |
GAO J T, LIU Y Y, GAO Y, et al. Cobalt-free fluorine doped Bi0.7Sr0.3FeO3 oxides for energetic cathodes of low-temperature solid oxide fuel cells. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 452(4): 139584.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 高源, 魏波, 金芳军, 吕喆, 凌意瀚. Ag掺杂调控中温固体氧化物燃料电池阴极酸性位点增强耐铬能力[J]. 无机材料学报, 2026, 41(1): 70-78. |
| [2] | 柴润宇, 张镇, 王孟龙, 夏长荣. 直接组装法制备氧化铈基金属支撑固体氧化物燃料电池[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 765-771. |
| [3] | 渠吉发, 王旭, 张维轩, 张康喆, 熊永恒, 谭文轶. 掺杂改性NaYTiO4增强固体氧化物燃料电池阳极抗硫中毒性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 489-496. |
| [4] | 薛柯, 蔡长焜, 谢满意, 李舒婷, 安胜利. 固体氧化物燃料电池Pr1+xBa1-xFe2O5+δ阴极材料的制备及电化学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 363-371. |
| [5] | 刘弘明, 张金柯, 陈正鹏, 李明飞, 钱秀洋, 孙传骐, 熊凯, 饶睦敏, 陈创庭, 高源, 凌意瀚. B位高熵策略提高La0.7Sr0.3FeO3-δ基阴极性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(12): 1433-1442. |
| [6] | 杨恒强, 张馨月, 马义初, 周青军. 铁基钙钛矿La0.25M0.75FeO3-δ (M=Ba, Sr, Ca)的制备及其作为固体氧化物燃料电池阴极材料的性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(12): 1365-1372. |
| [7] | 姜玥宏, 宋云峰, 张磊磊, 马季, 宋昭远, 龙文. 质子传导型固体氧化物燃料电池BaZr0.1Ce0.7Y0.1Yb0.1O3电解质的氟化研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(12): 1356-1364. |
| [8] | 薛子轩, 殷超凡, 姚跃超, 王彦敏, 孙跃跃, 刘峥嵘, 周玉存, 周峻, 吴锴. 泛氢燃料质子导体固体氧化物燃料电池研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(12): 1324-1340. |
| [9] | 刘通, 黄溯, 朱诗悦, 查方林, 胡学雷, 王瑶. 一锅法合成高温氢燃料电池用高效无钴复合阴极[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(12): 1349-1355. |
| [10] | 张婧慧, 陆晓彤, 毛海雁, 田亚州, 张山林. 烧结助剂对BaZr0.1Ce0.7Y0.2O3-δ电解质烧结行为及电导率的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(1): 84-90. |
| [11] | 潘建隆, 马官军, 宋乐美, 郇宇, 魏涛. 燃料还原法原位制备高稳定性/催化活性SOFC钴基钙钛矿阳极[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(8): 911-919. |
| [12] | 叶梓滨, 邹高昌, 吴琪雯, 颜晓敏, 周明扬, 刘江. 阳极支撑型锥管串接式直接碳固体氧化物燃料电池组的制备及性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 819-827. |
| [13] | 张琨, 王宇, 朱腾龙, 孙凯华, 韩敏芳, 钟秦. LaNi0.6Fe0.4O3阴极接触材料导电特性调控及其对SOFC电化学性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(4): 367-373. |
| [14] | 陈正鹏, 金芳军, 李明飞, 董江波, 许仁辞, 徐韩昭, 熊凯, 饶睦敏, 陈创庭, 李晓伟, 凌意瀚. 双钙钛矿Sr2CoFeO5+δ阴极材料的制备及其中温固体氧化物燃料电池性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(3): 337-344. |
| [15] | 薛顶喜, 伊炳尧, 李国君, 马帅, 刘克勤. 功能梯度阳极固体氧化物燃料电池热应力数值模拟研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(11): 1189-1196. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||