无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (12): 1324-1340.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250132 CSTR: 32189.14.jim20250132
• 专栏:高温燃料电池关键材料(客座编辑:凌意瀚) • 上一篇 下一篇
薛子轩1,2( ), 殷超凡1,2, 姚跃超2, 王彦敏2,3, 孙跃跃1, 刘峥嵘1, 周玉存2(
), 殷超凡1,2, 姚跃超2, 王彦敏2,3, 孙跃跃1, 刘峥嵘1, 周玉存2( ), 周峻1(
), 周峻1( ), 吴锴1
), 吴锴1
收稿日期:2025-03-29
修回日期:2025-06-04
出版日期:2025-12-20
网络出版日期:2025-06-27
通讯作者:
周玉存, 研究员. E-mail: zhouyucun@hrl.ac.cn;作者简介:薛子轩(1996-), 男, 博士研究生. E-mail: xuezixuanx@hotmail.com
基金资助:
XUE Zixuan1,2( ), YIN Chaofan1,2, YAO Yuechao2, WANG Yanmin2,3, SUN Yueyue1, LIU Zhengrong1, ZHOU Yucun2(
), YIN Chaofan1,2, YAO Yuechao2, WANG Yanmin2,3, SUN Yueyue1, LIU Zhengrong1, ZHOU Yucun2( ), ZHOU Jun1(
), ZHOU Jun1( ), WU Kai1
), WU Kai1
Received:2025-03-29
Revised:2025-06-04
Published:2025-12-20
Online:2025-06-27
Contact:
ZHOU Yucun, professor. E-mail: zhouyucun@hrl.ac.cn;About author:XUE Zixuan (1996-), male, PhD candidate. E-mail: xuezixuanx@hotmail.com
Supported by:摘要:
在全球能源结构转型与碳中和目标驱动下, 质子传导型固体氧化物燃料电池(Proton-conducting Solid Oxide Fuel Cells, P-SOFCs)兼具中低温(400~600 ℃)高效发电、出色的燃料兼容性与高能量转换效率的优势, 成为清洁能源技术的研究热点。本文分析了泛氢燃料P-SOFCs的发展前景, 围绕泛氢燃料电池技术瓶颈, 聚焦材料设计、反应机制以及表征手段三个核心维度, 综述了碳氢燃料与氨燃料P-SOFCs体系的研究进展与技术挑战。针对碳氢燃料电池碳沉积问题, 深入探讨了碳沉积的形成机理、表征手段以及影响因素, 指出了重整催化剂改性、质子导体电解质优化和新型电极设计等前沿改进策略; 针对直接氨燃料电池(Direct Ammonia Fuel Cells, DAFCs)性能问题, 系统阐述了催化剂活性、载体种类、氮化腐蚀机制、氢分压、氨气流量以及阳极微结构等关键影响因素; 根据DAFCs的前沿工作, 总结了阳极改性、阳极催化层构筑以及新型电池结构设计等新型改进策略, 为推动泛氢燃料P-SOFCs商业化应用指明未来发展方向。
中图分类号:
薛子轩, 殷超凡, 姚跃超, 王彦敏, 孙跃跃, 刘峥嵘, 周玉存, 周峻, 吴锴. 泛氢燃料质子导体固体氧化物燃料电池研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(12): 1324-1340.
XUE Zixuan, YIN Chaofan, YAO Yuechao, WANG Yanmin, SUN Yueyue, LIU Zhengrong, ZHOU Yucun, ZHOU Jun, WU Kai. Research Progress on Proton-conducting Solid Oxide Fuel Cells with Hydrogen-containing Fuel[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(12): 1324-1340.
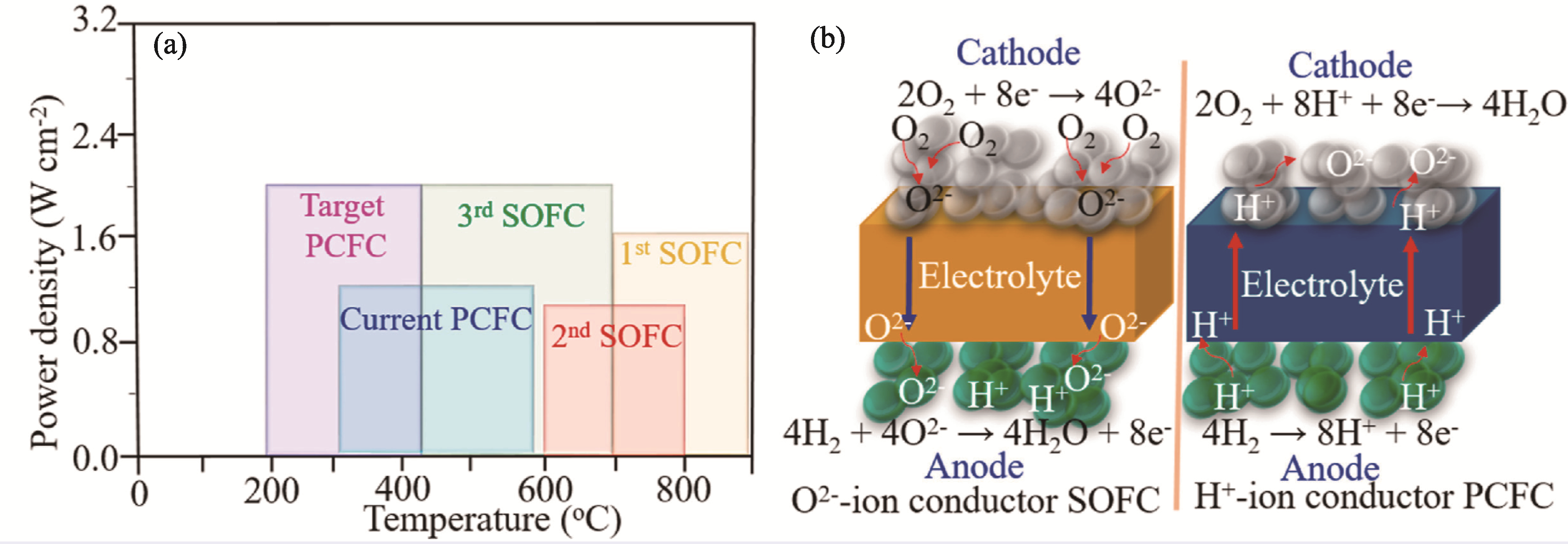
图1 P-SOFCs与O-SOFCs的比较[16]
Fig. 1 Comparison of P-SOFCs and O-SOFCs[16] (a) Performances comparison of P-SOFCs and O-SOFCs; (b) Schematic illustration of ionic transport mechanism of O-SOFCs and P-SOFCs
| Type | Hydrogen production technology | Cost/ (RMB·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|
| Grey hydrogen | Coal gasification | 7-11 |
| Steam methane reforming (SMR) | 9-18 | |
| Blue hydrogen | Coal gasification with carbon capture, utilization and storage | 9-20 |
| SMR with carbon capture storage | 13-24 | |
| Carbon capture storage | 2-9 | |
| Green hydrogen | Water electrolysis | 20-62 |
表1 不同产氢途径氢气成本[25]
Table 1 Hydrogen cost in different hydrogen production pathways[25]
| Type | Hydrogen production technology | Cost/ (RMB·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|
| Grey hydrogen | Coal gasification | 7-11 |
| Steam methane reforming (SMR) | 9-18 | |
| Blue hydrogen | Coal gasification with carbon capture, utilization and storage | 9-20 |
| SMR with carbon capture storage | 13-24 | |
| Carbon capture storage | 2-9 | |
| Green hydrogen | Water electrolysis | 20-62 |
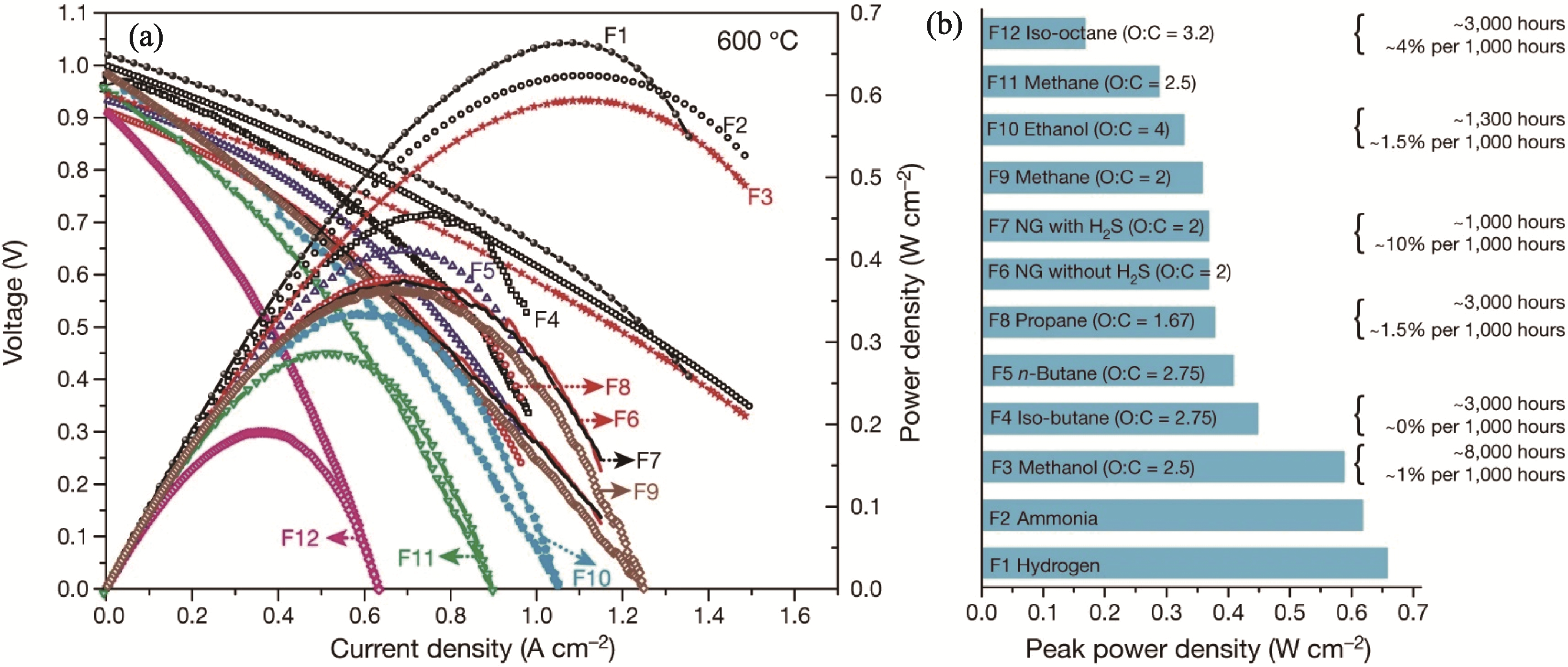
图2 燃料分子结构对P-SOFCs电化学性能的影响[33]
Fig. 2 P-SOFCs performance across a range of fuels[33] (a) Current density versus voltage (j-V) and current density versus power density (j-P) curves of P-SOFCs under a range of fuels; (b) Peak power densities, lifetime and degradation rates of P-SOFCs on 12 different fuel streams at 600 ℃
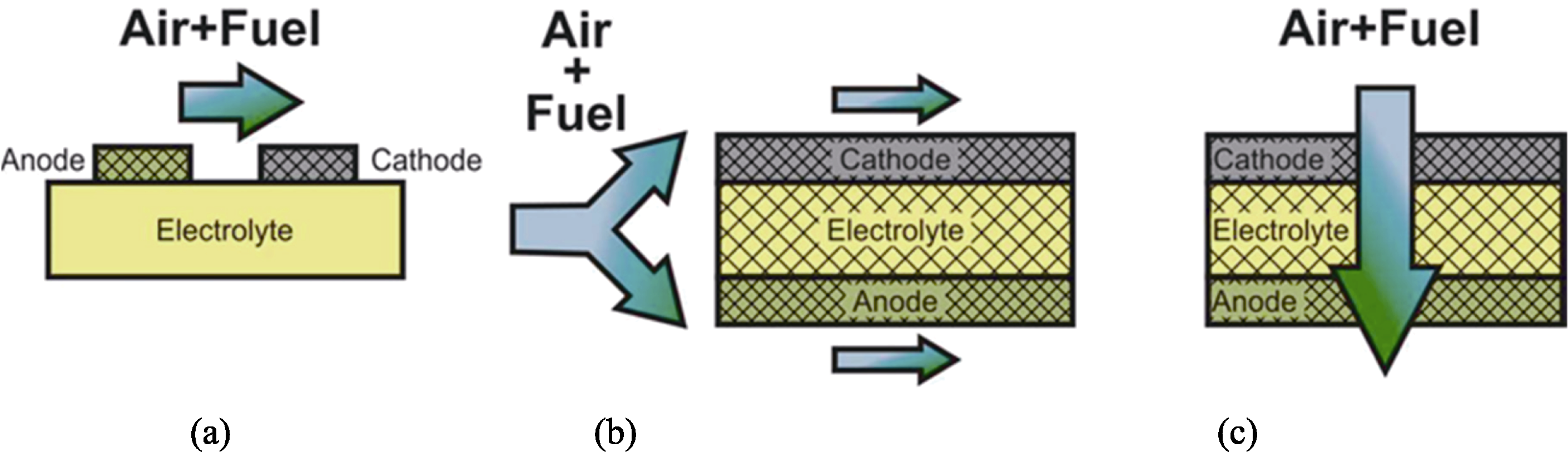
图3 单腔室SOFCs示意图[39]
Fig. 3 Schematics of single chamber SOFCs[39] (a) Single chamber SOFCs with coplanar electrodes; (b) Single chamber SOFCs with fully porous electrolyte in flow-by configuration; (c) Single chamber SOFCs with fully porous electrolyte in flow-through configuration
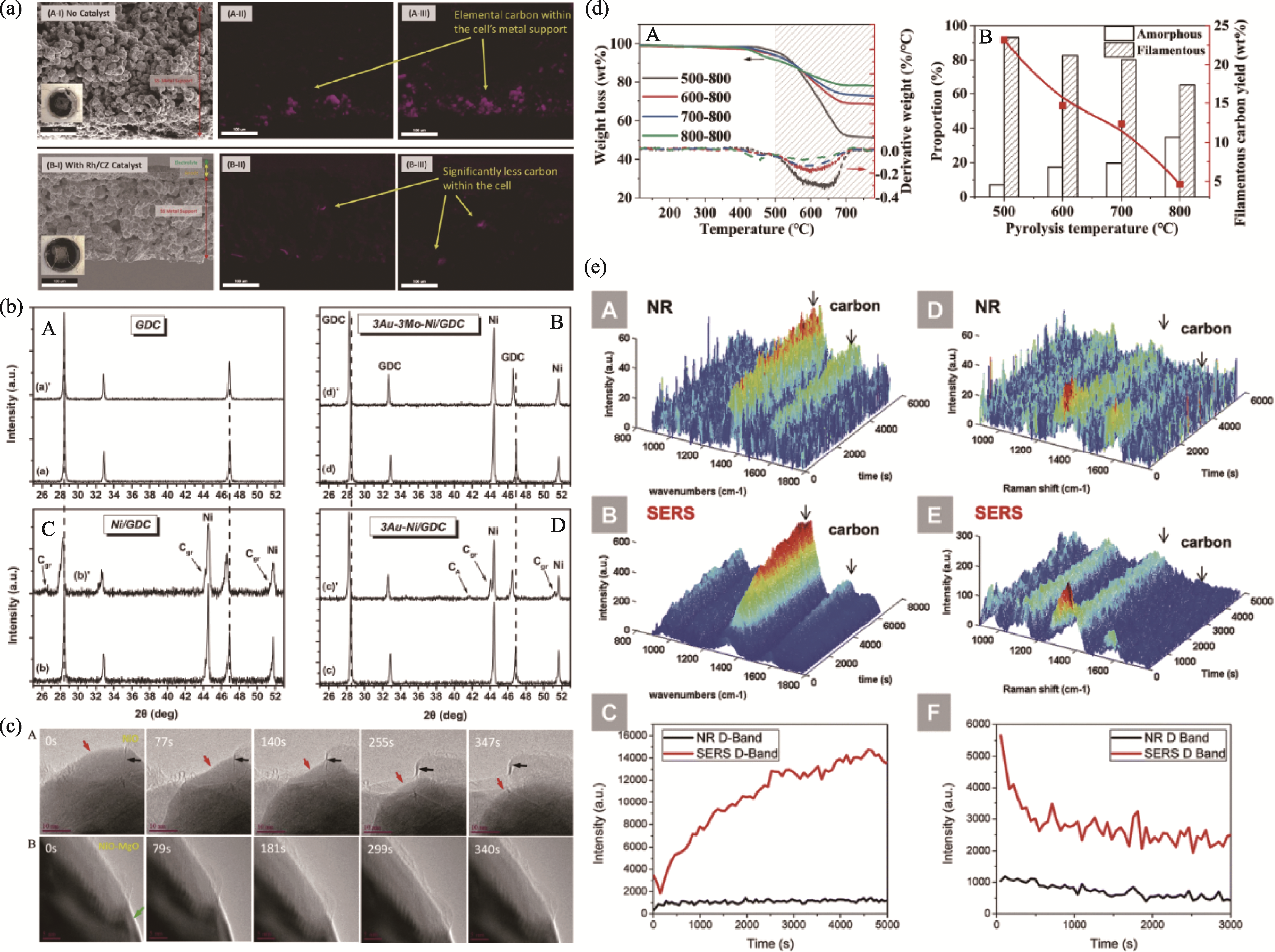
图4 常见的SOFCs阳极碳沉积表征手段[54,56,59,61,67]
Fig. 4 Common characterization methods for carbon deposition on SOFCs anodes[54,56,59,61,67] (a) SEM images and EDS carbon elemental mappings of the spent cell. (A-I, A-II and A-III: spent cell without catalyst; B-I, B-II and B-III: spent cell with catalyst)[54]; (b) XRD patterns of different SOFCs anode materials (A: GDC; B: Au-Mo-Ni/GDC; C: Ni/GDC; D: Au-Ni/GDC)[56]; (c) HR-TEM images of formation of the graphitic layer in NiO (A) and MgO-modified NiO (B)[59]; (d) TPO results of the carbon deposits (A: weight loss curves and derivative plots; B: yields of different types of carbons deposits at different pyrolysis temperatures)[61]; (e) Time-resolved normal Raman and SERS analysis of coking and carbon removal on nickel surface (carbon deposition on (A) blank Ni and (B) Ag@SiO2 loaded Ni, and (C) integrated intensity of the carbon D-band; removal of carbon deposition on (D) blank Ni and (E) Ag@SiO2 loaded Ni, and (F) integrated intensity of the carbon D-band)[67]
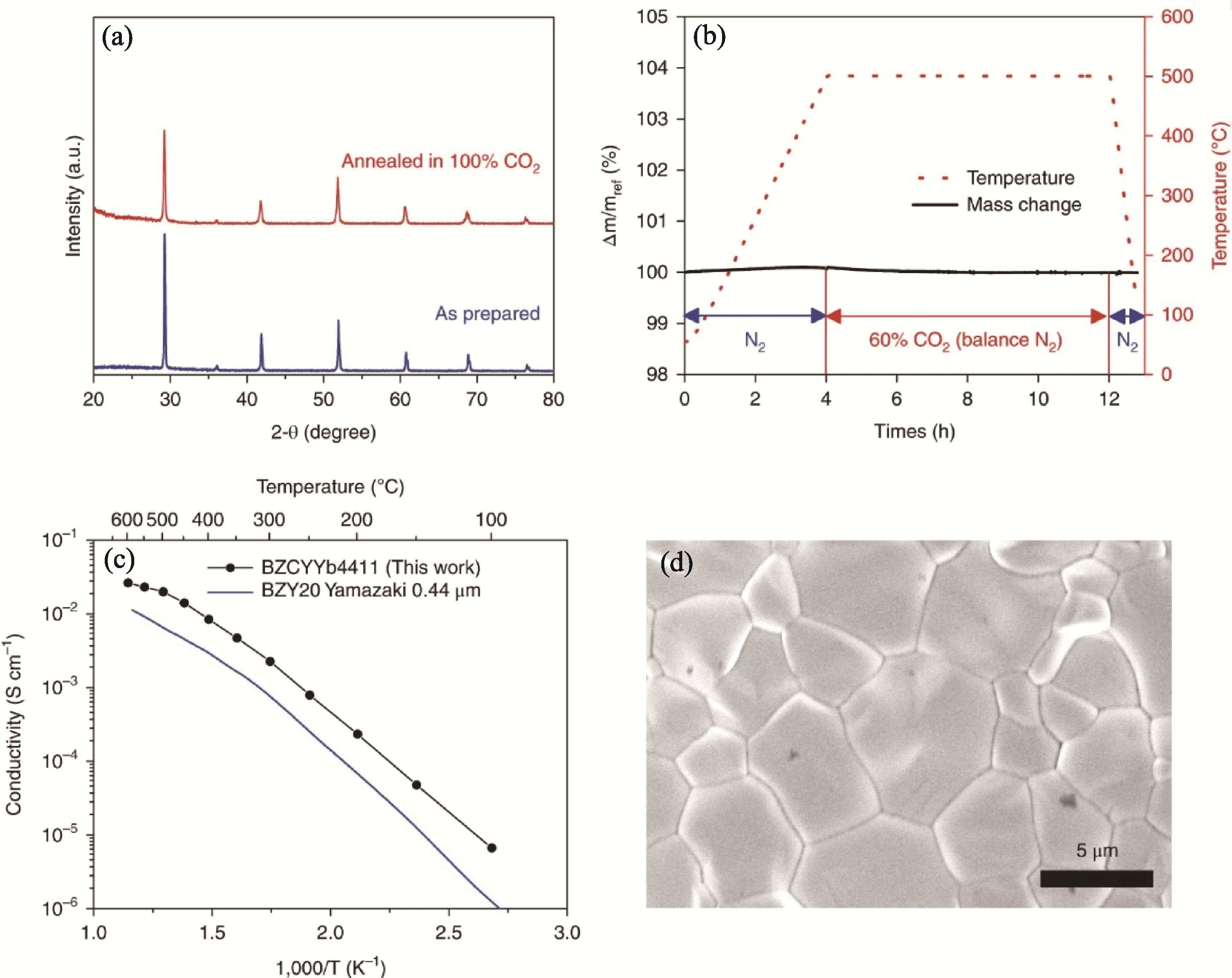
图5 BaZr0.4Ce0.4Y0.1Yb0.1O3-δ电解质的物化性质[76]
Fig. 5 Physicochemical properties of BaZr0.4Ce0.4Y0.1Yb0.1O3-δ electrolyte[76] (a) XRD patterns before and after exposure to 100% CO2 at 500 ℃; (b) Thermogravimetric analysis profile on exposure to 60% CO2 (balance N2) at 500 ℃; (c) Conductivity under humidified N2 atmosphere (pH2O=3.1×103 Pa) compared to that of BaZr0.8Y0.2O3-δ (BZY20) sintered under similar conditions; (d) SEM image of the as-sintered surface morphology
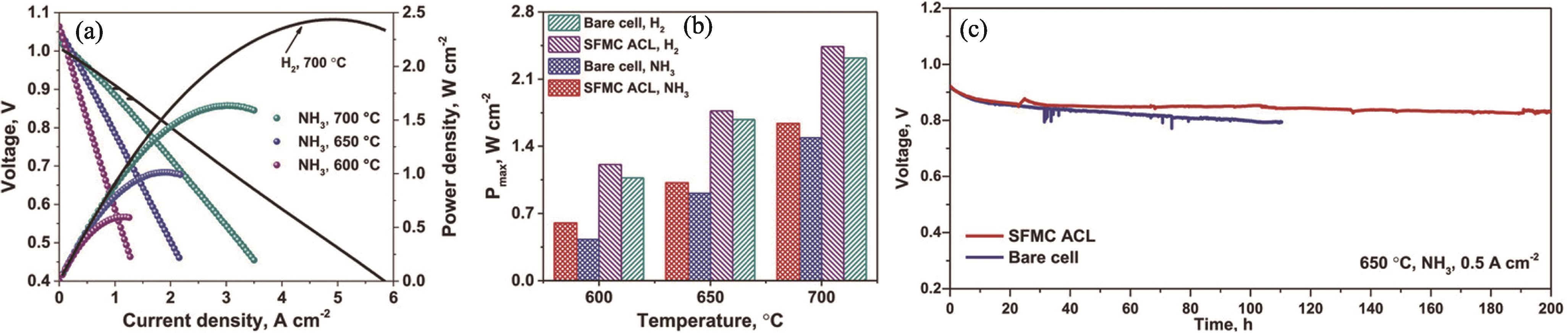
图8 SFMC修饰的P-SOFCs的电化学性能和耐久性[106]
Fig. 8 Electrochemical performance and durability of SFMC-modified P-SOFCs[106] (a) Current density versus voltage (j-V) and current density versus power density (j-P) curves of the cell with the SFMC-modified Ni-BZCYYb anode at 600-700 ℃ using wet H2 and dry NH3 as fuels and ambient air as an oxidant; (b) Comparisons on the PPD of the cells with the bare Ni-BZCYYb and SFMC active catalytic layer (ACL) modified Ni-BZCYYb anodes at 600-700 ℃ in wet H2 and dry NH3; (c) Operation stabilities of the single cells with the bare Ni-BZCYYb and SFMC-modified Ni-BZCYYb anodes at 650 ℃ under a current density of 0.5 A/cm2 using dry NH3 as fuel
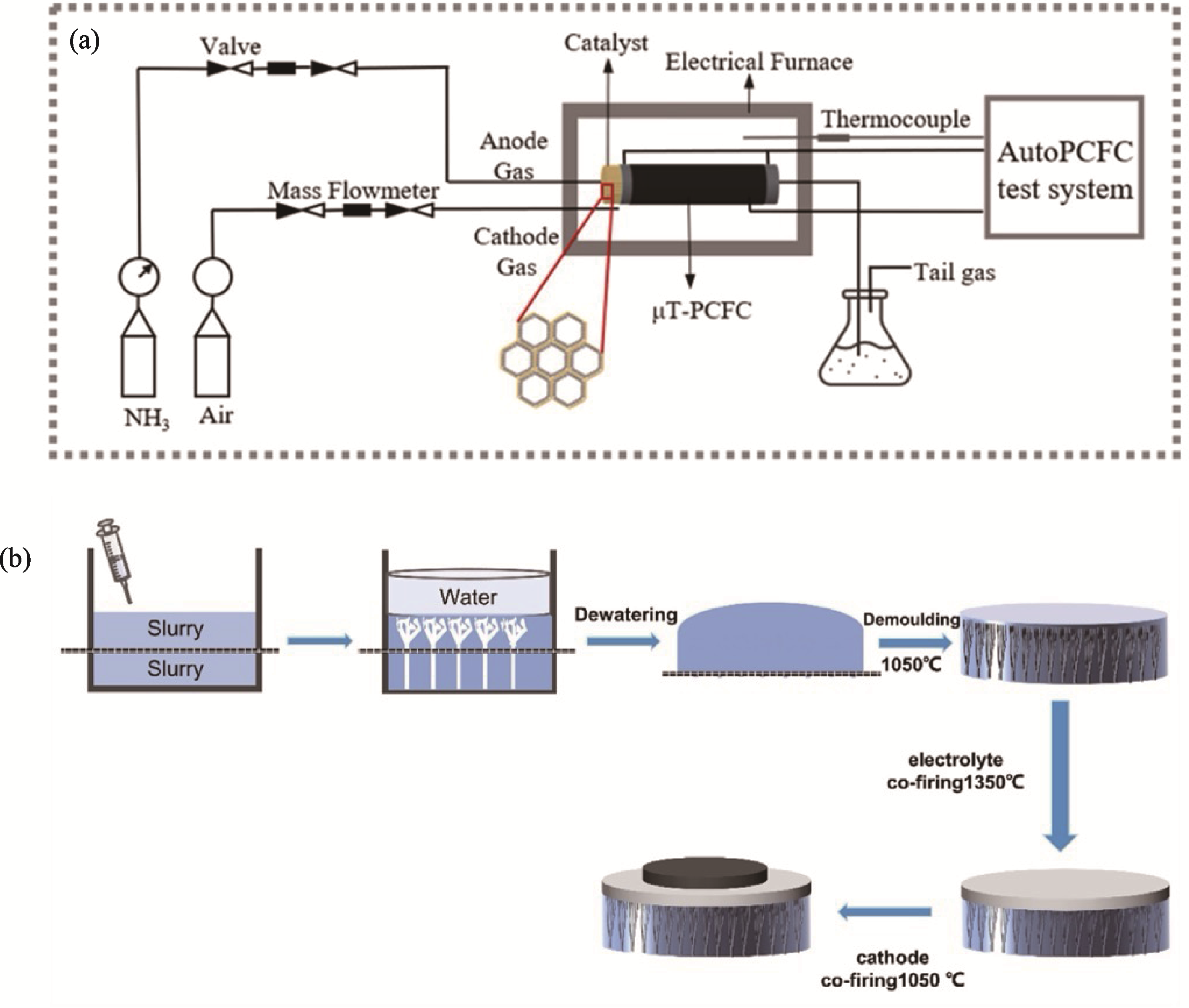
图9 新型DA-SOFCs结构设计方案[109-110]
Fig. 9 Novel structural design schemes for DA-SOFCs[109-110] (a) Test schematic diagram of tubular catalyst embedded P-SOFCs[109]; (b) Illustration of the cell anode preparation using the grid-assisted phase transformation method[110]
| [1] |
KOVAČ A, PARANOS M, MARCIUŠ D. Hydrogen in energy transition: a review. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(16): 10016.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
ALLAHVERDYAN A E, HOVHANNISYAN K V, MELKIKH A V, et al. Carnot cycle at finite power: attainability of maximal efficiency. Physical Review Letters, 2013, 111(5): 050601.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
FAYYAZBAKHSH A, BELL M L, ZHU X, et al. Engine emissions with air pollutants and greenhouse gases and their control technologies. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 376: 134260.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
WANG Z, DONG B, WANG Y, et al. Analysis and evaluation of fuel cell technologies for sustainable ship power: energy efficiency and environmental impact. Energy Conversion and Management: X, 2024, 21: 100482.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
TUOFU H, CHANGHAO H, QINGYUN H, et al. A coordination analysis of stakeholder interests on the new subsidy policy of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles in China: from the perspective of the evolutionary game theory. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(58): 24493.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
HASSAN Q, HSU C Y, MOUNICH K, et al. Enhancing smart grid integrated renewable distributed generation capacities: implications for sustainable energy transformation. Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments, 2024, 66: 103793.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
SINGH M, ZAPPA D, COMINI E. Solid oxide fuel cell: decade of progress, future perspectives and challenges. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(54): 27643.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
WEBER A. Fuel flexibility of solid oxide fuel cells. Fuel Cells, 2021, 21(5): 440.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
ZHANG D, WANG Z, CUI D, et al. Thermodynamic and electrochemical performance coupling analysis of single ammonia-fueled tubular solid oxide fuel cell toward low operating temperatures. Journal of Power Sources, 2024, 623: 235362.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
ABDELKAREEM M A, ELSAID K, WILBERFORCE T, et al. Environmental aspects of fuel cells: a review. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 752: 141803.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
ZHANG W, HU Y H. Progress in proton-conducting oxides as electrolytes for low-temperature solid oxide fuel cells: from materials to devices. Energy Science & Engineering, 2021, 9(7): 984.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
IWAHARA H, ESAKA T, UCHIDA H, et al. Proton conduction in sintered oxides and its application to steam electrolysis for hydrogen production. Solid State Ionics, 1981, 3/4: 359.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
IWAHARA H, UCHIDA H, TANAKA S. High temperature type proton conductor based on SrCeO3 and its application to solid electrolyte fuel cells. Solid State Ionics, 1983, 9/10: 1021.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
KREUER K D. Aspects of the formation and mobility of protonic charge carriers and the stability of perovskite-type oxides. Solid State Ionics, 1999, 125(1): 285.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
VIGNESH D, SONU B K, ROUT E. Factors constituting proton trapping in BaCeO3 and BaZrO3 perovskite proton conductors in fuel cell technology: a review. Energy & Fuels, 2022, 36(14): 7219.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
RASAKI S A, LIU C, LAO C, et al. A review of current performance of rare earth metal-doped barium zirconate perovskite: the promising electrode and electrolyte material for the protonic ceramic fuel cells. Progress in Solid State Chemistry, 2021, 63: 100325.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
WANG M, SU C, ZHU Z, et al. Composite cathodes for protonic ceramic fuel cells: rationales and materials. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2022, 238: 109881.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
WANG B, LI T, GONG F, et al. Ammonia as a green energy carrier: electrochemical synthesis and direct ammonia fuel cell - a comprehensive review. Fuel Processing Technology, 2022, 235: 107380.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
ZHAO Y, MAO Y, ZHANG W, et al. Reviews on the effects of contaminations and research methodologies for PEMFC. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45(43): 23174.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
FERGUSON K, DUBOIS A, ALBRECHT K, et al. High performance protonic ceramic fuel cell systems for distributed power generation. Energy Conversion and Management, 2021, 248: 114763.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
GUILBERT D, VITALE G. Hydrogen as a clean and sustainable energy vector for global transition from fossil-based to zero-carbon. Clean Technologies, 2021, 3(4): 881.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
BORETTI A. There are hydrogen production pathways with better than green hydrogen economic and environmental costs. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(46): 23988.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
EL-ADAWY M, DALHA I B, ISMAEL M A, et al. Review of sustainable hydrogen energy processes: production, storage, transportation, and color-coded classifications. Energy & Fuels, 2024, 38(23): 22686.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
AZIZ M, WIJAYANTA A T, NANDIYANTO A B D. Ammonia as effective hydrogen storage: a review on production, storage and utilization. Energies, 2020, 13(12): 3062.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
HUI Y, WANG M, GUO S, et al. Comprehensive review of development and applications of hydrogen energy technologies in China for carbon neutrality: technology advances and challenges. Energy Conversion and Management, 2024, 315: 118776.
DOI URL |
| [26] | LIU H, CLAUSEN L R, WANG L, et al. Pathway toward cost-effective green hydrogen production by solid oxide electrolyzer. Energy & Environmental Science, 2023, 16(5): 2090. |
| [27] |
MEGÍA P J, VIZCAíNO A J, CALLES J A, et al. Hydrogen production technologies: from fossil fuels toward renewable sources. A mini review. Energy & Fuels, 2021, 35(20): 16403.
DOI URL |
| [28] | RONG H, ZHAO D, BECKER S, et al. Entropy production and thermodynamics exergy investigation on an ammonia-methane fueled micro-combustor with porous medium for thermophotovoltaic applications. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 49: 384. |
| [29] |
MONTAZERINEJAD H, EICKER U. Recent development of heat and power generation using renewable fuels: a comprehensive review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2022, 165: 112578.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
WANG B, GUPTA R, BEI L, et al. A review on gasification of municipal solid waste (MSW): syngas production, tar formation, mineral transformation and industrial challenges. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2023, 48(69): 26676.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
RAVINDRAN M X Y, ASIKIN-MIJAN N, ABDULKAREEM- ALSULTAN G, et al. A review of carbon-based catalyst for production of renewable hydrocarbon rich fuel. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2024, 12(2): 112330.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
YE Z B, ZOU G C, WU Q W, et al. Preparation and performances of tubular cone-shaped anode-supported segmented-in-series direct carbon solid oxide fuel cell. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(7): 819.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
DUAN C, KEE R J, ZHU H, et al. Highly durable, coking and sulfur tolerant, fuel-flexible protonic ceramic fuel cells. Nature, 2018, 557(7704): 217.
DOI |
| [34] |
MOGENSEN M, KAMMER K. Conversion of hydrocarbons in solid oxide fuel cells. Annual Review of Materials Research, 2003, 33: 321.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
YANG H, HAN C, LI W, et al. Experimental evaluation of SOFC fuel adaptability and power generation performance based on MSR. Fuel Processing Technology, 2023, 250: 107919.
DOI URL |
| [36] | LEI F, GU Y, ASHAR A, et al. Integrated autothermal reformer, heat exchanger and solid oxide fuel cell in single-stack for aircraft gas-turbine applications. ECS Meeting Abstracts, 2024, MA 2024- 02(48): 3340. |
| [37] |
HAO N H, KIM Y, LEE K, et al. High performance of direct ethanol-fueled protonic ceramic fuel cells via ethanol steam reforming using non-noble metal catalysts. Electrochimica Acta, 2024, 481: 143994.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
WANG C, LIAO M, JIANG Z, et al. Sorption-enhanced propane partial oxidation hydrogen production for solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) applications. Energy, 2022, 247: 123463.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
KUTERBEKOV K A, NIKONOV A V, BEKMYRZA K Z, et al. Classification of solid oxide fuel cells. Nanomaterials, 2022, 12(7): 1059.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
QIU P, SUN S, YANG X, et al. A review on anode on-cell catalyst reforming layer for direct methane solid oxide fuel cells. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(49): 25208.
DOI URL |
| [41] | BAHARUDIN L, RAHMAT N, OTHMAN N H, et al. Formation, control, and elimination of carbon on Ni-based catalyst during CO2 and CH4 conversion via dry reforming process: a review. Journal of CO2 Utilization, 2022, 61: 102050. |
| [42] |
HONG K, SUTANTO S N, LEE J A, et al. Ni-based bimetallic nano-catalysts anchored on BaZr0.4Ce0.4Y0.1Yb0.1O3-δ for internal steam reforming of methane in a low-temperature proton-conducting ceramic fuel cell. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2021, 9(10): 6139.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
SHISHKIN M, ZIEGLER T. Direct modeling of the electrochemistry in the three-phase boundary of solid oxide fuel cell anodes by density functional theory: a critical overview. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2014, 16(5): 1798.
DOI PMID |
| [44] |
GALEA N M, KNAPP D, ZIEGLER T. Density functional theory studies of methane dissociation on anode catalysts in solid-oxide fuel cells: suggestions for coke reduction. Journal of Catalysis, 2007, 247(1): 20.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
OLMOS-ASAR J A, MONACHINO E, DRI C, et al. CO on supported Cu nanoclusters: coverage and finite size contributions to the formation of carbide via the Boudouard process. ACS Catalysis, 2015, 5(5): 2719.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
SKABELUND B B, MILCAREK R J. Review of thermal partial oxidation reforming with integrated solid oxide fuel cell power generation. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2022, 168: 112852.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
SHABRI H A, OTHMAN M H D, MOHAMED M A, et al. Recent progress in metal-ceramic anode of solid oxide fuel cell for direct hydrocarbon fuel utilization: a review. Fuel Processing Technology, 2021, 212: 106626.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
MOSEENKOV S I, KUZNETSOV V L, ZOLOTAREV N A, et al. Investigation of amorphous carbon in nanostructured carbon materials (a comparative study by TEM, XPS, Raman spectroscopy and XRD). Materials, 2023, 16(3): 1112.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
YAO D, WU C, YANG H, et al. Co-production of hydrogen and carbon nanotubes from catalytic pyrolysis of waste plastics on Ni-Fe bimetallic catalyst. Energy Conversion and Management, 2017, 148: 692.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
JIAO Z, SHIKAZONO N, KASAGI N. Study on degradation of solid oxide fuel cell anode by using pure nickel electrode. Journal of Power Sources, 2011, 196(20): 8366.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
KUHN J, KESLER O. Method for in situ carbon deposition measurement for solid oxide fuel cells. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 246: 430.
DOI URL |
| [52] | DYUKOV V G, NEPIJKO S A. Chapter four - progress in determining of compound composition by BSE imaging in a SEM and the relevant detector disadvantages//HŸTCH M, HAWKES P W. Advances in imaging and electron physics. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2020, 215: 107. |
| [53] |
BROWN H G, D'ALFONSO A J, ALLEN L J. Secondary electron imaging at atomic resolution using a focused coherent electron probe. Physical Review B, 2013, 87(5): 054102.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
DEWA M, ELHARATI M A, HUSSAIN A M, et al. Metal-supported solid oxide fuel cell system with infiltrated reforming catalyst layer for direct ethanol feed operation. Journal of Power Sources, 2022, 541: 231625.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
DUDEK M, TOMCZYK P, SOCHA R, et al. Biomass fuels for direct carbon fuel cell with solid oxide electrolyte. International Journal of Electrochemical Science, 2013, 8(3): 3229.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
NEOFYTIDIS C, DRACOPOULOS V, NEOPHYTIDES S G, et al. Electrocatalytic performance and carbon tolerance of ternary Au-Mo-Ni/GDC SOFC anodes under CH4-rich internal steam reforming conditions. Catalysis Today, 2018, 310: 157.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
GONG Y, PATEL R L, LIANG X, et al. Atomic layer deposition functionalized composite SOFC cathode La0.6Sr0.4Fe0.8Co0.2O3-δ- Gd0.2Ce0.8O1.9: enhanced long-term stability. Chemistry of Materials, 2013, 25(21): 4224.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
PAN J L, MA G J, SONG L M, et al. High stability/catalytic activity Co-based perovskite as SOFC anode: in-situ preparation by fuel reducing method. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(8): 911.
DOI URL |
| [59] |
SUN C, SU R, CHEN J, et al. Carbon formation mechanism of C2H2 in Ni-based catalysts revealed by in situ electron microscopy and molecular dynamics simulations. ACS Omega, 2019, 4(5): 8413.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
YOU X, WANG X, MA Y, et al. Ni-Co/Al2O3 bimetallic catalysts for CH4 steam reforming: elucidating the role of Co for improving coke resistance. ChemCatChem, 2014, 6(12): 3377.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
XIAO H, ZHU L, LI S, et al. Influence of pyrolysis temperature on carbon deposition from the perspective of volatile evolution during the ex-situ pyrolysis-catalysis of plastic. Combustion and Flame, 2024, 265: 113480.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
HUANG Y, LI X, ZHANG Q, et al. Carbon deposition behaviors in dry reforming of CH4 at elevated pressures over Ni/MoCeZr/ MgAl2O4-MgO catalysts. Fuel, 2022, 310: 122449.
DOI URL |
| [63] |
LI X, BLINN K, CHEN D, et al. In situ and surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy study of electrode materials in solid oxide fuel cells. Electrochemical Energy Reviews, 2018, 1(3): 433.
DOI |
| [64] |
DRESSELHAUS M S, JORIO A, HOFMANN M, et al. Perspectives on carbon nanotubes and graphene Raman spectroscopy. Nano Letters, 2010, 10(3): 751.
DOI PMID |
| [65] |
DRASBÆK D B, WELANDER M M, TRAULSEN M L, et al. Operando characterization of metallic and bimetallic electrocatalysts for SOFC fuel electrodes operating under internal methane reforming conditions. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2022, 10(10): 5550.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
STILES P L, DIERINGER J A, SHAH N C, et al. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Annual Review of Analytical Chemistry, 2008, 1: 601.
DOI URL |
| [67] | LI X, LEE J P, BLINN K S, et al. High-temperature surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy for in situ study of solid oxide fuel cell materials. Energy & Environmental Science, 2014, 7(1): 306. |
| [68] | SASAKI K, TERAOKA Y. Equilibria in fuel cell gases: II. The C-H-O ternary diagrams. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2003, 150(7): A885. |
| [69] |
KIM S, KIM C, LEE J H, et al. Tailoring Ni-based catalyst by alloying with transition metals (M=Ni, Co, Cu, and Fe) for direct hydrocarbon utilization of energy conversion devices. Electrochimica Acta, 2017, 225: 399.
DOI URL |
| [70] |
ZHANG W, WEI J, YIN F, et al. Recent advances in carbon-resistant anodes for solid oxide fuel cells. Materials Chemistry Frontiers, 2023, 7(10): 1943.
DOI URL |
| [71] |
BABAKOUHI R, ALAVI S M, REZAEI M, et al. Hydrogen production through combined dry reforming and partial oxidation of methane over the Ni/Al2O3-CeO2 catalysts. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 60: 503.
DOI URL |
| [72] |
GUO Z, CHEN T, LI X, et al. Ni-Mo/Al2O3 catalyst for partial oxidation reforming of low concentration coal bed methane and its application on SOFC. Fuel, 2024, 378: 132857.
DOI URL |
| [73] |
GUTTA N, VELISOJU V K, TARDIO J, et al. CH4 cracking over the Cu-Ni/Al-MCM-41 catalyst for the simultaneous production of H2 and highly ordered graphitic carbon nanofibers. Energy & Fuels, 2019, 33(12): 12656.
DOI URL |
| [74] |
NIE S, XIANG Y, WU L, et al. Active learning guided discovery of high entropy oxides featuring high H2-production. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2024, 146(43): 29325.
DOI URL |
| [75] |
NIE H, LIU Z, XIAO M, et al. Recent advances and challenges in perovskite-based protonic ceramic electrolytes: design strategies and fabrication innovations. Advanced Functional Materials, 2025, 35(10): 2416651.
DOI URL |
| [76] |
CHOI S, KUCHARCZYK C J, LIANG Y, et al. Exceptional power density and stability at intermediate temperatures in protonic ceramic fuel cells. Nature Energy, 2018, 3(3): 202.
DOI |
| [77] |
MURPHY R, ZHOU Y, ZHANG L, et al. A new family of proton-conducting electrolytes for reversible solid oxide cells: BaHfxCe0.8-xY0.1Yb0.1O3-δ. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(35): 2002265.
DOI URL |
| [78] |
CHOI S M, LEE J H, AN H, et al. Fabrication of anode-supported protonic ceramic fuel cell with Ba(Zr0.85Y0.15)O3-δ- Ba(Ce0.9Y0.1)O3-δ dual-layer electrolyte. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014, 39(24): 12812.
DOI URL |
| [79] |
LUO Z, HU X, ZHOU Y, et al. Harnessing high-throughput computational methods to accelerate the discovery of optimal proton conductors for high-performance and durable protonic ceramic electrochemical cells. Advanced Materials, 2024, 36(18): 2311159.
DOI URL |
| [80] |
CHENG P C, LEE S W, LEE K R, et al. Carbon resistant Ni1-xCux- BCZY anode for methane-fed protonic ceramic fuel cell. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2023, 48(30): 11455.
DOI URL |
| [81] |
WANG J, ZHANG D, LIU T, et al. Self-assembled FeRu bimetallic nanocatalysts for efficient and durable mutual CO-CO2 conversion in a reversible solid oxide electrochemical cell. Science China Materials, 2024, 67(5): 1471.
DOI |
| [82] |
LUO Y, CHANG X, WANG J, et al. Precise regulation of in situ exsolution components of nanoparticles for constructing active interfaces toward carbon dioxide reduction. ACS Nano, 2025, 19(1): 1463.
DOI URL |
| [83] |
HONG K, CHOI M, BAE Y, et al. Direct methane protonic ceramic fuel cells with self-assembled Ni-Rh bimetallic catalyst. Nature Communications, 2023, 14: 7485.
DOI PMID |
| [84] |
WANG A, LI T, WANG X, et al. Enhanced stability of a direct- methane and carbon dioxide protonic ceramic fuel cell with a PrCrO3 based reforming layer. Ceramics International, 2023, 49(15): 25240.
DOI URL |
| [85] |
AWAD O I, ZHOU B, HARRATH K, et al. Characteristics of NH3/H2 blend as carbon-free fuels: a review. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2023, 48(96): 38077.
DOI URL |
| [86] |
JIAO F, XU B. Electrochemical ammonia synthesis and ammonia fuel cells. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(31): 1805173.
DOI URL |
| [87] |
DUAN X, JI J, QIAN G, et al. Ammonia decomposition on Fe(110), Co(111) and Ni(111) surfaces: a density functional theory study. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical, 2012, 357: 81.
DOI URL |
| [88] | SCHÜTH F, PALKOVITS R, SCHLÖGL R, et al. Ammonia as a possible element in an energy infrastructure: catalysts for ammonia decomposition. Energy & Environmental Science, 2012, 5(4): 6278. |
| [89] |
WU H, LIU C, GUO W. Computational screening of bimetallic catalysts: application to ammonia decomposition. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2022, 126(1): 192.
DOI URL |
| [90] |
SAIDI W A, SHADID W, VESER G. Optimization of high-entropy alloy catalyst for ammonia decomposition and ammonia synthesis. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2021, 12(21): 5185.
DOI URL |
| [91] |
PAN C J, TSAI M C, SU W N, et al. Tuning/exploiting strong metal-support interaction (SMSI) in heterogeneous catalysis. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2017, 74: 154.
DOI URL |
| [92] |
OKURA K, OKANISHI T, MUROYAMA H, et al. Ammonia decomposition over nickel catalysts supported on rare-earth oxides for the on-site generation of hydrogen. ChemCatChem, 2016, 8(18): 2988.
DOI URL |
| [93] |
OKURA K, MIYAZAKI K, MUROYAMA H, et al. Ammonia decomposition over Ni catalysts supported on perovskite-type oxides for the on-site generation of hydrogen. RSC Advances, 2018, 8(56): 32102.
DOI URL |
| [94] |
LI X, CHEN J, HUANG Y, et al. Performance-enhanced direct ammonia protonic ceramic fuel cells using CeO2-supported Ni and Ru catalyst layer. Frontiers in Energy, 2024, 18(6): 875.
DOI |
| [95] |
ZHAO X, TENG Q, TAO H, et al. FeCo alloy-decorated proton- conducting perovskite oxide as an efficient and low-cost ammonia decomposition catalyst. Catalysts, 2024, 14(12): 850.
DOI URL |
| [96] | YANG J, MOLOUK A F S, OKANISHI T, et al. Electrochemical and catalytic properties of Ni/BaCe0.75Y0.25O3-δ anode for direct ammonia-fueled solid oxide fuel cells. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(13): 7406. |
| [97] |
LEE H, KIM J, BAEK J, et al. Effects of water on the degradations in the Ni-YSZ anode of the direct ammonia solid oxide fuel cells. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 497: 154764.
DOI URL |
| [98] |
SINGH V, MUROYAMA H, MATSUI T, et al. Influence of cell design on the performance of direct ammonia-fueled solid oxide fuel cell: anode- vs. electrolyte-supported cell. ECS Transactions, 2017, 78(1): 2527.
DOI URL |
| [99] |
YUN J, XIONG G, KIM S, et al. Understanding direct-ammonia protonic ceramic fuel cells: high-performance in the absence of precious metal catalysts. ACS Energy Letters, 2024, 9(11): 5520.
DOI URL |
| [100] |
KISHIMOTO M, FURUKAWA N, KUME T, et al. Formulation of ammonia decomposition rate in Ni-YSZ anode of solid oxide fuel cells. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(4): 2370.
DOI URL |
| [101] | ZHANG H, ZHOU Y, PEI K, et al. An efficient and durable anode for ammonia protonic ceramic fuel cells. Energy & Environmental Science, 2022, 15(1): 287. |
| [102] | ZHANG H, XU K, XU Y, et al. In situ formed catalysts for active, durable, and thermally stable ammonia protonic ceramic fuel cells at 550 ℃. Energy & Environmental Science, 2024, 17(10): 3433. |
| [103] |
JEONG H J, CHANG W, SEO B G, et al. High-performance ammonia protonic ceramic fuel cells using a Pd inter-catalyst. Small, 2023, 19(22): 2208149.
DOI URL |
| [104] |
SONG Y, CHEN J, YANG M, et al. Realizing simultaneous detrimental reactions suppression and multiple benefits generation from nickel doping toward improved protonic ceramic fuel cell performance. Small, 2022, 18(16): 2200450.
DOI URL |
| [105] |
LIU Z, DI H, LIU D, et al. Boosting ammonia-fueled protonic ceramic fuel cells with RuFe nanoparticle exsolution: enhanced performance via secondary redox treatment. Advanced Functional Materials, 2025, 35(15): 2420214.
DOI URL |
| [106] |
HE F, HOU M, DU Z, et al. Self-construction of efficient interfaces ensures high-performance direct ammonia protonic ceramic fuel cells. Advanced Materials, 2023, 35(42): 2304957.
DOI URL |
| [107] |
LAN H, CHU J, CHEN X, et al. Effect of increasing Fe catalytic decomposition layer of ammonia on the performance and stability of ammonia electrode. Journal of Power Sources, 2024, 593: 233987.
DOI URL |
| [108] |
LIANG M, SONG Y, XIONG B, et al. In situ exsolved CoFeRu alloy decorated perovskite as an anode catalyst layer for high- performance direct-ammonia protonic ceramic fuel cells. Advanced Functional Materials, 2024, 34(48): 2408756.
DOI URL |
| [109] |
LIU Y, JIAN J, XU X, et al. An anode-supported tubular proton conductor fuel cell with an inner ceramic ammonia cracking component. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2025, 22(2): e14969.
DOI URL |
| [110] |
DANG H, SONG L, SHI G. Efficient ammonia conversion in proton conducting fuel cells: combined application of dendritic anodes and nanofiber catalysts. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 85: 715.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 范雨竹, 王媛, 王林燕, 向美玲, 鄢雨婷, 黎本慧, 李敏, 文志东, 王海超, 陈永福, 邱会东, 赵波, 周成裕. 氧化石墨烯基吸附材料去除水体中Pb(II): 制备、性能及机理[J]. 无机材料学报, 2026, 41(1): 12-26. |
| [2] | 高源, 魏波, 金芳军, 吕喆, 凌意瀚. Ag掺杂调控中温固体氧化物燃料电池阴极酸性位点增强耐铬能力[J]. 无机材料学报, 2026, 41(1): 70-78. |
| [3] | 邬博宇, 张深根, 张生杨, 刘波, 张柏林. CeO2对MnOx催化剂低温脱硝性能的影响及其机理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2026, 41(1): 87-95. |
| [4] | 徐锦涛, 高攀, 何唯一, 蒋圣楠, 潘秀红, 汤美波, 陈锟, 刘学超. 3C-SiC晶体制备研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2026, 41(1): 1-11. |
| [5] | 余升阳, 苏海军, 姜浩, 余明辉, 姚佳彤, 杨培鑫. 激光增材制造超高温氧化物陶瓷孔隙缺陷形成及抑制研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(9): 944-956. |
| [6] | 刘江平, 管鑫, 唐振杰, 朱文杰, 罗永明. 含氮挥发性有机化合物催化氧化的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(9): 933-943. |
| [7] | 肖晓琳, 王玉祥, 谷佩洋, 朱圳荣, 孙勇. 二维无机材料调控病损皮肤组织再生的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 860-870. |
| [8] | 马景阁, 吴成铁. 无机生物材料用于毛囊和毛发再生的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 901-910. |
| [9] | 张洪健, 赵梓壹, 吴成铁. 无机生物材料调控神经细胞功能及神经化组织再生的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 849-859. |
| [10] | 艾敏慧, 雷波. 微纳米生物活性玻璃: 功能化设计与血管化皮肤再生[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 921-932. |
| [11] | 王宇彤, 常江, 徐合, 吴成铁. 硅酸盐生物陶瓷/玻璃促创面修复的研究进展:作用、机制和应用方式[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 911-920. |
| [12] | 马文平, 韩雅卉, 吴成铁, 吕宏旭. 无机活性材料在类器官研究领域的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 888-900. |
| [13] | 罗晓民, 乔志龙, 刘颍, 杨晨, 常江. 无机生物活性材料调控心肌再生的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 871-887. |
| [14] | 朱文杰, 唐璐, 陆继长, 刘江平, 罗永明. 钙钛矿型氧化物催化氧化挥发性有机化合物的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [15] | 柴润宇, 张镇, 王孟龙, 夏长荣. 直接组装法制备氧化铈基金属支撑固体氧化物燃料电池[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 765-771. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||