无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (11): 1245-1251.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250036 CSTR: 32189.14.jim20250036
张海丰1( ), 蒋蒙1, 孙婷婷3(
), 蒋蒙1, 孙婷婷3( ), 王连军1(
), 王连军1( ), 江莞1,2
), 江莞1,2
收稿日期:2025-01-25
修回日期:2025-03-31
出版日期:2025-11-20
网络出版日期:2025-04-15
通讯作者:
孙婷婷, 讲师. E-mail: tingtingsun@dhu.edu.cn;作者简介:张海丰(2000-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: zhanghf2025@163.com
基金资助:
ZHANG Haifeng1( ), JIANG Meng1, SUN Tingting3(
), JIANG Meng1, SUN Tingting3( ), WANG Lianjun1(
), WANG Lianjun1( ), JIANG Wan1,2
), JIANG Wan1,2
Received:2025-01-25
Revised:2025-03-31
Published:2025-11-20
Online:2025-04-15
Contact:
SUN Tingting, lecturer. E-mail: tingtingsun@dhu.edu.cn;About author:ZHANG Haifeng (2000-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: zhanghf2025@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
p型GeTe基热电材料在中低温区(300~800 K)具有良好的热电性能, 受到了广泛关注。然而, 在600~700 K温度区间, 该化合物易从菱方相转变为立方相, 导致热膨胀系数变化, 这限制了其在热电器件领域的应用。因此, 获得稳定无相变的GeTe基热电材料至关重要。本研究利用高温熔融结合放电等离子体烧结制备了GeMnTe2材料。合成的样品存在MnTe2第二相, 导致其总热导率从800 K下的1.34 W·m-1·K-1增大到1.81 W·m-1·K-1。本研究通过优化不同元素化学计量比, 抑制了MnTe2第二相的生成, 获得了稳定立方相GeMnTe1.96材料。制备的GeMnTe1.96化合物样品最高zT达到~0.85(800 K), 这为中温区废热高效稳定回收利用提供了有发展潜力的热电材料。
中图分类号:
张海丰, 蒋蒙, 孙婷婷, 王连军, 江莞. 稳定立方相p型GeMnTe2基热电材料制备[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(11): 1245-1251.
ZHANG Haifeng, JIANG Meng, SUN Tingting, WANG Lianjun, JIANG Wan. Preparation of p-type GeMnTe2 Based Thermoelectric Materials with Stable Cubic Phase[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(11): 1245-1251.
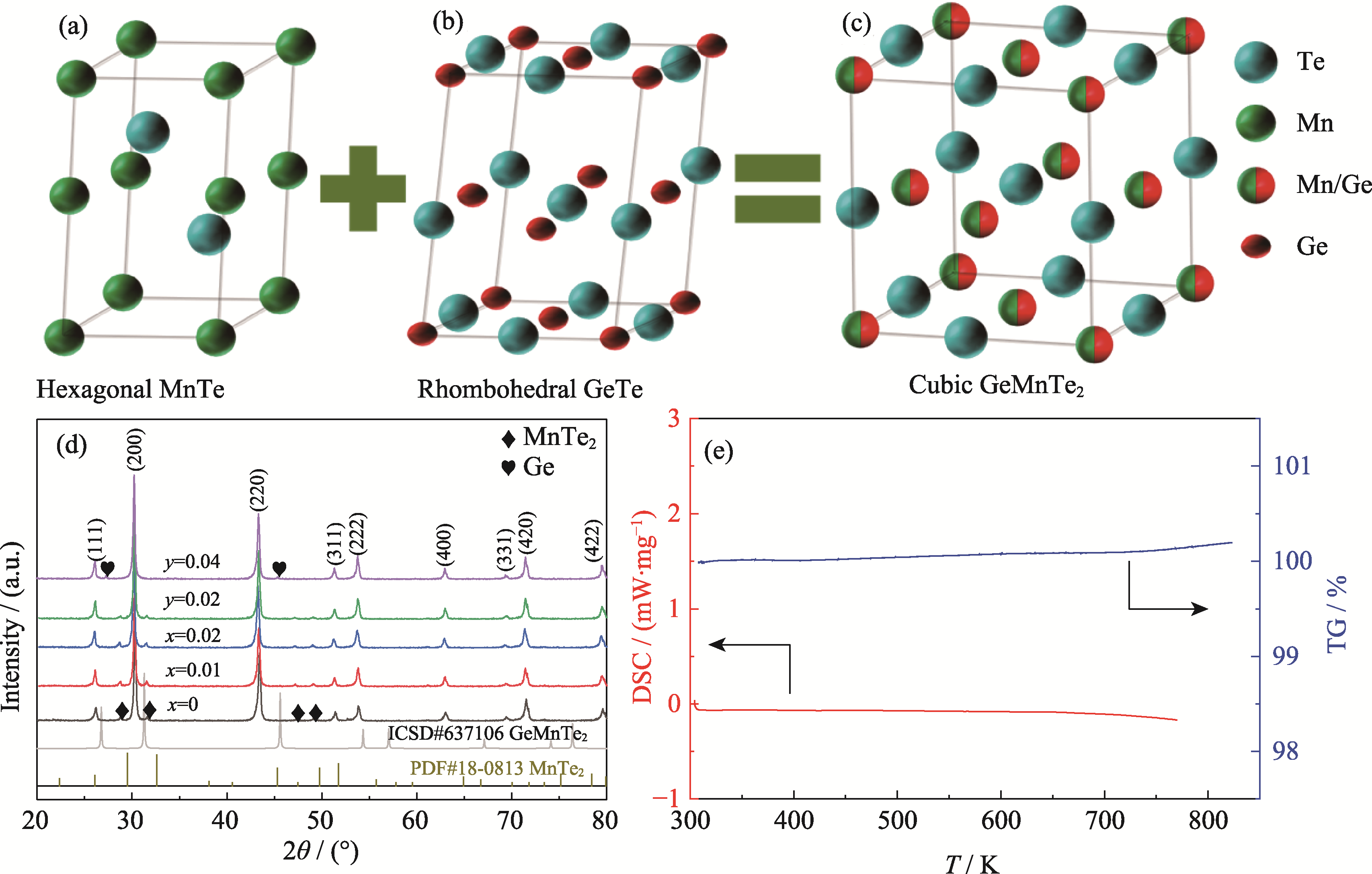
图1 室温下(a)六方相MnTe、(b)菱方相GeTe和(c)立方相GeMnTe2的晶体结构; (d)室温下样品GeMn1-xTe2-2x与GeMnTe2-y的粉末XRD图谱; (e)GeMnTe1.96样品的差示扫描热流曲线和热重曲线
Fig. 1 Room temperature crystal structures for (a) hexagonal MnTe, (b) rhombohedral GeTe and (c) cubic GeMnTe2; (d) Powder XRD patterns of GeMn1-xTe2-2x and GeMnTe2-y at room temperature;(e) Differential scanning calorimetry and thermogravimetric heat flow curves of GeMnTe1.96

图2 (a) GeMnTe2、(b) GeMn0.98Te1.96和(c) GeMnTe1.96样品的BSE照片和EDS面扫描元素分布图
Fig. 2 BSE images and surface scan EDS element distributions of (a) GeMnTe2, (b) GeMn0.98Te1.96 and (c) GeMnTe1.96 samples
| Point | Mn/% | Ge/% | Te/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 34.39 | 4.04 | 61.56 |
| 2 | 34.50 | / | 65.50 |
| 3 | 34.74 | 5.76 | 59.49 |
表1 图2(a)中对应位置的EDS点扫描元素含量(原子分数)
Table 1 Element contents of the points in Fig. 2(a) by EDS point scanning (in atom)
| Point | Mn/% | Ge/% | Te/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 34.39 | 4.04 | 61.56 |
| 2 | 34.50 | / | 65.50 |
| 3 | 34.74 | 5.76 | 59.49 |

图3 样品GeMnTe1.96(a)沿[$0\bar{1}1$]方向的(a)FFT图像以及对应的(b)HRTEM照片和(c)元素分布图
Fig. 3 (a) FFT image along [$0\bar{1}1$] zone axes, (b) HRTEM image and (c) elemental distribution images for GeMnTe1.96 sample
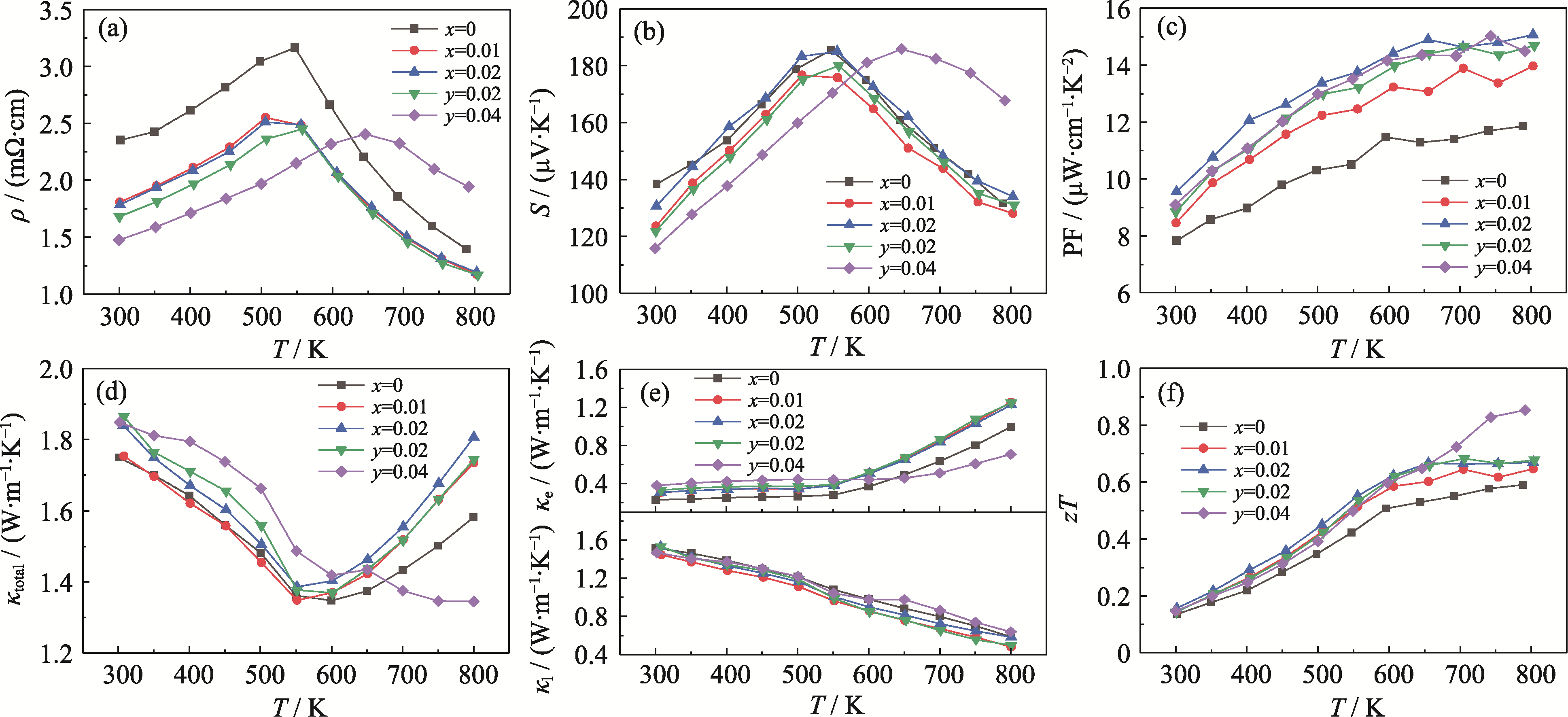
图4 样品GeMn1-xTe2-2x与GeMnTe2-y的(a)电阻率、(b) Seebeck系数、(c)功率因子、(d)总热导率、(e)晶格热导率和电子热导率、(f) zT随温度的变化关系
Fig. 4 Temperature dependent (a) electrical resistivity, (b) Seebeck coefficient, (c) power factor, (d) total thermal conductivity, (e) lattice and electronic thermal conductivity, and (f) zT for GeMn1-xTe2-2x and GeMnTe2-y samples
| [1] |
SHI X L, ZOU J, CHEN Z G. Advanced thermoelectric design: from materials and structures to devices. Chemical Reviews, 2020, 120(15): 7399.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
ZHUANG H L, CAI B, PAN Y, et al. Strong and efficient bismuth telluride-based thermoelectrics for Peltier microcoolers. National Science Review, 2024, 11(10): nwae329.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
ZHANG Q, YUAN M, PANG K, et al. High-performance industrial-grade p-type (Bi,Sb)2Te3 thermoelectric enabled by a stepwise optimization strategy. Advanced Materials, 2023, 35(21): 2300338.
DOI URL |
| [4] | HAO F, QIU P, TANG Y, et al. High efficiency Bi2Te3-based materials and devices for thermoelectric power generation between 100 and 300 ℃. Energy & Environmental Science, 2016, 9(10): 3120. |
| [5] |
ZHANG Z, SUN T, WANG L, et al. Flexible thermoelectric films with different Ag2Se dimensions: performance optimization and device integration. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(11): 1221.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
BU Z, ZHANG X, HU Y, et al. A record thermoelectric efficiency in tellurium-free modules for low-grade waste heat recovery. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 237.
DOI PMID |
| [7] |
JIANG M, FU Y T, ZHANG Q H, et al. High-efficiency and reliable same-parent thermoelectric modules using Mg3Sb2-based compounds. National Science Review, 2023, 10(6): nwad095.
DOI URL |
| [8] | MAO J, LIU Z, ZHOU J, et al. Advances in thermoelectrics. Advances in Physics, 2018, 67(2): 69. |
| [9] |
YAN X, PAN H, ZHANG Y, et al. Highly enhanced thermoelectric and mechanical performance of copper sulfides via natural mineral in-situ phase separation. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2024, 13(5): 641.
DOI URL |
| [10] | DUAN B, YANG J, SALVADOR J R, et al. Electronegative guests in CoSb3. Energy & Environmental Science, 2016, 9(6): 2090. |
| [11] | FU Y T, ZHANG Q H, HU Z L, et al. Mg3(Bi,Sb)2-based thermoelectric modules for efficient and reliable waste-heat utilization up to 750 K. Energy & Environmental Science, 2022, 15(8): 3265. |
| [12] |
WU D, XIE L, XU X, et al. High thermoelectric performance achieved in GeTe-Bi2Te3 pseudo-binary via van der Waals gap-induced hierarchical ferroelectric domain structure. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29(18): 1806613.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
LI J, ZHANG X, WANG X, et al. High-performance GeTe thermoelectrics in both rhombohedral and cubic phases. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2018, 140(47): 16190.
DOI PMID |
| [14] |
HONG M, WANG Y, LIU W, et al. Arrays of planar vacancies in superior thermoelectric Ge1-x-yCdxBiyTe with band convergence. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(30): 1801837.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
LI J, ZHANG X, CHEN Z, et al. Low-symmetry rhombohedral GeTe thermoelectrics. Joule, 2018, 2(5): 976.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
LI J, CHEN Z, ZHANG X, et al. Electronic origin of the high thermoelectric performance of GeTe among the p-type group IV monotellurides. NPG Asia Materials, 2017, 9(3): e353.
DOI |
| [17] |
LEE J K, OH M W, KIM B S, et al. Influence of Mn on crystal structure and thermoelectric properties of GeTe compounds. Electronic Materials Letters, 2014, 10(4): 813.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
LIU Z, SUN J, MAO J, et al. Phase-transition temperature suppression to achieve cubic GeTe and high thermoelectric performance by Bi and Mn codoping. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2018, 115(21): 5332.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
CHENG J, YIN L, WANG X, et al. Realizing a superior conversion efficiency of ≈11.3% in the group IV-VI thermoelectric module. Small, 2024, 20(27): 2312145.
DOI URL |
| [20] | LI X, CHEN C, YIN L, et al. Realizing an excellent conversion efficiency of 14.5% in the Mg3Sb2/GeTe-based thermoelectric module for waste heat recovery. Energy & Environmental Science, 2023, 16(12): 6147. |
| [21] |
WANG S, J M, WANG L, et al. n-Type Pb-free AgBiSe2 based thermoelectric materials with stable cubic phase structure. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(7): 807.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
ZHENG Z, SU X, DENG R, et al. Rhombohedral to cubic conversion of GeTe via MnTe alloying leads to ultralow thermal conductivity, electronic band convergence, and high thermoelectric performance. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2018, 140(7): 2673.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
LIU X, WANG W, WANG Y, et al. Realizing high thermoelectric performance in GeTe-based supersaturated solid solutions. Advanced Energy Materials, 2024, 14(16): 2304029.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
CHEN S, ZHONG Y, CAI J, et al. High thermoelectric performance of GeTe-MnTe alloy driven by spin degree of freedom. Materials Today Physics, 2024, 43: 101393.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
WU G, CAI J, CHEN L, et al. Defect engineering realizes superior thermoelectric performance of GeTe. Advanced Functional Materials, 2024, 34(46): 2407818.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
HONG M, CHEN Z G, YANG L, et al. Realizing zT of 2.3 in Ge1-x-ySbxInyTe via reducing the phase-transition temperature and introducing resonant energy doping. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(11): 1705942.
DOI URL |
| [27] | SARKAR D, SAMANTA M, GHOSH T, et al. All-scale hierarchical nanostructures and superior valence band convergence lead to ultra-high thermoelectric performance in cubic GeTe. Energy & Environmental Science, 2022, 15(11): 4625. |
| [28] | DUAN S, YIN Y, LIU G Q, et al. Anomalous thermopower and high ZT in GeMnTe2 driven by spin’s thermodynamic entropy. Research, 2021, 2021: 1949070. |
| [29] |
MEI Q, XIE C, CUI J, et al. Locally off-centered Ge atoms contribute to high thermoelectric performance of globally averaged cubic MnGeTe2 alloys. Acta Materialia, 2025, 285: 120694.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
CHEN H, ZHAO E, WEN X, et al. Phase engineering on high- entropy transition metal dichalcogenides and the entropy-enhanced thermoelectric performance. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2024, 13: 1985.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
XU Y, LI W, WANG C, et al. MnTe2 as a novel promising thermoelectric material. Journal of Materiomics, 2018, 4(3): 215.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
ZHOU B, LI W, WANG X, et al. Promising cubic MnGeTe2 thermoelectrics. Science China Materials, 2019, 62(3): 379.
DOI |
| [33] |
DONG J F, PEI J, LI J F, et al. High-performance electron-doped GeMnTe2: hierarchical structure and low thermal conductivity. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(48): 27361.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
DONG J, JIANG Y, SUN Y, et al. Discordant distortion in cubic GeMnTe2 and high thermoelectric properties of GeMnTe2-x%SbTe. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2023, 145(3): 1988.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
YIN L C, LIU W D, LI M, et al. Interstitial Cu: an effective strategy for high carrier mobility and high thermoelectric performance in GeTe. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(25): 2301750.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
ZHANG Q, WANG R, SONG K, et al. Raised solubility in SnTe by GeMnTe2 alloying enables converged valence bands, low thermal conductivity, and high thermoelectric performance. Nano Energy, 2022, 94: 106940.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
ZHONG Y, CHEN S, CAI J, et al. Bipolar-like effect and its suppression in magnetic thermoelectrics GeMnTe2. ACS Applied Electronic Materials, 2024, 6(4): 2552.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
LI M, HONG M, TANG X, et al. Crystal symmetry induced structure and bonding manipulation boosting thermoelectric performance of GeTe. Nano Energy, 2020, 73: 104740
DOI URL |
| [1] | 王伟明, 王为得, 粟毅, 马青松, 姚冬旭, 曾宇平. 以非氧化物为烧结助剂制备高导热氮化硅陶瓷的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 634-646. |
| [2] | 金敏, 马玉鹏, 魏天然, 林思琪, 白旭东, 史迅, 刘学超. 非化学计量溶液区熔法生长大尺寸InSe晶体及表征[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(5): 554-560. |
| [3] | 王姝灵, 蒋蒙, 王连军, 江莞. 稳定立方相结构的n型无铅AgBiSe2基热电材料[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(7): 807-814. |
| [4] | 付师, 杨增朝, 李江涛. 功率模块封装用高强度高热导率Si3N4陶瓷的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(10): 1117-1132. |
| [5] | 孙小凡, 陈小武, 靳喜海, 阚艳梅, 胡建宝, 董绍明. 低温反应熔渗工艺制备AlN-SiC复相陶瓷及其性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(10): 1223-1229. |
| [6] | 付师, 杨增朝, 李宏华, 王良, 李江涛. 复合烧结助剂对Si3N4陶瓷力学性能和热导率的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(9): 947-953. |
| [7] | 胡佳军, 王凯, 侯鑫广, 杨婷, 夏鸿雁. 熔盐法合成高导热磷化硼及其热管理性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(9): 933-940. |
| [8] | 王鹏将, 康慧君, 杨雄, 刘颖, 程成, 王同敏. 熵调控抑制ZrNiSn基half-Heusler热电材料的晶格热导率[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 717-723. |
| [9] | 阮景, 杨金山, 闫静怡, 游潇, 王萌萌, 胡建宝, 张翔宇, 丁玉生, 董绍明. 碳化硅纳米线增强多孔碳化硅陶瓷基复合材料的制备[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(4): 459-466. |
| [10] | 娄许诺, 邓后权, 李爽, 张青堂, 熊文杰, 唐国栋. Ge掺杂MnTe材料的热电输运性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(2): 209-214. |
| [11] | 王为得, 陈寰贝, 李世帅, 姚冬旭, 左开慧, 曾宇平. 以YbH2-MgO体系为烧结助剂制备高热导率高强度氮化硅陶瓷[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(9): 959-966. |
| [12] | 桑玮玮, 张红松, 陈华辉, 温斌, 李新春. (Sm0.2Gd0.2Dy0.2Y0.2Yb0.2)3TaO7高熵陶瓷的制备及热物理性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(4): 405-410. |
| [13] | 牟庭海, 许文涛, 凌军荣, 董天文, 秦梓轩, 周有福. 微波烧结制备ZrO2-AlN复合陶瓷的微观结构与性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(11): 1231-1236. |
| [14] | 邱小小,周细应,傅赟天,孙晓萌,王连军,江莞. Ge1-xInxTe微观结构对热电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(8): 916-922. |
| [15] | 周星圆, 柳伟, 张程, 华富强, 张敏, 苏贤礼, 唐新峰. Nb掺杂Mo1-xWxSeTe固溶体的热-电输运性能优化[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(12): 1373-1379. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||