无机材料学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (7): 717-723.DOI: 10.15541/jim20210610 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20210610
王鹏将1( ), 康慧君1(
), 康慧君1( ), 杨雄1, 刘颖2, 程成1, 王同敏1
), 杨雄1, 刘颖2, 程成1, 王同敏1
收稿日期:2021-10-05
修回日期:2021-11-28
出版日期:2022-07-20
网络出版日期:2021-12-02
通讯作者:
康慧君, 教授. E-mail: kanghuijun@dlut.edu.cn作者简介:王鹏将(1996-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: wpj@mail.dlut.edu.cn
基金资助:
WANG Pengjiang1( ), KANG Huijun1(
), KANG Huijun1( ), YANG Xiong1, LIU Ying2, CHENG Cheng1, WANG Tongmin1
), YANG Xiong1, LIU Ying2, CHENG Cheng1, WANG Tongmin1
Received:2021-10-05
Revised:2021-11-28
Published:2022-07-20
Online:2021-12-02
Contact:
KANG Huijun, professor. E-mail: kanghuijun@dlut.edu.cnAbout author:WANG Pengjiang (1996-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: wpj@mail.dlut.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
ZrNiSn基half-Heusler热电材料具有较高的热导率, 限制了其热电性能进一步提高。为了降低晶格热导率, 本研究采用磁悬浮熔炼和放电等离子烧结的方法制备ZrNiSn和Zr0.5Hf0.5Ni1-xPtxSn (x=0, 0.1, 0.15, 0.2, 0.25, 0.3)高熵half-Heusler热电合金。在Zr位进行Hf原子替代, Ni位进行Pt原子替代以调控该合金的构型熵, 并研究构型熵对热电性能的影响。本工作优化了Zr0.5Hf0.5Ni0.85Pt0.15Sn在673 K的最小晶格热导率和双极扩散热导率之和为2.1 W·m-1·K-1, 与ZrNiSn相比降低了约58%。这一发现为降低ZrNiSn基合金的晶格热导率提供了一种有效的策略, 有助于改善材料的热电性能。
中图分类号:
王鹏将, 康慧君, 杨雄, 刘颖, 程成, 王同敏. 熵调控抑制ZrNiSn基half-Heusler热电材料的晶格热导率[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 717-723.
WANG Pengjiang, KANG Huijun, YANG Xiong, LIU Ying, CHENG Cheng, WANG Tongmin. Inhibition of Lattice Thermal Conductivity of ZrNiSn-based Half-Heusler Thermoelectric Materials by Entropy Adjustment[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 717-723.
图2 Zr0.5Hf0.5Ni1-xPtxSn的二次电子照片
Fig. 2 Secondary electron images of Zr0.5Hf0.5Ni1-xPtxSn (a) x=0; (b) x=0.1; (c) x=0.15; (d) x=0.2; (e) x=0.25; (f) x=0.3

图4 ZrNiSn和Zr0.5Hf0.5Ni1-xPtxSn试样的(a)电导率与温度的变化关系, (b)室温载流子浓度和迁移率与Pt掺杂量的变化关系, (c)Seebeck系数和(d)功率因子与温度的变化关系
Fig. 4 (a) Temperature dependence of electrical conductivity, (b) room temperature carrier concentration and carrier mobility varied with Pt content, temperature dependence of (c) Seebeck coefficient and (d) power factor of ZrNiSn and Zr0.5Hf0.5Ni1-xPtxSn

图5 ZrNiSn和Zr0.5Hf0.5Ni1-xPtxSn试样的(a)热扩散系数和(b)比热容与温度的变化关系
Fig. 5 Temperature dependence of (a) thermal diffusivity and (b) specific heat capacity for ZrNiSn and Zr0.5Hf0.5Ni1-xPtxSn samples
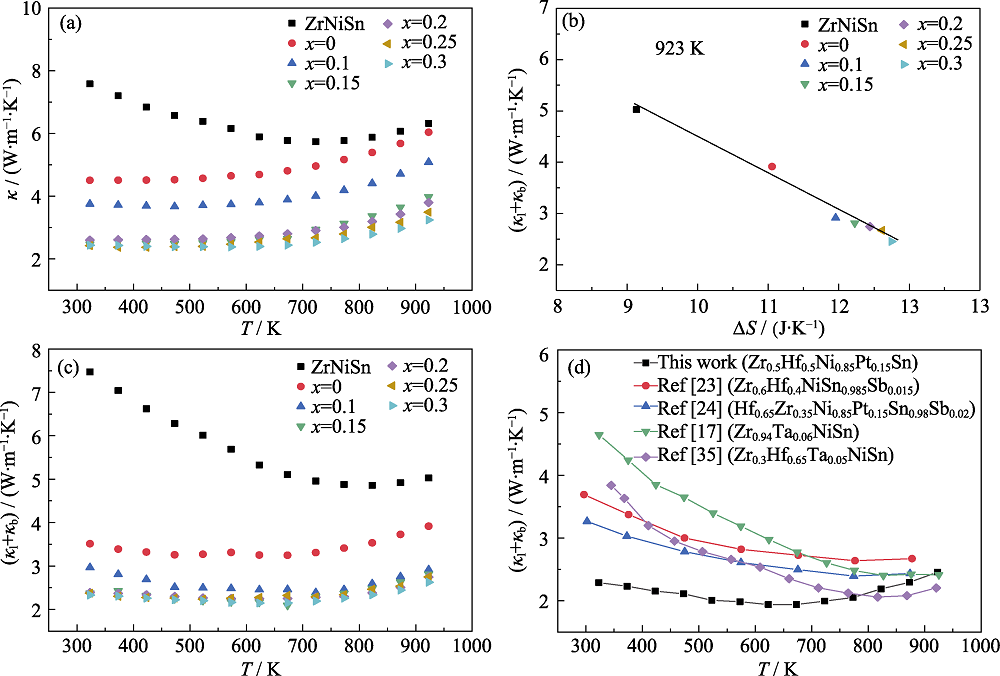
图6 (a)ZrNiSn和Zr0.5Hf0.5Ni1-xPtxSn试样总热导率与温度的变化关系, (b) 923 K时(κl+κb)随构型熵的变化关系, (c) (κl+κb)与温度的变化关系, (d) 不同样品的(κl+κb)的对比[17,23-24,35]
Fig. 6 (a) Temperature dependence of total thermal conductivity, (b) change of lattice thermal conductivity with configuration entropy at 923 K, (c) temperature dependence of lattice thermal conductivity of Zr0.5Hf0.5Ni1-xPtxSn (x=0, 0.1, 0.15, 0.2, 0.25, 0.3), and (d) comparison of lattice thermal conductivity of different samples [17,23-24,35]
| [1] | CHEN Z Y, GAO B, TANG J, et al. Low lattice thermal conductivity by alloying SnTe with AgSbTe2 and CaTe/MnTe. Applied Physics Letters, 2019, 115(7): 0739031. |
| [2] | GLEN A S. New Materials and Performance Limits for Thermoelectric Cooling. CRC Handbook of Thermoelectrics. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 1995. |
| [3] |
SNYDER G J, TOBERER E S. Complex thermoelectric materials. Nature Materials, 2008, 7(2): 105-114.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
CHANG C, WU M H, HE D S, et al. 3D charge and 2D phonon transports leading to high out-of-plane ZT in n-type SnSe crystals. Science, 2018, 360(6390): 778-782.
DOI URL |
| [5] | LI J, WANG Y, YANG X, et al. Processing bulk insulating CaTiO3 into a high-performance thermoelectric material. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 428: 131121. |
| [6] |
MA Y, HEIJL R, PALMQVIST A E C. Composite thermoelectric materials with embedded nanoparticles. Journal of Materials Science, 2013, 48(7): 2767-2778.
DOI URL |
| [7] | ZHU T J, LIU Y T, FU C G, et al. Compromise and synergy in high-efficiency thermoelectric materials. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(14): 1605884. |
| [8] |
FANG T, ZHENG S Q, ZHOU T, et al. Computational prediction of high thermoelectric performance in p-type half-Heusler compounds with low band effective mass. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2017, 19(6): 4411-4417.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
MAKONGO J P A, MISRA D K, ZHOU X Y, et al. Simultaneous large enhancements in thermopower and electrical conductivity of bulk nanostructured half-Heusler alloys. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011, 133(46): 18843-18852.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
GALAZKA K, XIE W J, POPULOH S, et al. Tailoring thermoelectric properties of Zr0.43Hf0.57NiSn half-Heusler compound by defect engineering. Rare Metals, 2020, 39(6): 659-670.
DOI URL |
| [11] | BOS J W G, DOWNIE R A. Half-Heusler thermoelectrics: a complex class of materials. Journal of Physics-Condensed Matter, 2014, 26(43): 433201. |
| [12] | ZHU T J, FU C G, XIE H H, et al. High efficiency half-Heusler thermoelectric materials for energy harvesting. Advanced Energy Materials, 2015, 5(19): 1500588. |
| [13] |
LIU Y F, SAHOO P, MAKONGO J P A, et al. Large enhancements of thermopower and carrier mobility in quantum dot engineered bulk semiconductors. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2013, 135(20): 7486-7495.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
ALIABAD H A R, NODEHI Z, MALEKI B, et al. Electronical and thermoelectric properties of half-Heusler ZrNiPb under pressure in bulk and nanosheet structures for energy conversion. Rare Metals, 2019, 38(11): 1015-1023.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
GRAF T, FELSER C, PARKIN S S P. Simple rules for the understanding of Heusler compounds. Progress in Solid State Chemistry, 2011, 39(1): 1-50.
DOI URL |
| [16] | YANG X, LIU D Q, LI J B, et al. Top-down method to fabricate TiNi1+xSn half-Heusler alloy with high thermoelectric performance. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2021, 87: 39-45. |
| [17] |
YANG X, JIANG Z, KANG H J, et al. Enhanced thermoelectric performance of Zr1-xTaxNiSn half-Heusler alloys by diagonal-rule doping. ACS Applied Materials Interfaces, 2020, 12(3): 3773-3783.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
YAN J L, LIU F S, MA G H, et al. Suppression of the lattice thermal conductivity in NbFeSb-based half-Heusler thermoelectric materials through high entropy effects. Scripta Materialia, 2018, 157: 129-134.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
SHEN Q, CHEN L, GOTO T, et al. Effects of partial substitution of Ni by Pd on the thermoelectric properties of ZrNiSn-based half-Heusler compounds. Applied Physics Letters, 2001, 79(25): 4165-4167.
DOI URL |
| [20] | YANG X, JIANG Z, LI J B, et al. Identification of the intrinsic atomic disorder in ZrNiSn-based alloys and their effects on thermoelectric properties. Nano Energy, 2020, 78: 105372. |
| [21] |
SCHWALL M, BALKE B. Phase separation as a key to a thermoelectric high efficiency. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2013, 15(6): 1868-1872.
DOI URL |
| [22] | XIE W J, WEIDENKAFF A, TANG X F, et al. Recent advances in nanostructured thermoelectric half-Heusler compounds. Nanomaterials- Basel, 2012, 2(4): 379-412. |
| [23] |
LIU Y T, XIE H H, FU C G, et al. Demonstration of a phonon-glass electron-crystal strategy in (Hf,Zr)NiSn half-Heusler thermoelectric materials by alloying. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2015, 3(45): 22716-22722.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
XIE H H, WANG H, PEI Y Z, et al. Beneficial contribution of alloy disorder to electron and phonon transport in half-Heusler thermoelectric materials. Advanced Functional Materials, 2013, 23(41): 5123-5130.
DOI URL |
| [25] | SENKOV O N, MILLER J D, MIRACLE D B, et al. Accelerated exploration of multi-principal element alloys with solid solution phases. Nature Communications, 2015, 6: 6529. |
| [26] |
ZHANG Y, ZUO T T, TANG Z, et al. Microstructures and properties of high-entropy alloys. Progress in Materials Science, 2014, 61: 1-93.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
YEH J W, CHEN S K, LIN S J, et al. Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2004, 6(5): 299-303.
DOI URL |
| [28] | CANTOR B, CHANG I T H, KNIGHT P, et al. Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Materials Science and Engineering A-Structural Materials Properties Microstructure and Processing, 2004, 375: 213-218. |
| [29] | KOZELJ P, VRTNIK S, JELEN A, et al. Discovery of a superconducting high-entropy alloy. Physical Review Letters, 2014, 113(10): 107001. |
| [30] |
KAO Y F, CHEN S K, SHEU J H, et al. Hydrogen storage properties of multi-principal-component CoFeMnTixVyZrz alloys. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2010, 35(17): 9046-9059.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
BERARDAN D, FRANGER S, MEENA A K, et al. Room temperature lithium superionic conductivity in high entropy oxides. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2016, 4(24): 9536-9541.
DOI URL |
| [32] | LIU R H, CHEN H Y, ZHAO K P, et al. Entropy as a gene-like performance indicator promoting thermoelectric materials. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(38): 1702712. |
| [33] | SHAFEIE S, GUO S, HU Q, et al. High-entropy alloys as high- temperature thermoelectric materials. Journal of Applied Physics, 2015, 118(18): 184905. |
| [34] |
YANG Q Y, QIU P F, SHI X, et al. Application of entropy engineering in thermoelectrics. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(4): 347-354.
DOI URL |
| [35] | GALAZKA K, POPULOH S, XIE W J, et al. Improved thermoelectric performance of (Zr0.3Hf0.7)NiSn half-Heusler compounds by Ta substitution. Journal of Applied Physics, 2014, 115(18): 183704. |
| [36] |
XIE W J, YAN Y G, ZHU S, et al. Significant ZT enhancement in p-type Ti(Co,Fe)Sb-InSb nanocomposites via a synergistic high-mobility electron injection, energy-filtering and boundary- scattering approach. Acta Materialia, 2013, 61(6): 2087-2094.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
YANG J, MEISNER G P, CHEN L. Strain field fluctuation effects on lattice thermal conductivity of ZrNiSn-based thermoelectric compounds. Applied Physics Letters, 2004, 85(7): 1140-1142.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 余乐洋阳, 赵芳霞, 张舒心, 徐以祥, 牛亚然, 张振忠, 郑学斌. 感应等离子球化技术制备喷涂用高熵硼化物粉体[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 808-816. |
| [2] | 崔宁, 张玉新, 王鲁杰, 李彤阳, 于源, 汤华国, 乔竹辉. (TiVNbMoW)Cx高熵陶瓷的单相形成过程与碳空位调控[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 511-520. |
| [3] | 李紫薇, 弓伟露, 崔海峰, 叶丽, 韩伟健, 赵彤. 前驱体法制备(Zr, Hf, Nb, Ta, W)C-SiC复相陶瓷及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 271-280. |
| [4] | 樊文楷, 杨潇, 李宏华, 李永, 李江涛. 无压烧结制备(Y0.2Gd0.2Er0.2Yb0.2Lu0.2)2Zr2O7高熵陶瓷及其高温抗CMAS腐蚀性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 159-167. |
| [5] | 鲍伟超, 郭晓杰, 辛晓婷, 彭湃, 王新刚, 刘吉轩, 张国军, 许钫钫. 在碳化物陶瓷中构筑金属原子层分相共生结构[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(1): 17-22. |
| [6] | 程俊, 张家伟, 仇鹏飞, 陈立东, 史迅. P掺杂β-FeSi2材料的制备与热电输运性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(8): 895-902. |
| [7] | 李刘媛, 黄开明, 赵秀艺, 刘会超, 王超. RE-Si-Al-O玻璃相对高熵稀土双硅酸盐微结构及耐CMAS腐蚀性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 793-802. |
| [8] | 蔡飞燕, 倪德伟, 董绍明. 高熵碳化物超高温陶瓷的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 591-608. |
| [9] | 刘国昂, 王海龙, 方成, 黄飞龙, 杨欢. B4C含量对(Ti0.25Zr0.25Hf0.25Ta0.25)B2-B4C陶瓷力学性能及抗氧化性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 697-706. |
| [10] | 张睿, 张侃, 袁梦雅, 谷鑫磊, 郑伟涛. 氮空位调控晶格畸变度强化(NbMoTaW)Nx薄膜的力学性质和耐磨损性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 715-725. |
| [11] | 陈浩, 樊文浩, 安德成, 陈少平. 能带优化和载流子调控改善SnTe的热电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(3): 306-312. |
| [12] | 田震, 蒋全伟, 李建波, 于砺锋, 康慧君, 王同敏. 热变形协同优化BiSbSe1.50Te1.50材料电热输运[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(12): 1316-1324. |
| [13] | 张文宇, 郭瑞华, 岳全鑫, 黄雅荣, 张国芳, 关丽丽. 高熵磷化物双功能催化剂的制备及高效电解水性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(11): 1265-1274. |
| [14] | 张哲, 孙婷婷, 王连军, 江莞. 不同维度Ag2Se构筑柔性热电薄膜的性能优化与器件集成研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(11): 1221-1227. |
| [15] | 孟雨婷, 王雪梅, 章淑娴, 陈志炜, 裴艳中. Bi2Te3基热电材料的单带和双带传输特性转变[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(11): 1283-1291. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||