无机材料学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (9): 959-966.DOI: 10.15541/jim20200705 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20200705
王为得1,2( ), 陈寰贝3, 李世帅1,2, 姚冬旭1(
), 陈寰贝3, 李世帅1,2, 姚冬旭1( ), 左开慧1, 曾宇平1
), 左开慧1, 曾宇平1
收稿日期:2020-12-08
修回日期:2021-01-31
出版日期:2021-09-20
网络出版日期:2021-03-01
通讯作者:
姚冬旭, 副研究员. E-mail: yaodongxu@mail.sic.ac.cn
作者简介:王为得, 博士研究生. E-mail: wangweide@student.sic.ac.cn
基金资助:
WANG Weide1,2( ), CHEN Huanbei3, LI Shishuai1,2, YAO Dongxu1(
), CHEN Huanbei3, LI Shishuai1,2, YAO Dongxu1( ), ZUO Kaihui1, ZENG Yuping1
), ZUO Kaihui1, ZENG Yuping1
Received:2020-12-08
Revised:2021-01-31
Published:2021-09-20
Online:2021-03-01
Contact:
YAO Dongxu, associate professor. E-mail: yaodongxu@mail.sic.ac.cn
About author:WANG Weide, PhD candidate. E-mail: wangweide@student.sic.ac.cn
Supported by:摘要:
以YbH2-MgO体系为烧结助剂, 采用两步法烧结制备了高热导率高强度氮化硅陶瓷, 研究了YbH2-MgO对氮化硅致密化行为、相组成、微观形貌、热导率和抗弯强度的影响。在预烧结阶段, YbH2在还原SiO2的同时原位生成了Yb2O3, 进而形成“缺氧-富氮”液相。该液相不仅有利于晶粒的生长, 更有利于阻碍晶格氧的生成, 相较于Yb2O3-MgO助剂体系, β-Si3N4晶粒尺寸更大, 晶格缺陷更少, 低热导晶间相更少, 在1900 ℃保温24 h后, 热导率最优可达131.15 W·m-1·K-1, 较Yb2O3-MgO体系提升13.7%。用YbH2代替Yb2O3, 在低温条件下烧结制备得到的氮化硅抗弯强度有所改善, 在1800 ℃保温4 h的抗弯强度可达(1008±35) MPa; 但在高温烧结时强度略有下降, 这与微观结构的变化密切相关。研究表明, YbH2-MgO体系是制备高热导率高强度氮化硅陶瓷的有效烧结助剂。
中图分类号:
王为得, 陈寰贝, 李世帅, 姚冬旭, 左开慧, 曾宇平. 以YbH2-MgO体系为烧结助剂制备高热导率高强度氮化硅陶瓷[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(9): 959-966.
WANG Weide, CHEN Huanbei, LI Shishuai, YAO Dongxu, ZUO Kaihui, ZENG Yuping. Preparation of Silicon Nitride with High Thermal Conductivity and High Flexural Strength Using YbH2-MgO as Sintering Additive[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(9): 959-966.
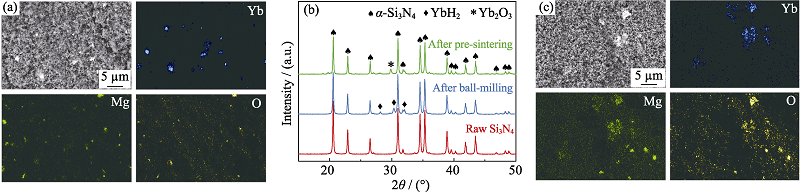
图1 (a)YbHM球磨后的元素分布图, (b)α-Si3N4原料、YbHM球磨及预烧结后XRD图谱, (c)YbHM预烧结后的元素分布图
Fig. 1 (a) Elemental distributions of YbHM after ball milling, (b) XRD patterns of α-Si3N4 raw powder, YbHM after ball milling, and YbHM after pre-sintering, (c) elemental distributions of YbHM after pre-sintering
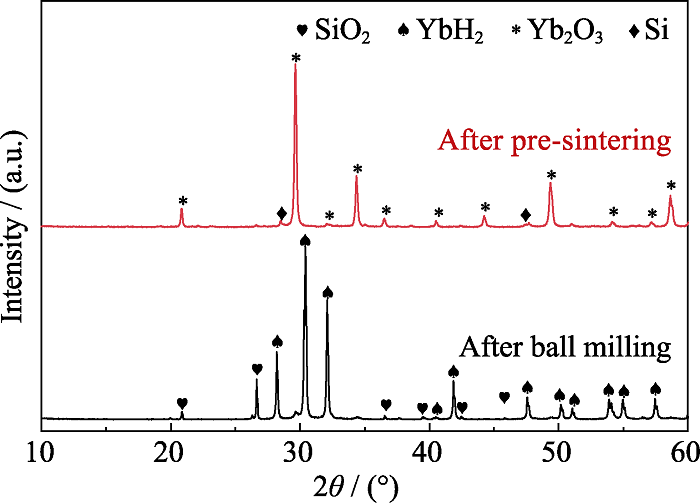
图2 摩尔比为n(YbH2) : n(SiO2)=1 : 1的混合物热处理前后的XRD图谱
Fig. 2 XRD patterns of powder mixture of YbH2 and SiO2 with moler ratio of 1 : 1 before and after pre-sintering
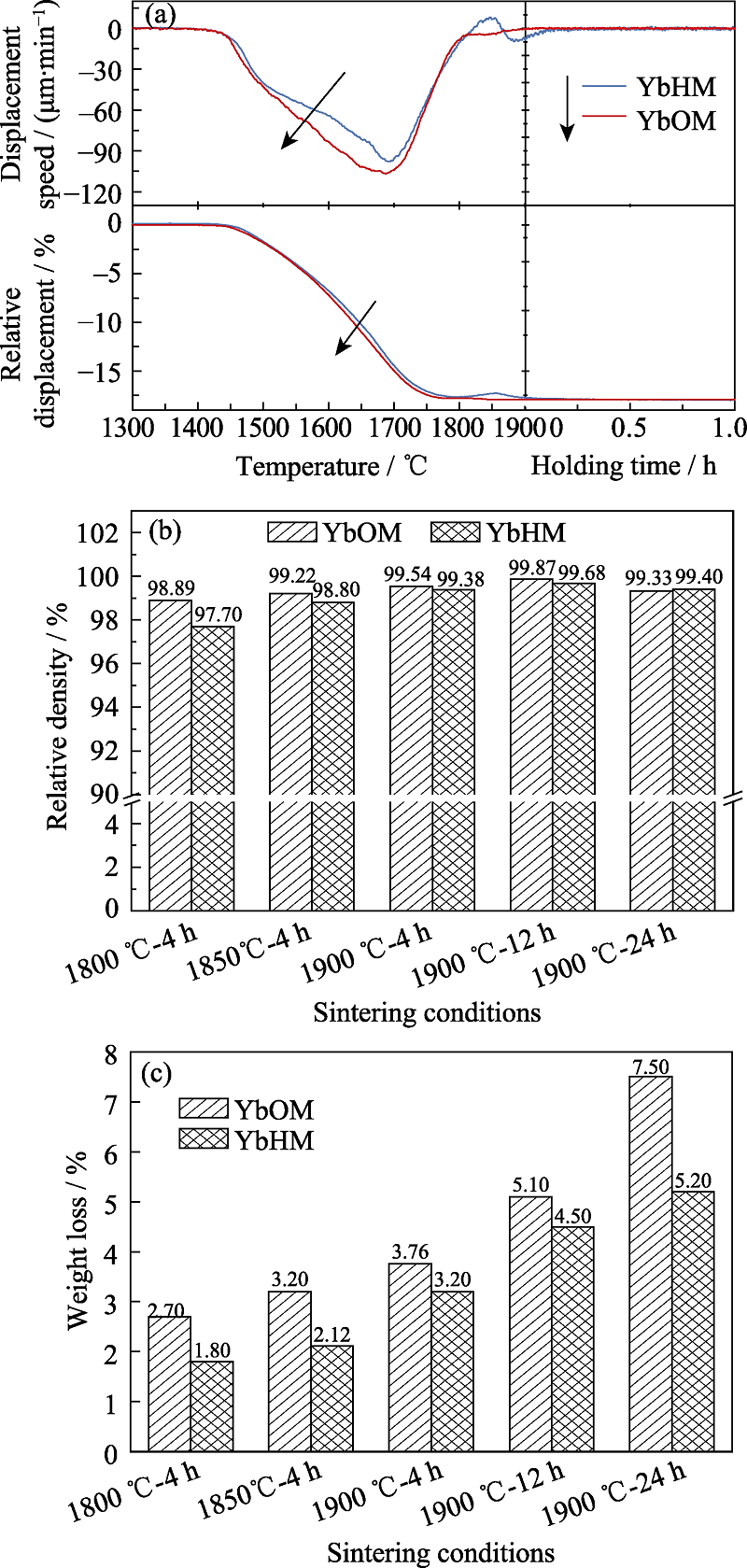
图3 (a)样品原位热收缩行为, (b)不同烧结条件下样品的相对密度, (c)不同烧结条件下样品的失重率
Fig. 3 (a) In-situ observation of shrinkage behaviors of the Si3N4 ceramics, (b) relative density after gas-pressure sintering, and (c) weight loss after gas-pressure sintering
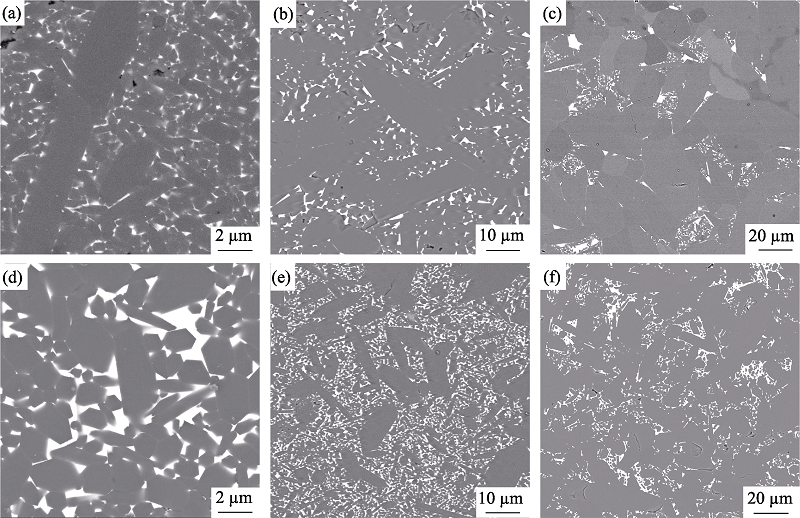
图6 样品抛光面的SEM照片
Fig. 6 SEM images of the polished surfaces (a) 1900 ℃-4 h-YbHM; (b) 1900 ℃-12 h-YbHM; (c) 1900 ℃-24 h-YbHM; (d) 1900 ℃-4 h-YbOM; (e) 1900 ℃-12 h-YbOM; (f) 1900 ℃-24 h-YbOM
| Additive | Ionic radius /nm | Annealing time at 1900 ℃/h | Thermal conductivity /(W·m-1·K-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GdH2 [ | 0.094 | 4 h | 98.07 |
| 12 h | 119.07 | ||
| 24 h | 134.90 | ||
| YH2 [ | 0.089 | 4 h | 101.80 |
| 12 h | 123.00 | ||
| 24 h | 131.60 | ||
| YbH2 | 0.086 | 4 h | 100.20 |
| 12 h | 118.90 | ||
| 24 h | 131.15 |
表1 添加不同种类稀土氢化物作为烧结助剂制备得到氮化硅陶瓷的热导率
Table 1 Thermal conductivities of Si3N4 doped with different rare-earth hydride
| Additive | Ionic radius /nm | Annealing time at 1900 ℃/h | Thermal conductivity /(W·m-1·K-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GdH2 [ | 0.094 | 4 h | 98.07 |
| 12 h | 119.07 | ||
| 24 h | 134.90 | ||
| YH2 [ | 0.089 | 4 h | 101.80 |
| 12 h | 123.00 | ||
| 24 h | 131.60 | ||
| YbH2 | 0.086 | 4 h | 100.20 |
| 12 h | 118.90 | ||
| 24 h | 131.15 |
| [1] |
EDDY C, GASKILL D. Silicon carbide as a platform for power electronics. Science, 2009, 324(5933):1398-1400.
DOI URL |
| [2] | OKUMURA H. Present status and future prospect of widegap semiconductor high-power devices. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics Part 1-Regular Papers Brief Communications & Review Papers, 2006, 45(10A):7565-7586. |
| [3] |
RILEY F L. Silicon nitride and related materials. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2000, 83(2):245-265.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
KRSTIC Z, KRSTIC V D. Silicon nitride: the engineering material of the future. Journal of Materials Science, 2012, 47(2):535-552.
DOI URL |
| [5] | HAGGERTY J S, LIGHTFOOT A. Opportunities for enhancing the thermal conductivities of SiC and Si3N4 ceramics through improved processing. Ceramic Engineering and Science Proceedings, 1995, 16(4):475-487. |
| [6] |
KITAYAMA M, HIRAO K, TORIYAMA M, et al. Thermal conductivity of β-Si3N4: I, effects of various microstructural factors. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1999, 82(11):3105-3112.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
KITAYAMA M, HIRAO K, TSUGE A, et al. Thermal conductivity of β-Si3N4: II, Effect of lattice oxygen. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2000, 83(8):1985-1992.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
ZHU X W, ZHOU Y, HIRAO K. Effects of processing method and additive composition on microstructure and thermal conductivity of Si3N4 ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2006, 26(4/5):711-718.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
ZHOU Y, HYUGA H, KUSANO D, et al. A tough silicon nitride ceramic with high thermal conductivity. Advanced Materials, 2011, 23(39):4563-4567.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
KIM H D, HAN B D, PARK D S, et al. Novel two-step sintering process to obtain a bimodal microstructure in silicon nitride. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2002, 85(1):245-252.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
LI Y S, KIM H N, WU H B, et al. Enhanced thermal conductivity in Si3N4 ceramic by addition of a small amount of carbon. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(2/3):157-164.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
WANG W, YAO D, LIANG H, et al. Novel silicothermic reduction method to obtain Si3N4 ceramics with enhanced thermal conductivity and fracture toughness. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 41(2):1735-1738.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
LIANG H, WANG W, ZUO K, et al. Effect of LaB6 addition on mechanical properties and thermal conductivity of silicon nitride ceramics. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(11):17776-17783.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
LIANG H, WANG W, ZUO K, et al. YB2C2: a new additive for fabricating Si3N4 ceramics with superior mechanical properties and medium thermal conductivity. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(4):5239-5243.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
WANG W, YAO D, CHEN H, et al. ZrSi2-MgO as novel additives for high thermal conductivity of β-Si3N4 ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2020, 103(3):2090-2100.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
WANG W, YAO D, LIANG H, et al. Effect of the binary non-oxide additives on the densification behavior and thermal conductivity of Si3N4 ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2020, 103(10):5891-5899.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
LIANG H, ZENG Y, ZUO K, et al. Mechanical properties and thermal conductivity of Si3N4 ceramics with YF3 and MgO as sintering additives. Ceramics International, 2016, 42(14):15679-15686.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
LEE H M, LEE E B, KIM D L, et al. Comparative study of oxide and non-oxide additives in high thermal conductive and high strength Si3N4 ceramics. Ceramics International, 2016, 42(15):17466-17471.
DOI URL |
| [19] | HU F, ZHAO L, XIE Z P. Silicon nitride ceramics with high thermal conductivity and excellent mechanical properties fabriccated with MgF2 sintering aid and post-sintering heat treatment. Journal of Ceramic Science and Technology, 2016, 7(4):423-428. |
| [20] |
RATZKER B, SOKOL M, KALABUKHOV S, et al. High- pressure spark plasma sintering of silicon nitride with LiF additive. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2018, 38(4):1271-1277.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
ZHANG J, CUI W, LI F, et al. Effects of MgSiN2 addition and post-annealing on mechanical and thermal properties of Si3N4 ceramics. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(10):15719-15722.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
LI Y, KIM H N, WU H, et al. Enhanced thermal conductivity in Si3N4 ceramic with the addition of Y2Si4N6C. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2018, 101(9):4128-4136.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
WANG W, YAO D, LIANG H, et al. Effect of in-situ formed Y2O3 by metal hydride reduction reaction on thermal conductivity of β-Si3N4 ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(15):5316-5323.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
WANG W, YAO D, LIANG H, et al. Improved thermal conductivity of β-Si3N4 ceramics by lowering SiO2/Y2O3 ratio using YH2 as sintering additive. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2020, 103(10):5567-5572.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
WANG W, YAO D, LIANG H, et al. Improved thermal conductivity of β-Si3N4 ceramics through the modification of the liquid phase by using GdH2 as a sintering additive. Ceramics International, 2020, 47(4):5631-5638.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
WANG W, YAO D, LIANG H, et al. Enhanced thermal conductivity in Si3N4 ceramics prepared by using ZrH2 as an oxygen getter. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 855:157451.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
LIU Y, LIU Y B, WANG B, et al. Rare earth element: is it a necessity for PM Ti alloys? Key Engineering Materials, 2012, 520:41-48.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
ROBERTSON I, SCHAFFER G. Comparison of sintering of titanium and titanium hydride powders. Powder Metallurgy, 2010, 53(1):12-19.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
ZHU X W, ZHOU Y, HIRAO K. Effect of sintering additive composition on the processing and thermal conductivity of sintered reaction-bonded Si3N4. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2004, 87(7):1398-1400.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
LINDSAY R, MOYER R O, THOMPSON J S, et al. Preparation, structure, and properties of ytterbium ruthenium hydride. Inorganic Chemistry, 1976, 15(12):3050-3053.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
HAKEEM A S, DAUCÉ R, LEONOVA E, et al. Silicate glasses with unprecedented high nitrogen and electropositive metal contents obtained by using metals as precursors. Advanced Materials, 2005, 17(18):2214-2216.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
ZHU X W, HAYASHI H, ZHOU Y, et al. Influence of additive composition on thermal and mechanical properties of β-Si3N4 ceramics. Journal of Materials Research, 2004, 19(11):3270-3278.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
KITAYAMA M, HIRAO K, WATARI K, et al. Thermal conductivity of β-Si3N4: III, effect of rare-earth (RE = La, Nd, Cd, Y, Yb, and Sc) oxide additives. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2001, 84(2):353-358.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 王伟明, 王为得, 粟毅, 马青松, 姚冬旭, 曾宇平. 以非氧化物为烧结助剂制备高导热氮化硅陶瓷的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 634-646. |
| [2] | 金敏, 马玉鹏, 魏天然, 林思琪, 白旭东, 史迅, 刘学超. 非化学计量溶液区熔法生长大尺寸InSe晶体及表征[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(5): 554-560. |
| [3] | 王姝灵, 蒋蒙, 王连军, 江莞. 稳定立方相结构的n型无铅AgBiSe2基热电材料[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(7): 807-814. |
| [4] | 付师, 杨增朝, 李江涛. 功率模块封装用高强度高热导率Si3N4陶瓷的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(10): 1117-1132. |
| [5] | 李宏华, 东婉茹, 王良, 杨增朝, 李江涛. 燃烧合成氮化硅粉体的性能一致性评价方法和应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(10): 1169-1175. |
| [6] | 孙小凡, 陈小武, 靳喜海, 阚艳梅, 胡建宝, 董绍明. 低温反应熔渗工艺制备AlN-SiC复相陶瓷及其性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(10): 1223-1229. |
| [7] | 付师, 杨增朝, 李宏华, 王良, 李江涛. 复合烧结助剂对Si3N4陶瓷力学性能和热导率的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(9): 947-953. |
| [8] | 胡佳军, 王凯, 侯鑫广, 杨婷, 夏鸿雁. 熔盐法合成高导热磷化硼及其热管理性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(9): 933-940. |
| [9] | 张叶, 曾宇平. 自蔓延高温合成氮化硅多孔陶瓷的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(8): 853-864. |
| [10] | 王鹏将, 康慧君, 杨雄, 刘颖, 程成, 王同敏. 熵调控抑制ZrNiSn基half-Heusler热电材料的晶格热导率[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 717-723. |
| [11] | 阮景, 杨金山, 闫静怡, 游潇, 王萌萌, 胡建宝, 张翔宇, 丁玉生, 董绍明. 碳化硅纳米线增强多孔碳化硅陶瓷基复合材料的制备[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(4): 459-466. |
| [12] | 李萌, 黄海露, 吴甲民, 刘春磊, 吴亚茹, 张景贤, 史玉升. 浆料固相含量对数字光处理成形Si3N4陶瓷性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(3): 310-316. |
| [13] | 娄许诺, 邓后权, 李爽, 张青堂, 熊文杰, 唐国栋. Ge掺杂MnTe材料的热电输运性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(2): 209-214. |
| [14] | 梁汉琴, 尹金伟, 左开慧, 夏咏锋, 姚冬旭, 曾宇平. 添加BaTiO3的热压烧结Si3N4陶瓷的力学和介电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(5): 535-540. |
| [15] | 刘洋, 陆有军, 李彦瑞, 林立群, 袁振侠, 黄振坤. Hf-Si-La-O-N体系中HfN的形成及相关系[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(4): 443-448. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||