无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (11): 1261-1267.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250018 CSTR: 32189.14.jim20250018
胡清豪1( ), 刘兴翀1(
), 刘兴翀1( ), 彭永珊1, 侯孟君1, 何堂贵2, 汤安民2
), 彭永珊1, 侯孟君1, 何堂贵2, 汤安民2
收稿日期:2025-01-13
修回日期:2025-05-05
出版日期:2025-11-20
网络出版日期:2025-05-22
通讯作者:
刘兴翀, 副教授. E-mail: liuxingchong@126.com作者简介:胡清豪(1998-), 女, 硕士研究生. E-mail: 2073147278@qq.com
基金资助:
HU Qinghao1( ), LIU Xingchong1(
), LIU Xingchong1( ), PENG Yongshan1, HOU Mengjun1, HE Tanggui2, TANG Anmin2
), PENG Yongshan1, HOU Mengjun1, HE Tanggui2, TANG Anmin2
Received:2025-01-13
Revised:2025-05-05
Published:2025-11-20
Online:2025-05-22
Contact:
LIU Xingchong, associate professor. E-mail: liuxingchong@126.comAbout author:HU Qinghao (1998-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: 2073147278@qq.com
Supported by:摘要:
作为钙钛矿太阳能电池(PSCs)的电子传输层(ETL)材料, 二氧化锡(SnO2)表面及晶界处的氧空位缺陷会引发非辐射复合, 从而限制器件效率的进一步提升。本研究提出了一种低成本、高效的安赛蜜(ACE-K)修饰ETL策略。研究结果表明, ACE-K分子中的C=O和S=O与SnO2表面未配位Sn4+相互作用, 显著钝化了SnO2的氧空位缺陷, 薄膜电导率由4.60×10-6 S·cm-1提升至6.23×10-6 S·cm-1。同时ACE-K修饰改善了SnO2薄膜的粗糙度(20.6 nm降低至14.0 nm)和润湿性, 为钙钛矿薄膜生长提供了更优质的基底。基于此ETL生长的钙钛矿薄膜晶粒尺寸从970.90 nm增大到1071.20 nm, 且薄膜吸光能力得到增强。空间限制电流(SCLC)测试发现优化后薄膜缺陷密度从4.84×1016 cm-3降低至3.83×1016 cm-3, 电化学阻抗谱(EIS)测试也证实载流子输运过程中的非辐射复合得到明显抑制。最终PSCs的光电转换效率(PCE)从19.27%提升至21.60%。此外, 未封装的ACE-K修饰器件在氮气氛围下储存2160 h后, 仍能保持初始效率的91.67%, 展现出优异的长期稳定性。
中图分类号:
胡清豪, 刘兴翀, 彭永珊, 侯孟君, 何堂贵, 汤安民. 安赛蜜修饰SnO2电子传输层对钙钛矿太阳能电池性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(11): 1261-1267.
HU Qinghao, LIU Xingchong, PENG Yongshan, HOU Mengjun, HE Tanggui, TANG Anmin. Effect of Acesulfame Potassium Modified SnO2 Electron Transport Layer on Performance of Perovskite Solar Cells[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(11): 1261-1267.
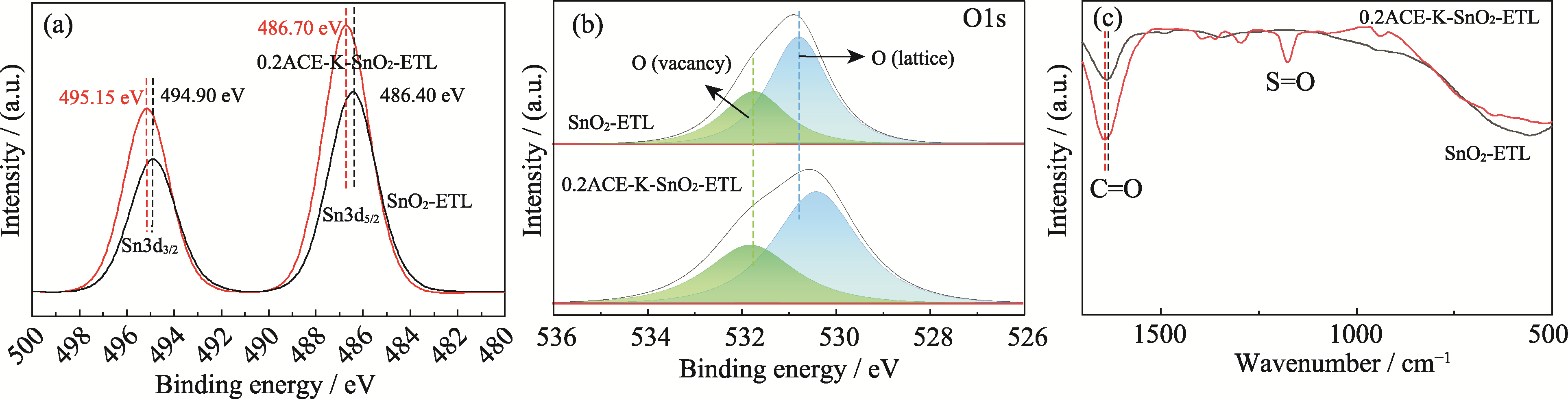
图2 SnO2-ETL和0.2ACE-K-SnO2-ETL的(a) Sn3d XPS谱图、(b) O1s XPS谱图、(c) FT-IR谱图(500~2000 cm-1)
Fig. 2 (a) Sn3d XPS spectra, (b) O1s XPS spectra and (c) FT-IR spectra (500-2000 cm-1) of SnO2-ETL and 0.2ACE-K-SnO2-ETL
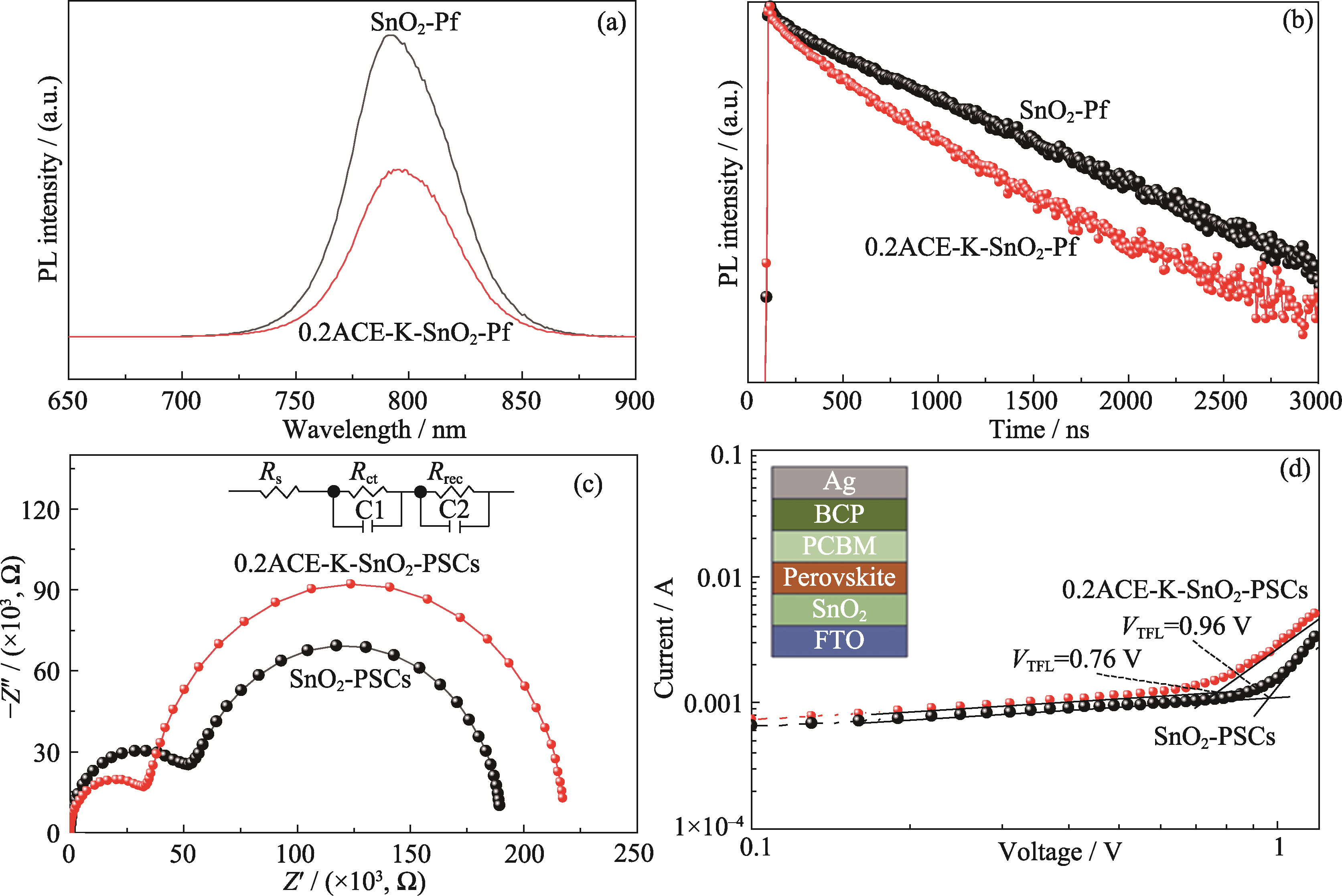
图5 SnO2-Pf和0.2ACE-K-SnO2-Pf的(a) PL曲线、(b) TRPL曲线; SnO2-PSCs和0.2ACE-K-SnO2-PSCs的(c) EIS谱图、(d) SCLC曲线
Fig. 5 (a) PL curves and (b) TRPL curves of SnO2-Pf and 0.2ACE-K-SnO2-Pf; (c) EIS spectra and (d) SCLC curves of SnO2-PSCs and 0.2ACE-K-SnO2-PSCs
| x | VOC/V | JSC/(mA·cm-2) | PCE/% | FF/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1.112 | 22.85 | 19.27 | 75.90 |
| 0.05 | 1.127 | 23.84 | 20.68 | 77.00 |
| 0.1 | 1.128 | 24.32 | 20.87 | 76.10 |
| 0.2 | 1.135 | 23.97 | 21.60 | 79.30 |
| 0.4 | 1.129 | 23.71 | 20.72 | 77.40 |
表1 最优xACE-K-SnO2-PSCs的光伏参数
Table 1 Photovoltaic parameters of champion xACE-K-SnO2-PSCs
| x | VOC/V | JSC/(mA·cm-2) | PCE/% | FF/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1.112 | 22.85 | 19.27 | 75.90 |
| 0.05 | 1.127 | 23.84 | 20.68 | 77.00 |
| 0.1 | 1.128 | 24.32 | 20.87 | 76.10 |
| 0.2 | 1.135 | 23.97 | 21.60 | 79.30 |
| 0.4 | 1.129 | 23.71 | 20.72 | 77.40 |
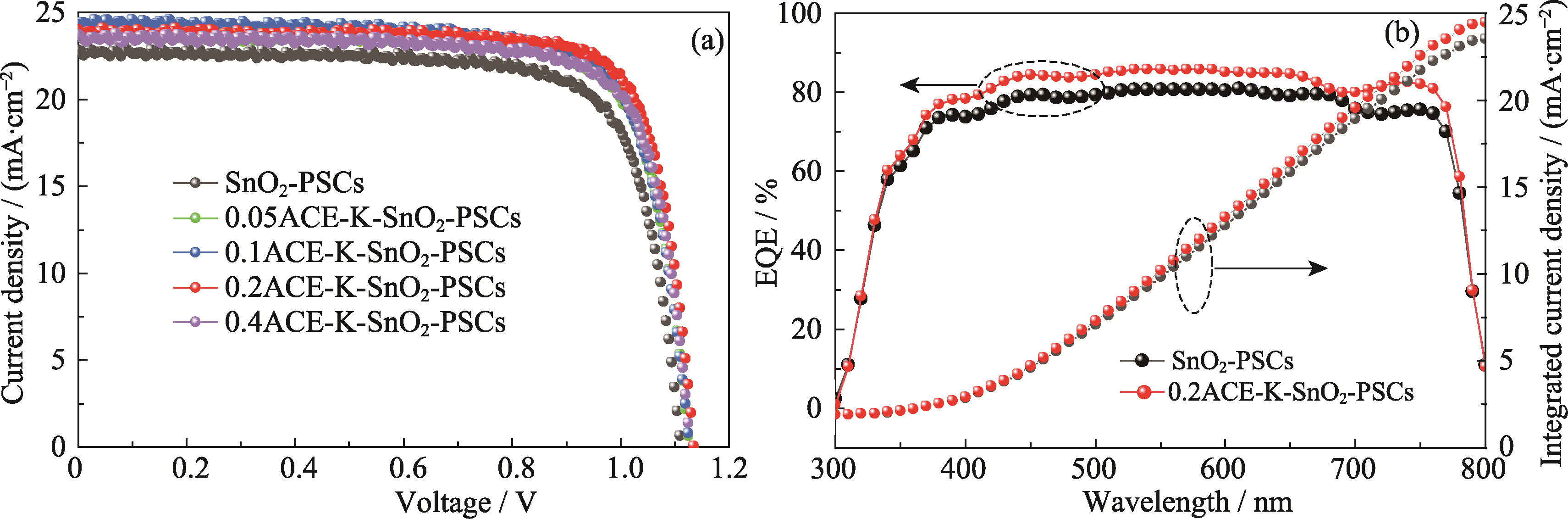
图7 SnO2-PSCs和0.2ACE-K-SnO2-PSCs的(a) J-V曲线、(b) EQE曲线
Fig. 7 (a) J-V curves and (b) EQE curves of SnO2-PSCs and 0.2ACE-K-SnO2-PSCs Colorful figures are available on website
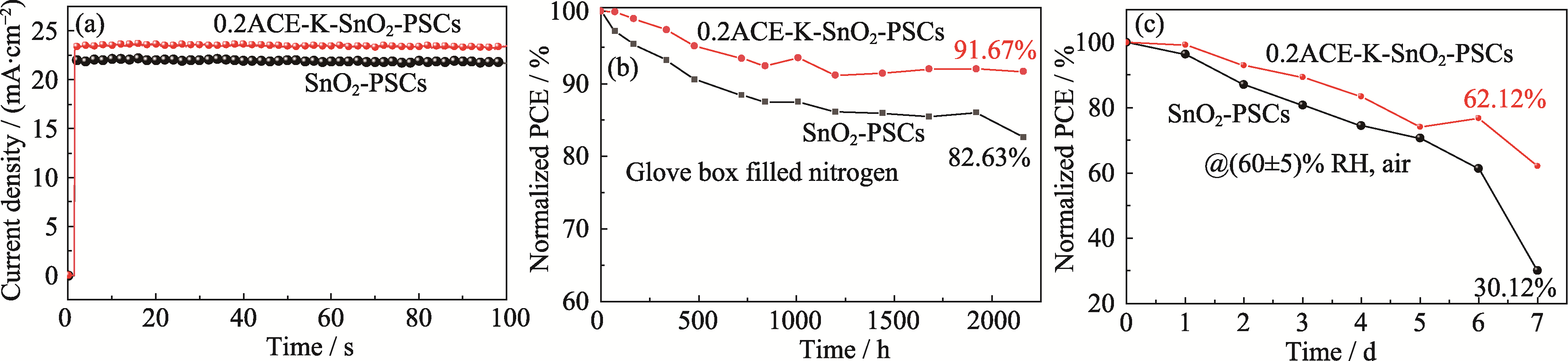
图8 SnO2-PSCs和0.2ACE-K-SnO2-PSCs的(a) 100 s电流稳定性曲线、(b)长期稳定性曲线、(c)湿度稳定性曲线
Fig. 8 (a) Current stability curves during 100 s, (b) long-term stability curves and (c) humidity stability curves of SnO2-PSCs and 0.2ACE-K-SnO2-PSCs
| Sample | Rs/Ω | Rct/Ω | Rrec/Ω | C1/(×10-9, F) | C2/(×10-8, F) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SnO2-PSCs | 23.3 | 53972 | 136090 | 5.0 | 8.52 |
| 0.2ACE-K-SnO2-PSCs | 17.79 | 38465 | 154690 | 3.96 | 6.7 |
表S1 EIS曲线的拟合数据
Table S1 Fitting data for EIS curves
| Sample | Rs/Ω | Rct/Ω | Rrec/Ω | C1/(×10-9, F) | C2/(×10-8, F) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SnO2-PSCs | 23.3 | 53972 | 136090 | 5.0 | 8.52 |
| 0.2ACE-K-SnO2-PSCs | 17.79 | 38465 | 154690 | 3.96 | 6.7 |
| [1] |
JEONG J, KIM M, SEO J, et al. Pseudo-halide anion engineering for α-FAPbI3 perovskite solar cells. Nature, 2021, 592(7854): 381.
DOI |
| [2] |
LIU Z H, QIU L B, ONO L K, et al. A holistic approach to interface stabilization for efficient perovskite solar modules with over 2,000-hour operational stability. Nature Energy, 2020, 5(8): 596.
DOI |
| [3] |
BU T L, LI J, LI H Y, et al. Lead halide-templated crystallization of methylamine-free perovskite for efficient photovoltaic modules. Science, 2021, 372(6548): 1327.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
KOJIMA A, TESHIMA K, SHIRAI Y, et al. Organometal halide perovskites as visible-light sensitizers for photovoltaic cells. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2009, 131(17): 6050.
DOI PMID |
| [5] | NREL. Best research-cell efficiency chart. [2025-05-05]. https://www.nrel.gov/pv/cell-efficiency.html. |
| [6] |
ZHANG H L, JI X, YAO H Y, et al. Review on efficiency improvement effort of perovskite solar cell. Solar Energy, 2022, 233: 421.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
HAGHIGHI M, GHAZYANI N, MAHMOODPOUR S, et al. Low-temperature processing methods for tin oxide as electron transporting layer in scalable perovskite solar cells. Solar RRL, 2023, 7(10): 2201080.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
TROST S, BEHRENDT A, BECKER T, et al. Tin oxide (SnOx) as universal "light-soaking" free electron extraction material for organic solar cells. Advanced Energy Materials, 2015, 5(17): 1500277.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
ZHANG J J, FU J F, CHEN Q Y, et al. 3,5-Difluorophenylboronic acid-modified SnO2 as ETLs for perovskite solar cells: PCE>22.3%, T82>3000 h. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 433: 133744.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
ALTINKAYA C, AYDIN E, UGUR E, et al. Tin oxide electron- selective layers for efficient, stable, and scalable perovskite solar cells. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(15): 2005504.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
GODINHO K G, WALSH A, WATSON G W. Energetic and electronic structure analysis of intrinsic defects in SnO2. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2009, 113(1): 439.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
PARIDA B, JIN I S, JUNG J W. Dual passivation of SnO2 by tetramethylammonium chloride for high-performance CsPbI2Br- based inorganic perovskite solar cells. Chemistry of Materials, 2021, 33(15): 5850.
DOI URL |
| [13] | DONG H Y, WANG J L, LI X Y, et al. Modifying SnO2 with polyacrylamide to enhance the performance of perovskite solar cells. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(29): 34143. |
| [14] |
XIA H R, LI X, ZHOU J Y, et al. Interfacial chemical bridge constructed by zwitterionic sulfamic acid for efficient and stable perovskite solar cells. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2020, 3(4): 3186.
DOI URL |
| [15] | CHOI K, LEE J, KIM H I, et al. Thermally stable, planar hybrid perovskite solar cells with high efficiency. Energy & Environmental Science, 2018, 11(11): 3238. |
| [16] |
YANG D, YANG R X, WANG K, et al. High efficiency planar- type perovskite solar cells with negligible hysteresis using EDTA- complexed SnO2. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 3239.
DOI |
| [17] |
FU P, HUANG L Q, YU W, et al. Efficiency improved for inverted polymer solar cells with electrostatically self-assembled BenMelm- Cl ionic liquid layer as cathode interface layer. Nano Energy, 2015, 13: 275.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
HUANG X K, HU Z Y, XU J, et al. Low-temperature processed SnO2 compact layer by incorporating TiO2 layer toward efficient planar heterojunction perovskite solar cells. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2017, 164: 87.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
AN Z Q, CHEN S Y, LU T, et al. Interfacial modification via aniline molecules with multiple active sites for performance enhancement of n-i-p perovskite solar cells. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2023, 11(37): 12750.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
BI H, GUO Y, GUO M N, et al. Highly efficient and low hysteresis methylammonium-free perovskite solar cells based on multifunctional oteracil potassium interface modification. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 439: 135671.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
BOB B, SONG T B, CHEN C C, et al. Nanoscale dispersions of gelled SnO2: material properties and device applications. Chemistry of Materials, 2013, 25(23): 4725.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
HUANG H, CUI P, CHEN Y, et al. 24.8%-efficient planar perovskite solar cells via ligand-engineered TiO2 deposition. Joule, 2022, 6(9): 2186.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
PENG X, LU H L, ZHUANG J, et al. Enhanced performance of perovskite solar cells using DNA-doped mesoporous-TiO2 as electron transporting layer. Solar Energy, 2020, 206: 855.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
YOU S, ZENG H P, KU Z L, et al. Multifunctional polymer-regulated SnO2 nanocrystals enhance interface contact for efficient and stable planar perovskite solar cells. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(43): 2003990.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
QIU Z W, GONG H B, ZHENG G H J, et al. Enhanced physical properties of pulsed laser deposited NiO films via annealing and lithium doping for improving perovskite solar cell efficiency. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2017, 5(28): 7084.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
ZHAO S H, QIN M C, WANG H, et al. Cascade type-II 2D/3D perovskite heterojunctions for enhanced stability and photovoltaic efficiency. Solar RRL, 2020, 4(10): 2000282.
DOI URL |
| [27] | MA Z, ZHOU W Y, HUANG D J, et al. Nicotinamide as additive for microcrystalline and defect passivated perovskite solar cells with 21.7% efficiency. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(47): 52500. |
| [28] |
LIU W, LIU N J, JI S L, et al. Perfection of perovskite grain boundary passivation by rhodium incorporation for efficient and stable solar cells. Nano-Micro Letters, 2020, 12(1): 119.
DOI PMID |
| [29] |
YANG Z R, XIE J S, ARIVAZHAGAN V, et al. Efficient and highly light stable planar perovskite solar cells with graphene quantum dots doped PCBM electron transport layer. Nano Energy, 2017, 40: 345.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 肖梓晨, 何世豪, 邱诚远, 邓攀, 张威, 戴维德仁, 缑炎卓, 李金华, 尤俊, 王贤保, 林俍佑. 钙钛矿太阳能电池纳米纤维改性电子传输层研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 828-834. |
| [2] | 张慧, 许志鹏, 朱从潭, 郭学益, 杨英. 大面积有机-无机杂化钙钛矿薄膜及其光伏应用研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(5): 457-466. |
| [3] | 陈甜, 罗媛, 朱刘, 郭学益, 杨英. 有机-无机共添加增强柔性钙钛矿太阳能电池机械弯曲及环境稳定性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(5): 477-484. |
| [4] | 于嫚, 高荣耀, 秦玉军, 艾希成. 上转换发光纳米材料对钙钛矿太阳能电池迟滞效应和离子迁移动力学的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(4): 359-366. |
| [5] | 刘锁兰, 栾福园, 吴子华, 寿春晖, 谢华清, 杨松旺. 原位生长钙钛矿太阳能电池共形氧化锡薄膜[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(12): 1397-1403. |
| [6] | 周泽铸, 梁子辉, 李静, 吴聪聪. 基于挥发性溶剂制备MAPbI3钙钛矿太阳能电池/模组[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(11): 1197-1204. |
| [7] | 厉佥元, 李纪伟, 张钰涵, 刘焱康, 孟阳, 储余, 朱一佳, 徐诺言, 朱亮, 张传香, 陶海军. PbTiO3修饰和极化处理提升钙钛矿太阳能电池性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(11): 1205-1211. |
| [8] | 韩旭, 姚恒大, 吕梅, 陆红波, 朱俊. 单分子液晶添加剂在甲脒铅碘钙钛矿太阳能电池中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(9): 1097-1102. |
| [9] | 方万丽, 沈黎丽, 李海艳, 陈薪羽, 陈宗琦, 寿春晖, 赵斌, 杨松旺. NiOx介孔层的成膜过程对碳电极钙钛矿太阳能电池性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(9): 1103-1109. |
| [10] | 丁统顺, 丰平, 孙学文, 单沪生, 李琪, 宋健. Fmoc-FF-OH钝化钙钛矿薄膜及其太阳能电池性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(9): 1076-1082. |
| [11] | 陈雨, 林埔安, 蔡冰, 张文华. 钙钛矿太阳能电池无机空穴传输材料的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(9): 991-1004. |
| [12] | 张万文, 罗建强, 刘淑娟, 马建国, 张小平, 杨松旺. 氧化锆间隔层的低温喷涂制备及其三层结构钙钛矿太阳能电池应用性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(2): 213-218. |
| [13] | 马婷婷, 汪志鹏, 张梅, 郭敏. 超长稳定的混合阳离子钙钛矿太阳能电池性能优化研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(12): 1387-1395. |
| [14] | 王烨, 焦忆楠, 郭军霞, 刘欢, 李睿, 尚子璇, 张士东, 王永浩, 耿海川, 侯登录, 赵晋津. 钙钛矿太阳能电池界面工程优化研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(11): 1323-1330. |
| [15] | 焦博新, 刘兴翀, 全子威, 彭永姗, 周若男, 李海敏. L-精氨酸掺杂钙钛矿太阳电池性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(6): 669-675. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||