无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (11): 1252-1260.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250045 CSTR: 32189.14.jim20250045
吴明轩1,2( ), 李珺杰1,2(
), 李珺杰1,2( ), 陈硕1,2, 鄢永高1,2, 苏贤礼1,2(
), 陈硕1,2, 鄢永高1,2, 苏贤礼1,2( ), 张清杰2, 唐新峰1,2
), 张清杰2, 唐新峰1,2
收稿日期:2025-02-07
修回日期:2025-05-14
出版日期:2025-11-20
网络出版日期:2025-06-05
通讯作者:
苏贤礼, 研究员. E-mail: suxianli@whut.edu.cn;作者简介:吴明轩(2000-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: krenwu_u@whut.edu.cn
基金资助:
WU Mingxuan1,2( ), LI Junjie1,2(
), LI Junjie1,2( ), CHEN Shuo1,2, YAN Yonggao1,2, SU Xianli1,2(
), CHEN Shuo1,2, YAN Yonggao1,2, SU Xianli1,2( ), ZHANG Qingjie2, TANG Xinfeng1,2
), ZHANG Qingjie2, TANG Xinfeng1,2
Received:2025-02-07
Revised:2025-05-14
Published:2025-11-20
Online:2025-06-05
Contact:
SU Xianli, professor. E-mail: suxianli@whut.edu.cn;About author:WU Mingxuan (2000-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: krenwu_u@whut.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
区熔制备技术是商业化制备Bi2Te3基热电材料的重要方法, 区熔纯化过程受材料分凝的影响, 但迄今为止, 区熔工艺对Bi2Te3基材料分凝机制影响的研究尚未形成统一认识, 特别是材料组元增加后会显著影响分凝过程和均匀性。本研究以n型Bi1.96Sb0.04Te2.694Se0.3Br0.006材料为研究对象, 采用熔融-区熔-退火工艺, 系统探讨了区熔温度对材料组成和热电性能均匀性的影响规律, 发现区熔温度对棒材均匀性有很大影响, 轴向组成分凝是影响其均匀性的重要因素, 在高区熔温度(≥988 K)下, 棒材顶部出现了Bi2Te3富集相的分凝, 这种组成分凝现象导致材料热电性能的均匀性变差。区熔温度为988和1003 K样品的室温ZT在不同区域(中心顶部、边缘顶部(ET)、中心底部、边缘底部)最大差异达到了31.5%和28.6%。降低区熔温度至958 K显著抑制了Bi2Te3富集相分凝, 制备得到具有优异热电性能和均匀性的圆柱型锭体(内径16 mm, 高55 mm), 样品不同区域的室温ZT最大差异仅为14%, 并且958 K-ET样品在350 K下获得最大ZT为1.05。本研究揭示了区熔温度对多组元n型(Bi, Sb)2(Te, Se)3基材料组成成分及热电性能均匀性的调控机制, 为制备具有优异均匀性的高性能热电材料提供了重要指导。
中图分类号:
吴明轩, 李珺杰, 陈硕, 鄢永高, 苏贤礼, 张清杰, 唐新峰. 区熔n型Bi1.96Sb0.04Te2.70Se0.30热电材料均匀性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(11): 1252-1260.
WU Mingxuan, LI Junjie, CHEN Shuo, YAN Yonggao, SU Xianli, ZHANG Qingjie, TANG Xinfeng. Homogeneity of Zone-melted n-type Bi1.96Sb0.04Te2.70Se0.30 Thermoelectric Material[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(11): 1252-1260.

图2 (a) 958、(b) 973、(c) 988和(d) 1003 K区熔温度制备的Bi1.96Sb0.04Te2.694Se0.3Br0.006不同区域样品的σ、S和PF
Fig. 2 σ, S and PF of different regions in Bi1.96Sb0.04Te2.694Se0.3Br0.006 with zone melting temperatures of (a) 958, (b) 973, (c) 988, and (d) 1003 K

图3 Bi1.96Sb0.04Te2.694Se0.3Br0.006样品的(a, d)热导率κ, (b, e) κL+κb和(c, f) ZT
Fig.3 (a, d) Thermal conductivities κ, (b, e) κL+κb and (c, f) ZT of Bi1.96Sb0.04Te2.694Se0.3Br0.006 samples

图5 不同区熔温度制备的Bi1.96Sb0.04Te2.694Se0.3Br0.006不同区域样品的Bi/Sb和Te/Se变化趋势
Fig. 5 Variation trends of Bi/Sb and Te/Se of different regions in Bi1.96Sb0.04Te2.694Se0.3Br0.006 samples prepared under different zone melting temperatures Colorful figures are available on website
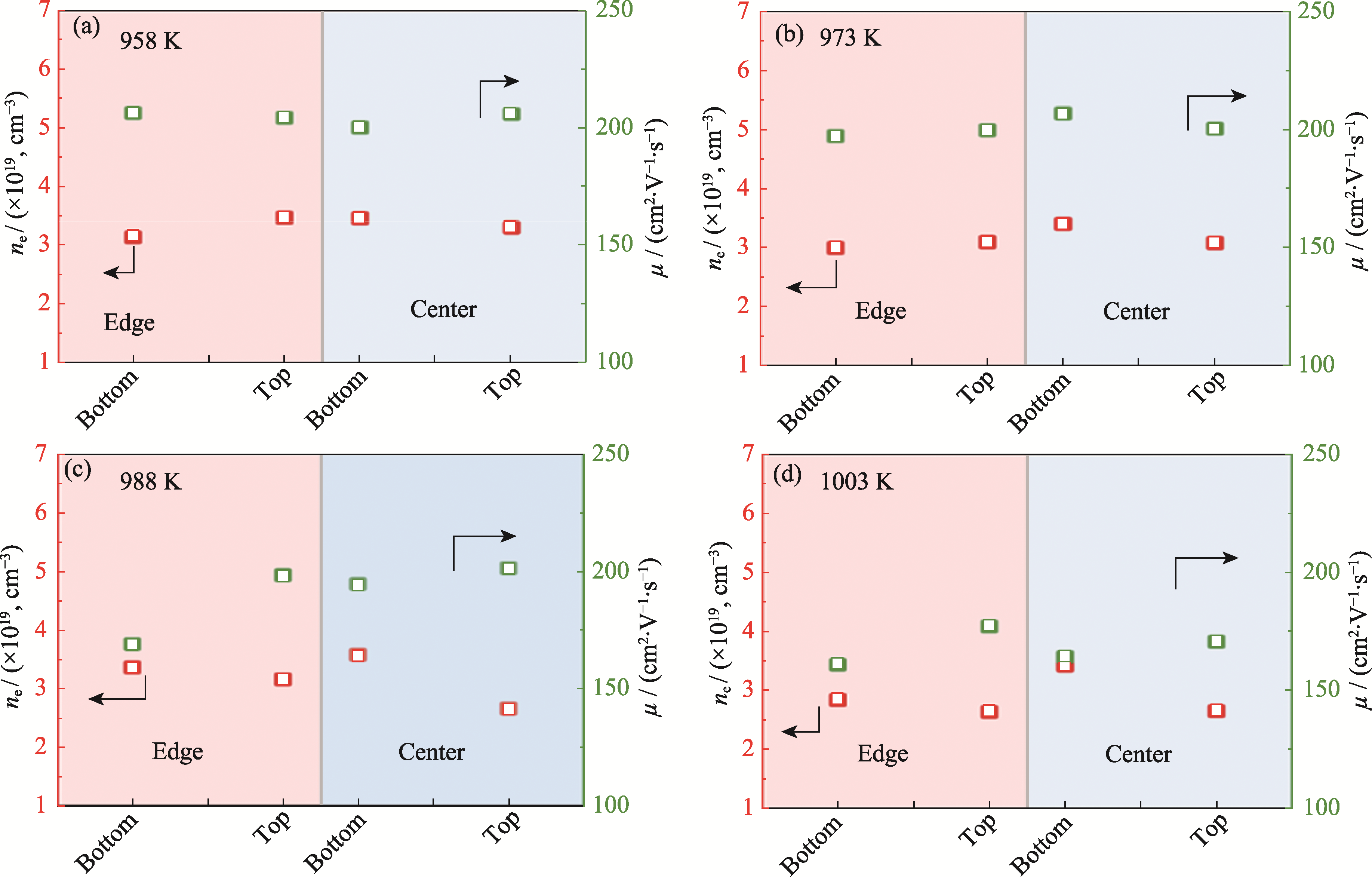
图6 不同区熔温度制备的Bi1.96Sb0.04Te2.694Se0.3Br0.006不同区域样品的ne和μ
Fig. 6 ne and μ of different regions in Bi1.96Sb0.04Te2.694Se0.3Br0.006 samples prepared under different zone melting temperatures
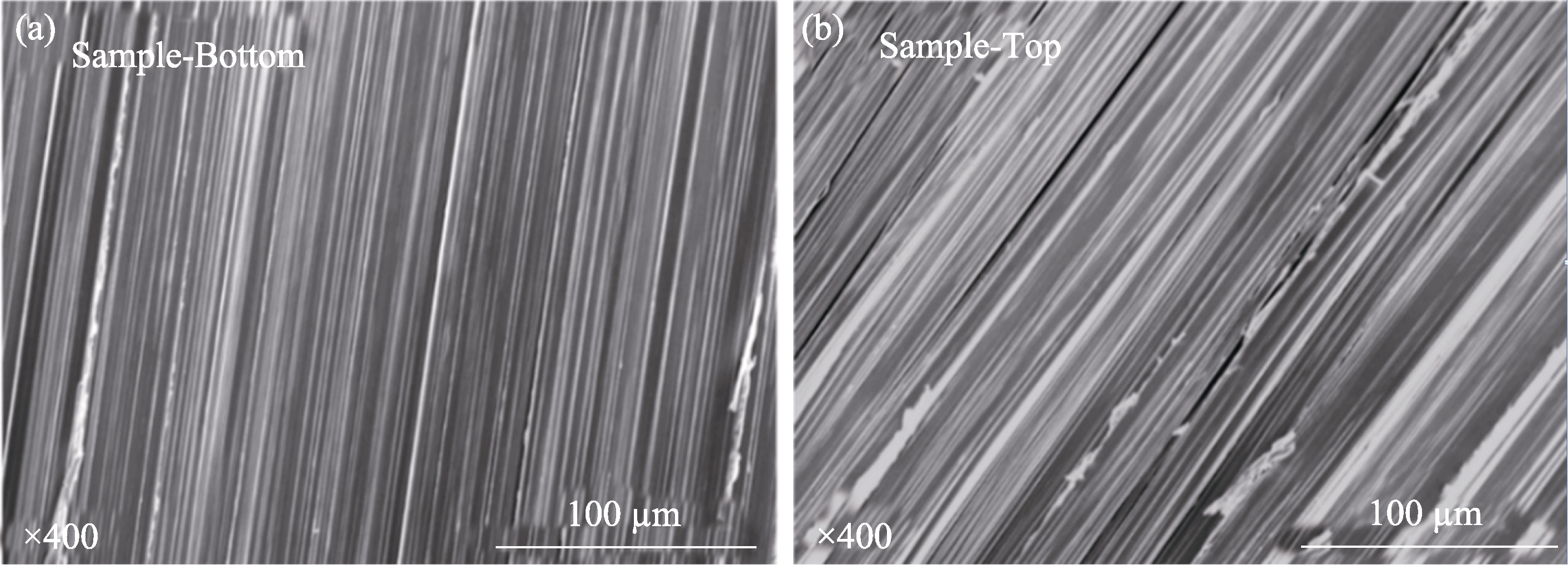
图S1 (a) 1003 K-CB和(b) 1003 K-CT样品的自由断裂截面FESEM照片
Fig. S1 Cross-sectional FESEM images of the free fracture cross sections of (a) 1003 K-CB and (b) 1003 K-CT samples
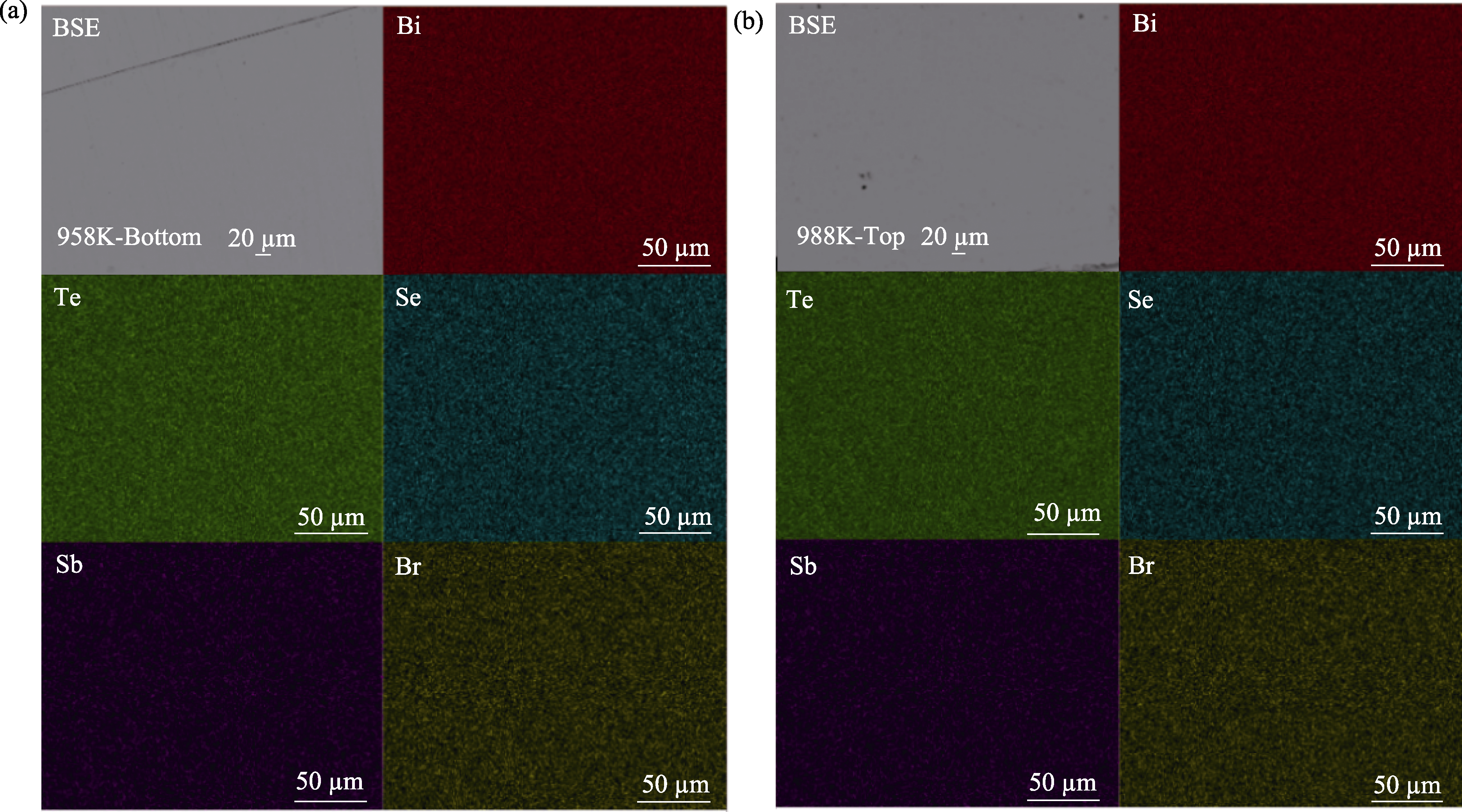
图S2 (a) 958 K-Bottom和(b) 988 K-Top样品的抛光表面BSE图像及对应区域Bi、Sb、Se、Te和Br元素面分布图
Fig. S2 BSE images of polished surface and surface distributions of Bi, Sb, Se, Te and Br elements in the corresponding regions for (a) 958 K-Bottom and (b) 988 K-Top
| Sample | σ/(×104, S·m−1) | S/(μV·K-1) | κ/(W·m-1·K-1) | ZT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 958 K-CB | 11.1 | -186 | 1.37 | 0.86 |
| 958 K-CT | 10.9 | -195 | 1.43 | 0.89 |
| 958 K-EB | 10.4 | -195 | 1.38 | 0.88 |
| 958 K-ET | 11.4 | -199 | 1.42 | 0.98 |
| 973 K-CB | 11.2 | -197 | 1.50 | 0.89 |
| 973 K-CT | 9.86 | -201 | 1.48 | 0.82 |
| 973 K-EB | 9.45 | -196 | 1.50 | 0.74 |
| 973 K -ET | 9.88 | -204 | 1.48 | 0.85 |
| 988 K-CB | 11.1 | -205 | 1.47 | 0.96 |
| 988 K-CT | 8.54 | -202 | 1.44 | 0.73 |
| 988 K-EB | 9.98 | -200 | 1.48 | 0.76 |
| 988 K-ET | 9.05 | -201 | 1.43 | 0.86 |
| 1003 K-CB | 9.00 | -206 | 1.47 | 0.80 |
| 1003 K-CT | 7.27 | -216 | 1.39 | 0.74 |
| 1003 K-EB | 7.34 | -202 | 1.47 | 0.63 |
| 1003 K-ET | 7.51 | -214 | 1.39 | 0.76 |
表S1 Bi1.96Sb0.04Te2.694Se0.3Br0.006样品在室温下的σ、S、κ和ZT
Table S1 σ, S, κ and ZT of Bi1.96Sb0.04Te2.694Se0.3Br0.006 samples at room temperature
| Sample | σ/(×104, S·m−1) | S/(μV·K-1) | κ/(W·m-1·K-1) | ZT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 958 K-CB | 11.1 | -186 | 1.37 | 0.86 |
| 958 K-CT | 10.9 | -195 | 1.43 | 0.89 |
| 958 K-EB | 10.4 | -195 | 1.38 | 0.88 |
| 958 K-ET | 11.4 | -199 | 1.42 | 0.98 |
| 973 K-CB | 11.2 | -197 | 1.50 | 0.89 |
| 973 K-CT | 9.86 | -201 | 1.48 | 0.82 |
| 973 K-EB | 9.45 | -196 | 1.50 | 0.74 |
| 973 K -ET | 9.88 | -204 | 1.48 | 0.85 |
| 988 K-CB | 11.1 | -205 | 1.47 | 0.96 |
| 988 K-CT | 8.54 | -202 | 1.44 | 0.73 |
| 988 K-EB | 9.98 | -200 | 1.48 | 0.76 |
| 988 K-ET | 9.05 | -201 | 1.43 | 0.86 |
| 1003 K-CB | 9.00 | -206 | 1.47 | 0.80 |
| 1003 K-CT | 7.27 | -216 | 1.39 | 0.74 |
| 1003 K-EB | 7.34 | -202 | 1.47 | 0.63 |
| 1003 K-ET | 7.51 | -214 | 1.39 | 0.76 |
| [1] |
YANG D, XING Y, WANG J, et al. Multifactor roadmap for designing low-power-consumed micro thermoelectric thermostats in a closed-loop integrated 5G optical module. Interdisciplinary Materials, 2024, 3(2): 326.
DOI URL |
| [2] | 范人杰, 江先燕, 陶奇睿, 等. In1+xTe化合物的结构及热电性能研究. 物理学报, 2021, 70(13): 393. |
| [3] |
LIU Z, HONG T, XU L, et al. Lattice expansion enables interstitial doping to achieve a high average ZT in n-type PbS. Interdisciplinary Materials, 2023, 2(1): 161.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
QIU J, YAN Y, XIE H, et al. Achieving superior performance in thermoelectric Bi0.4Sb1.6Te3.72 by enhancing texture and inducing high-density line defects. Science China Materials, 2021, 64: 1507.
DOI |
| [5] | 唐新峰, 柳伟, 谭刚健, 等. 热电材料物理化学. 北京: 科学出版社, 2024: 1-30. |
| [6] | 陈立东, 刘睿恒, 史迅. 热电材料与器件. 北京: 科学出版社, 2018: 1-18. |
| [7] | 张建中. 温差电技术. 电源技术, 2016(3): 754. |
| [8] |
LIN L, ZHANG Y F, LIU H B, et al. A new configuration design of thermoelectric cooler driven by thermoelectric generator. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2019, 160: 114087.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
LIU W D, WANG D Z, LIU Q, et al. High-performance GeTe- based thermoelectrics: from materials to devices. Advanced Energy Materials, 2020, 10(19): 2000367.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
TAN G, ZHAO L D, KANATZIDIS M G. Rationally designing high-performance bulk thermoelectric materials. Chemical Reviews, 2016, 116(19): 12123.
PMID |
| [11] |
HE J, TRITT T M. Advances in thermoelectric materials research: looking back and moving forward. Science, 2017, 357(6358): eaak9997.
DOI URL |
| [12] | ROWE D M. Thermoelectrics handbook:macro to nano. Boston: CRC press, 2018: 1008. |
| [13] | 訾鹏, 白辉, 汪聪, 等. AgyIn3.33-y/3Se5化合物结构和热电性能. 物理学报, 2022, 71(11): 326. |
| [14] |
XIE H, ZHAO L D, KANATZIDIS M G. Lattice dynamics and thermoelectric properties of diamondoid materials. Interdisciplinary Materials, 2024, 3(1): 5.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
HUANG Y, LYU T, ZENG M, et al. Manipulation of metavalent bonding to stabilize metastable phase: a strategy for enhancing ZT in GeSe. Interdisciplinary Materials, 2024: 3(4): 607.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
YANG D, LUO T, SU X, et al. Unveiling the intrinsic low thermal conductivity of BiAgSeS through entropy engineering in SHS kinetic process. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(9): 991.
DOI |
| [17] |
GONG H, SU X L, YAN Y G, et al. Ultra-fast synthesis of Cu2S thermoelectric materials under pulsed electric field. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(12): 1295.
DOI |
| [18] |
PEIAN R, CONG W, PENG Z, et al. Effect of Te and In co-doping on thermoelectric properties of Cu2SnSe3 compounds. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(10): 1079.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
YANG J, CAILLAT T. Thermoelectric materials for space and automotive power generation. MRS Bulletin, 2006, 31(3): 224.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
WANG W C, CHANG Y L. Experimental investigation of thermal deformation in thermoelectric coolers. Strain, 2011, 47: 232.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
SNYDER G J, URSELL T S. Thermoelectric efficiency and compatibility. Physical Review Letters, 2003, 91(14): 148301.
DOI URL |
| [22] | SNYDER G J, SNYDER A H. Figure of merit ZT of a thermoelectric device defined from materials properties. Energy & Environmental Science, 2017, 10(11): 2280. |
| [23] |
郭凯, 骆军, 赵景泰. 热电材料的基本原理, 关键问题及研究进展. 自然杂志, 2015, 37(3): 175.
DOI |
| [24] | 唐昊, 白辉, 吕嘉南, 等. 表面修饰工程协同优化Bi2Te3基微型热电器件的界面性能. 物理学报, 2022, 71(16): 330. |
| [25] |
YANG X, SU X L, YAN Y G, et al. Structures and thermoelectric properties of (GeTe)(n)Bi2Te3. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(1): 75.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
CHEN Y, SHI Q, ZHONG Y, et al. Ga intercalation in van der Waals layers for advancing p-type Bi2Te3-based thermoelectrics. Chinese Physics B, 2023, 32(6): 067201.
DOI |
| [27] |
CHI H, LIU W, SUN K, et al. Low-temperature transport properties of Tl-doped Bi2Te3 single crystals. Physical Review B—Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 2013, 88(4): 045202.
DOI URL |
| [28] | LIU F, ZHANG M, NAN P, et al. Unraveling the origin of donor- like effect in bismuth-telluride-based thermoelectric materials. Small Science, 2023, 3(8): 2300082. |
| [29] |
LIU D, BAI S, WEN Y, et al. Lattice plainification and band engineering lead to high thermoelectric cooling and power generation in n-type Bi2Te3 with mass production. National Science Review, 2025, 12(2): nwae448.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
ZHANG Z, SUN M, LIU J, et al. Ultra-fast fabrication of Bi2Te3 based thermoelectric materials by flash-sintering at room temperature combining with spark plasma sintering. Scientific Reports, 2022, 12: 10045.
DOI |
| [31] |
CHEN C, WANG B, YING P, et al. Microstructure engineered Bi2Te3-based materials with outstanding mechanical and thermoelectric properties. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2025, 1020: 179543.
DOI URL |
| [32] | SHI Q, LI J, ZHAO X, et al. Comprehensive insight into p-type Bi2Te3-based thermoelectrics near room temperature. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(44): 49425. |
| [33] |
LU Z Q, LIU K K, LI Q, et al. Donor-like effect and thermoelectric performance in p-type Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3 alloy. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(11): 1331.
DOI URL |
| [34] | 李强, 陈硕, 刘可可, 等. n型Bi2Te3基化合物的类施主效应和热电性能. 物理学报, 2023, 72(9): 135. |
| [35] |
ZHANG Q, FANG T, LIU F, et al. Tuning optimum temperature range of Bi2Te3-based thermoelectric materials by defect engineering. Chemistry-An Asian Journal, 2020, 15(18): 2775.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
HUANG W, TAN X, CAI J, et al. Synergistic effects improve thermoelectric properties of zone-melted n-type Bi2Te2.7Se0.3. Materials Today Physics, 2023, 32: 101022.
DOI URL |
| [37] | 田源, 汪波, 李存成, 等. 区熔n型碲化铋材料的制备及性能优化. 材料科学与工程学报, 2024, 42(2): 186. |
| [38] |
LIU D, STÖTZEL J, SEYRING M, et al. Anisotropic n-type Bi2Te3-In2Te3 thermoelectric material produced by seeding zone melting and solid state transformation. Crystal Growth & Design, 2016, 16(2): 617.
DOI URL |
| [39] | WANG T, ZHOU C, HUANG W, et al. Synergistic improvement of BiI3 and In on thermoelectric properties of zone-melted n-type Bi2Te2.7Se0.3. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2024, 16(31): 41080. |
| [40] |
LIU D, LI X, BORLIDO P M D C, et al. Anisotropic layered Bi2Te3-In2Te3 composites: control of interface density for tuning of thermoelectric properties. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 43611.
DOI |
| [41] |
HA H P, HYUN D B, BYUN J Y, et al. Enhancement of the yield of high-quality ingots in the zone-melting growth of p-type bismuth telluride alloys. Journal of Materials Science, 2002, 37(21): 4691.
DOI |
| [42] |
KIM H S, HEINZ N A, GIBBS Z M, et al. High thermoelectric performance in (Bi0.25Sb0.75)2Te3 due to band convergence and improved by carrier concentration control. Materials Today, 2017, 20(8): 452.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
PERRIN D, CHITROUB M, SCHERRER S, et al. Study of the n-type Bi2Te2.7Se0.3 doped with bromine impurity. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 2000, 61(10): 1687.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
KAVEI G, KARAMI M. Thermoelectric crystals Bi2Te2.88Se0.12 undoped and doped by CdCl2 or CdBr2 impurities, fabricated and characterized by XRD and Hall effect. Materials Research Bulletin, 2008, 43(2): 239.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
CHEN Y R, HWANG W S, HSIEH H L, et al. Thermal and microstructure simulation of thermoelectric material Bi2Te3 grown by zone- melting technique. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2014, 402: 273.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
KAVEI G, AHMADI K, KAVEI A. Electrical conductivity variation of (Bi2Te3)0.25(Sb2Te3)0.75 crystal grown using the zone melting method. International Journal of Materials Research, 2013, 104(3): 314.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
XIA H, LI X, XU Q. Macro-micro-coupling simulation and space experiment study on zone melting process of bismuth telluride-based crystal materials. Metals, 2022, 12(5): 886.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
GUO X, QIN J, JIA X, et al. Quaternary thermoelectric materials: synthesis, microstructure and thermoelectric properties of the (Bi,Sb)2(Te,Se)3 alloys. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 705: 363.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
CHAUHAN N S, PYRLIN S V, LEBEDEV O I, et al. Compositional fluctuations mediated by excess tellurium in bismuth antimony telluride nanocomposites yield high thermoelectric performance. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2021, 125(37): 20184.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
LIU Y, ZHANG Y, LIM K H, et al. High thermoelectric performance in crystallographically textured n-type Bi2Te3-xSex produced from asymmetric colloidal nanocrystals. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(7): 7174.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
VASIL’EV A, IVANOV O, YAPRYNTSEV M, et al. Aspects of the microstructure and thermoelectric properties of a two-phase ceramic material based on the high-entropy system Bi-Sb-Te-Se-S. Glass and Ceramics, 2023, 80(1): 52.
DOI |
| [52] |
CHEN H W, CHEN B C, WU H J. Dilute Sb doping yields softer p-type Bi2Te3 thermoelectrics. Advanced Electronic Materials, 2024, 10(6): 2300793.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
GUAN X, LIU Z, MA N, et al. High-performance p-type Bi2Te3- based thermoelectric materials with a wide temperature range obtained by direct Sb doping. Acta Metallurgica Sinica (English Letters), 2025, 38: 849.
DOI |
| [54] | WITTING I T, RICCI F, CHASAPIS T C, et al. The thermoelectric properties of n-type bismuth telluride: bismuth selenide alloys Bi2Te3-xSex. Research, 2020, 2020: 4361703. |
| [55] |
LI Y, BAI S, WEN Y, et al. Realizing high-efficiency thermoelectric module by suppressing donor-like effect and improving preferred orientation in n-type Bi2(Te,Se)3. Science Bulletin, 2024, 69(11): 1728.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 吴华鑫, 张骐昊, YAN Haixue, 王连军, 江莞. 纳米复合MgAgSb基合金的热电输运性能优化[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(9): 997-1004. |
| [2] | 缪鹏程, 王丽君, 沈紫怡, 黄莉, 袁宁一, 丁建宁. 微球状Ag2Se的溶剂热合成及其热电性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(12): 1373-1378. |
| [3] | 郑元顺, 余健, 叶先峰, 梁栋, 朱婉婷, 聂晓蕾, 魏平, 赵文俞, 张清杰. V取代Al位提升全赫斯勒合金Fe2VAl的热电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(12): 1425-1432. |
| [4] | 薛轶凡, 李玮洁, 张中伟, 庞旭, 刘愚. 碳纤维布表面PyC界面相微观结构及均匀性的工艺调控[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(4): 399-408. |
| [5] | 汪波, 余健, 李存成, 聂晓蕾, 朱婉婷, 魏平, 赵文俞, 张清杰. Gd/Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3热电磁梯度复合材料的服役稳定性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 663-670. |
| [6] | 贺丹琪, 魏明旭, 刘蕤之, 汤志鑫, 翟鹏程, 赵文俞. 一步法制备重费米子YbAl3热电材料及其性能提升[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 577-582. |
| [7] | 林思琪, 李艾燃, 付晨光, 李荣斌, 金敏. Zintl相Mg3X2(X=Sb, Bi)基晶体生长及热电性能研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 270-279. |
| [8] | 产思义, 屠菊萍, 黄珂, 邵思武, 杨志亮, 刘鹏, 刘金龙, 陈良贤, 魏俊俊, 安康, 郑宇亭, 李成明. 2英寸MPCVD光学级均匀金刚石膜的制备研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(12): 1413-1419. |
| [9] | 鲁志强, 刘可可, 李强, 胡芹, 冯利萍, 张清杰, 吴劲松, 苏贤礼, 唐新峰. p型多晶Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3合金类施主效应与热电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(11): 1331-1337. |
| [10] | 江润璐, 吴鑫, 郭昊骋, 郑琦, 王连军, 江莞. UiO-67基导电复合材料的制备及其热电性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(11): 1338-1344. |
| [11] | 邓陶丽, 陈河莘, 黑玲丽, 李淑星, 解荣军. 第二相引入荧光转换材料实现激光驱动高均匀性白光光源[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(8): 891-896. |
| [12] | 程成, 李建波, 田震, 王鹏将, 康慧君, 王同敏. In2O3/InNbO4复合材料的热电性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 724-730. |
| [13] | 刘丹, 赵亚欣, 郭锐, 刘艳涛, 张志东, 张增星, 薛晨阳. 退火条件对磁控溅射MgO-Ag3Sb-Sb2O4柔性薄膜热电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(12): 1302-1310. |
| [14] | 任培安, 汪聪, 訾鹏, 陶奇睿, 苏贤礼, 唐新峰. Te与In共掺杂对Cu2SnSe3热电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(10): 1079-1086. |
| [15] | 逯旭, 侯绩翀, 张强, 樊建锋, 陈少平, 王晓敏. Mg含量对Mg3(1+z)Sb2化合物热电传输性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(8): 835-840. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||