无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (9): 1005-1012.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240499 CSTR: 32189.14.jim20240499
闫共芹1,2( ), 王晨1, 蓝春波1,2, 洪雨昕1, 叶维超1, 付向辉1
), 王晨1, 蓝春波1,2, 洪雨昕1, 叶维超1, 付向辉1
收稿日期:2024-12-02
修回日期:2025-02-03
出版日期:2025-09-20
网络出版日期:2025-03-06
作者简介:闫共芹(1982-), 男, 副教授. E-mail: ygq@gxust.edu.cn
基金资助:
YAN Gongqin1,2( ), WANG Chen1, LAN Chunbo1,2, HONG Yuxin1, YE Weichao1, FU Xianghui1
), WANG Chen1, LAN Chunbo1,2, HONG Yuxin1, YE Weichao1, FU Xianghui1
Received:2024-12-02
Revised:2025-02-03
Published:2025-09-20
Online:2025-03-06
About author:YAN Gongqin (1982-), male, associate professor. E-mail: ygq@gxust.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
钠离子电池(SIBs)具有低廉的成本和良好的安全性, 在储能领域极具发展前景, 有望替代锂离子电池。P2型Ni/Mn基氧化物具有高理论容量和宽工作电压的优点, 然而, 高压下P2-O2相变和Jahn-Teller畸变严重影响了循环可逆性和结构稳定性。针对上述问题, 本研究通过高温固相法制备了不同Al掺杂量的P2型Na0.8Ni0.33Mn0.67-xAlxO2, 并将其用作SIBs正极材料, 表征了它们的形貌、成分、元素价态和结构特征。研究发现, Al掺杂增强了金属-氧键(M-O键), 增大了Na层距离, 有助于Na+扩散和结构稳定。电化学性能测试结果表明, Al掺杂可以抑制高压相变, 触发Mn的电化学活性, 降低电荷转移电阻, 从而增强材料的电化学性能。其中, Na0.8Ni0.33Mn0.62Al0.05O2正极表现出最佳的循环性能, 在2.0~4.2 V范围内和0.1C(1C=200 mA·g-1)条件下循环200 次后容量保持率为87.3%, 并且具有良好的倍率性能, 在2.0~4.2 V范围内和2C条件下放电比容量达到100.9 mAh·g-1。
中图分类号:
闫共芹, 王晨, 蓝春波, 洪雨昕, 叶维超, 付向辉. Al掺杂P2型Na0.8Ni0.33Mn0.67-xAlxO2钠离子电池正极材料的制备与电化学性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(9): 1005-1012.
YAN Gongqin, WANG Chen, LAN Chunbo, HONG Yuxin, YE Weichao, FU Xianghui. Al-doped P2-type Na0.8Ni0.33Mn0.67-xAlxO2 as Cathode for Sodium-ion Batteries: Synthesis and Electrochemical Properties[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(9): 1005-1012.
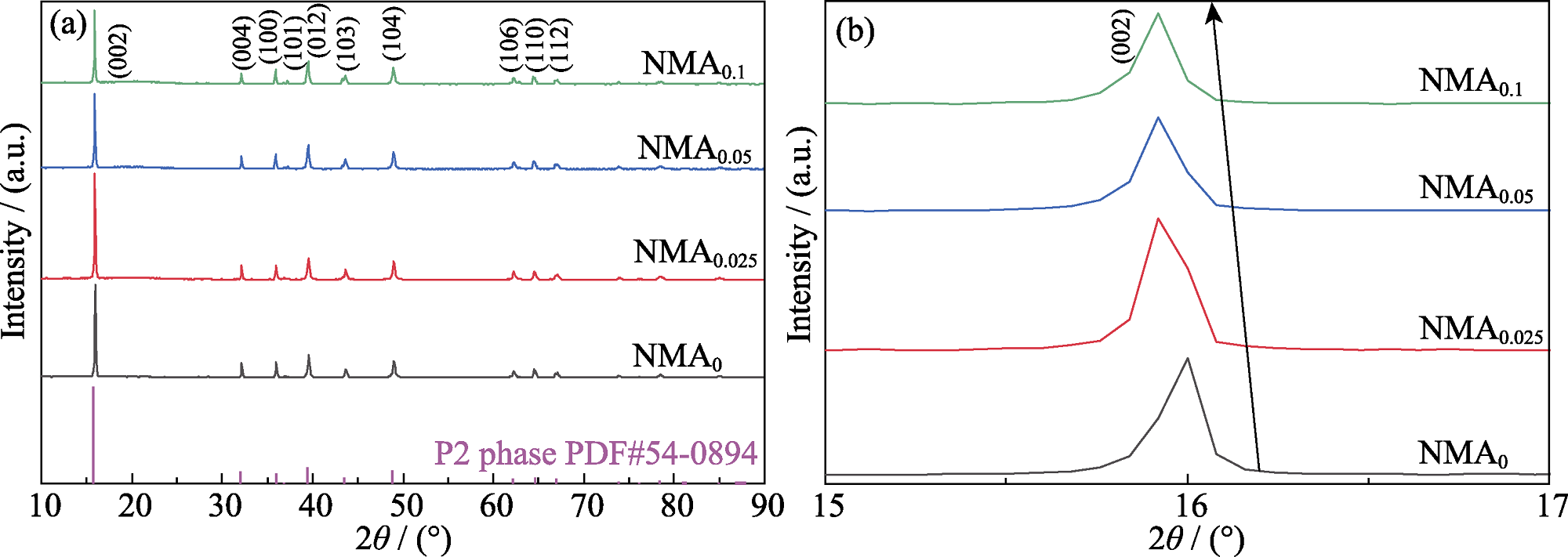
图2 NMAx (x=0, 0.025, 0.05, 0.1)样品的XRD图谱
Fig. 2 XRD patterns of NMAx (x=0, 0.025, 0.05, 0.1) (a) Survey XRD patterns; (b) Regional enlargement patterns in the range of 2θ=15°-17°
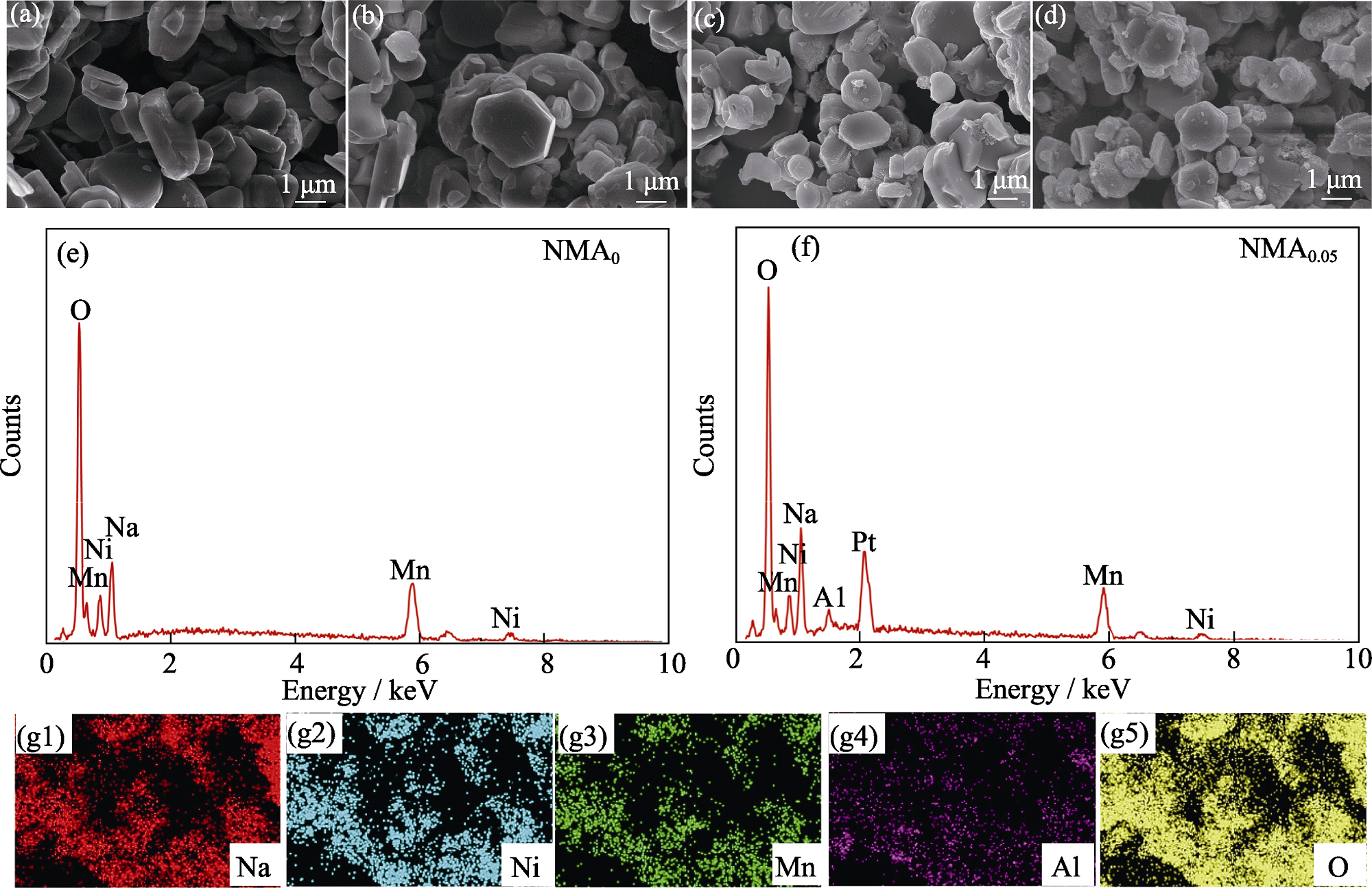
图3 NMAx(x=0, 0.025, 0.05, 0.1)样品的SEM照片及EDS谱图
Fig. 3 SEM images and EDS spectra of NMAx (x=0, 0.025, 0.05, 0.1) (a-d) SEM images of (a) NMA0, (b) NMA0.025, (c) NMA0.05, and (d) NMA0.1; (e, f) EDS spectra of (e) NMA0 and (f) NMA0.05; (g1-g5) EDS elemental mappings of NMA0.05
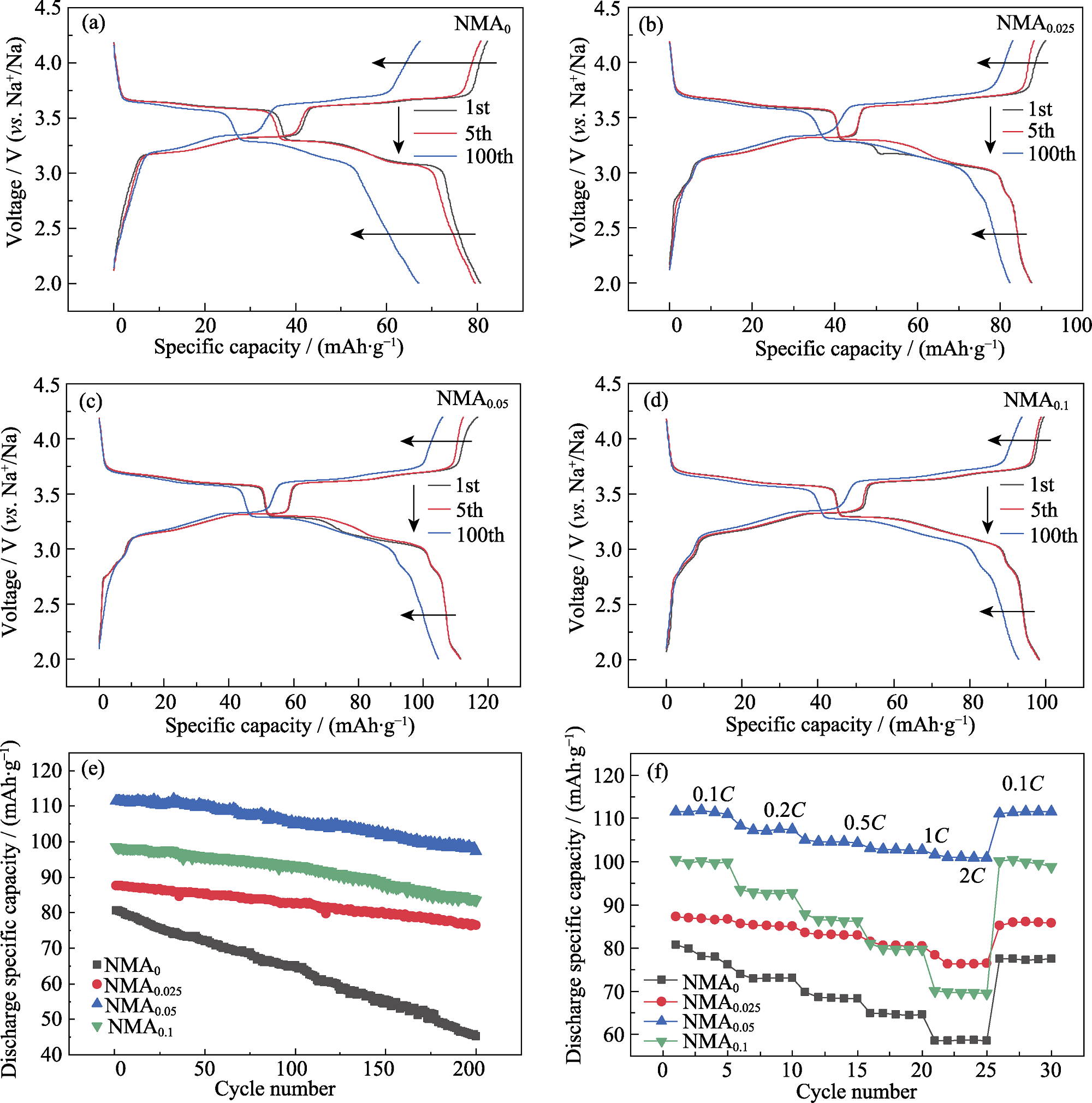
图5 NMAx(x=0, 0.025, 0.05, 0.1)样品的电化学性能
Fig. 5 Electrochemical performance of NMAx (x=0, 0.025, 0.05, 0.1) (a-d) GCD curves of SIBs with NMAx as cathodes for the 1st, 5th, and 100th cycles at 0.1C; (e) Cycling performance at 0.1C; (f) Rate performance. Colorful figures are available on website
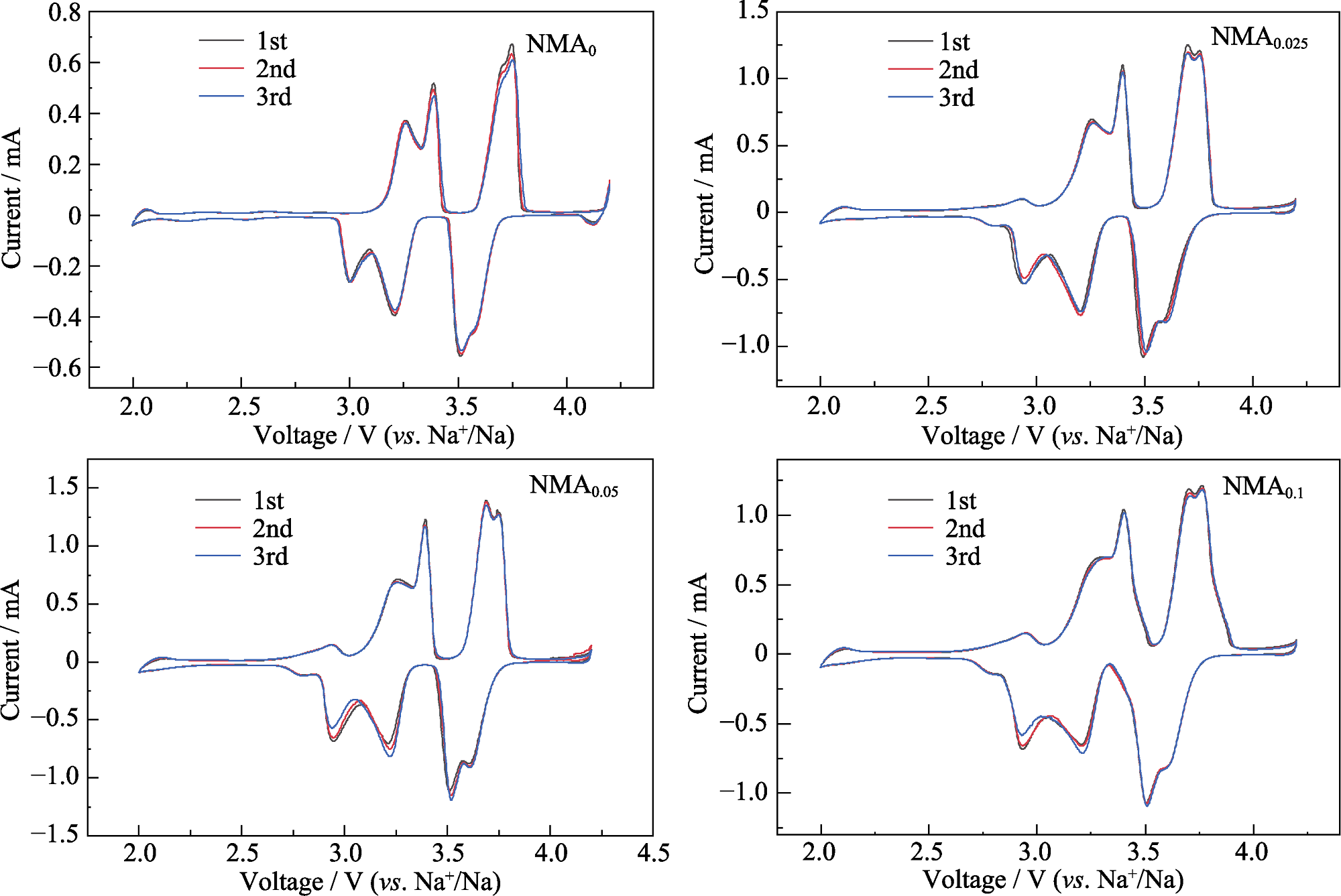
图6 以NMAx(x=0, 0.025, 0.05, 0.1)为正极的SIBs在2.0~4.2 V电压范围内和0.1 mV·s-1扫描速率下的CV曲线
Fig. 6 CV curves of SIBs with NMAx (x=0, 0.025, 0.05, 0.1) as cathodes at 0.1 mV·s-1 within a voltage range of 2.0-4.2 V Colorful figures are available on website
| Sample | a/Å | b/Å | c/Å | α/(°) | β/(°) | γ/(°) | MO2 layer /Å | Na layer/Å |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NMA0 | 3.524154 | 3.524154 | 10.279081 | 90 | 90 | 120 | 2.143 | 2.997 |
| NMA0.025 | 3.514988 | 3.514988 | 10.281807 | 90 | 90 | 120 | 2.139 | 3.002 |
| NMA0.05 | 3.511682 | 3.511682 | 10.281813 | 90 | 90 | 120 | 2.128 | 3.013 |
| NMA0.1 | 3.501512 | 3.501512 | 10.282081 | 90 | 90 | 120 | 2.118 | 3.023 |
表S1 NMAx样品的MO2层、Na层距离及晶格参数
Table S1 Distances of MO2 layers, Na layers and lattice parameters of NMAx samples
| Sample | a/Å | b/Å | c/Å | α/(°) | β/(°) | γ/(°) | MO2 layer /Å | Na layer/Å |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NMA0 | 3.524154 | 3.524154 | 10.279081 | 90 | 90 | 120 | 2.143 | 2.997 |
| NMA0.025 | 3.514988 | 3.514988 | 10.281807 | 90 | 90 | 120 | 2.139 | 3.002 |
| NMA0.05 | 3.511682 | 3.511682 | 10.281813 | 90 | 90 | 120 | 2.128 | 3.013 |
| NMA0.1 | 3.501512 | 3.501512 | 10.282081 | 90 | 90 | 120 | 2.118 | 3.023 |
| Sample | Cycle number | Discharge specific capacity/(mAh·g-1) | Coulombic efficiency/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| NMA0 | 1st | 80.7 | 98.07 |
| 5th | 80.1 | 98.74 | |
| 100th | 65.2 | 99.45 | |
| NMA0.025 | 1st | 87.7 | 98.53 |
| 5th | 87.5 | 98.74 | |
| 100th | 82.6 | 99.68 | |
| NMA0.05 | 1st | 111.6 | 98.11 |
| 5th | 111.5 | 98.42 | |
| 100th | 105.5 | 99.01 | |
| NMA0.1 | 1st | 98.5 | 98.85 |
| 5th | 98.1 | 99.25 | |
| 100th | 93.3 | 99.54 |
表S2 NMAx(x=0, 0.025, 0.05, 0.1)第1、5、100次循环的放电比容量和库仑效率
Table S2 Discharge specific capacity and Coulombic efficiency of NMAx (x=0, 0.025, 0.05, 0.1) for the 1st, 5th, and 100th cycles
| Sample | Cycle number | Discharge specific capacity/(mAh·g-1) | Coulombic efficiency/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| NMA0 | 1st | 80.7 | 98.07 |
| 5th | 80.1 | 98.74 | |
| 100th | 65.2 | 99.45 | |
| NMA0.025 | 1st | 87.7 | 98.53 |
| 5th | 87.5 | 98.74 | |
| 100th | 82.6 | 99.68 | |
| NMA0.05 | 1st | 111.6 | 98.11 |
| 5th | 111.5 | 98.42 | |
| 100th | 105.5 | 99.01 | |
| NMA0.1 | 1st | 98.5 | 98.85 |
| 5th | 98.1 | 99.25 | |
| 100th | 93.3 | 99.54 |
| Sample | Rs/Ω | Rct/Ω |
|---|---|---|
| NMA0 | 26.57 | 497.4 |
| NMA0.025 | 5.912 | 459.6 |
| NMA0.05 | 7.725 | 414.2 |
| NMA0.1 | 15.23 | 422.9 |
表S3 NMAx(x=0, 0.025, 0.05, 0.1)样品的欧姆电阻(Rs)和电荷转移电阻(Rct)
Table S3 Ohmic resistance (Rs) and charge transfer resistance (Rct) of NMAx (x=0, 0.025, 0.05, 0.1) samples
| Sample | Rs/Ω | Rct/Ω |
|---|---|---|
| NMA0 | 26.57 | 497.4 |
| NMA0.025 | 5.912 | 459.6 |
| NMA0.05 | 7.725 | 414.2 |
| NMA0.1 | 15.23 | 422.9 |
| [1] | ŞEN M, ÖZCAN M, EKER Y R. A review on the lithium-ion battery problems used in electric vehicles. Next Sustainability, 2024, 3: 100036. |
| [2] | KHAN F M N U, RASUL M G, SAYEM A S M, et al. Design and optimization of lithium-ion battery as an efficient energy storage device for electric vehicles: a comprehensive review. Journal of Energy Storage, 2023, 71: 108033. |
| [3] | LIU J H, WANG P, GAO Z, et al. Review on electrospinning anode and separators for lithium ion batteries. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2024, 189: 113939. |
| [4] | GAO H, ZENG J, SUN Z, et al. Advances in layered transition metal oxide cathodes for sodium-ion batteries. Materials Today Energy, 2024, 42: 101551. |
| [5] | YU T, LI G, DUAN Y, et al. The research and industrialization progress and prospects of sodium ion battery. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2023, 958: 170486. |
| [6] | CHEN X, LIN G, LIU P, et al. Synergetic enhancement of structural stability and kinetics of P’2-type layered cathode for sodium-ion batteries via cation-anion co-doping. Energy Storage Materials, 2024, 67: 103303. |
| [7] | MATHIYALAGAN K, SHIN D, LEE Y C. Difficulties, strategies, and recent research and development of layered sodium transition metal oxide cathode materials for high-energy sodium-ion batteries. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2024, 90: 40. |
| [8] | LU Y, SONG M, HUANG J, et al. K/Zn dual-site doping toward ultralow-strain P2-type Ni/Mn-based cathode materials for sodium- ion batteries. Journal of Energy Storage, 2024, 77: 109933. |
| [9] | WANG H, YANG B, LIAO X Z, et al. Electrochemical properties of P2-Na2/3[Ni1/3Mn2/3]O2 cathode material for sodium ion batteries when cycled in different voltage ranges. Electrochimica Acta, 2013, 113: 200. |
| [10] | LUO R, ZHANG N, WANG J, et al. Insight into effects of divalent cation substitution stabilizing P2-Type layered cathode materials for sodium-ion batteries. Electrochimica Acta, 2021, 368: 137614. |
| [11] | ANILKUMAR A, NAIR N, NAIR S V, et al. Tailoring high Na content in P2-type layered oxide cathodes via Cu-Li dual doping for sodium-ion batteries. Journal of Energy Storage, 2023, 72: 108291. |
| [12] | YANG L, LUO S H, WANG Y, et al. Cu-doped layered P2-type Na0.67Ni0.33-xCuxMn0.67O2 cathode electrode material with enhanced electrochemical performance for sodium-ion batteries. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 404: 126578. |
| [13] | LI Z Y, ZHANG J, GAO R, et al. Unveiling the role of Co in improving the high-rate capability and cycling performance of layered Na0.7Mn0.7Ni0.3-xCoxO2 cathode materials for sodium-ion batteries. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(24): 15439. |
| [14] | SUN J, SHEN J, WANG T. Electrochemical study of Na0.66Ni0.33-Mn0.67-xMoxO2 as cathode material for sodium-ion battery. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 709: 481. |
| [15] | SU G, ZHENG H, CHEN H, et al. Ca/Mg dual-doping P2-type Na0.67Ni0.17Co0.17Mn0.66O2 cathode material for sodium ion batteries. Materials Letters, 2023, 331: 133425. |
| [16] | YU L, CHENG Z, XU K, et al. Interlocking biphasic chemistry for high-voltage P2/O3 sodium layered oxide cathode. Energy Storage Materials, 2022, 50: 730. |
| [17] | XU J, LEE D H, CLÉMENT R J, et al. Identifying the critical role of Li substitution in P2-Nax[LiyNizMn1-y-z]O2 (0 < x, y, z < 1) intercalation cathode materials for high-energy Na-ion batteries. Chemistry of Materials, 2014, 26(2): 1260. |
| [18] | FU J, HUANG H, SHI K, et al. Al-doped walnut-shell-like P2-type Na2/3Ni1/3Co(1/3-x)Mn1/3AlxO2 as advanced sodium ion battery cathode materials with enhanced rate and cycling performance. Electrochimica Acta, 2020, 349: 136347. |
| [19] | LIU J, QIN W, YANG Z, et al. Enhanced structural and cycling stability of O3-type NaNi1/3Mn1/3Fe1/3O2 cathode by Al replacement of Mn studied in half cell/full sodium-ion batteries. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2023, 933: 167714. |
| [20] | PENG B, CHEN Y, ZHAO L, et al. Regulating the local chemical environment in layered O3-NaNi0.5Mn0.5O2 achieves practicable cathode for sodium-ion batteries. Energy Storage Materials, 2023, 56: 631. |
| [21] | LI G, ZHU W, LIU W. First-principles calculations of the Ti-doping effects on layered NaNiO2 cathode materials for advanced Na-ion batteries. Journal of the Indian Chemical Society, 2022, 99(5): 100424. |
| [22] |
ZHAO C, WANG Q, YAO Z, et al. Rational design of layered oxide materials for sodium-ion batteries. Science, 2020, 370(6517): 708.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | ZHOU C, YANG L, ZHOU C, et al. Fluorine-substituted O3-type NaNi0.4Mn0.25Ti0.3Co0.05O2-xFx cathode with improved rate capability and cyclic stability for sodium-ion storage at high voltage. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2021, 60: 341. |
| [24] | ZHOU J, LIU J, LI Y, et al. Reaching the initial coulombic efficiency and structural stability limit of P2/O3 biphasic layered cathode for sodium-ion batteries. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2023, 638: 758. |
| [25] | XU J, CHEN J, ZHANG K, et al. Nax(Cu-Fe-Mn)O2 system as cathode materials for Na-ion batteries. Nano Energy, 2020, 78: 105142. |
| [26] | QIAO D, ZHANG Y, SU C, et al. Study on the different effects of aluminum doping on Fe-Mn and Ni-Mn based compounds as cathode material for sodium-ion batteries. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2023, 124: 287. |
| [27] | LIU J, ZHOU J, ZHAO Z, et al. Deciphering the formation process and electrochemical behavior of novel P2/O3 biphasic layered cathode with long cycle life for sodium-ion batteries. Journal of Power Sources, 2023, 560: 232686. |
| [28] | JIANG C, CHEN B, XU M, et al. Elevating both capacity and voltage tolerance of P2-type layered cathodes with cooperative Al cation/F anion co-doping for advanced sodium-ion batteries. Energy Storage Materials, 2024, 70: 103518. |
| [29] | YANG Y, YAN C, HUANG J. Research progress of solid electrolyte interphase in lithium batteries. Acta Physico Chimica Sinica, 2021, 37(11): 2010076. |
| [30] | FENG L, LIU Y, ZHANG D, et al. Al substituted Mn position on Li[Ni0.5Co0.2Mn0.3]O2 for high rates performance of cathode material. Vacuum, 2021, 188: 110168. |
| [31] | LI G, ZHANG Z, WANG R, et al. Effect of trace Al surface doping on the structure, surface chemistry and low temperature performance of LiNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2 cathode. Electrochimica Acta, 2016, 212: 399. |
| [32] | WEN Y, WANG B, ZENG G, et al. Electrochemical and structural study of layered P2-type Na2/3Ni1/3Mn2/3O2 as cathode material for sodium-ion battery. Chemistry-An Asian Journal, 2015, 10(3): 661. |
| [33] | SHI S, YANG B, BAI S, et al. Ti-doped O3-NaNi0.5Mn0.5O2 as high-performance cathode materials for sodium-ion batteries. Solid State Ionics, 2024, 411: 116554. |
| [1] | 万俊池, 杜路路, 张永上, 李琳, 刘建德, 张林森. Na4FexP4O12+x/C钠离子电池正极材料的结构演变及其电化学性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 497-503. |
| [2] | 薛柯, 蔡长焜, 谢满意, 李舒婷, 安胜利. 固体氧化物燃料电池Pr1+xBa1-xFe2O5+δ阴极材料的制备及电化学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 363-371. |
| [3] | 张继国, 吴田, 赵旭, 杨钒, 夏天, 孙士恩. 钠离子电池正极材料循环稳定性提升策略及产业化进程[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 348-362. |
| [4] | 杨舒琪, 杨存国, 牛慧祝, 石唯一, 舒珂维. GeP3/科琴黑复合材料作为钠离子电池高性能负极材料[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 329-336. |
| [5] | 朱志杰, 申明远, 吴涛, 李文翠. Cu和Mg协同取代抑制钠离子电池正极材料P2-Na2/3Ni1/3Mn2/3O2的P2-O2相变[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 184-195. |
| [6] | 杨恒强, 张馨月, 马义初, 周青军. 铁基钙钛矿La0.25M0.75FeO3-δ (M=Ba, Sr, Ca)的制备及其作为固体氧化物燃料电池阴极材料的性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(12): 1365-1372. |
| [7] | 姜玥宏, 宋云峰, 张磊磊, 马季, 宋昭远, 龙文. 质子传导型固体氧化物燃料电池BaZr0.1Ce0.7Y0.1Yb0.1O3电解质的氟化研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(12): 1356-1364. |
| [8] | 凌意瀚, 郭胜, 曹志强, 田云峰, 刘方升, 金芳军, 高源. 固体氧化物电池直孔电极结构的制备技术与性能研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(12): 1311-1323. |
| [9] | 张宇婷, 李晓斌, 刘尊义, 李宁, 赵鹬. 复合蛋黄壳型NiCo2V2O8@TiO2@NC材料用作锂离子电池负极研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(11): 1221-1228. |
| [10] | 唐阳, 刘立敏, 周晓亮, 张搏, 蒋星洲, 贾浩义, 罗延麟庆. 质子陶瓷膜反应器的制备及低温氨分解性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(11): 1277-1284. |
| [11] | 王琨鹏, 刘兆林, 林存生, 王治宇. 基于低含水量普鲁士蓝正极的准固态钠离子电池[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(9): 1005-1012. |
| [12] | 陈正鹏, 金芳军, 李明飞, 董江波, 许仁辞, 徐韩昭, 熊凯, 饶睦敏, 陈创庭, 李晓伟, 凌意瀚. 双钙钛矿Sr2CoFeO5+δ阴极材料的制备及其中温固体氧化物燃料电池性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(3): 337-344. |
| [13] | 孔剑锋, 黄杰成, 刘兆林, 林存生, 王治宇. 基于DPEPA聚合物凝胶电解质的准固态钠离子电池[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(12): 1331-1338. |
| [14] | 周靖渝, 李兴宇, 赵晓琳, 王有伟, 宋二红, 刘建军. Ti和Cu掺杂β-NaMnO2正极材料:钠离子电池的倍率和循环性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(12): 1404-1412. |
| [15] | 胡梦菲, 黄丽萍, 李贺, 张国军, 吴厚政. 锂/钠离子电池硬碳负极材料的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(1): 32-44. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||