无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (11): 1277-1284.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250057 CSTR: 32189.14.jim20250057
唐阳1( ), 刘立敏1,2(
), 刘立敏1,2( ), 周晓亮1,2,3, 张搏3, 蒋星洲1, 贾浩义1, 罗延麟庆1
), 周晓亮1,2,3, 张搏3, 蒋星洲1, 贾浩义1, 罗延麟庆1
收稿日期:2025-02-14
修回日期:2025-04-17
出版日期:2025-11-20
网络出版日期:2025-05-22
通讯作者:
刘立敏, 副教授. E-mail: liulimin_ly@126.com作者简介:唐 阳(2001-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: 2630565355@qq.com
基金资助:
TANG Yang1( ), LIU Limin1,2(
), LIU Limin1,2( ), ZHOU Xiaoliang1,2,3, ZHANG Bo3, JIANG Xingzhou1, JIA Haoyi1, LUO Yanlinqing1
), ZHOU Xiaoliang1,2,3, ZHANG Bo3, JIANG Xingzhou1, JIA Haoyi1, LUO Yanlinqing1
Received:2025-02-14
Revised:2025-04-17
Published:2025-11-20
Online:2025-05-22
Contact:
LIU Limin, associate professor. E-mail: liulimin_ly@126.comAbout author:TANG Yang (2001-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: 2630565355@qq.com
Supported by:摘要:
氨气(NH3)作为一种储氢材料, 具有高储氢密度、易液化等优点, 因此利用氨分解制氢是一种理想的氢气(H2)制备方法。但传统氨分解的工作温度过高, 中低温下NH3转化效率过低且H2纯度较低, 无法实现H2的有效制取。本研究通过共压法制备了具有多孔电极Ni-BZCY/BZCY/Ni-BZCY(BZCY: BaZr0.1Ce0.7Y0.2O3-δ)对称结构的质子陶瓷膜反应器(PCMR)。在600 ℃时, PCMR在H2与NH3气氛下分别实现了0.11和0.23 Ω·cm2的极化阻抗(Rp), 在0.8 V外加电压下其电流密度分别达到1.87和1.56 A·cm-2; 在300 ℃、0.8 V外加电压下, H2与NH3中的电流密度仍能分别达到0.16和0.06 A·cm-2。通过共压法所制备的PCMR在600 ℃下的NH3分解转化效率达到80%, 比裸催化剂材料提升了8%, 在350 ℃仍能实现0.3%的提升, 即使在300 ℃下NH3转化效率也达到约1%。本研究为实现低温氨分解制氢提供了新的思路。
中图分类号:
唐阳, 刘立敏, 周晓亮, 张搏, 蒋星洲, 贾浩义, 罗延麟庆. 质子陶瓷膜反应器的制备及低温氨分解性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(11): 1277-1284.
TANG Yang, LIU Limin, ZHOU Xiaoliang, ZHANG Bo, JIANG Xingzhou, JIA Haoyi, LUO Yanlinqing. Proton Ceramic Membrane Reactor: Preparation and Low-temperature Ammonia Decomposition Performance[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(11): 1277-1284.
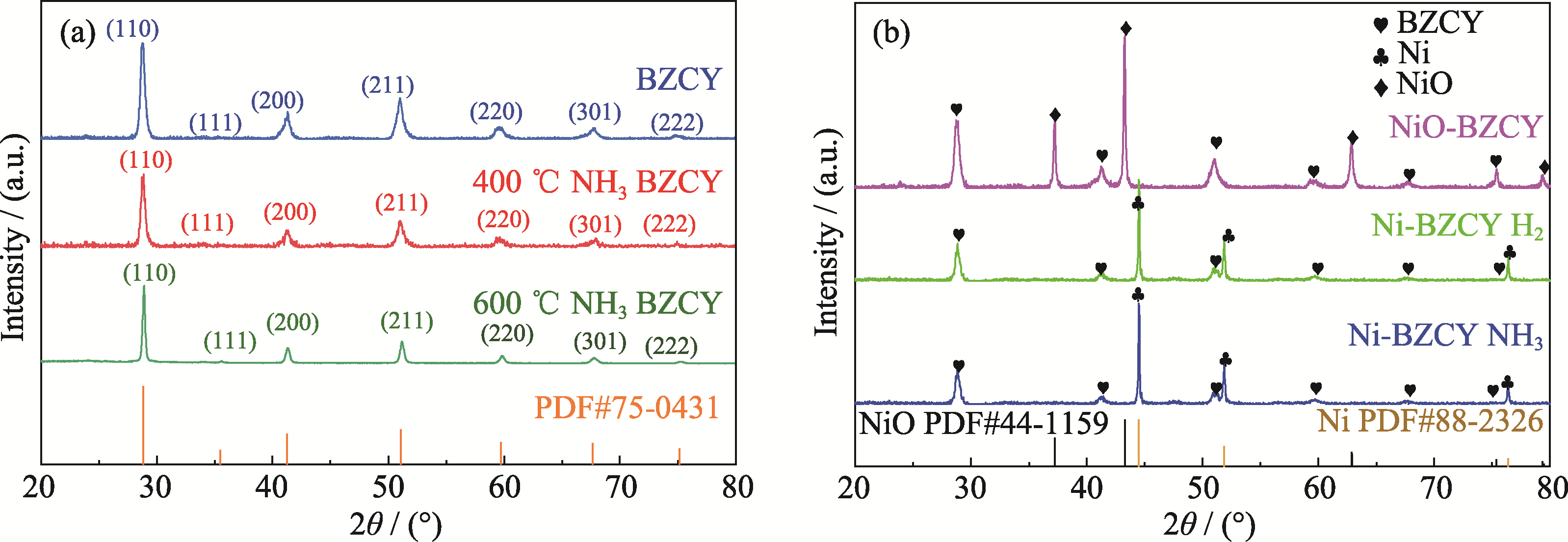
图2 样品的XRD图谱
Fig. 2 XRD patterns of samples (a) BZCY calcined at 1000 ℃ for 5 h in air and calcined at 400 and 600 ℃ for 4 h in NH3; (b) NiO-BZCY and Ni-BZCY treated with H2 and NH3 for 4 h at 400 ℃
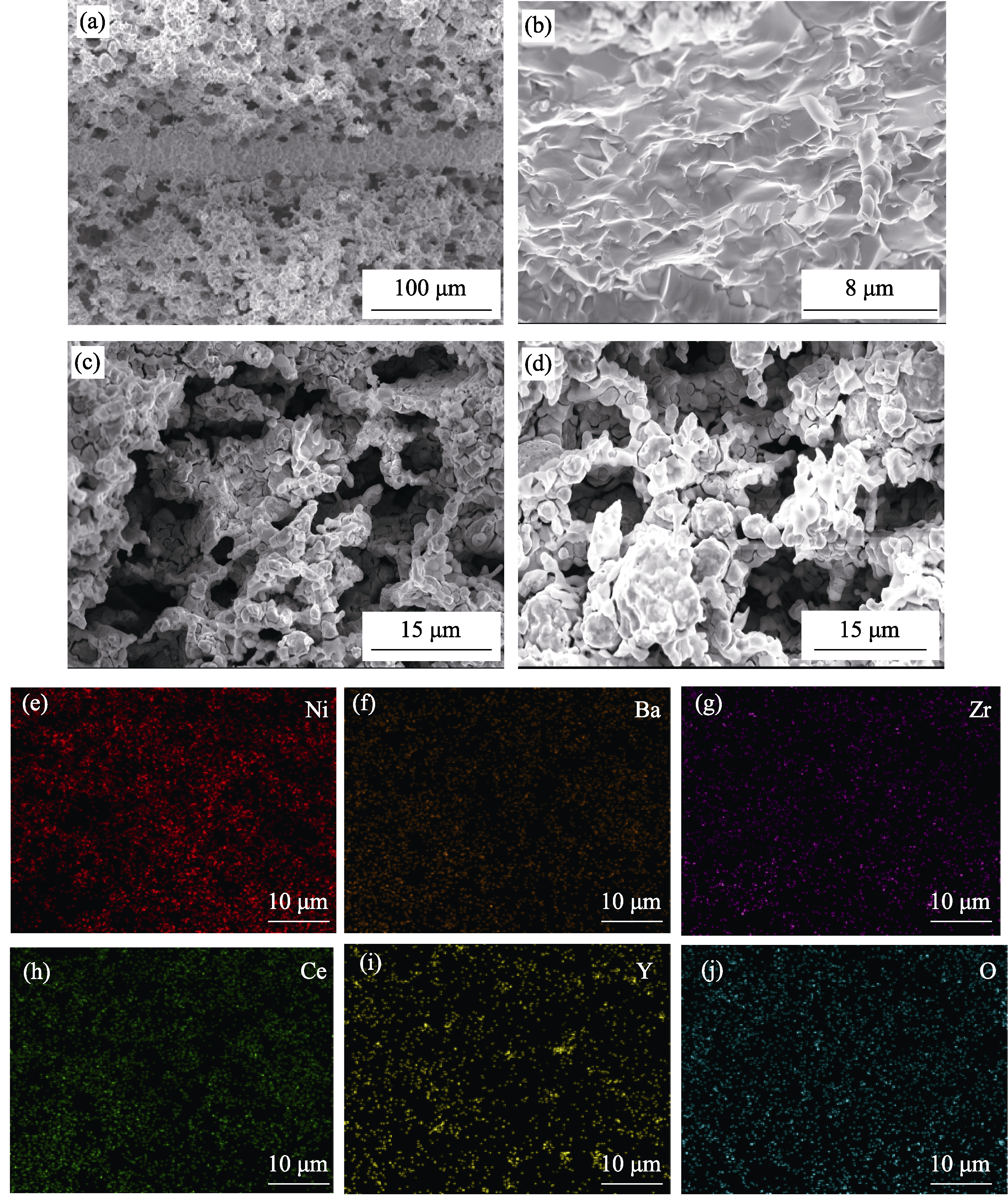
图3 PCMR (a)截面、(b)电解质、(c, d)两侧电极的SEM照片和(e~j) NiO-BZCY电极的EDS元素分布图
Fig. 3 SEM images of (a) cross-section, (b) electrolyte, and (c, d) electrodes on both sides of PCMR, and (e-j) EDS elemental mappings of NiO-BZCY electrode
| Reactor structure | Temperature/℃, gas environment | Voltage/V | Current density/ (A·cm-2) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni-BZCY/BZCY/Ni-BZCY | 650, 50% H2-N2 (measured at only 650 ℃) | 0.8 | 2.0 | [ |
| LSV-Ce-Pd/BZCYCu/LSV-Ce-Pd | 600, H2 (3% H2O) | 1.0 | 0.92 | [ |
| Ni-BZCY/BZCY/Ni-BZCY | 450, 60% H2 (maximum testing temperature of 450 ℃) | 1.0 | 0.53 | [ |
| Ni-BZCYYb/BZCYYb/Ni-BZCYYb | 600, 50% H2-N2 | 0.8 | 1.78 | [ |
| Ni-BZCY/BZCY/Ni-BZCY | 600, H2 (3% H2O) | 0.8 | 1.87 | This work |
| Ni-BZCY/BZCY/Ni-BZCY | 600, NH3 | 0.8 | 1.56 | This work |
表1 部分对称型PCMR的电流密度
Table 1 Current density of partially symmetrical PCMR
| Reactor structure | Temperature/℃, gas environment | Voltage/V | Current density/ (A·cm-2) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni-BZCY/BZCY/Ni-BZCY | 650, 50% H2-N2 (measured at only 650 ℃) | 0.8 | 2.0 | [ |
| LSV-Ce-Pd/BZCYCu/LSV-Ce-Pd | 600, H2 (3% H2O) | 1.0 | 0.92 | [ |
| Ni-BZCY/BZCY/Ni-BZCY | 450, 60% H2 (maximum testing temperature of 450 ℃) | 1.0 | 0.53 | [ |
| Ni-BZCYYb/BZCYYb/Ni-BZCYYb | 600, 50% H2-N2 | 0.8 | 1.78 | [ |
| Ni-BZCY/BZCY/Ni-BZCY | 600, H2 (3% H2O) | 0.8 | 1.87 | This work |
| Ni-BZCY/BZCY/Ni-BZCY | 600, NH3 | 0.8 | 1.56 | This work |
| Temperature/℃ | H2 | NH3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rtotal | RΩ | Rp | Rtotal | RΩ | Rp | |
| 600 | 0.48 | 0.37 | 0.11 | 0.67 | 0.44 | 0.23 |
| 500 | 0.72 | 0.47 | 0.25 | 1.28 | 0.61 | 0.67 |
| 400 | 1.98 | 0.81 | 1.17 | 3.31 | 1.09 | 2.22 |
| 300 | 9.23 | 1.54 | 7.69 | 17.31 | 2.80 | 14.51 |
表2 PCMR在H2、NH3气氛下的阻抗(Ω·cm2)
Table 2 Resistances under H2 and NH3 environments for PCMR (Ω·cm2)
| Temperature/℃ | H2 | NH3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rtotal | RΩ | Rp | Rtotal | RΩ | Rp | |
| 600 | 0.48 | 0.37 | 0.11 | 0.67 | 0.44 | 0.23 |
| 500 | 0.72 | 0.47 | 0.25 | 1.28 | 0.61 | 0.67 |
| 400 | 1.98 | 0.81 | 1.17 | 3.31 | 1.09 | 2.22 |
| 300 | 9.23 | 1.54 | 7.69 | 17.31 | 2.80 | 14.51 |
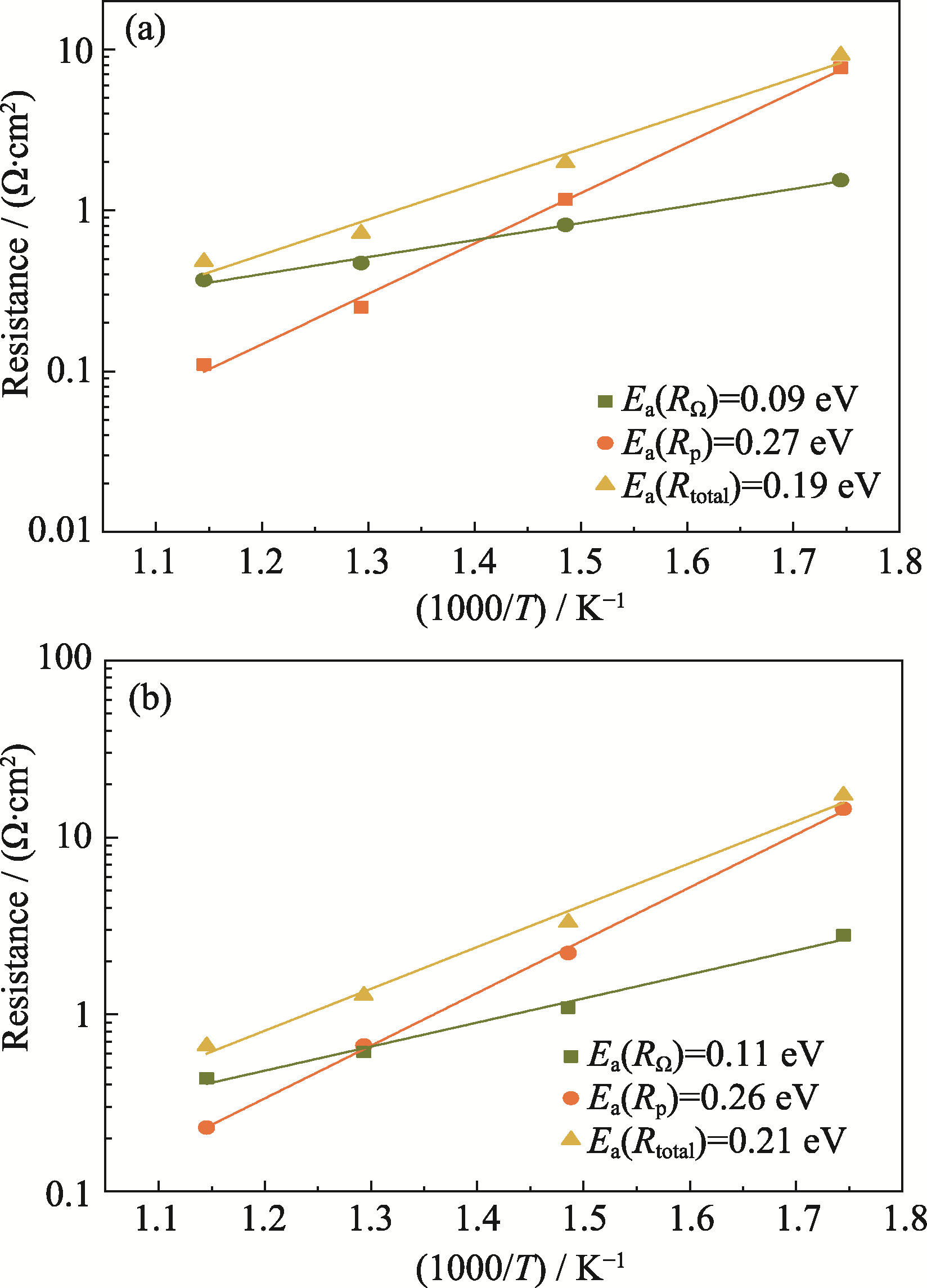
图6 PCMR在(a) H2和(b) NH3气氛下温度与Rp、RΩ以及Rtotal的阿伦尼乌斯曲线
Fig. 6 Arrhenius curves of temperature vs. Rp, RΩ and Rtotal of PCMR under (a) H2 and (b) NH3 environments
| [13] |
LI Y F, ZHANG W S, REN J, et al. Ammonia decomposition for carbon-free hydrogen production over Ni/Al-Ce catalysts: synergistic effect between Al and Ce. Fuel, 2024, 358: 130176.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
BUONOMENNA M G. Proton-conducting ceramic membranes for the production of hydrogen via decarbonized heat: overview and prospects. Hydrogen, 2023, 4(4): 807.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
WANG H N, WANG X B, MENG B, et al. Perovskite-based mixed protonic-electronic conducting membranes for hydrogen separation: recent status and advances. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2018, 60: 297.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
LI N N, ZARKADOULAS A, KYRIAKOU V. Opportunities and challenges for direct electrification of chemical processes with protonic ceramic membrane reactors. Progress in Energy, 2024, 6(4): 043007.
DOI |
| [17] |
LI F R, DUAN G X, WANG Z G, et al. Highly efficient recovery of hydrogen from dilute H2-streams using BaCe0.7Zr0.1Y0.2O3-δ/ Ni-BaCe0.7Zr0.1Y0.2O3-δ dual-layer hollow fiber membrane. Separation and Purification Technology, 2022, 287: 120602.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
WANG Q J, LUO T, TONG Y C, et al. Large-area protonic ceramic cells for hydrogen purification. Separation and Purification Technology, 2022, 295: 121301.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
TONG Y C, WANG Y, CUI C S, et al. Preparation and characterization of symmetrical protonic ceramic fuel cells as electrochemical hydrogen pumps. Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 457: 228036.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
LIANG M Z, SONG Y F, XIONG B C, et al. In situ exsolved CoFeRu alloy decorated perovskite as an anode catalyst layer for high-performance direct-ammonia protonic ceramic fuel cells. Advanced Functional Materials, 2024, 34(48): 2408756.
DOI URL |
| [21] | 曹希文, 罗凌虹, 曾小军, 等. 固体氧化物燃料电池Ni基阳极抗积碳的研究进展. 陶瓷学报, 2024, 45(1): 72. |
| [22] | 蓝海洋, 陈星余, 张博, 等. 固体氧化物直接氨燃料电池阳极材料的研究进展. 陶瓷学报, 2023, 44(6): 1078. |
| [23] |
PENG C X, ZHAO B X, MENG X, et al. Effect of NiO addition on the sintering and electrochemical properties of BaCe0.55Zr0.35Y0.1O3-δ proton-conducting ceramic electrolyte. Membranes, 2024, 14(3): 61.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
DANILOV N A, STAROSTINA I A, STAROSTIN G N, et al. Fundamental understanding and applications of protonic Y- and Yb-coped Ba(Ce, Zr)O3 perovskites: state-of-the-art and perspectives. Advanced Energy Materials, 2023, 13(47): 2302175.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
YANG Y M, LU J C, ZHANG X Y, et al. Symmetry-induced modulation of proton conductivity in Y-doped Ba(Zr, Ce)O3: insights from Raman spectroscopy. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2024, 12(21): 12599.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
ZHANG J H, LU X T, MAO H Y, et al. Effect of sintering additives on sintering behavior and conductivity of BaZr0.1Ce0.7Y0.2O3-δ electrolytes. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 84.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
ZHU D C, LIU Z Q, ZHU C J, et al. Construction of a novel BaZr0.1Ce0.7Y0.2O3-δ-SnO2 heterojunction composite electrolyte for advanced semiconductor ion fuel cells operating at lower temperature down to 350 ℃. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2025, 505: 159368.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
HOU J, GONG J Y, BI L. Advancing cathodic electrocatalysis via an in situ generated dense active interlayer based on CuO5 pyramid-structured Sm2Ba1.33Ce0.67Cu3O9. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2022, 10(30): 15949.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
HOU J, DONG K, MIAO L N, et al. Rationally structuring proton-conducting solid oxide fuel cell anode with Ni metal catalyst and porous skeleton. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(15): 24038.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
ZHANG G J, CHEN T, GUO Z Z, et al. A 10 × 10 cm2 protonic ceramic electrochemical hydrogen pump for efficient and durable hydrogen purification. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 495: 153521.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
CHOI J, SHIN M, KIM B, et al. High-performance ceramic composite electrodes for electrochemical hydrogen pump using protonic ceramics. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(18): 13092.
DOI URL |
| [32] | MUSHTAQ U, WELZEL S, SHARMA R K, et al. Development of electrode-supported proton conducting solid oxide cells and their evaluation as electrochemical hydrogen pumps. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(34): 38938. |
| [1] |
SADEQ A M, HOMOD R Z, HUSSEIN A K, et al. Hydrogen energy systems: technologies, trends, and future prospects. Science of the Total Environment, 2024, 939: 173622.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
YUE M L, LAMBERT H, PAHON E, et al. Hydrogen energy systems: a critical review of technologies, applications, trends and challenges. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2021, 146: 111180.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
AGYEKUM E B, ODOI-YORKE F, ABBEY A A, et al. A review of the trends, evolution, and future research prospects of hydrogen fuel cells-a focus on vehicles. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 72: 918.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
LI N, ZHANG C, LI D, et al. Review of reactor systems for hydrogen production via ammonia decomposition. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 495: 153125.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
ZAINAL N A, ZULKIFLI N W M, GULZAR M, et al. A review on the chemistry, production, and technological potential of bio-based lubricants. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2018, 82: 80.
DOI URL |
| [6] | LIANG D T, FENG C, XU L, et al. Promotion effects of different methods in COx-free hydrogen production from ammonia decomposition. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2023, 13(12): 3614. |
| [7] |
ZHANG X S, LIU Y T, WANG Y Y, et al. Self-assembled platinum-iridium alloy aerogels and their efficient electrocatalytic ammonia oxidation performance. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 511.
DOI |
| [8] |
MUKHERJEE S, DEVAGUPTAPU S V, SVIRIPA A, et al. Low-temperature ammonia decomposition catalysts for hydrogen generation. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2018, 226: 162.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
LIAN M L, SU J X, HUANG H Y, et al. Supported Ni catalysts from Ni-Mg-Al hydrotalcite-like compounds: preparation and catalytic performance for ammonia decomposition. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 53.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
SUN S C, JIANG Q Q, ZHAO D Y, et al. Ammonia as hydrogen carrier: advances in ammonia decomposition catalysts for promising hydrogen production. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2022, 169: 112918.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
YUN J, XIONG G, KIM S, et al. Understanding direct-ammonia protonic ceramic fuel cells: high-performance in the absence of precious metal catalysts. ACS Energy Letters, 2024, 9(11): 5520.
DOI URL |
| [34] | ZHOU Y C, LIU E Z, CHEN Y, et al. An active and robust air electrode for reversible protonic ceramic electrochemical cells. ACS Energy Letters, 2021, 6(4): 1511. |
| [11] |
CECHETTO V, DI FELICE L, MARTINEZ G R, et al. Ultra-pure hydrogen production via ammonia decomposition in a catalytic membrane reactor. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(49): 21220.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
SHEN M H, AI F J, MA H L, et al. Progress and prospects of reversible solid oxide fuel cell materials. iScience, 2021, 24(12): 103464.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 闫共芹, 王晨, 蓝春波, 洪雨昕, 叶维超, 付向辉. Al掺杂P2型Na0.8Ni0.33Mn0.67-xAlxO2钠离子电池正极材料的制备与电化学性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(9): 1005-1012. |
| [2] | 李汶金, 娄程广, 张帅, 苏兴华. 金属Cu和5YSZ陶瓷的“闪连”研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(9): 957-963. |
| [3] | 杨燕, 张发强, 马名生, 王墉哲, 欧阳琪, 刘志甫. 基于CuO-TiO2-Nb2O5复合氧化物烧结助剂的ZnAl2O4陶瓷低温烧结研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 711-718. |
| [4] | 姜昆, 李乐天, 郑木鹏, 胡永明, 潘勤学, 吴超峰, 王轲. PZT陶瓷的低温烧结研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| [5] | 尹长志, 成名飞, 雷微程, 蔡弋炀, 宋小强, 付明, 吕文中, 雷文. Ga3+掺杂对SrAl2Si2O8陶瓷晶体结构及微波介电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 704-710. |
| [6] | 陈莉波, 盛盈, 伍明, 宋季岭, 蹇建, 宋二红. Na和O元素共掺杂氮化碳高效光催化制氢[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 552-562. |
| [7] | 万俊池, 杜路路, 张永上, 李琳, 刘建德, 张林森. Na4FexP4O12+x/C钠离子电池正极材料的结构演变及其电化学性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 497-503. |
| [8] | 薛柯, 蔡长焜, 谢满意, 李舒婷, 安胜利. 固体氧化物燃料电池Pr1+xBa1-xFe2O5+δ阴极材料的制备及电化学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 363-371. |
| [9] | 杨恒强, 张馨月, 马义初, 周青军. 铁基钙钛矿La0.25M0.75FeO3-δ (M=Ba, Sr, Ca)的制备及其作为固体氧化物燃料电池阴极材料的性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(12): 1365-1372. |
| [10] | 姜玥宏, 宋云峰, 张磊磊, 马季, 宋昭远, 龙文. 质子传导型固体氧化物燃料电池BaZr0.1Ce0.7Y0.1Yb0.1O3电解质的氟化研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(12): 1356-1364. |
| [11] | 于泽龙, 唐春, 饶家豪, 郭恒, 周莹. 碱性电解水大电流密度电催化剂的制备及经济性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(12): 1405-1413. |
| [12] | 凌意瀚, 郭胜, 曹志强, 田云峰, 刘方升, 金芳军, 高源. 固体氧化物电池直孔电极结构的制备技术与性能研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(12): 1311-1323. |
| [13] | 张宇婷, 李晓斌, 刘尊义, 李宁, 赵鹬. 复合蛋黄壳型NiCo2V2O8@TiO2@NC材料用作锂离子电池负极研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(11): 1221-1228. |
| [14] | 连敏丽, 苏佳欣, 黄鸿杨, 嵇玉寅, 邓海帆, 张彤, 陈崇启, 李达林. Ni-Mg-Al类水滑石衍生镍基催化剂的制备及其氨分解性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(1): 53-60. |
| [15] | 陈正鹏, 金芳军, 李明飞, 董江波, 许仁辞, 徐韩昭, 熊凯, 饶睦敏, 陈创庭, 李晓伟, 凌意瀚. 双钙钛矿Sr2CoFeO5+δ阴极材料的制备及其中温固体氧化物燃料电池性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(3): 337-344. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||