无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (12): 1311-1323.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250123 CSTR: 32189.14.jim20250123
所属专题: 【能源环境】燃料电池(202512)
• 专栏:高温燃料电池关键材料(客座编辑:凌意瀚) • 上一篇 下一篇
凌意瀚( ), 郭胜, 曹志强, 田云峰(
), 郭胜, 曹志强, 田云峰( ), 刘方升, 金芳军, 高源
), 刘方升, 金芳军, 高源
收稿日期:2025-03-24
修回日期:2025-07-07
出版日期:2025-12-20
网络出版日期:2025-07-16
通讯作者:
田云峰, 副教授. E-mail: yunfengup@cumt.edu.cn;作者简介:凌意瀚(1986-), 男, 教授. E-mail: lyhyy@cumt.edu.cn
基金资助:
LING Yihan( ), GUO Sheng, CAO Zhiqiang, TIAN Yunfeng(
), GUO Sheng, CAO Zhiqiang, TIAN Yunfeng( ), LIU Fangsheng, JIN Fangjun, GAO Yuan
), LIU Fangsheng, JIN Fangjun, GAO Yuan
Received:2025-03-24
Revised:2025-07-07
Published:2025-12-20
Online:2025-07-16
Contact:
TIAN Yunfeng, associate professor. E-mail: yunfengup@cumt.edu.cn;About author:LING Yihan (1986-), male, professor. E-mail: lyhyy@cumt.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
固体氧化物电池(Solid Oxide Cell, SOC)因其燃料电池(SOFC)模式下的高效清洁发电能力和电解池(SOEC)模式下的优异制氢及储能潜力, 近年来受到广泛关注。传统SOC通常采用石墨、碳粉等造孔剂制备多孔电极支撑体, 存在孔隙无序分布、孔结构复杂的问题, 从而产生较高的曲折因子, 尤其在稀薄燃料或高电流密度条件下, 容易引发浓差极化, 这限制了电池性能的进一步提升。为解决这一问题, 近年来直孔结构的应用得到了广泛关注。该结构通过有序的孔道设计, 有效促进了气体扩散与传输, 减轻了浓差极化现象, 并提高了电极材料的浸渍效率及活性位点的利用率, 从而显著提升了SOC的电化学性能。本文系统综述了直孔结构SOC的最新制备技术研究进展, 详细阐述了相转化法、冷冻干燥法及海藻酸盐离子凝胶法等关键技术的成孔机理、工艺特点及其在平板式和管式SOC中的应用; 深入分析了直孔结构在SOFC和SOEC两种模式下对氢气、碳氢燃料适应性和电解性能(包括传统水/CO2电解及燃料辅助电解)的提升作用与机制。尽管直孔结构在SOC应用中展现出巨大的潜力, 但目前关于这一制备技术的系统性综述仍较为缺乏。本文旨在总结直孔结构SOC的最新制备技术进展, 分析其技术优势与存在的问题, 并提出未来的发展方向, 以期为相关研究提供参考。
中图分类号:
凌意瀚, 郭胜, 曹志强, 田云峰, 刘方升, 金芳军, 高源. 固体氧化物电池直孔电极结构的制备技术与性能研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(12): 1311-1323.
LING Yihan, GUO Sheng, CAO Zhiqiang, TIAN Yunfeng, LIU Fangsheng, JIN Fangjun, GAO Yuan. Research Progress on Preparation Technologies and Performance of Straight-pore Electrode Structures for Solid Oxide Cells[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(12): 1311-1323.
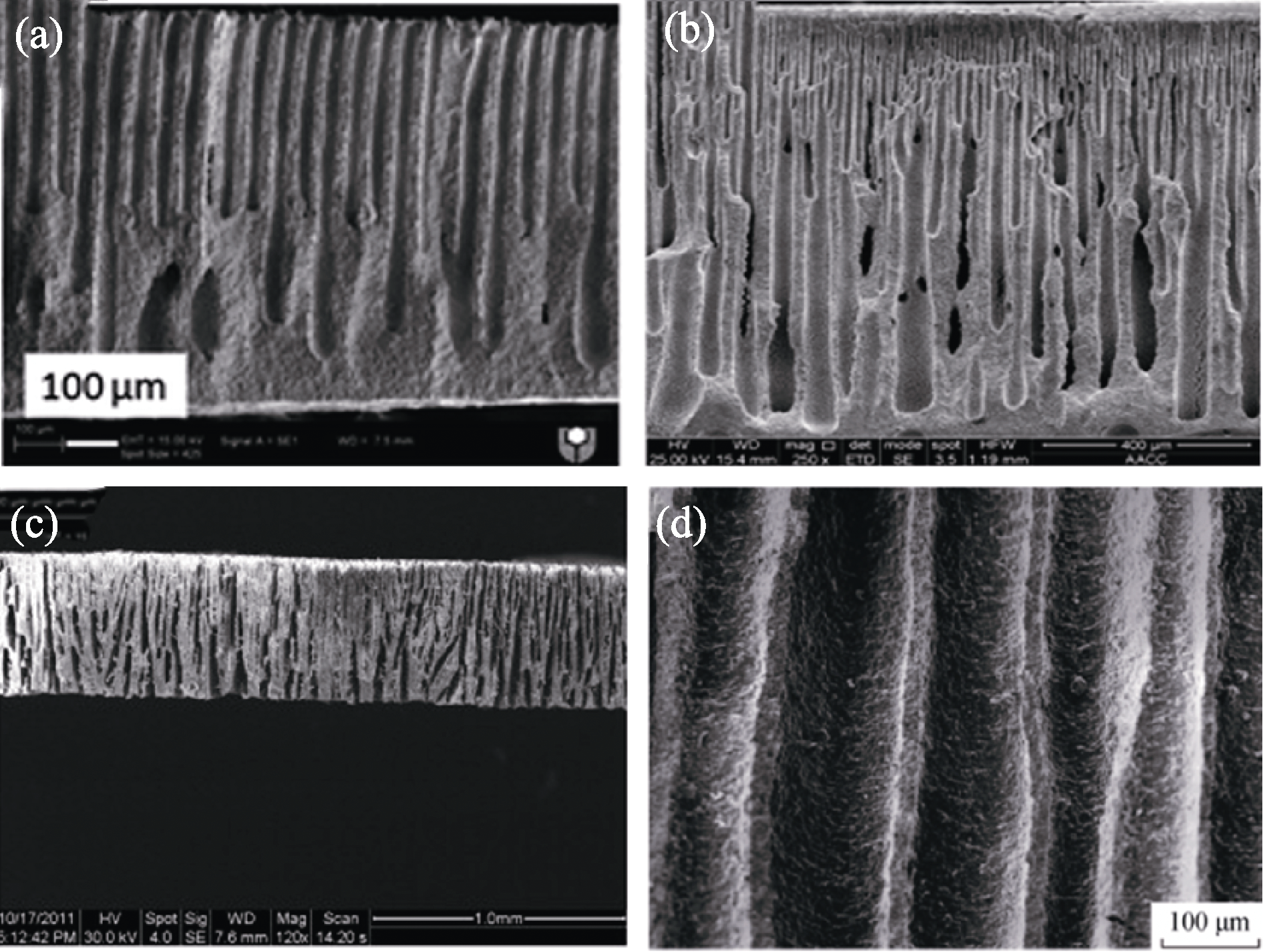
图2 不同孔结构的SEM照片[9-12]
Fig. 2 SEM images of different pore structures[9-12] (a) Microchannel pore structure[9]; (b) Dendritic pore structure[10]; (c) Gradient needle-like pore structure[11]; (d) Straight-through pore structure[12]
| Type | Fabrication technique | Technical advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planar | Stainless steel mesh-assisted phase inversion | Simple removal of skin/sponge layer | Difficult mass-production; Mechanical weakness |
| Phase inversion tape casting method | High consistency; Suitable for mass production; Low cost; High porosity and permeability | Poor consistency; Sponge layer removal difficulty; Mechanical weakness | |
| Freeze-drying method | Membrane formed without post- processing; High porosity and permeability | High process complexity; High cost; Being only suitable for producing thick films (>3 mm); Mechanical weakness | |
| Alginate ion gelation method | Simple operation; Low cost | Difficult commercialization; Relatively large functional layer thickness | |
| Tubular | Phase inversion combined with extrusion technology | Suitable for mass production; Simple operation | Small pore size; Difficult current collection |
| Phase inversion combined with dip coating | Simple operation; Low cost | Difficult mass-production; High cost |
表1 各种制备技术的优缺点比较
Table 1 Comparison of advantages and disadvantages of various preparation techniques
| Type | Fabrication technique | Technical advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planar | Stainless steel mesh-assisted phase inversion | Simple removal of skin/sponge layer | Difficult mass-production; Mechanical weakness |
| Phase inversion tape casting method | High consistency; Suitable for mass production; Low cost; High porosity and permeability | Poor consistency; Sponge layer removal difficulty; Mechanical weakness | |
| Freeze-drying method | Membrane formed without post- processing; High porosity and permeability | High process complexity; High cost; Being only suitable for producing thick films (>3 mm); Mechanical weakness | |
| Alginate ion gelation method | Simple operation; Low cost | Difficult commercialization; Relatively large functional layer thickness | |
| Tubular | Phase inversion combined with extrusion technology | Suitable for mass production; Simple operation | Small pore size; Difficult current collection |
| Phase inversion combined with dip coating | Simple operation; Low cost | Difficult mass-production; High cost |
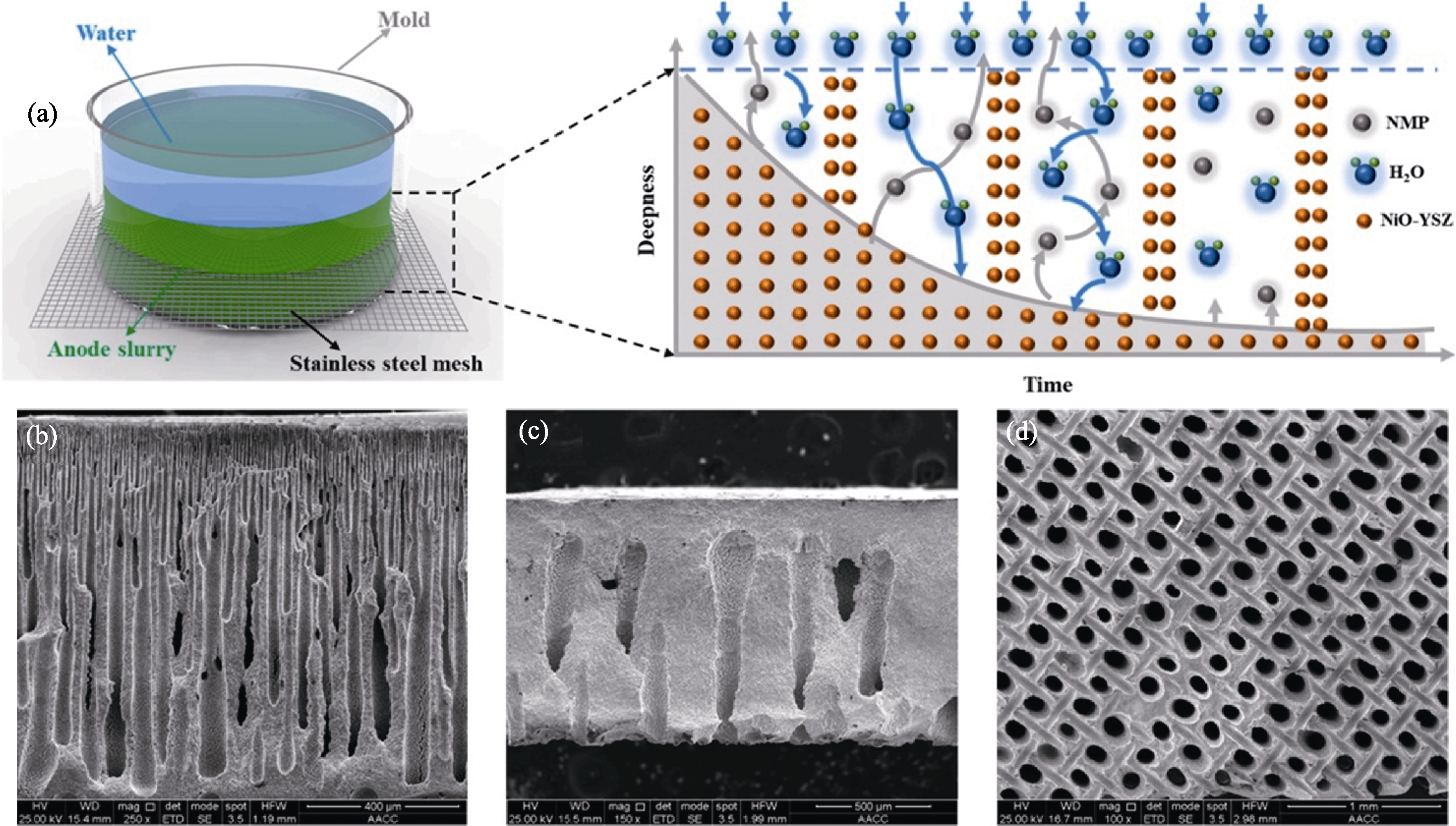
图4 (a)不锈钢网辅助相转化法制备树枝状燃料电极支撑体的过程示意图以及(b)顶部基底、(c)底部基底和(d)基底表面的SEM照片[10]
Fig. 4 (a) Schematic diagram of stainless steel mesh-assisted phase inversion method for preparing dendritic fuel electrode supports, along with SEM images of (b) top substrate, (c) bottom substrate, and (d) substrate surface[10]
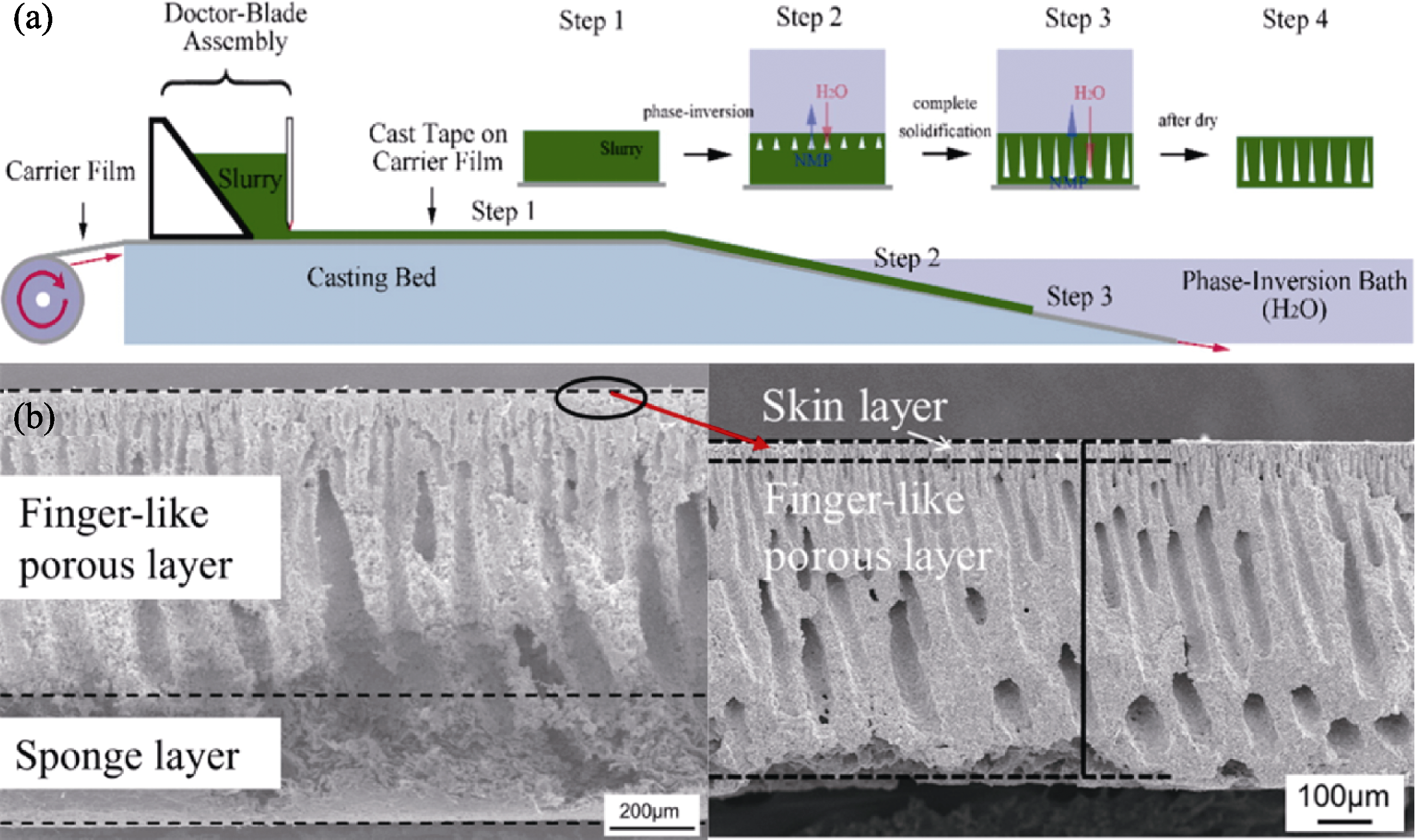
图5 (a)相转化流延法制备流程示意图[25]以及(b)电极横截面的SEM照片[26]
Fig. 5 (a) Schematic illustration of phase inversion tape casting fabrication process[25] and (b) cross-sectional SEM images of electrode[26]
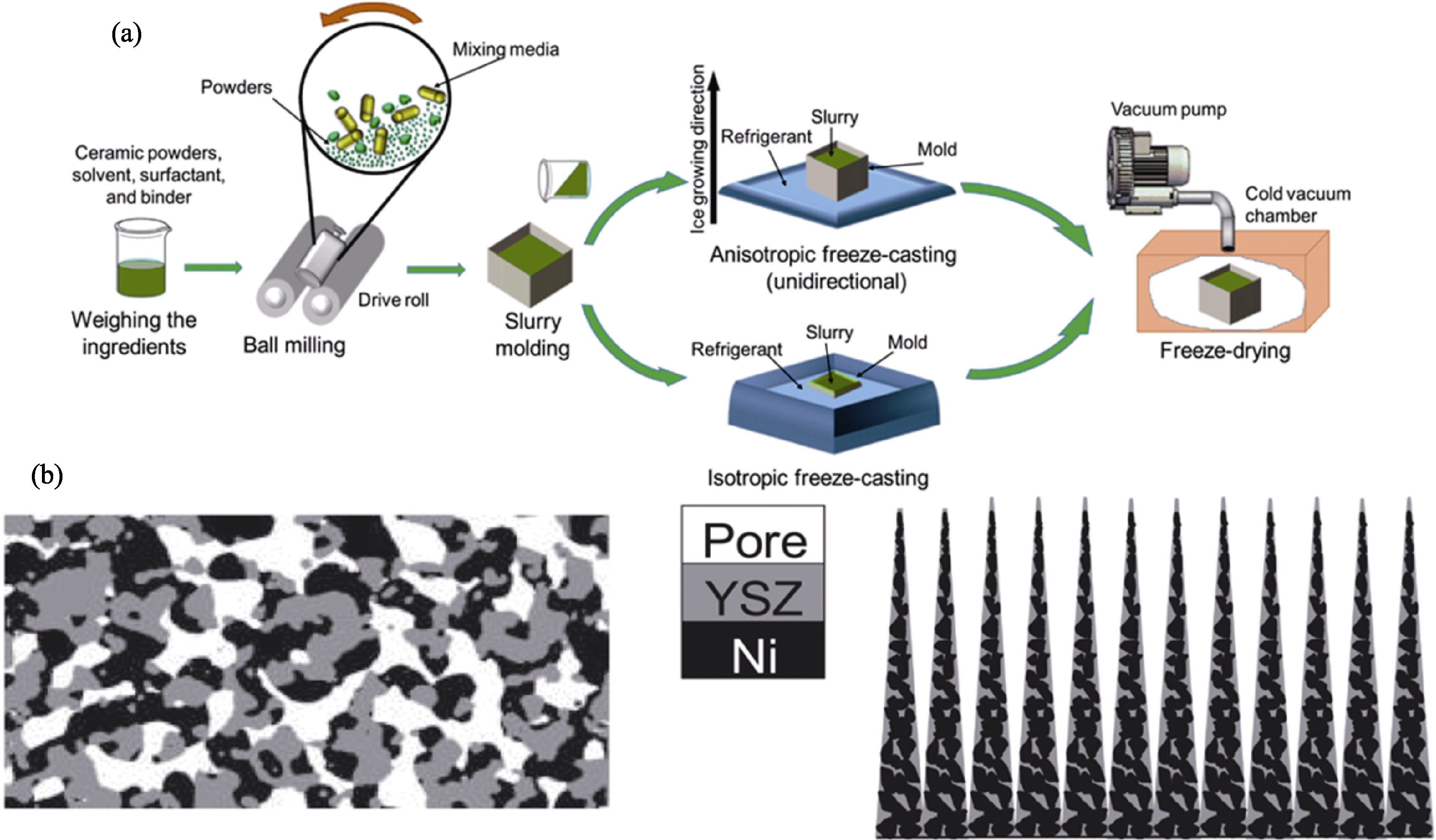
图6 (a)冷冻干燥法制备支撑体的步骤示意图和(b)无规则多孔结构电极与梯度针状结构电极[37]
Fig. 6 (a) Schematic diagram of the steps for preparing support by freeze-drying and (b) random porous structure of electrode and gradient needle-like structure of freeze-dried electrode[37]
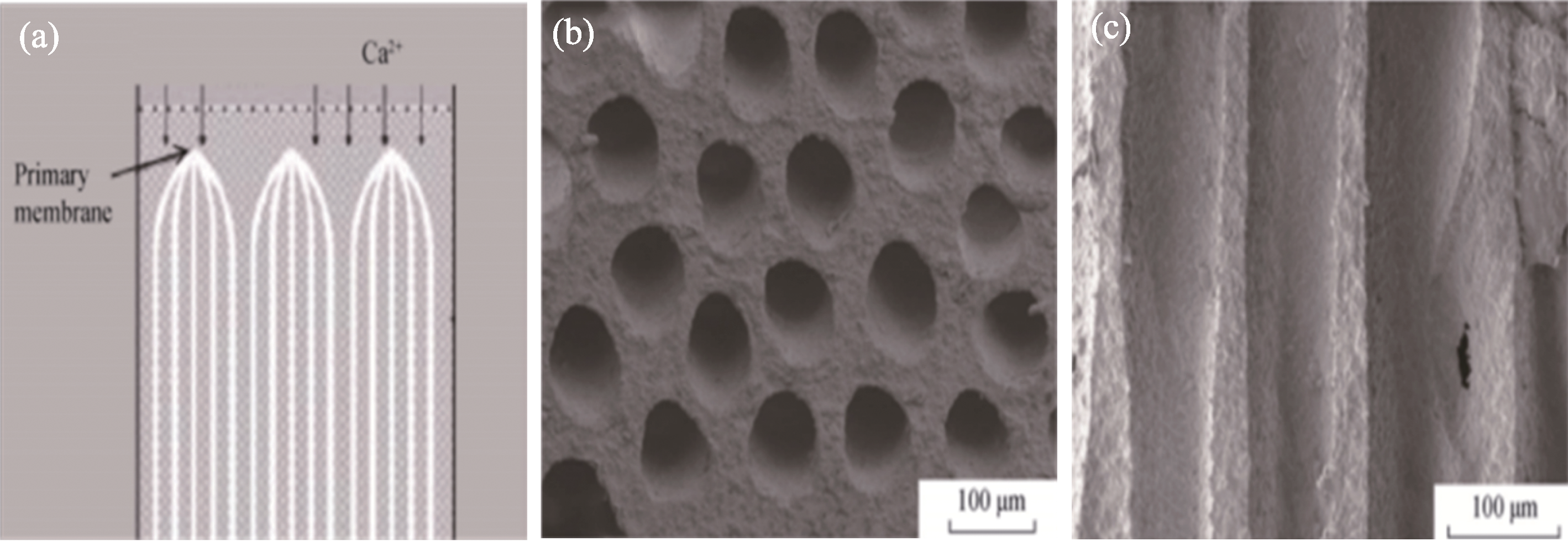
图8 (a)直孔燃料电极支撑体的形成过程示意图; (b, c)未还原的直孔NiO-YSZ燃料电极支撑体的(b)横向截面和(c)纵向表面的SEM照片[53]
Fig. 8 (a) Schematic diagram illustrating the formation process of a straight-pore fuel electrode support; (b, c) SEM images of (b) transverse cross-section and (c) longitudinal surface of unreduced straight-pore NiO-YSZ fuel electrode support[53]
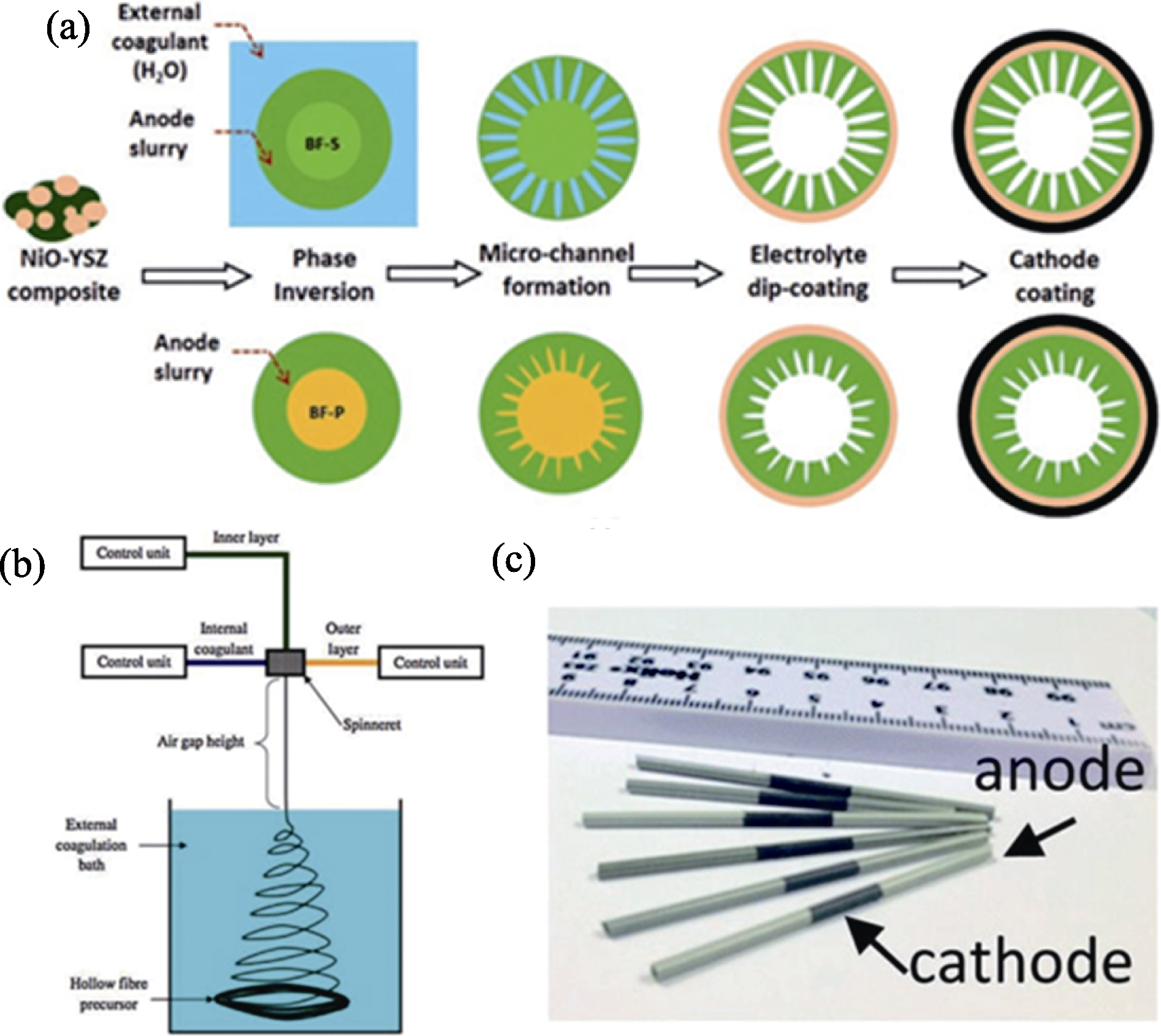
图9 相转化法结合挤出技术的(a)制作工艺、(b)实验装置示意图以及(c)管式电池的照片[58]
Fig. 9 Schematic diagrams of phase inversion method combined with extrusion technology for (a) fabrication process, (b) experimental device, and (c) photograph of tubular cells[58]

图10 (a)相转化结合挤出成型技术制备的单SOFC结构图和(b)电池横截面及(c)管壁多孔区域的SEM照片[59]
Fig. 10 (a) Schematic diagram of single SOFC prepared by phase transformation combined extrusion molding technology and SEM images of (b) cell cross-section and (c) porous region of tube wall[59]
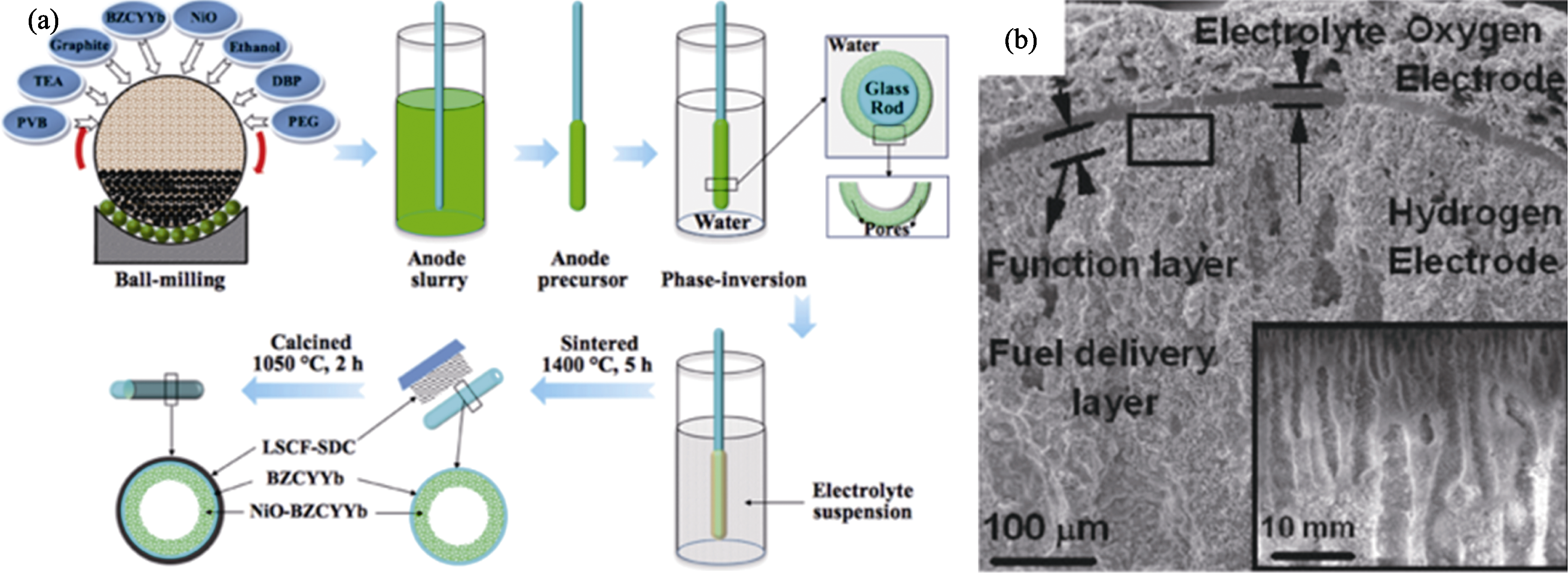
图11 (a)通过相转化浸渍工艺制备的管式直孔SOFC的典型制造工艺[62]; (b)管式直孔SOC横截面的SEM照片[66]
Fig. 11 (a) Typical manufacturing process of tubular straight hole structure SOFC prepared by phase transformation impregnation process[62]; (b) SEM image of the cross-section of a tubular straight hole SOC[66]
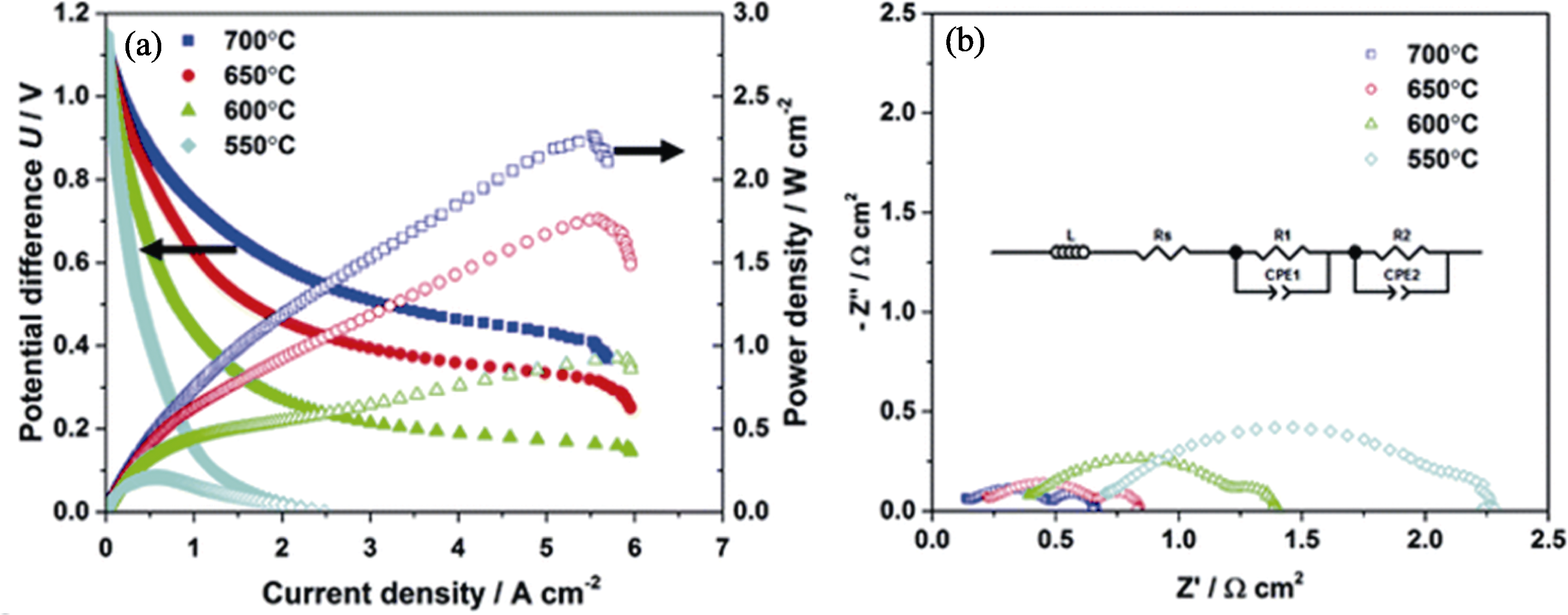
图12 (a)在550~700 ℃下电流密度对SOFC电势差及功率密度的影响; (b) 550~700 ℃下的EIS谱图[59]
Fig. 12 (a) Effect of current density on cell potential difference and power densities of micro-monolithic SOFC at 550-700 ℃; (b) EIS spectra at 550-700 ℃[59]
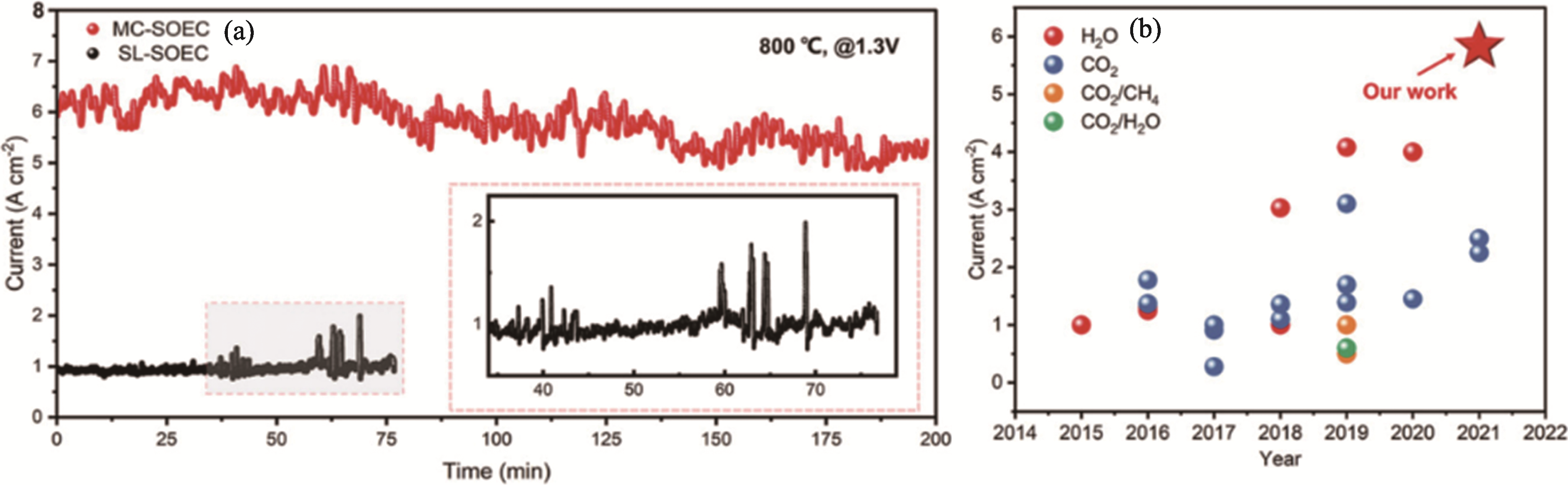
图14 (a)在1.3 V、800 ℃条件下新型SOEC(MC-SOEC)与传统海绵状SOEC(SL-SOEC)的电流密度随时间的变化曲线; (b) MC-SOEC在1.3 V下的高电流密度与以前的工作对比[69]
Fig. 14 (a) Time dependence curves of current density for novel SOEC (MC-SOEC) and conventional sponge-like SOEC (SL-SOEC) under 1.3 V at 800 ℃; (b) High current density of MC-SOEC at 1.3 V compared with previous work[69]

图15 (a) SOEC在800 ℃、2 A·cm-2下CH4辅助CO2电解的长期稳定性[70]; (b) SOEC在800 ℃、3.0 A·cm-2下乙醇辅助电解水的长期稳定性[71]
Fig. 15 Long-term stability of (a) CH4-assisted CO2 electrolysis at 800 ℃ and 2 A·cm-2 for SOEC[70] and (b) ethanol-assisted water electrolysis at 800 ℃ and 3.0 A·cm-2 for SOEC[71]
| [1] | WANG Z, HAO H R, WU Z H, et al. Enhancing Cr-tolerance ability of double perovskite cathodes through configuration entropy engineering. Journal of Inorganic Materials, DOI: 10.15541/jim20240542. |
| [2] |
VINCHHI P, KHANDLA M, CHAUDHARY K, et al. Recent advances on electrolyte materials for SOFC: a review. Inorganic Chemistry Communications, 2023, 152: 110724.
DOI URL |
| [3] | ZHANG J, RICOTE S, HENDRIKSEN P V, et al. Advanced materials for thin-film solid oxide fuel cells: recent progress and challenges in boosting the device performance at low temperatures. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(22): 2111205. |
| [4] | JIANG Y H, SONG Y F, ZHANG L L, et al. Fluorination of BaZr0.1Ce0.7Y0.1Yb0.1O3 as electrolyte material for proton conducting solid oxide fuel cell. Journal of Inorganic Materials, DOI: 10.15541/jim20240535. |
| [5] |
GÓMEZ S Y, HOTZA D. Current developments in reversible solid oxide fuel cells. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2016, 61: 155.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
ZHANG K, WANG Y, ZHU T L, et al. LaNi0.6Fe0.4O3 cathode contact material: electrical conducting property manipulation and its effect on SOFC electrochemical performance. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(4): 367.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
CHEN C S, ZHAN Z L, BAN X K, et al. Preparation and property of GDC-LSF dual-phase composite membrane with straight pores and sandwich structure. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(5): 497.
DOI |
| [8] |
夏美荣, 田丰源, 颜晓敏, 等. 造孔剂对流延法制备的阳极支撑SOFC性能的影响. 电源技术, 2022, 46(5): 492.
DOI |
| [9] |
SHAO X, DONG D H, PARKINSON G, et al. A microchanneled ceramic membrane for highly efficient oxygen separation. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2013, 1(34): 9641.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
YANG Y, LIU F S, HAN X, et al. Highly efficient and stable fuel-catalyzed dendritic microchannels for dilute ethanol fueled solid oxide fuel cells. Applied Energy, 2022, 307: 118222.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
CHEN Y, BUNCH J, LI T S, et al. Novel functionally graded acicular electrode for solid oxide cells fabricated by the freeze- tape-casting process. Journal of Power Sources, 2012, 213: 93.
DOI URL |
| [12] | 张月, 马宁, 王亚利, 等. 利用海藻酸钠自组装凝胶法制备YSZ多孔陶瓷. 硅酸盐学报, 2016, 44(6): 785. |
| [13] |
JAMIL S M, OTHMAN M H D, RAHMAN M A, et al. Recent fabrication techniques for micro-tubular solid oxide fuel cell support: a review. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2015, 35(1): 1.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
CHAI R Y, ZHANG Z, WANG M L, et al. Preparation of Ceria based metal supported solid oxide fuel cells by direct assembly method. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 765.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
SOYDAN A M, YILDIZ O, DURĞUN A, et al. Production, performance and cost analysis of anode-supported NiO-YSZ micro- tubular SOFCs. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(57): 30339.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
SHAO X, WANG Z T, XU S S, et al. Microchannel structure of ceramic membranes for oxygen separation. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2016, 36(13): 3193.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
DONG D H, SHAO X, XIE K, et al. Microchanneled anode supports of solid oxide fuel cells. Electrochemistry Communications, 2014, 42: 64.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
DONG D H, SHAO X, HU X, et al. Improved gas diffusion within microchanneled cathode supports of SOECs for steam electrolysis. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 41(44): 19829.
DOI URL |
| [19] | YU L B, WANG J J, YE Z M, et al. Electrochemical conversion of CO2 over microchanneled cathode supports of solid oxide electrolysis cells. Journal of CO2 Utilization, 2018, 26: 179. |
| [20] | WANG T P, TIAN Y Y, LI T P, et al. Essential microstructure of cathode functional layers of solid oxide electrolysis cells for CO2 electrolysis. Journal of CO2 Utilization, 2019, 32: 214. |
| [21] | WANG T P, WANG R Z, XIE X Y, et al. Robust direct hydrocarbon solid oxide fuel cells with exsolved anode nanocatalysts. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(51): 56735. |
| [22] |
FAN D J, GAO Y, LIU F S, et al. Autothermal reforming of methane over an integrated solid oxide fuel cell reactor for power and syngas co-generation. Journal of Power Sources, 2021, 513: 230536.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
ZHENG G Z, CHEN T, ZHANG G J, et al. High strength bilayer finger-like ceramic supported reversible solid oxide cells via phase inversion tape-casting technology. Journal of Power Sources, 2024, 599: 234232.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
JIN C, LIU J, LI L H, et al. Electrochemical properties analysis of tubular NiO-YSZ anode-supported SOFCs fabricated by the phase inversion method. Journal of Membrane Science, 2009, 341(1/2): 233.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
LIU T, WANG Y, ZHANG Y X, et al. Steam electrolysis in a solid oxide electrolysis cell fabricated by the phase-inversion tape casting method. Electrochemistry Communications, 2015, 61: 106.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
HUANG H, LIN J, WANG Y L, et al. Facile one-step forming of NiO and yttrium-stabilized zirconia composite anodes with straight open pores for planar solid oxide fuel cell using phase-inversion tape casting method. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 274: 1114.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
HE W, LIU J J, CHEN C S, et al. Oxygen permeation modeling for Zr0.84Y0.16O1.92-La0.8Sr0.2Cr0.5Fe0.5O3-asymmetric membrane made by phase-inversion. Journal of Membrane Science, 2015, 491: 90.
DOI URL |
| [28] | DING R G, CUI S S, LIN J, et al. Improving the water splitting performance of nickel electrodes by optimizing their pore structure using a phase inversion method. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2017, 7(14): 3056. |
| [29] | SHI N, XIE Y, YANG Y, et al. Infiltrated Ni0.08Co0.02CeO2-x@Ni0.8Co0.2 catalysts for a finger-like anode in direct methane-fueled solid oxide fuel cells. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(4): 4943. |
| [30] |
ZHANG H L, CHEN T, HUANG Z H, et al. A cathode-supported solid oxide fuel cell prepared by the phase-inversion tape casting and impregnating method. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(43): 18810.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
SHA Y H, LING Y H, YANG Y, et al. A finger-like anode with infiltrated Ni0.1Ce0.9O2-δ catalyst using new phase inversion combined tape-casting technology for optimized dry reforming of methane. Ceramics International, 2023, 49(17): 29155.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
PAN Y X, PEI K, ZHOU Y C, et al. A straight, open and macro- porous fuel electrode-supported protonic ceramic electrochemical cell. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2021, 9(17): 10789.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
DEVILLE S, SAIZ E, TOMSIA A P. Ice-templated porous alumina structures. Acta Materialia, 2007, 55(6): 1965.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
SUN H B, CHEN Y, CHEN F L, et al. High-performance solid oxide fuel cells based on a thin La0.8Sr0.2Ga0.8Mg0.2O3-δ electrolyte membrane supported by a nickel-based anode of unique architecture. Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 301: 199.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
LIU R P, XU T T, WANG C A. A review of fabrication strategies and applications of porous ceramics prepared by freeze-casting method. Ceramics International, 2016, 42(2): 2907.
DOI URL |
| [36] | GAUDILLERE C, SERRA J M. Freeze-casting: fabrication of highly porous and hierarchical ceramic supports for energy applications. Bulletin of the Spanish Society of Ceramics and Glass, 2016, 55(2): 45. |
| [37] |
DU Y H, HEDAYAT N, PANTHI D, et al. Freeze-casting for the fabrication of solid oxide fuel cells: a review. Materialia, 2018, 1: 198.
DOI URL |
| [38] | BUNCH J, CHEN Y, CHEN F L, et al. Freeze-tape casting for the design of anode-delivery layer in solid oxide fuel cells//SINGH P, BANSAL N P, HALBIG M, et al. Advances in solid oxide fuel cells VIII. Hoboken: Wiley, 2012: 13-21. |
| [39] |
CHEN Y, LIU Q, YANG Z B, et al. High performance low temperature solid oxide fuel cells with novel electrode architecture. RSC Advances, 2012, 2(32):12118.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
SAMMES N M, DU Y, BOVE R. Design and fabrication of a 100 W anode supported micro-tubular SOFC stack. Journal of Power Sources, 2005, 145(2): 428.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
HEDAYAT N, DU Y H, ILKHANI H, et al. Review on fabrication techniques for porous electrodes of solid oxide fuel cells by sacrificial template methods. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2017, 77: 1221.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
HEDAYAT N, DU Y H, ILKHANI H. Pyrolyzable pore-formers for the porous-electrode formation in solid oxide fuel cells: a review. Ceramics International, 2018, 44(5): 4561.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
NISHIHORA R K, RACHADEL P L, QUADRI M G N, et al. Manufacturing porous ceramic materials by tape casting-a review. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2018, 38(4): 988.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
WEI P, SOFIE S, ZHANG Q, et al. Metal supported solid oxide fuel cell by freeze tape casting. ECS Transactions, 2011, 35(1): 379.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
HU L F, WANG C A, HUANG Y, et al. Control of pore channel size during freeze casting of porous YSZ ceramics with unidirectionally aligned channels using different freezing temperatures. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2010, 30(16): 3389.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
CHEN Y, LIN Y, ZHANG Y X, et al. Low temperature solid oxide fuel cells with hierarchically porous cathode nano-network. Nano Energy, 2014, 8: 25.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
XUE W J, SUN Y, HUANG Y, et al. Preparation and properties of porous alumina with highly ordered and unidirectional oriented pores by a self-organization process. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2011, 94(7): 1978.
DOI URL |
| [48] | LONG M L, MA N, YANG J L. Preparation of unidirectional aligned alumina ceramics with micron pores. Journal of the Chinese Chemical Society, 2014, 42(3): 261. |
| [49] | ZHANG Y, MA N, WANG L Y, et al. Preparation of unidirectional porous yttria-stabilized zirconia ceramics by an alginate self- assemble method. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2016, 44(6): 785. |
| [50] | 郭祥, 田彦婷, 吴萍萍, 等. 直通孔陶瓷在固体氧化物燃料电池中的应用. 硅酸盐学报, 2020, 48(6): 887. |
| [51] |
CHANG H, YAN J, CHEN H L, et al. Preparation of thin electrolyte film via dry pressing/heating/quenching/calcining for electrolyte- supported SOFCs. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(8): 9866.
DOI URL |
| [52] | 吴萍萍, 田彦婷, 郭祥, 等. 直孔阳极支撑体及阳极功能层的制备方法及其单电池性能. 硅酸盐学报, 2021, 49(7): 1493. |
| [53] |
ELJAOUHARI A A, MULLER R, KELLERMEIER M, et al. New anisotropic ceramic membranes from chemically fixed dissipative structures. Langmuir, 2006, 22(26): 11353.
PMID |
| [54] | SUZUKI T, YAMAGUCHI T, FUJISHIRO Y, et al. Improvement of SOFC performance using a microtubular, anode-supported SOFC. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2006, 153(5): A925. |
| [55] |
YANG N T, TAN X Y, MA Z F. A phase inversion/sintering process to fabricate nickel/yttria-stabilized zirconia hollow fibers as the anode support for micro-tubular solid oxide fuel cells. Journal of Power Sources, 2008, 183(1): 14.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
LAWLOR V, GRIESSER S, BUCHINGER G, et al. Review of the micro-tubular solid oxide fuel cell: Part I. Stack design issues and research activities. Journal of Power Sources, 2009, 193(2): 387.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
RAHMAN A M, OTHMAN M H D, FANSURI H, et al. Development of high-performance anode/electrolyte/cathode micro- tubular solid oxide fuel cell via phase inversion-based co-extrusion/ co-sintering technique. Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 467: 228345.
DOI URL |
| [58] | LU X K, LI T, BERTEI A, et al. The application of hierarchical structures in energy devices: new insights into the design of solid oxide fuel cells with enhanced mass transport. Energy & Environmental Science, 2018, 11(9): 2390. |
| [59] | LI T, LU X K, RABUNI M F, et al. High-performance fuel cell designed for coking-resistance and efficient conversion of waste methane to electrical energy. Energy & Environmental Science, 2020, 13(6): 1879. |
| [60] |
JARDIEL T, LEVENFELD B, JIMENEZ R, et al. Fabrication of 8-YSZ thin-wall tubes by powder extrusion moulding for SOFC electrolytes. Ceramics International, 2009, 35(6): 2329.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
MENG X X, YAN W, YANG N T, et al. Highly stable microtubular solid oxide fuel cells based on integrated electrolyte/anode hollow fibers. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 275: 362.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
HOU M Y, ZHU F, LIU Y, et al. A high-performance fuel electrode-supported tubular protonic ceramic electrochemical cell. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2023, 43(14): 6200.
DOI URL |
| [63] |
ZHANG L, HE H Q, KWEK W R, et al. Fabrication and characterization of anode-supported tubular solid-oxide fuel cells by slip casting and dip coating techniques. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2009, 92(2): 302.
DOI URL |
| [64] |
CHEN C C, DONG Y, LI L, et al. Electrochemical properties of micro-tubular intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cell with novel asymmetric structure based on BaZr0.1Ce0.7Y0.1Yb0.1O3-δ proton conducting electrolyte. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(31): 16887.
DOI URL |
| [65] |
PAN Y X, ZHANG H, XU K, et al. A high-performance and durable direct NH3 tubular protonic ceramic fuel cell integrated with an internal catalyst layer. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2022, 306: 121071.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
YANG C H, JIN C, CHEN F L. Performances of micro-tubular solid oxide cell with novel asymmetric porous hydrogen electrode. Electrochimica Acta, 2010, 56(1): 80.
DOI URL |
| [67] |
LIN Q Y, LIN J, LIU T, et al. Solid oxide fuel cells supported on cathodes with large straight open pores and catalyst-decorated surfaces. Solid State Ionics, 2018, 323: 130.
DOI URL |
| [68] |
CHEN X, WANG J T, YU N, et al. A robust direct-propane solid oxide fuel cell with hierarchically oriented full ceramic anode consisting with in-situ exsolved metallic nano-catalysts. Journal of Membrane Science, 2023, 677: 121637.
DOI URL |
| [69] |
CAO J W, LI Y F, ZHENG Y, et al. A novel solid oxide electrolysis cell with micro-/nano channel anode for electrolysis at ultra-high current density over 5 A cm-2. Advanced Energy Materials, 2022, 12(28): 2200899.
DOI URL |
| [70] |
LIU F S, CHEN Z P, ZHOU H H, et al. Highly efficient CH4-assisted CO2 electrolysis for syngas production in a quasi- symmetric Ni-ceramic electrolyzer. Journal of Power Sources, 2024, 609: 234703.
DOI URL |
| [71] |
LIU F S, WANG T P, LI J J, et al. Elevated-temperature bio- ethanol-assisted water electrolysis for efficient hydrogen production. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 434: 134699.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 范雨竹, 王媛, 王林燕, 向美玲, 鄢雨婷, 黎本慧, 李敏, 文志东, 王海超, 陈永福, 邱会东, 赵波, 周成裕. 氧化石墨烯基吸附材料去除水体中Pb(II): 制备、性能及机理[J]. 无机材料学报, 2026, 41(1): 12-26. |
| [2] | 徐锦涛, 高攀, 何唯一, 蒋圣楠, 潘秀红, 汤美波, 陈锟, 刘学超. 3C-SiC晶体制备研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2026, 41(1): 1-11. |
| [3] | 余升阳, 苏海军, 姜浩, 余明辉, 姚佳彤, 杨培鑫. 激光增材制造超高温氧化物陶瓷孔隙缺陷形成及抑制研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(9): 944-956. |
| [4] | 闫共芹, 王晨, 蓝春波, 洪雨昕, 叶维超, 付向辉. Al掺杂P2型Na0.8Ni0.33Mn0.67-xAlxO2钠离子电池正极材料的制备与电化学性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(9): 1005-1012. |
| [5] | 刘江平, 管鑫, 唐振杰, 朱文杰, 罗永明. 含氮挥发性有机化合物催化氧化的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(9): 933-943. |
| [6] | 肖晓琳, 王玉祥, 谷佩洋, 朱圳荣, 孙勇. 二维无机材料调控病损皮肤组织再生的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 860-870. |
| [7] | 马景阁, 吴成铁. 无机生物材料用于毛囊和毛发再生的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 901-910. |
| [8] | 张洪健, 赵梓壹, 吴成铁. 无机生物材料调控神经细胞功能及神经化组织再生的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 849-859. |
| [9] | 艾敏慧, 雷波. 微纳米生物活性玻璃: 功能化设计与血管化皮肤再生[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 921-932. |
| [10] | 王宇彤, 常江, 徐合, 吴成铁. 硅酸盐生物陶瓷/玻璃促创面修复的研究进展:作用、机制和应用方式[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 911-920. |
| [11] | 马文平, 韩雅卉, 吴成铁, 吕宏旭. 无机活性材料在类器官研究领域的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 888-900. |
| [12] | 罗晓民, 乔志龙, 刘颍, 杨晨, 常江. 无机生物活性材料调控心肌再生的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(8): 871-887. |
| [13] | 朱文杰, 唐璐, 陆继长, 刘江平, 罗永明. 钙钛矿型氧化物催化氧化挥发性有机化合物的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [14] | 胡智超, 杨鸿宇, 杨鸿程, 孙成礼, 杨俊, 李恩竹. P-V-L键理论在微波介质陶瓷性能调控中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [15] | 吴琼, 沈炳林, 张茂华, 姚方周, 邢志鹏, 王轲. 铅基织构压电陶瓷研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||