无机材料学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (4): 407-416.DOI: 10.15541/jim20180280 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20180280
马志军,莽昌烨,赵海涛,关智浩,程亮
收稿日期:2018-06-22
修回日期:2018-10-22
出版日期:2019-04-20
网络出版日期:2019-04-15
作者简介:马志军(1969-), 男, 博士, 教授. E-mail:zhijunma0930@126.com
基金资助:Zhi-Jun MA,Chang-Ye MANG,Hai-Tao ZHAO,Zhi-Hao GUAN,Liang CHENG
Received:2018-06-22
Revised:2018-10-22
Published:2019-04-20
Online:2019-04-15
Supported by:摘要:
以天然鳞片石墨为原料制备氧化石墨(GO), 应用水热法制备钴锌铁氧体(Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4), 并将两者制备成石墨烯(rGO)/Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4复合材料。采用X射线衍射(XRD)、拉曼光谱(Raman)、红外光谱(FT-IR)研究rGO/Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4的结构; 应用透射电子显微镜(TEM)和矢量网络分析仪(VNA)研究不同复合比例对rGO/Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4复合材料形貌、电磁损耗特性、德拜弛豫模型及电磁响应行为的影响。结果表明: 复合反应后的GO在XRD图谱中主衍射峰由2θ=9.74°变化为2θ=24.15°, 且红外光谱图中显示含氧官能团消失, 均说明GO成功还原为rGO。透射电子显微镜图中可以看到Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4嵌布在rGO上。复合反应过程中, 当钴锌铁氧体的含量增大, 分散性逐渐减弱。Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4与GO质量比为2 : 1时制备的rGO/Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4复合材料的吸波性能最佳, 在15.11 GHz处反射率达到最小值-36.89 dB, 有效吸波频带宽为3.74。
中图分类号:
马志军, 莽昌烨, 赵海涛, 关智浩, 程亮. 石墨烯装载不同含量钴锌铁氧体及其电磁行为对比[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(4): 407-416.
Zhi-Jun MA, Chang-Ye MANG, Hai-Tao ZHAO, Zhi-Hao GUAN, Liang CHENG. Comparison of Electromagnetism Behavior of Different Content Cobalt-zinc Ferrite Loaded with Graphene[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(4): 407-416.
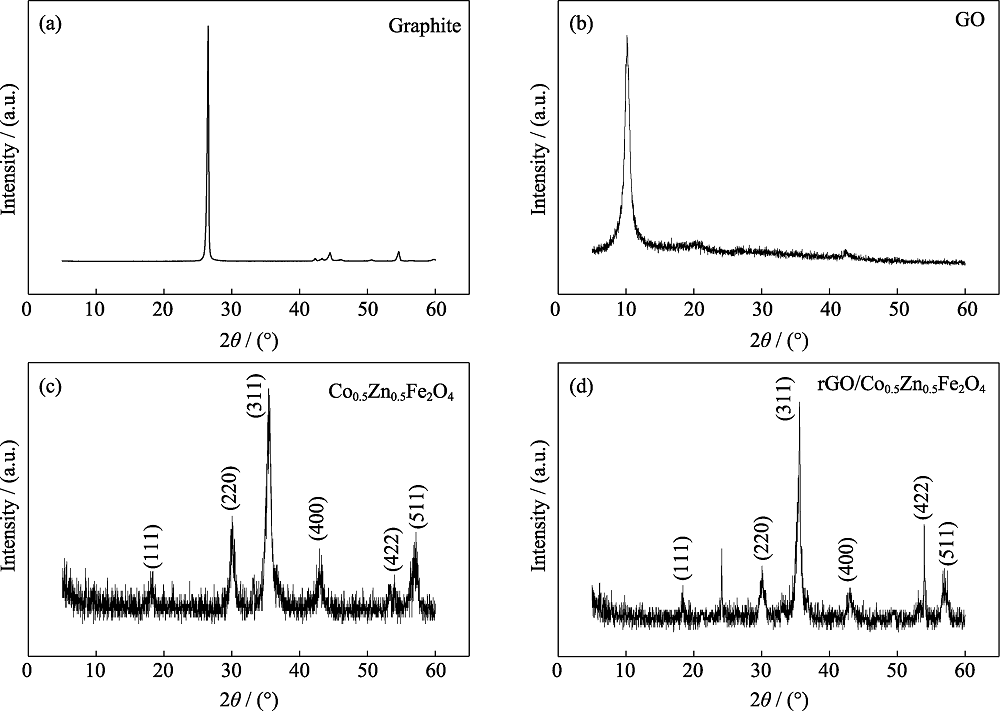
图1 天然鳞片石墨(a)、GO(b)、Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4(c)和rGO/Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4复合材料(d)的XRD图谱
Fig. 1 XRD patterns of natural flake graphite (a), GO (b), Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 (c), and rGO/Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 composite (d)
| Structural formula | 2θ/(°) | a/nm | (311) Priority crystallization diffraction peak | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FWHM/rad | Intensity/(a.u.) | Size/nm | |||
| Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 | 35.597 | 0.8391 | 0.618 | 86 | 13.8 |
| rGO/Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 | 35.595 | 0.8358 | 0.466 | 94 | 17.7 |
表1 铁氧体的组分和结构参数
Table 1 Composition and structure parameters of ferrite
| Structural formula | 2θ/(°) | a/nm | (311) Priority crystallization diffraction peak | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FWHM/rad | Intensity/(a.u.) | Size/nm | |||
| Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 | 35.597 | 0.8391 | 0.618 | 86 | 13.8 |
| rGO/Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 | 35.595 | 0.8358 | 0.466 | 94 | 17.7 |
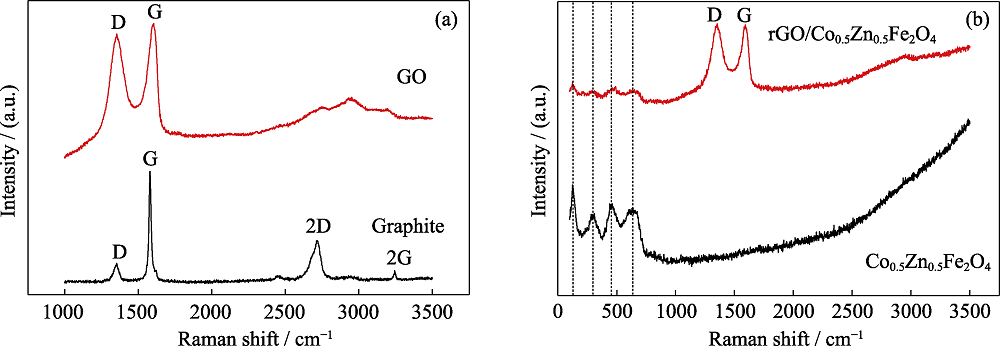
图2 天然鳞片石墨、GO(a)和Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4、rGO/Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4复合材料(b)的拉曼光谱
Fig. 2 Raman spectra of natural flake graphite, GO (a) and Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4, rGO/Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 composite (b)
| Samples | Graphite | GO | rGO/Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ID/IG | 0.21 | 0.95 | 1.02 |
表2 天然鳞片石墨、GO和rGO/Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4复合材料的ID值与IG值的比率
Table 2 ID/IG ratios of natural flake graphite, GO and rGO/Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 composite
| Samples | Graphite | GO | rGO/Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ID/IG | 0.21 | 0.95 | 1.02 |
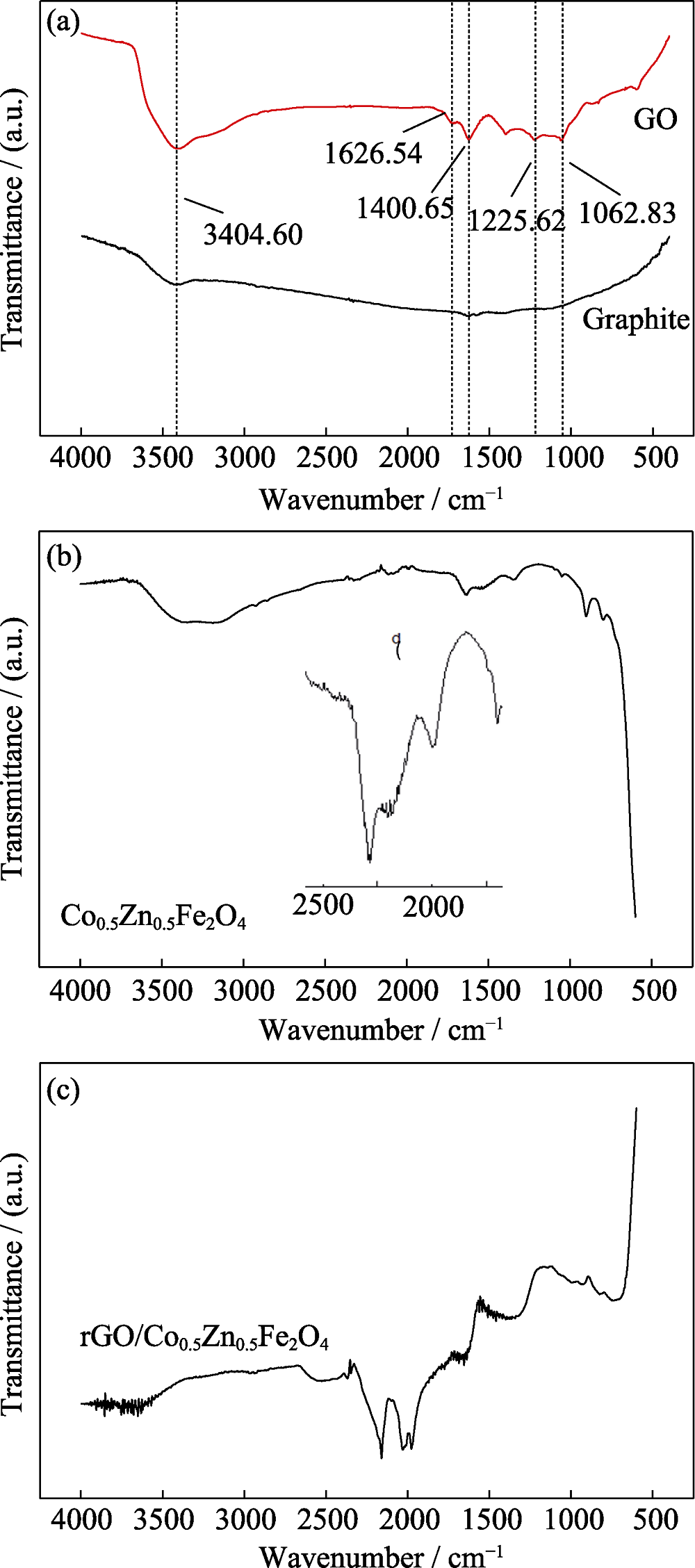
图3 天然鳞片石墨、GO (a)、Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 (b)和rGO/Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 (c)的FT-IR谱图
Fig. 3 FT-IR spectra of natural flake graphite, GO (a), Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 (b) and rGO/Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 (c)
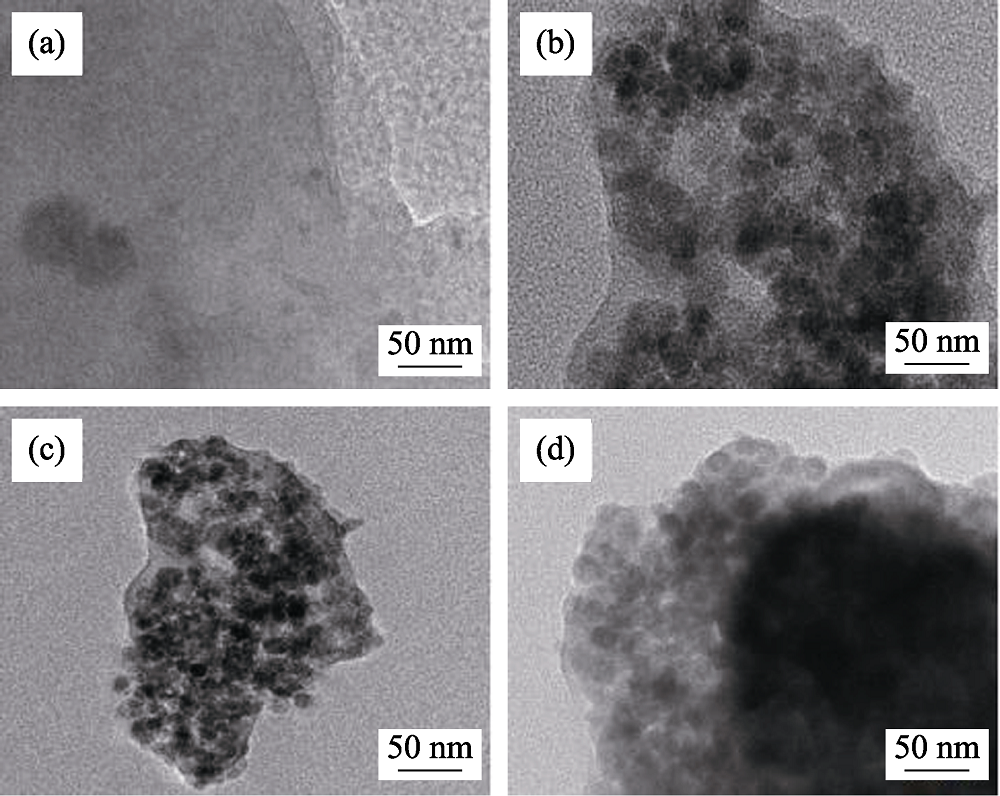
图4 rGO/Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4-1(a)、rGO/Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4-2(b)、rGO/Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4-3(c)和rGO/Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4-4(d)的TEM照片
Fig. 4 TEM images of rGO/Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4-1(a), rGO/ Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4-2 (b), rGO/Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4-3 (c), and rGO/ Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4-4 (d)
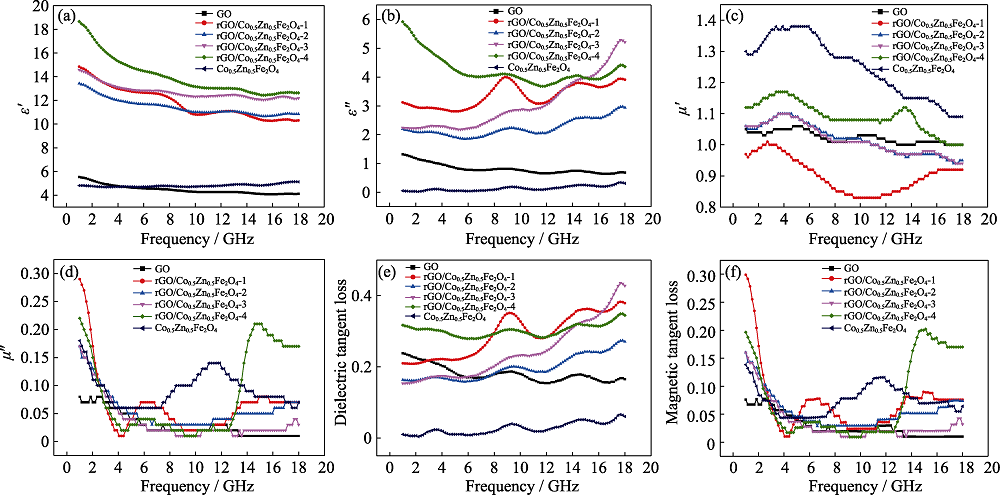
图5 GO、Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4和不同比例的rGO/Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4复合材料的复介电常数实部(a)、复介电常数虚部(b)、磁导率实部(c)、磁导率虚部(d)、介电损耗(e)和磁滞损耗(f)
Fig. 5 Real part of complex permittivity (a), imaginary part of complex permittivity (b), real part of complex permeability (c), imaginary part of complex permeability (d), dielectric loss tangent (e) and magnetic loss tangent (f) of GO、Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 and rGO/Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 composite with different ratios
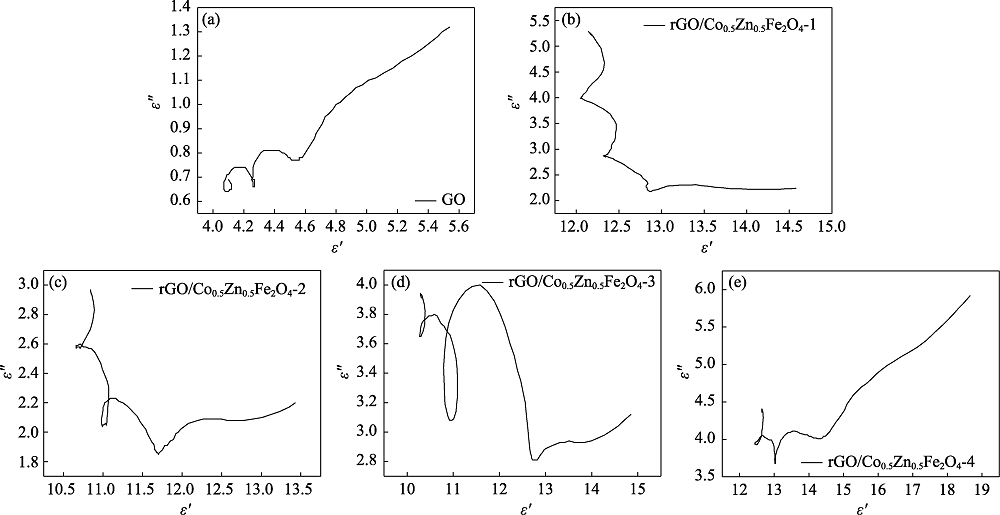
图6 GO和不同复合比例rGO/Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4复合材料的复介电常数(ε°)-复介电常数虚部(ε?)曲线
Fig. 6 Real part of complex permittivity (ε°)-imaginary part of complex permittivity (ε?) curves of GO and rGO/Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 composites with different ratios
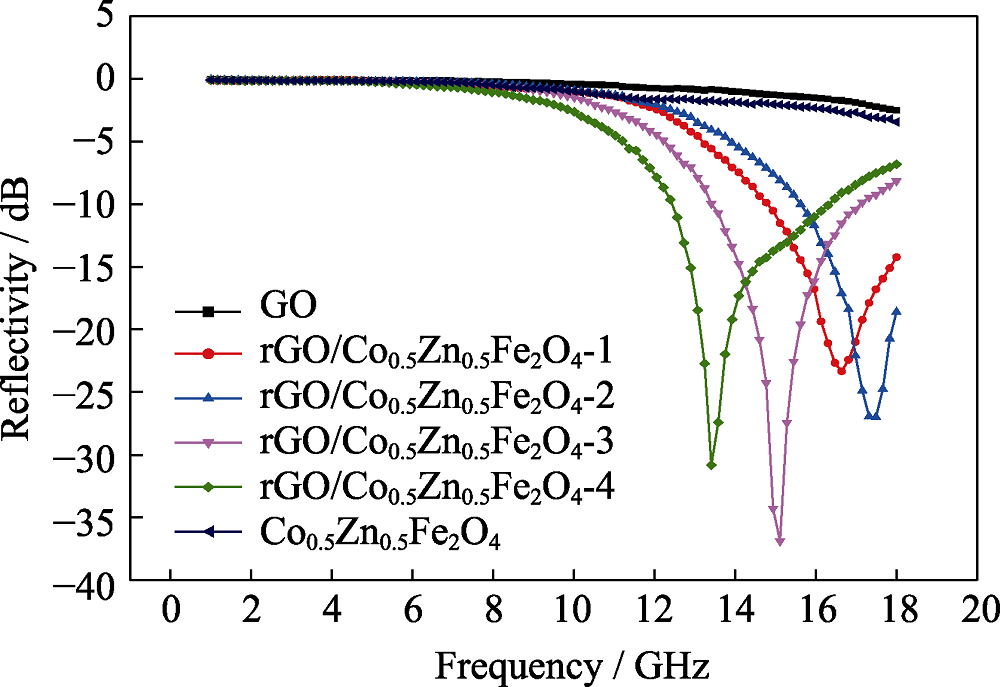
图7 GO和不同复合比例rGO/Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4复合材料的反射率与曲线频率的关系曲线
Fig. 7 Curves of reflectivity and frequency of GO and rGO/Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 composites with different ratios
| [1] | WU G L, CHENG Y H, XIANG F , et al. Morphology controlled synthesis, characterization and microwave absorption properties of nanostructured 3D CeO2. Mat. Sci. Semicond. Process, 2016,41(2):6-11. |
| [2] | FU W, LIU S, FAN W , et al. Hollow glass microspheres coated with CoFe2O4 and its microwave absorption property.[J]. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2007,316(1):54-58. |
| [3] | HAJALILOU A, HASHIM M, MASOUDI M T . A comparative study of in-situ mechanochemically synthesized Mn0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 ferrite nanoparticles in the MnO/ZnO/Fe2O3 and MnO2/Zn/Fe2O3 systems. Ceramics International, 2015,41(6):8070-8079. |
| [4] | ZHANG X C, WANG D P, YAO A H , et al. Optimization on preparation process of Mn-Zn ferrite powder by Sol-Gel method. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2008,27(5):937-940. |
| [5] | ZHAO H T, ZHANG Q, LIU R P , et al. Synthesis and magnetic properties of monodisperse ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2016,44(01):103-107. |
| [6] | LIU J, CHE R, CHEN H , et al. Microwave absorption enhancement of multifunctional composite microspheres with spinel Fe3O4 cores and anatase TiO2 shells. Small, 2012,8(8):1214-1221. |
| [7] | GUO J, WU H, LIAO X , et al. Facile synthesis of size-controlled silver nanoparticles using plant tannin grafted collagen fiber as reductant and stabilizer for microwave absorption application in the whole Ku band. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2011,115(48):23688-23694. |
| [8] | KONG L, YIN X, ZHANG Y , et al. Electromagnetic wave absorption properties of reduced graphene oxide modified by Maghemite colloidal nanoparticle clusters. J. Phys. Chem.C, 2013,117(38):19701-19711. |
| [9] | SCHEDIN F, GEIM A K, MOROZOV S V , et al. Detection of individual gas molecules adsorbed on graphene. Nat. Mater., 2007,6(9):652-655. |
| [10] | ANG P K, CHEN W, WEE A , et al. Solution-gated epitaxial graphene as pH sensor.[J]. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008,130(44):14392-14393. |
| [11] | STOLLER M D, PARK S J, ZHU Y W , et al. Graphene-based ultracapacitors. Nano Lett., 2008,8(10):3498-3502. |
| [12] | EDA G, FANCHINI G, CHHOWALLA M . Large-area ultrathin films of reduced graphene oxide as a transparent and flexible electronic material. Nat. Nanotechnol., 2008,3(5):270-274. |
| [13] | YOO E, KIM J, HOSONO E , et al. Large reversible Li storage of graphene nanosheet families for use in rechargeable lithium ion batteries. Nano Lett., 2008,8(8):2277-2282. |
| [14] | GEIM A K . Graphene: status and prospects. Science, 2009,324(5934):1530-1534. |
| [15] | BALANDIN A A, GHOSH S, BAO W Z , et al. Lausuperior thermal conductivity of single layer graphene. Nano Lett., 2008,8(3):902-907. |
| [16] | LEE C, WEI X D, KYSAR J W , et al. Measurement of the elastic properties and intrinsic strength of monolayer graphene. Science, 2008,321(5887):385-388. |
| [17] | LI D, MULLER M B, GILJE S , et al. Processable aqueous dispersions of graphene nanosheets. Nat. Nanotechnol., 2008,3(2):101-105. |
| [18] | JUNG I, DIKIN D A, PINER R D , et al. Tunable electrical conductivity of individual graphene oxide sheets reduced at “low” temperatures. Nano Lett., 2008,8(12):4283-4287. |
| [19] | CHEN H, MULLER M B, GILMORE K J , et al. Mechanically strong, electrically conductive, and biocompatible graphene paper. Adv. Mater., 2008,20(18):3557-3561. |
| [20] | LIAN P C, ZHU X F, XIANG H F , et al. Enhanced cycling performance of Fe3O4-graphene nanocomposite as an anode material for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim.Acta, 2010,56(2):834-840. |
| [21] | LI N W, ZHENG M B, CHANG X F , et al. Preparation of magnetic CoFe2O4-functionalized graphene sheets via a facile hydrothermal method and their adsorption properties.[J]. Solid State Chem., 2011,184(4):953-958. |
| [22] | ZONG M, HUANG Y, ZHANG N , et al. Influence of (RGO)/(Ferrite) ratios and graphene reduction degree on microwave absorption properties of graphene composites. J. Alloys Compd., 2015,644(25):491-501. |
| [23] | DAN C, LIU X, YU R , et al. Enhanced microwave absorption properties of flake-shaped FePCB metallic glass/graphene composites. Composites Part A, 2016,89:33-39. |
| [24] | AN R, WEI H Y, HE M , et al. The progress analysis of carbon- based composites used for electromagnetic wave absorption. Materials Review, 2017,31(21):46-53, 61. |
| [25] | HUMMERS W S, OFFEMAN R E . Preparation of graphitic oxide. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1958,80(6):1339. |
| [26] | KOVTYUKHOVA N I, OLLIVIER P J . Layer-by-layer assembly of ultrathin composite films from micron-sized graphite oxide sheets and polycations. Chemical Materials, 1999,11(3):71-78. |
| [27] | GENG Y, WANG S J, KIM J K . Preparation of graphite nanoplatelets and graphene sheets.[J]. Colloid Interface Sci., 2009,336(2):592-598. |
| [28] | SU J, CAO M H, REN L , et al. Fe3O4-graphene nanocomposites with improved Lithium storage and Magnetism properties. J. Phys. Chem.C, 2011,115(30):14469-14477. |
| [29] | GABAL M A, EL-SHISHTAWY R M, ANGARI YM . Structural and magnetic properties of nano-crystalline Ni-Zn ferrites synthesized using egg-white precursor.[J]. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2012,324(14):2258-2264. |
| [30] | YANG H B, YE T, LIN Y , et al. Microwave absorbing properties of the ferrite composites based on graphene.[J]. Alloys Compd., 2016,683:567-574. |
| [31] | GRAF D, MOLITOR F, ENSSLIN K , et al. Spatially resolved raman spectroscopy of single and few-layer graphene. Nano Lett., 2007,7(2):238-242. |
| [32] | BELL N J, HG Y H, DU A J , et al. Understanding the enhancement in photoelectrochemical properties of photocatalytically prepared TiO2-reduced graphene oxide composite. J. Phys. Chem.C, 2011,115(13):6004-6009. |
| [33] | FU MIN, JIAO QINGZE, ZHAO YUN . Preparation of NiFe2O4 nanorod-graphene compoites via an ionic liquid assisted one-step hydrothermal approch and their microwave absorbing properties. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2013,1(18):5577-5586. |
| [34] | FERRARI AC, ROBERTSON A . Interpretation of Raman spectra of disordered and amorphous carbon. J. Physiol. Rev.B, 2000,61(20):14095-14107. |
| [35] | SUN XIN, HE JIANPING, LI GUOXIAN , et al. Laminated magnetic graphene with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2013,1(4):765-777. |
| [36] | TUINSTRA F, KOENIG J L . Raman spectrum of graphite.[J]. Chem. Phys., 1970,53(3):1126-1130. |
| [37] | MURUGAN A V, MURALIGANTH T, MANTHIRAM A . Rapid, facile microwave-solvothermal synthesis of graphene nanosheets and their polyaniline nanocomposites for energy strorage. Chem. Mater., 2009,22(8):5004-5006. |
| [38] | FU MIN, JIAO QINGZE, ZHAO YUN . In situ fabrication and characterization of cobalt ferrite nanorods/graphene composites. Materials Characterization, 2013,86(8):303-315. |
| [39] | JEONG H K, LEE Y P, LAHAYE R J , et al. Evidence of graphitic AB stacking order of graphite oxides.[J]. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008,130(4):1362-1366. |
| [40] | NETHRAVATHI C, NISHA T, RAVISHANKAR N , et al. Graphene- nanocrystalline metal sulphide composites produced by a one-pot reaction starting from graphite oxide. Carbon, 2009,47(8):2054-2059. |
| [41] | BOURLINOS A B, GOURNIS D, PETRIDIS D , et al. Graphite oxide: chemical reduction to graphite and surface modification with primary aliphatic amines and amino acids. Langmuir, 2003,19(15):6050-6055. |
| [42] | ZHANG X F, DONG X L, HUANG H , et al. Microwave absorption properties of the carbon-coated nickel nanocapsules. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2006, 89(5): 053115-1-3. |
| [43] | TIANJIAO B, YAN Z, XIAOFENG S , et al. A study of the electromagnetic properties of cobalt-multiwalled carbon nanotubes(co-mwcnts)composites. Materials Science And Engineering: B, 2011,176(12):906-912. |
| [44] | HASSAN A, KHAN M A, ASGHAR M , et al. Nanocrystalline Zn1-xCo0.5xNi0.5xFe2O4 ferrites: fabrication via co-precipitation route with enhanced magnetic and electrical properties.[J]. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2015,393:56-77. |
| [45] | FRENKEL J, DORFMAN J . Spontaneous and induced magnetisation in ferromagnetic bodies. Nature, 1930,126(3173):274-275. |
| [46] | YANG HAIBO, YE TING, LIN YING , et al. Microwave absorbing properties of the ferrite composites based on grapheme.[J]. Alloys Compd., 2016,683:567-574. |
| [47] | MILES P A, WESTPHAL W B, VON HIPPEL A . Dielectric spectroscopy of ferromagnetic semiconductors rev. Mod. Phys., 1957,29(3):279-307. |
| [48] | MA Z, WANG J B, LIU Q F , et al. Microwave absorption of electroless Ni-Co-P-coated SiO2 powder. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2009,255(13):6629-6633. |
| [49] | RUTTER G M, CRAIN J N, GUISINGER N P , et al. Scattering and interference in epitaxial graphene. Science, 2007,317(5835):219-222. |
| [50] | SUN S L, HE Q, XIAO S Y , et al. Gradient-index meta-surfaces as a bridge linking propagating waves and surface waves. Nat. Mater., 2012,11(5):426-431. |
| [1] | 陈义, 邱海鹏, 陈明伟, 徐昊, 崔恒. SiC/SiC复合材料基体硼改性方法及其力学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 504-510. |
| [2] | 杨茗凯, 黄泽皑, 周芸霄, 刘彤, 张魁魁, 谭浩, 刘梦颖, 詹俊杰, 陈国星, 周莹. 基于Cu与金属氧化物-KCl熔融介质的甲烷热解制备少层石墨烯与氢气联产研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 473-480. |
| [3] | 穆爽, 马沁, 张禹, 沈旭, 杨金山, 董绍明. Yb2Si2O7改性SiC/SiC复合材料的氧化行为研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 323-328. |
| [4] | 杨舒琪, 杨存国, 牛慧祝, 石唯一, 舒珂维. GeP3/科琴黑复合材料作为钠离子电池高性能负极材料[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 329-336. |
| [5] | 高晨光, 孙晓亮, 陈君, 李达鑫, 陈庆庆, 贾德昌, 周玉. 基于湿法纺丝技术的SiBCN-rGO陶瓷纤维的组织结构、力学和吸波性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 290-296. |
| [6] | 谌广昌, 段小明, 朱金荣, 龚情, 蔡德龙, 李宇航, 杨东雷, 陈彪, 李新民, 邓旭东, 余瑾, 刘博雅, 何培刚, 贾德昌, 周玉. 直升机特定结构先进陶瓷材料研究进展与应用展望[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 225-244. |
| [7] | 王悦, 王欣, 于显利. 室温铁磁性还原氧化石墨烯基全碳膜[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 305-313. |
| [8] | 栾新刚, 何典蔚, 涂建勇, 成来飞. 2D平纹和3D针刺C/SiC复合材料的低速冲击破坏行为和失效机理[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 205-214. |
| [9] | 王文婷, 徐敬军, 马科, 李美栓, 李兴超, 李同起. 原位反应/热压合成Ti2AlC-20TiB2复合材料在1000~1300 ℃空气中的高温氧化行为[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(1): 31-38. |
| [10] | 全文心, 余艺平, 方冰, 李伟, 王松. 管状C/SiC复合材料高温空气氧化行为与宏细观建模研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(8): 920-928. |
| [11] | 何思哲, 王俊舟, 张勇, 费嘉维, 吴爱民, 陈意峰, 李强, 周晟, 黄昊. 高频低损耗的Fe/亚微米FeNi软磁复合材料[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(8): 871-878. |
| [12] | 孙海洋, 季伟, 王为民, 傅正义. TiB-Ti周期序构复合材料设计、制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 662-670. |
| [13] | 吴晓晨, 郑瑞晓, 李露, 马浩林, 赵培航, 马朝利. SiCf/SiC陶瓷基复合材料高温环境损伤原位监测研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 609-622. |
| [14] | 粟毅, 史扬帆, 贾成兰, 迟蓬涛, 高扬, 马青松, 陈思安. 浆料浸渍辅助PIP工艺制备C/HfC-SiC复合材料的微观结构及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 726-732. |
| [15] | 赵日达, 汤素芳. 多孔碳陶瓷化改进反应熔渗法制备陶瓷基复合材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 623-633. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||