无机材料学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (6): 571-590.DOI: 10.15541/jim20230609 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20230609
所属专题: 【结构材料】超高温结构陶瓷(202506)
收稿日期:2023-12-31
修回日期:2024-03-18
出版日期:2024-06-20
网络出版日期:2024-03-22
通讯作者:
胡平, 教授. E-mail: huping@hit.edu.cn作者简介:张幸红(1972-), 男, 博士, 教授. E-mail: zhangxh@hit.edu.cn
基金资助:
ZHANG Xinghong( ), WANG Yiming, CHENG Yuan, DONG Shun, HU Ping(
), WANG Yiming, CHENG Yuan, DONG Shun, HU Ping( )
)
Received:2023-12-31
Revised:2024-03-18
Published:2024-06-20
Online:2024-03-22
Contact:
HU Ping, professor. E-mail: huping@hit.edu.cnAbout author:ZHANG Xinghong (1972-), male, PhD, professor. E-mail: zhangxh@hit.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
随着高速飞行器朝着更宽空域、更长时间和更高速度的方向发展, 对飞行器的鼻锥、前缘和发动机燃烧室等关键结构的热防护性能提出了更加严苛的要求, 发展在极端环境下使用的高性能热防护材料是当前的研究重点。超高温陶瓷复合材料具有优异的抗氧化烧蚀性能, 是一类极具应用潜力的非烧蚀型热防护材料。然而, 本征脆性问题限制了超高温陶瓷复合材料的工程化应用, 需通过组分结构调控对其进行强韧化。同时, 飞行器有效载荷提升也对超高温陶瓷复合材料提出了轻量化的要求。本文系统概述了超高温陶瓷复合材料近年来取得的主要研究进展, 包括压力烧结、泥浆浸渍、前驱体浸渍裂解、反应熔渗、化学气相渗透/沉积与“固-液”组合工艺等制备方法, 颗粒、晶须、软相物质、短切纤维和连续纤维等强韧化方法及其机制, 抗氧化烧蚀性能与机理, 以及轻量化设计等。讨论了超高温陶瓷复合材料组分、微结构和性能之间的关系, 并指出了超高温陶瓷复合材料目前存在的挑战以及未来的发展趋势。
中图分类号:
张幸红, 王义铭, 程源, 董顺, 胡平. 超高温陶瓷复合材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(6): 571-590.
ZHANG Xinghong, WANG Yiming, CHENG Yuan, DONG Shun, HU Ping. Research Progress on Ultra-high Temperature Ceramic Composites[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(6): 571-590.

图1 热压烧结制备的3D Cf/ZrC-SiC复合材料微观结构[31]
Fig. 1 Microstructures of 3D Cf/ZrC-SiC composites prepared by hot pressing sintering[31] (a, b) Carbon fiber surface at different magnifications; (c, d) Carbon fiber-ceramic interface at different magnifications
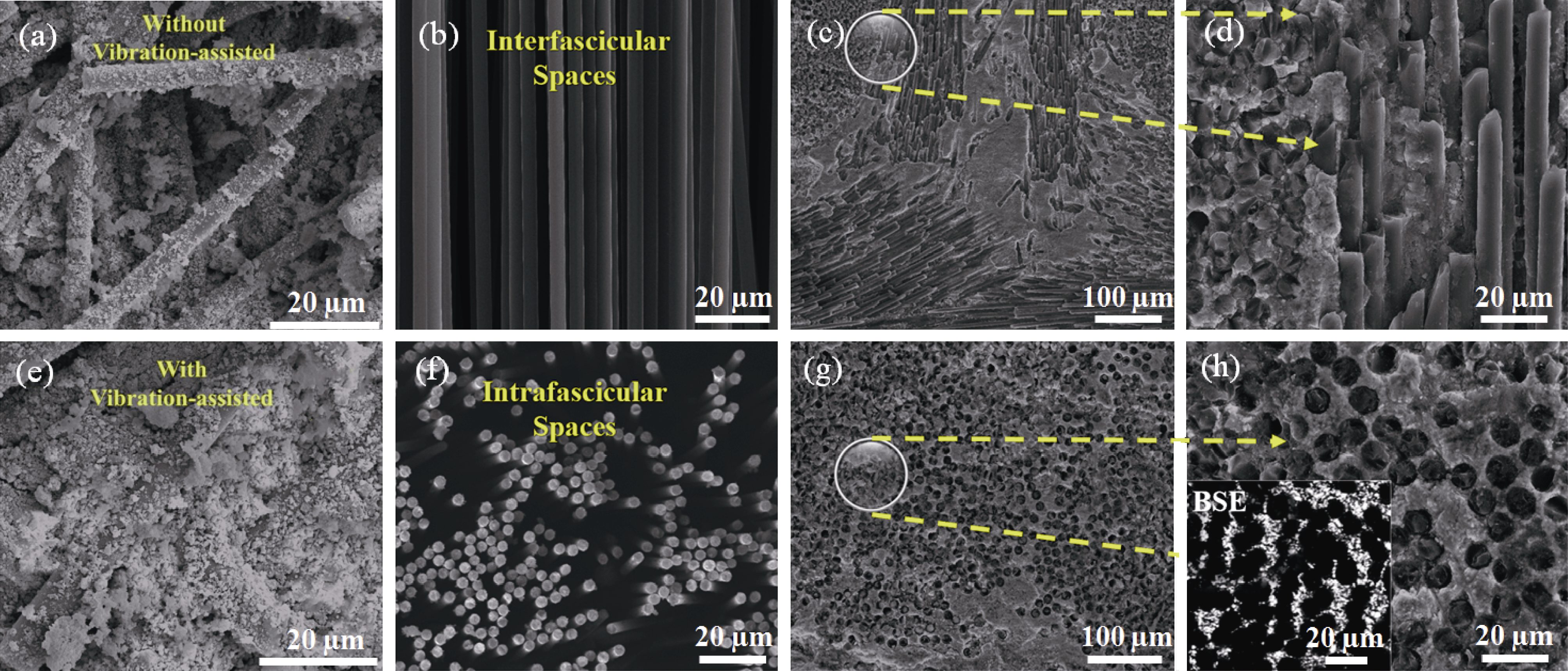
图3 “固-液”组合工艺微结构表征[70-71]
Fig. 3 Microstructure characterization of “solid-liquid” combination process[70-71] (a, e) Microscopic comparison with/without vibration-assisted[70]; (b-d, f-h)Interfascicular (b-d) and intrafascicular (f-h) microstructures of fibers before (b, f) and after (c, d, g, h) densification[71]
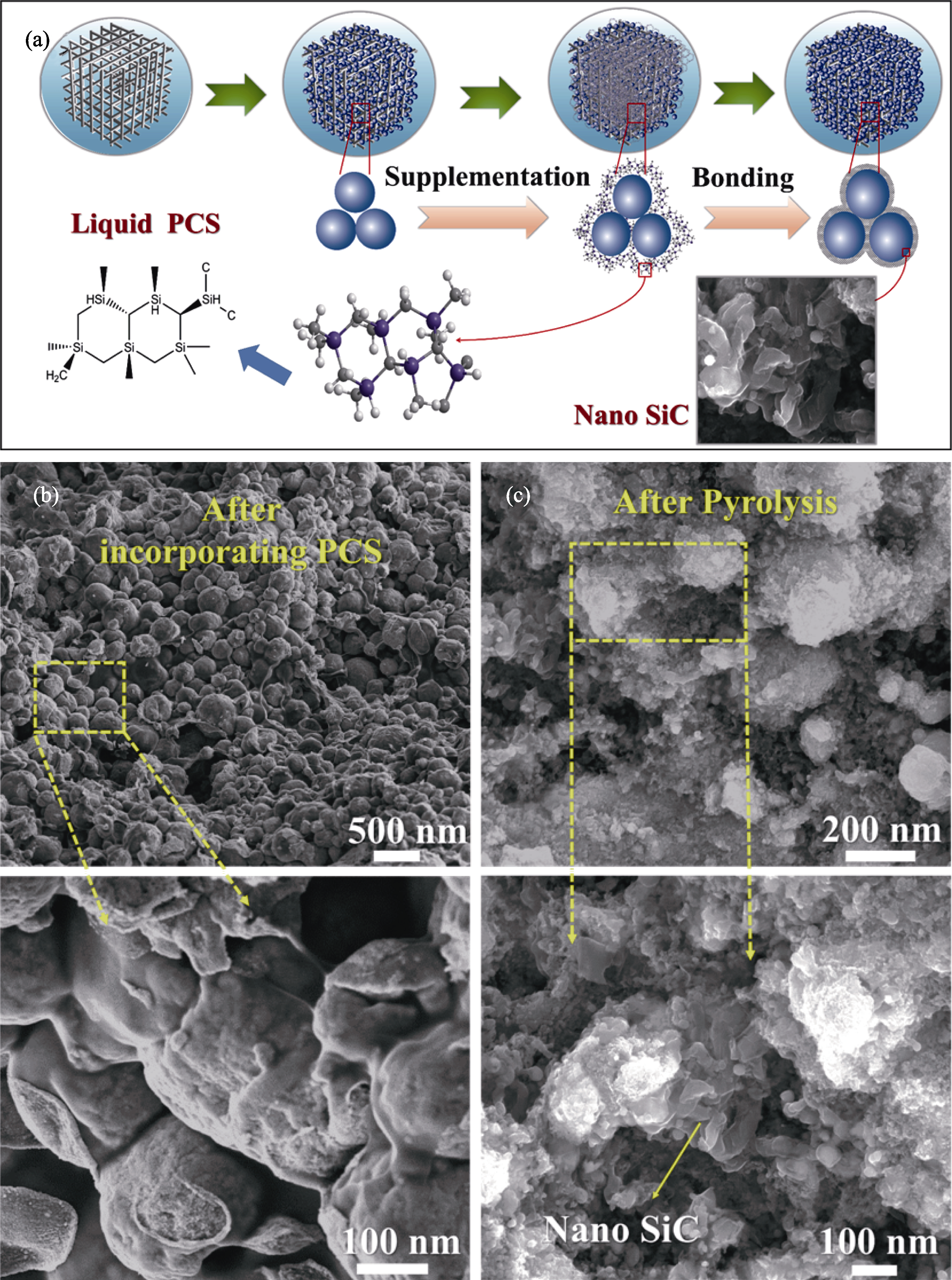
图4 “固-液”组合工艺致密化机理与微观结构[71]
Fig. 4 Densification mechanism and microstructure of "solid-liquid" combination process[71] (a) Mechanism of densification; (b) Microstructure after addition of polycarbosilane (PCS); (c) Microstructure after pyrolysis
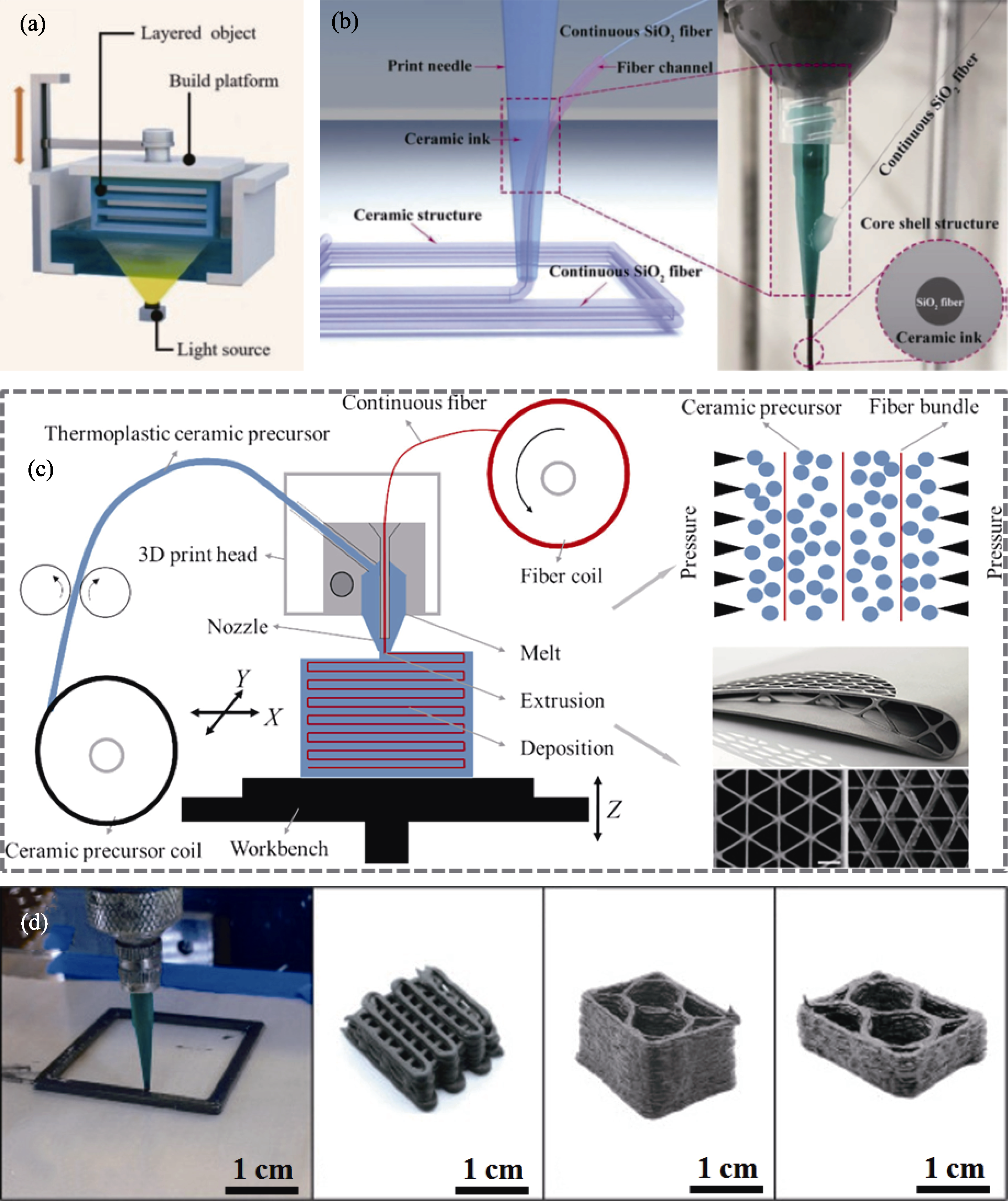
图5 用于超高温陶瓷复合材料的增材制造技术[75,78⇓ -80]
Fig. 5 Additive manufacturing technologies for ultra-high temperature ceramic composite materials[75,78⇓ -80] (a) DLP printer[75]; (b) Schematic of SiO2/phosphate ceramic matrix composites fabricated by DIW[78]; (c) Schematic of Cf/SiC ceramic matrix composites fabricated by FDM[80]; (d) Examples of SiCf/ZrB2-SiC composites with ink being printed and pyrolytic structures fabricated[79]

图6 超高温陶瓷复合材料强韧化机制[71,85,87,90,93 -94,100,115]
Fig. 6 Mechanisms for toughening ultra-high temperature ceramic composites[71,85,87,90,93 -94,100,115] (a) Particle toughening[85]; (b) Whisker toughening[87]; (c) Graphene toughening[93]; (d) Graphite flakes toughening[90]; (e) Carbon nanotube toughening[94]; (f) Short cut fiber toughening[100]; (g) Continuous fiber toughening[71]; (h) Fibrous monolith structure toughening[115]
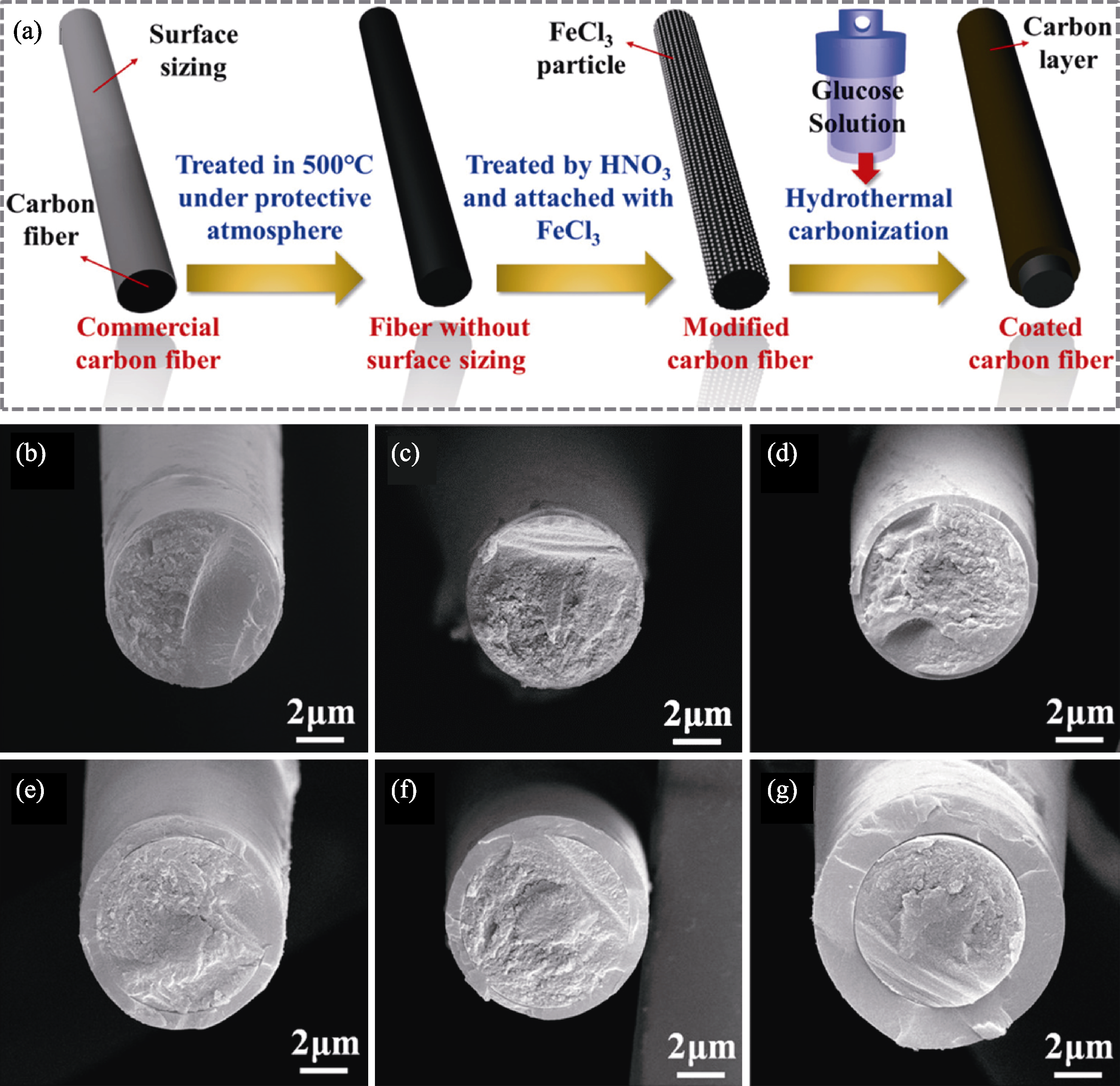
图7 糖-碳转化工艺过程与结果[111]
Fig. 7 Sugar-carbon conversion process and results[111] (a) Process; (b-g) Hydrothermal coatings with different thicknesses of (b) 70 nm, (c) 160 nm, (d) 300 nm, (e) 1 μm, (f) 1.3 μm, and (g) 1.8 μm
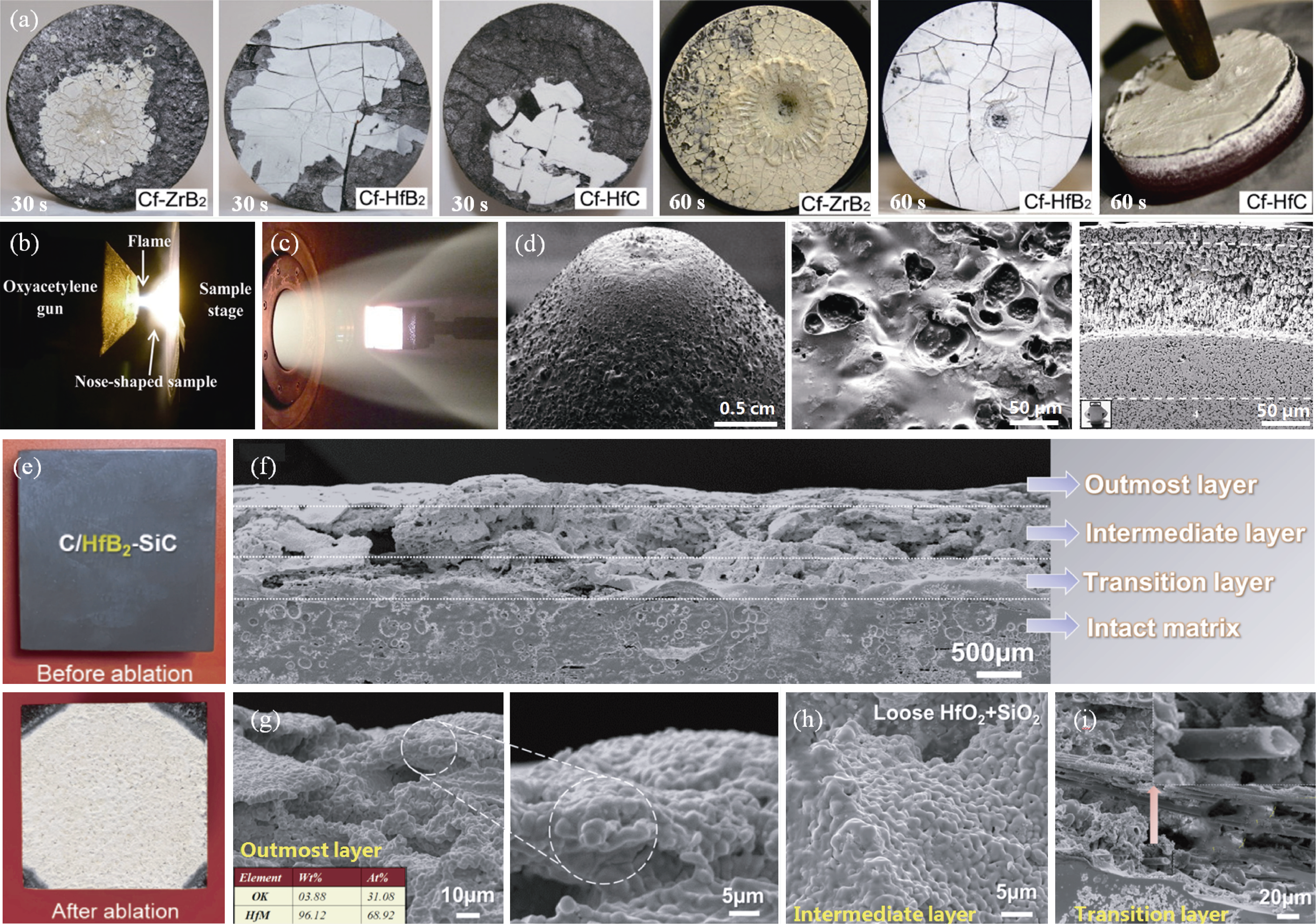
图8 超高温陶瓷复合材料抗氧化烧蚀宏微观表征
Fig. 8 Macro-micro characterization of ultra-high temperature ceramic composites against oxidative ablation (a) Cf/ultra-high temperature ceramic composites ablated under oxyacetylene flame after 30 and 60 s with diameter of 30 mm[118]; (b) Oxyacetylene ablation test[119]; (c) Arc jet plasma wind tunnel in German Aerospace Agency (DLR); (d) Microscopic morphology of ZrB2-SiC material after plasma wind tunnel ablation[120]; (e) Macroscopic morphologies of Cf/HfB2-SiC composites before and after oxyacetylene ablation[128]; (f-i) Micro-morphologies of Cf/HfB2-SiC composites after oxyacetylene ablation[128]
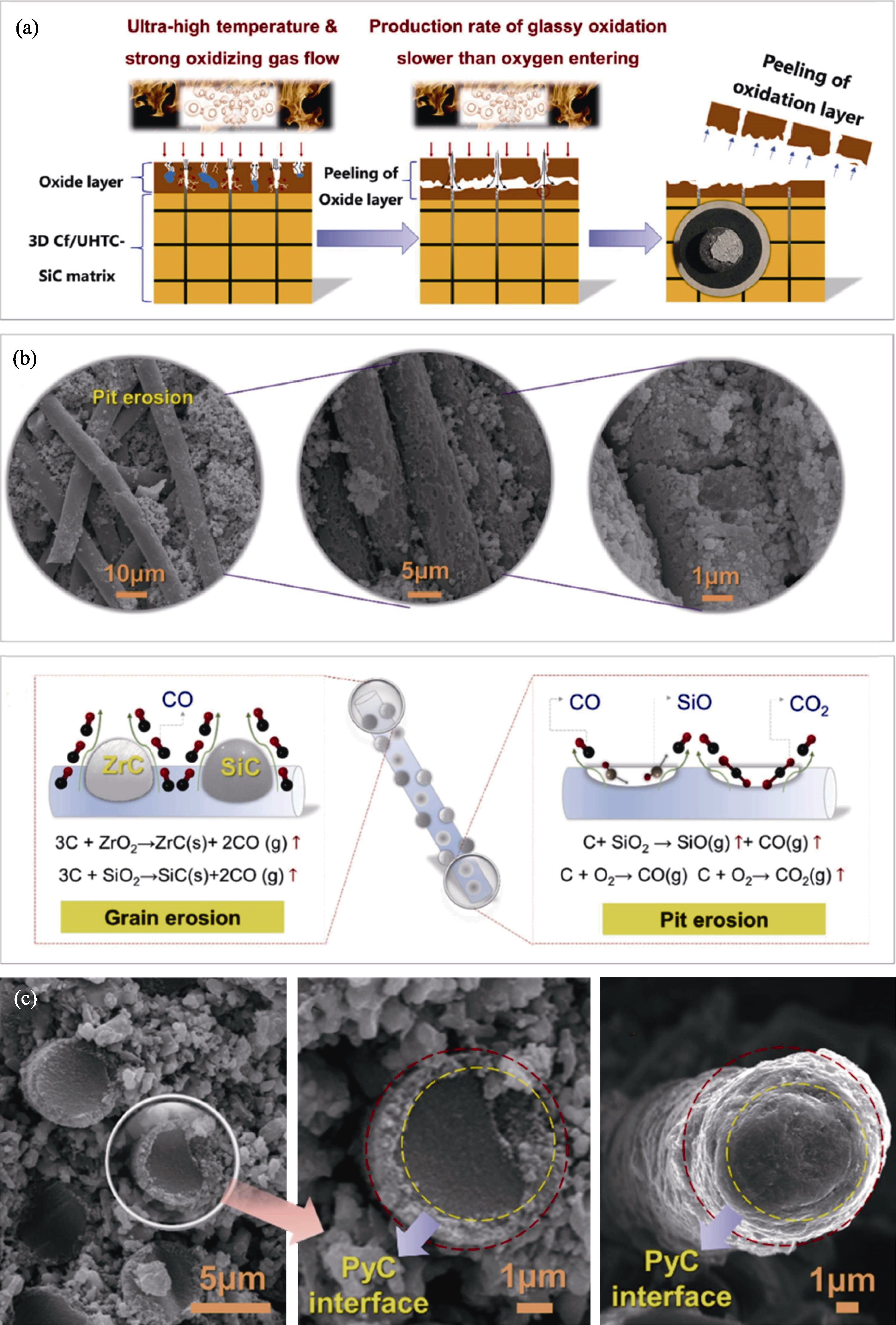
图9 Cf/ZrC-SiC复合材料烧蚀机理[135]
Fig. 9 Ablation mechanism of Cf/ZrC-SiC composites[135] (a) Oxide ablation mechanism; (b) Carbon fiber ablation mechanism; (c) PyC ablation microscopic morphologies

图10 梯度化Cf/超高温陶瓷复合材料[128]
Fig. 10 Gradientised Cf/ultra-high temperature ceramic composites[128] (a) Long-distance and ultrafast antigravity transport of slurries inside the fibrous framework; (b) Images for gradiented C/ZrB2-SiC and C/HfB2-SiC; (c) SEM images of cross-profile for final Cf/ZrB2-SiC and Cf/HfB2-SiC composites
| [1] | STOLLERY J L. Hypersonic viscous interaction on curved surfaces. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1970, 43(3):497. |
| [2] | OPEKA M M, TALMY I G, ZAYKOSKI J. Oxidation-based materials selection for 2000 ℃+hypersonic aerosurfaces: theoretical considerations and historical experience. Journal of Materials Science, 2004, 39: 5887. |
| [3] | SUTTON G P, BIBLARZ O. Rocket propulsion elements. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2016: 540. |
| [4] | SCHMIDT D L. Ablative polymers in aerospace technology. Journal of Macromolecular Science—Chemistry, 1969, 3(3):327. |
| [5] | SCITI D, ZOLI L, SILVESTRONI L, et al. Design, fabrication and high velocity oxy-fuel torch tests of a Cf-ZrB2-fiber nozzle to evaluate its potential in rocket motors. Materials & Design, 2016, 109: 709. |
| [6] | LIFANOV I, YURISHCHEVA A, ASTAPOV A. High-temperature protective coatings on carbon composites. Russian Engineering Research, 2019, 39: 804. |
| [7] | YOO H I, KIM H S, HONG B G, et al. Hafnium carbide protective layer coatings on carbon/carbon composites deposited with a vacuum plasma spray coating method. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2016, 36(7):1581. |
| [8] | ABDOLLAHI A, EHSANI N, VALEFI Z. High temperature ablation-oxidation performance of SiC nanowhisker toughened- SiC/ZrB2-SiC ultra-high temperature multilayer coatings under supersonic flame. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 745: 798. |
| [9] | JIN X, FAN X, LU C, et al. Advances in oxidation and ablation resistance of high and ultra-high temperature ceramics modified or coated carbon/carbon composites. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2018, 38(1):1. |
| [10] | PAUL A, RUBIO V, BINNER J, et al. Evaluation of the high temperature performance of HfB2 UHTC particulate filled Cf/C composites. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2017, 14(3):344. |
| [11] | FAHRENHOLTZ W G, WUCHINA E J, LEE W E, et al. Ultra- high temperature ceramics:materials for extreme environment applications. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2014. |
| [12] | FAHRENHOLTZ W, HILMAS G. Oxidation of ultra-high temperature transition metal diboride ceramics. International Materials Reviews, 2012, 57(1):61. |
| [13] | EAKINS E, JAYASEELAN D D, LEE W E. Toward oxidation- resistant ZrB2-SiC ultra high temperature ceramics. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2011, 42: 878. |
| [14] | OPEKA M M, TALMY I G, WUCHINA E J, et al. Mechanical, thermal, and oxidation properties of refractory hafnium and zirconium compounds. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 1999, 19(13/14):2405. |
| [15] | FAHRENHOLTZ W G, HILMAS G E, TALMY I G, et al. Refractory diborides of zirconium and hafnium. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2007, 90(5):1347. |
| [16] | LIN J, ZHANG X, HAN W. Comparison of ZrB2-ZrO2f ceramics prepared by hot pressing and pressureless sintering. International Journal of Refractory Metals & Hard Materials, 2012, 35: 102. |
| [17] | LIN J, ZHANG X, WANG Z, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of hot-pressed ZrB2-SiC-ZrO2f ceramics with different sintering temperatures. Materials & Design, 2012, 34: 853. |
| [18] | HU P, GUI K, HONG W, et al. High-performance ZrB2-SiC-Cf composite prepared by low-temperature hot pressing using nanosized ZrB2 powder. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2017, 37(6):2317. |
| [19] | BELLOSI A, MONTEVERDE F, SCITI D. Fast densification of ultra-high-temperature ceramics by spark plasma sintering. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2006, 3(1):32. |
| [20] | HU P, CHENG Y, WANG P, et al. Rolling compacted fabrication of carbon fiber reinforced ultra-high temperature ceramics with highly oriented architectures and exceptional mechanical feedback. Ceramics International, 2018, 44(12):14907. |
| [21] | ZHANG G J, DENG Z Y, KONDO N, et al. Reactive hot pressing of ZrB2-SiC composites. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2000, 83(9):2330. |
| [22] | QU Q, HAN J, HAN W, et al. In situ synthesis mechanism and characterization of ZrB2-ZrC-SiC ultra high-temperature ceramics. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2008, 110(2/3):216. |
| [23] | WU H Y, ZOU J, ERIKSSON M, et al. Reactive sintering of 2.5D Cf/ZrC-SiC ceramic matrix composite. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(13):6189. |
| [24] | EINARSRUD M A, HAGEN E, PETTERSEN G, et al. Pressureless sintering of titanium diboride with nickel, nickel boride and iron additives. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1997, 80(12):3013. |
| [25] | RODRíGUEZ-SÁNCHEZ J, SÁNCHEZ-GONZÁLEZ E, GUIBERTEAU F, et al. Contact-mechanical properties at intermediate temperatures of ZrB2 ultra-high-temperature ceramics pressureless sintered with Mo, Ta, or Zr disilicides. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2015, 35(11):3179. |
| [26] | ZHANG S C, HILMAS G, FAHRENHOLTZ W. Pressureless densification of zirconium diboride with boron carbide additions. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2006, 89(5):1544. |
| [27] | HE R, ZHANG X, HU P, et al. Aqueous gelcasting of ZrB2-SiC ultra high temperature ceramics. Ceramics International, 2012, 38(7):5411. |
| [28] | CHEN X, CHENG G, ZHANG J, et al. Residual stress variation in SiCf/SiC composite during heat treatment and its effects on mechanical behavior. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2020, 9: 567. |
| [29] | WANG C, PING W, BAI Q, et al. A general method to synthesize and sinter bulk ceramics in seconds. Science, 2020, 368: 521. |
| [30] | WANG R, DONG Q, WANG C, et al. High-temperature ultrafast sintering: exploiting a new kinetic region to fabricate porous solid- state electrolyte scaffolds. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33: 2008161. |
| [31] | 程源.Cf/ZrC-SiC复合材料的强韧化与抗氧化性能研究. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学博士论文, 2020. |
| [32] | BAKER B, RUBIO V, RAMANUJAM P, et al. Development of a slurry injection technique for continuous fibre ultra-high temperature ceramic matrix composites. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(14):3927. |
| [33] | SERVADEI F, ZOLI L, GALIZIA P, et al. Development of UHTCMCs via water based ZrB2 powder slurry infiltration and polymer infiltration and pyrolysis. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(15):5076. |
| [34] | LI L, WANG Y, CHENG L, et al. Preparation and properties of 2D C/SiC-ZrB2-TaC composites. Ceramics International, 2011, 37(3):891. |
| [35] | UHLMANN F, WILHELMI C, SCHMIDT-WIMMER S, et al. Preparation and characterization of ZrB2 and TaC containing Cf/SiC composites via polymer-infiltration-pyrolysis process. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2017, 37(5): 1955. |
| [36] | LESLIE C J, BOAKYE E E, KELLER K A, et al. Development of continuous SiC fiber reinforced HfB2-SiC composites for aerospace applications. Processing and Properties of Advanced Ceramics and Composites V: Ceramic Transactions, 2013, 240: 1. |
| [37] | TAMMANA S M, DUAN M, ZOU J, et al. Ablation behaviour of Cf-ZrC-SiC with and without rare earth metal oxide dopants. Open Ceramics, 2022, 10: 100270. |
| [38] | ZHOU H, NI D, HE P, et al. Ablation behavior of C/C-ZrC and C/SiC-ZrC composites fabricated by a joint process of slurry impregnation and chemical vapor infiltration. Ceramics International, 2018, 44(5):4777. |
| [39] | ZHU Y, HUANG Z, DONG S, et al. Manufacturing 2D carbon- fiber-reinforced SiC matrix composites by slurry infiltration and PIP process. Ceramics International, 2008, 34(5):1201. |
| [40] | ZHANG D, HU P, DONG S, et al. Microstructures and mechanical properties of Cf/ZrB2-SiC composite fabricated by nano slurry brushing combined with low-temperature hot pressing. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 789: 755. |
| [41] | ZHAO X, WANG Y, DUAN L, et al. Improved ablation resistance of C/SiC-ZrB2 composites via polymer precursor impregnation and pyrolysis. Ceramics International, 2017, 43(15):12480. |
| [42] | YAN C, LIU R, ZHA B, et al. Fabrication and properties of 3-dimensional 4-directional Cf/HfC-SiC composites by precursor impregnation and pyrolysis process. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 739: 955. |
| [43] | ZHANG J P, FU Q G, WANG L. Preparation, ablation behavior and thermal retardant ability of C/C-HfB2-SiC composites. Materials & Design, 2017, 132: 552. |
| [44] | JIA Y, YAO X, SUN J, et al. Effect of ZrC particle size on the ablation resistance of C/C-ZrC-SiC composites. Materials & Design, 2017, 129: 15. |
| [45] | WANG Z, DONG S, ZHANG X, et al. Fabrication and properties of Cf/SiC-ZrC composites. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2008, 91(10):3434. |
| [46] | NASLAIN R. Design, preparation and properties of non-oxide CMCs for application in engines and nuclear reactors: an overview. Composites Science and Technology, 2004, 64(2):155. |
| [47] | ZHAO D, ZHANG C, HU H, et al. Preparation and characterization of three-dimensional carbon fiber reinforced zirconium carbide composite by precursor infiltration and pyrolysis process. Ceramics International, 2011, 37(7): 2089. |
| [48] | YANG Y, JAYARAMAN S, KIM D Y, et al. CVD growth kinetics of HfB2 thin films from the single-source precursor Hf(BH4)4. Chemistry of Materials, 2006, 18(21):5088. |
| [49] | WANG H, CHEN X, GAO B, et al. Synthesis and characterization of a novel precursor-derived ZrC/ZrB2 ultra-high-temperature ceramic composite. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 2013, 27(2):79. |
| [50] | ZHOU H, YANG J, LE G, et al. Effect of ZrC amount and distribution on the thermomechanical properties of Cf/SiC-ZrC composites. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2019, 16(4):1321. |
| [51] | NISAR A, ZHANG C, BOESL B, et al. A perspective on challenges and opportunities in developing high entropy-ultra high temperature ceramics. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(16):25845. |
| [52] | TONG Y, BAI S, CHEN K. C/C-ZrC composite prepared by chemical vapor infiltration combined with alloyed reactive melt infiltration. Ceramics International, 2012, 38(7):5723. |
| [53] | CHEN X, FENG Q, GAO L, et al. Interphase degradation of three-dimensional Cf/SiC-ZrC-ZrB2 composites fabricated via reactive melt infiltration. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2017, 100(10):4816. |
| [54] | KÜTEMEYER M, SCHOMER L, HELMREICH T, et al. Fabrication of ultra high temperature ceramic matrix composites using a reactive melt infiltration process. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2016, 36(15):3647. |
| [55] | VINCI A, ZOLI L, GALIZIA P, et al. Reactive melt infiltration of carbon fibre reinforced ZrB2/B composites with Zr2Cu. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2020, 137: 105973. |
| [56] | Ceramic-matrix-composites[2023-12-31]. https://ultramet.com/ceramic-matrix-composites/. |
| [57] | ZOU L, WALI N, YANG J M, et al. Microstructural characterization of a Cf/ZrC composite manufactured by reactive melt infiltration. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2011, 8(2):329. |
| [58] | Liquid-rocket-engines[2023-12-31]. https://ultramet.com/propulsion-system-components/liquid-rocket-engines/. |
| [59] | CHEN B W, NI D W, WANG J X, et al. Ablation behavior of Cf/ZrC-SiC-based composites fabricated by an improved reactive melt infiltration. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(15):4617. |
| [60] | BINNER J, PORTER M, BAKER B, et al. Selection, processing, properties and applications of ultra-high temperature ceramic matrix composites, UHTCMCs—a review. International Materials Reviews, 2020, 65(7):389. |
| [61] | RUBIO V, RAMANUJAM P, BINNER J. Ultra-high temperature ceramic composite. Advances in Applied Ceramics, 2018, 117(sup1):s56. |
| [62] | REN J, FENG E, ZHANG Y, et al. Microstructure and anti-ablation performance of HfC-TaC and HfC-ZrC coatings synthesized by CVD on C/C composites. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(8):10147. |
| [63] | TONG M, FU Q, ZHOU L, et al. Ablation behavior of a novel HfC-SiC gradient coating fabricated by a facile one-step chemical vapor co-deposition. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2018, 38(13):4346. |
| [64] | HU H, ZHANG Y, HE X, et al. Rapid densification of C/SiC composites by joint processes of CLVD and PIP. Materials Letters, 2011, 65(19/20):3137. |
| [65] | VIGNOLES G L, DUCLOUS R, GAILLARD S. Analytical stability study of the densification front in carbon-or ceramic- matrix composites processing by TG-CVI. Chemical Engineering Science, 2007, 62(22):6081. |
| [66] | TANG Z H, QU D N, XIONG J, et al. Effects of infiltration conditions on the densification behavior of carbon/carbon composites prepared by a directional-flow thermal gradient CVI process. Carbon, 2003, 41(14):2703. |
| [67] | TAGUCHI T, NOZAWA T, IGAWA N, et al. Fabrication of advanced SiC fiber/F-CVI SiC matrix composites with SiC/C multi- layer interphase. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2004, 329: 572. |
| [68] | VENKATACHALAM V, BLEM S, GÜLHAN A, et al. Thermal qualification of the UHTCMCs produced using RF-CVI technique with VMK facility at DLR. Journal of Composites Science, 2022, 6(1):24. |
| [69] | NASLAIN R R, PAILLER R, BOURRAT X, et al. Synthesis of highly tailored ceramic matrix composites by pressure-pulsed CVI. Solid State Ionics, 2001, 141: 541. |
| [70] | CHENG Y, HU P, ZHANG W, et al. One-step introduction of ZrC-SiC inside carbon fabric to fabricate high homogeneous and damage-tolerant composite inspired by vibration. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(7):2251. |
| [71] | HU P, CHENG Y, ZHANG D, et al. From ferroconcrete to Cf/UHTC-SiC: a totally novel densification method and mechanism at 1300 °C without pressure. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2019, 174: 107023. |
| [72] | HU P, ZHANG D, DONG S, et al. A novel vibration-assisted slurry impregnation to fabricate Cf/ZrB2-SiC composite with enhanced mechanical properties. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(4):798. |
| [73] | ZHANG D, HU P, DONG S, et al. Oxidation behavior and ablation mechanism of Cf/ZrB2-SiC composite fabricated by vibration- assisted slurry impregnation combined with low-temperature hot pressing. Corrosion Science, 2019, 161: 108181. |
| [74] | ZHANG D, FENG J, HU P, et al. Enhanced mechanical properties and thermal shock resistance of Cf/ZrB2-SiC composite via an efficient slurry injection combined with vibration-assisted vacuum infiltration. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(15):5059. |
| [75] | SUN J, YU S, WADE-ZHU J, et al. 3D printing of layered ceramic/carbon fiber composite with improved toughness. Additive Manufacturing, 2022, 50: 102543. |
| [76] | FU H, ZHU W, XU Z, et al. Effect of silicon addition on the microstructure, mechanical and thermal properties of Cf/SiC composite prepared via selective laser sintering. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 792: 1045. |
| [77] | LV X, YE F, CHENG L, et al. 3D printing “wire-on-sphere” hierarchical SiC nanowires/SiC whiskers foam for efficient high-temperature electromagnetic wave absorption. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2022, 109: 94. |
| [78] | ZHAO Z, ZHOU G, YANG Z, et al. Direct ink writing of continuous SiO2 fiber reinforced wave-transparent ceramics. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2020, 9: 403. |
| [79] | KEMP J W, DIAZ A A, MALEK E C, et al. Direct ink writing of ZrB2-SiC chopped fiber ceramic composites. Additive Manufacturing, 2021, 44: 102049. |
| [80] |
MEI H, YAN Y, FENG L, et al. First printing of continuous fibers into ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2019, 102(6):3244.
DOI |
| [81] | HAN J, LIU C, BRADFORD-VIALVA R L, et al. Additive manufacturing of advanced ceramics using preceramic polymers. Materials, 2023, 16(13):4636. |
| [82] | LIU Y, CHENG Y, MA D, et al. Continuous carbon fiber reinforced ZrB2-SiC composites fabricated by direct ink writing combined with low-temperature hot-pressing. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2022, 42(9):3699. |
| [83] | ALFANO D, GARDI R, SCATTEIA L, et al. UHTC-based hot structures: characterization, design, and on-ground/in-flight testing. Ultra-High Temperature Ceramics: Materials for Extreme Environment Applications, 2014: 416. |
| [84] | 张东洋.多维度Cf/ZrB2-SiC复合材料的微结构构筑及性能研究. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学博士论文, 2020. |
| [85] | ASL M S, KAKROUDI M G, NOORI S. Hardness and toughness of hot pressed ZrB2-SiC composites consolidated under relatively low pressure. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2015, 619: 481. |
| [86] | KIM S, CHAE J M, LEE S M, et al. Change in microstructures and physical properties of ZrB2-SiC ceramics hot-pressed with a variety of SiC sources. Ceramics International, 2014, 40(2):3477. |
| [87] | SILVESTRONI L, SCITI D, MELANDRI C, et al. Toughened ZrB2- based ceramics through SiC whisker or SiC chopped fiber additions. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2010, 30(11): 2155. |
| [88] | SCITI D, PIENTI L, DALLE FABBRICHE D, et al. Combined effect of SiC chopped fibers and SiC whiskers on the toughening of ZrB2. Ceramics International, 2014, 40(3):4819. |
| [89] | GOLLA B R, MUKHOPADHYAY A, BASU B, et al. Review on ultra-high temperature boride ceramics. Progress in Materials Science, 2020, 111: 100651. |
| [90] | VAFA N P, KAKROUDI M G, ASL M S. Advantages and disadvantages of graphite addition on the characteristics of hot-pressed ZrB2-SiC composites. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(7):8561. |
| [91] | CHENG Y, LYU Y, ZHOU S, et al. Non-axially aligned ZrB2-SiC/ZrB2-SiC-graphene short fibrous monolithic ceramics with isotropic in-plane properties. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(3):4113. |
| [92] | FARAHBAKHSH I, AHMADI Z, ASL M S. Densification, microstructure and mechanical properties of hot pressed ZrB2-SiC ceramic doped with nano-sized carbon black. Ceramics International, 2017, 43(11):8411. |
| [93] | CHENG Y, HU P, ZHOU S, et al. Using macroporous graphene networks to toughen ZrC-SiC ceramic. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2018, 38(11):3752. |
| [94] | TIAN W B, KAN Y M, ZHANG G J, et al. Effect of carbon nanotubes on the properties of ZrB2-SiC ceramics. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2008, 487(1/2):568. |
| [95] | JIN H, MENG S, XIE W, et al. HfB2-CNTs composites with enhanced mechanical properties prepared by spark plasma sintering. Ceramics International, 2017, 43(2): 2170. |
| [96] | ZHOU P, HU P, ZHANG X, et al. R-curve behavior of laminated ZrB2-SiC ceramic with strong interfaces. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2015, 52: 12. |
| [97] | GUI K, LIU F, WANG G, et al. Microstructural evolution and performance of carbon fiber-toughened ZrB2 ceramics with SiC or ZrSi2 additive. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2018, 7: 343. |
| [98] |
KARIMIRAD S, BALAK Z. Characteristics of spark plasma sintered ZrB2-SiC-SCFs composites. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(5):6275
DOI |
| [99] | YANG F, ZHANG X, HAN J, et al. Characterization of hot-pressed short carbon fiber reinforced ZrB2-SiC ultra-high temperature ceramic composites. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 472: 395. |
| [100] | MOR M, VINCI A, FAILLA S, et al. A novel approach for manufacturing of layered, ultra-refractory composites using pliable, short fibre-reinforced ceramic sheets. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2023, 12(1):155. |
| [101] | CHENG Y, LIU C, HU P, et al. Using PyC coated short chopped carbon fiber to tackle the dilemma between toughness and strength of ZrC-SiC. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(1):503. |
| [102] | NI D, CHENG Y, ZHANG J, et al. Advances in ultra-high temperature ceramics composites and coatings. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2022, 11: 1. |
| [103] | LI C, LI G, OUYANG H, et al. Microstructure and properties of C/C-ZrC composites prepared by hydrothermal deposition combined with carbothermal reduction. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 741: 323. |
| [104] | GALIZIA P, FAILLA S, ZOLI L, et al. Tough salami-inspired Cf/ZrB2 UHTCMCs produced by electrophoretic deposition. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2018, 38(2):403. |
| [105] | MATVEEVA A Y, LOMOV S V, GORBATIKH L. Debonding at the fiber/matrix interface in carbon nanotube reinforced composites: modelling investigation. Computational Materials Science, 2019, 159: 412. |
| [106] | LI J, ZHANG Y, FU Y, et al. A simple and efficient route to synthesize hafnium carbide nanowires by catalytic pyrolysis of a polymer precursor. Ceramics International, 2018, 44(11):13335. |
| [107] | WANG D, DONG S, ZHOU H, et al. Effect of pyrolytic carbon interface on the properties of 3D C/ZrC-SiC composites fabricated by reactive melt infiltration. Ceramics International, 2016, 42(8):10272. |
| [108] | BOITIER G, DARZENS S, CHERMANT J L, et al. Microstructural investigation of interfaces in CMCs. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2002, 33(10):1467. |
| [109] | KERANS R J, HAY R S, PARTHASARATHY T A, et al. Interface design for oxidation-resistant ceramic composites. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2002, 85(11):2599. |
| [110] | NI D W, WANG J X, DONG S M, et al. Fabrication and properties of Cf/ZrC-SiC-based composites by an improved reactive melt infiltration. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2018, 101(8):3253. |
| [111] | FANG C, HU P, DONG S, et al. An efficient hydrothermal transformation approach for construction of controllable carbon coating on carbon fiber from renewable carbohydrate. Applied Surface Science, 2019, 491: 478. |
| [112] | BOULIGAND Y. Twisted fibrous arrangements in biological materials and cholesteric mesophases. Tissue and Cell, 1972, 4(2):189. |
| [113] | AN Y, SONG M, WAN K, et al. Anisotropic friction properties of biomimetic Cf/ZrB2-SiC ceramic composites with bouligand structures. Tribology International, 2023, 186: 108638. |
| [114] | AN Y, WAN K, YANG Y, et al. Fabrication method and mechanical properties of biomimetic Cf/ZrB2-SiC ceramic composites with bouligand structures. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2023, 43(2):283. |
| [115] | ZIMMERMANN J W, HILMAS G E, FAHRENHOLTZ W G. Thermal shock resistance and fracture behavior of ZrB2-based fibrous monolith ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2009, 92(1):161. |
| [116] | ZHOU P, HU P, ZHANG X, et al. Laminated ZrB2-SiC ceramic with improved strength and toughness. Scripta Materialia, 2011, 64(3):276. |
| [117] | HAN Y, LIU X, ZHANG Q, et al. Ultra-dense dislocations stabilized in high entropy oxide ceramics. Nature Communications, 2022, 13: 2871. |
| [118] | PAUL A, VENUGOPAL S, BINNER J, et al. UHTC-carbon fibre composites: preparation, oxyacetylene torch testing and characterisation. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2013, 33(2):423. |
| [119] | ZHANG J P, QU J L, FU Q G. Ablation behavior of nose-shaped HfB2-SiC modified carbon/carbon composites exposed to oxyacetylene torch. Corrosion Science, 2019, 151: 87. |
| [120] | MONTEVERDE F, SAVINO R, FUMO M D S, et al. Plasma wind tunnel testing of ultra-high temperature ZrB-SiC composites under hypersonic re-entry conditions. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2010, 30(11):2313. |
| [121] | LI Q, DONG S, WANG Z, et al. Fabrication and properties of 3D Cf/SiC-ZrC composites using ZrC precursor and polycarbosilane. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2012, 95(4):1216. |
| [122] | MUNGIGUERRA S, DI MARTINO G, CECERE A, et al. Arc-jet wind tunnel characterization of ultra-high-temperature ceramic matrix composites. Corrosion Science, 2019, 149: 18. |
| [123] | SAVINO R, CRISCUOLO L, DI MARTINO G D, et al. Aero-thermo-chemical characterization of ultra-high-temperature ceramics for aerospace applications. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2018, 38(8):2937. |
| [124] | TANG S, DENG J, WANG S, et al. Fabrication and characterization of an ultra-high-temperature carbon fiber-reinforced ZrB2-SiC matrix composite. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2007, 90(10):3320. |
| [125] | TANG S, DENG J, WANG S, et al. Ablation behaviors of ultra-high temperature ceramic composites. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2007, 465(1/2):1. |
| [126] | ZENG Y, WANG D, XIONG X, et al. Ultra-high-temperature ablation behavior of SiC-ZrC-TiC modified carbon/carbon composites fabricated via reactive melt infiltration. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(3):651. |
| [127] | 杜百合.ZrB2基超高温陶瓷的力学性能与热响应行为研究. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学博士论文, 2021. |
| [128] | CHENG Y, HU P, DONG S, et al. Dual bionics of structure and preparation: gradient architectured carbon/ceramic composite as light as water but bearing ultra-high temperature max to 2500 °C. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2023, 265: 110963. |
| [129] | GILD J, ZHANG Y, HARRINGTON T, et al. High-entropy metal diborides: a new class of high-entropy materials and a new type of ultrahigh temperature ceramics. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 37946. |
| [130] | WANG F, XU L, ZOU J, et al. Pressureless densification and properties of high-entropy boride ceramics with B4C additions. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2024, 190: 1. |
| [131] | BACKMAN L, GILD J, LUO J, et al. Part I: theoretical predictions of preferential oxidation in refractory high entropy materials. Acta Materialia, 2020, 197: 20. |
| [132] | ZENG Y, WANG D, XIONG X, et al. Ablation-resistant carbide Zr0.8Ti0.2C0.74B0.26 for oxidizing environments up to 3000 ℃. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 15836. |
| [133] | CAI F, NI D, CHEN B, et al. Fabrication and properties of Cf/(Ti0.2Zr0.2Hf0.2Nb0.2Ta0.2) C-SiC high-entropy ceramic matrix composites via precursor infiltration and pyrolysis. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(12):5863. |
| [134] | ZHANG C, BOESL B, AGARWAL A. Oxidation resistance of tantalum carbide-hafnium carbide solid solutions under the extreme conditions of a plasma jet. Ceramics International, 2017, 43(17):14798. |
| [135] | CHENG Y, LYU Y, XIE Y, et al. Starting from essence to reveal the ablation behavior and mechanism of 3D PyC Cf/ZrC-SiC composite. Corrosion Science, 2022, 201: 110261. |
| [136] | BOSE D, OLSON M, LAUB B, et al. Initial assessment of Mars Science Laboratory heatshield instrumentation and flight data. 51st AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting including the New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition, Texas, 2013: 908. |
| [137] | TRUMBLE K A, COZMUTA I, SEPKA S, et al. Postflight aerothermal analysis of the stardust sample return capsule. Journal of Spacecraft and Rockets, 2010, 47(5):765. |
| [138] | GUO P, LI J, PANG S, et al. Ultralight carbon fiber felt reinforced monolithic carbon aerogel composites with excellent thermal insulation performance. Carbon, 2021, 183: 525. |
| [139] | LEVENTIS N, SADEKAR A, CHANDRASEKARAN N, et al. Click synthesis of monolithic silicon carbide aerogels from polyacrylonitrile-coated 3D silica networks. Chemistry of Materials, 2010, 22(9):2790. |
| [140] | WANG X, LIU J, HOU F, et al. Manufacture of porous SiC/C ceramics with excellent damage tolerance by impregnation of LPCS into carbonized pinewood. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2015, 35(6):1751. |
| [141] | LI F, LIU J X, HUANG X, et al. Carbothermal conversion of self-supporting organic/inorganic interpenetrating networks to porous metal boride monoliths. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2019, 102(10):5746. |
| [142] |
CAHILL J T, TURNER S, YE J, et al. Ultrahigh-temperature ceramic aerogels. Chemistry of Materials, 2019, 31(10):3700.
DOI |
| [143] | BENAD A, JÜRRIES F, VETTER B, et al. Mechanical properties of metal oxide aerogels. Chemistry of Materials, 2018, 30(1):145. |
| [144] | ZHANG M, WANG Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Conductive and elastic TiO2 nanofibrous aerogels: a new concept toward self-supported electrocatalysts with superior activity and durability. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(51):23252. |
| [145] | KIDCHOB T, MALFATTI L, SERRA F, et al. Hafnia sol-gel films synthesized from HfCl4: changes of structure and properties with the firing temperature. Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology, 2007, 42: 89. |
| [146] | ZHAO K, YE F, CHENG L, et al. Formation of ultra-high temperature ceramic hollow microspheres as promising lightweight thermal insulation materials via a molten salt-assisted template method. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(31):37388. |
| [147] | WEI K, CHENG X, MO F, et al. Design and analysis of integrated thermal protection system based on lightweight C/SiC pyramidal lattice core sandwich panel. Materials & Design, 2016, 111: 435. |
| [148] | WEI K, HE R, CHENG X, et al. A lightweight, high compression strength ultra high temperature ceramic corrugated panel with potential for thermal protection system applications. Materials & Design, 2015, 66: 552. |
| [149] | SHIMODA N. Functionally graded materials. Functionally Graded Materials Forum, 1990. |
| [150] | NAIK A K, NAZEER M, PRASAD D, et al. Development of functionally graded ZrB2-B4C composites for lightweight ultrahigh-temperature aerospace applications. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(22):33332. |
| [1] | 朱文杰, 唐璐, 陆继长, 刘江平, 罗永明. 钙钛矿型氧化物催化氧化挥发性有机化合物的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [2] | 胡智超, 杨鸿宇, 杨鸿程, 孙成礼, 杨俊, 李恩竹. P-V-L键理论在微波介质陶瓷性能调控中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [3] | 吴琼, 沈炳林, 张茂华, 姚方周, 邢志鹏, 王轲. 铅基织构压电陶瓷研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [4] | 张碧辉, 刘小强, 陈湘明. Ruddlesden-Popper结构杂化非常规铁电体的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| [5] | 吴杰, 杨帅, 王明文, 李景雷, 李纯纯, 李飞. 铅基织构压电陶瓷的发展历程、现状与挑战[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 575-586. |
| [6] | 姜昆, 李乐天, 郑木鹏, 胡永明, 潘勤学, 吴超峰, 王轲. PZT陶瓷的低温烧结研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| [7] | 陈义, 邱海鹏, 陈明伟, 徐昊, 崔恒. SiC/SiC复合材料基体硼改性方法及其力学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 504-510. |
| [8] | 田睿智, 兰正义, 殷杰, 郝南京, 陈航榕, 马明. 基于微流控技术的纳米无机生物材料制备: 原理及其研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 337-347. |
| [9] | 张继国, 吴田, 赵旭, 杨钒, 夏天, 孙士恩. 钠离子电池正极材料循环稳定性提升策略及产业化进程[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 348-362. |
| [10] | 穆爽, 马沁, 张禹, 沈旭, 杨金山, 董绍明. Yb2Si2O7改性SiC/SiC复合材料的氧化行为研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 323-328. |
| [11] | 殷杰, 耿佳毅, 王康龙, 陈忠明, 刘学建, 黄政仁. SiC陶瓷的3D打印成形与致密化新进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 245-255. |
| [12] | 杨舒琪, 杨存国, 牛慧祝, 石唯一, 舒珂维. GeP3/科琴黑复合材料作为钠离子电池高性能负极材料[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 329-336. |
| [13] | 谌广昌, 段小明, 朱金荣, 龚情, 蔡德龙, 李宇航, 杨东雷, 陈彪, 李新民, 邓旭东, 余瑾, 刘博雅, 何培刚, 贾德昌, 周玉. 直升机特定结构先进陶瓷材料研究进展与应用展望[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 225-244. |
| [14] | 范晓波, 祖梅, 杨向飞, 宋策, 陈晨, 王子, 罗文华, 程海峰. 质子调控型电化学离子突触研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(3): 256-270. |
| [15] | 栾新刚, 何典蔚, 涂建勇, 成来飞. 2D平纹和3D针刺C/SiC复合材料的低速冲击破坏行为和失效机理[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 205-214. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||