
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2026, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (1): 113-118.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250142
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
HAN Weiwei1,2( ), HUANG Dong2, LI Tingsong2, LI Jiang2,3(
), HUANG Dong2, LI Tingsong2, LI Jiang2,3( )
)
Received:2025-04-06
Revised:2025-05-04
Published:2026-01-20
Online:2025-06-10
Contact:
LI Jiang, professor. E-mail: lijiang@mail.sic.ac.cnAbout author:HAN Weiwei (1998-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: hw18800205253@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
HAN Weiwei, HUANG Dong, LI Tingsong, LI Jiang. Sm:LuAG/Nd:LuAG Composite Laser Ceramics with Cladding Structure: Fabrication and Properties[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2026, 41(1): 113-118.
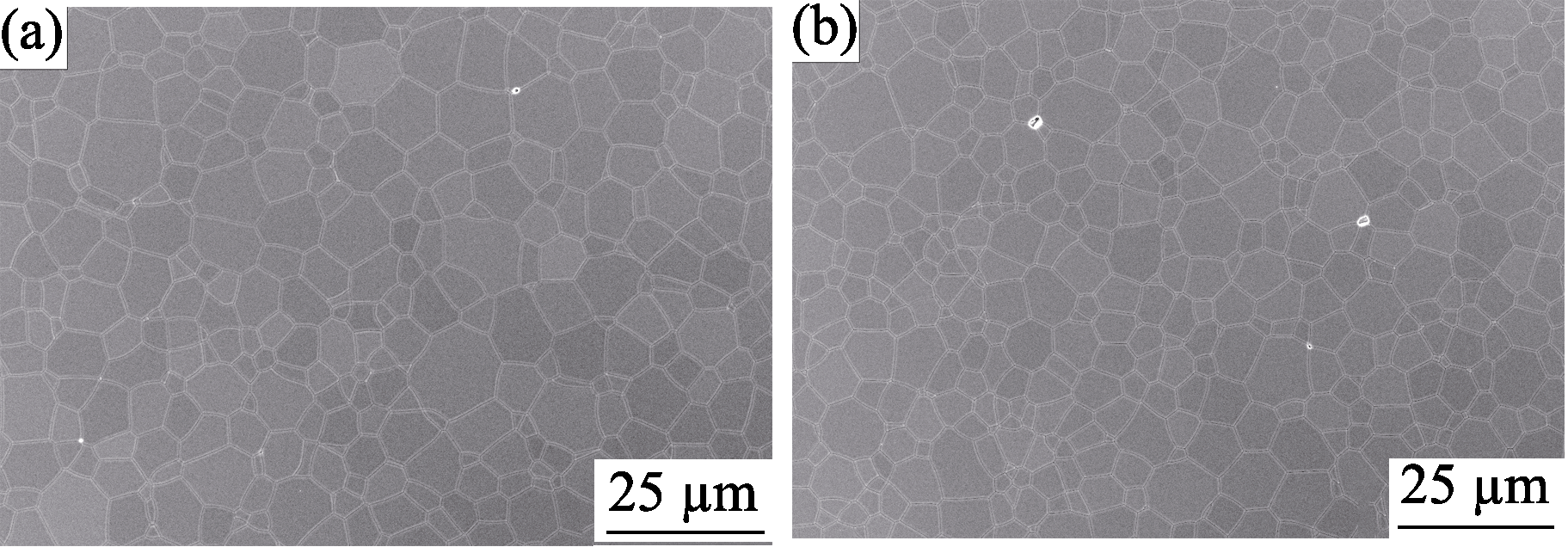
Fig. 2 FESEM images of the 5% Sm:LuAG/1% Nd:LuAG cladding structure composite ceramics pre-sintered at 1825 ℃ for 20 h (a) Gain area; (b) Cladding area
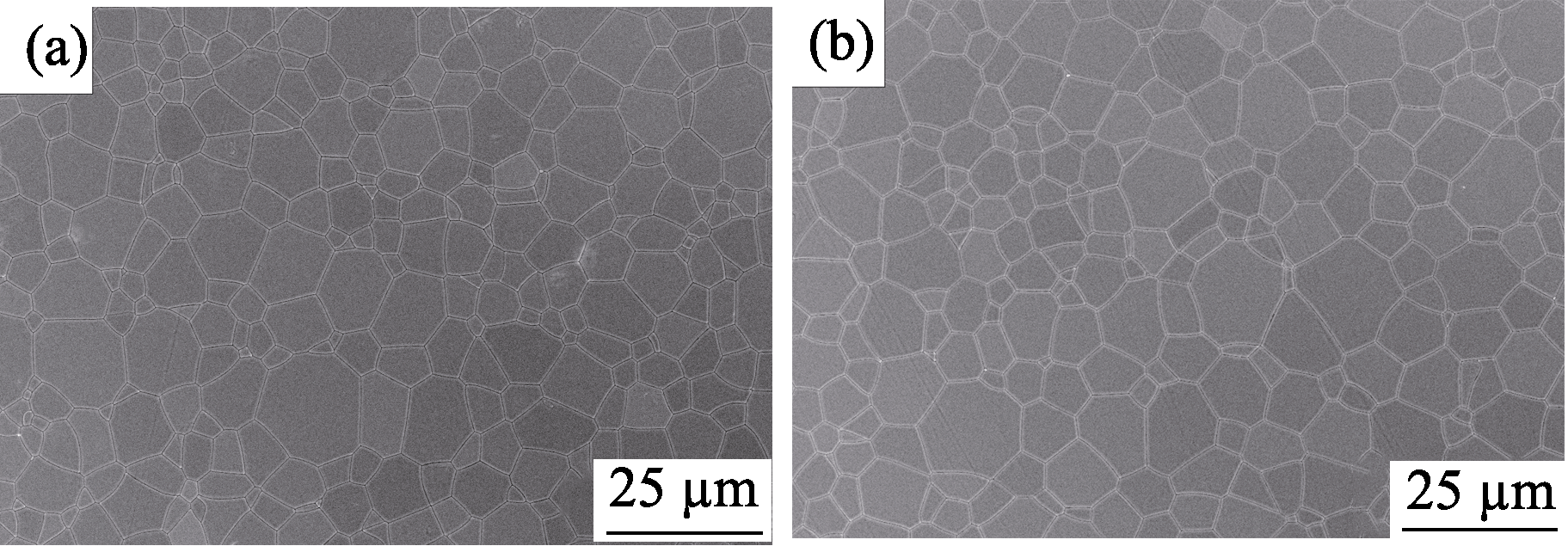
Fig. 3 FESEM images of the 5% Sm:LuAG/1% Nd:LuAG cladding structure composite ceramics pre-sintered at 1825 ℃ for 20 h and HIP post-treated at 1750 ℃ for 3 h (a) Gain area; (b) Cladding area
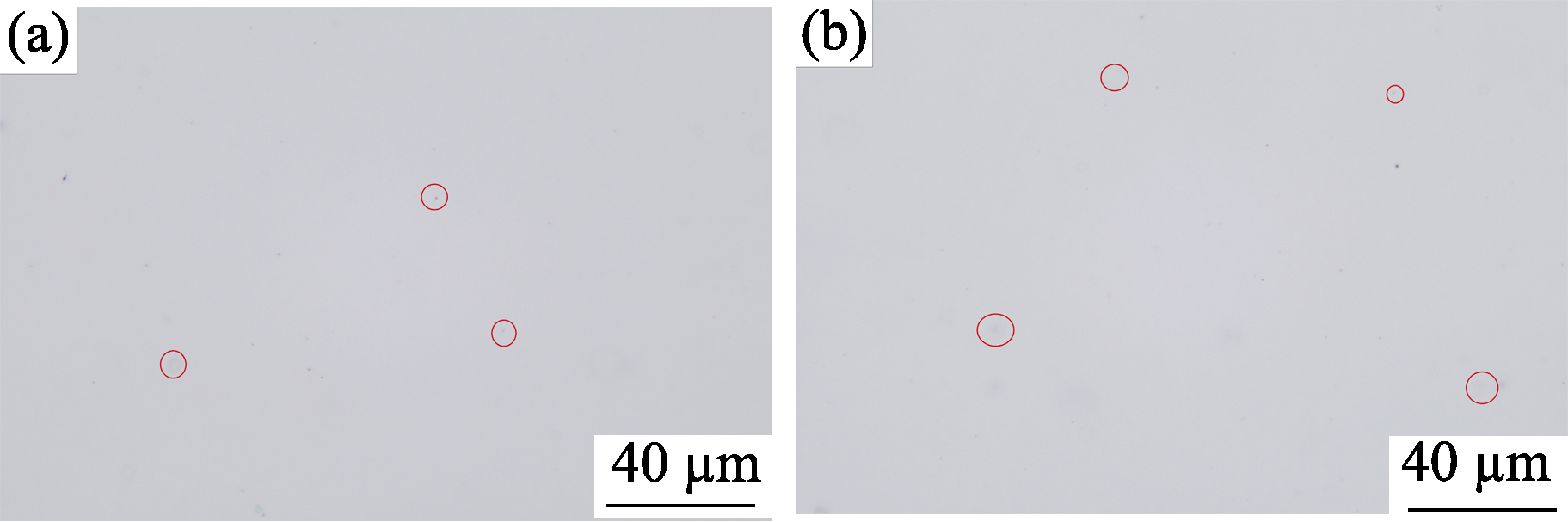
Fig. 5 Optical microscopic images of the 5% Sm:LuAG/1% Nd:LuAG cladding structure composite ceramics after HIP post- treatment (a) Gain area; (b) Cladding area
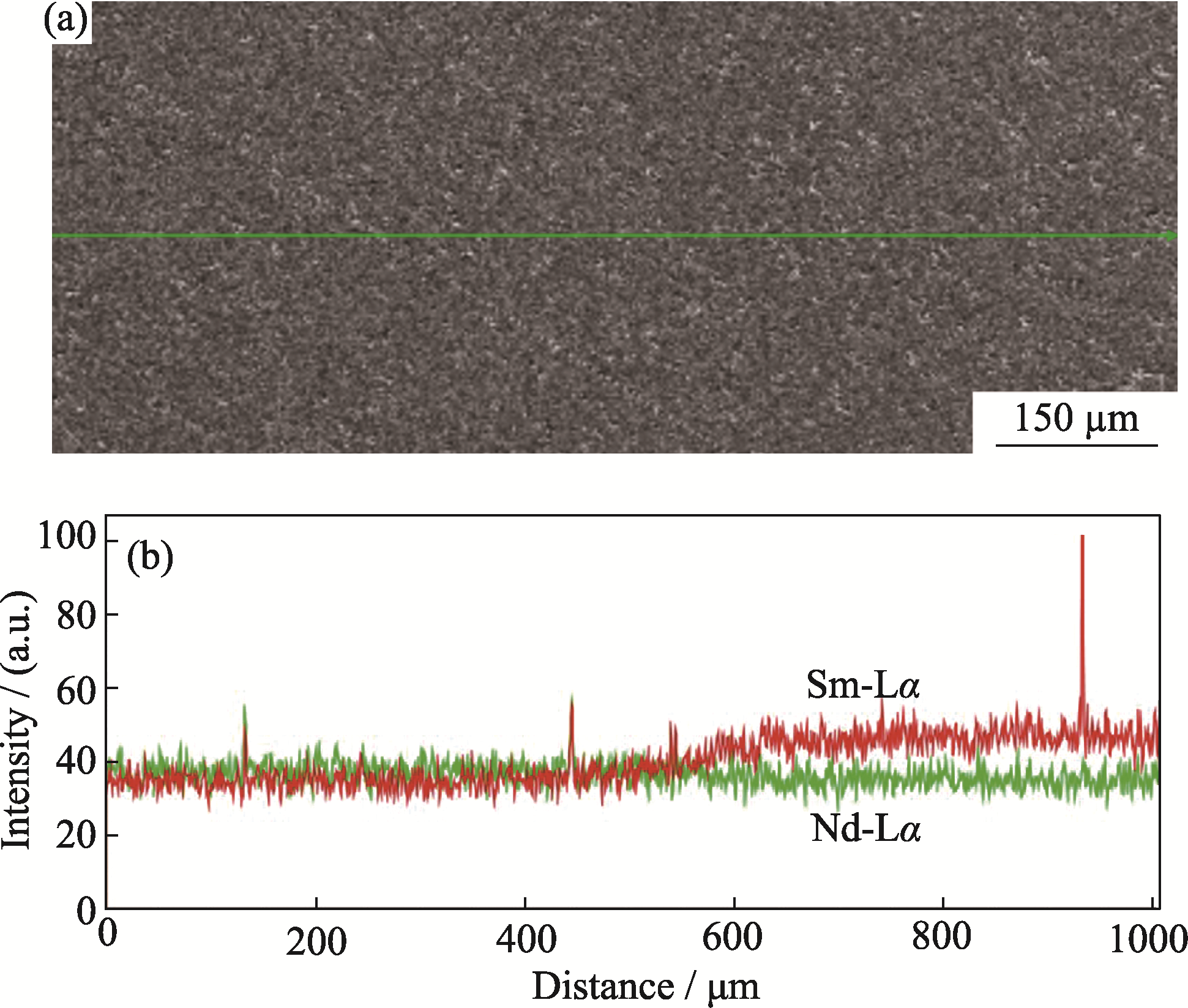
Fig. 6 FESEM image (a) and linear scanning image (b) of the interface for the 5% Sm:LuAG/1% Nd:LuAG cladding structure composite ceramics after HIP post-treatment
| [1] |
SPAETH M L, MANES K R, KALANTAR D H, et al. Description of the NIF laser. Fusion Science and Technology, 2016, 69(1): 25.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
BAYRAMIAN A, ACEVES S, ANKLAM T, et al. Compact, efficient laser systems required for laser inertial fusion energy. Fusion Science and Technology, 2011, 60(1): 28.
DOI URL |
| [3] | DANSON C N, HAEFNER C, BROMAGE J, et al. Petawatt and exawatt class lasers worldwide. High Power Laser Science and Engineering, 2019, 7(3): 172. |
| [4] |
ZHU Z D, LV S W, ZHANG H Y, et al. Highly efficient actively Q-switched Nd:YAG laser. Optics Express, 2021, 29(20): 32325.
DOI PMID |
| [5] |
BANERJEES, ERTEL K, MASON P D, et al. DiPOLE: a 10 J, 10 Hz cryogenic gas cooled multi-slab nanosecond Yb:YAG laser. Optics Express, 2015, 23(15): 19542.
DOI PMID |
| [6] |
BROWND C, MCMILLEN C D, MOORE C, et al. Spectral properties of hydrothermally-grown Nd:LuAG, Yb:LuAG, and Yb:Lu2O3 laser materials. Journal of Luminescence, 2014, 148: 26.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
GONCALVES T, ALBACH D, VINCENT B, et al. 14 J/2 Hz Yb3+:YAG diode pumped solid state laser chain. Optics Express, 2013, 21(1): 855.
DOI URL |
| [8] | 冯亚刚, 田丰, 刘子玉, 等. 层状复合结构YAG/Yb:YAG透明陶瓷的制备与性能研究. 人工晶体学报, 2024, 53(11): 1901. |
| [9] |
YAGI H, BISSON J F, UEDA K, et al. Y3Al5O12 ceramic absorbers for the suppression of parasitic oscillation in high-power Nd:YAG lasers. Journal of Luminescence, 2006, 121(1): 88.
DOI URL |
| [10] | HAEFNER C L, BAYRAMIAN A, BETTS S, et al. High average power diode pumped petawatt laser systems a new generation of lasers enabling precision science and commercial applications. Proceedings of SPIE, 2017, 10241: 1024102. |
| [11] | LEBEGUE P, DE SOUSA J, RAPENOU C. Coherent combining of large-aperture high-energy Nd:glass laser amplifiers. High Power Laser Science and Engineering, 2025, 13: 4. |
| [12] | RONG X F, YANG Y M, PENG S Z, et al. Sub-nanosecond diode-pumped passively Q-switched Nd:LuAG ceramic microchip lasers. Optics & Laser Technology, 2023, 158:108901. |
| [13] |
FU Y L, LI J, LIU Y, et al. Fabrication, microstructure and laser performance of Nd3+-doped Lu3Al5O12 transparent ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2016, 36(3): 655.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
LIU T H, FENG T, SUI Z, et al. 50 mm-aperture Nd:LuAG ceramic nanosecond laser amplifier producing 10 J at 10 Hz. Optics Express, 2019, 27(11): 15595.
DOI PMID |
| [15] | ZHANG W S, LI L J, LIANG H. Efficient acousto-optically Q-switched Tm:LuAG laser end-pumped by a laser diode at 1.7 μm. Applied Physics B-Lasers and Optics, 2025, 131(3): 65. |
| [16] |
IKESUEA, FURUSATO I, KAMATA K, et al. Fabrication of polycrystal line, transparent YAG ceramics by a solid-state reaction method. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1995, 78(1): 225.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
TIAN F, IKESUEA , LI J. Progress and perspectives on composite laser ceramics: a review. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2022, 42(5): 1833.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
LIU Z Y, FENG Y G, CHEN H H, et al. Microstructure and properties characterization of Yb:Lu2O3 transparent ceramics from co-precipitated nano-powders. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2023, 20(6): 3365.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
LI X Y, ZHANG L X, HU D J, et al. Fabrication and characterizations of Tb3Al5O12-based magneto-optical ceramics. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2023, 20(1): 493.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
LI X, HU C, LIU Q, et al. Fluoride transparent ceramics for solid-state lasers: a review. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2024, 13(12): 1891.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
YE J H, ZHOU Z Z, HU C, et al. Yb:Sc2O3 Transparent ceramics fabricated from co-precipitated nano-powders: microstructure and optical property. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 215.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
HUSS R, WILHELM R, KOLLECK C, et al. Suppression of parasitic oscillations in a core-doped ceramic Nd:YAG laser by Sm:YAG cladding. Optics Express, 2010, 18(12): 13094.
DOI PMID |
| [23] |
TIMOSHENKO A D, MATVIENKO O O, DOROSHENKO A G, et al. Highly-doped YAG:Sm3+ transparent ceramics: effect of Sm3+ ions concentration. Ceramics International, 2023, 49(5): 7524.
DOI URL |
| [24] | WANG X, YU H, LI P, et al. Femtosecond laser-based processing methods and their applications in optical device manufacturing: a review. Optics & Laser Technology, 2021, 135: 106687. |
| [25] | JI S H, HUANG W F, FENG T, et al. Modeling and measurement of thermal effect in a flashlamp-pumped direct-liquid-cooled split-disk Nd:LuAG ceramic laser amplifier. Nature Photonics, 2021, 8(4): 97. |
| [26] | HUß R, WILHELM R, NEUMANN J, et al. Passively Q-switched core-doped ceramic Nd:YAG laser with Sm:YAG cladding. Lasers and Electro-Optics, 2007, 5:1303. |
| [27] | YAGI H, YANAGITANI T. Recent progress in transparent polycrystalline ceramics for optical applications. Laser & Photonics Reviews, 2011, 39(5): 300. |
| [28] |
MA J, LU T T, ZHU X L, et al. 1.57 MW peak power pulses generated by a diode-pumped Q-switched Nd:LuAG ceramic laser. Chinese Optics Letters, 2017, 15(12): 121402.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
KONG W, TSUNEKANE M, TAIRA T, et al. Diode edge-pumped passively Q-switched microchip laser. Optical Engineering, 2015, 54(9): 090501.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
STEVENSON A J, LI X, MARTINEZ M A, et al. Effect of SiO2 on densification and microstructure development in Nd:YAG transparent ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2011, 94(5): 1380.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
JING Y Q, TIAN F, GUO L H, et al. Effect of TEOS content on microstructure evolution and optical properties of Sm:YAG transparent ceramics. Optical Materials, 2024, 147: 114681.
DOI URL |
| [32] | LIN Z, HUANG X, LAN J, et al. Efficient and compact diode-pumped Nd:YAG lasers at 1073 and 1078 nm. IEEE Photonic, 2016, 8(2): 1500808. |
| [1] | YUAN Wang, HU Jianbao, ZHOU Liang, KAN Yanmei, ZHANG Xiangyu, DONG Shaoming. Effect of Argon Atmosphere Heat Treatment on Mechanical Properties and Microstructural Evolution of Shicolon-II SiC Fibers [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2026, 41(1): 119-128. |
| [2] | ZHONG Weimin, ZHAO Ke, WANG Kewei, LIU Dianguang, LIU Jinling, AN Linan. Effect of Oscillatory Pressure Amplitude on Microstructures and Wear Resistance of Tungsten Carbide [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(9): 964-970. |
| [3] | MU Haojie, ZHANG Yuanjiang, YU Bin, FU Xiumei, ZHOU Shibin, LI Xiaodong. Preparation and Properties of ZrO2 Doped Y2O3-MgO Nanocomposite Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 281-289. |
| [4] | YE Junhao, ZHOU Zhenzhen, HU Chen, WANG Yanbin, JING Yanqiu, LI Tingsong, CHENG Ziqiu, WU Junlin, IVANOV Maxim, HRENIAK Dariusz, LI Jiang. Yb:Sc2O3 Transparent Ceramics Fabricated from Co-precipitated Nano-powders: Microstructure and Optical Property [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 215-224. |
| [5] | ZHENG Yuanshun, YU Jian, YE Xianfeng, LIANG Dong, ZHU Wanting, NIE Xiaolei, WEI Ping, ZHAO Wenyu, ZHANG Qingjie. Boosting the Thermoelectric Performance of Full-Heusler Fe2VAl Alloy via Substituting Al Site with V [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(12): 1425-1432. |
| [6] | FAN Wugang, CAO Xiong, ZHOU Xiang, LI Ling, ZHAO Guannan, ZHANG Zhaoquan. Anticorrosion Performance of 8YSZ Ceramics in Simulated Aqueous Environment of Pressurized Water Reactor [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(7): 803-809. |
| [7] | CHEN Qian, SU Haijun, JIANG Hao, SHEN Zhonglin, YU Minghui, ZHANG Zhuo. Progress of Ultra-high Temperature Oxide Ceramics: Laser Additive Manufacturing and Microstructure Evolution [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(7): 741-753. |
| [8] | JIANG Lingyi, PANG Shengyang, YANG Chao, ZHANG Yue, HU Chenglong, TANG Sufang. Preparation and Oxidation Behaviors of C/SiC-BN Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(7): 779-786. |
| [9] | ZHENG Yawen, ZHANG Cuiping, ZHANG Ruijie, XIA Qian, RU Hongqiang. Fabrication of Boron Carbide Ceramic Composites by Boronic Acid Carbothermal Reduction and Silicon Infiltration Reaction Sintering [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(6): 707-714. |
| [10] | LÜ Zhaoyang, XU Yong, YANG Jiuyan, TU Guangsheng, TU Bingtian, WANG Hao. Effect of MgF2 Additive on Preparation and Optical Properties of MgAl1.9Ga0.1O4 Transparent Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(5): 531-538. |
| [11] | XUE Yifan, LI Weijie, ZHANG Zhongwei, PANG Xu, LIU Yu. Process Control of PyC Interphases Microstructure and Uniformity in Carbon Fiber Cloth [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(4): 399-408. |
| [12] | SUN Chuan, HE Pengfei, HU Zhenfeng, WANG Rong, XING Yue, ZHANG Zhibin, LI Jinglong, WAN Chunlei, LIANG Xiubing. SiC-based Ceramic Materials Incorporating GNPs Array: Preparation and Mechanical Characterization [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(3): 267-273. |
| [13] | ZHENG Jiaqian, LU Xiao, LU Yajie, WANG Yingjun, WANG Zhen, LU Jianxi. Functional Bioadaptability in Medical Bioceramics: Biological Mechanism and Application [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(1): 1-16. |
| [14] | GU Junyi, FAN Wugang, ZHANG Zhaoquan, YAO Qin, ZHAN Hongquan. Structure and Optical Property of Pr2O3 Powder Prepared by Reduction [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(7): 771-777. |
| [15] | HE Danqi, WEI Mingxu, LIU Ruizhi, TANG Zhixin, ZHAI Pengcheng, ZHAO Wenyu. Heavy-Fermion YbAl3 Materials: One-step Synthesis and Enhanced Thermoelectric Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 577-582. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||