
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2018, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (12): 1360-1364.DOI: 10.15541/jim20180375
• RESEARCH LETTER • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Jia-Ke, HAN Xiao-Qi, LIU Xin, WANG Yan-Xiang, GUO Ping-Chun, YANG Zhi-Sheng
Received:2018-08-16
Published:2018-12-20
Online:2018-11-27
About author:LI Jia-Ke (1973-), male, PhD, associate professor. E-mail: jiakeli.jci@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
LI Jia-Ke, HAN Xiao-Qi, LIU Xin, WANG Yan-Xiang, GUO Ping-Chun, YANG Zhi-Sheng. Preparation of High Specific Surface Area Micro/Meso-porous SiOC Ceramics by the Low Temperature Phase Separation Method[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(12): 1360-1364.
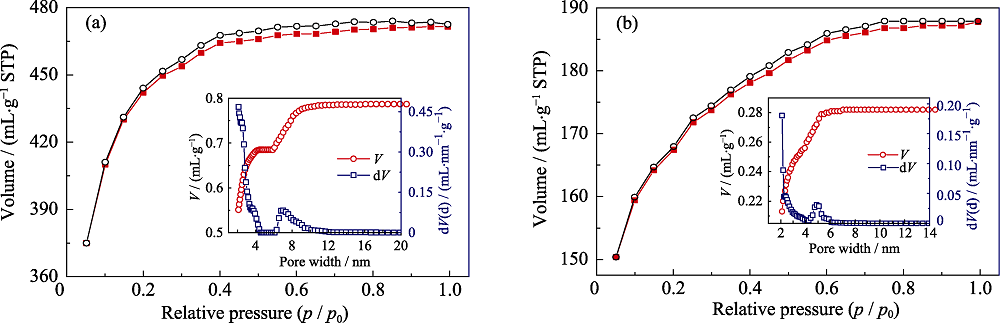
Fig. 5 N2 adsorption (solid symbols) and desorption (open symbols) isotherms for the samples obtained from SiOC ceramics pyrolyzed in (a) Ar +H2O and (b) Ar at 1300℃ after etching
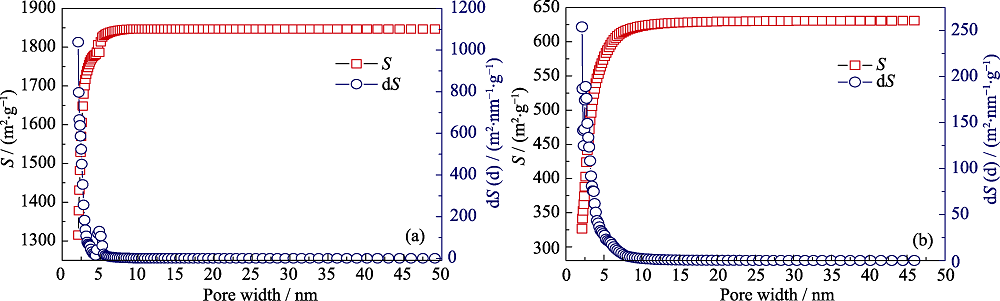
Fig. 6 Cumulative specific surface area (S), interval specific surface area (dS) and pore size distribution (PSD) for SiOC ceramics pyrolyzed in Ar +H2O (a) and in Ar (b) at 1300℃ after etching
| Temperature/℃ | Specific surface area/ (m2·g-1) | Average pore size/nm | Pore volume/(cm3·g-1)) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ar | Ar +H2O | Ar | Ar +H2O | Ar | Ar +H2O | |
| 900 | - | 58.6 | - | 2.05 | - | 0.105 |
| 1100 | - | 435.23 | - | 2.16 | - | 0.142 |
| 1200 | 53.65 | 654.16 | 1.43 | 2.23 | 0.015 | 0.202 |
| 1300 | 635.13 | 1845.50 | 2.25 | 2.83 | 0.282 | 0.788 |
| 1400 | 632.24 | 1817.20 | 2.18 | 2.75 | 0.286 | 0.764 |
| 1500 | 633.52 | 1805.60 | 2.15 | 2.77 | 0.288 | 0.756 |
Table 1 BET results of SiOC ceramics after etching with different pyrolysis temperatures in Ar and Ar+H2O
| Temperature/℃ | Specific surface area/ (m2·g-1) | Average pore size/nm | Pore volume/(cm3·g-1)) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ar | Ar +H2O | Ar | Ar +H2O | Ar | Ar +H2O | |
| 900 | - | 58.6 | - | 2.05 | - | 0.105 |
| 1100 | - | 435.23 | - | 2.16 | - | 0.142 |
| 1200 | 53.65 | 654.16 | 1.43 | 2.23 | 0.015 | 0.202 |
| 1300 | 635.13 | 1845.50 | 2.25 | 2.83 | 0.282 | 0.788 |
| 1400 | 632.24 | 1817.20 | 2.18 | 2.75 | 0.286 | 0.764 |
| 1500 | 633.52 | 1805.60 | 2.15 | 2.77 | 0.288 | 0.756 |
| [1] | IONESCU E, KLEEBE H J, RIEDEL R.Silicon-containing polymer- derived ceramic nanocomposites (PDC-NCs): preparative approaches and properties.Chem. Soc. Rev., 2012, 41(15): 5032-5052. |
| [2] | FENG Y, LAI S Y, YANG L,et al. Polymer-derived porous Bi2WO6/SiC (O) ceramic nanocomposites with high photodegradation efficiency towards Rhodamine B. Ceram. Int., 2018, 44(7): 8562-8569. |
| [3] | COLOMBO P.Conventional and novel processing methods for cellular ceramics.Philos. Trans., 2006, 364(1838): 109-124. |
| [4] | YAN X J, SAHIMI M, TSOTSIS T T.Fabrication of high-surface area nanoporous SiOC ceramics using preceramic polymer precursors and a sacrificial template: precursor effects.Micropor. Mesopor. Mat., 2017, 241: 338-345. |
| [5] | VAKIFAHMETOGLU C, COLOMBO P.A direct method for the fabrication of macro-porous SiOC ceramics from preceramic polymers.Adv. Eng. Mater., 2008, 10(3): 256-259. |
| [6] | DIBANDJO P, DIRE S, BABONNEAU F,et al. Influence of the polymer architecture on the high temperature behavior of SiCO glasses: a comparison between linear- and cyclic-derived precursors. J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 2010, 356(3): 132-140. |
| [7] | FORTUNIAK W, POSPIECH P, MIZERSKA U,et al. Generation of meso- and microporous structures by pyrolysis of polysiloxane microspheres and by HF etching of SiOC microspheres. Ceram. Int., 2018, 44(1): 374-383. |
| [8] | VAKIFAHMETOGLU C, PRESSER V, YEON S H,et al. Enhanced hydrogen and methane gas storage of silicon oxycarbide derived carbon. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat., 2011, 144(1): 105-112. |
| [9] | SORARU G D, PENA-ALONSO R, LEONI M.C-rich micro/ mesoporous Si(B)OC:in situ diffraction analysis of the HF etching process. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat., 2013, 172: 125-130. |
| [10] | XU T H, MA Q S, CHEN Z H.High-temperature behavior of silicon oxycarbide glasses in air environment.Ceram. Int., 2011, 37(7): 2555-2559. |
| [11] | SAHA A, RAJ R.Crystallization maps for SiCO amorphous ceramics.J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2007, 90(2): 578-583. |
| [12] | LI J K, LU K, LIN T S,et al. Preparation of micro-/meso porous SiOC bulk ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2015, 98(6): 1753-1761. |
| [13] | WU J Q, LI Y M, CHEN L M,et al. Simple fabrication of micro/ nano-porous SiOC foam from polysiloxane. J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22(14): 6542-6545. |
| [14] | LIANG T, LI Y L, SU D,et al. Silicon oxycarbide ceramics with reduced carbon by pyrolysis of polysiloxanes in water vapor. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2010, 30(12): 2677-2682. |
| [1] | MU Haojie, ZHANG Yuanjiang, YU Bin, FU Xiumei, ZHOU Shibin, LI Xiaodong. Preparation and Properties of ZrO2 Doped Y2O3-MgO Nanocomposite Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 281-289. |
| [2] | MA Wen, SHEN Zhe, LIU Qi, GAO Yuanming, BAI Yu, LI Rongxing. Preparation of Y2O3 Coating by Suspension Plasma Spraying and Its Resistance to Plasma Etching [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(8): 929-936. |
| [3] | FAN Wugang, CAO Xiong, ZHOU Xiang, LI Ling, ZHAO Guannan, ZHANG Zhaoquan. Anticorrosion Performance of 8YSZ Ceramics in Simulated Aqueous Environment of Pressurized Water Reactor [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(7): 803-809. |
| [4] | CHEN Qian, SU Haijun, JIANG Hao, SHEN Zhonglin, YU Minghui, ZHANG Zhuo. Progress of Ultra-high Temperature Oxide Ceramics: Laser Additive Manufacturing and Microstructure Evolution [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(7): 741-753. |
| [5] | JIANG Lingyi, PANG Shengyang, YANG Chao, ZHANG Yue, HU Chenglong, TANG Sufang. Preparation and Oxidation Behaviors of C/SiC-BN Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(7): 779-786. |
| [6] | ZHENG Yawen, ZHANG Cuiping, ZHANG Ruijie, XIA Qian, RU Hongqiang. Fabrication of Boron Carbide Ceramic Composites by Boronic Acid Carbothermal Reduction and Silicon Infiltration Reaction Sintering [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(6): 707-714. |
| [7] | XUE Yifan, LI Weijie, ZHANG Zhongwei, PANG Xu, LIU Yu. Process Control of PyC Interphases Microstructure and Uniformity in Carbon Fiber Cloth [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(4): 399-408. |
| [8] | SUN Chuan, HE Pengfei, HU Zhenfeng, WANG Rong, XING Yue, ZHANG Zhibin, LI Jinglong, WAN Chunlei, LIANG Xiubing. SiC-based Ceramic Materials Incorporating GNPs Array: Preparation and Mechanical Characterization [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(3): 267-273. |
| [9] | ZHENG Jiaqian, LU Xiao, LU Yajie, WANG Yingjun, WANG Zhen, LU Jianxi. Functional Bioadaptability in Medical Bioceramics: Biological Mechanism and Application [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(1): 1-16. |
| [10] | HE Danqi, WEI Mingxu, LIU Ruizhi, TANG Zhixin, ZHAI Pengcheng, ZHAO Wenyu. Heavy-Fermion YbAl3 Materials: One-step Synthesis and Enhanced Thermoelectric Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 577-582. |
| [11] | WU Shuang, GOU Yanzi, WANG Yongshou, SONG Quzhi, ZHANG Qingyu, WANG Yingde. Effect of Heat Treatment on Composition, Microstructure and Mechanical Property of Domestic KD-SA SiC Fibers [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 569-576. |
| [12] | XIE Jiaye, LI Liwen, ZHU Qiang. Contrastive Study on in Vitro Antibacterial Property and Biocompatibility of Three Clinical Pulp Capping Agents [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(12): 1449-1456. |
| [13] | LI Jianbo, TIAN Zhen, JIANG Quanwei, YU Lifeng, KANG Huijun, CAO Zhiqiang, WANG Tongmin. Effects of Different Element Doping on Microstructure and Thermoelectric Properties of CaTiO3 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(12): 1396-1404. |
| [14] | WU Dongjiang, ZHAO Ziyuan, YU Xuexin, MA Guangyi, YOU Zhulin, REN Guanhui, NIU Fangyong. Direct Additive Manufacturing of Al2O3-TiCp Composite Ceramics by Laser Directed Energy Deposition [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(10): 1183-1192. |
| [15] | ZHANG Ye, ZENG Yuping. Progress of Porous Silicon Nitride Ceramics Prepared via Self-propagating High Temperature Synthesis [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(8): 853-864. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||