
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (11): 1171-1177.DOI: 10.15541/jim20210090
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
LAN Qing1,2( ), SUN Shengrui1, WU Ping1, YANG Qingfeng3(
), SUN Shengrui1, WU Ping1, YANG Qingfeng3( ), LIU Yangqiao1(
), LIU Yangqiao1( )
)
Received:2021-02-08
Revised:2021-03-15
Published:2021-11-20
Online:2021-03-15
Contact:
LIU Yangqiao, professor. E-mail: yqliu@mail.sic.ac.cn;YANG Qingfeng, professor. E-mail: yangqf@sari.ac.cn
About author:LAN Qing(1996-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: lanqing@student.sic.ac.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
LAN Qing, SUN Shengrui, WU Ping, YANG Qingfeng, LIU Yangqiao. Co-doped CuO/Visible Light Synergistic Activation of PMS for Degradation of Rhodamine B and Its Mechanism[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(11): 1171-1177.
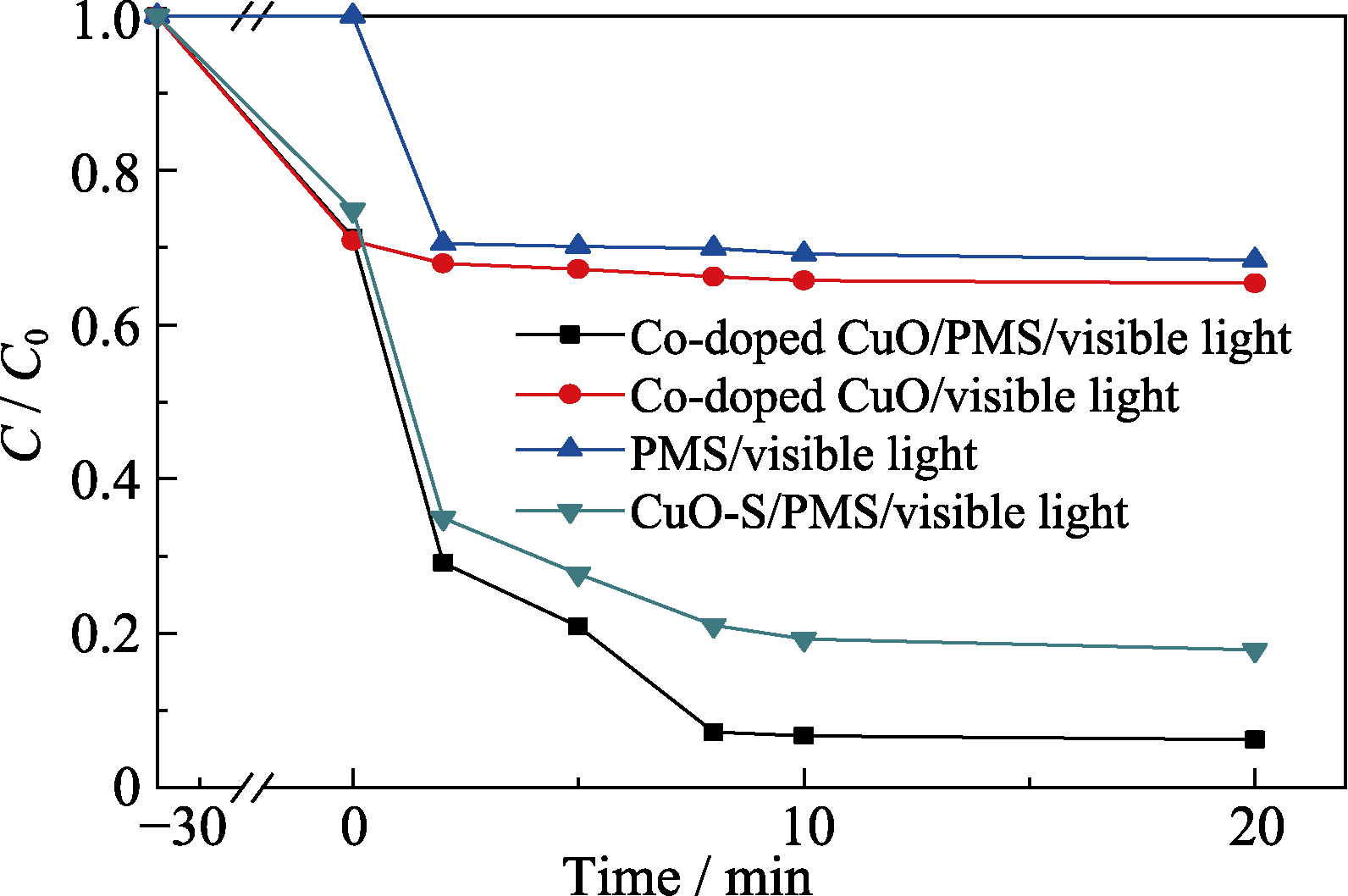
Fig. 3 Comparison of the catalytic performance of Co-doped CuO and CuO-S under visible light illumination (PMS concentration=0.4 g/L; Initial RhB concentration=25 mg/L, catalyst dosage=0.4 g/L)
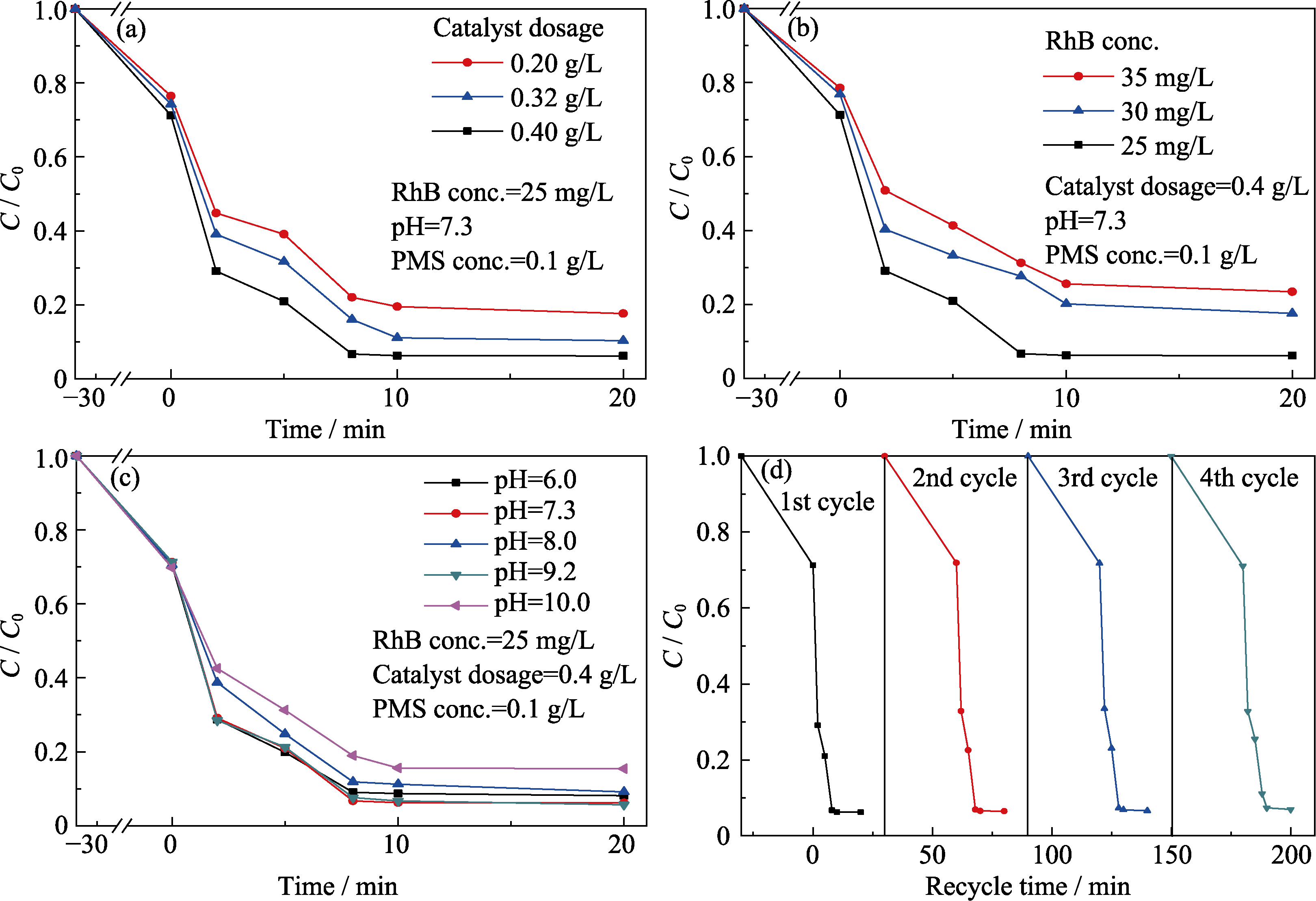
Fig. 4 Influences of catalyst dosage (a), initial dye concentration (b), solution pH (c) on catalytic performance, the recycling experiment results (d)
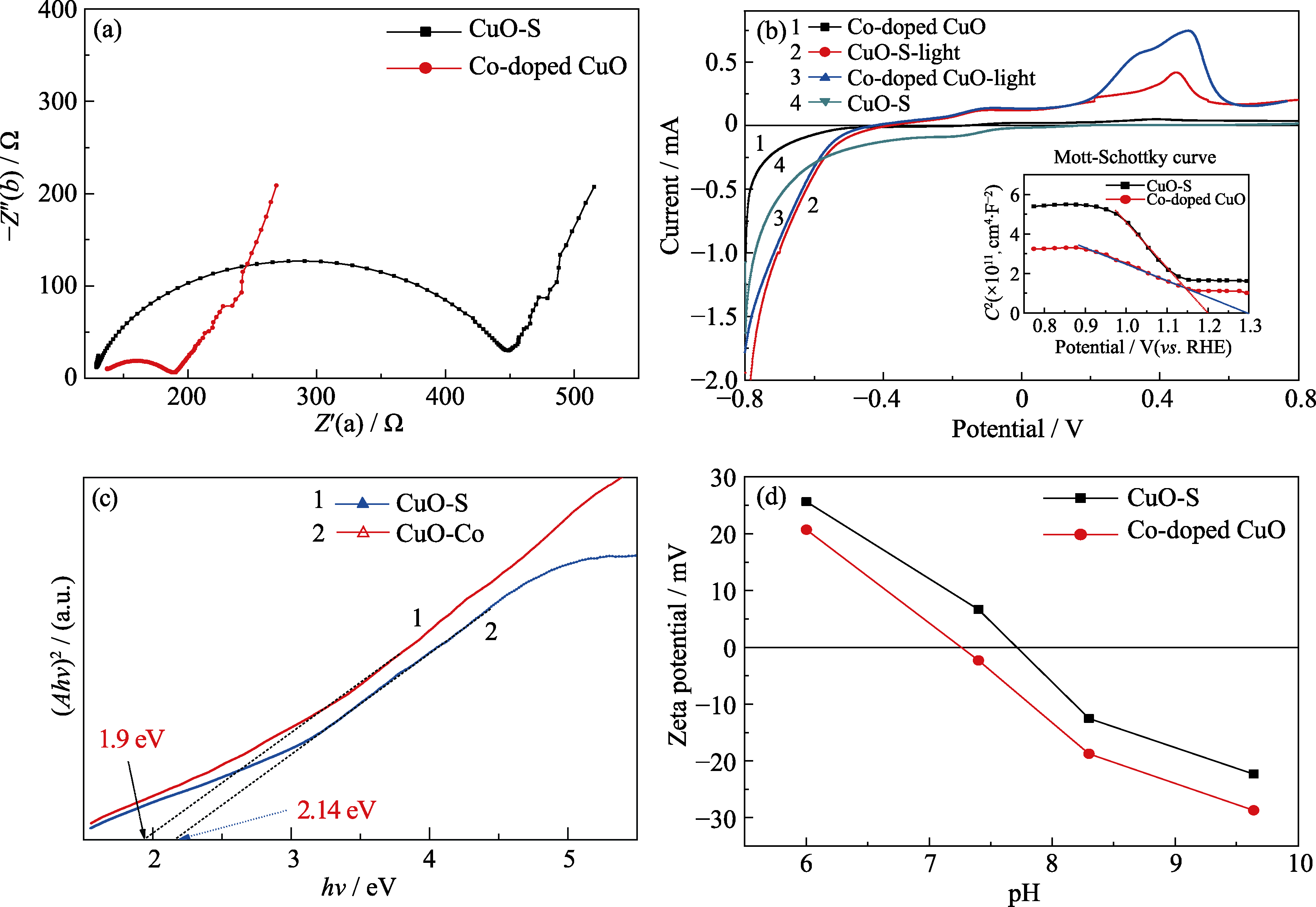
Fig. 5 Electrochemical impedance spectra (a), photocurrent(inset showing Mott-Schottky) curves (b), Diffuse reflection spectra (c), Zeta potential curves (d) of CuO-S and Co-doped CuO
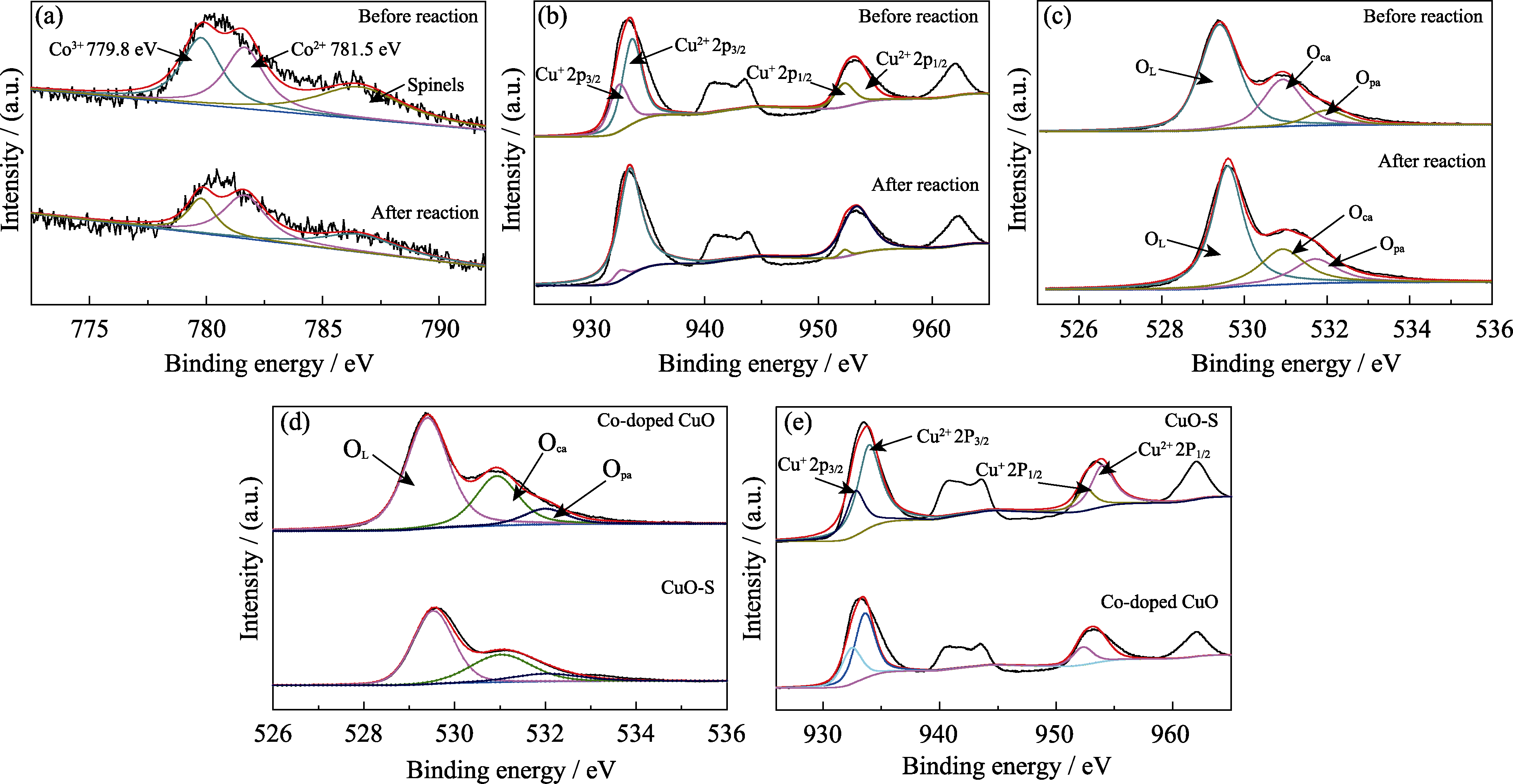
Fig. 6 Comparation of XPS spectra of Co-doped CuO before and after reaction (Co2p (a), Cu2p (b), O1s (c)) XPS spectra of catalysts Co-doped CuO and CuO-S before reaction(O1s (d), Cu2p (e))
| [1] |
BABUPONNUSAMI A, MUTHUKUMAR K. A review on Fenton and improvements to the Fenton process for wastewater treatment. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2014, 2:557-572.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
GHANBARI F, MORADI M. Application of peroxymonosulfate and its activation methods for degradation of environmental organic pollutants: Review. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 310:41-62.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
NIDHEESH P V, GANDHIMATHI R, RAMESH S T. Degradation of dyes from aqueous solution by Fenton processes: a review. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2013, 20:2099-2132.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
CHI F, SONG B, YANG B, et al. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by BiFeO3 microspheres under visible light irradiation for decomposition of organic pollutants. RSC Advances, 2015, 5:67412-67417.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
PHAM H H, YOU S J, WANG Y F, et al. Activation of potassium peroxymonosulfate for rhodamine B photocatalytic degradation over visible-light-driven conjugated polyvinyl chloride/Bi2O3 hybrid structure. Sustainable Chemistry and Pharmacy, 2021, 19:100367-100376.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
YAN J F, LI J, PENG J L, et al. Efficient degradation of sulfamethoxazole by the CuO@Al2O3(EPC) coupled PMS system: optimization, degradation pathways and toxicity evaluation. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 359:1097-1110.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
WANG J L, WANG S Z. Activation of persulfate (PS) and peroxymonosulfate (PMS) and application for the degradation of emerging contaminants. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 334:1502-1517.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
PENG C, WEI P, LI X Y, et al. High efficiency photocatalytic hydrogen production over ternary Cu/TiO2@Ti3C2Tx enabled by low-work-function 2D titanium carbide. Nano Energy, 2018, 53:97-107.
DOI URL |
| [9] | VILLANI M, ALABI A B, ZAPPETTINI A, et al. Facile synthesis of hierarchical CuO nanostructures with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Crystal Research& Technology, 2014, 49:594-598. |
| [10] |
YANG Z Y, DAI D J, YAO Y Y, et al. Extremely enhanced generation of reactive oxygen species for oxidation of pollutants from peroxymonosulfate induced by a supported copper oxide catalyst. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 322:546-555.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
SUN M Y, LEI Y, CHENG H, et al. Mg doped CuO-Fe2O3 composites activated by persulfate as highly active heterogeneous catalysts for the degradation of organic pollutants. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 825:154036-154044.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
WANG S X, TIAN J Y, WANG Q, et al. Development of CuO coated ceramic hollow fiber membrane for peroxymonosulfate activation: a highly efficient singlet oxygen-dominated oxidation process for bisphenol a degradation. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2019, 256:117783-117793.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
YANG Q J, CHOI H, DIONYSIOU D D, et al. Iron-cobalt mixed oxide nanocatalysts: heterogeneous peroxymonosulfate activation, cobalt leaching, and ferromagnetic properties for environmental applications. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2009, 88:462-469.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
KHAN A, LIAO Z W, LIU Y, et al. Synergistic degradation of phenols using peroxymonosulfate activated by CuO-Co3O4@MnO2. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 329:262-271.
DOI URL |
| [15] | DONG Q, QIAO N, LIU Y H. Spongelike porous CuO as an efficient peroxymonosulfate activator for degradation of Acid Orange 7. Applied Surface Science, 2020, 202:25-34. |
| [16] |
LIU Y, GUO H G, ZHANG Y L, et al. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by BiVO4 under visible light for degradation of Rhodamine B. Chemical Physics Letters, 2016, 653:101-107.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
KUSHWAHA A, MOAKHAR R S, DALAPATI G K, et al. Morphologically tailored CuO photocathode using aqueous solution technique for enhanced visible light driven water splitting. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 2017, 337:54-61.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
LEE P Y, CHANG S P, CHANG S J. Photoelectrochemical characterization of n-type and p-type thin-film nanocrystalline Cu2ZnSnSe4 photocathodes. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2015, 3:297-303.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
LUO X S, LIANG H, QU F S, et al. Free-standing hierarchical a-MnO2@CuO membrane for catalytic filtration degradation of organic pollutants. Chemosphere, 2018, 200:237-247.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
JURISTIĆ A B, Choy W C H, ROY V A L. Photoluminescence and electron paramagnetic resonance of ZnO tetrapod structures. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2004, 14:856-864.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
MORAZONNI F, SCOTTI R, NOLA D P, et al. Electron paramagnetic resonance study of the interaction of the ZnO surface with air and air-reducing gas mixtures. J. Chem. Soc., Faraday Trans., 1992, 88:1691-1694.
DOI URL |
| [1] | YANG Yan, ZHANG Faqiang, MA Mingsheng, WANG Yongzhe, OUYANG Qi, LIU Zhifu. Low Temperature Sintering of ZnAl2O4 Ceramics with CuO-TiO2-Nb2O5 Composite Oxide Sintering Aid [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 711-718. |
| [2] | TANG Ya, SUN Shengrui, FAN Jia, YANG Qingfeng, DONG Manjiang, KOU Jiahui, LIU Yangqiao. PEI Modified Hydrated Calcium Silicate Derived from Fly Ash and Its adsorption for Removal of Cu (II) and Catalytic Degradation of Organic Pollutants [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(11): 1281-1291. |
| [3] | ZHANG Qingming, ZHU Min, ZHOU Xiaoxia. CuO/ZnO Composite Electrocatalyst: Preparation and Reduction of CO2 to Syngas [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(11): 1145-1153. |
| [4] | ZHANG Xincong,GUO Ke,PENG Lianlian,WU Jieyu,ZHANG Fumin,ZHU Weidong,FU Yanghe. Degradation of Dye Wastewater over NH2-UiO-66: Piezoelectrically Induced Mechano-Catalytic Effect [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(9): 1023-1028. |
| [5] | LI Rui,WANG Hao,FU Qiang,TIAN Ziyu,WANG Jianxu,MA Xiaojian,YANG Jian,QIAN Yitai. Stable Li-metal Depositon on Lithiophilic 3D CuO Nanosheet-decorated Cu Mesh [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(8): 882-888. |
| [6] | DENG Min, JIANG Qi, DUAN Zhi-Hong, LIU Qing-Qing, JIANG Li, LU Xiao-Ying. Rice-like CuO Chemically Modified Electrode: Preparation and Detection for Glucose [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(2): 152-158. |
| [7] | CHENG Dan, HUANG Bin, CHEN Tao, JING Feng-Juan, XIE Dong, LENG Yong-Xiang, HUANG Nan. Microstructure of TiCuO Films on Copper Ion Release and Endothelial Cell Behavior [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(10): 1089-1096. |
| [8] | LI Shu-Ling, YUAN Xian-Xia, KONG Hai-Chuan, XU Jin, MA Zi-Feng. Fe-PPy-TsOH/C as Cathode Catalyst for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(4): 393-399. |
| [9] | YANG Shuai, XU Pan-Pan, WANG Ming-Wen, HAO Wen-Tao, SUN Li, CAO En-Si, ZHANG Yong-Jia. High Dielectric-permittivity Properties and Relevant Mechanism of NaCu3Ti3Sb0.5Nb0.5O12 Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(10): 1029-1035. |
| [10] |
ZENG Tao, BAI Yang, LI Hao, YAO Wei-Feng, DONG Xian-Lin.
Preparation of Polyhedral Copper Oxide Nanoparticles by Molten-salt Method and Their Catalytic Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(4): 439-442. |
| [11] | LI Xiao-Yan, YAN Jian-Hui, ZHANG Li, ZHOU Ming-Jie, LIU You-Nian. Preparation and Photocatalytic Properties of Hollow Spheres-like Zn-doped CuO/CuAl2O4 Composite Photocatalysts [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(10): 1055-1060. |
| [12] | YE Yun, CHEN Tian-Yuan, CAI Shou-Jin, YAN Min, LIU Yu-Hui, GUO Tai-Liang. Effects of Different Humidity on the Growth and Field Emission Properties of CuO Nanowires [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(12): 1359-1363. |
| [13] | YUAN Chang-Lai,WU Xiu-Fang,LIU Xin-Yu,HUANG Jing-Yue,LI Bo,LIANG Mei-Fang,MO Chong-Gui. Electrical Properties of CuO-doped SrFe0.9Sn0.1O3- δ Thick Film NTC Thermistors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2011, 26(4): 387-392. |
| [14] | LIU Bin, HU Wen-Sheng, SONG Bin, JIA Dian-Zeng. Preparation and Electrochemical Properties of Tin-copper Nanocomposite Oxides Material [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2010, 25(7): 729-732. |
| [15] | ZHANG Zhao-Chun,ZHANG Yi-Chao,ZHANG Qi-Xian. Catalytic Activity of Water Gas Shift and Characteristic Analysis of Complex Network from Surface Morphology of CuO+ZnO/CeO2/Al2O3 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2009, 24(1): 182-186. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||