
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2014, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (10): 1055-1060.DOI: 10.15541/jim20140008
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Xiao-Yan1,2, YAN Jian-Hui1,2, ZHANG Li1,2, ZHOU Ming-Jie2, LIU You-Nian1
Received:2014-01-06
Revised:2014-03-14
Published:2014-10-20
Online:2014-09-22
About author:LI Xiao-Yan. E-mail: yuyicaocao@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
LI Xiao-Yan, YAN Jian-Hui, ZHANG Li, ZHOU Ming-Jie, LIU You-Nian. Preparation and Photocatalytic Properties of Hollow Spheres-like Zn-doped CuO/CuAl2O4 Composite Photocatalysts[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(10): 1055-1060.
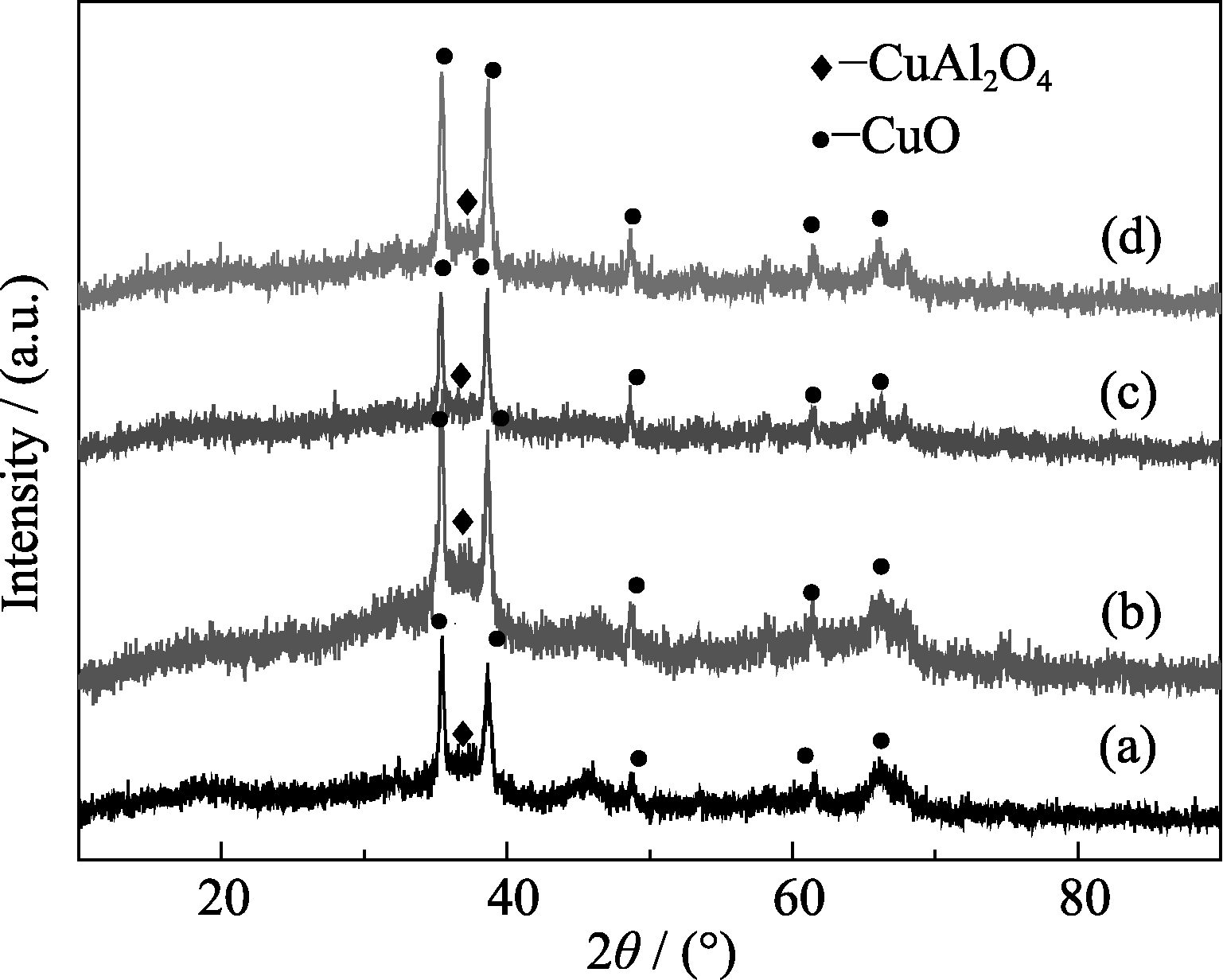
Fig. 2 XRD patterns of Zn-doped CuO/CuAl2O4 samples calcined at 600℃ (a) 0wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4; (b) 0.5wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4; (c) 1wt% Zn- CuO/CuAl2O4; (d) 2wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4
| Element | Area 1 | Area 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt% | at% | wt% | at% | |
| O | 32.00 | 52.78 | 30.99 | 51.06 |
| Al | 33.76 | 33.01 | 36.15 | 35.32 |
| Cu | 33.30 | 13.83 | 32.03 | 13.29 |
| Zn | 0.94 | 0.38 | 0.83 | 0.34 |
Table 1 EDS analyses of 1wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4 samples
| Element | Area 1 | Area 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt% | at% | wt% | at% | |
| O | 32.00 | 52.78 | 30.99 | 51.06 |
| Al | 33.76 | 33.01 | 36.15 | 35.32 |
| Cu | 33.30 | 13.83 | 32.03 | 13.29 |
| Zn | 0.94 | 0.38 | 0.83 | 0.34 |

Fig. 3 SEM images of Zn microspheres (a, b), Zn microspheres calcined at 500℃(c), 0.5wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4 samples (d, e) and HRTEM images of 0.5wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4 samples (f)
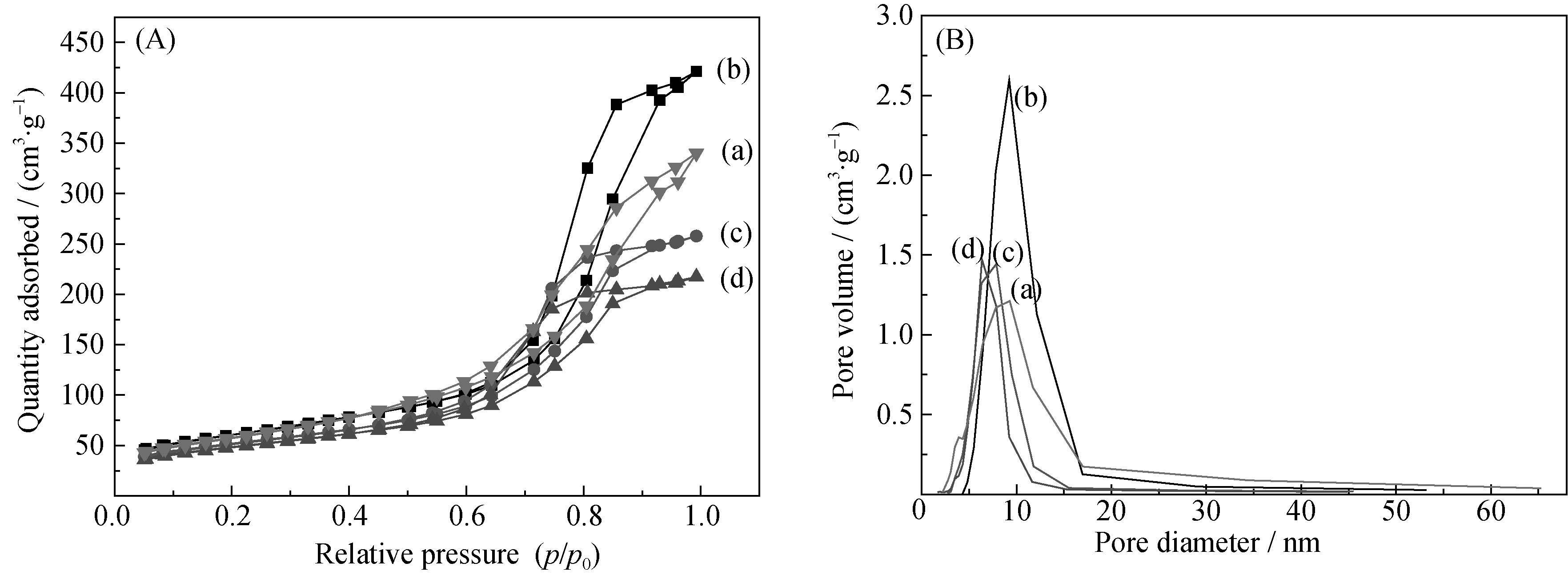
Fig. 4 (A) N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms and (B) pore size distribution curves of Zn-doped CuO/CuAl2O4 samples (a) 0wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4; (b) 0.5wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4; (c) 1wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4; (d) 2wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4
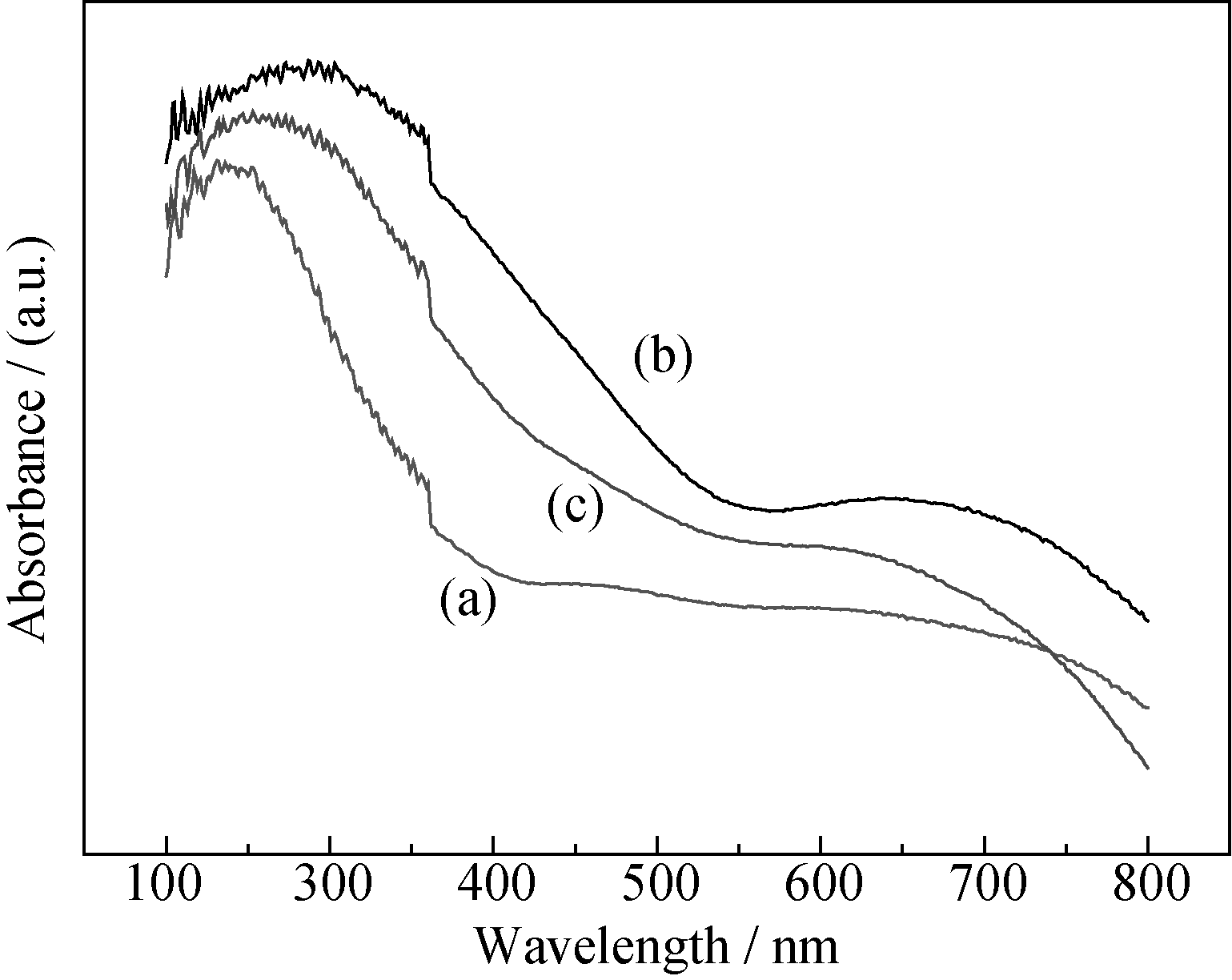
Fig. 5 UV-Vis DRS spectra of Zn-doped CuO/CuAl2O4 samples (a) 0wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4; (b) 0.5wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4; (c) 1wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4 calcined at 600℃
| Sample | SBET/(m2·g-1) | Adsorption average pore width / nm | Pore volume /(cm3·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.3wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4 | 208.25 | 7.7 | 0.59 |
| 0.5wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4 | 214.97 | 9.2 | 0.71 |
| 1wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4 | 182.92 | 7.0 | 0.45 |
| 2wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4 | 171.42 | 6.5 | 0.37 |
Table 2 Physical property of Zn-doped CuO/CuAl2O4 samples
| Sample | SBET/(m2·g-1) | Adsorption average pore width / nm | Pore volume /(cm3·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.3wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4 | 208.25 | 7.7 | 0.59 |
| 0.5wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4 | 214.97 | 9.2 | 0.71 |
| 1wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4 | 182.92 | 7.0 | 0.45 |
| 2wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4 | 171.42 | 6.5 | 0.37 |
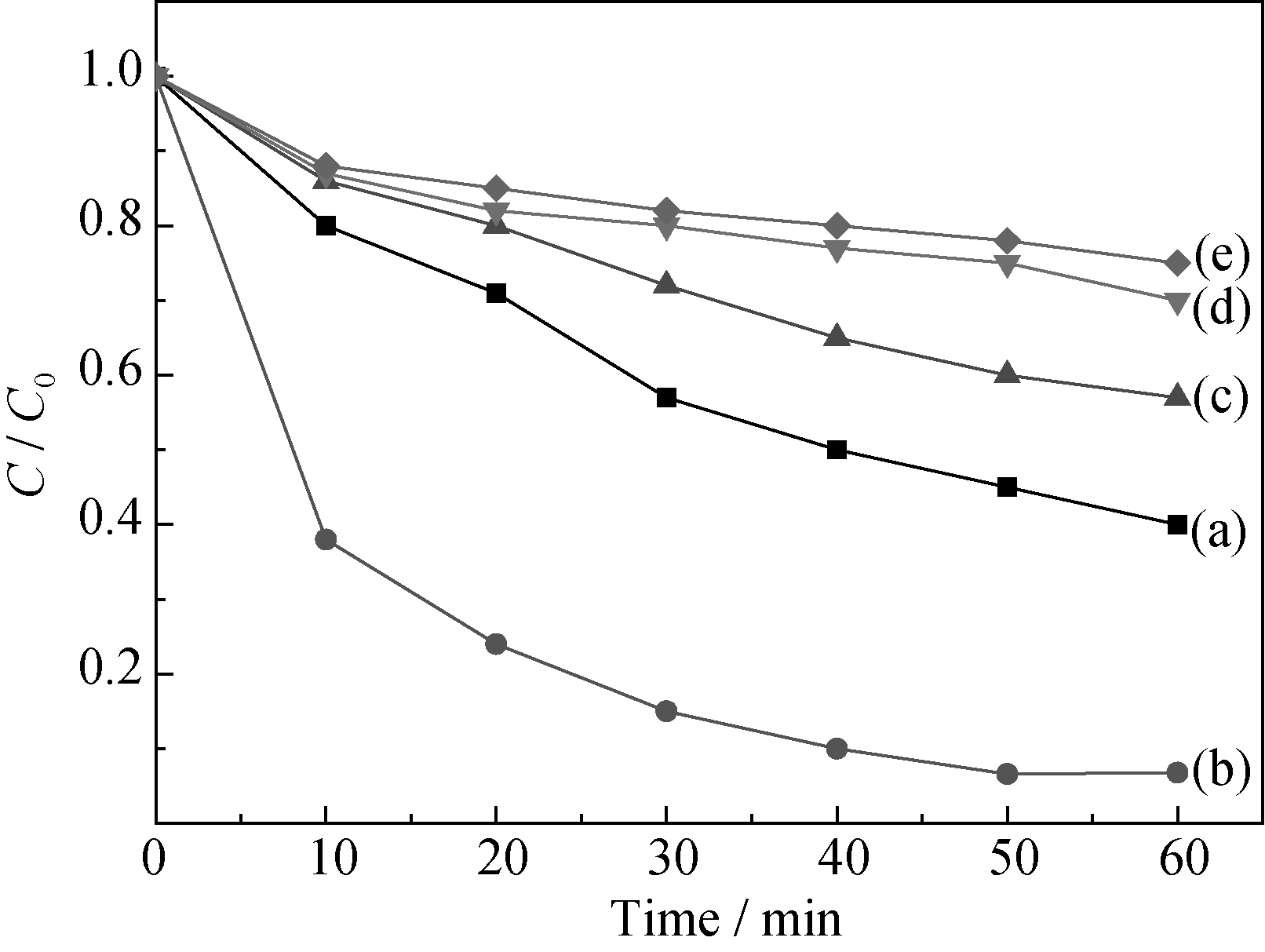
Fig. 7 Effect of calcination temperatures on methyl orange degradation of 0.5wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4 samples (a) 500℃; (b) 600℃; (c) 700℃; (d) 800℃; (e) 900℃
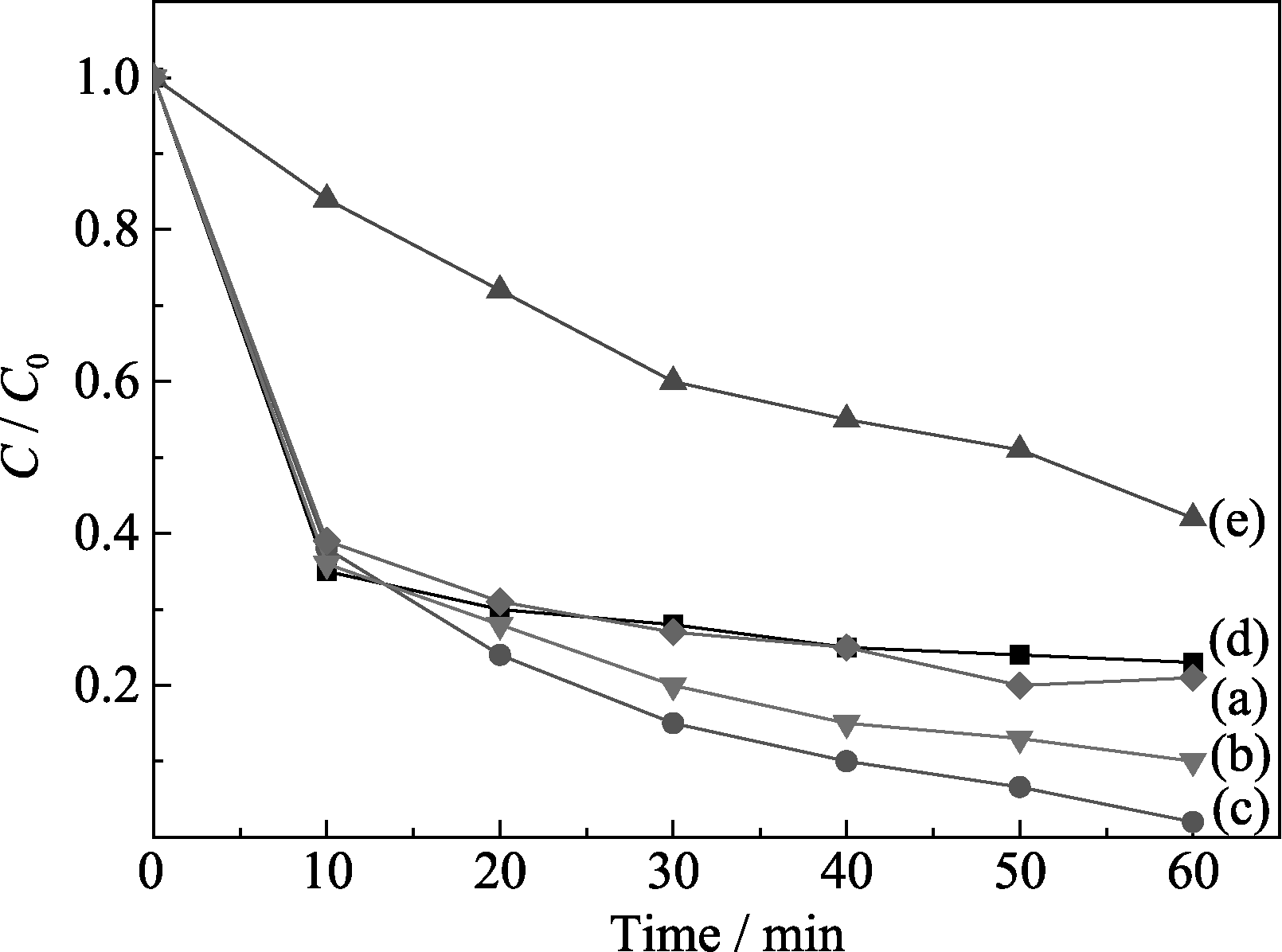
Fig. 8 Effect of Zn doped content on methyl orange degradation of Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4 samples (a) 0wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4; (b) 0.3wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4; (c) 0.5wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4; (d) 1wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4; (e) 2wt% Zn-CuO/ CuAl2O4 calcined at 600℃
| [1] | LI F H, LIN H, LI J F, et al. Influence of LiF on the infrared transmissivity of magnesia alumina spinel transparent ceramics. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(4): 417-421. |
| [2] | TORKIAN L, AMINI M M, BAHRAMI Z. Synthesis of nano crystalline MgAl2O4 spinel powder by microwave assisted combustion. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2011, 26(5): 550-554. |
| [3] | BAYAL N, JEEVANANDAM P. Synthesis of metal aluminate nanoparticles by Sol-Gel method and studies on their reactivity. J. Alloys Compd., 2012, 516: 27-32. |
| [4] | NADERI M, SHAMIRIAN A, EDRISI M. Synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic properties of nanoparticles CuAl2O4 by pechini method using taguchi statistical design. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol., 2011, 58(2): 557-563. |
| [5] | EDRISI M, TAJIK S, SOLEYMANI M. Synthesis of CuAl2O4 nanoparticles by mixed chelates thermolysis and homogeneous precipitation using solubility difference reactions; taguchi optimization and photocatalytic application. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2013, 24(10): 3914-3920. |
| [6] | LIANG C X, LI X Y, QU Z P, et al. The role of copper species on Cu/γ-Al2O3 catalysts for NH3-SCO reaction. Applied Surface Science, 2012, 258(8): 3738-3743. |
| [7] | SHANG H X, TIAN Y, WANG X T, et al. Photocatalytic H2 evolution from glycerol solution over Bi3+-doped TiO2 nanoparti-cles. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(12): 1283-1288. |
| [8] | YIN J, ZANG Y S, YUE C, et al. Ag nanoparticle/ZnO hollow nanosphere arrays: large scale synthesis and surface plasmon resonance effect induced Raman scattering enhancement. J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22(16): 7902-7909. |
| [9] | ZHAO G, LIU S W, LU Q F. Synthesis of TiO2/Bi2WO6 nanofibers with electrospinning technique for photocatalytic methyl blue degradation. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol., 2013, 66(3): 406-412. |
| [10] | LI Z Q, CHEN X T, XUE Z L. Microwave-assisted synthesis and photocatalytic properties of flower-like Bi2WO6 and Bi2O3-Bi2WO6 composite. J. Colloid Interface sci., 2013, 394: 69-77. |
| [11] | TIAN G H, CHEN Y J, MENG X Y, et al. Hierarchical composite of Ag/AgBr nanoparticles supported on Bi2MoO6 hollow spheres for enhanced visible-light photocatalytic performance. ChemPlusChem, 2013, 78(1): 117-123. |
| [12] | BAO Y, YANG Y Q, MA J Z. Research progress of hollow structural materials prepared via templating method. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(5): 459-468. |
| [13] | ZHAO B, LIN L, CHEN C, et al. Research progress on crystal growth mechanism of titania/titanate nano-powder materials. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(7): 683-690. |
| [14] | MENG H X, WANG B B, LIU S, et al. Hydrothermal preparation, characterization and photocatalytic activity of TiO2/Fe-TiO2 composite catalysts. Ceram. Int., 2013, 39(5): 5785-5793. |
| [15] | YIN B, WANG J T, XU W, et al. Preparation of TiO2/mesoporous carbon composites and their photocatalytic performance for methyl orange degradation. New Carbon Materials, 2013, 28(1): 47-54. |
| [16] | ZHANG L, YAN J H, ZHOU M J, et al. Fabrication and photocatalytic properties of spheres-in-spheres ZnO/ZnAl2O4 composite hollow microspheres. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2013, 268: 237-245. |
| [17] | ZHANG L, YAN J H, ZHOU M J, et al. Preparation and photocatalytic property of hollow sphere-like ZnO/ZnAl2O4 composite photocatalysts with high specific surface area. Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2012, 28(9): 1827-1834. |
| [18] | LV K, YU J, DENG K, et al. Synergistic effects of hollow structure and surface fluorination on the photocatalytic activity of titania. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 173(1): 539-543. |
| [19] | ZHANG Y J, XU Y, LI T, et al. Preparation of ternary Cr2O3-SiC-TiO2 composites for the photocatalytic production of hydrogen. Particuology, 2012, 10(1): 46-50. |
| [20] | DONG F, SUN Y J, FU M, et al. Room temperature synthesis and highly enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity of porous BiOI/BiOCl composites nanoplates microflowers. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2012, 219: 26-34. |
| [21] | LEE S S, BAI H W, LIU Z Y, et al. Novel-structured electrospun TiO2/CuO composite nanofibers for high efficient photocatalytic cogeneration of clean water and energy from dye wastewater. Water Research, 2013, 47(12): 4059-4073. |
| [1] | FAN Xiaoxuan, ZHENG Yonggui, XU Lirong, YAO Zimin, CAO Shuo, WANG Kexin, WANG Jiwei. Organic Pollutant Fenton Degradation Driven by Self-activated Afterglow from Oxygen-vacancy-rich LiYScGeO4: Bi3+ Long Afterglow Phosphor [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 481-488. |
| [2] | JIA Xianghua, ZHANG Huixia, LIU Yanfeng, ZUO Guihong. Cu2O/Cu Hollow Spherical Heterojunction Photocatalysts Prepared by Wet Chemical Approach [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 397-404. |
| [3] | LIU Huilai, LI Zhihao, KONG Defeng, CHEN Xing. Preparation of FePc/MXene Composite Cathode and Electro-Fenton Degradation of Sulfadimethoxine [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 61-69. |
| [4] | MA Binbin, ZHONG Wanling, HAN Jian, CHEN Liangyu, SUN Jingjing, LEI Caixia. ZIF-8/TiO2 Composite Mesocrystals: Preparation and Photocatalytic Activity [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(8): 937-944. |
| [5] | CAO Qingqing, CHEN Xiangyu, WU Jianhao, WANG Xiaozhuo, WANG Yixuan, WANG Yuhan, LI Chunyan, RU Fei, LI Lan, CHEN Zhi. Visible-light Photodegradation of Tetracycline Hydrochloride on Self-sensitive Carbon-nitride Microspheres Enhanced by SiO2 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(7): 787-792. |
| [6] | WANG Zhaoyang, QIN Peng, JIANG Yin, FENG Xiaobo, YANG Peizhi, HUANG Fuqiang. Sandwich Structured Ru@TiO2 Composite for Efficient Photocatalytic Tetracycline Degradation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(4): 383-389. |
| [7] | YE Maosen, WANG Yao, XU Bing, WANG Kangkang, ZHANG Shengnan, FENG Jianqing. II/Z-type Bi2MoO6/Ag2O/Bi2O3 Heterojunction for Photocatalytic Degradation of Tetracycline under Visible Light Irradiation [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(3): 321-329. |
| [8] | YOU Bojie, LI Bo, LI Xuqin, MA Xuehan, ZHANG Yi, CHENG Laifei. Thermal Shock Damage and In-plane Shear Performance Degradation of 2D SiCf/SiC at Medium Temperature [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(12): 1367-1376. |
| [9] | CHEN Mengjie, WANG Qianqian, WU Chengtie, HUANG Jian. Predicting the Degradability of Bioceramics through a DFT-based Descriptor [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(10): 1175-1181. |
| [10] | CAI Mengyu, LI-YANG Hongmiao, YANG Caiyun, ZHOU Yuting, WU Hao. Activated Sludge Incineration Ash Derived Fenton-like Catalyst: Preparation and Degradation Performance on Methylene Blue [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(10): 1135-1142. |
| [11] | ZHENG Jiaqian, LU Xiao, LU Yajie, WANG Yingjun, WANG Zhen, LU Jianxi. Functional Bioadaptability in Medical Bioceramics: Biological Mechanism and Application [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(1): 1-16. |
| [12] | WU Lin, HU Minglei, WANG Liping, HUANG Shaomeng, ZHOU Xiangyuan. Preparation of TiHAP@g-C3N4 Heterojunction and Photocatalytic Degradation of Methyl Orange [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 503-510. |
| [13] | WANG Lei, LI Jianjun, NING Jun, HU Tianyu, WANG Hongyang, ZHANG Zhanqun, WU Linxin. Enhanced Degradation of Methyl Orange with CoFe2O4@Zeolite Catalyst as Peroxymonosulfate Activator: Performance and Mechanism [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 469-476. |
| [14] | LING Jie, ZHOU Anning, WANG Wenzhen, JIA Xinyu, MA Mengdan. Effect of Cu/Mg Ratio on CO2 Adsorption Performance of Cu/Mg-MOF-74 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(12): 1379-1386. |
| [15] | SUN Chen, ZHAO Kunfeng, YI Zhiguo. Research Progress in Catalytic Total Oxidation of Methane [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(11): 1245-1256. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||