
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2017, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (4): 393-399.DOI: 10.15541/jim20160399
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Shu-Ling, YUAN Xian-Xia, KONG Hai-Chuan, XU Jin, MA Zi-Feng
Received:2016-06-29
Revised:2016-09-07
Published:2017-04-20
Online:2017-03-24
About author:LI Shu-Ling. E-mail: l_nicola@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
LI Shu-Ling, YUAN Xian-Xia, KONG Hai-Chuan, XU Jin, MA Zi-Feng. Fe-PPy-TsOH/C as Cathode Catalyst for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(4): 393-399.
| Catalyst | Fe/mmol | Co/mmol | Fe:Co | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| synthesis | ICP | |||
| 1 | 1.000 | 0 | 1:0 | 1:0 |
| 2 | 0.750 | 0.250 | 3:1 | 3.127:1 |
| 3 | 0.667 | 0.333 | 2:1 | 2.066:1 |
| 4 | 0.500 | 0.500 | 1:1 | 1.077:1 |
Table 1 Content of Fe and Co in Fe1-xCox-PPy-TsOH/C catalysts
| Catalyst | Fe/mmol | Co/mmol | Fe:Co | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| synthesis | ICP | |||
| 1 | 1.000 | 0 | 1:0 | 1:0 |
| 2 | 0.750 | 0.250 | 3:1 | 3.127:1 |
| 3 | 0.667 | 0.333 | 2:1 | 2.066:1 |
| 4 | 0.500 | 0.500 | 1:1 | 1.077:1 |
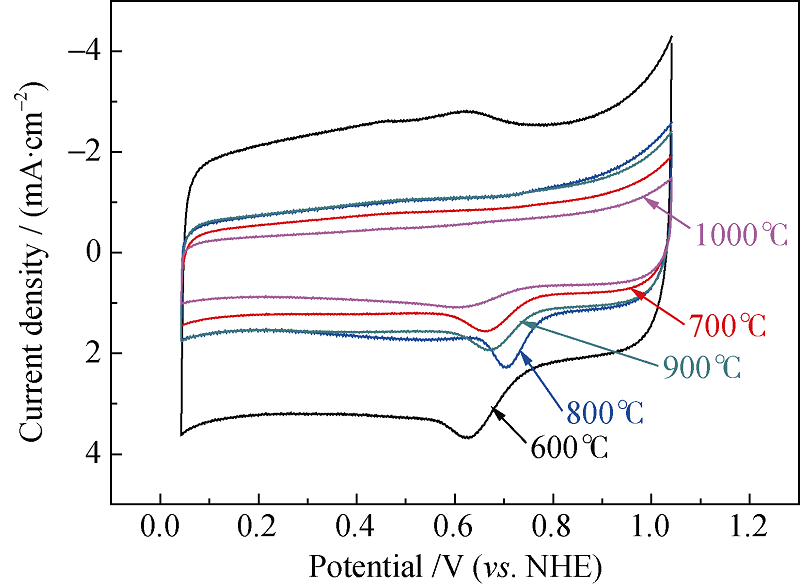
Fig. 4 Cyclic voltammograms of Fe-PPy-TsOH/C catalysts synthesized at various temperatures in oxygen saturated 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 solution at a potential scanning rate of 5 mV/s
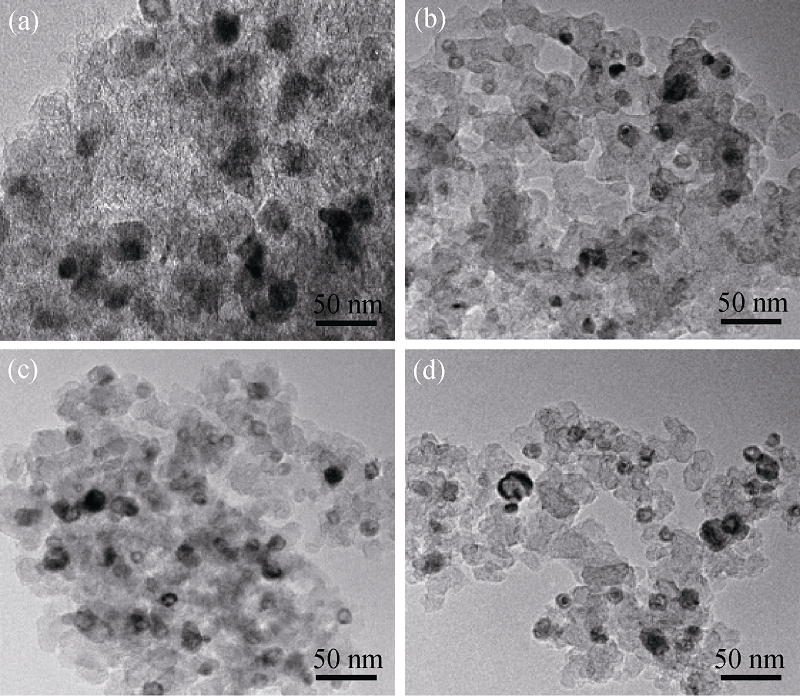
Fig. 6 TEM images of Fe1-xCox-PPy-TsOH /C catalysts with various Co contents(a) Fe1Co0-PPy-TsOH/C; (b) Fe0.75:Co0.25-PPy-TsOH/C; (c) Fe0.666Co0.333- PPy-TsOH /C; (d) Fe0.5:Co0.5-PPy-TsOH/C
| [1] | JAOUEN F, PROIETTI E, LEFEVRE M, et al.Recent advances in non-precious metal catalysis for oxygen-reduction reaction in polymer electrolyte fuel cells. Energy Environ. Sci., 2011, 4(1): 114-130. |
| [2] | KRAMM U I, LEFÈVRE M, BOGDANOFF P, et al. Analyzing structural changes of Fe-N-C cathode catalysts in PEM fuel cell by Mößbauer spectroscopy of complete membrane electrode assemblies. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2014, 5(21): 3750-3756. |
| [3] | FAN R J, RUI L, ZHEN H, et al.Preparation and characterization of Pt catalysts supported on cobalt-polypyrrole-carbon for fuel cells. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin., 2014, 30(7): 1259-1266. |
| [4] | WU G, ZELENAY P.High-performance electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction derived from polyaniline, iron, and cobalt. Science, 2011, 332(6028): 443-447. |
| [5] | APPLEBY A J, TWIDELL J.Recent developments and applications of the polymer fuel cell and discussion. Philos. Trans. R. Soc., A, 1996, 354(1712): 1693. |
| [6] | HOGARTH M P, RALPH T R.Catalysis for low temperature fuel cells. Platinum Met. Rev., 2002, 46(4): 146-164. |
| [7] | YUAN X X, XIA X Y, ZENG X, et al.Catalysts for oxygen electrode in low tempera ture fuel cells. Prog. Chem., 2010, 22(1): 19-31. |
| [8] | SHAO M, CHANG Q, DODELET J P, et al.Recent advances in electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. Chem. Rev., 2016, 116(6): 3594. |
| [9] | YUAN X X, HU X X, DING X L, et al.Effects of cobalt precursor on pyrolyzed carbon-supported cobalt-polypyrrole as electrocatalyst toward oxygen reduction reaction. Nanoscale Res. Lett., 2013, 8(1): 1-11. |
| [10] | KRAMM U I, ZANA A, VOSCH T, et al.On the structural composition and stability of Fe-N-C catalysts prepared by an intermediate acid leaching. J. Solid State Electrochem., 2015: 1-13. |
| [11] | WANG J, LI S, ZHU G, et al.Novel non-noble metal electrocatalysts synthesized by heat-treatment of iron terpyridine complexes for the oxygen reduction reaction. J. Power Sources, 2013, 240(31): 381-389. |
| [12] | YUAN X X, SHA H D, DING X L, et al.Comparative investigation on the properties of carbon-supported cobalt- polypyrrole pyrolyzed at various conditions as electrocatalyst towards oxygen reduction reaction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2014, 39(28): 15937-15947. |
| [13] | SHA H D, YUAN X X, LI L, et al.Experimental identification of the active sites in pyrolyzed carbon-supported cobalt-polypyrrole- 4-toluenesulfinic acid as electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. J. Power Sources, 2014, 255(7): 76-84. |
| [14] | SHA H D, YUAN X X, HU X X, et al.Effects of pyrrole polymerizing oxidant on the properties of pyrolysed carbon-supported cobalt-polypyrrole as electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. J. Electrochem. Soc., 2013, 160(6): F507-F513. |
| [15] | LEI Z, KIM J, DY E, et al.Synthesis of novel mesoporous carbon spheres and their supported Fe-based electrocatalysts for PEM fuel cell oxygen reduction reaction. Electrochim. Acta, 2013, 108(10): 480-485. |
| [16] | YIN W W, DAUD W R W, MOHAMAD A B, et al. Nitrogen- containing carbon nanotubes as cathodic catalysts for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Diamond Relat. Mater., 2011, 22: 12-22. |
| [17] | MILLÁN W M, THOMPSON T T, ARRIAGA L G, et al. Characterization of composite materials of electroconductive polymer and cobalt as electrocatalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2009, 34(2): 694-702. |
| [18] | LEE K, LEI Z, LUI H, et al.Oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) catalyzed by carbon-supported cobalt polypyrrole (Co-PPy/C) electrocatalysts. Electrochim. Acta, 2009, 54(20): 4704-4711. |
| [19] | LIU H S, SHI Z, ZHANG J L, et al.Ultrasonic spray pyrolyzed iron-polypyrrole mesoporous spheres for fuel cell oxygen reduction electrocatalysts. J. Mater. Chem., 2009, 19(4): 468-470. |
| [20] | YUASA M, OYAIZU K, MURATA H, et al.Electrocatalytic activities for the reduction of oxygen of carbon particles modified with polypyrrole including various metal ions as electrocatalytic sites. Electrochemistry, 2007, 75(10): 800-806. |
| [21] | YUAN X X, ZENG X, ZHANG H J, et al.Improved performance of proton exchange membrane fuel cells with p-Toluenesulfonic acid-doped Co-PPy/C as cathode electrocatalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132(6): 1754. |
| [22] | LIU Y C, YANG K H, LIN L H, et al.Studies of thermal decay of electropolymerized polypyrrole using in situ surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Electrochem. Commun., 2008, 10(1): 161-164. |
| [23] | WANG J Z, CHOU S L, CHEN J, et al.Paper-like free-standing polypyrrole and polypyrrole-liFePO4 composite films for flexible and bendable rechargeable battery. Electrochem. Commun., 2008, 10(11): 1781-1784. |
| [24] | JAOUEN F, MARCOTTE S, DODELET J P, et al.Oxygen reduction catalysts for polymer electrolyte fuel cells from the pyrolysis of iron acetate adsorbed on various carbon supports. J. Phys. Chem. B, 2003, 107(6): 1376-1386. |
| [25] | BEZERRA C W B, LEI Z, LEE K, et al. A review of Fe-N/C and Co-N/C catalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction. Electrochim. Acta, 2008, 53(15): 4937-4951. |
| [1] | LIU Lei, GUO Ruihua, WANG Li, WANG Yan, ZHANG Guofang, GUAN Lili. Oxygen Reduction Reaction on Pt3Co High-index Facets by Density Functional Theory [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 39-46. |
| [2] | WU Shuang, GOU Yanzi, WANG Yongshou, SONG Quzhi, ZHANG Qingyu, WANG Yingde. Effect of Heat Treatment on Composition, Microstructure and Mechanical Property of Domestic KD-SA SiC Fibers [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 569-576. |
| [3] | YANG Daihui, SUN Tian, TIAN Hexin, SHI Xiaofei, MA Dongwei. Iron-nitrogen-codoped Mesoporous Carbon: Facile Synthesis and Catalytic Performance of Oxygen Reduction Reaction [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(11): 1309-1315. |
| [4] | SUN Lian, GU Quanchao, YANG Yaping, WANG Honglei, YU Jinshan, ZHOU Xingui. Two-dimensional Transition Metal Dichalcogenides for Electrocatalytic Oxygen Reduction Reaction [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 697-709. |
| [5] | JIANG Lili, XU Shuaishuai, XIA Baokai, CHEN Sheng, ZHU Junwu. Defect Engineering of Graphene Hybrid Catalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reactions [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(2): 215-222. |
| [6] | LIU Ziruo, LIU Wei, HAO Ce, HU Jinwen, SHI Yantao. Honeycomb-like Carbon-supported Fe Single Atom Catalyst: Preparation and Electrocatalytic Performance in Oxygen Reduction Reaction [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(9): 943-949. |
| [7] | HAO Ce, LIU Ziruo, LIU Wei, SHI Yantao. Research Progress of Carbon-supported Metal Single Atom Catalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reaction [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(8): 820-834. |
| [8] | ZHU Yong, GU Jun, YU Tao, HE Haitong, YAO Rui. Synthesis and Property of Platinum-cobalt Alloy Nano Catalyst [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(3): 299-305. |
| [9] | LAN Qing, SUN Shengrui, WU Ping, YANG Qingfeng, LIU Yangqiao. Co-doped CuO/Visible Light Synergistic Activation of PMS for Degradation of Rhodamine B and Its Mechanism [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(11): 1171-1177. |
| [10] | WEI Yuquan,YANG Yong,LIU Meng,LI Qile,HUANG Zhengren. Effect of High Temperature Heat Treatment on Phase Composition and Microstructure of SiBCN/HfC Ceramic Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(8): 931-938. |
| [11] | DING Sheng, NING Kai, YUAN Binxia, PAN Weiguo, YIN Shibin, LIU Jianfeng. Durability of Fe-N/C Catalysts with Different Nanostructures for Electrochemical Oxygen Reduction in Alkaline Solution [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(8): 953-958. |
| [12] | FU Ya-Kang,WENG Jie,LIU Yao-Wen,ZHANG Ke-Hong. hBMP-2 Contained Composite Coatings on Titanium Mesh Surface: Preparation and hBMP-2 Release [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(2): 173-178. |
| [13] | WANG Dan-Dan, TIAN Wu-Bian, DING Jian-Xiang, MA Ai-Bin, ZHANG Pei-Gen, HE Wei, SUN Zheng-Ming. Ag/Ti3AlC2 Composites Prepared by Equal Channel Angular Pressing Followed by Heat Treatment [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(1): 46-52. |
| [14] | LIAO Chun-Jing, DONG Shao-Ming, JIN Xi-Hai, HU Jian-Bao, ZHANG Xiang-Yu, WU Hui-Xia. Deposition Temperature and Heat Treatment on Silicon Nitride Coating Deposited by LPCVD [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(11): 1231-1237. |
| [15] | HE Wang-Tao, MA Ru-Guang, ZHU Yu-Fang, YANG Ming-Jie, WANG Jia-Cheng. Renewable Porous Carbons Prepared by KOH Activation as Oxygen Reduction Electrocatalysts [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(10): 1115-1122. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||