
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (6): 711-718.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240517
• RESEARCH LETTER • Previous Articles Next Articles
YANG Yan1,2( ), ZHANG Faqiang1, MA Mingsheng1(
), ZHANG Faqiang1, MA Mingsheng1( ), WANG Yongzhe1, OUYANG Qi1, LIU Zhifu1(
), WANG Yongzhe1, OUYANG Qi1, LIU Zhifu1( )
)
Received:2024-12-12
Revised:2025-02-19
Published:2025-06-20
Online:2025-02-25
Contact:
LIU Zhifu, professor. E-mail: liuzf@mail.sic.ac.cn;About author:YANG Yan (1994-), female, PhD. E-mail: yan.yang@hongxing799.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
YANG Yan, ZHANG Faqiang, MA Mingsheng, WANG Yongzhe, OUYANG Qi, LIU Zhifu. Low Temperature Sintering of ZnAl2O4 Ceramics with CuO-TiO2-Nb2O5 Composite Oxide Sintering Aid[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 711-718.
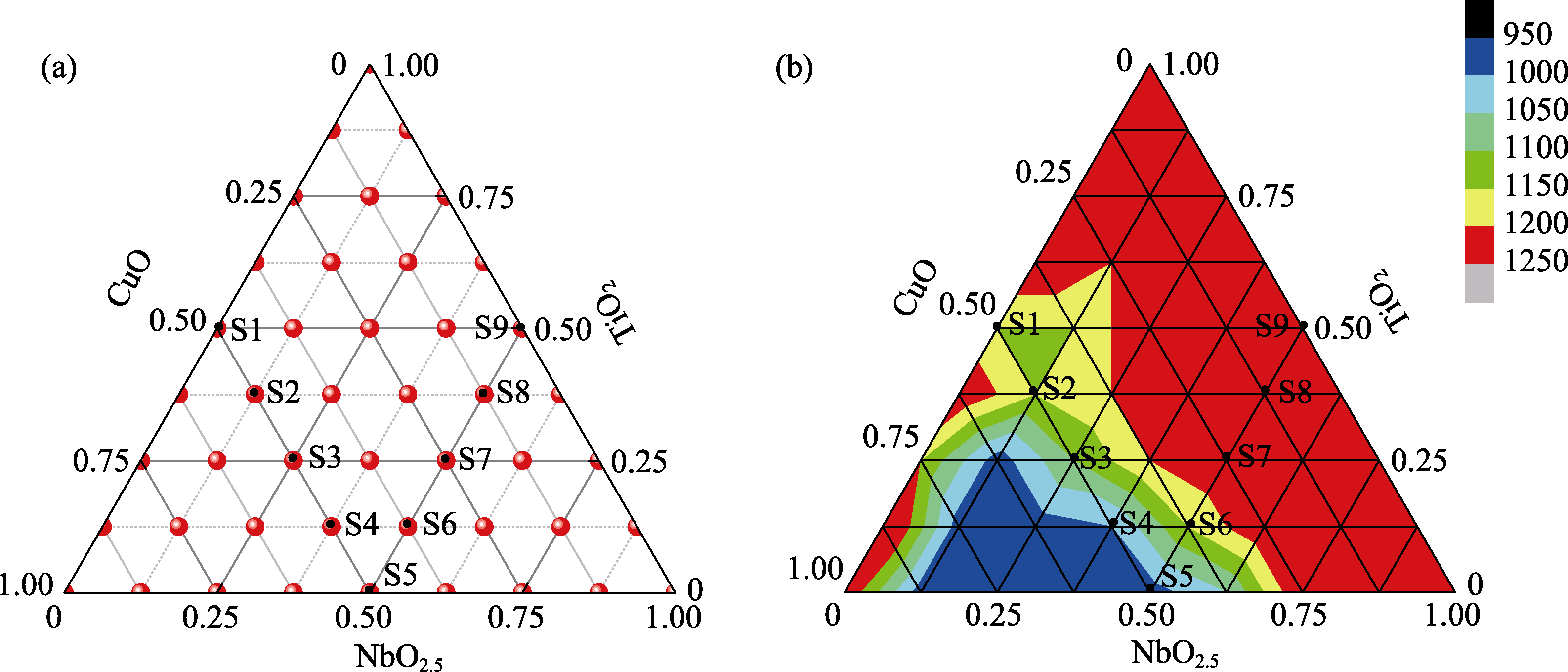
Fig. 1 (a) Compositions of CTN additives for ZnAl2O4; (b) Nephogram of sintering temperature of ZnAl2O4 ceramics with 5% CTN additives and different compositions Colorful figures are available on website
| Sample ID | Sintering temperature/℃ | Molar fraction | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | Ti | Nb | ||
| S1 | 1150 | 0.500 | 0.500 | 0 |
| S2 | 1150 | 0.500 | 0.375 | 0.125 |
| S3 | 1100 | 0.500 | 0.250 | 0.250 |
| S4 | 1000 | 0.500 | 0.125 | 0.375 |
| S5 | 975 | 0.500 | 0 | 0.500 |
| S6 | 1150 | 0.375 | 0.125 | 0.500 |
| S7 | 1250 | 0.250 | 0.250 | 0.500 |
| S8 | 1250 | 0.125 | 0.375 | 0.500 |
| S9 | 1250 | 0 | 0.500 | 0.500 |
Table 1 Sintering temperatures of ZnAl2O4 ceramics mixed 5% CTN additives with different formulas
| Sample ID | Sintering temperature/℃ | Molar fraction | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | Ti | Nb | ||
| S1 | 1150 | 0.500 | 0.500 | 0 |
| S2 | 1150 | 0.500 | 0.375 | 0.125 |
| S3 | 1100 | 0.500 | 0.250 | 0.250 |
| S4 | 1000 | 0.500 | 0.125 | 0.375 |
| S5 | 975 | 0.500 | 0 | 0.500 |
| S6 | 1150 | 0.375 | 0.125 | 0.500 |
| S7 | 1250 | 0.250 | 0.250 | 0.500 |
| S8 | 1250 | 0.125 | 0.375 | 0.500 |
| S9 | 1250 | 0 | 0.500 | 0.500 |
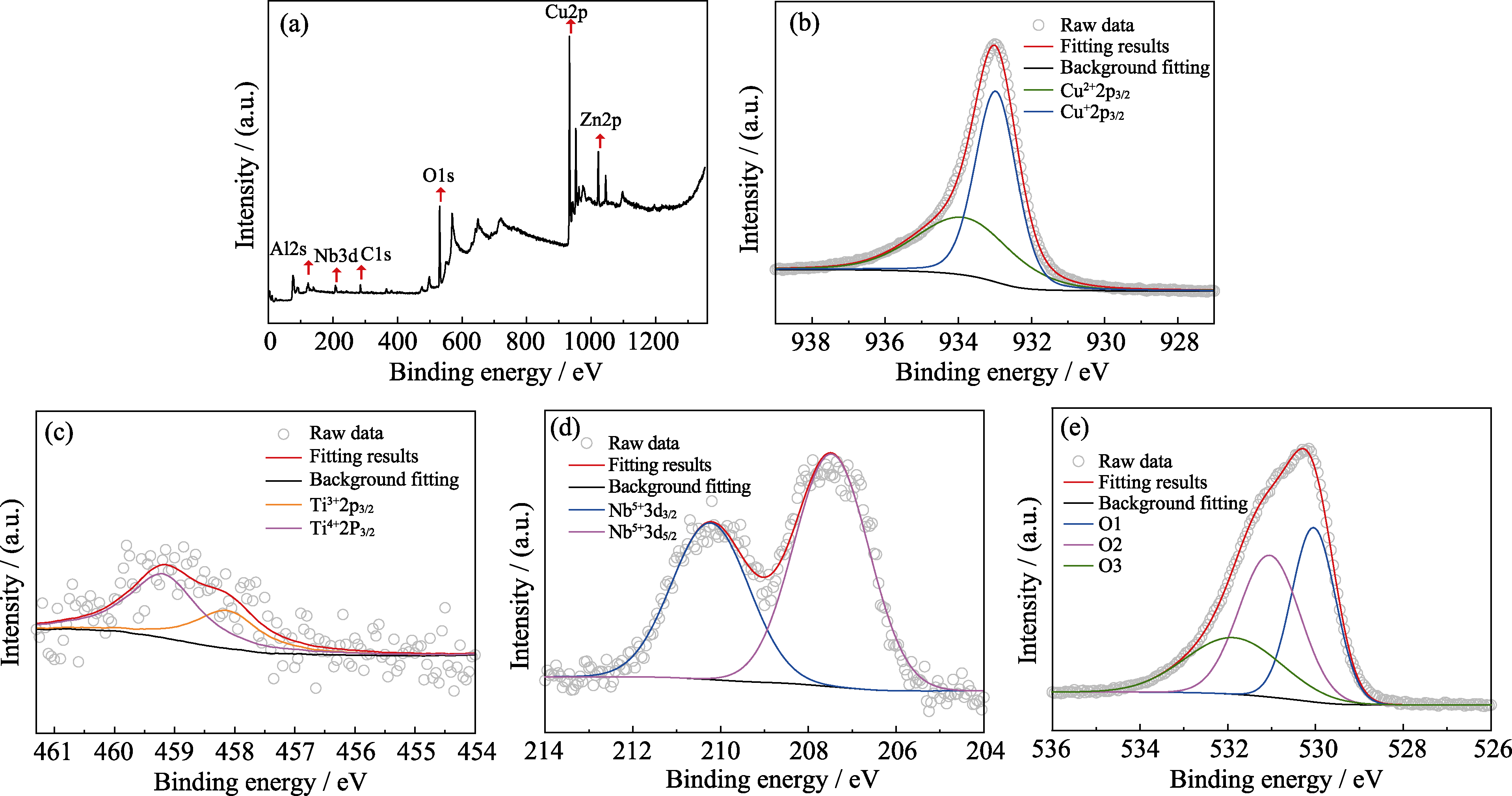
Fig. 4 XPS spectra of sample S4 sintered at 1000 ℃ for 2 h (a) and (b-e) detailed XPS spectra of Cu ion (b), Ti ion (c), Nb ion (d) and O1s (e) Colorful figures are available on website
| Sample ID | Sintering temperature/℃ | Density/(g·cm-3) | εr(@10 GHz) | Q׃/GHz | CTE/(×10-6, ℃-1) (25-350 ℃) | Flexural strength/MPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 1150 | 4.46±0.17 | 10.18 | 17811 | 7.66 | 246±34 |
| S2 | 1150 | 4.49±0.02 | 9.00 | 41673 | 7.34 | 230±10 |
| S3 | 1100 | 4.49±0.01 | 10.10 | 17150 | 7.65 | 233±10 |
| S4 | 1000 | 4.54±0.03 | 9.52 | 22249 | 7.49 | 161±25 |
| S5 | 975 | 4.50±0.04 | 11.36 | 8245 | 7.56 | 200±14 |
| S6 | 1150 | 4.54±0.01 | 9.67 | 30021 | 7.45 | 186±10 |
| S7 | 1250 | 4.17±0.02 | - | - | 7.47 | 215±20 |
| S8 | 1250 | 4.19±0.02 | - | - | 7.53 | 199±8 |
| S9 | 1250 | 3.51±0.03 | - | - | 7.29 | 195±17 |
Table S1 Properties of ZnAl2O4 ceramics with different formulas of CTN additives
| Sample ID | Sintering temperature/℃ | Density/(g·cm-3) | εr(@10 GHz) | Q׃/GHz | CTE/(×10-6, ℃-1) (25-350 ℃) | Flexural strength/MPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 1150 | 4.46±0.17 | 10.18 | 17811 | 7.66 | 246±34 |
| S2 | 1150 | 4.49±0.02 | 9.00 | 41673 | 7.34 | 230±10 |
| S3 | 1100 | 4.49±0.01 | 10.10 | 17150 | 7.65 | 233±10 |
| S4 | 1000 | 4.54±0.03 | 9.52 | 22249 | 7.49 | 161±25 |
| S5 | 975 | 4.50±0.04 | 11.36 | 8245 | 7.56 | 200±14 |
| S6 | 1150 | 4.54±0.01 | 9.67 | 30021 | 7.45 | 186±10 |
| S7 | 1250 | 4.17±0.02 | - | - | 7.47 | 215±20 |
| S8 | 1250 | 4.19±0.02 | - | - | 7.53 | 199±8 |
| S9 | 1250 | 3.51±0.03 | - | - | 7.29 | 195±17 |
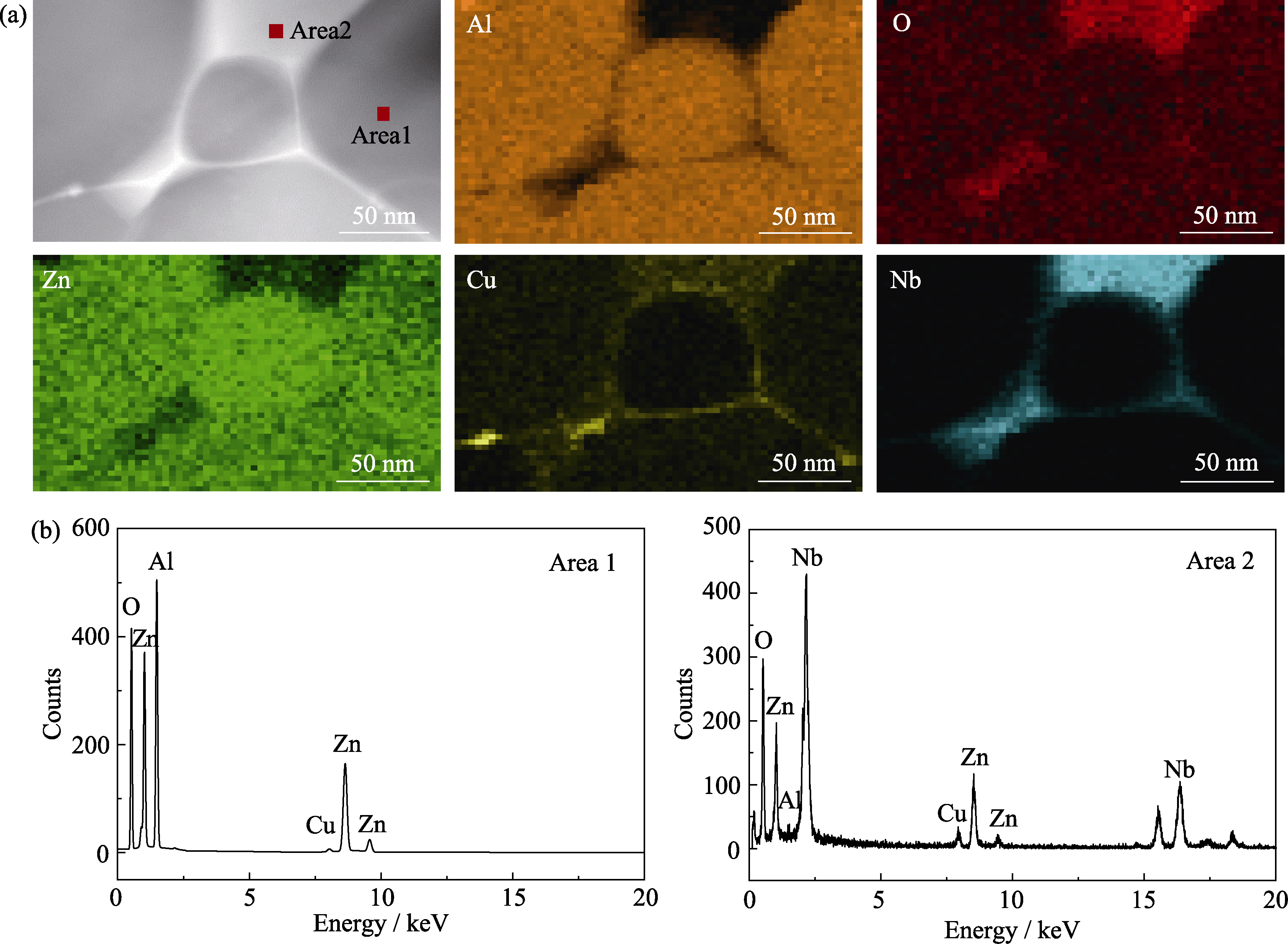
Fig. S4 EDS element mappings of sample S5 sintered at 975 ℃ for 2 h (a) and EDS spectra of the grain phase (Area 1) and the adjacent second phase (Area 2) (b)
| Element | Al (K) | Zn(K) | O (K) | Nb (K) | Cu (K) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atomic/% | Area 1 | 28.63 | 13.50 | 57.47 | 0.00 | 0.38 |
| Area 2 | 1.44 | 4.43 | 88.90 | 4.04 | 1.17 | |
| Uncertainty/% | Area 1 | 0.31 | 0.42 | 0.49 | 100.00 | 0.05 |
| Area 2 | 0.11 | 0.43 | 1.14 | 0.78 | 0.19 | |
Table S2 EDS analysis results for the grain (Area 1) and the adjacent second phase (Area 2)
| Element | Al (K) | Zn(K) | O (K) | Nb (K) | Cu (K) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atomic/% | Area 1 | 28.63 | 13.50 | 57.47 | 0.00 | 0.38 |
| Area 2 | 1.44 | 4.43 | 88.90 | 4.04 | 1.17 | |
| Uncertainty/% | Area 1 | 0.31 | 0.42 | 0.49 | 100.00 | 0.05 |
| Area 2 | 0.11 | 0.43 | 1.14 | 0.78 | 0.19 | |
| [1] | NAGATSUMA T, DUCOURNAU G, RENAUD C C. Advances in terahertz communications accelerated by photonics. Nature Photonics, 2016, 10: 371. |
| [2] | MA M S, WANG Y, NAVARRO-CÍA M, et al. The dielectric properties of some ceramic substrate materials at terahertz frequencies. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39: 4424. |
| [3] | TAJIMA T, SONG H J, YAITA M. Compact THz LTCC receiver module for 300 GHz wireless communications. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 2016, 26: 291. |
| [4] | CHEN X, ZHANG W, BAI S, et al. Densification and characterization of SiO2-B2O3-CaO-MgO glass/Al2O3 composites for LTCC application. Ceramics International, 2013, 39: 6355. |
| [5] | ARCARO S, CESCONETO FR, PEREIRA F R, et al. Synthesis and characterization of LZS/Α-Al2O3 glass-ceramic composites for applications in the LTCC technology. Ceramics International, 2014, 40: 5269. |
| [6] | SEBASTIAN M T, JANTUNEN H. Low loss dielectric materials for LTCC applications: a review. International Materials Reviews, 2008, 53: 57. |
| [7] | ZHOU J. Towards rational design of low-temperature co-fired ceramic (LTCC) materials. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2012, 1: 89. |
| [8] | RABE T, GEMEINERT M, SCHILLER W A. Development of advanced low temperature cofired ceramics (LTCC). Key Engineering Materials, 2004, 264-268: 1181. |
| [9] | SHIGENO K, KATSUMURA H, KAGATA H, et al. Low temperature sintering of alumina by CuO-TiO2-Nb2O5 additives. Key Engineering Materials, 2006, 320: 181. |
| [10] | SHIGENO K, KOJIMA E, FUJIMORI H. Improvement in the low-temperature sintering performance and characteristics of alumina with CuO-TiO2-Nb2O5 additive by controlling the firing atmosphere. Journal of the Japan Society of Powder and Powder Metallurgy, 2016, 63: 701. |
| [11] | YANG Y, MA M S, ZHANG F Q, et al. Low-temperature sintering of Al2O3 ceramics doped with 4CuO-TiO2-2Nb2O5 composite oxide sintering aid. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40: 5504. |
| [12] | LEI W, LU W Z, ZHU J H, et al. Microwave dielectric properties of ZnAl2O4-TiO2 spinel-based composites. Materials Letters, 2007, 61: 4066. |
| [13] | SURENDRAN K P, SANTHA N, MOHANAN P, et al. Temperature stable low loss ceramic dielectrics in (1-x)ZnAl2O4-xTiO2 system for microwave substrate applications. European Physical Journal B, 2004, 41: 301. |
| [14] | QIN T Y, ZHONG C W, QIN Y, et al. Low-temperature sintering mechanism and microwave dielectric properties of ZnAl2O4-LMZBS composites. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 797: 744. |
| [15] | ROSHNI S B, SEBASTIAN M T, SURENDRAN K P. Can zinc aluminate-titania composite be an alternative for alumina as microelectronic substrate? Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 40839. |
| [16] | WU J M, LU W Z, LEI W, et al. Preparation of ZnAl2O4-based microwave dielectric ceramics and GPS antenna by aqueous gel casting. Materials Research Bulletin, 2011, 46: 1485. |
| [17] | THOMAS S, SEBASTIAN M T. Effect of B2O3-Bi2O3-SiO2- ZnO glass on the sintering and microwave dielectric properties of 0.83ZnAl2O4-0.17TiO2. Materials Research Bulletin, 2008, 43: 843. |
| [18] | YANG Y, MA M S, WANG Y Z, et al. Low-temperature sintering of ZnAl2O4 ceramics with 4CuO-TiO2-2Nb2O5 composite oxide sintering aid. Ferroelectrics, 2022, 586: 190. |
| [19] | COURTNEY W E. Analysis and evaluation of a method of measuring the complex permittivity and permeability microwave insulators. IEEE Transaction on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 1970, 18: 476. |
| [20] | HAKKI B W, COLEMAN P D. A dielectric resonator method of measuring inductive capacitance in the millimeter range. IEEE Transaction on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 1960, 8: 402. |
| [21] | DIFEO M, RAMAJO L, CASTRO M. Influence of CuO addition on dielectric and piezoelectric properties of (Bi0.5Na0.5) TiO3- BaTiO3 lead-free piezoceramics. Journal of Advanced Dielectrics, 2021, 11: 2140004. |
| [22] | MCLNTYRE N S, COOK M G. X-ray photoelectron studies on some oxides and hydroxides of cobalt, nickel, and copper. Analytical Chemistry, 1975, 47: 2208. |
| [23] | SUZANA M, FRANCISCO P, MASTERARO V R. Activity and characterization by XPS, HRTEM, Raman spectroscopy, and BET surface area of CuO/CeO2-TiO2 catalysts. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2001, 105: 10515. |
| [24] | SANJINÉS R, TANG H, BERGER H, et al. Electronic structure of anatase TiO2 oxide. Journal of Applied Physiology, 1994, 75: 2945. |
| [25] | MOREAU P, OUVRARD G, GRESSIER P, et al. Electronic structures and charge transfer in lithium and mercury intercalated titanium disulfides. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 1996, 57: 1117. |
| [26] | UEKAWA N, WATANABE M, KANEKO K. Mixed-valence formation in highly oriented Ti-doped iron oxide film. Journal of the Chemical Society, Faraday Transaction, 1995, 91: 2161. |
| [27] | WERFEL F, BRUMMER O. Corundum structure oxides studied by XPS. Physical Scripta, 1983, 28: 92. |
| [28] | LU F H, FANG F X, CHEN Y S. Eutectic reaction between copper oxide and titanium dioxide. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2001, 21: 1093. |
| [29] | YOSHIDA H, YAMAMOTO T. Densification behavior of Ti-doped polycrystalline alumina in a nitrogen-hydrogen atmosphere. Materials Transactions, 2009, 50: 1032. |
| [30] | PULLAR R C, PENN S J, WANG X, et al. Dielectric loss caused by oxygen vacancies in titania ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2009, 29: 419. |
| [31] | POLLAK R A, STOLZ H J, RAIDER S I, et al. Chemical composition and interface chemistry of very thin Nb2O5 films prepared by RF plasma oxidation. Oxidation of Metals, 1983, 20: 185. |
| [32] | OU G, XU YS, WEN B, et al. Tuning defects in oxides at room temperature by lithium reduction. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 1302. |
| [33] | CHEN, X B, LIU L, YU P Y, et al. Increasing solar absorption for photocatalysis with black hydrogenated titanium dioxide nanocrystals. Science, 2011, 331: 746. |
| [34] | HU W B, LIU Y, WITHERS R L, et al. Electron-pinned defect- dipoles for high-performance colossal permittivity materials. Nature Materials, 2013, 12: 821. |
| [35] | THIRUMAL M, MURUGAN G S, VARMA K B R, et al. Ba3ZnTa2-xNbxO9 and Ba3MgTa2-xNbxO9: synthesis, structural and dielectric studies. Materials Research Bulletin, 2000, 35: 2423. |
| [36] | NIE J Y, CHAN J M, QIN M D, et al. Liquid-like grain boundary complexion and sub-eutectic activated sintering in CuO-doped TiO2. Acta Materials, 2017, 130: 329. |
| [37] | KINGERY W D, BOWEN H K, UHLMANN D R. Introduction to Ceramics, 2nd edition. New York: John Wiley and Sons, 1976: 478-482. |
| [38] | GUPTA V K, YOON D H, MEYER H M, et al. Thin intergranular films and solid state activated sintering in nickel- doped tungsten. Acta Materials, 2007, 55: 3131. |
| [39] | LUO J, WANG H, CHIANG Y M. Origin of solid-state activated sintering in Bi2O3-doped ZnO. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1999, 82: 916. |
| [1] | HU Zhichao, YANG Hongyu, YANG Hongcheng, SUN Chengli, YANG Jun, LI Enzhu. Usage of the P-V-L Bond Theory in Regulating Properties of Microwave Dielectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [2] | HE Guoqiang, ZHANG Kaiheng, WANG Zhentao, BAO Jian, XI Zhaochen, FANG Zhen, WANG Changhao, WANG Wei, WANG Xin, JIANG Jiapei, LI Xiangkun, ZHOU Di. Ba(Nd1/2Nb1/2)O3: Au Underrated K40 Microwave Dielectric Ceramic [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 639-646. |
| [3] | TANG Ying, LI Jie, XIANG Huaicheng, FANG Weishuang, LIN Huixing, YANG Junfeng, FANG Liang. Rattling Effect: A New Mechanism Affecting the Resonant Frequency Temperature Coefficient of Microwave Dielectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 656-666. |
| [4] | JIANG Kun, LI Letian, ZHENG Mupeng, HU Yongming, PAN Qinxue, WU Chaofeng, WANG Ke. Research Progress on Low-temperature Sintering of PZT Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| [5] | YIN Changzhi, CHENG Mingfei, LEI Weicheng, CAI Yiyang, SONG Xiaoqiang, FU Ming, LÜ Wenzhong, LEI Wen. Effect of Ga3+ Doping on Crystal Structure Evolution and Microwave Dielectric Properties of SrAl2Si2O8 Ceramic [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 704-710. |
| [6] | JIANG Qiang, SHI Lizhi, CHEN Zhengran, ZHOU Zhiyong, LIANG Ruihong. Preparation and Properties of Hard PZT Piezoelectric Ceramics Poled above Curie Temperature and Multilayer Actuators [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(10): 1091-1099. |
| [7] | KE Xin, XIE Bingqing, WANG Zhong, ZHANG Jingguo, WANG Jianwei, LI Zhanrong, HE Huijun, WANG Limin. Progress of Interconnect Materials in the Third-generation Semiconductor and Their Low-temperature Sintering of Copper Nanoparticles [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(1): 17-31. |
| [8] | LUO Shuwen, MA Mingsheng, LIU Feng, LIU Zhifu. Corrosion Behavior and Mechanism of LTCC Materials in Ca-B-Si System [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 553-560. |
| [9] | LI Hai-Tao, LI Qian, YAN Yan-Fu, XU Rong-Hui. Effect of ZnO-doping on Sinterability and Microwave Dielectric Property of Ca0.25(Li0.43Sm0.57)0.75TiO3 Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(4): 369-373. |
| [10] | FANG Ai-Hua, XIE Xiao-Ming, HUANG Fu-Qiang, JIANG Mian-Heng. High Upper Critical Field of Sm0.85Nd0.15FeAsO0.85F0.15 Superconductors by Mechanical Alloying Synthesis [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(4): 439-444. |
| [11] | LIU Lin, FANG You-Wei, DENG Xin-Feng, ZHUANG Wen-Dong, TANG Bin, ZHANG Shu-Ren. Crystal Structures and Microwave Dielectric Properties of (Ba1-xSrx)La4Ti4O15 (x=0.8-0.95) Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(3): 281-284. |
| [12] | YAO Xiao-Gang, LIN Hui-Xing, JIANG Shao-Hu, CHEN Wei, LUO Lan. Effects of Al2O3-doping on the Microstructure and Dielectric Properties of Ba4Sm9.33Ti18O54 Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(12): 1266-1270. |
| [13] | LIU Hao, SHEN Chun-Ying, LU Zheng-Dong, QIU Tai. Microwave Dielectric Properties of the (1-x)(Mg0.9Co0.1)TiO3-x(Ca0.61La0.26)TiO3 Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2011, 26(6): 664-668. |
| [14] |
LEI Wen,LVWen-Zhong,WANG Xiao-Chuan,LIANG Jun,JIANG Jian-Jun.
Effects of CaTiO3 on Microstructures and Properties of (1-x)ZnAl2O4-xMg2TiO4(x=0.21) Microwave Dielectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2009, 24(5): 957-961. |
| [15] | LI Yue-Ming,SONG Ting-Ting,YOU Yuan,HU Yuan-Yun,LIU Wei-Liang,TANG Chun-Bao. Research on Low-temperature Sintering of Ca0.3(Li1/2Sm1/2)0.7TiO3 Microwave Dielectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2008, 23(6): 1293-1297. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||