
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (2): 125-136.DOI: 10.15541/jim20220338
Special Issue: 【信息功能】纪念殷之文先生诞辰105周年虚拟学术专辑
• REVIEW • Previous Articles Next Articles
FENG Jingjing1( ), ZHANG Youran1,2, MA Mingsheng1, LU Yiqing1, LIU Zhifu1,2(
), ZHANG Youran1,2, MA Mingsheng1, LU Yiqing1, LIU Zhifu1,2( )
)
Received:2022-06-17
Revised:2022-07-29
Published:2023-02-20
Online:2022-09-15
Contact:
LIU Zhifu, professor. E-mail: liuzf@mail.sic.ac.cnAbout author:FENG Jingjing (1989-), female, PhD. E-mail: fengjingjing@mail.sic.ac.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
FENG Jingjing, ZHANG Youran, MA Mingsheng, LU Yiqing, LIU Zhifu. Current Status and Development Trend of Cold Sintering Process[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(2): 125-136.
| Technique | Name (Abbreviation) | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional sintering | Conventional sintering (ConvS) | Thermal sintering at heating rate of 1-10 ℃/min |
| Two step sintering (TSS) | Thermal sintering divided in two steps (heating; cooling and densification) | |
| Fast firing (FF) | Rapid sintering with short soaking times and high heating rates | |
| Sinter forging (SF) | Sintering in presence of uniaxial pressure in die-less configuration | |
| Hot pressing (HP) | Sintering at high temperature and in presence of uniaxial pressure | |
| Hydrothermal hot pressing (HIP) | Sintering at high temperature and in presence of hydrostatic pressure | |
| Liquid phase sintering | Cold sintering process (CSP) | Sintering at T<400 ℃ in presence of solvent and uniaxial pressure |
| Cold hydrostatic consolidation (CHC) | Sintering at room temperature in presence of solvent and hydrostatic pressure | |
| Hydrothermal hot pressing (HHP) | Pressure-assisted sintering in hydrothermal conditions | |
| Hydrothermal reaction sintering (HRS) | Sintering of oxide ceramics in presence of supercritical water | |
| Water vapor-assisted sintering (WVAS) | Conventional sintering in a humid atmosphere | |
| Reactive hydrothermal liquid-phase densification (rHLPD) | Sintering at low temperature assisted by hydrothermal reaction | |
| Flash-like | Flash sintering (FS) | Rapid sintering at low furnace temperature in presence of electric field |
| Thermally insulated flash sintering (TIFS) | Flash sintering where the sample is thermally insulated from the environment | |
| Flash sinterforging (FSF) | Flash sintering in presence of uniaxial pressure in die-less configuration | |
| Sliding electrodes flash sintering (SEFS) | Flash sintering where the electrodes are in relative motion with respect to the sample | |
| Water-assisted flash sintering (WAFS) | Flash sintering in humid atmosphere | |
| Contactless flash sintering (CLFS) | Flash sintering with electrodes in non-contact mode | |
| SPS-like | Spark plasma sintering (SPS) | Sintering in presence of a DC electric potential and uniaxial pressure |
| Deformable punch spark plasma sintering (DPSPS) | Spark plasma sintering at very high pressure (1000-2000 MPa) | |
| Flash spark plasma sintering (FSPS) | Hybrid technique of flash sintering and spark plasma sintering | |
| Cool spark plasma sintering (CSPS) | Spark plasma sintering at T<400 ℃ and high pressure (300-600 MPa) | |
| High pressure spark plasma sintering (HPSPS) | Spark plasma sintering at high pressure (102-103 MPa) | |
| Sacrificial material spark plasma sintering (SMPS) | Spark plasma sintering with a sacrificial die to form samples with complex shapes | |
| Others | Ultrafast high-temperature sintering (UHS) | Rapid sintering at heating rate of 103-104 ℃/min |
| Cold sintering (CS) | Sintering of ductile materials at high pressure and low temperature | |
| Microwave sintering (MWS) | Densification assisted by heating with an electromagnetic radiation | |
| Induction sintering (IS) | Densification assisted by heating with an induction system | |
| Capacitor discharge sintering (CDS) | Rapid sintering with electric energy supplied by capacitor discharge |
Table 1 Definition table of sintering techniques[13-14]
| Technique | Name (Abbreviation) | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional sintering | Conventional sintering (ConvS) | Thermal sintering at heating rate of 1-10 ℃/min |
| Two step sintering (TSS) | Thermal sintering divided in two steps (heating; cooling and densification) | |
| Fast firing (FF) | Rapid sintering with short soaking times and high heating rates | |
| Sinter forging (SF) | Sintering in presence of uniaxial pressure in die-less configuration | |
| Hot pressing (HP) | Sintering at high temperature and in presence of uniaxial pressure | |
| Hydrothermal hot pressing (HIP) | Sintering at high temperature and in presence of hydrostatic pressure | |
| Liquid phase sintering | Cold sintering process (CSP) | Sintering at T<400 ℃ in presence of solvent and uniaxial pressure |
| Cold hydrostatic consolidation (CHC) | Sintering at room temperature in presence of solvent and hydrostatic pressure | |
| Hydrothermal hot pressing (HHP) | Pressure-assisted sintering in hydrothermal conditions | |
| Hydrothermal reaction sintering (HRS) | Sintering of oxide ceramics in presence of supercritical water | |
| Water vapor-assisted sintering (WVAS) | Conventional sintering in a humid atmosphere | |
| Reactive hydrothermal liquid-phase densification (rHLPD) | Sintering at low temperature assisted by hydrothermal reaction | |
| Flash-like | Flash sintering (FS) | Rapid sintering at low furnace temperature in presence of electric field |
| Thermally insulated flash sintering (TIFS) | Flash sintering where the sample is thermally insulated from the environment | |
| Flash sinterforging (FSF) | Flash sintering in presence of uniaxial pressure in die-less configuration | |
| Sliding electrodes flash sintering (SEFS) | Flash sintering where the electrodes are in relative motion with respect to the sample | |
| Water-assisted flash sintering (WAFS) | Flash sintering in humid atmosphere | |
| Contactless flash sintering (CLFS) | Flash sintering with electrodes in non-contact mode | |
| SPS-like | Spark plasma sintering (SPS) | Sintering in presence of a DC electric potential and uniaxial pressure |
| Deformable punch spark plasma sintering (DPSPS) | Spark plasma sintering at very high pressure (1000-2000 MPa) | |
| Flash spark plasma sintering (FSPS) | Hybrid technique of flash sintering and spark plasma sintering | |
| Cool spark plasma sintering (CSPS) | Spark plasma sintering at T<400 ℃ and high pressure (300-600 MPa) | |
| High pressure spark plasma sintering (HPSPS) | Spark plasma sintering at high pressure (102-103 MPa) | |
| Sacrificial material spark plasma sintering (SMPS) | Spark plasma sintering with a sacrificial die to form samples with complex shapes | |
| Others | Ultrafast high-temperature sintering (UHS) | Rapid sintering at heating rate of 103-104 ℃/min |
| Cold sintering (CS) | Sintering of ductile materials at high pressure and low temperature | |
| Microwave sintering (MWS) | Densification assisted by heating with an electromagnetic radiation | |
| Induction sintering (IS) | Densification assisted by heating with an induction system | |
| Capacitor discharge sintering (CDS) | Rapid sintering with electric energy supplied by capacitor discharge |
| Binary compound | Ternary compound | Quaternary compound | Quinary compound |
|---|---|---|---|
| MoO3 | Li2CO3 | LiFePO4 | LiAl0.5Ge1.5(PO4)3 |
| WO3 | CsSO4 | LiCoPO4 | Li0.5xBi1-0.5xMoxV1-xO4 |
| V2O3 | Li2MoO4 | KH2PO4 | (Bi0.95Li0.05)(V0.9Mo0.1)O4 |
| V2O5 | Na2Mo2O7 | Ca5(PO4)3(OH) | Li1.5Al0.5Ge1.5(PO4)3 |
| ZnO | K2Mo2O7 | (LiBi)0.5MoO4 | - |
| Bi2O3 | ZnMoO4 | CsH2PO4 | - |
| Fe2O3 | K2MoO4 | InGaZnO4 | - |
| SiO2 | Bi2Mo2O9 | K0.5Na0.5NbO3 | - |
| CsBr | Gd2(MoO4)3 | LiFePO4 | - |
| MgO | Li2WO4 | Li2Mg3TiO6 | - |
| PbTe | Na2WO4 | Na0.5Bi0.5MoO4 | - |
| Bi2Te3 | LiVO3 | Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3 | - |
| NaCl | BiVO4 | YBa2Cu3O7-x | - |
| ZnTe | AgVO3 | - | - |
| AgI | Na2ZrO3 | - | - |
| CuCl | BaTiO3 | - | - |
| ZrF4 | NaNO2 | - | - |
| ZrO2 | Mg2P2O7 | - | - |
| Al2O3 | BaMoO4 | - | - |
| CeO2 | Cs2WO4 | - | - |
| MnO | NaxCO2O4 | - | - |
| SnO | Ca3Co4O9 | - | - |
| TiO2 | KPO3 | - | - |
| MoS2 | Al2SiO5 | - | - |
| - | Ca3Co4O9 | - | - |
| - | CaCO3 | - | - |
| - | BaFe12O19 | - | - |
| - | ZrW2O8 | - | - |
| - | NaNbO3 | - | - |
| - | SrTiO3 | - | - |
Table 2 Ceramic materials prepared by CSP[29,38,50]
| Binary compound | Ternary compound | Quaternary compound | Quinary compound |
|---|---|---|---|
| MoO3 | Li2CO3 | LiFePO4 | LiAl0.5Ge1.5(PO4)3 |
| WO3 | CsSO4 | LiCoPO4 | Li0.5xBi1-0.5xMoxV1-xO4 |
| V2O3 | Li2MoO4 | KH2PO4 | (Bi0.95Li0.05)(V0.9Mo0.1)O4 |
| V2O5 | Na2Mo2O7 | Ca5(PO4)3(OH) | Li1.5Al0.5Ge1.5(PO4)3 |
| ZnO | K2Mo2O7 | (LiBi)0.5MoO4 | - |
| Bi2O3 | ZnMoO4 | CsH2PO4 | - |
| Fe2O3 | K2MoO4 | InGaZnO4 | - |
| SiO2 | Bi2Mo2O9 | K0.5Na0.5NbO3 | - |
| CsBr | Gd2(MoO4)3 | LiFePO4 | - |
| MgO | Li2WO4 | Li2Mg3TiO6 | - |
| PbTe | Na2WO4 | Na0.5Bi0.5MoO4 | - |
| Bi2Te3 | LiVO3 | Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3 | - |
| NaCl | BiVO4 | YBa2Cu3O7-x | - |
| ZnTe | AgVO3 | - | - |
| AgI | Na2ZrO3 | - | - |
| CuCl | BaTiO3 | - | - |
| ZrF4 | NaNO2 | - | - |
| ZrO2 | Mg2P2O7 | - | - |
| Al2O3 | BaMoO4 | - | - |
| CeO2 | Cs2WO4 | - | - |
| MnO | NaxCO2O4 | - | - |
| SnO | Ca3Co4O9 | - | - |
| TiO2 | KPO3 | - | - |
| MoS2 | Al2SiO5 | - | - |
| - | Ca3Co4O9 | - | - |
| - | CaCO3 | - | - |
| - | BaFe12O19 | - | - |
| - | ZrW2O8 | - | - |
| - | NaNbO3 | - | - |
| - | SrTiO3 | - | - |
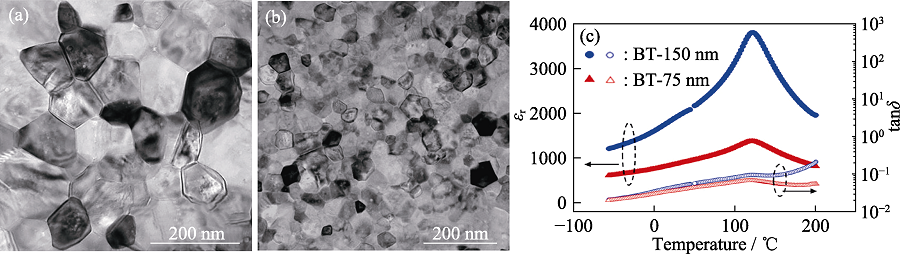
Fig. 5 Cold sintered BaTiO3 ceramics obtained by holding at 300 ℃ for 12 h[56] TEM images with grain size of 150 nm (a) and 75 nm (b); (c) Dielectric temperature spectra at 1 MHz
| Ceramic-polymer composite | Solvent | Processing conditions | Relative density | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li2MoO4-PTFE | Deionized (DI) water | 120 ℃, 350 MPa, 15-20 min | 96%-97% | Dielectrics | [19] |
| Li1.5Al0.5Ge1.5(PO4)3/PVDF-HFP | DI water | 120 ℃, 400 MPa, 60 min | 80%-86% | Li-ion battery electrolytes | [ |
| V2O5-PEDOT:PSS | DI water | 120 ℃, 350 MPa, 20-30 min | 91%-93% | Negative-temperature-resistance sensors | [ |
| (LiBi)0.5MoO4-PTFE | DI water | 120 ℃, 250-350 MPa, 20 min | >85% | Dielectrics | [ |
| Na2Mo2O7-PEI | DI water | 120 ℃, 175-350 MPa, 20 min | >90% | Dielectrics | [ |
| SiO2-PTFE | TEOS/NaOH | 270 ℃, 430 MPa, 60 min | 90%-99% | Dielectrics | [ |
| BaTiO3-PTFE | Ba(OH)2·8H2O | 225 ℃, 350 MPa, 120 min | >90% | Dielectrics | [ |
| ZnO-PTFE | Acetic acid | 300 ℃, 350 MPa, 30 min | 93%-99% | Varistors | [ |
| LiFePO4-C-PVDF | LiOH | 240 ℃, 30-750 MPa, 30 min | 89% | Li-ion electrodes | [ |
| NaNbO3-PVDF | DI water | 180 ℃, 550 MPa, 10 min | 97% | Dielectrics | [ |
| ZnO-PEEK | Acetic acid | 330 ℃, 300 MPa, 120 min | >98% | Varistors | [ |
| ZnO-PDMS | Acetic acid | 250 ℃, 320 MPa, 60 min | >90% | Varistors | [ |
| ZnO/PVDF-TrFE | Acetic acid | 140 ℃, 300 MPa, 240 min | >95% | Varistors | [ |
| ZnO-PEI-Mn2O3-CoO | Acetic acid | 150 ℃, 27 MPa, 60 min | 88% | Varistors | [ |
| LiFePO4-Li6.95Mg0.15La2.75Sr0.25Zr2O12-PPC-LiClO4 | DMF | 100-140℃, 400 MPa, 90-180 min | >85% | Li-ion battery electrolytes | [ |
Table 3 Composites prepared by CSP
| Ceramic-polymer composite | Solvent | Processing conditions | Relative density | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li2MoO4-PTFE | Deionized (DI) water | 120 ℃, 350 MPa, 15-20 min | 96%-97% | Dielectrics | [19] |
| Li1.5Al0.5Ge1.5(PO4)3/PVDF-HFP | DI water | 120 ℃, 400 MPa, 60 min | 80%-86% | Li-ion battery electrolytes | [ |
| V2O5-PEDOT:PSS | DI water | 120 ℃, 350 MPa, 20-30 min | 91%-93% | Negative-temperature-resistance sensors | [ |
| (LiBi)0.5MoO4-PTFE | DI water | 120 ℃, 250-350 MPa, 20 min | >85% | Dielectrics | [ |
| Na2Mo2O7-PEI | DI water | 120 ℃, 175-350 MPa, 20 min | >90% | Dielectrics | [ |
| SiO2-PTFE | TEOS/NaOH | 270 ℃, 430 MPa, 60 min | 90%-99% | Dielectrics | [ |
| BaTiO3-PTFE | Ba(OH)2·8H2O | 225 ℃, 350 MPa, 120 min | >90% | Dielectrics | [ |
| ZnO-PTFE | Acetic acid | 300 ℃, 350 MPa, 30 min | 93%-99% | Varistors | [ |
| LiFePO4-C-PVDF | LiOH | 240 ℃, 30-750 MPa, 30 min | 89% | Li-ion electrodes | [ |
| NaNbO3-PVDF | DI water | 180 ℃, 550 MPa, 10 min | 97% | Dielectrics | [ |
| ZnO-PEEK | Acetic acid | 330 ℃, 300 MPa, 120 min | >98% | Varistors | [ |
| ZnO-PDMS | Acetic acid | 250 ℃, 320 MPa, 60 min | >90% | Varistors | [ |
| ZnO/PVDF-TrFE | Acetic acid | 140 ℃, 300 MPa, 240 min | >95% | Varistors | [ |
| ZnO-PEI-Mn2O3-CoO | Acetic acid | 150 ℃, 27 MPa, 60 min | 88% | Varistors | [ |
| LiFePO4-Li6.95Mg0.15La2.75Sr0.25Zr2O12-PPC-LiClO4 | DMF | 100-140℃, 400 MPa, 90-180 min | >85% | Li-ion battery electrolytes | [ |
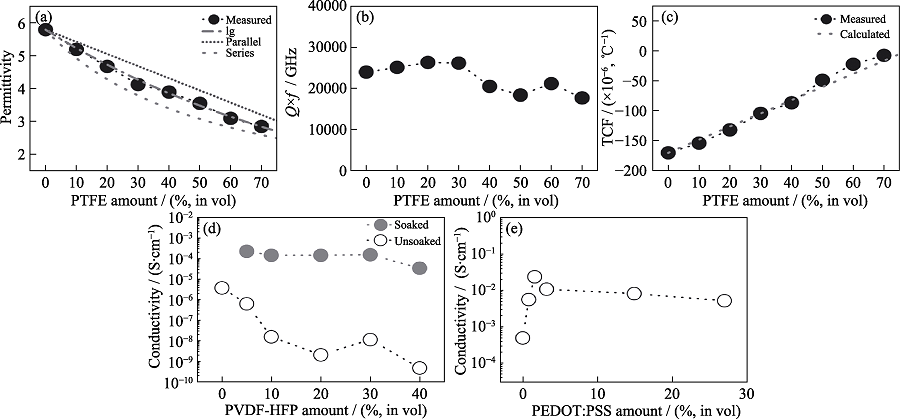
Fig. 8 Electrical properties of three composites prepared by cold sintering process[19] (a-c) εr, Q×f, TCF of (1-x)Li2MoO4-xPTFE; (d) Conductivity of (1-x)LAGP/xPVDF-HFP; (e) Conductivity of (1-x)V2O5-xPEDOT:PSS
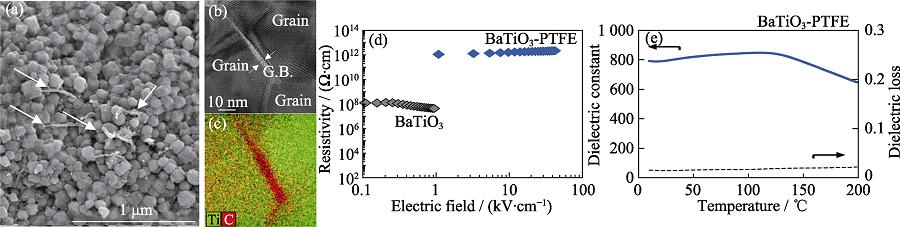
Fig. 10 Cold sintered BaTiO3-PTFE composites[57] (a) SEM image; (b) TEM image; (c) EDS image; (d) Relationship between resistivity and electric field strength comparing with BaTiO3 ceramics; (e) Dielectric temperature spectra
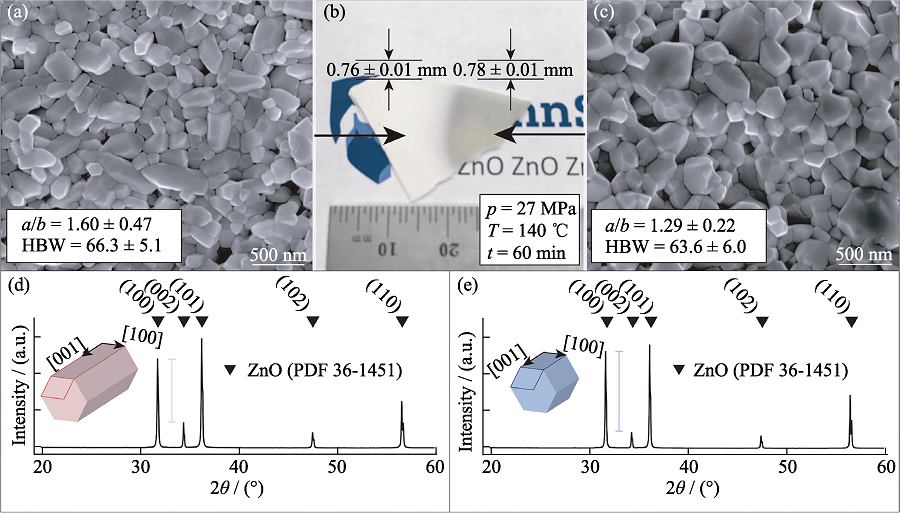
Fig. 12 Obvious inhomogeneity of cold sintered ZnO ceramics[69] (a) SEM image of opaque area; (b) Photograph; (c) SEM image of translucent area; (d) XRD pattern of opaque area; (e) XRD pattern of translucent area
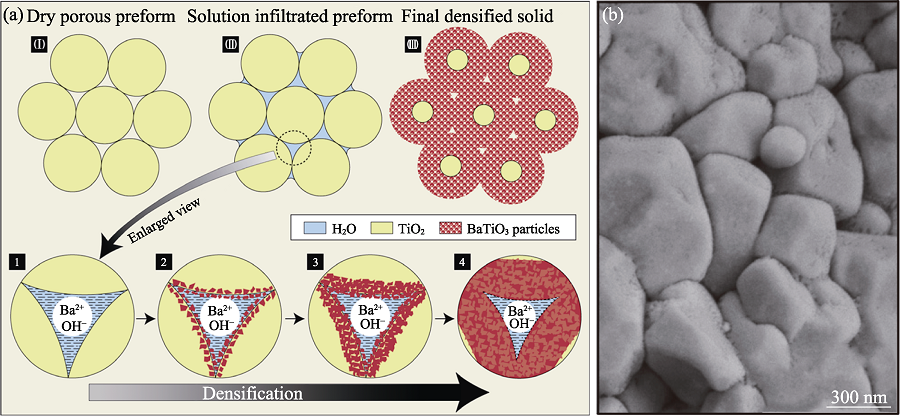
Fig. 13 Reactive hydrothermal liquid phase densification process[72] (a) Schematic of the HLPD process; (b) SEM image of BaTiO3/TiO2 ceramics prepared by rHLPD
| [1] |
VANDIVER P B, SOFFER O, KLIMA B, et al. The origins of ceramic technology at Dolni Věstonice, Czechoslovakia. Science, 1989, 246(4933): 1002.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
GERMAN R M. History of sintering: empirical phase. Powder Metallurgy, 2013, 56(2): 117.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
BORDIA R K, KANG S J L, OLEVSKY E A. Current understanding and future research directions at the onset of the next century of sintering science and technology. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2017, 100(6): 2314.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
NDAYISHIMIYE A, SENGUL M Y, BANG S H, et al. Comparing hydrothermal sintering and cold sintering process: mechanisms, microstructure, kinetics and chemistry. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(4): 1312.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
SMITH B L, SCHÄFFER T E, VIANI M, et al. Molecular mechanistic origin of the toughness of natural adhesives, fibres and composites. Nature, 1999, 399(6738): 761.
DOI URL |
| [6] | RENARD F, BERNARD D, THIBAULT X, et al. Synchrotron 3D microtomography of halite aggregates during experimental pressure solution creep and evolution of the permeability. Geophysical Research Letters, 2004, 31(7): L07607. |
| [7] | FU C L, LI X M, GUO J. Recent progress of dielectric materials prepared via cold sintering process. Journal of Shaanxi Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(4): 30. |
| [8] | JIANG R Z, LIU J. Research progress of cold sintering technology of ceramics. Journal of Guiyang University (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 16(4): 60. |
| [9] |
DURAN C, SATO K, HOTTA Y, et al. Eco-friendly processing and methods for ceramic materials: a review. Journal of the Ceramic Society of Japan, 2008, 116(1359): 1175.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
IBN-MOHAMMED T, RANDALL C A, MUSTAPHA K B, et al. Decarbonising ceramic manufacturing: a techno-economic analysis of energy efficient sintering technologies in the functional materials sector. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(16): 5213.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
TODD R I, ZAPATA-SOLVAS E, BONILLA R S, et al. Electrical characteristics of flash sintering: thermal runaway of Joule heating. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2015, 35(6): 1865.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
ZHANG Y, JUNG J I, LUO J. Thermal runaway, flash sintering and asymmetrical microstructural development of ZnO and ZnO- Bi2O3 under direct currents. Acta Materialia, 2015, 94: 87.
DOI URL |
| [13] | BIESUZ M, GRASSO S, SGLAVO V M. What’s new in ceramics sintering? A short report on the latest trends and future prospects. Current Opinion in Solid State & Materials Science, 2020, 24(5): 100868. |
| [14] |
GUO J, FLOYD R, LOWUM S, et al. Cold sintering: progress, challenges, and future opportunities. Annual Review of Materials Research, 2019, 49(1): 275.
DOI |
| [15] | COLOGNA M, RASHKOVA B, RAJ R. Flash sintering of nanograin zirconia in <5 s at 850 ℃. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2010, 93(11): 35569. |
| [16] |
BIESUZ M, SGLAVO V M. Flash sintering of ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(2): 115.
DOI |
| [17] |
GUO H Z, BAKER A, GUO J, et al. Protocol for ultralow- temperature ceramic sintering: an integration of nanotechnology and the cold sintering process. ACS Nano, 2016, 10(11): 10606.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
GUO H Z, BAKER A, GUO J, et al. Cold sintering process: a novel technique for low-temperature ceramic processing of ferroelectrics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2016, 99(11): 3489.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
GUO J, BERBANO S S, GUO H Z, et al. Cold sintering process of composites: bridging the processing temperature gap of ceramic and polymer materials. Advanced Functional Materials, 2016, 26(39): 7115.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
GUO J, GUO H Z, BAKER A L, et al. Cold sintering: a paradigm shift for processing and integration of ceramics. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2016, 55(38): 11457.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
GUO J, BAKER A L, GUO H Z, et al. Cold sintering process: a new era for ceramic packaging and microwave device development. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2017, 100(2): 669.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
MUNIR Z A, ANSELMI-TAMBURINI U, OHYANAGI M. The effect of electric field and pressure on the synthesis and consolidation of materials: a review of the spark plasma sintering method. Journal of Materials Science, 2006, 41(3): 763.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
GUILLON O, GONZALEZ-JULIAN J, DARGATZ B, et al. Field- assisted sintering technology/spark plasma sintering: mechanisms, materials, and technology developments. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2014, 16(7): 830.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
YANAGISAWA K, KANAHARA S, NISHIOKA M, et al. Immobilization of radioactive wastes in hydrothermal synthetic rock, (II). Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 1984, 21(7): 558.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
YAMASAKI N, YANAGISAWA K, NISHIOKA M, et al. A hydrothermal hot-pressing method: apparatus and application. Journal of Materials Science Letters, 1986, 5(3): 355.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
YAMASAKI N, KAI T, NISHIOKA M, et al. Porous hydroxyapatite ceramics prepared by hydrothermal hot-pressing. Journal of Materials Science Letters, 1990, 9(10): 1150.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
IOKU K, YAMAMOTO K, YANAGISAWA K, et al. Low temperature sintering of hydroxyapatite by hydrothermal hot-pressing. Phosphorus Research Bulletin, 1994, 4: 65.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
HOSOI K, HASHIDA T, TAKAHASHI H, et al. New processing technique for hydroxyapatite ceramics by the hydrothermal hot-pressing method. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1996, 79(10): 2771.
DOI URL |
| [29] | VAKIFAHMETOGLU C, KARACASULU L. Cold sintering of ceramics and glasses: a review. Current Opinion in Solid State & Materials Science, 2020, 24(1): 100807. |
| [30] |
BOUVILLE F, STUDART A R. Geologically-inspired strong bulk ceramics made with water at room temperature. Nature Communications, 2017, 8(1): 14655.
DOI PMID |
| [31] |
INDUJA I J, SEBASTIAN M T. Microwave dielectric properties of mineral sillimanite obtained by conventional and cold sintering process. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2017, 37(5): 2143.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
INDUJA I J, SEBASTIAN M T. Microwave dielectric properties of cold sintered Al2O3-NaCl composite. Materials Letters, 2018, 211: 55.
DOI URL |
| [33] | WANG D, ZHOU D, ZHANG S, et al. Cold-sintered temperature stable Na0.5Bi0.5MoO4-Li2MoO4 microwave composite ceramics. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2018, 6(2): 2438. |
| [34] |
GUO J, ZHAO X T, DE BEAUVOIR T H, et al. Recent progress in applications of the cold sintering process for ceramic-polymer composites. Advanced Functional Materials, 2018, 28(39): 1801724.
DOI URL |
| [35] | GUO H Z, GUO J, BAKER A, et al. Hydrothermal-assisted cold sintering process: a new guidance for low-temperature ceramic sintering. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(32): 20909. |
| [36] |
HUANG H, TANG J, LIU J. Preparation of Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3 ceramics by hydrothermal-assisted cold sintering. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(6): 6753.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
YU T, CHENG J, LI L, et al. Current understanding and applications of the cold sintering process. Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering, 2019, 13(4): 654.
DOI |
| [38] | GALOTTA A, SGLAVO V M. The cold sintering process: a review on processing features, densification mechanisms and perspectives. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(16): 1. |
| [39] |
NDAYISHIMIYE A, SENGUL M Y, SADA T, et al. Roadmap for densification in cold sintering: chemical pathways. Open Ceramics, 2020, 2: 100019.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
HONG W B, LI L, CAO M, et al. Plastic deformation and effects of water in room-temperature cold sintering of NaCl microwave dielectric ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2018, 101(9): 4038.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
HAUG M, BOUVILLE F, RUIZ-AGUDO C, et al. Cold densification and sintering of nanovaterite by pressing with water. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(3): 893.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
GONZALEZ-JULIAN J, NEUHAUS K, BERNEMANN M, et al. Unveiling the mechanisms of cold sintering of ZnO at 250 ℃ by varying applied stress and characterizing grain boundaries by Kelvin Probe Force Microscopy. Acta Materialia, 2018, 144: 116.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
KANG X, FLOYD R, LOWUM S, et al. Cold sintering with dimethyl sulfoxide solutions for metal oxides. Journal of Materials Science, 2019, 54(10): 7438.
DOI |
| [44] |
KANG S, GUO H, WANG J, et al. Influence of surface coating on the microstructures and dielectric properties of BaTiO3 ceramic via a cold sintering process. RSC Advances, 2020, 10: 30870.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
FAOURI S S, MOSTAED A, DEAN J S, et al. High quality factor cold sintered Li2MoO4-BaFe12O19 composites for microwave applications. Acta Materialia, 2019, 166: 202.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
ZHOU D, PANG L X, WANG D W, et al. Novel water-assisting low firing MoO3 microwave dielectric ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(7): 2374.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
LIU Y, SUN Q, WANG D, et al. Development of the cold sintering process and its application in solid-state lithium batteries. Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 393: 193.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
GUO J, GUO H, HEIDARY D S B, et al. Semiconducting properties of cold sintered V2O5 ceramics and Co-sintered V2O5-PEDOT: PSS composites. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2017, 37(4): 1529.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
LIU J A, LI C H, SHAN J J, et al. Preparation of high-density InGaZnO4 target by the assistance of cold sintering. Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing, 2018, 84: 17.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
MARIA J P, KANG X Y, FLOYD R D, et al. Cold sintering: current status and prospects. Journal of Materials Research, 2017, 32(17): 3205.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
KÄHÄRI H, TEIRIKANGAS M, JUUTI J, et al. Dielectric properties of lithium molybdate ceramic fabricated at room temperature. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2014, 97(11): 3378.
DOI URL |
| [52] | WU M W, ZHU H F, WANG J F, et al. Review on cold sintering process for preparation of ceramic materials. China Ceramics, 2021, 57(3): 1. |
| [53] | KANG S L, ZHAO X T, ZHANG J X, et al. Recent research progress of cold sintering process and its potential application in electrotechnical fields. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2022, 37(5): 10984. |
| [54] |
FUNAHASHI S, GUO J, GUO H, et al. Demonstration of the cold sintering process study for the densification and grain growth of ZnO ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2017, 100(2): 546.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
KANG X, FLOYD R, LOWUM S, et al. Mechanism studies of hydrothermal cold sintering of zinc oxide at near room temperature. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2019, 102(8): 4459.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
TSUJI K, NDAYISHIMIYE A, LOWUM S, et al. Single step densification of high permittivity BaTiO3 ceramics at 300 ºC. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(4): 1280.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
SADA T, TSUJI K, NDAYISHIMIYE A, et al. High permittivity BaTiO3 and BaTiO3-polymer nanocomposites enabled by cold sintering with a new transient chemistry: Ba(OH)2·8H2O. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2021, 41(1): 409.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
ZHAO Y Y, BERBANO S S, GAO L S, et al. Cold-sintered V2O5-PEDOT:PSS nanocomposites for negative temperature coefficient materials. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(4): 1257.
DOI URL |
| [59] |
GUO J, PFEIFFENBERGER N, BEESE A, et al. Cold sintering Na2Mo2O7 ceramic with poly(ether imide) (PEI) polymer to realize high-performance composites and integrated multilayer circuits. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2018, 1(8): 3837.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
NDAYISHIMIYE A, TSUJI K, WANG K, et al. Sintering mechanisms and dielectric properties of cold sintered (1-x)SiO2-xPTFE composites. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(15): 4743.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
SADA T, TSUJI K, NDAYISHIMIYE A, et al. Enhanced high permittivity BaTiO3-polymer nanocomposites from the cold sintering process. Journal of Applied Physics, 2020, 128(8): 084103.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
ZHAO X T, GUO J, WANG K, et al. Introducing a ZnO-PTFE (polymer) nanocomposite varistor via the cold sintering process. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2018, 20(7): 1700902.
DOI URL |
| [63] |
SEO J H, GUO J, GUO H Z, et al. Cold sintering of a Li-ion cathode: LiFePO4-composite with high volumetric capacity. Ceramics International, 2017, 43(17): 15370.
DOI URL |
| [64] |
GYAN D S, DWIVEDI A. Structural and electrical characterization of NaNbO3-PVDF nanocomposites fabricated using cold sintering synthesis route. Journal of Applied Physics, 2019, 125(2): 024103.
DOI URL |
| [65] |
SI M M, GUO J, HAO J Y, et al. Cold sintered composites consisting of PEEK and metal oxides with improved electrical properties via the hybrid interfaces. Composites Part B-Engineering, 2021, 226: 109349.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
SI M M, HAO J Y, ZHAO E D, et al. Preparation of zinc oxide/poly-ether-ether-ketone (PEEK) composites via the cold sintering process. Acta Materialia, 2021, 215: 117036.
DOI URL |
| [67] |
NDAYISHIMIYE A, GRADY Z A, TSUJI K, et al. Thermosetting polymers in cold sintering: the fabrication of ZnO-polydimethylsiloxane composites. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2020, 103(5): 3039.
DOI URL |
| [68] |
MENA-GARCIA J, DURSUN S, TSUJI K, et al. Integration and characterization of a ferroelectric polymer PVDF-TrFE into the grain boundary structure of ZnO via cold sintering. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2022, 42(6): 2789.
DOI URL |
| [69] |
BANG S H, TSUJI K, NDAYISHIMIYE A, et al. Toward a size scale-up cold sintering process at reduced uniaxial pressure. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2020, 103(4): 2322.
DOI URL |
| [70] |
SEO J H, NAKAYA H, TAKEUCHI Y, et al. Broad temperature dependence, high conductivity, and structure-property relations of cold sintering of LLZO-based composite electrolytes. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(15): 6241.
DOI URL |
| [71] |
DE BEAUVOIR T H, TSUJI K, ZHAO X, et al. Cold sintering of ZnO-PTFE: utilizing polymer phase to promote ceramic anisotropic grain growth. Acta Materialia, 2020, 186: 511.
DOI URL |
| [72] |
VAKIFAHMETOGLU C, ANGER J F, ATAKAN V, et al. Reactive hydrothermal liquid-phase densification (rHLPD) of ceramics: a study of the BaTiO3[TiO2] composite system. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2016, 99(12): 3893.
DOI URL |
| [73] | LI Q, GUPTA S, TANG L, et al. A novel strategy for carbon capture and sequestration by rHLPD processing. Frontiers in Energy Research, 2016, 3: 53. |
| [1] | ZHU Wenjie, TANG Lu, LU Jichang, LIU Jiangping, LUO Yongming. Research Progress on Catalytic Oxidation of Volatile Organic Compounds by Perovskite Oxides [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [2] | YU Leyangyang, ZHAO Fangxia, ZHANG Shuxin, XU Yixiang, NIU Yaran, ZHANG Zhenzhong, ZHENG Xuebin. Preparation of High-entropy Boride Powders for Plasma Spraying by Inductive Plasma Spheroidization [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 808-816. |
| [3] | WEI Zhifan, CHEN Guoqing, ZU Yufei, LIU Yuan, LI Minghao, FU Xuesong, ZHOU Wenlong. ZrB2-HfSi2 Ceramics: Microstructure and Formation Mechanism of Core-rim Structure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 817-825. |
| [4] | HU Zhichao, YANG Hongyu, YANG Hongcheng, SUN Chengli, YANG Jun, LI Enzhu. Usage of the P-V-L Bond Theory in Regulating Properties of Microwave Dielectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [5] | HE Guoqiang, ZHANG Kaiheng, WANG Zhentao, BAO Jian, XI Zhaochen, FANG Zhen, WANG Changhao, WANG Wei, WANG Xin, JIANG Jiapei, LI Xiangkun, ZHOU Di. Ba(Nd1/2Nb1/2)O3: Au Underrated K40 Microwave Dielectric Ceramic [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 639-646. |
| [6] | ZHANG Jiawei, CHEN Ning, CHENG Yuan, WANG Bo, ZHU Jianguo, JIN Cheng. Electrical Properties of Bismuth Layered Piezoelectric Bi4Ti3O12 Ceramics with A/B-site Doping [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 690-696. |
| [7] | TANG Ying, LI Jie, XIANG Huaicheng, FANG Weishuang, LIN Huixing, YANG Junfeng, FANG Liang. Rattling Effect: A New Mechanism Affecting the Resonant Frequency Temperature Coefficient of Microwave Dielectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 656-666. |
| [8] | WU Qiong, SHEN Binglin, ZHANG Maohua, YAO Fangzhou, XING Zhipeng, WANG Ke. Research Progress on Lead-based Textured Piezoelectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [9] | ZHANG Bihui, LIU Xiaoqiang, CHEN Xiangming. Recent Progress of Hybrid Improper Ferroelectrics with Ruddlesden-Popper Structure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| [10] | WU Jie, YANG Shuai, WANG Mingwen, LI Jinglei, LI Chunchun, LI Fei. Textured PT-based Piezoelectric Ceramics: Development, Status and Challenge [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 575-586. |
| [11] | ZHOU Yangyang, ZHANG Yanyan, YU Ziyi, FU Zhengqian, XU Fangfang, LIANG Ruihong, ZHOU Zhiyong. Enhancement of Piezoelectric Properties in CaBi4Ti4O15-based Ceramics through Bi3+ Self-doping Strategy [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 719-728. |
| [12] | YANG Yan, ZHANG Faqiang, MA Mingsheng, WANG Yongzhe, OUYANG Qi, LIU Zhifu. Low Temperature Sintering of ZnAl2O4 Ceramics with CuO-TiO2-Nb2O5 Composite Oxide Sintering Aid [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 711-718. |
| [13] | HUANG Zipeng, JIA Wenxiao, LI Lingxia. Crystal Structure and Terahertz Dielectric Properties of (Ti0.5W0.5)5+ Doped MgNb2O6 Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 647-655. |
| [14] | JIANG Kun, LI Letian, ZHENG Mupeng, HU Yongming, PAN Qinxue, WU Chaofeng, WANG Ke. Research Progress on Low-temperature Sintering of PZT Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| [15] | YIN Changzhi, CHENG Mingfei, LEI Weicheng, CAI Yiyang, SONG Xiaoqiang, FU Ming, LÜ Wenzhong, LEI Wen. Effect of Ga3+ Doping on Crystal Structure Evolution and Microwave Dielectric Properties of SrAl2Si2O8 Ceramic [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 704-710. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||