无机材料学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (1): 55-62.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250137 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20250137
葛烨明1( ), 汤哲1, 刘苗1, 娄四泽1, 刘振国2, 周岩3, 万舜4(
), 汤哲1, 刘苗1, 娄四泽1, 刘振国2, 周岩3, 万舜4( ), 宗鹏安1(
), 宗鹏安1( )
)
收稿日期:2025-04-01
修回日期:2025-06-05
出版日期:2026-01-20
网络出版日期:2025-06-27
通讯作者:
宗鹏安, 副教授. E-mail: pazong@njtech.edu.cn;作者简介:葛烨明(2000-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: 202261103011@njtech.edu.cn
基金资助:
GE Yeming1( ), TANG Zhe1, LIU Miao1, LOU Size1, LIU Zhenguo2, ZHOU Yan3, WAN Shun4(
), TANG Zhe1, LIU Miao1, LOU Size1, LIU Zhenguo2, ZHOU Yan3, WAN Shun4( ), ZONG Peng'an1(
), ZONG Peng'an1( )
)
Received:2025-04-01
Revised:2025-06-05
Published:2026-01-20
Online:2025-06-27
Contact:
ZONG Peng'an, associate professor. E-mail: pazong@njtech.edu.cn;About author:GE Yeming (2000-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: 202261103011@njtech.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
CoSb3基方钴矿材料因其生态友好性、热稳定性及优异的热电性能, 被广泛应用于热电器件。相比于n型方钴矿热电薄膜, 目前对于高热电性能的p型填充方钴矿柔性热电薄膜的研究尚不充分, 尤其是在柔性器件方面。本研究基于磁控溅射技术在玻璃基底上制备了p型Ce0.9Fe3CoSb12薄膜, 研究了不同溅射功率对薄膜成分、微观结构及热电性能的影响。研究结果表明, 随着溅射功率(100~120 W)的增加, Ce/Fe元素含量比逐渐下降, 空穴浓度随之提升, 导致薄膜电导率σ上升, 泽贝克系数S下降。其中110 W溅射功率制备的薄膜表现出最优的热电性能, 其室温功率因子(PF)达到76.7 μW∙m-1∙K-2, 随着温度的升高, 在500 K下其PF提升到103.5 μW∙m-1∙K-2。基于此, 本研究进一步利用柔性聚酰亚胺(PI)作为基底, 溅射时采用基板加热增强薄膜与基底之间的界面结合, 制备了柔性p型方钴矿薄膜, 并集成了薄膜热电发电器, 探究了其在温度传感器领域的应用。测试表明, 该器件在温度传感等领域具有良好的应用前景。
中图分类号:
葛烨明, 汤哲, 刘苗, 娄四泽, 刘振国, 周岩, 万舜, 宗鹏安. Ce0.9Fe3CoSb12薄膜的磁控溅射制备及其热电与传感性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2026, 41(1): 55-62.
GE Yeming, TANG Zhe, LIU Miao, LOU Size, LIU Zhenguo, ZHOU Yan, WAN Shun, ZONG Peng'an. Fabrication and Thermoelectric Performance of Ce0.9Fe3CoSb12 Thin Films via Magnetron Sputtering for Flexible Thermoelectric and Sensing Applications[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2026, 41(1): 55-62.
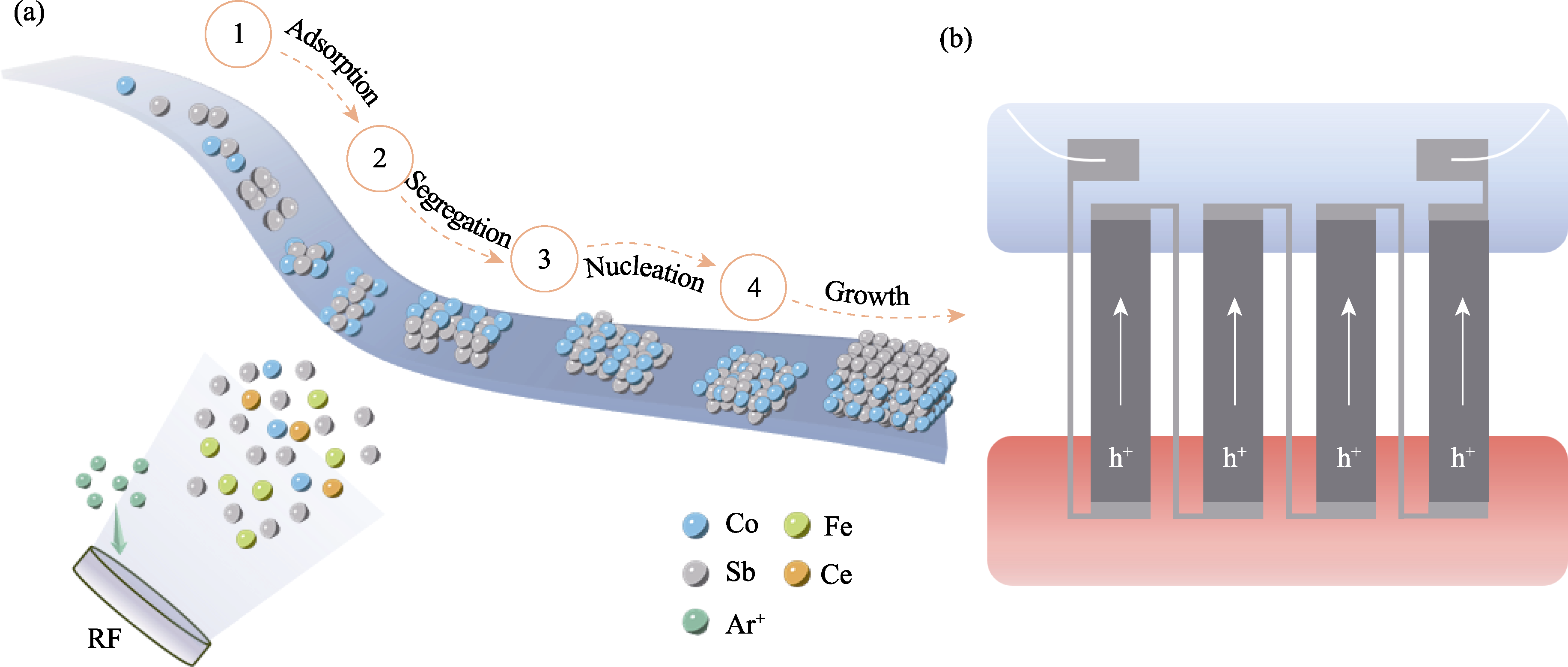
图1 薄膜与热电器件制备示意图
Fig. 1 Diagrams of thin film and thermoelectric device fabrication (a) Schematic diagram of fabrication of Ce0.9Fe3CoSb12 thin film by magnetron sputtering; (b) Schematic diagram of thermoelectric device
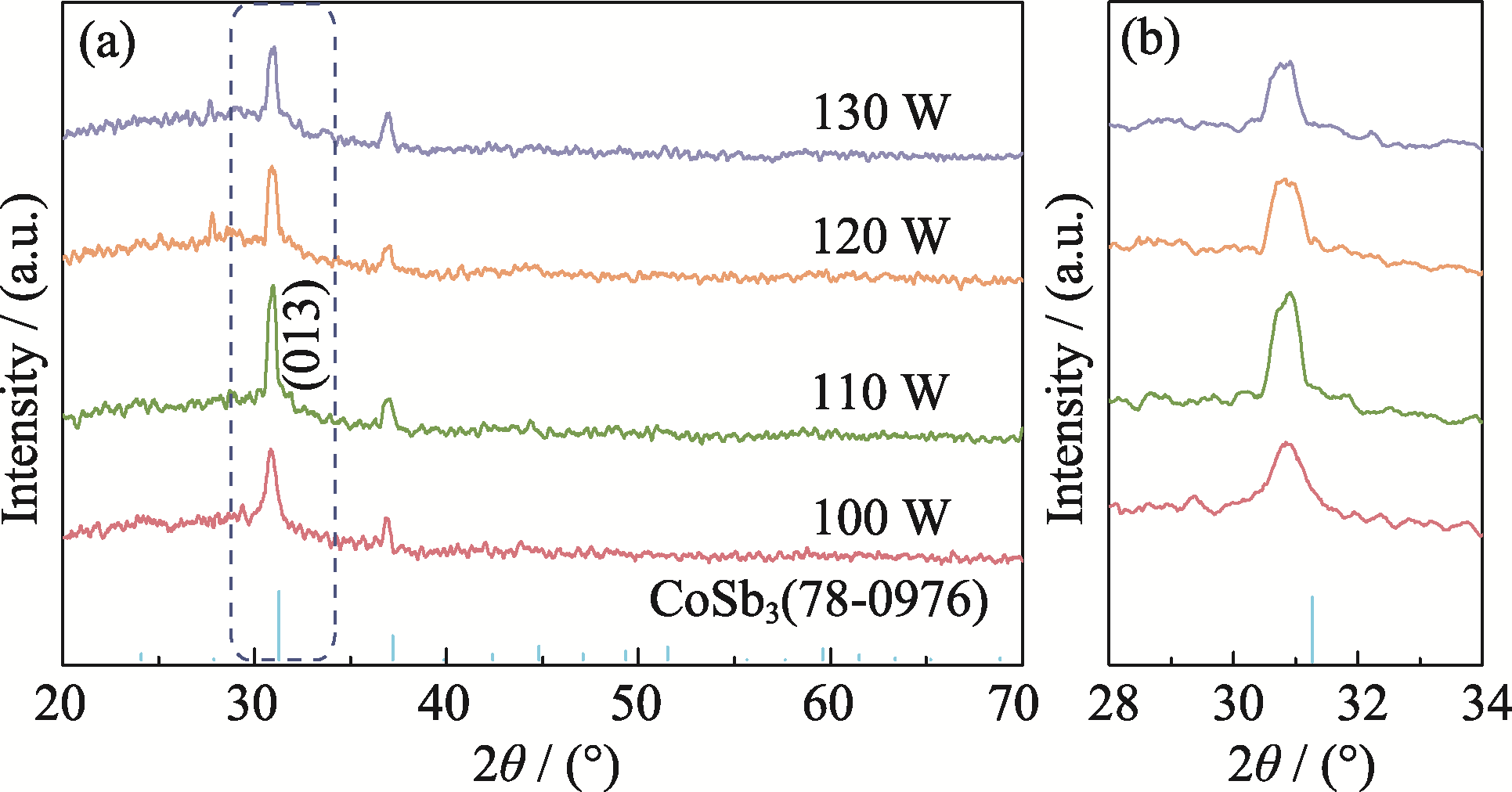
图2 不同溅射功率沉积的Ce0.9Fe3CoSb12薄膜样品的XRD图谱
Fig. 2 XRD patterns of Ce0.9Fe3CoSb12 thin films deposited at different sputtering powers (a) XRD patterns; (b) Localized enlargements of (013) crystal plane diffraction peak
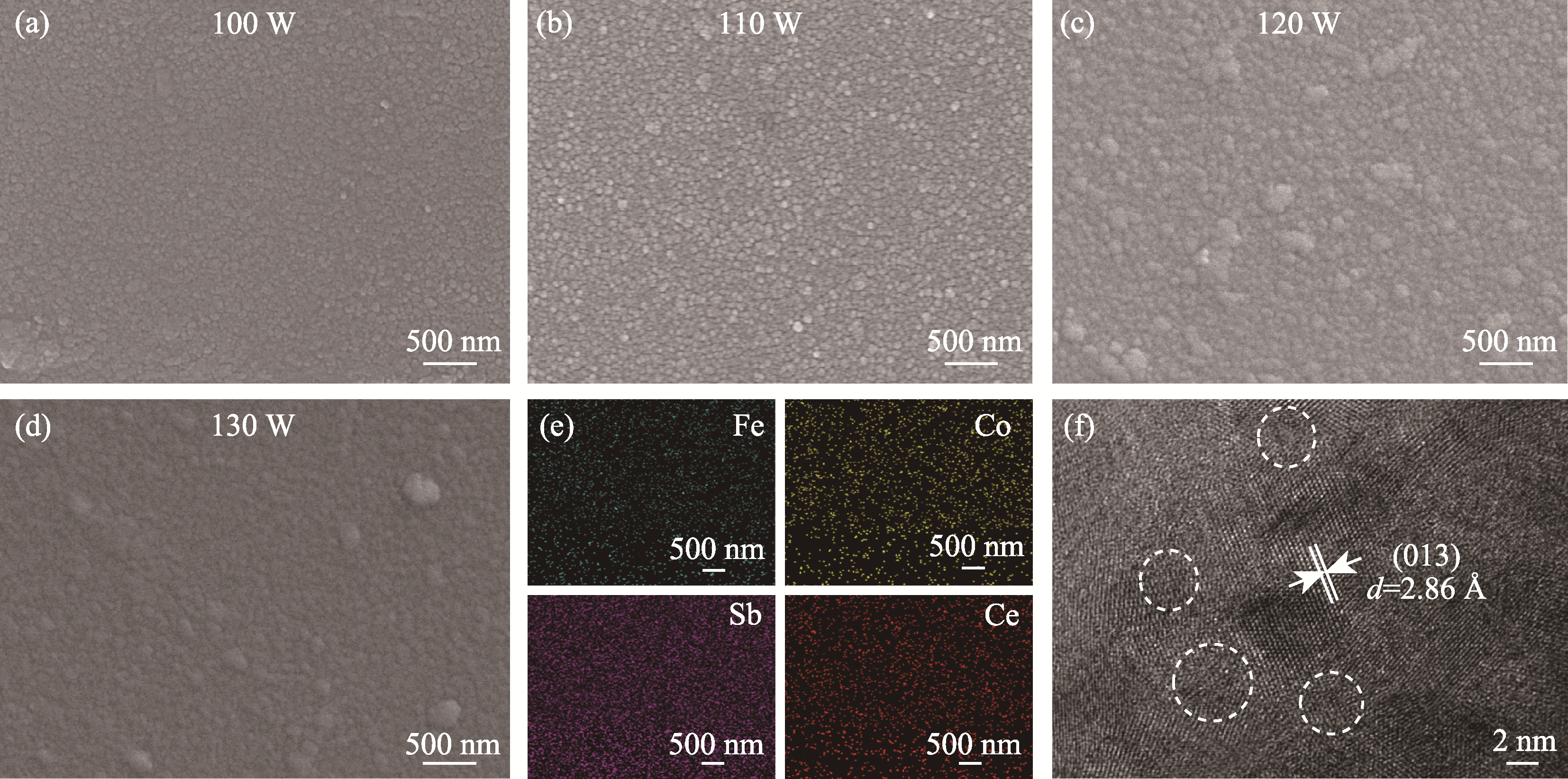
图3 Ce0.9Fe3CoSb12薄膜样品的微观表征
Fig. 3 Microstructure analyses of Ce0.9Fe3CoSb12 thin films (a-d) SEM images of Ce0.9Fe3CoSb12 thin films deposited at different sputtering powers; (e) EDS elemental mappings and (f) HRTEM image of Ce0.9Fe3CoSb12 thin film deposited at 110 W
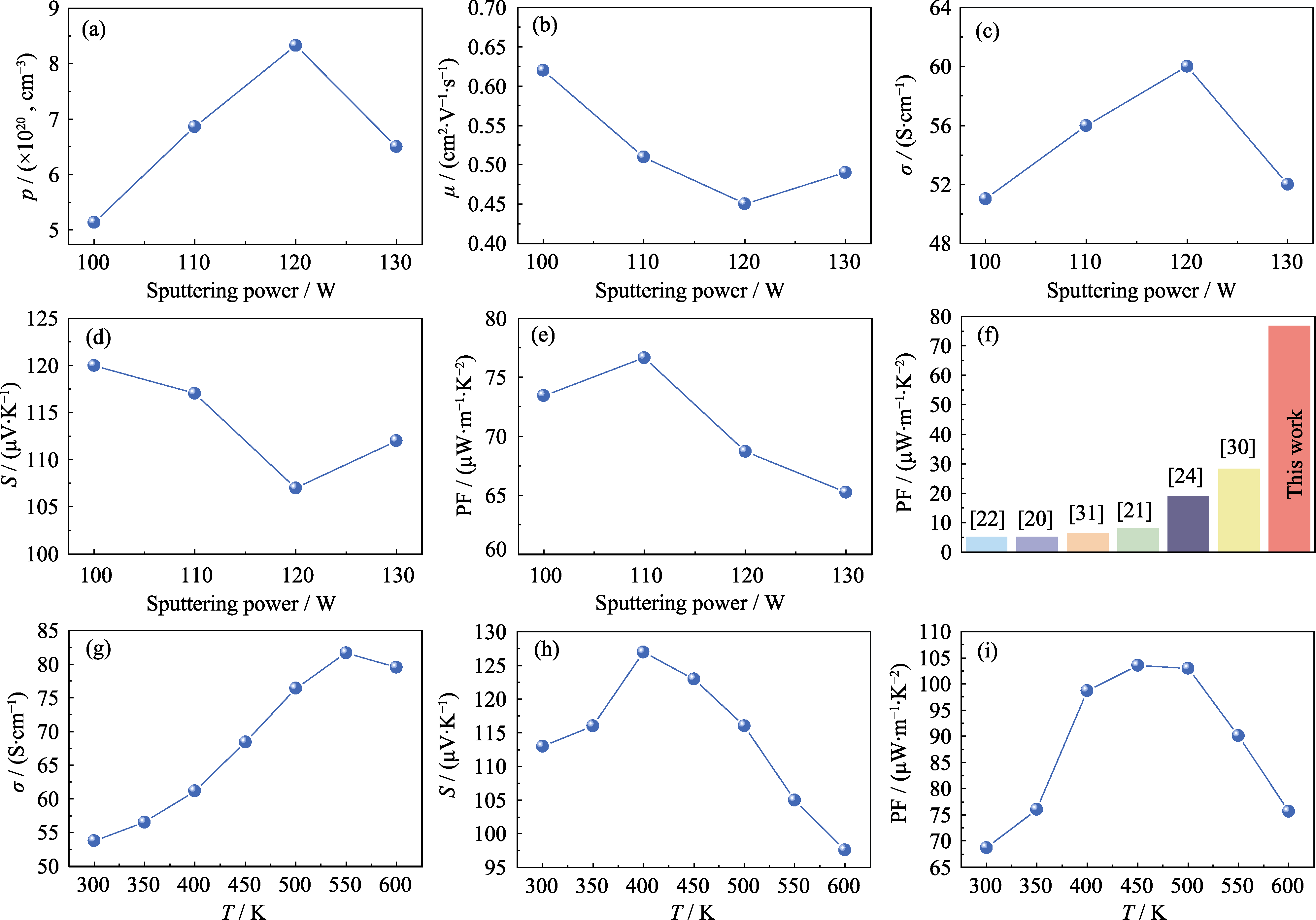
图4 不同溅射功率制备的Ce0.9Fe3CoSb12薄膜的热电性能
Fig. 4 Thermoelectric performance of Ce0.9Fe3CoSb12 thin films prepared at various sputtering powers (a-e) p, μ, σ, S, and PF of Ce0.9Fe3CoSb12 thin films prepared under different sputtering powers; (f) Comparison of PF of CoSb3-based films at room temperature[20-22,24,30 -31]; (g-i) Relationship between σ, S, and PF of the 110 W Ce0.9Fe3CoSb12 sample as a function of temperature
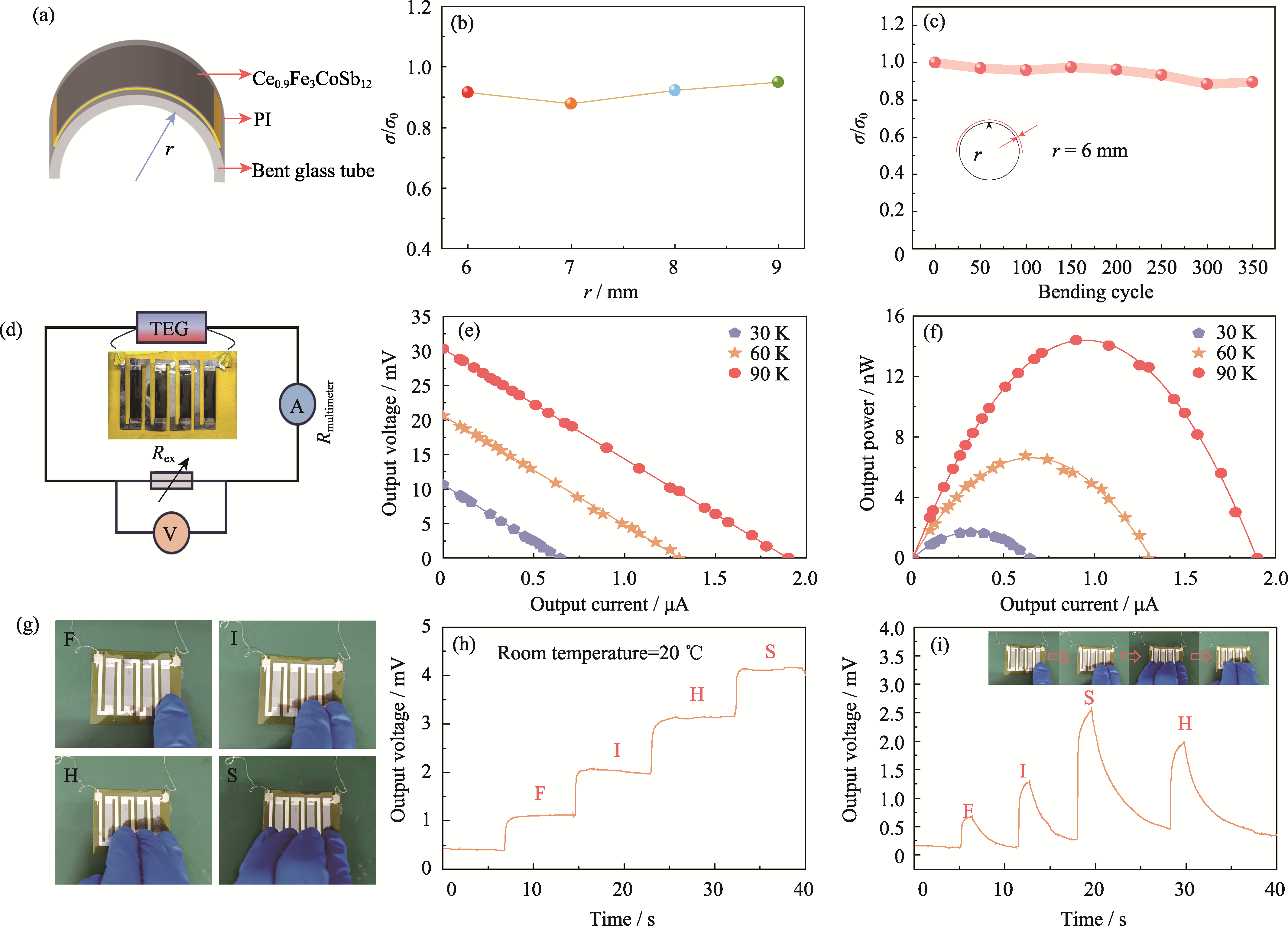
图5 Ce0.9Fe3CoSb12柔性热电器件的柔性、发电性能以及触碰测试
Fig. 5 Characterization of mechanical flexibility, thermoelectric output and touch sensing capability of the Ce0.9Fe3CoSb12 flexible thermoelectric device (a) Schematic diagram of Ce0.9Fe3CoSb12 flexible thin film placed on a bent tube during the bending test; (b) σ/σ0 varied with different curvature radii after 200 bending cycles on tubes; (c) σ/σ0 varied with bending cycles on a tube with a curvature radius of 6 mm; (d) Schematic diagram of the voltage-current circuit for device output performance testing; (e) Relationship between output voltage and output current under different ΔT; (f) Relationship between output power and output current under different ΔT; (g, h) Output voltage corresponding to different numbers of legs touched on the touch sensor; (i) Voltage signals converted into words by touch sensor, using "FISH" as an example
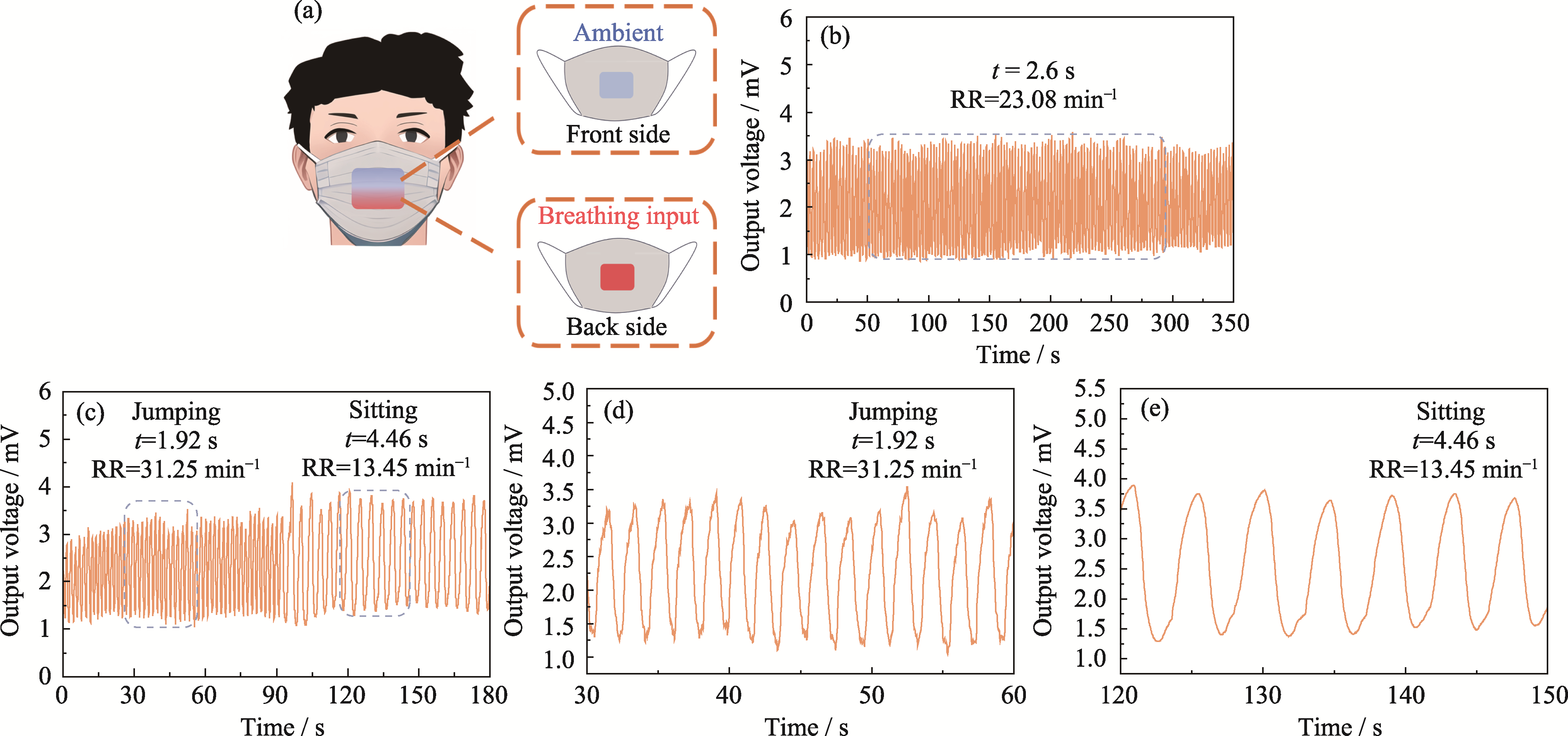
图6 呼吸传感输出测试
Fig. 6 Respiratory sensing output test (a) Integration of the respiratory sensor into a mask, with the backside positioned near the breathing inlet and the front side exposed to the ambient air; (b) Voltage signals detected by the sensor while worn in a resting state; (c-e) Voltage signals recorded during the transition from jumping to sitting while wearing the sensor
| Sputtering power/W | Ce/% | Fe/% | Co/% | Sb/% | Formula |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 7.23 | 8.91 | 3.24 | 80.62 | Ce0.938Fe2.9CoSb12.04 |
| 110 | 6.88 | 9.21 | 3.14 | 80.77 | Ce0.92Fe3.09CoSb12.43 |
| 120 | 6.82 | 9.98 | 3.38 | 79.81 | Ce0.85Fe3.14CoSb11.43 |
| 130 | 6.83 | 9.03 | 3.04 | 81.09 | Ce0.942Fe3.13CoSb12.9 |
表S1 不同溅射功率薄膜的各元素质量分数和以Co摩尔比为基准计算的薄膜化学式
Table S1 Mass fractions of various elements in thin films deposited at different sputtering powers and chemical formulas of films calculated with Co molar ratio as the base
| Sputtering power/W | Ce/% | Fe/% | Co/% | Sb/% | Formula |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 7.23 | 8.91 | 3.24 | 80.62 | Ce0.938Fe2.9CoSb12.04 |
| 110 | 6.88 | 9.21 | 3.14 | 80.77 | Ce0.92Fe3.09CoSb12.43 |
| 120 | 6.82 | 9.98 | 3.38 | 79.81 | Ce0.85Fe3.14CoSb11.43 |
| 130 | 6.83 | 9.03 | 3.04 | 81.09 | Ce0.942Fe3.13CoSb12.9 |
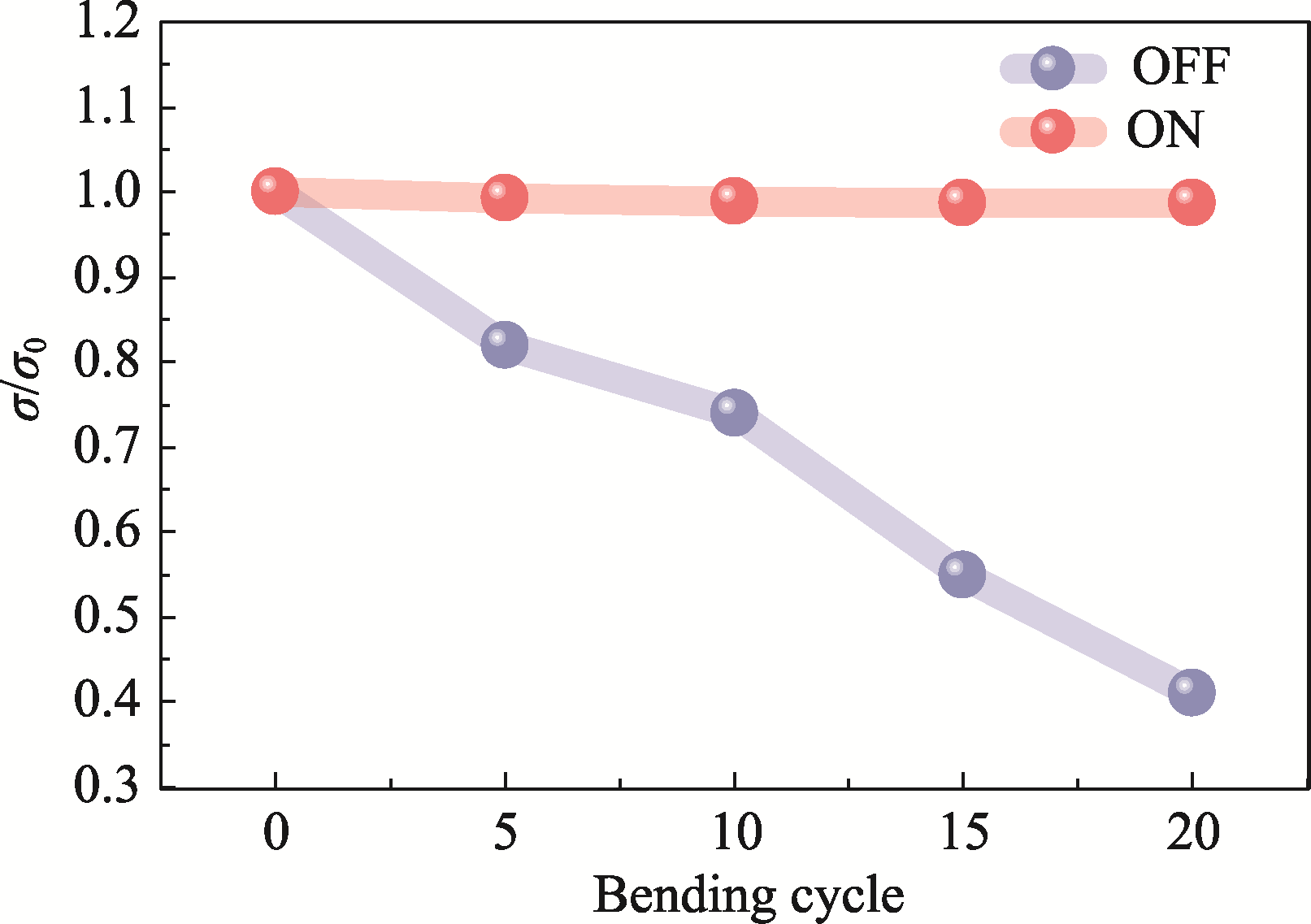
图S1 开启与关闭基板加热的Ce0.9Fe3CoSb12薄膜在多次弯折后的电导率变化
Fig. S1 Changes in conductivities of Ce0.9Fe3CoSb12 thin films on multiple bending cycles with substrate heating on and off
| [1] |
TAN G J, ZHAO L D, KANATZIDIS M G. Rationally designing high-performance bulk thermoelectric materials. Chemical Reviews, 2016, 116(19): 12123.
PMID |
| [2] |
SHI X, CHEN L, UHER C. Recent advances in high-performance bulk thermoelectric materials. International Materials Reviews, 2016, 61(6): 379.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
IBÁÑEZ M, LUO Z S, GENÇ A, et al. High-performance thermoelectric nanocomposites from nanocrystal building blocks. Nature Communications, 2016, 7: 10766.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
LIU B, HU J Z, ZHOU J, et al. Thermoelectric transport in nanocomposites. Materials, 2017, 10(4): 418.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
XIAO Y, ZHAO L D. Seeking new, highly effective thermoelectrics. Science, 2020, 367(6483): 1196.
DOI PMID |
| [6] |
JIANG B B, WANG W, LIU S X, et al. High figure-of-merit and power generation in high-entropy GeTe-based thermoelectrics. Science, 2022, 377(6602): 208.
DOI PMID |
| [7] |
CAO T Y, SHI X L, CHEN Z G. Advances in the design and assembly of flexible thermoelectric device. Progress in Materials Science, 2023, 131: 101003.
DOI URL |
| [8] | GAO M Y, WANG P, JIANG L L, et al. Power generation for wearable systems. Energy & Environmental Science, 2021, 14(4): 2114. |
| [9] | LIANG J S, WANG T, QIU P F, et al. Flexible thermoelectrics: from silver chalcogenides to full-inorganic devices. Energy & Environmental Science, 2019, 12(10): 2983. |
| [10] |
YANG Q Y, YANG S Q, QIU P F, et al. Flexible thermoelectrics based on ductile semiconductors. Science, 2022, 377(6608): 854.
DOI PMID |
| [11] |
WEI T R, JIN M, WANG Y C, et al. Exceptional plasticity in the bulk single-crystalline van der Waals semiconductor InSe. Science, 2020, 369(6503): 542.
DOI URL |
| [12] | NOLAS G S, MORELLI D T, TRITT T M. Skutterudites: a phonon-glass-electron crystal approach to advanced thermoelectric energy conversion applications. Annual Review of Materials Research, 1999, 29: 89. |
| [13] |
LIU Z Y, WANG Y G, YANG T, et al. Alloying engineering for thermoelectric performance enhancement in p-type skutterudites with synergistic carrier concentration optimization and thermal conductivity reduction. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2023, 12(3): 539.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
ROGL G, GRYTSIV A, ROGL P, et al. Nanostructuring of p- and n-type skutterudites reaching figures of merit of approximately 1.3 and 1.6, respectively. Acta Materialia, 2014, 76: 434.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
TANG Y L, GIBBS Z M, AGAPITO L A, et al. Convergence of multi-valley bands as the electronic origin of high thermoelectric performance in CoSb3 skutterudites. Nature Materials, 2015, 14(12): 1223.
DOI |
| [16] |
MENG X F, LIU Z H, CUI B, et al. Grain boundary engineering for achieving high thermoelectric performance in n-type skutterudites. Advanced Energy Materials, 2017, 7(13): 1602582.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
LIU Z Y, ZHU J L, TONG X, et al. A review of CoSb3-based skutterudite thermoelectric materials. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2020, 9(6): 647.
DOI |
| [18] |
ORTIZ B R, CRAWFORD C M, MCKINNEY R W, et al. Thermoelectric properties of bromine filled CoSb3 skutterudite. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2016, 4(21): 8444.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
HERMANN R P, JIN R Y, SCHWEIKA W, et al. Einstein oscillators in thallium filled antimony skutterudites. Physical Review Letters, 2003, 90(13): 135505.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
WEI M, MA H L, NIE M Y, et al. Enhanced thermoelectric performance of CoSb3 thin films by Ag and Ti co-doping. Materials, 2023, 16(3): 1271.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
LI D, SHI X L, ZHU J X, et al. Ce-filled Ni1.5Co2.5Sb12 skutterudite thin films with record-high figure of merit and device performance. Advanced Energy Materials, 2023, 13(37): 2301525.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
ZHENG Z H, SHI X L, AO D W, et al. Rational band engineering and structural manipulations inducing high thermoelectric performance in n-type CoSb3 thin films. Nano Energy, 2021, 81: 105683.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
AMIRGHASEMI F, KASSEGNE S. Effects of RF magnetron sputtering deposition power on crystallinity and thermoelectric properties of antimony telluride and bismuth telluride thin films on flexible substrates. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2021, 50(4): 2190.
DOI |
| [24] |
LI D, SHI X L, ZHU J X, et al. High-performance flexible p-type Ce-filled Fe3CoSb12 skutterudite thin film for medium-to-high- temperature applications. Nature Communications, 2024, 15: 4242.
DOI |
| [25] |
CAO X F, HE M K, MA B P, et al. Enhanced thermoelectric properties of Mm-filled p-type (Fe, Co)Sb3 skutterudites via Co/Fe ratio regulation and extra Sb compensation. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2024, 972: 172815.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
YADAV S, CHAUDHARY S, PANDYA D K. Enhancing thermoelectric properties of p-type CoSb3 skutterudite by Fe doping. Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing, 2021, 127: 105721.
DOI URL |
| [27] | RAUSCHENBACH B. Low-energy ion irradiation of materials. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2022: 123-174. |
| [28] |
JUNLABHUT P, NUTHONGKUM P, HARNWUNGGMOUNG A, et al. Thickness dependence of thermoelectric properties and maximum output power of single planar Sb2Te3 films. Materials, 2022, 15(24): 8850.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
SHI T F, CHEN M R, ZHANG C R, et al. Modifying carbon fiber fabric for flexible thermoelectric energy conversion. Applied Surface Science, 2023, 610: 155479.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
ZHENG Z H, WEI M, LUO J T, et al. An enhanced power factor via multilayer growth of Ag-doped skutterudite CoSb3 thin films. Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers, 2018, 5(6): 1409.
DOI URL |
| [31] | ZHENG Z H, NIU J Y, AO D W, et al. In-situ growth of high-performance (Ag, Sn) Co-doped CoSb3 thermoelectric thin films. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2021, 92: 178. |
| [32] |
LI X G, LIU W D, LI S M, et al. Ce filling limit and its influence on thermoelectric performance of Fe3CoSb12-based skutterudite grown by a temperature gradient zone melting method. Materials, 2021, 14(22): 6810.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
WANG Z W, ZHANG C R, ZHANG J, et al. Construction of an MXene/organic superlattice for flexible thermoelectric energy conversion. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2022, 5(9): 11351.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
ZHU J J, SUN C, FENG W L, et al. Permeable carbon fiber based thermoelectric film with exceptional EMI shielding performance and sensor capabilities. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2024, 13(8): 1119.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
ZHANG C R, ZONG P A, GE Z S, et al. MXene-based wearable thermoelectric respiration sensor. Nano Energy, 2023, 118: 109037.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 胡宇晨, 徐子硕, 胡悦娟, 陈立东, 姚琴. 单壁碳纳米管复合增强二维平面聚酞菁铜的热电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2026, 41(1): 63-69. |
| [2] | 吴华鑫, 张骐昊, YAN Haixue, 王连军, 江莞. 纳米复合MgAgSb基合金的热电输运性能优化[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(9): 997-1004. |
| [3] | 杨光, 张楠, 陈舒锦, 王义, 谢安, 严育杰. 基于多孔ITO电极的WO3薄膜的制备及其电致变色性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 781-789. |
| [4] | 董晨雨, 郑维杰, 马一帆, 郑春艳, 温峥. 压电力显微镜表征Pb(Mg,Nb)O3-PbTiO3超薄膜弛豫特性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 675-682. |
| [5] | 陶桂龙, 支国伟, 罗添友, 欧阳佩东, 衣新燕, 李国强. 空腔型薄膜体声波滤波器的关键技术进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(2): 128-144. |
| [6] | 缪鹏程, 王丽君, 沈紫怡, 黄莉, 袁宁一, 丁建宁. 微球状Ag2Se的溶剂热合成及其热电性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(12): 1373-1378. |
| [7] | 郑元顺, 余健, 叶先峰, 梁栋, 朱婉婷, 聂晓蕾, 魏平, 赵文俞, 张清杰. V取代Al位提升全赫斯勒合金Fe2VAl的热电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(12): 1425-1432. |
| [8] | 吴明轩, 李珺杰, 陈硕, 鄢永高, 苏贤礼, 张清杰, 唐新峰. 区熔n型Bi1.96Sb0.04Te2.70Se0.30热电材料均匀性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(11): 1252-1260. |
| [9] | 葛泽生, 刘苗, 汤哲, 周岩, 万舜, 宗鹏安. 柔性Cu0.005Bi0.5Sb1.495Te3薄膜的磁控溅射制备与热电性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(11): 1237-1244. |
| [10] | 程俊, 张家伟, 仇鹏飞, 陈立东, 史迅. P掺杂β-FeSi2材料的制备与热电输运性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(8): 895-902. |
| [11] | 赵志翰, 郭鹏, 魏菁, 崔丽, 刘山泽, 张文龙, 陈仁德, 汪爱英. Ti-DLC薄膜压阻性能及载流子输运行为研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(8): 879-886. |
| [12] | 苗鑫, 闫世强, 韦金豆, 吴超, 樊文浩, 陈少平. Te基热电器件反常界面层生长行为及界面稳定性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(8): 903-910. |
| [13] | 张慧, 许志鹏, 朱从潭, 郭学益, 杨英. 大面积有机-无机杂化钙钛矿薄膜及其光伏应用研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(5): 457-466. |
| [14] | 陈浩, 樊文浩, 安德成, 陈少平. 能带优化和载流子调控改善SnTe的热电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(3): 306-312. |
| [15] | 鲍可, 李西军. 化学气相沉积法制备智能窗用热致变色VO2薄膜的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(3): 233-258. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||