无机材料学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (8): 895-902.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240012 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20240012
所属专题: 【能源环境】热电材料(202506)
程俊1,2( ), 张家伟1,2(
), 张家伟1,2( ), 仇鹏飞1,2,3, 陈立东1,2, 史迅1,2(
), 仇鹏飞1,2,3, 陈立东1,2, 史迅1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2024-01-08
修回日期:2024-03-04
出版日期:2024-08-20
网络出版日期:2024-03-22
通讯作者:
张家伟, 研究员. E-mail: jiaweizhang@mail.sic.ac.cn;作者简介:程 俊(1997-), 男, 博士研究生. E-mail: chengjun@student.sic.ac.cn
基金资助:
CHENG Jun1,2( ), ZHANG Jiawei1,2(
), ZHANG Jiawei1,2( ), QIU Pengfei1,2,3, CHEN Lidong1,2, SHI Xun1,2(
), QIU Pengfei1,2,3, CHEN Lidong1,2, SHI Xun1,2( )
)
Received:2024-01-08
Revised:2024-03-04
Published:2024-08-20
Online:2024-03-22
Contact:
ZHANG Jiawei, professor. E-mail: jiaweizhang@mail.sic.ac.cn;About author:CHENG Jun (1997-), male, PhD candidate. E-mail: chengjun@student.sic.ac.cn
Supported by:摘要:
β-FeSi2作为一种绿色环保、高温抗氧化的热电材料, 在工业余热回收领域具有潜在的应用价值。虽然磷(P)是一种理想的β-FeSi2硅(Si)位的n型掺杂元素, 但是P掺杂β-FeSi2易出现第二相, 从而限制了其热电性能的提升。本研究采用感应熔炼法合成了一系列FeSi2-xPx (x=0, 0.02, 0.04, 0.06)样品, 极大程度地避免了第二相的产生, 并系统研究了P掺杂对β-FeSi2热电输运性能的影响。结果表明, P在β-FeSi2中的掺杂极限约为0.04, 与前期的理论缺陷计算结果相符。此外, P掺杂优化了β-FeSi2的热电性能, 在850 K时, FeSi1.96P0.04的最高热电优值ZT约为0.12, 远高于已有的研究结果(673 K, 最高ZT仅为0.03)。然而, 与同为n型Co和Ir掺杂的β-FeSi2相比(其载流子浓度可达1022 cm-3), P掺杂β-FeSi2的载流子浓度较低, 最高仅为1020 cm-3, 这导致其电声散射效应较弱, 从而限制了整体热电性能的提升。若能提高其载流子浓度, 则热电性能有望得到进一步提升。
中图分类号:
程俊, 张家伟, 仇鹏飞, 陈立东, 史迅. P掺杂β-FeSi2材料的制备与热电输运性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(8): 895-902.
CHENG Jun, ZHANG Jiawei, QIU Pengfei, CHEN Lidong, SHI Xun. Preparation and Thermoelectric Transport Properties of P-doped β-FeSi2[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(8): 895-902.
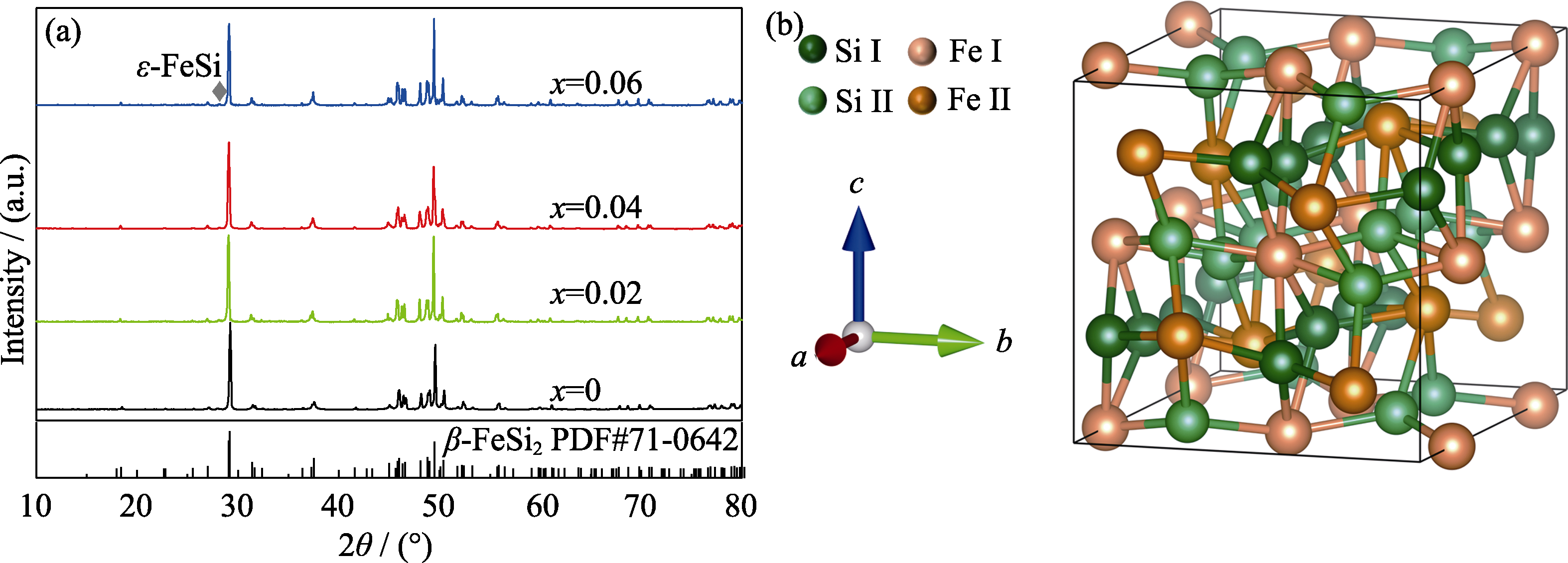
图1 (a) FeSi2-xPx (x=0, 0.02, 0.04, 0.06)的室温XRD图谱和(b) β-FeSi2的晶体结构示意图
Fig. 1 (a) Room-temperature XRD patterns of FeSi2-xPx (x=0, 0.02, 0.04, 0.06) and (b) crystal structure of β-FeSi2

图2 FeSi2-xPx (x=0.02, 0.04, 0.06)的SEM照片和对应的EDS元素分布图
Fig. 2 SEM images of as-synthesized FeSi2-xPx (x=0.02, 0.04, 0.06) and corresponding EDS elemental mappings
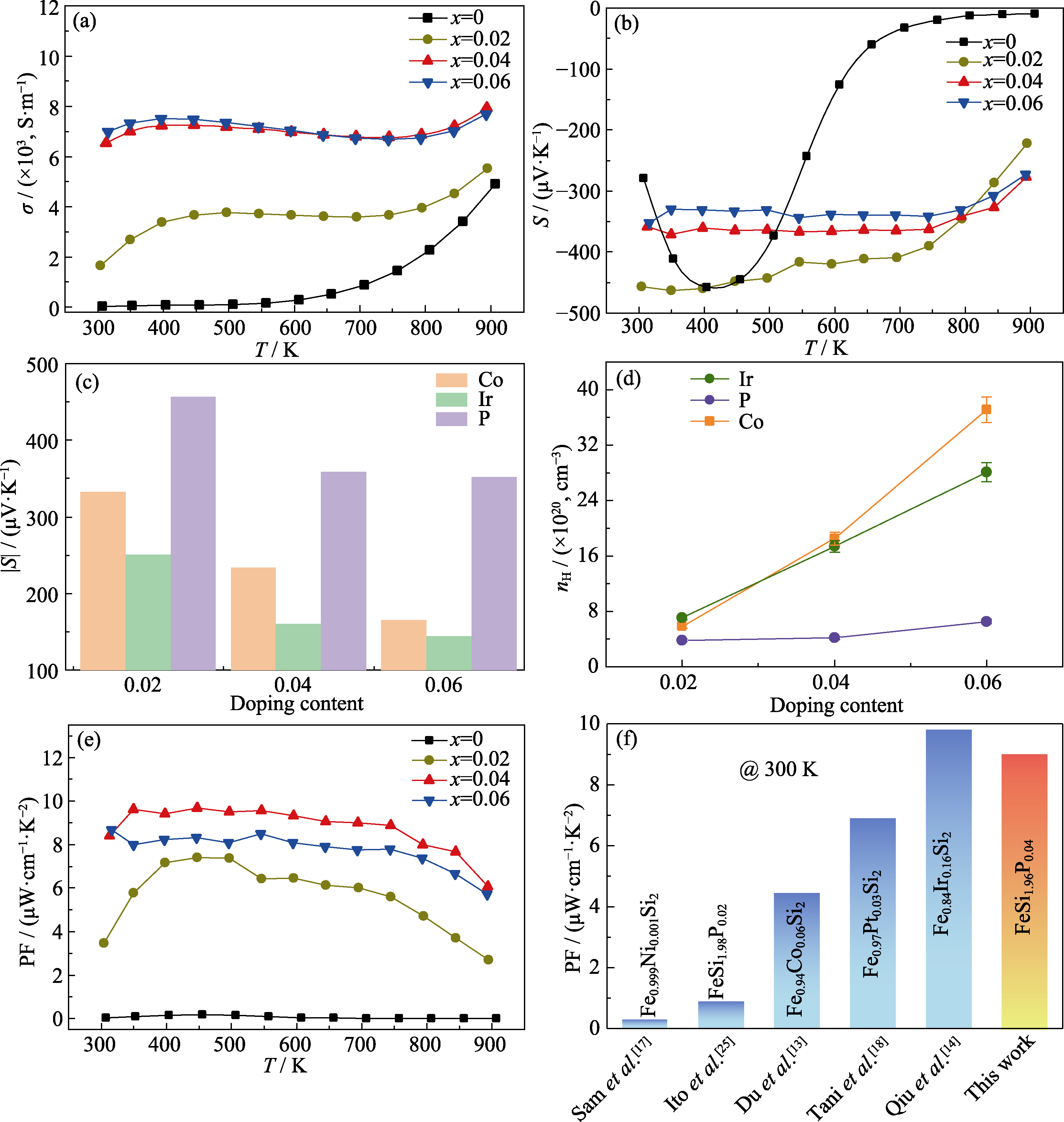
图3 样品的电输运性能
Fig. 3 Electrical transport properties of samples (a, b) Temperature dependences of electrical conductivity σ (a) and Seebeck coefficient S (b) for as-synthesized FeSi2-xPx (x=0, 0.02, 0.04, 0.06); (c, d) Comparison of the absolute values of Seebeck coefficients |S| (c) and carrier concentrations nH (d) for Co-, Ir-, and P-doped β-FeSi2 at 300 K; (e) Temperature dependence of power factor PF for as-synthesized FeSi2-xPx (x=0, 0.02, 0.04, 0.06); (f) Comparison of room-temperature power factor PF for various n-type doped β-FeSi2[13-14,17 -18,25]; Colorful figures are available on website
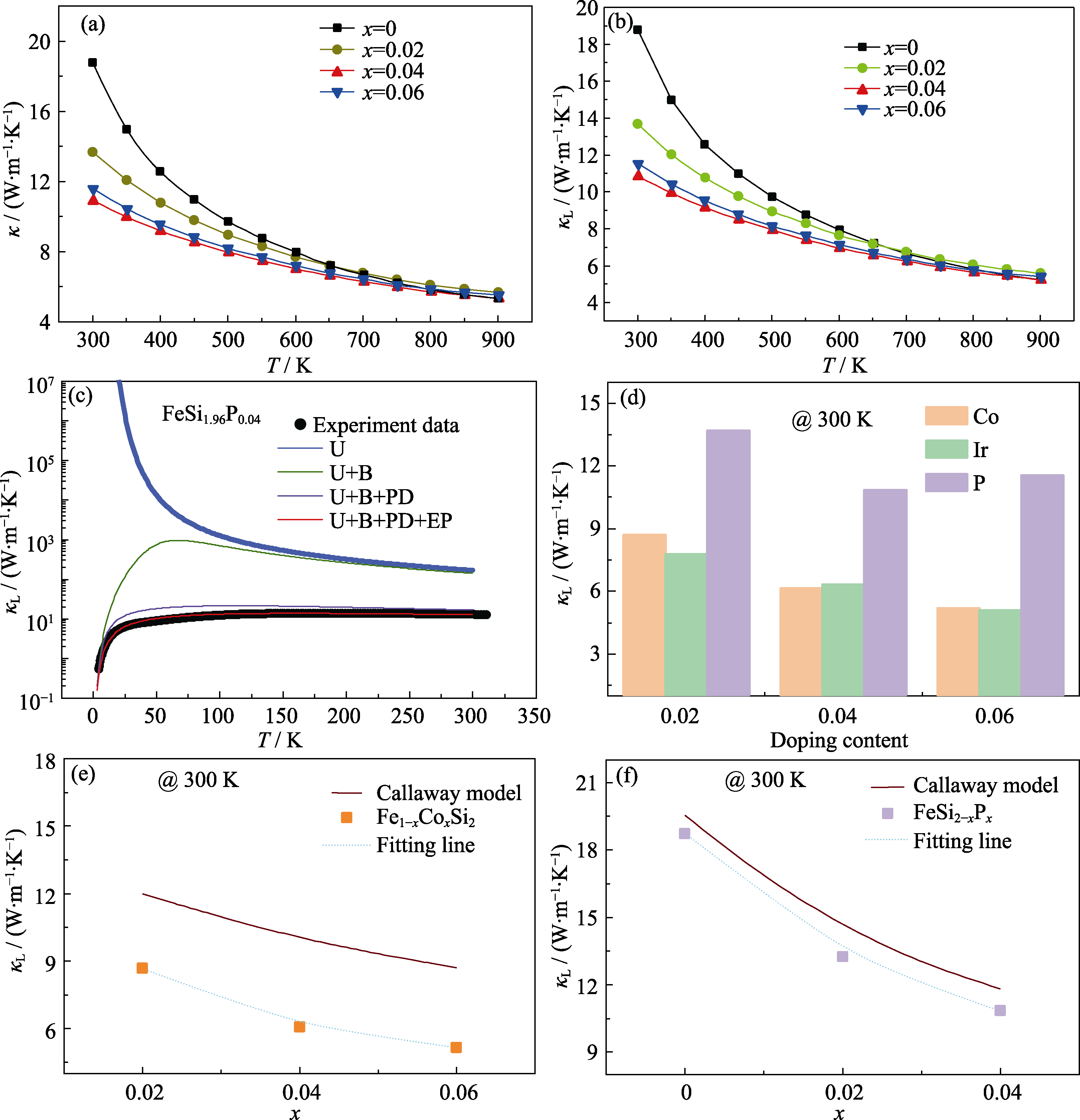
图4 样品的热输运性能
Fig. 4 Thermal transport properties of samples (a, b) Temperature dependences of total thermal conductivity κ (a) and lattice thermal conductivity κL (b) for as-synthesized FeSi2-xPx (x=0, 0.02, 0.04, 0.06); (c) Temperature dependence of the experimental and Debye model calculated lattice thermal conductivity κL for as-synthesized FeSi1.96P0.04 (U: Umklapp process; B: grain-boundary scattering; PD: point-defect scattering; EP: phonon-electron scattering); (d) Comparison of room temperature lattice thermal conductivity κL for Co-, Ir-, and P-doped β-FeSi2 at the same doping content; (e, f) Room-temperature lattice thermal conductivity κL as a function of the doping content of Co-doped β-FeSi2 (e) and P-doped β-FeSi2 (f), in which the solid square symbols represent the experimental data, while the red solid lines denote the Callaway model; Colorful figures are available on website
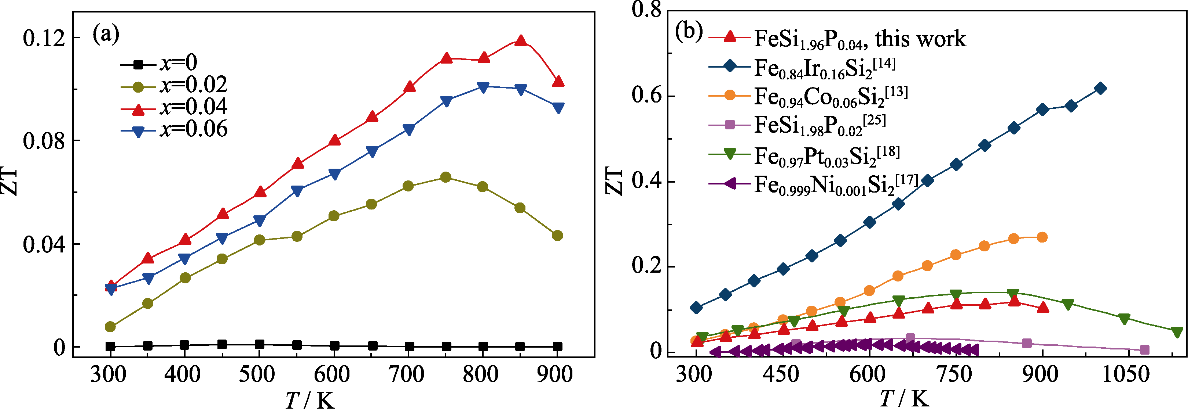
图5 样品的总热电性能
Fig. 5 Overall thermoelectric performance of samples (a) Temperature dependence of ZT for as-synthesized FeSi2-xPx (x=0, 0.02, 0.04, 0.06); (b) Comparison on ZT values of various n-type doped β-FeSi2[13-14,17 -18,25]
| Fitting parameter | FeSi1.96P0.04 |
|---|---|
| L/μm | 3 |
| A/(×10-41, s3) | 0.09 |
| B/(×10-18, s·K-1) | 0.48 |
| C/(×10-15, s-1) | 0.08 |
| R2 | 0.99642 |
| χ2 | 0.06560 |
表S1 FeSi1.96P0.04的晶格热导率拟合参数
Table S1 Parameters used to fit the lattice thermal conductivity κL of FeSi1.96P0.04
| Fitting parameter | FeSi1.96P0.04 |
|---|---|
| L/μm | 3 |
| A/(×10-41, s3) | 0.09 |
| B/(×10-18, s·K-1) | 0.48 |
| C/(×10-15, s-1) | 0.08 |
| R2 | 0.99642 |
| χ2 | 0.06560 |
| [1] | ZHANG Q H, BAI S Q, CHEN L D. Technologies and applications of thermoelectric devices: current status, challenges and prospects. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(3): 279. |
| [2] | SNYDER G J, TOBERER E S. Complex thermoelectric materials. Nature Materials, 2008, 7(2): 105. |
| [3] | WU Z, HU Z. Perspective—powerful micro/nano-scale heat engine: thermoelectric converter on chip. ECS Sensors Plus, 2022, 1(2): 023402. |
| [4] | ZHU T, LIU Y, FU C, et al. Compromise and synergy in high- efficiency thermoelectric materials. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(14): 1605884. |
| [5] | LIU Y, ZAMANIPOUR Z, VASHAEE D. Economical FeSi2-SiGe composites for thermoelectric power generation. 2012 IEEE Green Technologies Conference, Tulsa, 2012. |
| [6] | MAKITA Y, OOTSUKA T, FUKUZAWA Y, et al. β-FeSi2 as a Kankyo (environmentally friendly) semiconductor for solar cells in the space application. SPIE Proceedings: Photonics for Solar Energy Systems, Strasbourg, 2006. |
| [7] | CABALLERO-CALERO O, ARES J R, MARTÍN-GONZÁLEZ M. Environmentally friendly thermoelectric materials: high performance from inorganic components with low toxicity and abundance in the earth. Advanced Sustainable Systems, 2021, 5(11): 2100095. |
| [8] | ITO M, NAGAI H, ODA E, et al. Thermoelectric properties of β-FeSi2 with B4C and BN dispersion by mechanical alloying. Journal of Materials Science, 2002, 37(13): 2609. |
| [9] | LAILA A, NANKO M, TAKEDA M. Upgrade recycling of cast iron scrap chips towards β-FeSi2 thermoelectric materials. Materials, 2014, 7(9): 6304. |
| [10] | DUSAUSOY Y, PROTAS J, WANDJI R, et al. Structure cristalline du disiliciure de fer, FeSi2β. Acta Crystallographica Section B Structural Crystallography and Crystal Chemistry, 1971, 27(6): 1209. |
| [11] | CHAI J, MING C, DU X, et al. Thermodynamics, kinetics and electronic properties of point defects in β-FeSi2. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2019, 21(20): 10497. |
| [12] | DU X, QIU P, CHAI J, et al. Doubled thermoelectric figure of merit in p-type β-FeSi2 via synergistically optimizing electrical and thermal transports. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(11): 12901. |
| [13] | DU X, HU P, MAO T, et al. Ru alloying induced enhanced thermoelectric performance in FeSi2-based compounds. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(35): 32151. |
| [14] | QIU P, CHENG J, CHAI J, et al. Exceptionally heavy doping boosts the performance of iron silicide for refractory thermoelectrics. Advanced Energy Materials, 2022, 12(18): 2200247. |
| [15] | TANI J I, KIDO H. Electrical properties of Co-doped and Ni-doped β-FeSi2. Journal of Applied Physics, 1998, 84(3): 1408. |
| [16] | TANI J I, KIDO H. Thermoelectric properties of β-Fe1-xCoxSi2 semiconductors. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2001, 40(5R): 3236. |
| [17] | SAM S, ODAGAWA S, NAKATSUGAWA H, et al. Effect of Ni substitution on thermoelectric properties of bulk β-Fe1-xNixSi2 (0≤x≤0.03). Materials, 2023, 16(3): 927. |
| [18] | TANI J I, KIDO H. Thermoelectric properties of Pt-doped β-FeSi2. Journal of Applied Physics, 2000, 88(10): 5810. |
| [19] | TANI J I, KIDO H. Thermoelectric properties of Mn-doped β-FeSi2 fabricated by spark plasma sintering. Journal of the Ceramic Society of Japan, 2001, 109(1270): 557. |
| [20] | CHEN H Y, ZHAO X B, LU Y F, et al. Microstructures and thermoelectric properties of Fe0.92Mn0.08Six alloys prepared by rapid solidification and hot pressing. Journal of Applied Physics, 2003, 94(10): 6621. |
| [21] | TANI J I, KIDO H. Electrical properties of Cr-doped β-FeSi2. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 1999, 38(5R): 2717. |
| [22] | KIM S W, CHO M K, MISHIMA Y, et al. High temperature thermoelectric properties of p- and n-type β-FeSi2 with some dopants. Intermetallics, 2003, 11(5): 399. |
| [23] | EHARA T, NAITO S, NAKAGOMI S, et al. Phosphorous doping in beta-irondisilicide by co-sputtering method. Materials Letters, 2002, 56(4): 471. |
| [24] | EHARA T, NAKAGOMI S, KOKUBUN Y. Preparation of phosphorous dope beta-irondisilicide thin films and application for devices. Solid-State Electronics, 2003, 47(2): 353. |
| [25] | ITO M, NAGAI H, ODA E, et al. Effects of P doping on the thermoelectric properties of β-FeSi2. Journal of Applied Physics, 2002, 91(4): 2138. |
| [26] | GOLDBECK O K. Iron-Silicon//IRON-Binary Phase Diagrams. Heidelberg: Springer, 1982: 136. |
| [27] | YANG L, CHEN Z G, DARGUSCH M S, et al. High performance thermoelectric materials: progress and their applications. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(6): 1701797. |
| [28] | KIM H S, GIBBS Z M, TANG Y L, et al. Characterization of Lorenz number with Seebeck coefficient measurement. APL Materials, 2015, 3(4): 041506. |
| [29] | CALLAWAY J. Model for lattice thermal conductivity at low temperatures. Physical Review, 1959, 113(4): 1046. |
| [30] | LIU H, YANG J, SHI X, et al. Reduction of thermal conductivity by low energy multi-Einstein optic modes. Journal of Materiomics, 2016, 2(2): 187. |
| [31] | SHEN J J, FANG T, FU T Z, et al. Lattice thermal conductivity in thermoelectric materials. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(3): 260. |
| [32] | ZHOU Z Z, YAN Y C, YANG X L, et al. Anomalous lattice thermal conductivity driven by all-scale electron-phonon scattering in bulk semiconductors. Physical Review B, 2023, 107(19): 195113. |
| [33] | ZHU T, YU G, XU J, et al. The role of electron-phonon interaction in heavily doped fine-grained bulk silicons as thermoelectric materials. Advanced Electronic Materials, 2016, 2(8): 1600171. |
| [34] | QIN Y T, QIU P F, SHI X, et al. Thermoelectric properties for CuInTe2-xSx (x=0, 0.05, 0.1, 0.15) solid solution. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(11): 1171. |
| [35] | XIE H, SU X, ZHENG G, et al. The role of Zn in chalcopyrite CuFeS2: enhanced thermoelectric properties of Cu1-xZnxFeS2 with in situ nanoprecipitates. Advanced Energy Materials, 2017, 7(3): 1601299. |
| [36] | YANG J, MORELLI D T, MEISNER G P, et al. Influence of electron-phonon interaction on the lattice thermal conductivity of Co1-xNixSb3. Physical Review B, 2002, 65(9): 094115. |
| [37] | NAGAI H, TAKAMATSU T, IIJIMA Y, et al. Effects of Ge substitution on thermoelectric properties of CrSi2. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2016, 55(11): 111801. |
| [38] | ZHOU A J, ZHU T J, ZHAO X B, et al. Improved thermoelectric performance of higher manganese silicides with Ge additions. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2010, 39(9): 2002. |
| [39] | DU R, ZHANG G, HAO M, et al. Enhanced thermoelectric performance of Mg-doped AgSbTe2 by inhibiting the formation of Ag2Te. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2023, 15(7): 9508. |
| [40] | WANG Y, ZHANG X, LIU Y, et al. Optimizing the thermoelectric performance of p-type Mg3Sb2 by Sn doping. Vacuum, 2020, 177: 109388. |
| [41] | LI J C, LI D, QIN X Y, et al. Enhanced thermoelectric performance of p-type SnSe doped with Zn. Scripta Materialia, 2017, 126: 6. |
| [1] | 陈浩, 樊文浩, 安德成, 陈少平. 能带优化和载流子调控改善SnTe的热电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(3): 306-312. |
| [2] | 田震, 蒋全伟, 李建波, 于砺锋, 康慧君, 王同敏. 热变形协同优化BiSbSe1.50Te1.50材料电热输运[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(12): 1316-1324. |
| [3] | 张哲, 孙婷婷, 王连军, 江莞. 不同维度Ag2Se构筑柔性热电薄膜的性能优化与器件集成研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(11): 1221-1227. |
| [4] | 孟雨婷, 王雪梅, 章淑娴, 陈志炜, 裴艳中. Bi2Te3基热电材料的单带和双带传输特性转变[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(11): 1283-1291. |
| [5] | 苏浩健, 周敏, 李来风. 多元素掺杂优化SnTe的热电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(10): 1159-1166. |
| [6] | 肖娅妮, 吕嘉南, 李振明, 刘铭扬, 刘伟, 任志刚, 刘弘景, 杨东旺, 鄢永高. Bi2Te3基热电材料的湿热稳定性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(7): 800-806. |
| [7] | 贺丹琪, 魏明旭, 刘蕤之, 汤志鑫, 翟鹏程, 赵文俞. 一步法制备重费米子YbAl3热电材料及其性能提升[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 577-582. |
| [8] | 李建波, 田震, 蒋全伟, 于砺锋, 康慧君, 曹志强, 王同敏. 不同元素掺杂对CaTiO3微观结构及热电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(12): 1396-1404. |
| [9] | 鲁志强, 刘可可, 李强, 胡芹, 冯利萍, 张清杰, 吴劲松, 苏贤礼, 唐新峰. p型多晶Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3合金类施主效应与热电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(11): 1331-1337. |
| [10] | 王鹏将, 康慧君, 杨雄, 刘颖, 程成, 王同敏. 熵调控抑制ZrNiSn基half-Heusler热电材料的晶格热导率[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 717-723. |
| [11] | 程成, 李建波, 田震, 王鹏将, 康慧君, 王同敏. In2O3/InNbO4复合材料的热电性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 724-730. |
| [12] | 娄许诺, 邓后权, 李爽, 张青堂, 熊文杰, 唐国栋. Ge掺杂MnTe材料的热电输运性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(2): 209-214. |
| [13] | 金敏, 白旭东, 张如林, 周丽娜, 李荣斌. 区熔法制备金属硫化物Ag2S及其热电性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(1): 101-106. |
| [14] | 张岑岑, 王雪, 彭良明. 基于分步式双重调控n型(PbTe)1-x-y(PbS)x(Sb2Se3)y体系的热电传输特性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(9): 936-942. |
| [15] | 杨青雨, 仇鹏飞, 史迅, 陈立东. 熵工程在热电材料中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(4): 347-354. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||