无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (6): 675-682.DOI: 10.15541/jim20240471 CSTR: 32189.14.jim20240471
董晨雨1( ), 郑维杰1, 马一帆2, 郑春艳1, 温峥1,2(
), 郑维杰1, 马一帆2, 郑春艳1, 温峥1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2024-11-09
修回日期:2025-01-19
出版日期:2025-06-20
网络出版日期:2025-01-24
通讯作者:
温 峥, 教授. E-mail: zwen@qdu.edu.cn作者简介:董晨雨(1999-), 女, 硕士研究生. E-mail: 18244065981@163.com
基金资助:
DONG Chenyu1( ), ZHENG Weijie1, MA Yifan2, ZHENG Chunyan1, WEN Zheng1,2(
), ZHENG Weijie1, MA Yifan2, ZHENG Chunyan1, WEN Zheng1,2( )
)
Received:2024-11-09
Revised:2025-01-19
Published:2025-06-20
Online:2025-01-24
Contact:
WEN Zheng, professor. E-mail: zwen@qdu.edu.cnAbout author:DONG Chenyu (1999-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: 18244065981@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
弛豫铁电体因其卓越的介电和压电特性, 在传感器、光电器件、高密度存储器、类脑计算等领域展现出广泛的应用潜力。然而, 纳米尺度超薄膜的弛豫特性研究受到严重漏电流的限制, 基于Sawyer-Tower电路和Positive-Up-Negative-Down(PUND)脉冲波形的测试方法存在显著挑战。本研究提出了一种基于压电力显微镜(Piezoresponse Force Microscopy, PFM)的测试方法, 来研究纳米尺度弛豫薄膜的极化特性。以Pb(Mg,Nb)O3-PbTiO3 (PMN-PT)超薄膜为例, 比较了不同厚度的PMN-PT弛豫薄膜与铁电Pb(Zr,Ti)O3(PZT)薄膜在双频追踪PFM (DART-PFM)测量中On-field和Off-field两种模式下的极化回滞行为。通过调节PFM回线测量中的用于极化读出的交流信号电压振幅, 系统表征了纳米厚度PMN-PT薄膜的弛豫特性。进一步对不同面内应变和厚度的PMN-PT超薄膜进行PFM测试, 发现在较大压缩应变(3.19%)下, 弛豫特性被抑制, 表现出显著的铁电特性, 并观测到铁电-弛豫转变的临界厚度。这些实验结果验证了所提出测试方法的有效性。本研究不仅为超薄膜弛豫特性的探索提供了一种新的表征方法, 也为理解铁电材料的弛豫极化行为奠定了基础, 推动了弛豫铁电材料在低维电子学器件中的应用。
中图分类号:
董晨雨, 郑维杰, 马一帆, 郑春艳, 温峥. 压电力显微镜表征Pb(Mg,Nb)O3-PbTiO3超薄膜弛豫特性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 675-682.
DONG Chenyu, ZHENG Weijie, MA Yifan, ZHENG Chunyan, WEN Zheng. Characterizations by Piezoresponse Force Microscopy on Relaxor Properties of Pb(Mg,Nb)O3-PbTiO3 Ultra-thin Films[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 675-682.
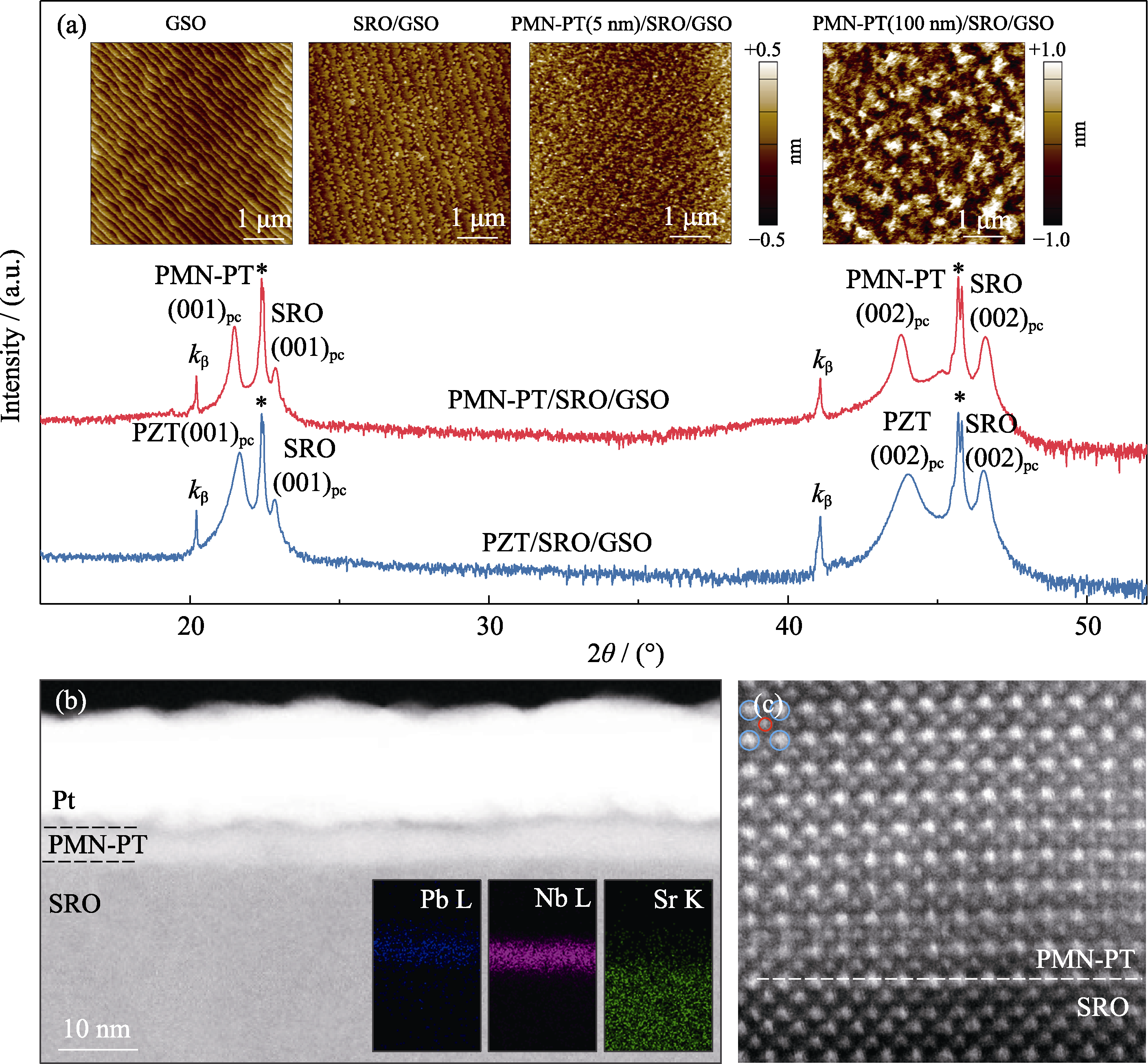
图1 (a) PMN-PT/SRO/GSO和PZT/SRO/GSO的XRD图谱(其中PMN-PT和PZT厚度均为100 nm, *代表GSO的(00l)衍射峰, 插图分别为GSO衬底、SRO/GSO、PMN-PT(5 nm)/SRO/GSO、PMN-PT(100 nm)/SRO/GSO薄膜异质结构的AFM表面形貌); (b) 5 nm厚度PMN-PT/SRO/GSO异质结构的截面STEM照片和元素分布图; (c) PMN-PT层的HAADF照片
Fig. 1 (a) XRD patterns of PMN-PT/SRO/GSO and PZT/SRO/GSO heterostructures, where PMN-PT and PZT are both 100 nm thick, in which the * symbols indicate the (00l) Bragg reflections peaks of GSO, with insets showing the AFM surface morphologies of GSO substrate, SRO/GSO, PMN-PT(5 nm)/SRO/GSO, PMN-PT(100 nm)/SRO/GSO thin-film heterostructures; (b) Cross-sectional STEM image and elemental distributions of the 5 nm thick PMN-PT/SRO/GSO heterostructure; (c) HAADF image of the PMN-PT layer
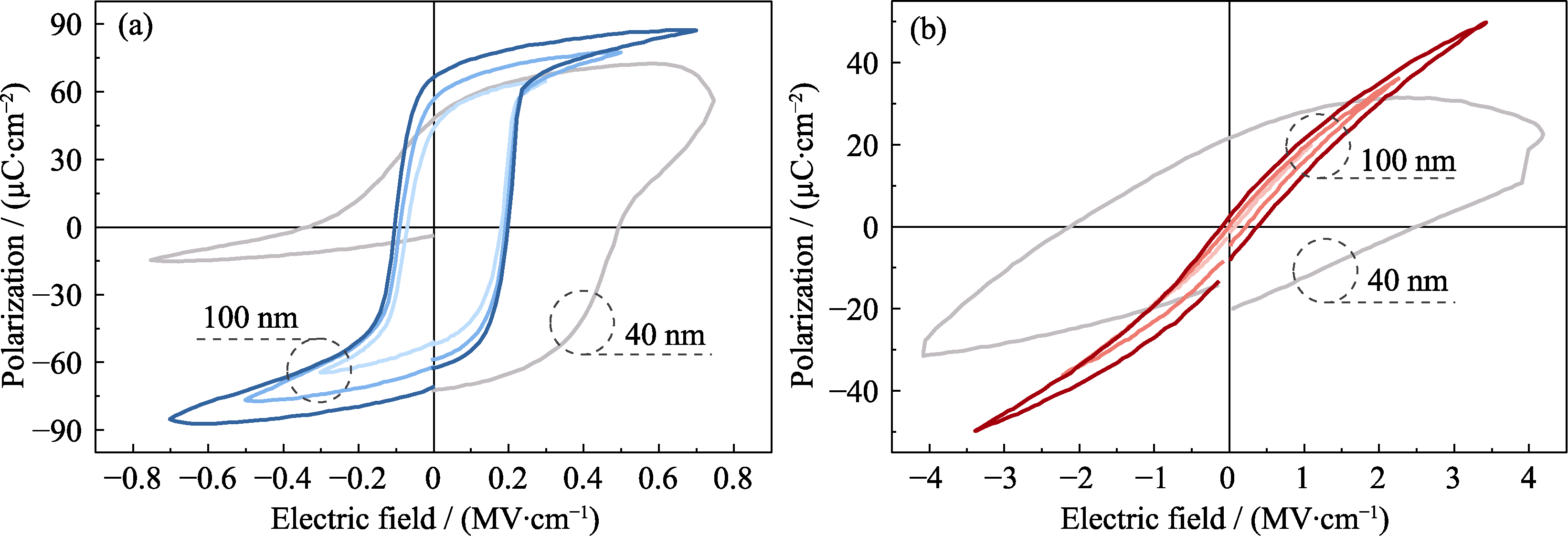
图2 不同厚度PZT (a)和PMN-PT (b)薄膜电容器的电滞回线
Fig. 2 Polarization-electric field hysteresis loops of PZT (a) and PMN-PT (b) thin-film capacitors with different thicknesses
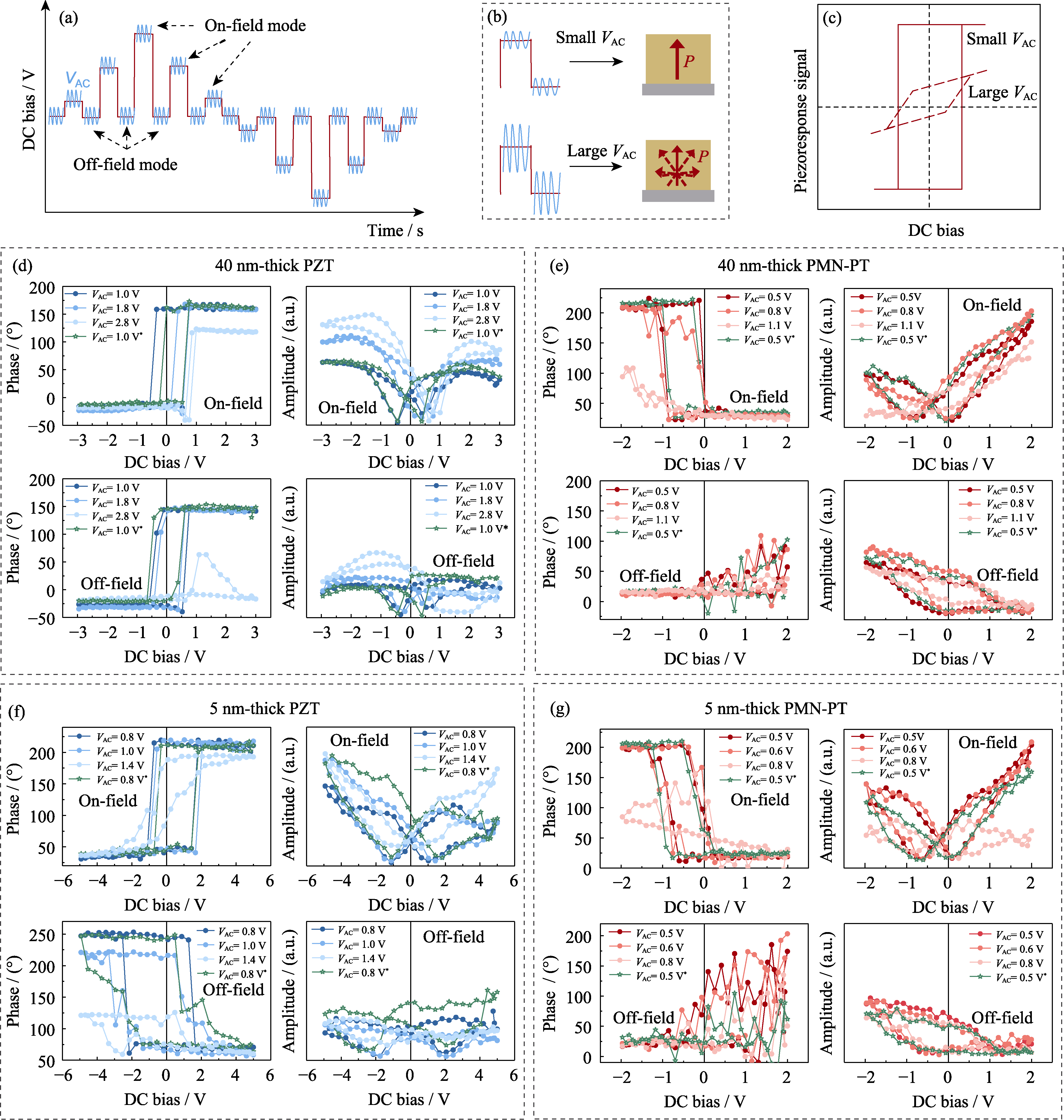
图3 不同厚度PZT、PMN-PT薄膜异质结构的PFM回线表征
Fig. 3 PFM hysteresis characterizations on PZT and PMN-PT thin-film heterostructures with different thicknesses (a) Triangular pulse waveform for PFM test, where the red line represents the DC bias to polarize sample and the blue line represents the AC signal (VAC) used for readout. The polarization is read out in the Off-field mode when the DC bias is zero, and in the On-field mode when the DC bias is non-zero; (b) Sketches of the polarization response of the sample; (c) PFM hysteresis loops with various VAC; (d-g) PFM phases and amplitude hysteresis loops obtained under On-field and Off-field modes with various VAC: 40 nm-thick PZT (d) and PMN-PT (e), 5 nm-thick PZT (f) and PMN-PT (g). Colorful figures are available on website
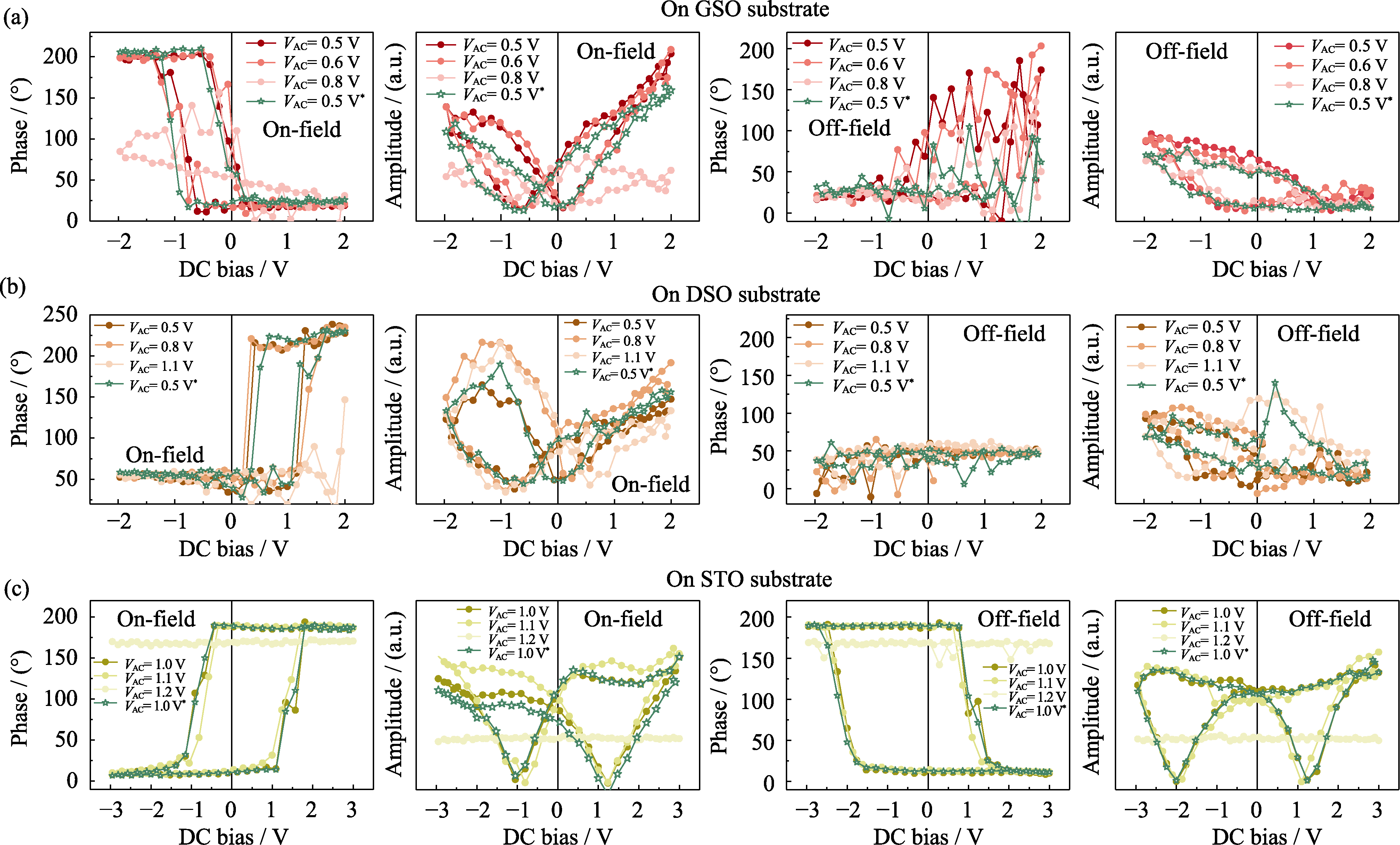
图4 不同衬底上5 nm厚度PMN-PT薄膜异质结构的PFM回线表征
Fig. 4 PFM hysteresis loops of 5 nm-thick PMN-PT films on various substrates (a) PMN-PT/SRO/GSO; (b) PMN-PT/SRO/DSO; (c) PMN-PT/SRO/STO. Colorful figures are available on website
| [1] | LI F, CABRAL M J, XU B, et al. Giant piezoelectricity of Sm-doped Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-PbTiO3 single crystals. Science, 2019, 364(6437): 264. |
| [2] | LI F, ZHANG S, YANG T, et al. The origin of ultrahigh piezoelectricity in relaxor-ferroelectric solid solution crystals. Nature Communications, 2016, 7: 13807. |
| [3] | TYUNINA M, LEVOSKA J, JANOLIN P E, et al. Low- temperature relaxor state induced by epitaxial compression in PbSc0.5Nb0.5O3 films. Physical Review B, 2013, 87(22): 224107. |
| [4] | THAKRE A, KUMAR A, LEE M Y, et al. Artificially induced normal ferroelectric behaviour in aerosol deposited relaxor 65PMN-35PT thick films by interface engineering. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2021, 9(10): 3403. |
| [5] | WANG Y J, LUO C T, WANG S H, et al. Large piezoelectricity in ternary lead-free single crystals. Advanced Electronic Materials, 2020, 6(1): 1900949. |
| [6] | MITTAL S K, JAMWAL U, YADAV D, et al. Enhanced sensitivity in capacitive temperature sensors through synergistic relaxor/ antiferroelectric composites. IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation, 2024, 31(3): 1119. |
| [7] | LU Y H, LIAO W Y, HE X C, et al. Piezoelectricity and up-conversion photoluminescence of Er3+-doped Pb(Zn1/3Nb2/3)O3- PbTiO3 single crystals. Ceramics International, 2024, 50(6): 9762. |
| [8] | NIU J G, JIANG Y X, SHI X H, et al. Domain-modified engineering for low-power resistive switching in ferroelectric diodes. Applied Physics Letters, 2024, 124(4): 043503. |
| [9] | YANG D, MOON Y, HAN N, et al. Solution-processable low-voltage carbon nanotube field-effect transistors with high-k relaxor ferroelectric polymer gate insulator. Nanotechnology, 2024, 35(29): 295202. |
| [10] | PROSANDEEV S, GROLLIER J, TALBAYEV D, et al. Ultrafast neuromorphic dynamics using hidden phases in the prototype of relaxor ferroelectrics. Physical Review Letters, 2021, 126(2): 027602. |
| [11] | NAGARAJAN V, GANPULE C S, NAGARAJ B, et al. Effect of mechanical constraint on the dielectric and piezoelectric behavior of epitaxial Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3(90%)-PbTiO3(10%) relaxor thin films. Applied Physics Letters, 1999, 75(26): 4183. |
| [12] | TRSTENJAK U, DANEU N, RAFALOVSKYI T, et al. Polarization in pseudocubic epitaxial relaxed PMN-PT thin films. Applied Physics Letters, 2022, 120(4): 042901. |
| [13] | WANG F F, WANG H N, YANG Q S, et al. Fine-grained relaxor ferroelectric PMN-PT ceramics prepared using hot-press sintering method. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(11): 15005 |
| [14] | RYAN K, CARL M, MARGEAUX W, et al. Thickness-dependent domain wall reorientation in 70/30 lead magnesium niobate-lead titanate thin films. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2017, 100(9): 3961. |
| [15] | ABEL F, JIEUN K, DEREK M, et al. Finite-size effects in lead scandium tantalate relaxor thin films. Physical Review B, 2020, 101(9): 094102. |
| [16] | KIM J, TAKENAKA H, QI Y, et al. Epitaxial strain control of relaxor ferroelectric phase evolution. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(21): 1901060. |
| [17] | NADAUD K, BORDERON C, RENOUD R, et al. Study of the long time relaxation of the weak ferroelectricity in PbZrO3 antiferroelectric thin film using positive up negative down and first order reversal curves measurements. Thin Solid Films, 2023, 773: 139817. |
| [18] | KANNAN V, KOCHMANN D M. Rate-dependent ferroelectric switching in barium titanate ceramics from modified PUND experiments. Extreme Mechanics Letters, 2022, 57: 101898. |
| [19] | DING Y R, WENG Z P, LAN Z S, et al. Wake-up and imprint effects in hafnium oxide-based ferroelectric capacitors during cycling with different interval times. Electronics, 2024, 13(6): 1021. |
| [20] | SINGH P, JHA R K, SINGH R K, et al. Electrical and ferroelectric properties of RF sputtered PZT/SBN on silicon for non-volatile memory applications. Materials Research Express, 2018, 5(2): 026301. |
| [21] | YU H F, ZENG H R, CHU R Q, et al. Progress in nanoscale piezoresponse force microscopy on ferroelectrics. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2005, 20(2): 257. |
| [22] | DENIS A, VIOLETTA S, ALEXANDER A, et al. Defining ferroelectric characteristics with reversible piezoresponse: PUND switching spectroscopy PFM characterization. Nanotechnology, 2024, 35(17): 175702. |
| [23] | GUAN Z, JIANG Z Z, TIAN B B, et al. Identifying intrinsic ferroelectricity of thin film with piezoresponse force microscopy. AIP Advances, 2017, 7(9): 095116. |
| [24] | ALEXEI G, MARIN A, DENNIS M. Piezoresponse force microscopy and nanoferroic phenomena. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 1661. |
| [25] | STRELCOV E, KIM Y, YANG J C, et al. Role of measurement voltage on hysteresis loop shape in piezoresponse force microscopy. Applied Physics Letters, 2012, 101(19): 192902. |
| [26] | MIAO P X, ZHAO Y G, LUO N N, et al. Ferroelectricity and self-polarization in ultrathin relaxor ferroelectric films. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 19965. |
| [1] | 王晓波, 朱于良, 薛稳超, 史汝川, 骆柏锋, 罗骋韬. PT含量变化对PMN-PT单晶的大功率性能影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 840-846. |
| [2] | 刘 颖, 龙西法. 新型铁电晶体铌镥酸铅-钛酸铅的生长与性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(1): 47-51. |
| [3] | 朱 哲, 郑学军, 张丹书. 外场下NBT-KBT100x压电薄膜畴变演化、保持特性及印记的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2013, 28(7): 707-712. |
| [4] | 徐 琴, 丁士华, 宋天秀, 彭 勇, 吴小亮. 复合掺杂BCZT陶瓷的介电弛豫行为研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2013, 28(4): 441-446. |
| [5] | 何 邕, 李效民, 高相东, 冷 雪, 王 炜. 氧等离子体辅助脉冲激光沉积法制备PMN-PT薄膜的微观结构和电学性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2011, 26(11): 1227-1232. |
| [6] | 叶 芸,蒋亚东. 静电自组装铁电复合超薄膜及特性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2009, 24(4): 741-744. |
| [7] | 王评初,孙士文,潘晓明,朱丽慧,李东林,温保松,黄清伟,殷之文. 高性能铌镁酸铅-钛酸铅定向压电陶瓷的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2004, 19(5): 1195-1198. |
| [8] | 黎辉东,冯楚德,向平华. 掺La3+对0.94(Na1/2Bi1/2)TiO3-0.06BaTiO3陶瓷介电行为和压电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2004, 19(3): 579-585. |
| [9] | 孙士文,潘晓明,李东林,李洪钧,朱丽慧,黄清伟,王评初. PMN-PT弛豫铁电固溶体的定向凝固组织与结晶习性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2004, 19(3): 541-545. |
| [10] | 曹虎,方必军,徐海清,罗豪甦. 四方相铌镁酸铅-钛酸铅(PMN-PT)铁电单晶的弹性、介电、压电和机电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2003, 18(2): 465-469. |
| [11] | 曹虎,方必军,徐海清,罗豪甦. 分凝对Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-38%PbTiO3单晶的成分及介电、压电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2003, 18(1): 50-56. |
| [12] | 王歆,庄志强,齐雪君. PMN-PT弛豫铁电粉体的溶胶-凝胶法制备及其性质[J]. 无机材料学报, 2002, 17(2): 306-310. |
| [13] | 邸利锋,丁爱丽,何夕云,罗维根. 溶胶-凝胶法中热处理对PMNT薄膜结构的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2002, 17(2): 299-305. |
| [14] | 李国荣,罗豪甦,殷庆瑞. PMN-PT驰豫铁电单晶及其超声换能器性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2001, 16(6): 1077-1083. |
| [15] | 蔡弘,桂治轮,李龙土. 复合X7R多层陶瓷电容器[J]. 无机材料学报, 2000, 15(6): 1117-1122. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||