无机材料学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (2): 186-192.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250108 CSTR: 32189.14.jim20250108
蒋君1( ), 杨攻旅1, 杨雨帆1, 李毅1, 袁宁一1(
), 杨攻旅1, 杨雨帆1, 李毅1, 袁宁一1( ), 丁建宁2(
), 丁建宁2( )
)
收稿日期:2025-03-12
修回日期:2025-07-07
出版日期:2026-02-20
网络出版日期:2025-08-01
通讯作者:
袁宁一, 教授. E-mail: nyyuan@cczu.edu.cn;作者简介:蒋 君(1991-), 女, 博士. E-mail: jiangjun@cczu.edu.cn
基金资助:
JIANG Jun1( ), YANG Gonglü1, YANG Yufan1, LI Yi1, YUAN Ningyi1(
), YANG Gonglü1, YANG Yufan1, LI Yi1, YUAN Ningyi1( ), DING Jianning2(
), DING Jianning2( )
)
Received:2025-03-12
Revised:2025-07-07
Published:2026-02-20
Online:2025-08-01
Contact:
YUAN Ningyi, professor. E-mail: nyyuan@cczu.edu.cn;About author:JIANG Jun (1991-), female, PhD. E-mail: jiangjun@cczu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
钙钛矿太阳能电池(Perovskite solar cells, PSCs)的光电转换效率(PCE)已达27%, 但其工业化进程仍受限于钙钛矿吸光层的薄膜质量与稳定性问题。本研究采用丁基碘化胺(BAI)作为添加剂, 通过延缓结晶速率和诱导择优取向生长, 实现了对钙钛矿薄膜的晶面取向调控, 使得晶粒尺寸显著增大和缺陷密度降低。得益于有机胺盐具有本征的高疏水性, 优化后的钙钛矿薄膜表现出更强的环境耐受性, PSCs的PCE从22.32%提升至23.46%, 迟滞效应得到显著抑制。并且, 柔性钙钛矿太阳能电池(F-PSCs)的PCE从21.51%提升至22.26%, 验证了该策略在不同基底上的普适性。稳定性测试表明, BAI处理钙钛矿薄膜后PSCs的环境稳定性、热稳定性、光照稳定性以及F-PSCs的机械稳定性同步提升。本研究为钙钛矿薄膜的结晶控制和稳定性提升提供了新的解决方案, 为高性能钙钛矿光伏器件的开发提供了新思路, 具有显著的产业化应用价值。
中图分类号:
蒋君, 杨攻旅, 杨雨帆, 李毅, 袁宁一, 丁建宁. 有机胺盐调控钙钛矿薄膜结晶提升太阳能电池光电转换效率和稳定性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2026, 41(2): 186-192.
JIANG Jun, YANG Gonglü, YANG Yufan, LI Yi, YUAN Ningyi, DING Jianning. Regulating Perovskite Film Crystallization via Organic Amine Salts for Enhanced Photoelectric Conversion Efficiency and Stability[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2026, 41(2): 186-192.
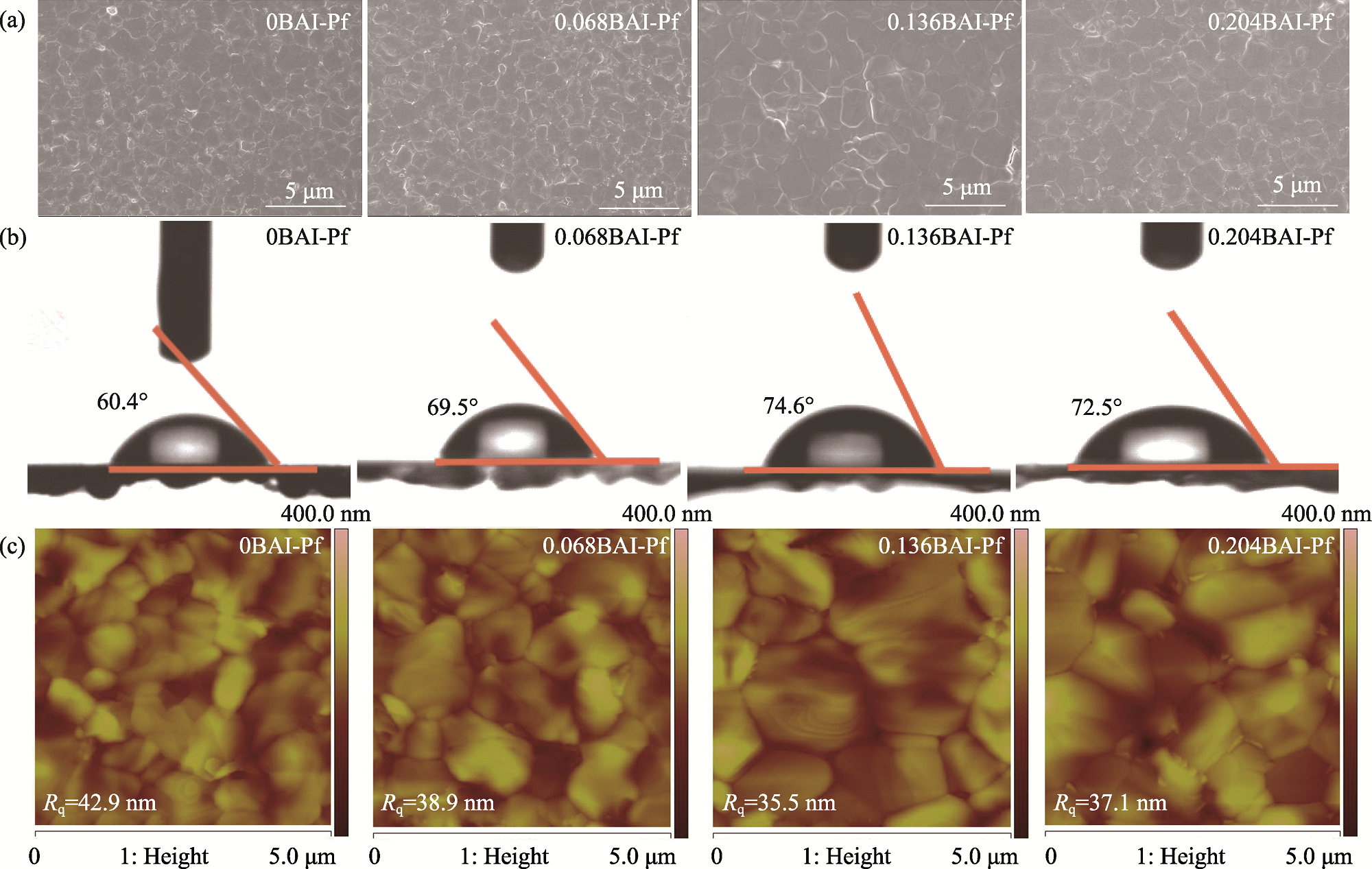
图1 xBAI-Pf(x=0, 0.068, 0.136, 0.204)的(a)表面SEM照片、(b)水接触角照片和(c)AFM图
Fig. 1 (a) SEM images, (b) water contact angles, and (c) AFM topographical images of xBAI-Pf (x=0, 0.068, 0.136, 0.204)
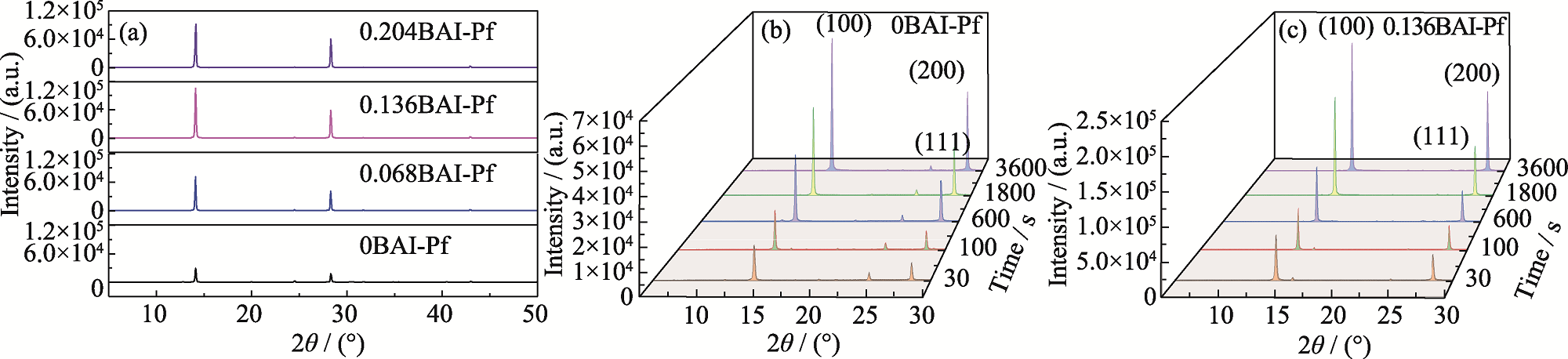
图2 (a) xBAI-Pf(x=0, 0.068, 0.136, 0.204)的XRD图谱; (b) 0BAI-Pf与(c) 0.136BAI-Pf在不同退火时间下的半原位3D XRD图谱
Fig. 2 (a) XRD patterns of xBAI-Pf (x=0, 0.068, 0.136, 0.204); (b, c) Semi-in situ 3D XRD patterns of (b) 0BAI-Pf and (c) 0.136BAI-Pf on different heating stages
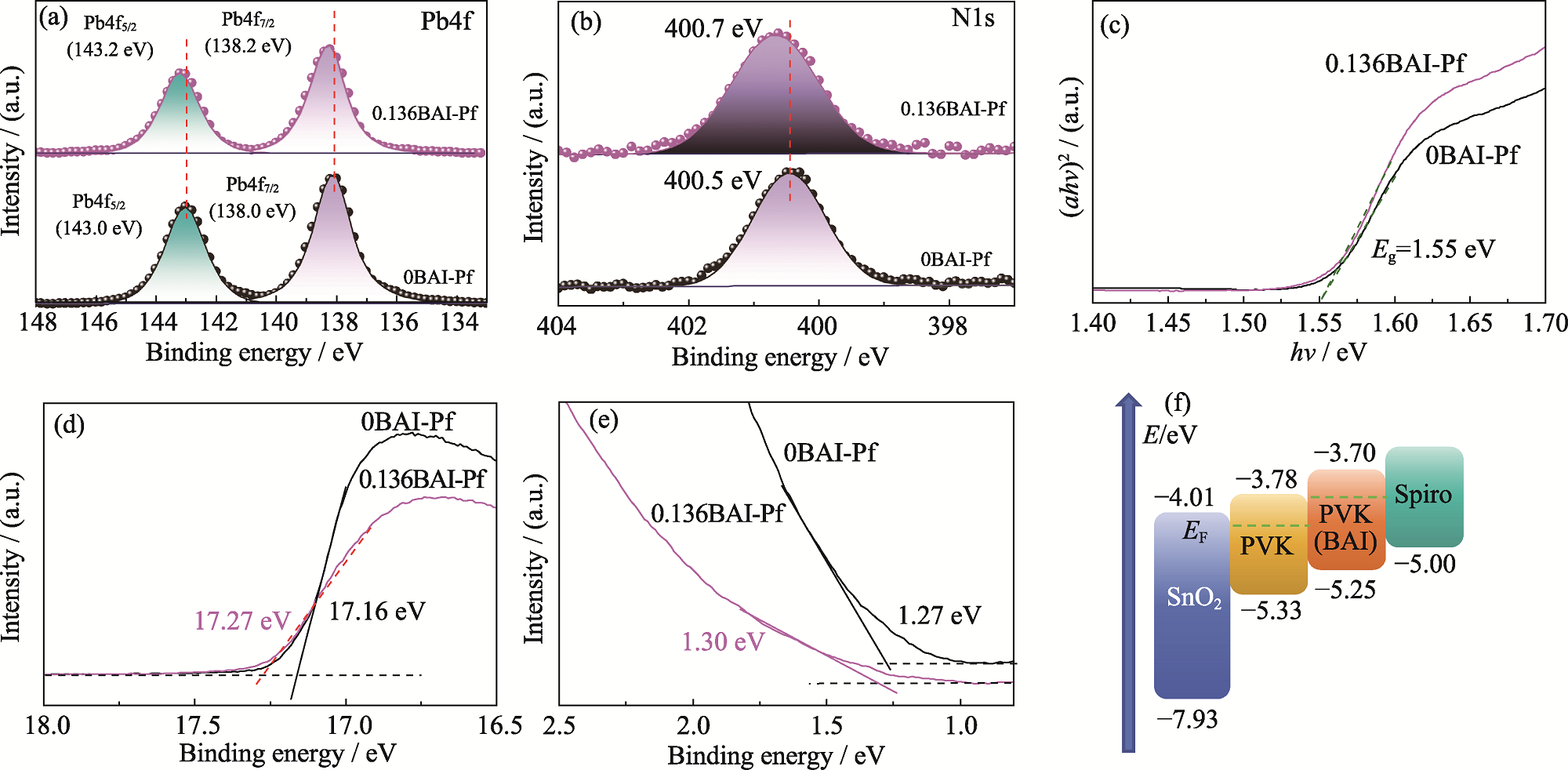
图3 0BAI-Pf与0.136BAI-Pf的(a, b) XPS谱图、(c) UV-Vis吸收光谱图对应的Tauc图、(d, e) UPS谱图和(f)能级示意图
Fig. 3 (a, b) XPS spectra, (c) Tauc plots corresponding to UV-Vis absorption spectra, (d, e) UPS spectra, and (f) schematic energy levels of 0BAI-Pf and 0.136BAI-Pf Colorful figures are available on website
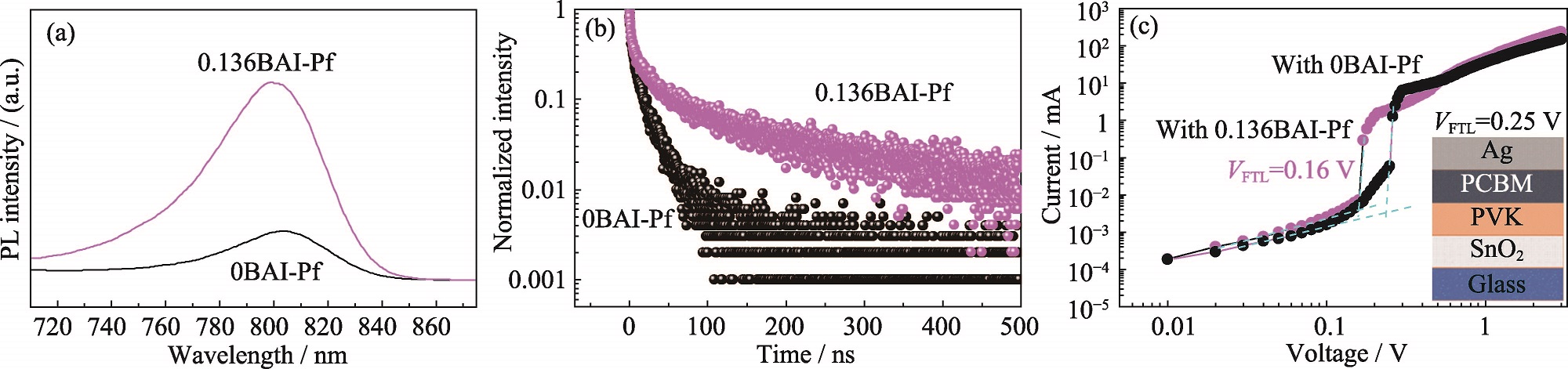
图4 0BAI-Pf与0.136BAI-Pf的(a) PL谱图、(b) TRPL谱图和(c)分别含两种薄膜的器件的SCLC谱图
Fig. 4 (a) PL spectra, (b) TRPL spectra of 0BAI-Pf and 0.136BAI-Pf; (c) SCLC spectra of devices containing two types of thin films Inset in (c): structural diagram of SCLC device. Colorful figures are available on website
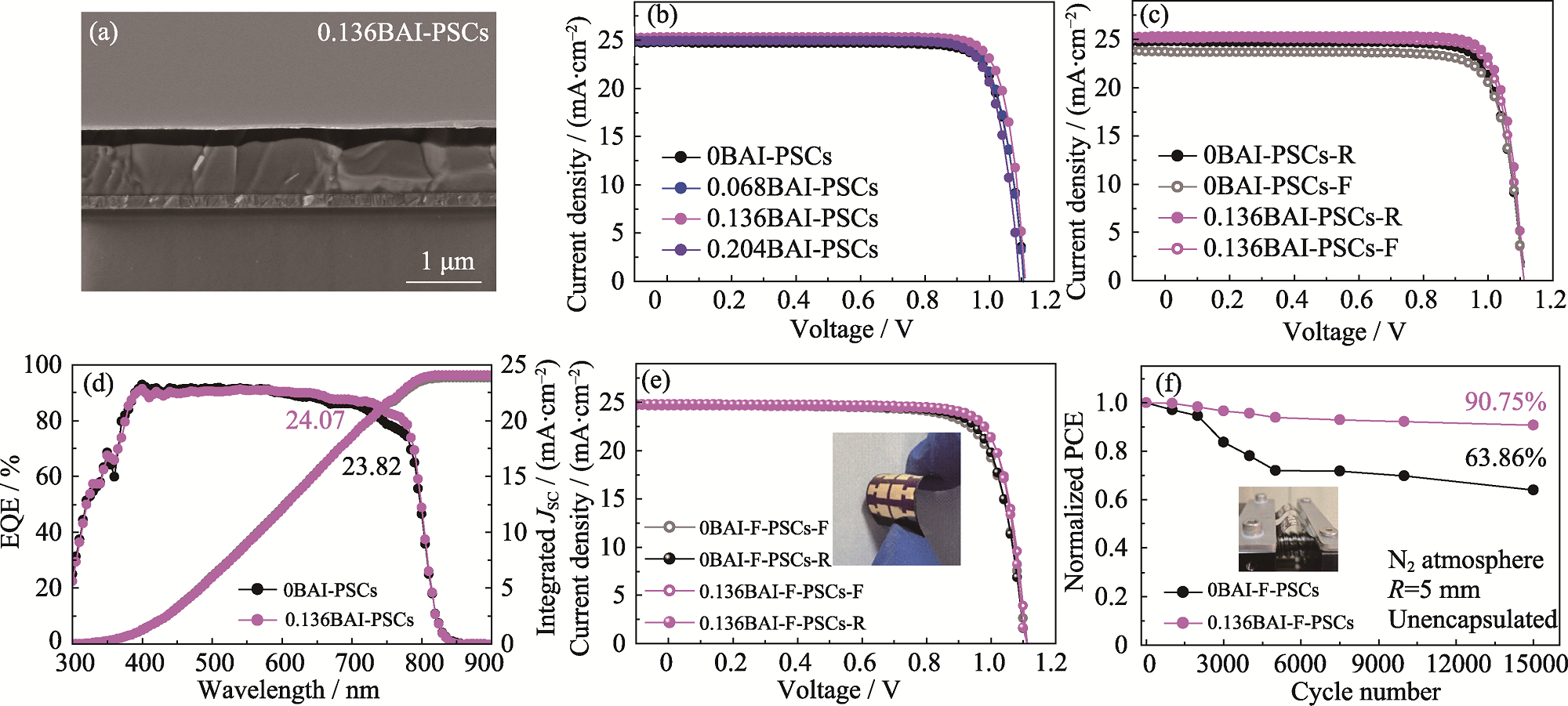
图5 (a) 0.136BAI-PSCs的截面SEM照片; (b) xBAI-PSCs的J-V曲线; (c, d) 0BAI-PSCs与0.136BAI-PSCs的(c)正反扫J-V曲线和(d) EQE谱图; (e, f) 0BAI-F-PSCs与0.136BAI-F-PSCs的(e)正反扫J-V曲线和(f) 5 mm弯曲半径下PCE随弯曲循环次数的衰减曲线
Fig. 5 (a) Cross section SEM image of 0.136BAI-PSCs; (b) J-V curves of xBAI-PSC; (c) Forward (F) and reverse (R) scanning J-V curves and (d) EQE spectra of 0BAI-PSCs and 0.136BAI-PSCs; (e) Forward and reverse scanning J-V curves and (f) attenuation curves of PCE with bending cycles at a bending radius of 5 mm for 0BAI-F-PSCs and 0.136BAI-F-PSCs Inset in (e): photograph of flexible PSCs; Inset in (f): bending experiment. Colorful figures are available on website
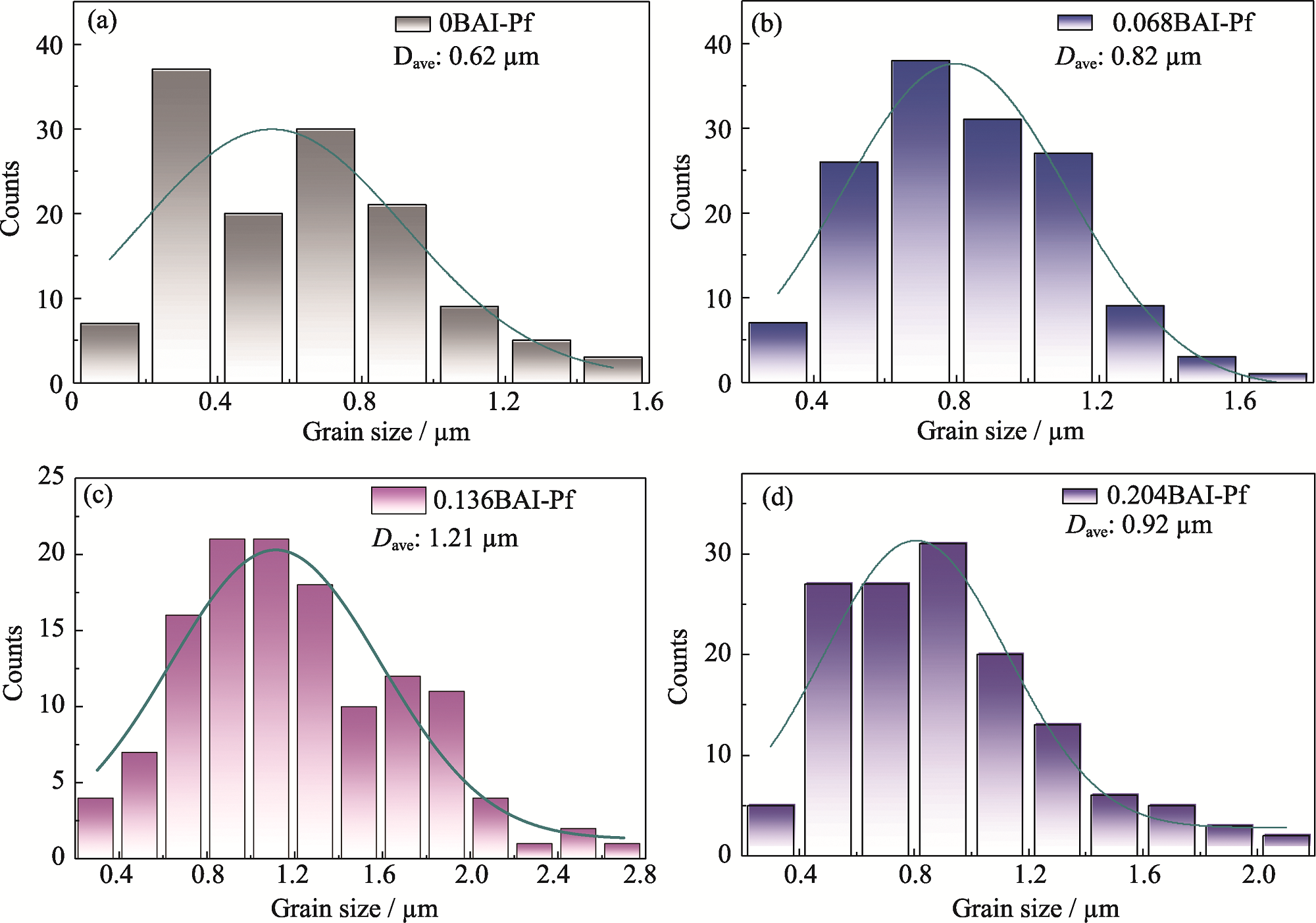
图S1 (a) 0BAI-Pf、(b) 0.068BAI-Pf、(c) 0.136BAI-Pf、(d) 0.204BAI-Pf的晶粒尺寸分布直方图
Fig. S1 Histograms of grain size distribution of (a) 0BAI-Pf, (b) 0.068BAI-Pf, (c) 0.136BAI-Pf, and (d) 0.204BAI-Pf
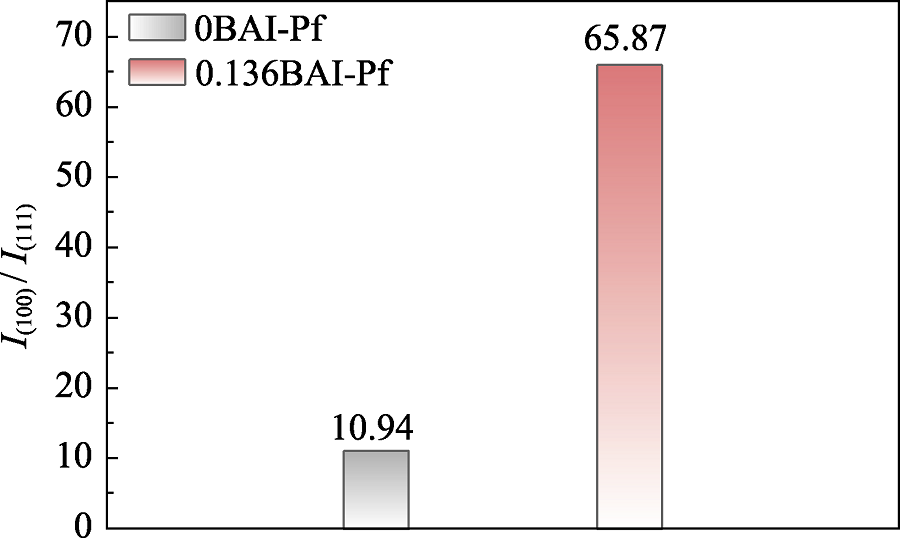
图S2 由XRD图谱获得的0BAI-Pf与0.136BAI-Pf的(100)和(111)晶面的峰强度比
Fig. S2 Peak intensity ratios of (100) to (111) crystal planes of 0BAI-Pf and 0.136BAI-Pf from XRD patterns
| Film | Ecutoff/eV | EFermi/eV | EVB/eV | ECB/eV | EF/eV | Eg/eV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0BAI-Pf | 17.16 | 1.27 | -5.33 | -3.78 | -4.06 | 1.55 |
| 0.136BAI-Pf | 17.27 | 1.30 | -5.25 | -3.70 | -3.95 | 1.55 |
表S1 0BAI-Pf与0.136BAI-Pf的能级结构参数
Table S1 Energy level structure parameters of 0BAI-Pf and 0.136BAI-Pf
| Film | Ecutoff/eV | EFermi/eV | EVB/eV | ECB/eV | EF/eV | Eg/eV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0BAI-Pf | 17.16 | 1.27 | -5.33 | -3.78 | -4.06 | 1.55 |
| 0.136BAI-Pf | 17.27 | 1.30 | -5.25 | -3.70 | -3.95 | 1.55 |
| Film | τ1/ns | A1 | τ2/ns | A2 | τave/ns |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0BAI-Pf | 33.13 | 0.40 | 40.49 | 0.40 | 37.18 |
| 0.136BAI-Pf | 83.67 | 0.36 | 102.27 | 0.36 | 109.80 |
表S2 0BAI-Pf与0.136BAI-Pf的TRPL寿命拟合参数
Table S2 TRPL lifetime fitting parameters of 0BAI-Pf and 0.136BAI-Pf
| Film | τ1/ns | A1 | τ2/ns | A2 | τave/ns |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0BAI-Pf | 33.13 | 0.40 | 40.49 | 0.40 | 37.18 |
| 0.136BAI-Pf | 83.67 | 0.36 | 102.27 | 0.36 | 109.80 |
| PSCs | VOC/V | FF/% | JSC/(mA·cm-2) | PCE/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0BAI-PSCs | 1.11 | 81.21 | 24.75 | 22.32 |
| 0.068BAI-PSCs | 1.11 | 82.67 | 24.92 | 22.85 |
| 0.136BAI-PSCs | 1.11 | 83.43 | 25.29 | 23.46 |
| 0.204BAI-PSCs | 1.09 | 82.07 | 24.96 | 22.41 |
表S3 xBAI-PSCs的光电性能参数
Table S3 Photovoltaic performance parameters of xBAI-PSCs
| PSCs | VOC/V | FF/% | JSC/(mA·cm-2) | PCE/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0BAI-PSCs | 1.11 | 81.21 | 24.75 | 22.32 |
| 0.068BAI-PSCs | 1.11 | 82.67 | 24.92 | 22.85 |
| 0.136BAI-PSCs | 1.11 | 83.43 | 25.29 | 23.46 |
| 0.204BAI-PSCs | 1.09 | 82.07 | 24.96 | 22.41 |
| PSCs | VOC/V | FF/% | JSC/(mA·cm-2) | PCE/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0BAI-PSCs-R | 1.11 | 81.21 | 24.75 | 22.32 |
| 0BAI-PSCs-F | 1.11 | 80.91 | 23.70 | 21.29 |
| 0.136BAI-PSCs-R | 1.11 | 83.43 | 25.29 | 23.46 |
| 0.136BAI-PSCs-F | 1.11 | 82.97 | 25.09 | 23.07 |
表S4 0BAI-PSCs与0.136BAI-PSCs的正反扫J-V参数
Table S4 Parameters of forward and backward scanning J-V curves of 0BAI-PSCs and 0.136BAI-PSCs
| PSCs | VOC/V | FF/% | JSC/(mA·cm-2) | PCE/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0BAI-PSCs-R | 1.11 | 81.21 | 24.75 | 22.32 |
| 0BAI-PSCs-F | 1.11 | 80.91 | 23.70 | 21.29 |
| 0.136BAI-PSCs-R | 1.11 | 83.43 | 25.29 | 23.46 |
| 0.136BAI-PSCs-F | 1.11 | 82.97 | 25.09 | 23.07 |
| PSCs | VOC/V | FF/% | JSC/(mA·cm-2) | PCE/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0BAI-F-PSCs-R | 1.11 | 78.64 | 24.74 | 21.51 |
| 0BAI-F-PSCs-F | 1.11 | 76.75 | 24.71 | 21.04 |
| 0.136BAI-F-PSCs-R | 1.11 | 81.24 | 24.82 | 22.26 |
| 0.136BAI-F-PSCs-F | 1.11 | 80.87 | 24.66 | 22.17 |
表S5 0BAI-F-PSCs与0.136BAI-F-PSCs的J-V曲线的参数
Table S5 Parameters of J-V curves of 0BAI-F-PSCs and 0.136BAI-F-PSCs
| PSCs | VOC/V | FF/% | JSC/(mA·cm-2) | PCE/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0BAI-F-PSCs-R | 1.11 | 78.64 | 24.74 | 21.51 |
| 0BAI-F-PSCs-F | 1.11 | 76.75 | 24.71 | 21.04 |
| 0.136BAI-F-PSCs-R | 1.11 | 81.24 | 24.82 | 22.26 |
| 0.136BAI-F-PSCs-F | 1.11 | 80.87 | 24.66 | 22.17 |
| [1] | The National Renewable Energy Laboratory. Best research-cell efficiency chart. (2025-01-21)[2025-03-12]. https://www.nrel.gov/pv/cell-efficiency.html. |
| [2] | HAILEGNAW B, DEMCHYSHYN S, PUTZ C, et al. Flexible quasi-2D perovskite solar cells with high specific power and improved stability for energy autonomous drones. Nature Energy, 2024, 9: 677. |
| [3] |
WU J, LIU Z, YANG Y, et al. Regulating precursor viscosity with inert solvent additives for efficient blade-coated perovskite solar cells. Small Methods, 2025, 9(8): 2500129.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
ZHANG Z, CHEN W, JIANG X, et al. Suppression of phase segregation in wide bandgap perovskites with thiocyanate ions for perovskite/organic tandems with 25.06% efficiency. Nature Energy, 2024, 9: 592.
DOI |
| [5] |
LIANG L, NAN Z, LI Y, et al. Formation dynamics of thermally stable 1D/3D perovskite interfaces for high-performance photovoltaics. Advanced Materials, 2025, 37(8): 2413841.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
WANG K, ZHENG L Y, HOU Y C, et al. Overcoming Shockley- Queisser limit using halide perovskite platform? Joule, 2022, 6(4): 756.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
ALLEN T G, BULLOCK J, YANG X, et al. Passivating contacts for crystalline silicon solar cells. Nature Energy, 2019, 4: 914.
DOI |
| [8] | XIE L, DU S, LI J, et al. Molecular dipole engineering-assisted strain release for mechanically robust flexible perovskite solar cells. Energy & Environment Science, 2023, 16(11): 5423. |
| [9] |
WANG S, TAN L, ZHOU J, et al. Over 24% efficient MA-free CsxFA1-xPbX3 perovskite solar cells. Joule, 2022, 6(6): 1344.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
ZHU H, WU S, YAO J, et al. An effective surface modification strategy with high reproducibility for simultaneously improving efficiency and stability of inverted MA-free perovskite solar cells. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(37): 21476.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
LI X, GAO S, WU X, et al. Bifunctional ligand-induced preferred crystal orientation enables highly efficient perovskite solar cells. Joule, 2024, 8(11): 3169.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
ZHANG X, SHANG C, WANG C, et al. Preferred crystallographic orientation via solution bathing for high-performance inverted perovskite photovoltaics. Advanced Functional Materials, 2024, 34(46): 2407732.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
HUANG S, QIAN C, LIU X, et al. A review on flexible solar cells. Science China Materials, 2024, 67(9): 2717.
DOI |
| [14] |
FAN Y, CHEN H, LIU X, et al. Myth behind metastable and stable n-hexylammonium bromide-based low-dimensional perovskites. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2023, 145 (14): 8209.
DOI URL |
| [15] | LEI Y S, CHEN Y, ZHANG R, et al. A fabrication process for flexible single-crystal perovskite devices. Nature, 2020, 583: 790. |
| [16] |
XU X, DU Q, KANG H, et al. Uniform molecular adsorption energy-driven homogeneous crystallization and dual-interface modification for high efficiency and thermal stability in inverted perovskite solar cells. Advanced Functional Materials, 2024, 34(44): 2408512.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
LIU H, JIN G, WANG J, et al. Quantum dots mediated crystallization enhancement in two-step processed perovskite solar cells. Nano-Micro Letters, 2025, 17: 169.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
LI S, XIAO Y, SU R, et al. Coherent growth of high-Miller-index facets enhances perovskite solar cells. Nature, 2024, 635: 874.
DOI |
| [19] |
PENG J, WALTER D, REN Y, et al. Nanoscale localized contacts for high fill factors in polymer-passivated perovskite solar cells. Science, 2021, 371(6527): 390.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
KANG D, PARK N. On the current-voltage hysteresis in perovskite solar cells: dependence on perovskite composition and methods to remove hysteresis. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(34): 1805214.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
ZHAO W, XU J, HE K, et al. A special additive enables all cations and anions passivation for stable perovskite solar cells with efficiency over 23%. Nano-Micro Letters, 2021, 13: 169.
DOI PMID |
| [22] | WANG C, GU J, LI J, et al. Two-dimensional (n=1) ferroelectric film solar cells. National Science Review, 2023, 10(7): nwad061. |
| [23] |
LIAO X, JIA X, LI W, et al. Methylammonium-free, high-efficiency, and stable all-perovskite tandem solar cells enabled by multifunctional rubidium acetate. Nature Communications, 2025, 16: 1164.
DOI |
| [1] | 马新超, 智清, 李威, 陈毛, 王海龙, 张锐, 张帆, 范冰冰. Fe2AlB2的高温氧化机制及吸波性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2026, 41(1): 45-54. |
| [2] | 江宗玉, 黄红花, 清江, 王红宁, 姚超, 陈若愚. 铝离子掺杂MIL-101(Cr)的制备及其VOCs吸附性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(7): 747-753. |
| [3] | 倪晓萌, 许方贤, 刘静静, 张帅, 郭华飞, 袁宁一. 甲脒亚磺酸添加剂提升Sb2(S,Se)3薄膜质量及其光伏性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 372-378. |
| [4] | 张继国, 吴田, 赵旭, 杨钒, 夏天, 孙士恩. 钠离子电池正极材料循环稳定性提升策略及产业化进程[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(4): 348-362. |
| [5] | 胡清豪, 刘兴翀, 彭永珊, 侯孟君, 何堂贵, 汤安民. 安赛蜜修饰SnO2电子传输层对钙钛矿太阳能电池性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(11): 1261-1267. |
| [6] | 瞿牡静, 张淑兰, 朱梦梦, 丁浩杰, 段嘉欣, 代恒龙, 周国红, 李会利. CsPbBr3@MIL-53纳米复合荧光粉的合成、性能及其白光LEDs应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(9): 1035-1043. |
| [7] | 潘建隆, 马官军, 宋乐美, 郇宇, 魏涛. 燃料还原法原位制备高稳定性/催化活性SOFC钴基钙钛矿阳极[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(8): 911-919. |
| [8] | 苗鑫, 闫世强, 韦金豆, 吴超, 樊文浩, 陈少平. Te基热电器件反常界面层生长行为及界面稳定性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(8): 903-910. |
| [9] | 肖梓晨, 何世豪, 邱诚远, 邓攀, 张威, 戴维德仁, 缑炎卓, 李金华, 尤俊, 王贤保, 林俍佑. 钙钛矿太阳能电池纳米纤维改性电子传输层研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 828-834. |
| [10] | 张慧, 许志鹏, 朱从潭, 郭学益, 杨英. 大面积有机-无机杂化钙钛矿薄膜及其光伏应用研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(5): 457-466. |
| [11] | 陈甜, 罗媛, 朱刘, 郭学益, 杨英. 有机-无机共添加增强柔性钙钛矿太阳能电池机械弯曲及环境稳定性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(5): 477-484. |
| [12] | 杨博, 吕功煊, 马建泰. 镍铁氢氧化物-磷化钴复合电极电催化分解水研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(4): 374-382. |
| [13] | 于嫚, 高荣耀, 秦玉军, 艾希成. 上转换发光纳米材料对钙钛矿太阳能电池迟滞效应和离子迁移动力学的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(4): 359-366. |
| [14] | 张宇晨, 陆知遥, 赫晓东, 宋广平, 朱春城, 郑永挺, 柏跃磊. 硫族MAX相硼化物的物相稳定性和性能预测[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 225-232. |
| [15] | 刘锁兰, 栾福园, 吴子华, 寿春晖, 谢华清, 杨松旺. 原位生长钙钛矿太阳能电池共形氧化锡薄膜[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(12): 1397-1403. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||