无机材料学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (2): 225-232.DOI: 10.15541/jim20230188 CSTR: 32189.14.10.15541/jim20230188
所属专题: 【材料计算】材料模拟计算(202506); 【信息功能】MAX、MXene及其他二维材料(202506)
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
张宇晨1( ), 陆知遥1, 赫晓东1, 宋广平1, 朱春城2, 郑永挺1, 柏跃磊1(
), 陆知遥1, 赫晓东1, 宋广平1, 朱春城2, 郑永挺1, 柏跃磊1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-04-14
修回日期:2023-07-07
出版日期:2023-08-21
网络出版日期:2023-08-21
通讯作者:
柏跃磊,教授. E-mail: baiyl@hit.edu.cn作者简介:张宇晨(2001-),男,本科生. E-mail: 1696409105@qq.com
基金资助:
ZHANG Yuchen1( ), LU Zhiyao1, HE Xiaodong1, SONG Guangping1, ZHU Chuncheng2, ZHENG Yongting1, BAI Yuelei1(
), LU Zhiyao1, HE Xiaodong1, SONG Guangping1, ZHU Chuncheng2, ZHENG Yongting1, BAI Yuelei1( )
)
Received:2023-04-14
Revised:2023-07-07
Published:2023-08-21
Online:2023-08-21
Contact:
BAI Yuelei, professor. E-mail: baiyl@hit.edu.cnAbout author:ZHANG Yuchen(2001-), male, undergraduate student. E-mail: 1696409105@qq.com
Supported by:摘要:
Zr2SB、Hf2SB、Zr2SeB、Hf2SeB、Hf2TeB都是近期发现的硫族MAX相硼化物, 与典型MAX相相比,具有明显不同的性质, 因此备受人们关注。本文采用第一性原理并结合“线性优化法”、键刚度模型和准简谐近似研究了MAX相硼化物(M = Zr, Hf; A = S, Se, Te)的物相稳定性、力学性能和热性能。理论分析结果与目前可用的实验结果一致。经热力学和本征稳定性分析后发现, 只有M2AB可以稳定存在。较短的M−A键与M−B键长使Hf系化合物的键刚度高于Zr系化合物, 这也同样导致Hf系化合物的硬度高于Zr系。随着A元素由S到Se再到Te, M−B与M−A键长逐渐增加, 键刚度减小导致弹性模量降低。而且, 这些化合物的体积模量取决于其平均化学键刚度。更加重要的是, 最弱键和最强键的刚度比(kmin/kmax)较高,显示这些MAX相硼化物不同于传统MAX相, 均呈本征脆性。考虑晶格振动(声子)和电子激发的贡献后计算得到M2AB等压热容及热膨胀系数(TEC), 均在300 K以下随温度升高先快速上升后上升速率逐渐降低, 这与其它MAX相类似。较低的键刚度导致Zr系MAX相硼化物的平均线热膨胀系数整体上高于Hf系, 而且在300~1300 K区间与大部分MAX和MAB相一致。
中图分类号:
张宇晨, 陆知遥, 赫晓东, 宋广平, 朱春城, 郑永挺, 柏跃磊. 硫族MAX相硼化物的物相稳定性和性能预测[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 225-232.
ZHANG Yuchen, LU Zhiyao, HE Xiaodong, SONG Guangping, ZHU Chuncheng, ZHENG Yongting, BAI Yuelei. Predictions of Phase Stability and Properties of S-group Elements Containing MAX Borides[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(2): 225-232.
| Compound | a/Å | c/Å | V/Å3 | Most competing phases | ΔHcomp/(eV·atom-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zr2SB | 3.521 | 12.302 | 132.12 | 0.6Zr2S + 0.1Zr3S4 + 0.5ZrB2 | -0.0749 |
| Exp.[ | 3.500 | 12.271 | 130.19 | ||
| Hf2SB | 3.484 | 12.122 | 127.40 | 0.5Hf2S + 0.5HfS + 0.5HfB2 | -0.0512 |
| Exp.[ | 3.467 | 12.105 | 126.01 | ||
| Zr2SeB | 3.573 | 12.733 | 140.78 | 0.5Zr2Se + 0.5ZrSe + 0.5ZrB2 | -0.0259 |
| Exp.[ | 3.644 | 12.632 | 145.27 | ||
| Hf2SeB | 3.538 | 12.544 | 136.01 | 0.0185Hf23Se25 + 0.5370Hf2Se + 0.5HfB2 | -0.0838 |
| Exp.[ | 3.523 | 12.478 | 134.11 | ||
| Hf2TeB | 3.619 | 13.239 | 150.14 | 0.5Hf3Te2 + 0.5HfB2 | -0.0100 |
| Exp.[ | 3.605 | 13.127 | 147.72 |
表1 M2AB (M = Zr, Hf; A = S, Se, Te)中形成焓ΔHcomp<0的化合物
Table 1 M2AB (M = Zr, Hf; A = S, Se, Te) of which formation enthalpy ΔHcomp<0
| Compound | a/Å | c/Å | V/Å3 | Most competing phases | ΔHcomp/(eV·atom-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zr2SB | 3.521 | 12.302 | 132.12 | 0.6Zr2S + 0.1Zr3S4 + 0.5ZrB2 | -0.0749 |
| Exp.[ | 3.500 | 12.271 | 130.19 | ||
| Hf2SB | 3.484 | 12.122 | 127.40 | 0.5Hf2S + 0.5HfS + 0.5HfB2 | -0.0512 |
| Exp.[ | 3.467 | 12.105 | 126.01 | ||
| Zr2SeB | 3.573 | 12.733 | 140.78 | 0.5Zr2Se + 0.5ZrSe + 0.5ZrB2 | -0.0259 |
| Exp.[ | 3.644 | 12.632 | 145.27 | ||
| Hf2SeB | 3.538 | 12.544 | 136.01 | 0.0185Hf23Se25 + 0.5370Hf2Se + 0.5HfB2 | -0.0838 |
| Exp.[ | 3.523 | 12.478 | 134.11 | ||
| Hf2TeB | 3.619 | 13.239 | 150.14 | 0.5Hf3Te2 + 0.5HfB2 | -0.0100 |
| Exp.[ | 3.605 | 13.127 | 147.72 |
| Compound | c11/GPa | c12/GPa | c13/GPa | c33/GPa | c44/GPa | G/GPa | B/GPa | E/GPa | μ | G/B | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zr2SB | 264 | 76 | 91 | 298 | 135 | 108 | 148 | 262 | 0.206 | 0.730 | This work |
| Hf2SB | 296 | 74 | 97 | 318 | 147 | 122 | 160 | 292 | 0.196 | 0.763 | This work |
| Zr2SeB | 252 | 64 | 83 | 277 | 125 | 105 | 137 | 250 | 0.197 | 0.766 | This work |
| Hf2SeB | 275 | 66 | 90 | 292 | 134 | 113 | 148 | 270 | 0.195 | 0.764 | This work |
| Zr2TeB | 198 | 67 | 78 | 225 | 104 | 79 | 118 | 194 | 0.226 | 0.669 | This work |
| Hf2TeB | 225 | 61 | 88 | 257 | 119 | 93 | 130 | 225 | 0.211 | 0.715 | This work |
| Ti3SiC2 | 366 | 94 | 100 | 352 | 153 | 142 | 187 | 339 | 0.192 | 0.759 | [ |
| Ti3GeC2 | 357 | 94 | 97 | 333 | 143 | 142 | 182 | 340 | 0.196 | 0.780 | [ |
| Hf2InC | 309 | 81 | 80 | 273 | 98 | 105 | 152 | 256 | 0.21 | 0.691 | [ |
| Hf2SnC | 251 | 71 | 107 | 238 | 101 | 87 | 145 | 218 | 0.25 | 0.600 | [ |
表2 M2AB (M = Zr, Hf; A = S, Se, Te)与几种典型MAX相的二阶弹性常数与工程弹性模量
Table 2 Second-order elastic constants and engineering elastic moduli of M2AB (M = Zr, Hf; A = S, Se, Te) and several typical MAX phases
| Compound | c11/GPa | c12/GPa | c13/GPa | c33/GPa | c44/GPa | G/GPa | B/GPa | E/GPa | μ | G/B | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zr2SB | 264 | 76 | 91 | 298 | 135 | 108 | 148 | 262 | 0.206 | 0.730 | This work |
| Hf2SB | 296 | 74 | 97 | 318 | 147 | 122 | 160 | 292 | 0.196 | 0.763 | This work |
| Zr2SeB | 252 | 64 | 83 | 277 | 125 | 105 | 137 | 250 | 0.197 | 0.766 | This work |
| Hf2SeB | 275 | 66 | 90 | 292 | 134 | 113 | 148 | 270 | 0.195 | 0.764 | This work |
| Zr2TeB | 198 | 67 | 78 | 225 | 104 | 79 | 118 | 194 | 0.226 | 0.669 | This work |
| Hf2TeB | 225 | 61 | 88 | 257 | 119 | 93 | 130 | 225 | 0.211 | 0.715 | This work |
| Ti3SiC2 | 366 | 94 | 100 | 352 | 153 | 142 | 187 | 339 | 0.192 | 0.759 | [ |
| Ti3GeC2 | 357 | 94 | 97 | 333 | 143 | 142 | 182 | 340 | 0.196 | 0.780 | [ |
| Hf2InC | 309 | 81 | 80 | 273 | 98 | 105 | 152 | 256 | 0.21 | 0.691 | [ |
| Hf2SnC | 251 | 71 | 107 | 238 | 101 | 87 | 145 | 218 | 0.25 | 0.600 | [ |
| Compound | M−A bond | M−B bond | kmin/kmax | Hmicro/GPa | Hmacro/GPa | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d/nm | k/GPa | d/nm | k/GPa | |||||
| Zr2SB | 0.26997 | 458.93 | 0.24124 | 612.75 | 0.7490 | 21.29 | 18.40 | |
| Exp.[ | 0.26844 | 0.24032 | 9-12[ | |||||
| Hf2SB | 0.26800 | 472.37 | 0.23722 | 652.32 | 0.7241 | 24.74 | 21.20 | |
| Exp.[ | 0.26643 | 0.23688 | ||||||
| Zr2SeB | 0.28062 | 442.87 | 0.24282 | 560.54 | 0.7901 | 21.09 | 19.30 | |
| Exp.[ | 0.28071 | 0.24729 | ||||||
| Hf2SeB | 0.27869 | 455.17 | 0.23899 | 595.24 | 0.7647 | 22.97 | 20.17 | |
| Exp.[ | 0.27735 | 0.23789 | ||||||
| Zr2TeB | 0.29743 | 432.53 | 0.24526 | 487.09 | 0.8880 | 14.45 | 13.12 | |
| Hf2TeB | 0.29604 | 439.17 | 0.24156 | 517.33 | 0.8489 | 17.90 | 16.16 | |
表3 M2AB (M = Zr, Hf; A = S, Se, Te)的键长、键刚度和kmin/kmax
Table 3 Bond length, bond stiffness and kmin/kmax in M2AB (M = Zr, Hf; A = S, Se, Te)
| Compound | M−A bond | M−B bond | kmin/kmax | Hmicro/GPa | Hmacro/GPa | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d/nm | k/GPa | d/nm | k/GPa | |||||
| Zr2SB | 0.26997 | 458.93 | 0.24124 | 612.75 | 0.7490 | 21.29 | 18.40 | |
| Exp.[ | 0.26844 | 0.24032 | 9-12[ | |||||
| Hf2SB | 0.26800 | 472.37 | 0.23722 | 652.32 | 0.7241 | 24.74 | 21.20 | |
| Exp.[ | 0.26643 | 0.23688 | ||||||
| Zr2SeB | 0.28062 | 442.87 | 0.24282 | 560.54 | 0.7901 | 21.09 | 19.30 | |
| Exp.[ | 0.28071 | 0.24729 | ||||||
| Hf2SeB | 0.27869 | 455.17 | 0.23899 | 595.24 | 0.7647 | 22.97 | 20.17 | |
| Exp.[ | 0.27735 | 0.23789 | ||||||
| Zr2TeB | 0.29743 | 432.53 | 0.24526 | 487.09 | 0.8880 | 14.45 | 13.12 | |
| Hf2TeB | 0.29604 | 439.17 | 0.24156 | 517.33 | 0.8489 | 17.90 | 16.16 | |
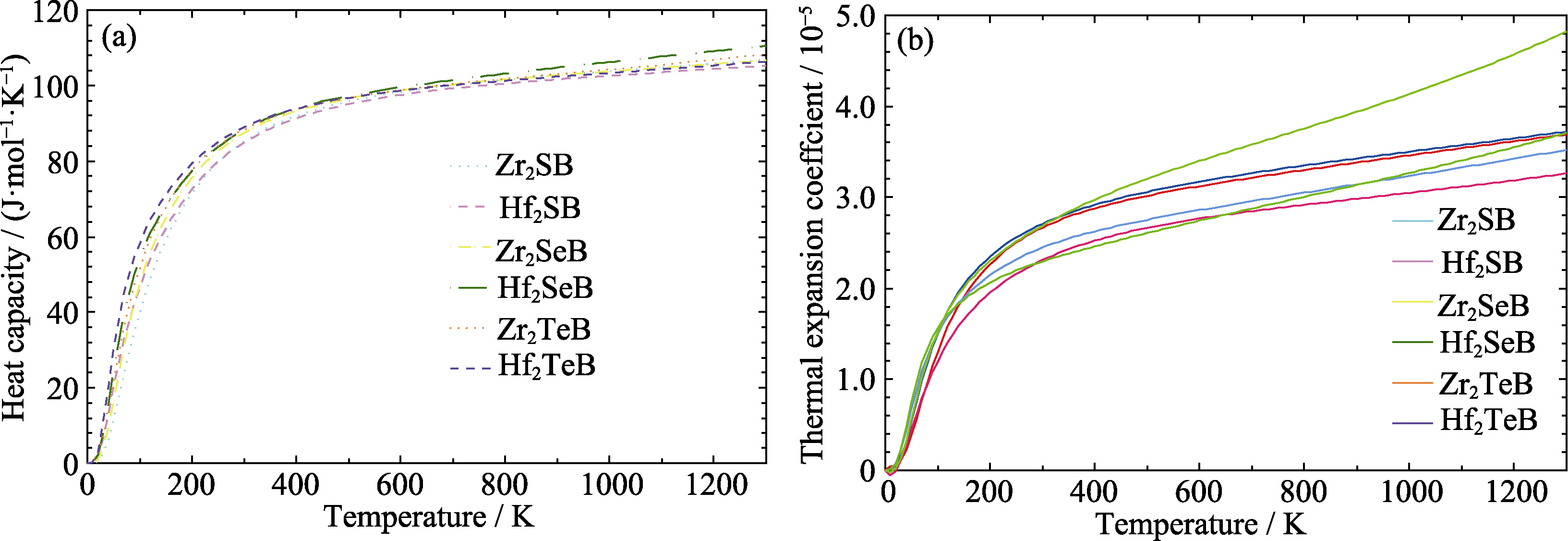
图2 M2AB (M = Zr, Hf; A = S, Se, Te)的(a)热容和(b)线热膨胀系数随温度的变化曲线
Fig. 2 Temperature dependence of (a) CP and (b) αl of M2AB (M = Zr, Hf; A = S, Se, Te) Colorful figures are available on website

图S2 (a) Zr2SB、(b) Hf2SB、(c) Zr2SeB、(d) Hf2SeB、(e) Zr2TeB和and (f) Hf2TeB沿高对称点方向的声子色散曲线(左)和态密度(右)
Fig. S2 Phonon dispersions (left) and density of states (right) of (a) Zr2SB, (b) Hf2SB, (c) Zr2SeB, (d) Hf2SeB, (e) Zr2TeB, and (f) Hf2TeB along the high symmetry directions

图S3 压力对M2AB (M = Zr, Hf; A = S, Se, Te)中(a) M-A和(b) M-B键归一化键长d/d0的影响
Fig. S3 Pressure dependence of normalized bond length d/d0 of (a) M-A and (b) M-B bonds in M2AB (M = Zr, Hf; A = S, Se, Te)
| Compound | Included phase | a/Å | c/Å | V/Å3 | Most competing phases | ΔHcomp/(eV·atom-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zr2SB | Zr, S, B, Zr2S, Zr3S4, Zr9S2, ZrS, ZrS2, ZrS3, ZrB2, B2S3, BS2 | 3.521 | 12.302 | 132.12 | 0.6Zr2S + 0.1Zr3S4 + 0.5ZrB2 | -0.0749 |
| Exp.[ | 3.500 | 12.271 | 130.19 | |||
| Zr3SB2 | 0.0833Zr9S2 + 0.5833ZrB2 + 0.8333Zr2SB | 0.0919 | ||||
| Zr4SB3 | 0.1667Zr9S2 + 1.1667ZrB2 + 0.6667Zr2SB | 0.1588 | ||||
| Hf2SB | Hf, S, B, Hf2S, HfS, HfS2, HfS3, HfB2, B2S3, BS2 | 3.484 | 12.122 | 127.40 | 0.5Hf2S + 0.5HfS + 0.5HfB2 | -0.0512 |
| Exp.[ | 3.467 | 12.105 | 126.01 | |||
| Hf3SB2 | 0.5Hf + 0.5HfB2 + Hf2SB | 0.0807 | ||||
| Hf4SB3 | Hf + HfB2 + Hf2SB | 0.1422 | ||||
| Zr2SeB | Zr, Se, B, Zr2Se, Zr2Se3, ZrSe, ZrSe2, ZrSe3, ZrB2, BSe2 | 3.573 | 12.733 | 140.78 | 0.5Zr2Se + 0.5ZrSe + 0.5ZrB2 | -0.0259 |
| Exp.[ | 3.644 | 12.632 | 145.27 | |||
| Zr3SeB2 | 0.5Zr + 0.5ZrB2 + Zr2SeB | 0.1649 | ||||
| Zr4SeB3 | Zr + ZrB2 + Zr2SeB | 0.1559 | ||||
| Hf2SeB | Hf, Se, B, Hf2Se, Hf2Se3, HfSe2, HfSe3, Hf23Se25, HfB2, BSe2 | 3.538 | 12.544 | 136.01 | 0.0185Hf23Se25 + 0.5370Hf2Se + 0.5HfB2 | -0.0838 |
| Exp.[ | 3.523 | 12.478 | 134.11 | |||
| Hf3SeB2 | 0.5Hf + 0.5HfB2 + Hf2SeB | 0.0836 | ||||
| Hf4SeB3 | Hf + HfB2 + Hf2SeB | 0.1457 | ||||
| Zr2TeB | Zr, Te, B, Zr2Te3, Zr3Te, Zr5Te4, ZrTe, ZrTe2, ZrTe3, ZrTe5, ZrB2 | 3.650 | 13.415 | 154.77 | 0.2143Zr5Te4 + 0.1429Zr3Te + 0.5ZrB2 | 0.0305 |
| Zr3TeB2 | 0.1429Zr5Te4 + 0.4286Zr3Te + ZrB2 | 0.1321 | ||||
| Zr4TeB3 | 0.0174Zr5Te4 + 0.7143Zr3Te + 1.5ZrB2 | 0.1960 | ||||
| Hf2TeB | Hf, Te, B, Hf3Te2,Hf5Te4, HfTe2, HfTe5, HfB2 | 3.619 | 13.239 | 150.14 | 0.5Hf3Te2 + 0.5HfB2 | -0.0100 |
| Exp.[ | 3.605 | 13.127 | 147.72 | |||
| Hf3TeB2 | 0.5Hf + 0.5HfB2 + Hf2TeB | 0.0994 | ||||
| Hf4TeB3 | Hf + HfB2 + Hf2TeB | 0.1613 |
表S1 M2AB、M3AB2和M4AB3 (M = Zr, Hf; A = S, Se, Te)的形成焓ΔHcomp
Table S1 Formation enthalpy ΔHcomp of M2AB, M3AB2 and M4AB3 (M = Zr, Hf; A = S, Se, Te)
| Compound | Included phase | a/Å | c/Å | V/Å3 | Most competing phases | ΔHcomp/(eV·atom-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zr2SB | Zr, S, B, Zr2S, Zr3S4, Zr9S2, ZrS, ZrS2, ZrS3, ZrB2, B2S3, BS2 | 3.521 | 12.302 | 132.12 | 0.6Zr2S + 0.1Zr3S4 + 0.5ZrB2 | -0.0749 |
| Exp.[ | 3.500 | 12.271 | 130.19 | |||
| Zr3SB2 | 0.0833Zr9S2 + 0.5833ZrB2 + 0.8333Zr2SB | 0.0919 | ||||
| Zr4SB3 | 0.1667Zr9S2 + 1.1667ZrB2 + 0.6667Zr2SB | 0.1588 | ||||
| Hf2SB | Hf, S, B, Hf2S, HfS, HfS2, HfS3, HfB2, B2S3, BS2 | 3.484 | 12.122 | 127.40 | 0.5Hf2S + 0.5HfS + 0.5HfB2 | -0.0512 |
| Exp.[ | 3.467 | 12.105 | 126.01 | |||
| Hf3SB2 | 0.5Hf + 0.5HfB2 + Hf2SB | 0.0807 | ||||
| Hf4SB3 | Hf + HfB2 + Hf2SB | 0.1422 | ||||
| Zr2SeB | Zr, Se, B, Zr2Se, Zr2Se3, ZrSe, ZrSe2, ZrSe3, ZrB2, BSe2 | 3.573 | 12.733 | 140.78 | 0.5Zr2Se + 0.5ZrSe + 0.5ZrB2 | -0.0259 |
| Exp.[ | 3.644 | 12.632 | 145.27 | |||
| Zr3SeB2 | 0.5Zr + 0.5ZrB2 + Zr2SeB | 0.1649 | ||||
| Zr4SeB3 | Zr + ZrB2 + Zr2SeB | 0.1559 | ||||
| Hf2SeB | Hf, Se, B, Hf2Se, Hf2Se3, HfSe2, HfSe3, Hf23Se25, HfB2, BSe2 | 3.538 | 12.544 | 136.01 | 0.0185Hf23Se25 + 0.5370Hf2Se + 0.5HfB2 | -0.0838 |
| Exp.[ | 3.523 | 12.478 | 134.11 | |||
| Hf3SeB2 | 0.5Hf + 0.5HfB2 + Hf2SeB | 0.0836 | ||||
| Hf4SeB3 | Hf + HfB2 + Hf2SeB | 0.1457 | ||||
| Zr2TeB | Zr, Te, B, Zr2Te3, Zr3Te, Zr5Te4, ZrTe, ZrTe2, ZrTe3, ZrTe5, ZrB2 | 3.650 | 13.415 | 154.77 | 0.2143Zr5Te4 + 0.1429Zr3Te + 0.5ZrB2 | 0.0305 |
| Zr3TeB2 | 0.1429Zr5Te4 + 0.4286Zr3Te + ZrB2 | 0.1321 | ||||
| Zr4TeB3 | 0.0174Zr5Te4 + 0.7143Zr3Te + 1.5ZrB2 | 0.1960 | ||||
| Hf2TeB | Hf, Te, B, Hf3Te2,Hf5Te4, HfTe2, HfTe5, HfB2 | 3.619 | 13.239 | 150.14 | 0.5Hf3Te2 + 0.5HfB2 | -0.0100 |
| Exp.[ | 3.605 | 13.127 | 147.72 | |||
| Hf3TeB2 | 0.5Hf + 0.5HfB2 + Hf2TeB | 0.0994 | ||||
| Hf4TeB3 | Hf + HfB2 + Hf2TeB | 0.1613 |
| Compound | Curve fitting equation (300-1300 K) | TEC (300-1300 K)/ K-1 |
|---|---|---|
| Zr2SB | CP = 0.83×10-2T + 96.9 - 1.28×106T-2 | 10.97×10-6 K-1 |
| Hf2SB | CP = 0.74×10-2T + 96.6 - 1.25×106T-2 | 9.66×10-6 K-1 |
| Zr2SeB | CP = 0.82×10-2T + 96.7 - 1.06×106T-2 | 11.11×10-6 K-1 |
| Hf2SeB | CP = 1.28×10-2T + 94.4 - 0.89×106T-2 | 10.17×10-6 K-1 |
| Zr2TeB | CP = 1.07×10-2T + 94.7 - 0.84×106T-2 | 12.63×10-6 K-1 |
| Hf2TeB | CP = 0.83×10-2T + 96.1 - 0.87×106T-2 | 10.07×10-6 K-1 |
表S2 M2AB (M = Zr, Hf; A = S, Se, Te)在300~1300 K温度区间的等压热容CP拟合式和平均线膨胀系数
Table S2 Heat capacity at constant pressure and the average linear thermal expansion coefficient of M2AB (M = Zr, Hf; A = S, Se, Te) in the temperature range of 300-1300 K
| Compound | Curve fitting equation (300-1300 K) | TEC (300-1300 K)/ K-1 |
|---|---|---|
| Zr2SB | CP = 0.83×10-2T + 96.9 - 1.28×106T-2 | 10.97×10-6 K-1 |
| Hf2SB | CP = 0.74×10-2T + 96.6 - 1.25×106T-2 | 9.66×10-6 K-1 |
| Zr2SeB | CP = 0.82×10-2T + 96.7 - 1.06×106T-2 | 11.11×10-6 K-1 |
| Hf2SeB | CP = 1.28×10-2T + 94.4 - 0.89×106T-2 | 10.17×10-6 K-1 |
| Zr2TeB | CP = 1.07×10-2T + 94.7 - 0.84×106T-2 | 12.63×10-6 K-1 |
| Hf2TeB | CP = 0.83×10-2T + 96.1 - 0.87×106T-2 | 10.07×10-6 K-1 |
| [1] |
OPEKA M M, TALMY I G, WUCHINA E J, et al. Mechanical, thermal, and oxidation properties of refractory hafnium and zirconium compounds. Journal of the European ceramic Society, 1999, 19(13/14): 2405.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
ZHOU H J, ZHANG X Y, GAO L, et al. Ablation properties of ZrB2-SiC ultra-high temperature ceramic coatings. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(3): 256.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
WILEY D, MANNING W, HUNTER JR O. Elastic properties of polycrystalline TiB2, ZrB2 and HfB2 from room temperature to 1300 K. Journal of the Less Common Metals, 1969, 18(2): 149.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
GAO Dong, ZHANG Y, XU C L, et al. Formation mechanism of zircon phase in ZrB2-SiC ceramic composites during oxidation. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2011, 26(4): 433.
DOI |
| [5] |
BARSOUM M W. The MN+1AXN phases: a new class of solids: thermodynamically stable nanolaminates. Progress in Solid State Chemistry, 2000, 28(1-4): 201.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
BAI Y, HE X, SUN Y, et al. Chemical bonding and elastic properties of Ti3AC2 phases (A= Si, Ge, and Sn): a first-principle study. Solid State Sciences, 2010, 12(7): 1220.
DOI URL |
| [7] | RACKL T, EISENBURGER L, NIKLAUS R, et al. Syntheses and physical properties of the MAX phase boride Nb2SB and the solid solutions Nb2SBxC1-x(x= 0-1). Physical Review Materials, 2019, 3(5): 054001. |
| [8] |
RACKL T, JOHRENDT D. The MAX phase borides Zr2SB and Hf2SB. Solid State Sciences, 2020, 106: 106316.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
ZHANG Q, ZHOU Y, SAN X, et al. Zr2SeB and Hf2SeB: two new MAB phase compounds with the Cr2AlC-type MAX phase (211 phase) crystal structures. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2022, 11(11): 1764.
DOI |
| [10] |
ZHANG Q, ZHOU Y, SAN X, et al. Thermal explosion synthesis of first Te-containing layered ternary Hf2TeB MAX phase. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2023, 43(1): 173.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
QIN Y, ZHOU Y, FAN L, et al. Synthesis and characterization of ternary layered Nb2SB ceramics fabricated by spark plasma sintering. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 878: 160344.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
ZHANG Q, FU S, WAN D, et al. Synthesis and property characterization of ternary laminar Zr2SB ceramic. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2022, 11(5): 825.
DOI |
| [13] | BARSOUM M W. MAX phases: properties of machinable ternary carbides and nitrides. John Wiley & Sons, 2013. |
| [14] |
BARSOUM M, ZHEN T, KALIDINDI S, et al. Fully reversible, dislocation-based compressive deformation of Ti3SiC2 to 1 GPa. Nature Materials, 2003, 2(2): 107.
DOI |
| [15] |
LIU Y, COOPER V R, WANG B, et al. Discovery of ABO3 perovskites as thermal barrier coatings through high-throughput first principles calculations. Materials Research Letters, 2019, 7(4): 145.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
TOGO A, CHAPUT L, TANAKA I, et al. First-principles phonon calculations of thermal expansion in Ti3SiC2, Ti3AlC2, and Ti3GeC2. Physical Review B, 2010, 81(17): 174301.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
BAI Y, HE X, WANG R. Lattice dynamics of Al-containing MAX-phase carbides: a first-principle study. Journal of Raman Spectroscopy, 2015, 46(9): 784.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
DAHLQVIST M, ALLING B, ROS N J. Stability trends of MAX phases from first principles. Physical Review B, 2010, 81(22): 220102.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
SHEN Y, SAUNDERS C N, BERNAL C M, et al. Anharmonic origin of the giant thermal expansion of NaBr. Physical Review Letters, 2020, 125(8): 085504.
DOI URL |
| [20] | QI X X, SONG G P, YIN W L, et al. Analysis on phase stability and mechanical property of newly-discovered ternary layered boride Cr4AlB4. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(1): 53. |
| [21] |
QI X, YIN W, JIN S, et al. Density-functional-theory predictions of mechanical behaviour and thermal properties as well as experimental hardness of the Ga-bilayer Mo2Ga2C. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2022, 11: 273.
DOI |
| [22] |
QI X, HE X, YIN W, et al. Stability trend, weak bonding, and magnetic properties of the Al-and Si-containing ternary-layered borides MAB phases. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2023, 106(2): 1513.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
KRESSE G, FURTHM LLER J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Physical Review B, 1996, 54(16): 11169.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
POPOOLA A, OLUYAMO S. Physical properties of some noble metal compounds from PAW-DFT calculations. Journal of Science and Technology (Ghana), 2014, 34(3): 47.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
ZECCA L, GORI-GIORGI P, MORONI S, et al. Local density functional for the short-range part of the electron-electron interaction. Physical Review B, 2004, 70(20): 205127.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
PERDEW J P, BURKE K, ERNZERHOF M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Physical Review Letters, 1996, 77(18): 3865.
DOI PMID |
| [27] |
TOGO A, OBA F, TANAKA I. First-principles calculations of the ferroelastic transition between rutile-type and CaCl2-type SiO2 at high pressures. Physical Review B, 2008, 78(13): 134106.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
HILL R. The elastic behaviour of a crystalline aggregate. Proceedings of the Physical Society Section A, 1952, 65(5): 349.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
WOLVERTON C, ZUNGER A. First-principles theory of short-range order, electronic excitations, and spin polarization in Ni-V and Pd-V alloys. Physical Review B, 1995, 52(12): 8813.
PMID |
| [30] |
WANG J, YE T N, GONG Y, et al. Discovery of hexagonal ternary phase Ti2InB2 and its evolution to layered boride TiB. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 2284.
DOI |
| [31] |
SAKAMAKI K, WADA H, NOZAKI H, et al. Carbosulfide superconductor. Solid State Communications, 1999, 112(6): 323.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
KHAZAEI M, WANG J, ESTILI M, et al. Novel MAB phases and insights into their exfoliation into 2D MBenes. Nanoscale, 2019, 11(23): 11305.
DOI PMID |
| [33] | BORN M, HUANG K, LAX M. Dynamical theory of crystal lattices. American Journal of Physics, 1955, 23(7): 474. |
| [34] |
BARSOUM M W, RADOVIC M. Elastic and mechanical properties of the MAX phases. Annual Review of Materials Research, 2011, 41: 195.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
PUGH S. XCII. Relations between the elastic moduli and the plastic properties of polycrystalline pure metals. The London, Edinburgh, and Dublin Philosophical Magazine and Journal of Science, 1954, 45(367): 823.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
BAI Y, QI X, DUFF A, et al. Density functional theory insights into ternary layered boride MoAlB. Acta Materialia, 2017, 132: 69.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
ALI M, HOSSAIN M, UDDIN M, et al. DFT insights into new B-containing 212 MAX phases: Hf2AB2 (A= In, Sn). Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 860: 158408.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
MIAO N, WANG J, GONG Y, et al. Computational prediction of boron-based MAX phases and MXene derivatives. Chemistry of Materials, 2020, 32(16): 6947.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
BOUHEMADOU A. First-principles study of structural, electronic and elastic properties of Nb4AlC3. Brazilian Journal of Physics, 2010, 40: 52.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
CHEN XQ, NIU H, LI D, et al. Modeling hardness of polycrystalline materials and bulk metallic glasses. Intermetallics, 2011, 19(9): 1275.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
GUO X, LI L, LIU Z, et al. Hardness of covalent compounds: roles of metallic component and d valence electrons. Journal of Applied Physics, 2008, 104(2): 023503.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
XIANG H, FENG Z, LI Z, et al. First-principles investigations on elevated temperature elastic and thermodynamic properties of ZrB2 and HfB2. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2017, 100(8): 3662.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
BLANCO M, FRANCISCO E, LUANA V. GIBBS: isothermal- isobaric thermodynamics of solids from energy curves using a quasi-harmonic Debye model. Computer Physics Communications, 2004, 158(1): 57.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 吴玉豪, 彭仁赐, 程春玉, 杨丽, 周益春. HfxTa1-xC体系力学性能及熔化曲线的第一性原理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 761-768. |
| [2] | 靳宇翔, 宋二红, 朱永福. 3d过渡金属单原子掺杂石墨烯缺陷电催化还原CO2的第一性原理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 845-852. |
| [3] | 王伟华, 张磊宁, 丁峰, 代兵, 韩杰才, 朱嘉琦, 贾怡, 杨宇. 铱衬底上金刚石外延形核与生长: 第一性原理计算[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(4): 416-422. |
| [4] | 周靖渝, 李兴宇, 赵晓琳, 王有伟, 宋二红, 刘建军. Ti和Cu掺杂β-NaMnO2正极材料:钠离子电池的倍率和循环性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(12): 1404-1412. |
| [5] | 陈梦杰, 王倩倩, 吴成铁, 黄健. 基于DFT的描述符预测生物陶瓷的降解性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(10): 1175-1181. |
| [6] | 周云凯, 刁亚琪, 王明磊, 张宴会, 王利民. 聚苯胺改性Ti3C2(OH)2抗氧化性的第一性原理计算研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(10): 1151-1158. |
| [7] | 吴晓维, 张涵, 曾彪, 明辰, 孙宜阳. 杂化泛函HSE和PBE0计算CsPbI3缺陷性质的比较研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(9): 1110-1116. |
| [8] | 张守超, 陈洪雨, 刘洪飞, 杨羽, 李欣, 刘德峰. 6H-SiC中子辐照肿胀高温回复及光学特性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 678-686. |
| [9] | 杨颖康, 邵怡晴, 李柏良, 吕志伟, 王路路, 王亮君, 曹逊, 吴宇宁, 黄荣, 杨长. Cl掺杂对CuI薄膜发光性能增强研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 687-692. |
| [10] | 文志勤, 黄彬荣, 卢涛仪, 邹正光. 压力对PbTiO3结构和热物性质影响的第一性原理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 787-794. |
| [11] | 孙铭, 邵溥真, 孙凯, 黄建华, 张强, 修子扬, 肖海英, 武高辉. RGO/Al复合材料界面性质第一性原理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(6): 651-659. |
| [12] | 肖美霞, 李苗苗, 宋二红, 宋海洋, 李钊, 毕佳颖. 表面端基卤化Ti3C2 MXene应用于锂离子电池高容量电极材料的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(6): 660-668. |
| [13] | 袁罡, 马新国, 贺华, 邓水全, 段汪洋, 程正旺, 邹维. 平面应变对二维单层MoSi2N4能带结构和光电性质的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(5): 527-533. |
| [14] | 冯清影, 刘东, 张莹, 冯浩, 李强. 太阳能驱动的两步热化学循环二氧化碳裂解反应活性材料的热力学与第一性原理评价[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(2): 223-229. |
| [15] | 彭军辉, TIKHONOV Evgenii. 空位对Hf-Ta-C体系的结构、力学性质及电子性质影响的第一性原理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(1): 51-57. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||