无机材料学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (12): 1414-1424.DOI: 10.15541/jim20250042 CSTR: 32189.14.jim20250042
郭佳芯1( ), 陈美娟1, 吴浩1, 郑潇然1, 闵楠1, 田辉1(
), 陈美娟1, 吴浩1, 郑潇然1, 闵楠1, 田辉1( ), 齐东丽1, 李全军2, 都时禹3,4, 沈龙海1(
), 齐东丽1, 李全军2, 都时禹3,4, 沈龙海1( )
)
收稿日期:2025-02-04
修回日期:2025-04-10
出版日期:2025-12-20
网络出版日期:2025-04-15
通讯作者:
沈龙海, 教授. E-mail: shenlonghai@sylu.edu.cn;作者简介:郭佳芯(2001-), 女, 硕士研究生. E-mail: 463256229@qq.com
基金资助:
GUO Jiaxin1( ), CHEN Meijuan1, WU Hao1, ZHENG Xiaoran1, MIN Nan1, TIAN Hui1(
), CHEN Meijuan1, WU Hao1, ZHENG Xiaoran1, MIN Nan1, TIAN Hui1( ), QI Dongli1, LI Quanjun2, DU Shiyu3,4, SHEN Longhai1(
), QI Dongli1, LI Quanjun2, DU Shiyu3,4, SHEN Longhai1( )
)
Received:2025-02-04
Revised:2025-04-10
Published:2025-12-20
Online:2025-04-15
Contact:
SHEN Longhai, professor. E-mail: shenlonghai@sylu.edu.cn;About author:GUO Jiaxin (2001-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: 463256229@qq.com
Supported by:摘要:
新型In基MAX相Zr3InC2因其优异的物理性能而受到广泛关注, 但其在高压下的研究仍较为有限。基于密度泛函理论(DFT)的第一性原理, 本工作系统研究了压力对新型MAX相Zr3InC2的晶体结构、力学性质、电子结构和热力学性质的影响。通过与Zr3AlC2进行对比, 揭示了A位元素由Al替换为In对MAX相材料的晶体结构、物理性质及两者在高压环境下响应的影响。计算得到的Zr3InC2和Zr3AlC2晶格参数与之前的实验报道相一致。晶格参数随压力的变化结果表明, Zr3InC2和Zr3AlC2存在明显的各向异性压缩, 即沿c轴方向的压缩率显著高于沿a轴方向。弹性常数和声子色散曲线的结果表明, Zr3InC2在0~50 GPa范围内保持力学稳定和动力学稳定。此外, 不同压力下的泊松比结果表明, Zr3InC2在常压下为脆性, 随着压力的增加, 其脆性逐渐减弱, 40 GPa时首次呈现韧性, 其中泊松比和柯西压力在50 GPa下存在差异, 表明Zr3InC2在高压下可能处于脆韧转变的临界区。经对比发现, Zr3InC2的力学性质比Zr3AlC2在高压下的响应更为敏感。电子结构的计算结果显示Zr3InC2具有金属性。热力学分析显示, Zr3InC2在常压下具有相对较低的热膨胀系数, 随着压力的增加, Zr3InC2的德拜温度和最小导热系数显著上升, 这表明压力能有效调节Zr3InC2的热力学性能, 为其在高温领域中的潜在应用提供了理论支持。
中图分类号:
郭佳芯, 陈美娟, 吴浩, 郑潇然, 闵楠, 田辉, 齐东丽, 李全军, 都时禹, 沈龙海. 高压下新型MAX相Zr3InC2的第一性原理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(12): 1414-1424.
GUO Jiaxin, CHEN Meijuan, WU Hao, ZHENG Xiaoran, MIN Nan, TIAN Hui, QI Dongli, LI Quanjun, DU Shiyu, SHEN Longhai. First-principles Study of Novel MAX Phase Zr3InC2 under High Pressure[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(12): 1414-1424.
| MAX | a/Å | c/Å | V/Å3 | c/a | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zr3InC2 | 3.332 | 20.177 | 200.776 | 6.055 | This work |
| 3.351 | 20.251 | 194.004 | 6.042 | [18] | |
| Zr3AlC2 | 3.337 | 19.940 | 192.362 | 5.975 | This work |
| 3.328 | 20.011 | 192.01 | 6.011 | [41] |
表1 0 GPa压力下Zr3InC2和Zr3AlC2的结构参数[18,41]
Table 1 Structural parameters of Zr3InC2 and Zr3AlC2 at 0 GPa pressure[18,41]
| MAX | a/Å | c/Å | V/Å3 | c/a | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zr3InC2 | 3.332 | 20.177 | 200.776 | 6.055 | This work |
| 3.351 | 20.251 | 194.004 | 6.042 | [18] | |
| Zr3AlC2 | 3.337 | 19.940 | 192.362 | 5.975 | This work |
| 3.328 | 20.011 | 192.01 | 6.011 | [41] |
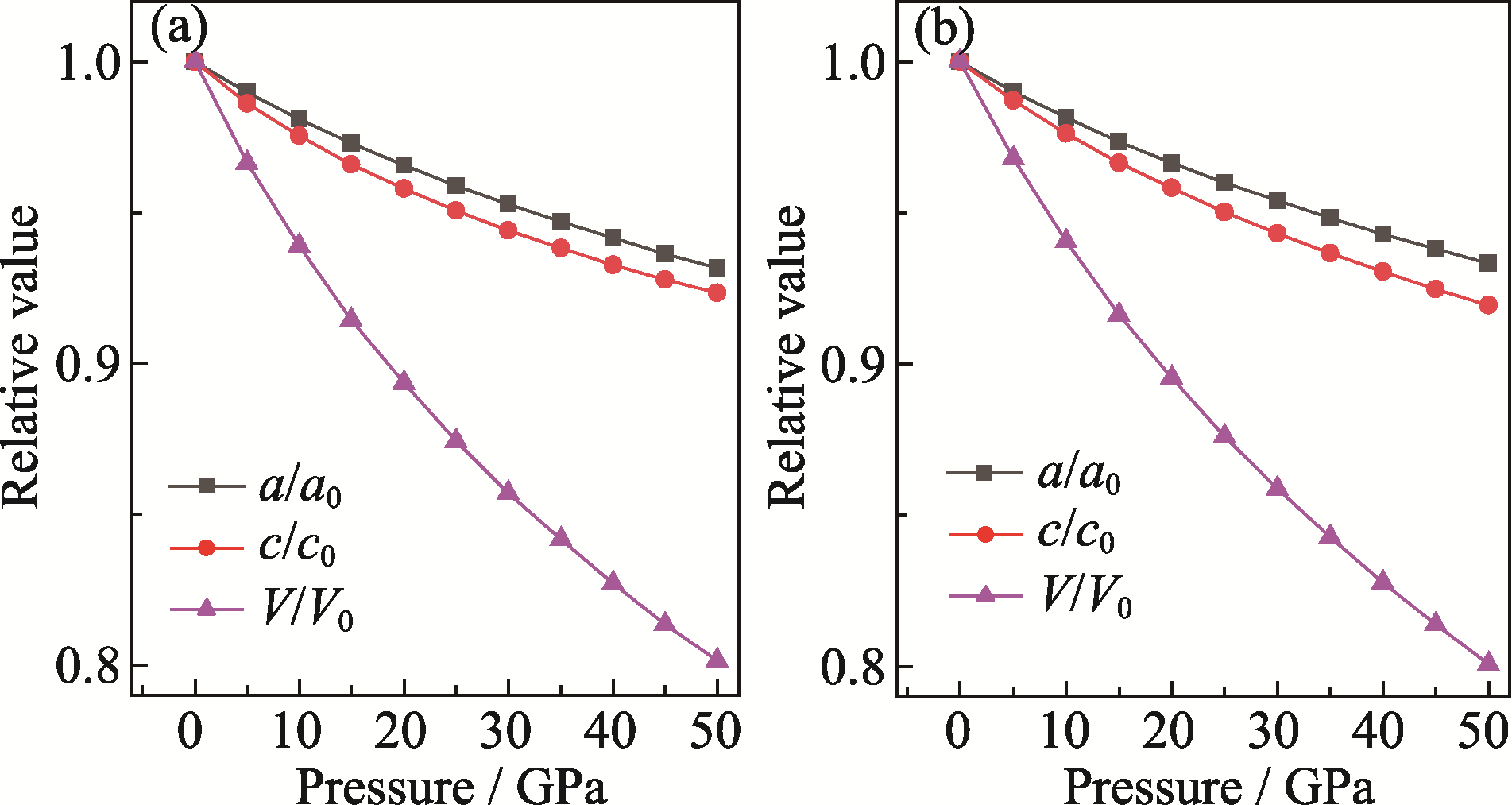
图2 (a) Zr3InC2和(b) Zr3AlC2的相对晶格参数和相对体积随压力变化的关系
Fig. 2 Variations of relative lattice parameters and relative volume of (a) Zr3InC2 and (b) Zr3AlC2 with pressure
| MAX | Pressure/ GPa | C11/ GPa | C12/ GPa | C13/ GPa | C33/ GPa | C44/ GPa | C66/ GPa | B/ GPa | G/ GPa | E/ GPa | Cauchy pressure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zr3InC2 | 0 | 300 | 73 | 65 | 243 | 87 | 114 | 138 | 100 | 241 | -14 |
| 5 | 308 | 96 | 80 | 277 | 102 | 106 | 156 | 104 | 256 | -6 | |
| 10 | 343 | 95 | 95 | 302 | 112 | 124 | 173 | 116 | 285 | -17 | |
| 15 | 360 | 104 | 106 | 326 | 121 | 128 | 186 | 122 | 301 | -17 | |
| 20 | 376 | 119 | 120 | 352 | 128 | 128 | 202 | 126 | 314 | -9 | |
| 25 | 401 | 124 | 134 | 376 | 139 | 138 | 218 | 135 | 337 | -15 | |
| 30 | 416 | 136 | 146 | 399 | 148 | 140 | 232 | 140 | 351 | -12 | |
| 35 | 435 | 142 | 157 | 418 | 154 | 147 | 244 | 146 | 366 | -12 | |
| 40 | 438 | 164 | 168 | 436 | 160 | 137 | 257 | 145 | 366 | 4 | |
| 45 | 471 | 159 | 184 | 457 | 172 | 156 | 273 | 158 | 396 | -13 | |
| 50 | 487 | 165 | 194 | 474 | 177 | 161 | 284 | 162 | 408 | -12 | |
| Zr3AlC2 | 0 | 310 | 72 | 71 | 253 | 103 | 119 | 144 | 108 | 260 | -31 |
| 5 | 331 | 82 | 82 | 272 | 112 | 125 | 158 | 115 | 278 | -30 | |
| 10 | 353 | 94 | 96 | 286 | 130 | 129 | 173 | 124 | 301 | -36 | |
| 15 | 373 | 99 | 107 | 316 | 134 | 137 | 187 | 130 | 317 | -35 | |
| 20 | 390 | 111 | 120 | 337 | 143 | 139 | 202 | 136 | 333 | -32 | |
| 25 | 402 | 128 | 133 | 355 | 152 | 137 | 216 | 139 | 342 | -24 | |
| 30 | 422 | 130 | 143 | 370 | 161 | 146 | 227 | 146 | 361 | -31 | |
| 35 | 432 | 143 | 154 | 384 | 164 | 145 | 239 | 147 | 366 | -21 | |
| 40 | 442 | 150 | 161 | 398 | 170 | 146 | 247 | 150 | 374 | -20 | |
| 45 | 444 | 166 | 170 | 401 | 172 | 139 | 255 | 147 | 371 | -6 | |
| 50 | 449 | 179 | 180 | 408 | 176 | 135 | 265 | 147 | 372 | 3 |
表2 0~50 GPa压力下Zr3InC2和Zr3AlC2的弹性常数和弹性模量
Table 2 Elastic constants and elastic moduli of Zr3InC2 and Zr3AlC2 under 0-50 GPa pressure
| MAX | Pressure/ GPa | C11/ GPa | C12/ GPa | C13/ GPa | C33/ GPa | C44/ GPa | C66/ GPa | B/ GPa | G/ GPa | E/ GPa | Cauchy pressure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zr3InC2 | 0 | 300 | 73 | 65 | 243 | 87 | 114 | 138 | 100 | 241 | -14 |
| 5 | 308 | 96 | 80 | 277 | 102 | 106 | 156 | 104 | 256 | -6 | |
| 10 | 343 | 95 | 95 | 302 | 112 | 124 | 173 | 116 | 285 | -17 | |
| 15 | 360 | 104 | 106 | 326 | 121 | 128 | 186 | 122 | 301 | -17 | |
| 20 | 376 | 119 | 120 | 352 | 128 | 128 | 202 | 126 | 314 | -9 | |
| 25 | 401 | 124 | 134 | 376 | 139 | 138 | 218 | 135 | 337 | -15 | |
| 30 | 416 | 136 | 146 | 399 | 148 | 140 | 232 | 140 | 351 | -12 | |
| 35 | 435 | 142 | 157 | 418 | 154 | 147 | 244 | 146 | 366 | -12 | |
| 40 | 438 | 164 | 168 | 436 | 160 | 137 | 257 | 145 | 366 | 4 | |
| 45 | 471 | 159 | 184 | 457 | 172 | 156 | 273 | 158 | 396 | -13 | |
| 50 | 487 | 165 | 194 | 474 | 177 | 161 | 284 | 162 | 408 | -12 | |
| Zr3AlC2 | 0 | 310 | 72 | 71 | 253 | 103 | 119 | 144 | 108 | 260 | -31 |
| 5 | 331 | 82 | 82 | 272 | 112 | 125 | 158 | 115 | 278 | -30 | |
| 10 | 353 | 94 | 96 | 286 | 130 | 129 | 173 | 124 | 301 | -36 | |
| 15 | 373 | 99 | 107 | 316 | 134 | 137 | 187 | 130 | 317 | -35 | |
| 20 | 390 | 111 | 120 | 337 | 143 | 139 | 202 | 136 | 333 | -32 | |
| 25 | 402 | 128 | 133 | 355 | 152 | 137 | 216 | 139 | 342 | -24 | |
| 30 | 422 | 130 | 143 | 370 | 161 | 146 | 227 | 146 | 361 | -31 | |
| 35 | 432 | 143 | 154 | 384 | 164 | 145 | 239 | 147 | 366 | -21 | |
| 40 | 442 | 150 | 161 | 398 | 170 | 146 | 247 | 150 | 374 | -20 | |
| 45 | 444 | 166 | 170 | 401 | 172 | 139 | 255 | 147 | 371 | -6 | |
| 50 | 449 | 179 | 180 | 408 | 176 | 135 | 265 | 147 | 372 | 3 |

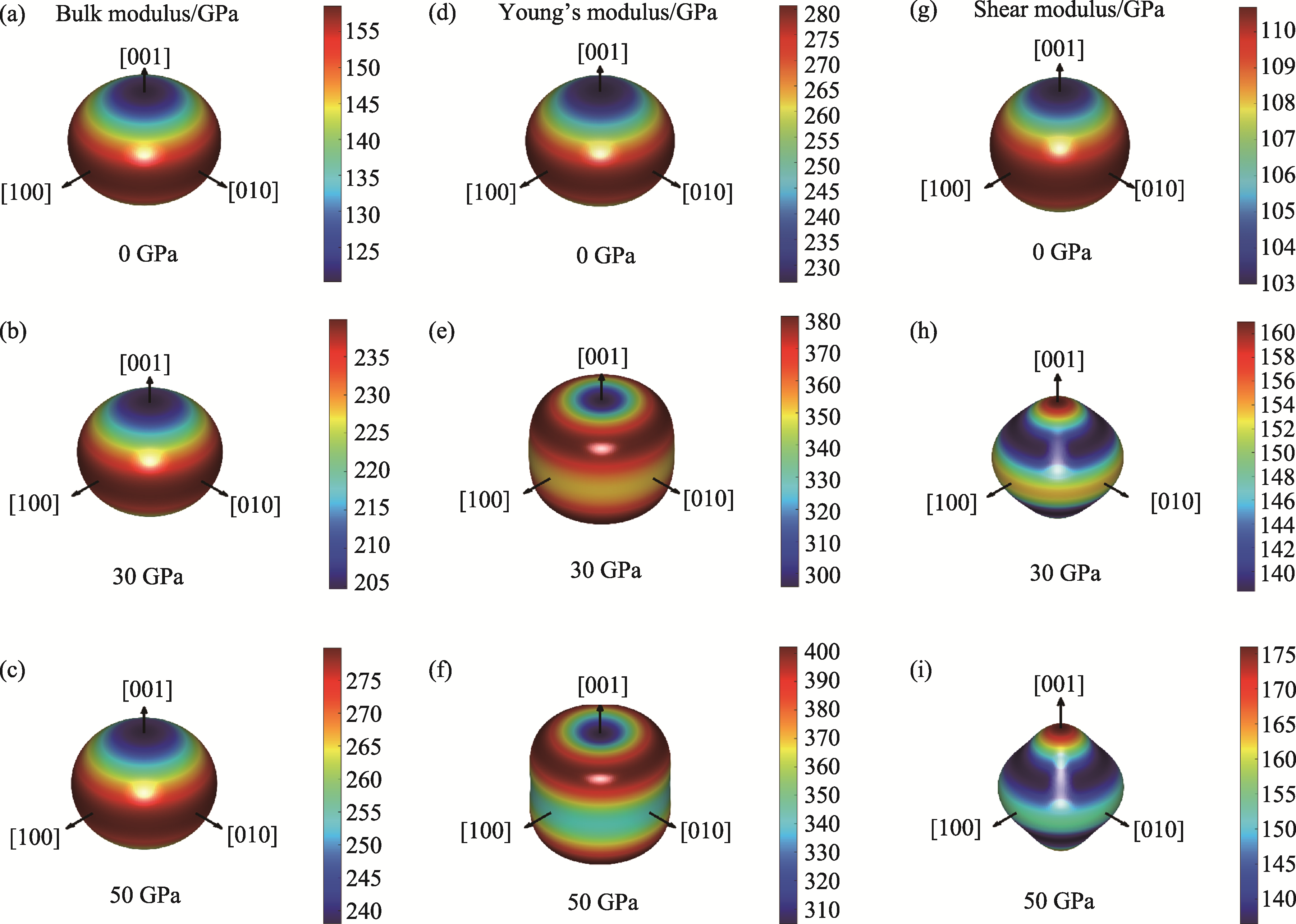
图7 Zr3InC2在0、30、50 GPa压力下的体积模量(a~c)、杨氏模量(d~f)和剪切模量(g~i)的三维曲面图
Fig. 7 3D surface plots of the bulk modulus (a-c), Young’s modulus (d-f), and shear modulus (g-i) of Zr3InC2 at 0, 30 and 50 GPa pressure
| MAX | Pressure/ GPa | ρ/ (kg·m-3) | vt/ (m·s-1) | vl/ (m·s-1) | vm/ (m·s-1) | ΘD/K | Kmin/ (W·m-1·K-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zr3InC2 | 0 | 3375.40 | 6301.53 | 3820.01 | 4221.57 | 491.4 | 0.89 |
| 5 | 3486.67 | 6461.24 | 3844.83 | 4256.71 | 501.2 | 0.92 | |
| 10 | 3588.36 | 6715.97 | 4001.02 | 4429.14 | 526.5 | 0.97 | |
| 15 | 3683.39 | 6846.77 | 4051.64 | 4488.03 | 538.2 | 1.01 | |
| 20 | 3769.65 | 6967.78 | 4065.94 | 4509.69 | 545.0 | 1.03 | |
| 25 | 3853.06 | 7143.07 | 4165.50 | 4620.38 | 562.5 | 1.07 | |
| 30 | 3931.13 | 7256.43 | 4200.63 | 4662.40 | 571.4 | 1.09 | |
| 35 | 4005.88 | 7360.26 | 4246.22 | 4714.42 | 581.2 | 1.12 | |
| 40 | 4078.30 | 7385.32 | 4190.43 | 4659.11 | 577.8 | 1.12 | |
| 45 | 4148.03 | 7585.61 | 4334.05 | 4815.97 | 600.5 | 1.17 | |
| 50 | 4215.80 | 7656.01 | 4356.83 | 4842.92 | 607.0 | 1.18 | |
| Zr3AlC2 | 0 | 3375.40 | 7176.31 | 4397.61 | 4854.54 | 573.2 | 1.05 |
| 5 | 3486.67 | 7333.83 | 4464.07 | 4931.28 | 588.6 | 1.09 | |
| 10 | 3588.36 | 7543.72 | 4569.82 | 5050.55 | 608.6 | 1.14 | |
| 15 | 3683.39 | 7684.20 | 4616.35 | 5106.18 | 620.7 | 1.17 | |
| 20 | 3769.65 | 7822.28 | 4657.67 | 5156.31 | 631.7 | 1.20 | |
| 25 | 3853.06 | 7914.84 | 4652.82 | 5157.13 | 636.4 | 1.22 | |
| 30 | 3931.13 | 8037.75 | 4727.22 | 5239.38 | 650.9 | 1.25 | |
| 35 | 4005.88 | 8080.91 | 4698.41 | 5212.88 | 651.7 | 1.26 | |
| 40 | 4078.30 | 8123.75 | 4703.44 | 5220.42 | 656.5 | 1.28 | |
| 45 | 4148.03 | 8097.81 | 4625.81 | 5140.25 | 650.1 | 1.28 | |
| 50 | 4215.80 | 8109.87 | 4578.04 | 5092.24 | 647.5 | 1.28 |
表3
0~50 GPa压力下Zr3InC2和Zr3AlC2的ρ、横向速度(vt)、纵向速度(vl)、平均声速(vm)、ΘD和Kmin Table 3 ρ, transverse velocity (vt), longitudinal velocity (vl), average sound velocity (vm), ΘD, and Kmin of Zr3InC2 and Zr3AlC2 under 0-50 GPa pressure
| MAX | Pressure/ GPa | ρ/ (kg·m-3) | vt/ (m·s-1) | vl/ (m·s-1) | vm/ (m·s-1) | ΘD/K | Kmin/ (W·m-1·K-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zr3InC2 | 0 | 3375.40 | 6301.53 | 3820.01 | 4221.57 | 491.4 | 0.89 |
| 5 | 3486.67 | 6461.24 | 3844.83 | 4256.71 | 501.2 | 0.92 | |
| 10 | 3588.36 | 6715.97 | 4001.02 | 4429.14 | 526.5 | 0.97 | |
| 15 | 3683.39 | 6846.77 | 4051.64 | 4488.03 | 538.2 | 1.01 | |
| 20 | 3769.65 | 6967.78 | 4065.94 | 4509.69 | 545.0 | 1.03 | |
| 25 | 3853.06 | 7143.07 | 4165.50 | 4620.38 | 562.5 | 1.07 | |
| 30 | 3931.13 | 7256.43 | 4200.63 | 4662.40 | 571.4 | 1.09 | |
| 35 | 4005.88 | 7360.26 | 4246.22 | 4714.42 | 581.2 | 1.12 | |
| 40 | 4078.30 | 7385.32 | 4190.43 | 4659.11 | 577.8 | 1.12 | |
| 45 | 4148.03 | 7585.61 | 4334.05 | 4815.97 | 600.5 | 1.17 | |
| 50 | 4215.80 | 7656.01 | 4356.83 | 4842.92 | 607.0 | 1.18 | |
| Zr3AlC2 | 0 | 3375.40 | 7176.31 | 4397.61 | 4854.54 | 573.2 | 1.05 |
| 5 | 3486.67 | 7333.83 | 4464.07 | 4931.28 | 588.6 | 1.09 | |
| 10 | 3588.36 | 7543.72 | 4569.82 | 5050.55 | 608.6 | 1.14 | |
| 15 | 3683.39 | 7684.20 | 4616.35 | 5106.18 | 620.7 | 1.17 | |
| 20 | 3769.65 | 7822.28 | 4657.67 | 5156.31 | 631.7 | 1.20 | |
| 25 | 3853.06 | 7914.84 | 4652.82 | 5157.13 | 636.4 | 1.22 | |
| 30 | 3931.13 | 8037.75 | 4727.22 | 5239.38 | 650.9 | 1.25 | |
| 35 | 4005.88 | 8080.91 | 4698.41 | 5212.88 | 651.7 | 1.26 | |
| 40 | 4078.30 | 8123.75 | 4703.44 | 5220.42 | 656.5 | 1.28 | |
| 45 | 4148.03 | 8097.81 | 4625.81 | 5140.25 | 650.1 | 1.28 | |
| 50 | 4215.80 | 8109.87 | 4578.04 | 5092.24 | 647.5 | 1.28 |
图S1 Zr3AlC2在0、30、50 GPa压力下的体积模量(a~c)、杨氏模量(d~f)和剪切模量(g~i)的三维曲面图
Fig. S1 3D surface plots of the bulk modulus (a-c), Young’s modulus (d-f), and shear modulus (g-i) of Zr3AlC2 at 0, 30 and 50 GPa pressure
| [1] |
DING H M, LI M, LI Y B, et al. Progress in structural tailoring and properties of ternary layered ceramics. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(8): 845.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
WANG X H, ZHOU Y C. Intermediate-temperature oxidation behavior of Ti2AlC in air. Journal of Materials Research, 2002, 17(11): 2974.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
BYEON J W, LIU J, HOPKINS M, et al. Microstructure and residual stress of alumina scale formed on Ti2AlC at high temperature in air. Oxidation of Metals, 2007, 68(1): 97.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
BARSOUM M W, YOO H I, POLUSHINA I K, et al. Electrical conductivity, thermopower, and Hall effect of Ti3AlC2, Ti4AlN3, and Ti3SiC2. Physical Review B, 2000, 62(15): 10194.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
BARSOUM M W, EL-RAGHY T, RAWN C J, et al. Thermal properties of Ti3SiC2. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 1999, 60(4): 429.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
ZAPATA-SOLVAS E, CHRISTOPOULOS S G, NI N, et al. Experimental synthesis and density functional theory investigation of radiation tolerance of Zr3(Al1-xSix)C2 MAX phases. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2017, 100(4): 1377.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
BARSOUM M W, EL-RAGHY T. The MAX phases: unique new carbide and nitride materials: ternary ceramics turn out to be surprisingly soft and machinable, yet also heat-tolerant, strong and lightweight. American Scientist, 2001, 89(4): 334.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
HAJAS D E, BABEN M T, HALLSTEDT B, et al. Oxidation of Cr2AlC coatings in the temperature range of 1230 to 1410 ℃. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2011, 206(4): 591.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
SHEIN I R, IVANOVSKII A L. Elastic properties of superconducting MAX phases from first-principles calculations. Physica Status Solidi: B, 2011, 248(1): 228.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
GALVIN T, HYATT N C, RAINFORTH W M, et al. Slipcasting of MAX phase tubes for nuclear fuel cladding applications. Nuclear Materials and Energy, 2020, 22: 100725.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
HUANG Q. MXene: coming up roses. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(2): 113.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
LI M, LI Y B, LUO K, et al. Synthesis of novel MAX phase Ti3ZnC2 via A-site-element-substitution approach. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(1): 60.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
DING H M, LI Y B, LU J, et al. Synthesis of MAX phases Nb2CuC and Ti2(Al0.1Cu0.9)N by A-site replacement reaction in molten salts. Materials Research Letters, 2019, 7(12): 510.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
LI Y B, LI M, LU J, et al. Single-atom-thick active layers realized in nanolaminated Ti3(AlxCu1-x)C2 and its artificial enzyme behavior. ACS Nano, 2019, 13(8): 9198.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
LI Y B, LIANG J H, DING H M, et al. Near-room temperature ferromagnetic behavior of single-atom-thick 2D iron in nanolaminated ternary MAX phases. Applied Physics Reviews, 2021, 8(3): 031418.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
FASHANDI H, DAHLQVIST M, LU J, et al. Synthesis of Ti3AuC2, Ti3Au2C2 and Ti3IrC2 by noble metal substitution reaction in Ti3SiC2 for high-temperature-stable Ohmic contacts to SiC. Nature Materials, 2017, 16: 814.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
CUSKELLY D T, RICHARDS E R, KISI E H, et al. Ti3GaC2 and Ti3InC2: first bulk synthesis, DFT stability calculations and structural systematics. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2015, 230: 418.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
ZHANG Q Q, LUO J, WEN B, et al. Determination of new α-312 MAX phases of Zr3InC2 and Hf3InC2. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2023, 43(15): 7228.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
BORTOLOZO A D, SANT’ANNA O H, DOS SANTOS C A M, et al. Superconductivity in the hexagonal-layered nanolaminates Ti2InC compound. Solid State Communications, 2007, 144(10/11): 419.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
BORTOLOZO A D, SERRANO G, SERQUIS A, et al. Superconductivity at 7.3 K in Ti2InN. Solid State Communications, 2010, 150(29/30): 1364.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
BORTOLOZO A D, FISK Z, SANT’ANNA O H, et al. Superconductivity in Nb2InC. Physica C: Superconductivity, 2009, 469(7/8): 256.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
BAKARDJIEVA S, CECCIO G, VACIK J, et al. Surface morphology and mechanical properties changes induced in Ti3InC2 (M3AX2) thin nanocrystalline films by irradiation of 100 keV Ne+ ions. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2021, 426: 127775.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
BAKARDJIEVA S, HORAK P, VACIK J, et al. Effect of Ar+ irradiation of Ti3InC2 at different ion beam fluences. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2020, 394: 125834.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
CANNAVÓ A, VACÍK J, BAKARDJIEVA S, et al. Effect of medium energy He+, Ne+ and Ar+ ion irradiation on the Hf-In-C thin film composites. Thin Solid Films, 2022, 743: 139052.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
LUO F, GUO Z C, ZHANG X L, et al. Ab initio predictions of structural and thermodynamic properties of Zr2AlC under high pressure and high temperature. Chinese Journal of Chemical Physics, 2015, 28(3): 263.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
QURESHI M W, MA X X, TANG G Z, et al. Structural stability, electronic, mechanical, phonon, and thermodynamic properties of the M2GaC (M=Zr, Hf) MAX phase: an ab initio calculation. Materials, 2020, 13(22): 5148.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
ALI M A, QURESHI M W. DFT insights into the new Hf-based chalcogenide MAX phase Hf2SeC. Vacuum, 2022, 201: 111072.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
ALI M A, QURESHI M W. Newly synthesized MAX phase Zr2SeC: DFT insights into physical properties towards possible applications. RSC Advances, 2021, 11(28): 16892.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
AZZOUZ-RACHED A, HADI M A, RACHED H, et al. Pressure effects on the structural, elastic, magnetic and thermodynamic properties of Mn2AlC and Mn2SiC MAX phases. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 885: 160998.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
KRESSE G, HAFNER J. Ab initio molecular dynamics for open- shell transition metals. Physical Review B, 1993, 48(17): 13115.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
KRESSE G, FURTHMÜLLER J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Physical Review B, 1996, 54(16): 11169.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
WU Z G, COHEN R E. More accurate generalized gradient approximation for solids. Physical Review B, 2006, 73(23): 235116.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
BLÖCHL P E. Projector augmented-wave method. Physical Review B, 1994, 50(24): 17953.
DOI PMID |
| [34] |
MONKHORST H J, PACK J D. Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations. Physical Review B, 1976, 13(12): 5188.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
REUSS A. Berechnung der fließgrenze von mischkristallen auf grund der plastizitätsbedingung für einkristalle. ZAMM - Journal of Applied Mathematics and Mechanics/Zeitschrift für Angewandte Mathematik und Mechanik, 1929, 9(1): 49.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
HILL R. The elastic behaviour of a crystalline aggregate. Proceedings of the Physical Society A, 1952, 65(5): 349.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
VOIGT W. Ueber die Beziehung zwischen den beiden Elasticitätsconstanten isotroper Körper. Annalen der Physik, 1889, 274(12): 573.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
WANG H Z, ZHAN Y Z, PANG M J. The structure, elastic, electronic properties and Debye temperature of M2AlC (M=Nb and Ta) under pressure from first-principles. Computational Materials Science, 2012, 54: 16.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
ANDERSON O L. A simplified method for calculating the Debye temperature from elastic constants. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 1963, 24(7): 909.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
CLARKE D R. Materials selection guidelines for low thermal conductivity thermal barrier coatings. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2003, 163/164: 67.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
ZAPATA-SOLVAS E, HADI M A, HORLAIT D, et al. Synthesis and physical properties of (Zr1-x, Tix)3AlC2 MAX phases. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2017, 100(8): 3393.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
WANG J, YIP S, PHILLPOT S R, et al. Crystal instabilities at finite strain. Physical Review Letters, 1993, 71(25): 4182.
PMID |
| [43] |
RANA M R, ISLAM S, HOQUE K, et al. DFT prediction of the stability and physical properties of M2GaB (M = Sc, V, Nb, Ta). Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2023, 24: 7795.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
PETTIFOR D G. Theoretical predictions of structure and related properties of intermetallics. Materials Science and Technology, 1992, 8(4): 345.
DOI URL |
| [45] | CHEN L L, DENG Z X, LI M, et al. Phase diagrams of novel MAX phases. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(1): 35. |
| [46] |
QI L, JIN Y C, ZHAO Y H, et al. The structural, elastic, electronic properties and Debye temperature of Ni3Mo under pressure from first-principles. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2015, 621: 383.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
CHEN Q, HUANG Z W, ZHAO Z D, et al. Thermal stabilities, elastic properties and electronic structures of B2-MgRE (RE=Sc, Y, La) by first-principles calculations. Computational Materials Science, 2013, 67: 196.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
HADI M A, AHMED I, ALI M A, et al. A comparative DFT exploration on M- and A-site double transition metal MAX phase, Ti3ZnC2. Open Ceramics, 2022, 12: 100308.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
HADI M A, ROKNUZZAMAN M, CHRONEOS A, et al. Elastic and thermodynamic properties of new (Zr3-xTix)AlC2 MAX-phase solid solutions. Computational Materials Science, 2017, 137: 318.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 胡智超, 杨鸿宇, 杨鸿程, 孙成礼, 杨俊, 李恩竹. P-V-L键理论在微波介质陶瓷性能调控中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [2] | 黄子鹏, 贾文晓, 李玲霞. (Ti0.5W0.5)5+掺杂MgNb2O6陶瓷的晶体结构与太赫兹介电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(6): 647-655. |
| [3] | 赵凯旋, 刘文鹏, 丁守军, 窦仁勤, 罗建乔, 高进云, 孙贵花, 任浩, 张庆礼. 熔融法制备Nd:YLF原料及其晶体生长和性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2025, 40(5): 529-535. |
| [4] | 黄建锋, 梁瑞虹, 周志勇. W/Cr共掺杂对CaBi2Nb2O9陶瓷晶体结构及电学性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(8): 887-894. |
| [5] | 吴玉豪, 彭仁赐, 程春玉, 杨丽, 周益春. HfxTa1-xC体系力学性能及熔化曲线的第一性原理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 761-768. |
| [6] | 靳宇翔, 宋二红, 朱永福. 3d过渡金属单原子掺杂石墨烯缺陷电催化还原CO2的第一性原理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(7): 845-852. |
| [7] | 王伟华, 张磊宁, 丁峰, 代兵, 韩杰才, 朱嘉琦, 贾怡, 杨宇. 铱衬底上金刚石外延形核与生长: 第一性原理计算[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(4): 416-422. |
| [8] | 张宇晨, 陆知遥, 赫晓东, 宋广平, 朱春城, 郑永挺, 柏跃磊. 硫族MAX相硼化物的物相稳定性和性能预测[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 225-232. |
| [9] | 刘艳艳, 谢曦, 刘增乾, 张哲峰. MAX相陶瓷增强金属基复合材料: 制备、性能与仿生设计[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(2): 145-152. |
| [10] | 周靖渝, 李兴宇, 赵晓琳, 王有伟, 宋二红, 刘建军. Ti和Cu掺杂β-NaMnO2正极材料:钠离子电池的倍率和循环性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(12): 1404-1412. |
| [11] | 陈梦杰, 王倩倩, 吴成铁, 黄健. 基于DFT的描述符预测生物陶瓷的降解性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(10): 1175-1181. |
| [12] | 周云凯, 刁亚琪, 王明磊, 张宴会, 王利民. 聚苯胺改性Ti3C2(OH)2抗氧化性的第一性原理计算研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2024, 39(10): 1151-1158. |
| [13] | 吴晓维, 张涵, 曾彪, 明辰, 孙宜阳. 杂化泛函HSE和PBE0计算CsPbI3缺陷性质的比较研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(9): 1110-1116. |
| [14] | 丁浩明, 李勉, 李友兵, 陈科, 肖昱琨, 周洁, 陶泉争, 尹航, 柏跃磊, 张毕堃, 孙志梅, 王俊杰, 张一鸣, 黄振莺, 张培根, 孙正明, 韩美康, 赵双, 王晨旭, 黄庆. 三元层状材料结构调控及性能研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(8): 845-884. |
| [15] | 宋云霞, 韩颖磊, 颜涛, 罗敏. Rb3Hg2(SO4)3Cl新型紫外非线性光学晶体材料[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(7): 778-784. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||